Abstract
The human-specific Alu elements, belonging to the class of Short INterspersed Elements (SINEs), have been shown to be a powerful tool for population genetic studies. An earlier study in this department showed that it was possible to analyze Alu presence/absence in 3000-year-old skeletal human remains from the Bronze Age Lichtenstein cave in Lower Saxony, Germany. We developed duplex Alu screening PCRs with flanking primers for two Alu elements, each combined with a single internal Alu primer. By adding an internal primer, the approximately 400–500 bp presence signals of Alu elements can be detected within a range of less than 200 bp. Thus, our PCR approach is suited for highly fragmented ancient DNA samples, whereas NGS analyses frequently are unable to handle repetitive elements. With this analysis system, we examined remains of 12 individuals from the Lichtenstein cave with different degrees of DNA degradation. The duplex PCRs showed fully informative amplification results for all of the chosen Alu loci in eight of the 12 samples. Our analysis system showed that Alu presence/absence analysis is possible in samples with different degrees of DNA degradation and it reduces the amount of valuable skeletal material needed by a factor of four, as compared with a singleplex approach.
Keywords:
Alu; SINE; retroposons; transposable elements; ancient DNA; aDNA; multiplex PCR; Lichtenstein cave 1. Introduction
Transposable elements (TEs) are widespread in prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms [1]. They affect the evolution of genomes [2,3] and alter gene expression [4,5,6]. Studies suggest that the human genome consists of between 45% [7] and 69% [8] TEs. They can be categorized in two classes based on their transposition mechanism [9]. Class II is the smaller group and consists of DNA transposons that move via a “cut and paste” mechanism [10]. Class I, or retroposons, move via a “copy and paste” mechanism [11]. Two major groups of retroposons in the human genome are the autonomous Long Interspersed Elements (LINEs) and the non-autonomous Short Interspersed Elements (SINEs) [7], which require enzymes provided by LINEs [12]. LINEs are transcribed by RNA polymerase II, which encode the enzymes reverse transcriptase and endonuclease, both of which are necessary for retrotransposition [11,13]. The 3′ end of SINEs is derived from partner LINEs [14]. Because both partner elements share a common recognition site, SINEs can be retrotransposed by the same enzymes as well [15]. L1s are partner LINEs for the primate-specific Alu elements [13,16]. For the retrotransposition of Alu elements, the RNA polymerase III transcribes the Alu element and creates an RNA sequence [11]. The RNA intermediate is retrotransposed, reverse-transcribed into cDNA, and reintegrated into a new genomic location. While LINEs require the Open-Reading-Frame-proteins ORF1p and ORF2p, Alu elements need only the latter [13]. The approximately 300-bp Alu element [17] is derived from the 7SL RNA gene [18]. Alu elements have a dimeric structure consisting of a free left Alu monomer (FLAM) and a free right Alu monomer (FRAM), separated by an A-rich region [19]. The left monomer contains the RNA polymerase III promoter boxes A and B. The 3′ end of the right monomer consists of a poly-A-tail of varying length, which has been found to be important for the transposition rate [20]. The whole Alu element is flanked by target-site duplications (TSDs) of variable length that are developed by duplication at the insertion site [21]. Alu elements consist of at least three subfamilies, starting with the oldest J, to the intermediate S, and the youngest Y subfamily [22,23]. While the AluJ subfamily is no longer active in humans, AluS has only a few and AluY possesses the greatest number of functional copies [24]. Within the AluY subfamily, AluYa5 and AluYb8 are the most active groups, with the largest number of polymorphic insertions [25]. Affiliation with a sub-subfamily is based on diagnostic changes in the sequence compared with the Alu consensus sequence [23]. A whole genome analysis has even identified 213 Alu sub-subfamilies [26]. No known mechanism of excision exists if an Alu element is integrated into the genome. However, a precise excision can occur rarely [27]. Nonetheless, the probability of two independent insertions occurring in the same genomic region is negligible [28]. Also, lateral transfer events are known for some retroposons [29], but they are extremely rare. The insertion (or presence) of one Alu element (or SINEs in general) in two different individuals (or taxa) is derived from the same initial insertion event in a common ancestor. For the last twenty years, SINEs have been successfully employed as molecular markers for evolutionary studies. For example, Alu insertions suggest that there was an early expansion of tropical populations of our species [30]; other SINEs show that hippopotamuses are the closest extant relatives of whales [31] and that the divergence of the common ancestor of placental mammals into three lineages occurred almost simultaneously [32].
TEs are not only a powerful tool for phylogeny and population genetics [33,34,35], but are also known to be associated with several diseases [21,36] and were used in a very recent forensic study dealing with quantity and sample quality in human DNA samples [37]. Large-scale analyses have already shown contributions to human genomic diversity [38,39,40]. For example, a recent bioinformatic study illustrated human evolution by analyzing TE polymorphisms based on the data of the 1000 genome project [41]. Thus, with next generation sequencing (NGS), whole genome sequencing (WGS) analyses can be accomplished, saving both money and time. However, TEs in WGS may cause difficulties because reads with similar sequences can be incorrectly assembled, excluding up to 420 Mbp of the genome [42]. For example, a disease called retinitis pigmentosa has been shown to be associated with a 353-bp Alu insertion between codons 428 and 429 in the male germ cell-associated kinase [43]. The TEs were removed during assembly and the insertion was found only by analyzing the raw data and confirmed using a PCR approach. A combination of several different methods can help to solve assembly problems of TEs [44], but the best solution is longer reads [45]. However, this only applies to modern DNA samples. Target hybridization enrichment has been used successfully in several studies analyzing mitochondrial genomes or exomes [46] for aDNA, but not for TEs. Further development of advanced analytical tools and DNA capture will improve whole genome analyses of aDNA [46]. Because of this, PCR approaches are still very useful for aDNA analyses (e.g., [47,48,49,50]) and are often an important complement for NGS analyses.
Our approach included the development of duplex Alu PCRs for degraded aDNA (Figure 1). Kothe et al. [50] demonstrated the possibility of Alu presence/absence analyses with singleplex PCRs in well-preserved aDNA samples. Hence, a long amplicon represents the insertion of the Alu element (presence), whereas a short amplicon represents the flanking regions of the Alu element only (absence). However, amplification of the insertion of an Alu element was not always possible due to fragmentation of the DNA at the beginning. In our approach, we aimed to decrease the needed amount of aDNA, as well as of the valuable skeletal material by amplifying two Alu loci simultaneously and by including an internal Alu primer (IAP). This latter method was used to detect the approximately 400- to 500-bp Alu insertion within a range of less than 200 bp, which is better suited for more fragmented aDNA samples. Besides the IAP, both duplex Alu PCRs consist of one primer set for an Alu element already investigated in the earlier study of Kothe et al. [50] and one newly designed primer set. The duplex PCRs used primer sets for these Alu elements, because amplicon lengths can be determined via a simple gel electrophoresis.
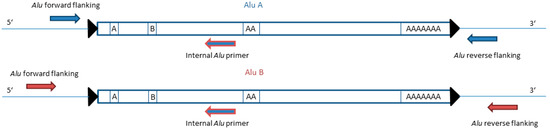
Figure 1.
Schema of the Alu duplex primer positioning. The dimeric structure is separated by an A-rich linker region. The left monomer contains Boxes A and B for the RNA polymerase III. The right monomer shows the recognition site displayed by a poly-A tail. The Alu elements are flanked by target-site duplications (TSDs) represented by black triangles. The two flanking Alu primer sets are placed in slightly different locations. The different-sized amplicons can be distinguished via gel electrophoresis. The internal Alu primer is specific for the sub-subfamily AluYa5 and is able to bind on both Alu elements (represented by blue and red coloring).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
The 3000-year-old skeletal human remains used in this study were found in the Bronze Age Lichtenstein cave close to the city Osterode in Lower Saxony, Germany. The cave has had a constant temperature of 8 °C, and the skeletal remains were coated with a gypsum layer [51,52], providing good conditions for DNA preservation [53,54]. The bone material has been stored at −20 °C in the department of Historical Anthropology and Human Ecology of Göttingen University, Lower Saxony, Germany. Twelve individuals were chosen with varying states of DNA preservation (Table S1), which were determined by earlier Short Tandem Repeat (STR) analyses [55]. In all of the cases, the DNA was extracted from the bone material located in the middle of the diaphysis. A full list of each bone and each individual used is provided in Table S1. To check whether environmental conditions from different burial sites might inhibit the PCR reaction, we added two samples from two additional burial sites. These samples originate from a cemetery in Eldagsen (EL) dated between the 9th and the 19th century, and a mass grave in Lübeck (HL) dated to the 14th century, both in Germany. DNA of EL 13 and EL 158 was extracted by Frischalowski, using the same extraction protocol as described below [56], whereas DNA of HL 1463 and HL 1751 was automatically extracted by Pepperl using the BioRobot® EZ1 (Qiagen) [57]. The DNA of the modern positive control of European origin was extracted from cells of the buccal mucosa.
2.2. DNA Extraction from Skeletal Material with the QIAvac-24-Plus
Fragments of about 0.5 cm2 of the diaphysis of each bone were sawn out. To reduce microorganisms and possible contamination on the bone, fragments were placed in 6% sodium hypochlorite solution (Aug. Hedinger GmbH Co. KG, Stuttgart, Germany) for 15 min, washed with water for 15 min, and dried at 37 °C for 3 h in an oven (B5028, Heraeus, Hanau, Germany). Fragments were powdered in a ball triturator (MM 200, Retsch, Haan, Germany) for 1 min at 24 Hz. Then, 0.25 g bone powder was transferred into a FalconTube with 3.9 mL EDTA UltraPure™ 0.5 M pH 8 (Invitrogen™, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and 100 μL Proteinase K (600 mAnson-U/mL, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany), followed by incubation at 37 °C for 18 h in a rotator. Afterward, another 50 μL of Proteinase K was added and incubated at 56 °C for 2 h. Subsequently, 50 μL sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS) (10 mg/mL, Sigma-Aldrich®, St. Louis, MO, USA) was added and incubated at 65 °C for 5 min. Lysate was centrifuged at 3300 rcf for 3 min to sediment surplus organic material. The lysate was transferred into a 50 mL FalconTube with 16 mL PB-Buffer (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) and 100 μL sodium acetate buffer (pH 5.2, 3 M, Sigma-Aldrich®). The lysate was mixed manually and centrifuged at 3300 rcf for 3 min. DNA was cleaned using minElute spin columns and funnels for large volumes on a QiaVac-24-plus (Qiagen). Three washing steps with 750 μL PE-Buffer (Qiagen) were performed. DNA was eluted in 60 µL RNase-free water (Qiagen) by centrifuging at 13,000 rpm for 1 min. The DNA extract was stored at −20 °C (cf. [55]).
2.3. Modern DNA
The buccal mucosa swab was placed in a 2-mL reaction tube; 400 µL G2-buffer (Qiagen) and 5 μL Proteinase K was added. The sample was incubated at 56 °C and 300 rpm for 2 h on a thermomixer (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany), followed by a centrifugation step at 3300 rcf for 3 min. Then, 200 μL of the supernatant was transferred to sample tubes and placed in the BioRobot EZ1® (Qiagen). Extraction was performed by using the trace protocol of the EZ1 DNA Forensic Card (Qiagen) with the EZ1 DNA Tissue Kit (Qiagen) Elution volume was 100 µL. The extract was stored at −20 °C.
2.4. Primer Design for Alu Duplex PCRs
All of the Alu loci used to develop the Alu duplex PCRs belong to the AluYa5 sub-subfamily. PCR procedures for primer sets Alu 9 and Alu 19 were designed by Kothe et al. [50]. Primers are named here as in the earlier study [50]. Further Alu loci were selected based on [40]. The Alu element was identified using RepeatMasker [58] to confirm whether the Alu element is inserted into a non-repetitive region of the genome. The primers were designed with PrimerSelect™, version 10.1.2 (DNASTAR, Madison, WI, USA). The primer design considered a strong 5′ binding, a weak 3′ binding, and the avoidance of primer dimerization and hairpin formation, in order to increase the specificity and sensitivity of the reaction [59].
Alu elements can be inserted reverse into the genomes [60]. Because of this, an IAP can potentially generate amplicons on its own, so to be specific for one sub-subfamily, the design of an IAP has to consider the following two points: Alu elements are dimeric, so a primer with binding sites in both monomers must be avoided (1); and, conserved regions like A and B Boxes for the RNA polymerase III must be avoided, as well (2). In this study, the IAP was specific for the AluYa5 family and was designed based on consensus sequences constructed by Price et al. [26]. A list of primer sets with amplicon lengths of both duplex PCRs is shown in Table 1. The accession number of the Alu loci used and the genomic position are provided in Table S2.

Table 1.
Primers of both duplex PCRs with expected amplicon lengths in bp for Alu presence (+), internal (+ int) and Alu absence (−) bands.
2.5. PCR
The IAP preliminary tests showed that 2.5 µL of a 20 µM primer working solution provided the most useful results in the Alu duplex PCR reactions. Further PCR amplifications were carried out in a final reaction volume of 25 µL, consisting of 5 µL DNA for aDNA samples and 0.1 µL modern DNA samples for the positive control; 12.5 µL Multiplex PCR Mastermix (Qiagen); 1 µL of a 20 μM working solution of each flanking primer of both Alu loci; 2.5 µL of the IAP; and 1 µL RNase-free water (Qiagen). PCR was performed under the following conditions: initial hot start at 95 °C for 5 min; 40 cycles with denaturation at 94 °C for 1 min, annealing at 58 °C for Alu duplex 1 and 60 °C for Alu duplex 2 for 1 min, and elongation at 72 °C for 40 s, followed by a final soak at 10 °C for 10 min. For the few samples in which the PCR was not successful, the annealing temperature was decreased by 2 °C. To check for possible allelic drop-out or false homozygous results, the PCRs were carried out at least twice.
To prove authenticity, all aDNA samples were subjected to STR typing by a multiplex amplification, as described in [48]. Deviating from this study, the primer set for the sex-discriminating amelogenin gene is labeled 6-FAM (cf. [55]). PCR amplifications were carried out in a final reaction volume of 25 µL consisting of 5 µL DNA (the amount of DNA of each sample is provided in Table S1, measured with a DS-11 FX, DeNovix Inc, Wilmingtion, DE, USA), 12.5 µL Multiplex PCR Mastermix (Qiagen), 2.85 µL multiplex primer mix, and 4.65 µL RNase-free water (Qiagen). PCR was performed under the following conditions: initial hot start at 95 °C for 5 min; 40 cycles with denaturation at 94 °C for 1 min, annealing and elongation at 59 °C for 2.5 min, followed by an end-elongation at 60 °C for 45 min, and final soak at 10 °C for 10 min. All PCRs were performed on a DNA thermal cycler of the type Mastercycler® Personal (Eppendorf).
2.6. Gel Electrophoresis and Fragment-Length Determination
Electrophoreses were performed and amplifications visualized using a 2.5% agarose gel stained with ethidium bromide. The Low Molecular Weight (LMW) DNA Ladder (New England BioLabs® Inc., Ipswich, MA, USA) was used to determine fragment length. The electrophoresis of Alu duplex amplifications had a run time of at least 90 min at 100 V to separate each band clearly. Electrophoresis of STR PCRs had a run time of 30 min at 100 V.
For Alu duplex 1, an Alu ladder for an easier determination of bands was constructed. Bands of the expected size (Alu presence, internal, and Alu absence) were extracted from gel electrophoresis using QIAquick® Gel Extraction Kit (Qiagen) following the manufacturer’s instructions [61] and eluted in 50 µl nuclease free water. The purified products were re-amplified using a modified PCR reaction, as described above. This singleplex PCR reaction used 5 µL of PCR product, 2 µL of each forward and reverse primer, and 35 cycles. Up to now, no absence bands for Alu duplex 2 were amplified. Thus, an Alu ladder could not be constructed.
STR fragments were separated in a 36-cm capillary performed on an ABI 3500 Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Waltham, MA, USA) using POP-7™ for 3500/3500xL Genetic Analyzers, the 3500 Data collection Software, and GeneScan™ 500 ROX™ as the size standard (all Applied Biosystems). GeneMapper® Software 5 (Applied Biosystems) was used for allele determination. Following parameters were applied: 1.2 kV injection voltage for 15 s and 15 kV run voltage for 14 min and 30 s.
2.7. PCR Purification and Sequencing
The whole 25 µL of PCR products were used for gel electrophoresis, cut out, and extracted using the Monarch® DNA Gel Extraction Kit (New England Biolabs® Inc.) following the manufacturer’s instructions [62], and eluted in 15 μL nuclease-free water. Sequencing reactions were carried out with the BigDye® Terminator (BDT) v1.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit (Applied Biosystems). The final reaction volume was 20 μL, consisting of 2 μL BDT, 4 μL Seq buffer (5×), 0.3 μL of a 20 μM working solution of the respective primer, 6.7 μL nuclease-free water, and 7 μL PCR product. Sequencing reactions were performed on a DNA thermal cycler of the type Mastercycler® (Eppendorf) under the following conditions: 96 °C for 10 min and 25 cycles of 96 °C for 10 s, 50 °C for 5 s, and 60 °C for 4 min. After sequencing, the samples were cooled to 10 °C. Sequencing products were purified using the NucleoSEQ® Kit (Macherey & Nagel, Düren, Germany), following the manufacturer’s instructions [63]. Capillary electrophoresis was performed on a 3500 Genetic Analyzer with a 36-cm capillary (Applied Biosystems) using POP-7™ polymer (Applied Biosystems), using following parameters: 1.2 kV injection voltage for 8 s, 8.5 kV run voltage for 21 min and 20 s, and 20 μL of the purified sequencing product. The sequences were analyzed using the software BioEdit v7.2.5 [64].
2.8. Laboratory Conditions
The laboratory was tested twice annually and certified by GEDNAP (German DNA Profiling Group). The laboratories are separated strictly into pre- and post-PCR area. The laboratory employees and all of the samples pass only in the direction from pre- to post-PCR. Only fully STR typed staff wearing laboratory coats, facemasks, and hairnets enter the pre-PCR area. All of the STR typing results from the samples were compared to the STR typed laboratory staff. All of the working surfaces and all non-disposables are cleaned with soap (Alconox®, Sigma-Aldrich®), bi-distilled water and 70% ethanol before and after treatment. Each PCR performed included a negative control.
3. Results
3.1. Alu Duplex PCRs
Amplification success of Alu duplex 1 for loci Alu 9 and Alu 34 was accomplished in 9 out of 12 Lichtenstein cave samples with varying degrees of DNA preservation (Figure 2, Table 2). In general, three amplification patterns are possible for each Alu locus: homozygous presence (1); homozygous absence (2); and, heterozygous (3). EL and HL samples shown in Figure 2 served as different aDNA controls. In all aDNA samples except DO 187, the presence of at least one Alu insertion can be seen with the combination of the IAP and one Alu flanking primer (Figure 2). In general, bands of internal Alu 34 are often more intense than internal bands of Alu 9 of the same sample. For sample DO 187, a partial success of the Alu duplex PCR was achieved only once, but could not be repeated (not shown in Figure 2).
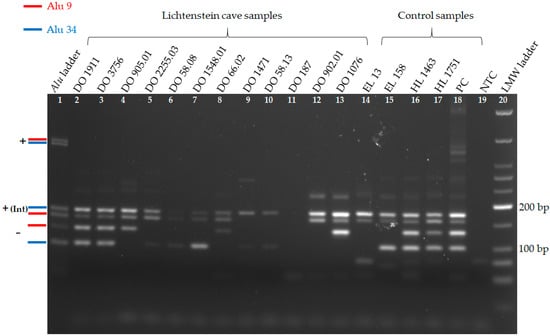
Figure 2.
Gel electrophoresis of Alu duplex 1, containing Alu 9 and 34 in twelve Lichtenstein cave samples and five control samples. Apart from the positive control samples, fully informative results of Lichtenstein cave samples can be seen in lanes 2–8 and 12–13. The most degraded samples (lane 9–11) show only partial results. Amplification results of Alu 34 are visible in 11 out of 12 Lichtenstein cave samples (lane 2–10 and 12–13). On the left in red and blue is the expected length of each possible amplicon illustrated by the Alu ladder. The insertion (+) of an Alu element is shown by the internal (Int) fragment. Some samples show weak unspecific bands longer than 200 bp. On the right is the modern DNA positive control sample (PC), the negative control sample (NTC), and the LMW ladder. The gel ran at 100 V for 90 min and had a UV light exposure time of 1.08 s.

Table 2.
Results for both duplex PCRs. “+” indicates that internal band was amplified. “−” represents the absence situation. No amplification success is displayed with “n.b.”. Results in parentheses were amplified only once.
Amplification success with Alu duplex 2 for loci Alu 19 and Alu 35 was accomplished in 8 out of 12 samples at 60 °C annealing temperature (Figure 3) and 9 out of 12 samples at 58 °C annealing temperature (Table 2, not shown in Figure 3). In contrast to Alu duplex 1, amplification failed with both annealing temperatures in DO 58.08. This sample shows a lower DNA preservation than estimated based on the previous study of [55].
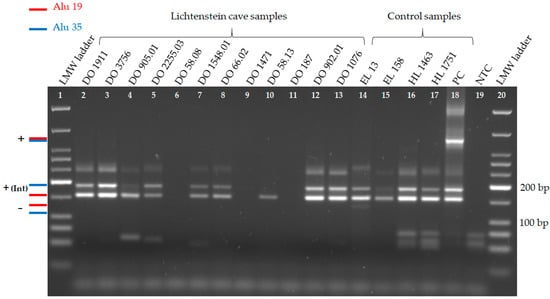
Figure 3.
Gel electrophoresis of Alu duplex 2, containing Alu 19 and 35 in twelve Lichtenstein cave samples and five control samples. Apart from the positive control samples, fully informative results of Lichtenstein cave samples can be seen in lanes 2–5, 7–8 and 12–13. Amplification results of Alu 19 are visible in 10 out of 12 Lichtenstein cave samples (lane 2–5, 7–8, 10 and 12–13). On the left in red and blue is the expected length of each possible amplicon. The insertion (+) of an Alu element is shown by the internal (Int) fragment. Some samples show weak unspecific bands longer than 200 bp. On the right is the modern DNA positive control sample (PC), the negative control sample (NTC), and the LMW ladder. The gel ran at 100 V for 90 min and had a UV light exposure time of 1.20 s. (Up to now, no absence bands for Alu duplex 2 were amplified. Thus, an Alu ladder could not be constructed).
In general, amplification success decreases with increasing degree of DNA degradation. Nonetheless, amplification of a 179-bp fragment was possible even in DO 58.13, which is one of the two most degraded DNA samples. However, the amount of DNA used in the PCRs (see Table S1) did not correlate with amplification success, providing support for DNA degradation being the primary factor affecting amplification success with these samples. To ensure the authenticity of the amplification of the duplex reaction, bands of Alu duplex 1 of DO 3756 (Figure 2, lane 3) were sequenced, showing the expected results, as found in Table S3. Moreover, in samples from further burial sites, both Alu duplex PCRs show fully informative results.
3.2. Proof of Authenticity
First STR typing of samples after DNA extraction showed only alleles that were congruent with previous results [55]. Subsequent to Alu screening, a second STR typing was carried out. It showed two incongruent alleles for DO 1471 and one incongruent allele for DO 187; this differs from previous results and must be discussed further. STR typing results are provided in Table S4.
4. Discussion
4.1. Alu Duplex PCRs
With the integration of an IAP, together with two flanking Alu primer sets, the duplex approach can be used to reduce the amount of DNA needed. Furthermore, the amplification of internal bands excludes the possibility of false negative presence bands of the Alu element. With this approach, only one PCR is necessary to show the presence or absence of two Alu elements simultaneously. This means that only a quarter as much DNA is needed.
The unsuccessful amplification of the presence bands might indicate that the fragment size of the aDNA is too short. However, Kothe et al. [50] showed that, for the samples DO 1911 and DO 3756, the presence band of Alu 19 can be amplified. Hence, the fragment sizes of the samples are not too short. Therefore, we assume that the amplification of the shorter internal bands is favored, due to more targets. Thus, an unsuccessful amplification of presence bands does not necessarily mean that the DNA of a sample has only short fragment sizes. However, when working with aDNA samples, the phenomenon of allelic drop-out is common. Especially large alleles are usually affected by allelic dropout [59]. As Kothe et al. [50] already mentioned in their study, loci with exclusively absence bands should be checked with an IAP. We can confirm this in case of Alu 9, the samples DO 1911 and DO 3756 are in fact heterozygous instead of homozygous absence.
Not every investigated locus showed the same results in terms of successful amplifications. The most successful screening was achieved with Alu 34. In this locus, the primer design was based on GenBank sequences with and without Alu 34 insertion. Usually primer design was based on sequences with the Alu insertion only, due to the lack of sequences of the ancestral (absence) state, in which the Alu element was not inserted. Alu 9 was chosen for a duplex PCR, because in the earlier study [50], singleplex PCR showed intensive bands. Further investigations of why this locus showed less intense internal bands than Alu 34 revealed that it is inserted into another TE. This led to the hypothesis that the flanking Alu primers could be consumed at unspecific amplicons, causing less intense signals from fragments. According to RepeatMasker, the TE belongs to the class of Long Terminal Repeats (LTRs), to the family of endogenous retrovirus elements (ERV), and to the subfamily of endogenous retrovirus-like elements (ERV-L). These elements have only a low copy number of 200 [65] and can be found in eutherian species. Therefore, it is evolutionarily older than the inserted Alu element. Many such TE in TE insertions are found in present-day genomes. For example, Alu retroposon activity can be investigated using a computational algorithm called TinT [66]. Moreover, the BLAST search showed only sequences and amplicons with the inserted Alu 9. This makes it unlikely that the primer set has multiple target sites in the human genome [65]. Besides, Alu insertions and other SINEs have been successfully used to explain events in evolution and are well-established molecular markers [50]. For example, they describe a greater genetic diversity in African human populations [30] and that a small population of common ancestors of all toothed whales diverged to launch the lineages of sperm whales and dolphins [34]. Furthermore, it was shown that human polymorphic TEs are substantial geographically differentiated with many population-specific TE insertions [41].
The unspecific amplicons in Alu duplex 1 and 2 can be observed between 200 and 300 bp. It is possible that the IAP alone generates amplicons by itself [60]. However, a PCR with this primer alone was carried out in a pretest. No unspecific amplicons could be observed as in both of the Alu duplex PCRs. Moreover, neither in the singleplex PCRs (Alu 9 and Alu 19) by Kothe et al. [50], nor in our singleplex pretests of all four investigated Alu elements could we observe these unspecific amplicons. The question of which primer set causes these unspecific amplicons remains unresolved, but sequencing results show that the absence and internal fragments are authentic.
Our study demonstrates the advantage of the duplex approach using aDNA, and therefore highlights a new aspect of TE research that was not investigated in our previous study by Kothe et al. [50]. In the latter study, the approximately 500-bp aDNA amplicon was occasionally detected using both Alu flanking primers, but only in well-preserved aDNA samples. We showed the possibility of duplex Alu screening in even more fragmented aDNA samples and of reducing the amount of material needed.
4.2. Authenticity of Samples
The second STR typing showed two incongruent results, in contrast to earlier genetic fingerprints. The incongruent alleles of DO 1471 and DO 187 did not match the known STR profiles of these two samples. The alleles do not match the researchers’ STR typing or any other sample used in this study, excluding this as a possible source of contamination. Therefore, it is likely that the contaminations were caused by allele drop-in [59,67] or that the non-concordant alleles are caused by stochastic effects because of a low amount of template [68,69]. However, measuring DNA quantities did not confirm this.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at www.mdpi.com/1424-2818/9/4/48/s1, Table S1: Individuals, bone numbers, bones, degrees of DNA preservation, and amount of DNA, Table S2: Alu positions, Table S3: Sequences of Alu duplex 1 bands of sample DO 3756, Table S4: STR typing.
Acknowledgments
First, thanks to the laboratory staff for help in various steps in the laboratory work. Furthermore, thanks to Verena Seidenberg for her advice concerning the Lichtenstein individuals used in this study. We also want to thank Stefan Flindt from the Landkreis Osterode am Harz (Kreisarchäologie) Lower Saxony for allowing the use of the invaluable sample material. Last, we thank Diana Kumar for language polishing of this manuscript.
Author Contributions
Fabian Haß, Susanne Hummel and Oliver Piskurek conceived and designed the experiments. Fabian Haß performed most of the experiments. Fabian Haß and Oliver Piskurek analyzed the data. Fabian Haß drafted most parts of the manuscript and Fabian Haß and Oliver Piskurek wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Miller, W.J.; Capy, P. Mobile Genetic Elements as Natural Tools for Genome Evolution. In Mobile Genetic Elements: Protocols and Genomic Applications; Miller, W.J., Capy, P., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 260, pp. 1–20. ISBN 978-1-58829-007-6. [Google Scholar]
- Volff, J.-N. Turning junk into gold: Domestication of transposable elements and the creation of new genes in eukaryotes. BioEssays News Rev. Mol. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2006, 28, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piskurek, O.; Jackson, D.J. Transposable elements: From DNA parasites to architects of metazoan evolution. Genes 2012, 3, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estecio, M.R.H.; Gallegos, J.; Dekmezian, M.; Lu, Y.; Liang, S.; Issa, J.-P.J. SINE retrotransposons cause epigenetic reprogramming of adjacent gene promoters. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 1332–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.S.; Boeke, J.D. LINE-1 retrotransposons: Modulators of quantity and quality of mammalian gene expression? BioEssays News Rev. Mol. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2005, 27, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peaston, A.E.; Evsikov, A.V.; Graber, J.H.; de Vries, W.N.; Holbrook, A.E.; Solter, D.; Knowles, B.B. Retrotransposons regulate host genes in mouse oocytes and preimplantation embryos. Dev. Cell 2004, 7, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lander, E.S.; Linton, L.M.; Birren, B.; Nusbaum, C.; Zody, M.C.; Baldwin, J.; Devon, K.; Dewar, K.; Doyle, M.; FitzHugh, W.; et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 2001, 409, 860–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Koning, A.P.J.; Gu, W.; Castoe, T.A.; Batzer, M.A.; Pollock, D.D. Repetitive Elements May Comprise Over Two-Thirds of the Human Genome. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Flores, I.; Garrido-Ramos, M.A. The Repetitive DNA Content of Eukaryotic Genomes; Karger Publishers: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 7, ISBN 978-3-318-02150-9. [Google Scholar]
- Feschotte, C.; Pritham, E.J. DNA Transposons and the Evolution of Eukaryotic Genomes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2007, 41, 331–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostertag, E.M.; Kazazian, H.H., Jr. Biology of mammalian L1 retrotransposons. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2001, 35, 501–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohshima, K.; Hamada, M.; Teral, Y.; Okada, N. The 3′ Ends of tRNA-Derived Short Interspersed Repetitive Elements Are Derived from the 3′ Ends of Long Interspersed Repetitive Elements. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 3756–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewannieux, M.; Esnault, C.; Heidmann, T. LINE-mediated retrotransposition of marked Alu sequences. Nat. Genet. 2003, 35, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, N.; Hamada, M.; Ogiwara, I.; Ohshima, K. SINEs and LINEs share common 3′ sequences: A review. Gene 1997, 205, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajikawa, M.; Okada, N. LINEs Mobilize SINEs in the Eel through a Shared 3′ Sequence. Cell 2002, 111, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriegs, J.O.; Churakov, G.; Jurka, J.; Brosius, J.; Schmitz, J. Evolutionary history of 7SL RNA-derived SINEs in Supraprimates. Trends Genet. TIG 2007, 23, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houck, C.M.; Rinehart, F.P.; Schmid, C.W. A ubiquitous family of repeated DNA sequences in the human genome. J. Mol. Biol. 1979, 132, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullu, E.; Tschudi, C. Alu sequences are processed 7SL RNA genes. Nature 1984, 312, 171–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quentin, Y. Origin of the Alu family: A family of Alu-like monomers gave birth to the left and the right arms of the Alu elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 3397–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewannieux, M.; Heidmann, T. Role of poly(A) tail length in Alu retrotransposition. Genomics 2005, 86, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deininger, P. Alu elements: Know the SINEs. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurka, J.; Smith, T. A fundamental division in the Alu family of repeated sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 4775–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batzer, M.A.; Deininger, P.L.; Hellmann-Blumberg, U.; Jurka, J.; Labuda, D.; Rubin, C.M.; Schmid, C.W.; Ziętkiewicz, E.; Zuckerkandl, E. Standardized nomenclature for Alu repeats. J. Mol. Evol. 1996, 42, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, E.A.; Keller, H.; Mills, R.E.; Schmidt, S.; Moran, J.V.; Weichenrieder, O.; Devine, S.E. Active Alu retrotransposons in the human genome. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 1875–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Song, L.; Gonder, M.K.; Azrak, S.; Ray, D.A.; Batzer, M.A.; Tishkoff, S.A.; Liang, P. Whole genome computational comparative genomics: A fruitful approach for ascertaining Alu insertion polymorphisms. Gene 2006, 365, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, A.L.; Eskin, E.; Pevzner, P.A. Whole-genome analysis of Alu repeat elements reveals complex evolutionary history. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 2245–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Lagemaat, L.N.; Gagnier, L.; Medstrand, P.; Mager, D.L. Genomic deletions and precise removal of transposable elements mediated by short identical DNA segments in primates. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batzer, M.A.; Deininger, P.L. Alu repeats and human genomic diversity. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piskurek, O.; Okada, N. Poxviruses as possible vectors for horizontal transfer of retroposons from reptiles to mammals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 12046–12051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoneking, M.; Fontius, J.J.; Clifford, S.L.; Soodyall, H.; Arcot, S.S.; Saha, N.; Jenkins, T.; Tahir, M.A.; Deininger, P.L.; Batzer, M.A. Alu Insertion Polymorphisms and Human Evolution: Evidence for a Larger Population Size in Africa. Genome Res. 1997, 7, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikaido, M.; Rooney, A.P.; Okada, N. Phylogenetic relationships among cetartiodactyls based on insertions of short and long interpersed elements: Hippopotamuses are the closest extant relatives of whales. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 10261–10266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishihara, H.; Maruyama, S.; Okada, N. Retroposon analysis and recent geological data suggest near-simultaneous divergence of the three superorders of mammals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5235–5240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shedlock, A.M.; Okada, N. SINE insertions: Powerful tools for molecular systematics. BioEssays News Rev. Mol. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2000, 22, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikaido, M.; Piskurek, O.; Okada, N. Toothed whale monophyly reassessed by SINE insertion analysis: The absence of lineage sorting effects suggests a small population of a common ancestral species. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 43, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rishishwar, L.; Wang, L.; Clayton, E.A.; Mariño-Ramírez, L.; McDonald, J.F.; Jordan, I.K. Population and clinical genetics of human transposable elements in the (post) genomic era. Mob. Genet. Elem. 2017, 7, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancks, D.C.; Kazazian, H.H. Roles for retrotransposon insertions in human disease. Mob. DNA 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftus, A.; Murphy, G.; Brown, H.; Montgomery, A.; Tabak, J.; Baus, J.; Carroll, M.; Green, A.; Sikka, S.; Sinha, S. Development and validation of InnoQuant® HY, a system for quantitation and quality assessment of total human and male DNA using high copy targets. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2017, 29, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, M.L.; Roy-Engel, A.M.; Nguyen, S.V.; Salem, A.H.; Vogel, E.; Vincent, B.; Myers, J.; Ahmad, Z.; Nguyen, L.; Sammarco, M.; et al. Large-scale analysis of the Alu Ya5 and Yb8 subfamilies and their contribution to human genomic diversity. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 311, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, A.B.; Salem, A.H.; Hedges, D.J.; Keegan, C.N.; Kimball, B.; Walker, J.A.; Watkins, W.S.; Jorde, L.B.; Batzer, M.A. Genome-wide analysis of the human Alu Yb-lineage. Hum. Genom. 2004, 1, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otieno, A.C.; Carter, A.B.; Hedges, D.J.; Walker, J.A.; Ray, D.A.; Garber, R.K.; Anders, B.A.; Stoilova, N.; Laborde, M.E.; Fowlkes, J.D.; et al. Analysis of the human Alu Ya-lineage. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 342, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rishishwar, L.; Tellez Villa, C.E.; Jordan, I.K. Transposable element polymorphisms recapitulate human evolution. Mob. DNA 2015, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkan, C.; Sajjadian, S.; Eichler, E.E. Limitations of next-generation genome sequence assembly. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, B.A.; Scheetz, T.E.; Mullins, R.F.; DeLuca, A.P.; Hoffmann, J.M.; Johnston, R.M.; Jacobson, S.G.; Sheffield, V.C.; Stone, E.M. Exome sequencing and analysis of induced pluripotent stem cells identify the cilia-related gene male germ cell-associated kinase (MAK) as a cause of retinitis pigmentosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E569–E576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treangen, T.J.; Salzberg, S.L. Repetitive DNA and next-generation sequencing: Computational challenges and solutions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 13, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huddleston, J.; Ranade, S.; Malig, M.; Antonacci, F.; Chaisson, M.; Hon, L.; Sudmant, P.H.; Graves, T.A.; Alkan, C.; Dennis, M.Y.; et al. Reconstructing complex regions of genomes using long-read sequencing technology. Genome Res. 2014, 24, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofreiter, M.; Paijmans, J.L.A.; Goodchild, H.; Speller, C.F.; Barlow, A.; Fortes, G.G.; Thomas, J.A.; Ludwig, A.; Collins, M.J. The future of ancient DNA: Technical advances and conceptual shifts. BioEssays News Rev. Mol. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2015, 37, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakuda, T.; Shojo, H.; Tanaka, M.; Nambiar, P.; Minaguchi, K.; Umetsu, K.; Adachi, N. Multiplex APLP System for High-Resolution Haplogrouping of Extremely Degraded East-Asian Mitochondrial DNAs. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidenberg, V.; Schilz, F.; Pfister, D.; Georges, L.; Fehren-Schmitz, L.; Hummel, S. A new miniSTR heptaplex system for genetic fingerprinting of ancient DNA from archaeological human bone. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2012, 39, 3224–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Talwar, I.; Sandhu, H.S.; Matharoo, K.; Bhanwer, A.J.S. Genetic dissection of five ethnic groups from Punjab, North-West India—A study based on Autosomal Markers. Leg. Med. 2017, 26, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kothe, M.; Seidenberg, V.; Hummel, S.; Piskurek, O. Alu SINE analyses of 3000-year-old human skeletal remains: A pilot study. Mob. DNA 2016, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flindt, S. Die Lichtensteinhöhle bei Osterode, Landkreis Osterode am Harz: Eine Opferhöhle der jüngeren Bronzezeit im Gipskarst des südwestlichen Harzrandes: Forschungsgeschite und erste Grabungsergebnisse. Die Kunde N. F. 1996, 47, 435–466. [Google Scholar]
- Flindt, S.; Hummel, S. Die Lichtensteinhöhle: Bestattungsplatz einer Großfamilie aus der Bronzezeit; HöhlenErlebnisZentrum: Bad Grund, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Höss, M.; Jaruga, P.; Zastawny, T.H.; Dizdaroglu, M.; Paabo, S. DNA Damage and DNA Sequence Retrieval from Ancient Tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996, 24, 1304–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, J.; Hummel, S.; Hermann, B.; Henke, W. DNA preservation: A microsatellite-DNA study on ancient skeletal remains. Electrophoresis 1999, 20, 1722–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidenberg, V. Ein Bronzezeitlicher Familienclan als Genetisches Archiv—Morphologisch-Paläogenetische Bearbeitung des Skelettkollektivs aus der Lichtensteinhöhle. Ph.D. Thesis, Georg-August-Universität, Göttingen, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Frischalowski, M. Examinaton of DNA Preservation in the Skeletal Remains from a Historic Burial Site in Eldagsen/Lower Saxony. Master’s Thesis, Georg-August-Universität, Göttingen, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pepperl, J. Immungenetische Marker im Wandel der Zeit. Ph.D. Dissertation, Georg-August-Universität, Göttingen, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Smit, A.F.A.; Hubley, R.; Green, P. Repeatmasker. 2013. Available online: http://www.repeatmasker.org (accessed on 27 July 2016).
- Hummel, S. Ancient DNA Typing: Methods, Strategies and Applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003; ISBN 3-662-05050-1. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.L.; Ledbetter, S.A.; Corbo, L.; Victoria, M.F.; Ramírez-Solis, R.; Webster, T.D.; Ledbetter, D.H.; Caskey, C.T. Alu polymerase chain reaction: A method for rapid isolation of human-specific sequences from complex DNA sources. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 6686–6690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiagen. Qiagen QIAquick Gel Extraction Kit. QIAquick® Spin Handbook; Qiagen: Hilden, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- New England Biolabs® Inc. Monarch® DNA Gel Extraction Kit: Instruction Manual; New England Biolabs® Inc.: Ipswich, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Macherey & Nagel. Macherey-Nagel NucleoSEQ®: Clean-Up of Sequencing Reactions User Manual; Macherey & Nagel: Düren, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hall BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98.
- Bénit, L.; Lallemand, J.-B.; Casella, J.-F.; Philippe, H.; Heidmann, T. ERV-L Elements: A Family of Endogenous Retrovirus-Like Elements Active throughout the Evolution of Mammals. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 3301–3308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Churakov, G.; Grundmann, N.; Kuritzin, A.; Brosius, J.; Makalowski, W.; Schmitz, J. A novel web-based TinT application and the chronology of the Primate Alu retroposon activity. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, T.; Hummel, S.; Herrmann, B. Evidence of contamination in PCR laboratory disposables. Naturwissenschaften 1995, 82, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, P.; Whitaker, J.; Flaxman, C.; Brown, N.; Buckleton, J. An investigation of the rigor of interpretation rules for STRs derived from less than 100 pg of DNA. Forensic Sci. Int. 2000, 112, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J. Advanced Topics in Forensic DNA Typing: Interpretation; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-0-12-405213-0. [Google Scholar]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).