Abstract
Outbreaks of the coral-eating crown-of-thorns seastar (Acanthaster cf. solaris) threaten coral reefs of the Indo-Pacific. Movement patterns may play an important role in the spread of outbreak populations, but studies investigating adult movement behavior are scarce. It remains unknown if Acanthaster cf. solaris orientates in inter-reef areas using chemical, visual, or mechanical cues (e.g., water currents) or which trigger is used for the onset of movement. We investigated the movement patterns of adult starved, fed, and blinded A. cf. solaris on sand at two sites with different unidirectional water current strengths. We found that the movement direction of the seastars in strong currents was downstream, whereas movement in weaker currents was random and independent from the current direction. However, the directionality of movement was consistently high, independent of the nutritional state, its visual abilities, or current strength. Starved A. cf. solaris started to move significantly faster compared to fed individuals. Therefore, starvation might trigger the onset of movement. Our findings indicate that navigation of A. cf. solaris in inter-reef areas is inefficient. Movements between reefs may be random or current-dependent and finding a new reef from a distance subject to chance, unless it is only few meters away.
1. Introduction
Coral eating crown-of-thorns seastars (Acanthaster cf. solaris) are abundant inhabitants of many coral reefs. Their specialized diet and frequent occurrence in high-density populations have caused extensive damage to coral reefs in the Indo-Pacific region for several decades [1]. During population outbreaks thousands of adult individuals may appear on a reef and move across it in feeding-bands [2]. Over time, local coral resources get depleted and the moving seastars reach the end of a reef or face a channel. In these situations A. cf. solaris may leave its preferred reef substrate and move on the bare sandy bottom in the search of reef areas with sufficient coral cover [3,4,5,6]. Although the spatial scales and individual numbers of migrations are not yet known, migrating adult A. cf. solaris may subsequently contribute to the spread of outbreak populations or cause other reefs to be infected [7,8]. Therefore, it is of considerable interest what triggers the onset of their movement and what cues might be used by A. cf. solaris to direct their movement and orientate themselves between reefs, on sandy substrate bare of suitable food.
Several variables have been proposed to influence the movements of A. cf. solaris: density of corals, exposure to wave action, temperature, time of day, light, and type of substratum, but also age or size, condition, or nutritional state [9,10,11]. Most of these variables, however, only influence the speed of seastar movement or cause the seastar to actively avoid unpleasant areas. The direction of movement, however, may be guided by the presence of visual cues [12,13,14], chemical cues (from food [15], predators [16], or conspecifics [17]), or water currents [18]. The visual sense of A. cf. solaris was shown to be involved in navigation on sand towards reef structures from a distance of several meters [13,14]. To successfully navigate between reefs, however, the reef structures have to be in sight, limiting the use of visual cues for long distance orientation on large, bare, sandy areas [14]. It is commonly assumed that A. cf. solaris navigate using their well-developed chemical sense [19]. However, chemoreception in seastars has only proven its functionality over short distances [20]. If chemoreception is used from a distance, then chemical cues need to be carried towards the seastar by water currents. The seastars may then follow a gradient of prey odors towards their source [21]. For A. cf. solaris navigating towards its coral food on the reef using chemoreception may be difficult, as the cues from corals are omnipresent and the flow patterns may be intricate and turbulent [14,22]. However, localization of prey using chemical cues is most effective in subtidal environments and where currents flow in one direction [20], and this may be the case in inter-reef areas. Seastars are also known to combine chemotaxis with their ability to perceive the mechanical stimulation by currents (rheotaxis). In the presence of chemical cues from food they may show positive rheotaxis (moving against the current) [22,23,24] or cross-current movement [18]. Stronger currents may thereby enhance the capability of seastars to locate their prey [18]. In this context, the responsiveness to chemical cues from food is frequently increased by starvation [25,26,27,28] and also results in a more consistent movement behavior [18]. This may help A. cf. solaris to overcome even larger distances between reefs where no food is available.
We aimed to investigate the potential of adult A. cf. solaris to navigate between reefs. In particular, we tried to identify cues, which may be used for orientation and factors, which trigger the onset of movement. We therefore analyzed the movement patterns of starved, fed and blinded A. cf. solaris in the field on sandy substrates under different strengths of water currents. Depending on the senses (vision, chemoreception, or mechanoreception) A. cf. solaris might use for orientation, we expected to see differences in movement patterns between treatments, such as an orientation of the seastars towards the reef or along water currents. In particular, we expected starved seastars to show the most directional movement and an orientation towards the reef (food source), while fed seastars may be less directed in their movement, but still being oriented towards the reef (seeking food and shelter). Blinded seastars should either not differ in their movement patterns from starved or fed, if the chemical sense is primarily used for orientation between reefs, or should show different movement patterns, if the visual sense is used for orientation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
Two sites on the island Mo’orea, Society Islands, French Polynesia (Figure 1a,c), named Temae (in the northwest; 17°29′52.43′′ S; 149°45′28.61′′ W) and Maharepa (in the north; 17°28′52.79′′ S; 149°48′56.99′′ W) were chosen for the experiments. Both areas consisted of sandy ground with few interspersed living coral heads. At both sites the water carried towards the seastars had to pass the reef crest before entering the sandy experimental area and may, therefore, have carried chemical cues from corals.
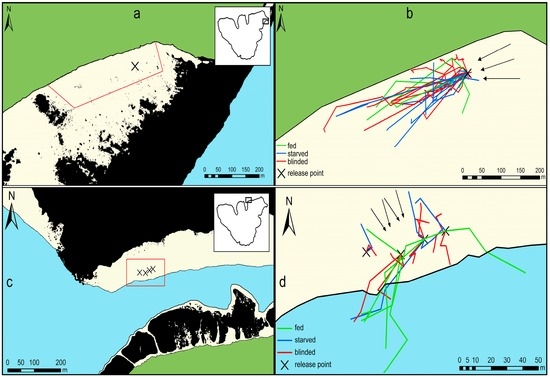
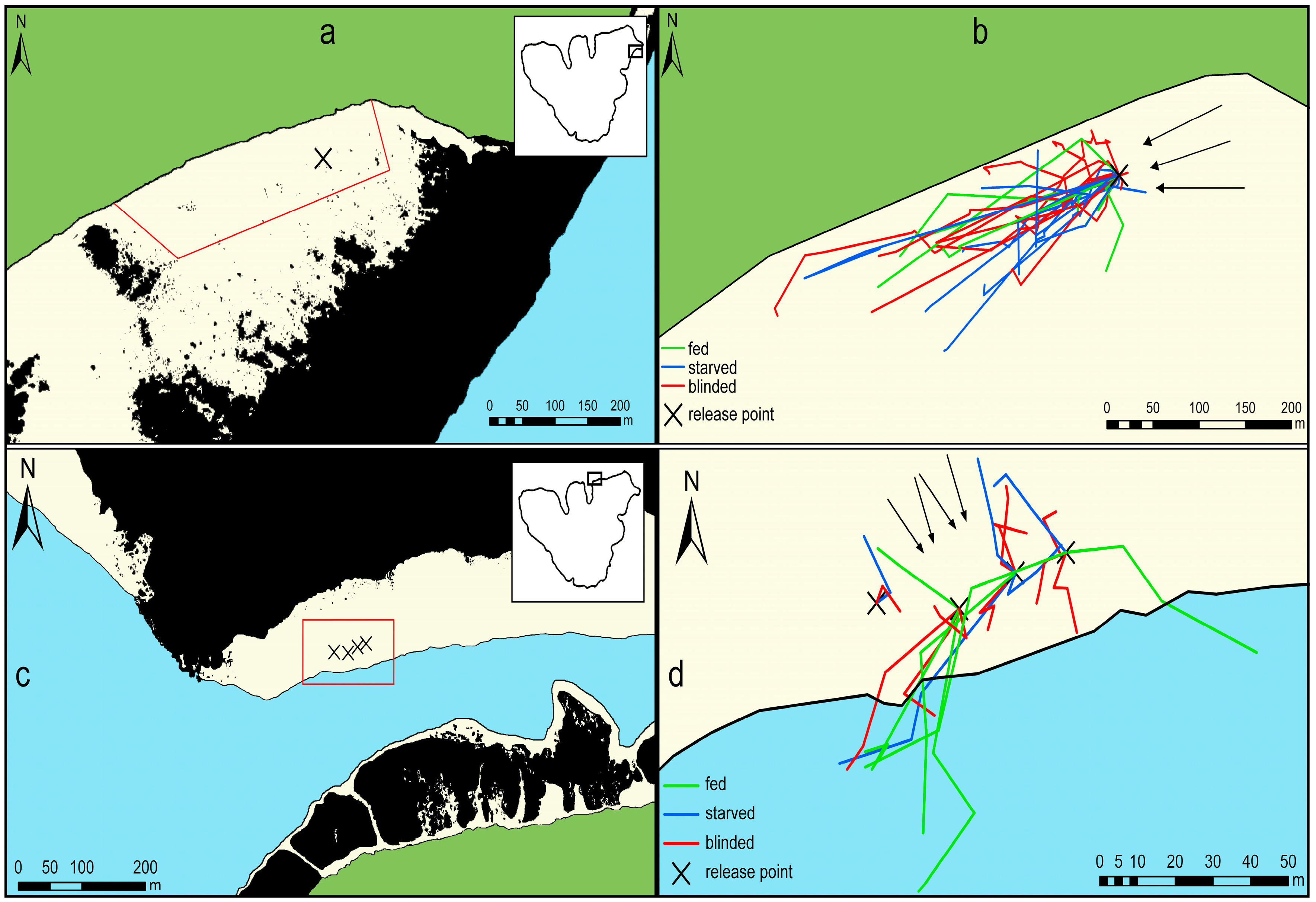
Figure 1.
Experimental sites and movement tracks of Acanthaster cf. solaris on sand. The green-colored area is land and the beige-colored areas consist of sandy substrate at water depths of 0–5 m. The blue-colored area represents water depths of >5 m. The black line represents the shoreline or the division of water depth greater or smaller than 5 m. Black areas represent reef areas with >30% hard substrate. (a) Overview of the experimental site Temae. The red line indicates the area that was systematically searched for A. cf. solaris six times a day. The box in the upper right shows the position of the experimental site around the Island of Mo’orea; (b) movement tracks of A. cf. solaris in Temae (strong current) recorded during a 2.5-week period. Arrows indicate the direction of the current; (c) overview of the experimental site Maharepa. The red box indicates the area that was systematically searched for A. cf. solaris hourly for 3 h. The box in the upper right shows the position of the experimental site around the Island of Mo’orea; and (d) movement tracks of A. cf. solaris in Maharepa (weaker current) recorded during 3 h over a period of three days. Arrows indicate the direction of the current.
Temae was situated in a large lagoon that was delimited by a sandy beach to the west and otherwise surrounded by fringing or patch reefs on each side. The starting point was located approximately 50 m from the beach and 370 m from the surrounding atoll reef crest at a water depth of about 2.5 m. A consistent, relatively strong current (>0.15 m·s−1), whose direction was independent from the tides was running from north to south, more or less parallel to the beach (Figure 1a,b).
Maharepa was located at a sandflat behind a backreef in about 3–5 m depth. To the south of the sandflat the ground dropped into a channel, which was approximately 25 m deep. The incoming tides produced a current, approximately 40% weaker than in Temae, that ran over the fringing reef towards to shore. We timed the experiments with the incoming tides so that they produced a consistent current over the reef perpendicular to the shore (Figure 1c,d).
Although one location was chosen in the lagoon and the other at the backreef, both areas provided similar conditions as both were downstream of an outer reef (for Maharepa this accounts only for the incoming tide), both had comparable water depths (2.5 m vs. 3–5 m), and at both the ground was covered to almost 100% by sand.
2.2. General Experimental Procedure
The experiments took place in November and December 2013. A. cf. solaris were collected at several locations around Mo’orea and transported to the R.B. Gump South Pacific Research Station. Eleven individuals each (diameter ~25–45 cm) were randomly assigned to the treatments ‘starved’, ‘fed’, and ‘blinded’ for each of the two experimental sites. Individuals of the “starved” treatment were kept without food in large plastic bins supplied with seawater from the ocean for 3–6 weeks. Individuals for the “fed” and “blinded” treatment were collected 1–4 days prior to the experiment and transported to the station. Individuals in the ‘blinded’ treatment were anaesthetized using 3.5% magnesium-chloride hexahydrate (Mg2Cl × 6H2O) mixed with seawater (procedure adapted from Messenger et al. [29]) prior to dissection. Subsequently the terminal ossicle harboring the terminal tube foot containing the compound eye was carefully removed using a pair of scissors one day prior to the experiments.
Depending on the experimental site the seastars were transported either by car (Temae) or by boat (Maharepa) in large coolers filled with seawater (duration of transport approximately 25 min and 15 min, respectively). A. cf. solaris were marked individually using numbered plastic tags (~12 × 15 mm pieces of flagging tape) pulled over an aboral spine. The seastars were released in a shelter (size approximately 50 × 50 × 30 cm) built out of dead coral rock that was collected within a radius of 150 m. The shelter was used to allow the seastars to start moving freely without influencing their initial movement direction and to provide them with a safe hiding place so that the onset of movement was not influenced by handling and exposure. At the same time this design had the disadvantage that not all individuals actually had moved out of the shelters after 1–3 h, therefore, different sample sizes emerged for the observations on movement directions. Additionally, not all seastars could be recaptured after 3 h.
In Temae one shelter was constructed and three seastars (one individual from each treatment) were placed in the shelter on each day a trial was conducted. In total, 11 trials were conducted during 2.5 weeks (Supplementary Materials Figure S1) resulting in 33 individuals released during this period of time. The tagged individuals were not collected after release to enable the recording of their movement over the period of 2.5 weeks. The experiment always started at 10 a.m. and the shelters were visited hourly until 1 p.m. Moreover, they were also checked once in the afternoon (3–4 p.m.) and in the evening (9–10 p.m.), in order to record how long A. cf. solaris individuals were staying in the shelters, if they had not left after 3 h. Additionally, at these times a large area around the release point was searched systematically by snorkeling transects parallel to the shore using a compass and underwater landmarks and the positions of the seastars were recorded (Figure 1a).
The experiment in Maharepa consisted of 10 trials, which were performed during three consecutive days. Four shelters were built in a line parallel to the reef of which only three were used in the first two days and the fourth only at the third day of the experiment. After each trial the released individuals were collected and transported back to the research station. The shelters were slightly smaller than the one built in Temae, measuring approximately 30 × 30 × 30 cm. To prevent potential effects of higher densities of conspecifics in the area as compared to Temae, shelters were set up approximately 20 m apart. This ensured that individuals were not able to detect each other by visual means [14]. In addition, the direction of the prevailing current should have prevented the seastars released in each shelter to sense each other chemically because it ran perpendicular to the row of shelters. The release procedure was identical to that described in Temae, placing one individual of each treatment in one shelter, with the only exception that all three to four shelters were equipped with seastars quickly one after another. A. cf. solaris movements were tracked using GPS (GPSMap 60 CSx; Garmin International, Inc., Olathe, KS, USA) hourly for 3 h after they were released.
The displacement and the direction of movement were analyzed using ArcMap (ArcGIS 10.2.1, ESRI, Redlands, CA, USA) and the ArcMET tool [30]. The water current direction was determined to the nearest 5° using a compass and an underwater plastic flag and checked during the experiments to ensure it was not changing. The strength of the current was determined each day prior to the start of the experiment using a neutrally buoyant plastic piece allowed to drift underwater for 2 m and a stopwatch. The mean of three such measurements was considered as the current velocity.
2.3. Data Analysis
To test for a preferred movement direction in A. cf. solaris the compass headings obtained after one and three hours, and several days of movement, were analyzed using the Rao’s spacing test. This test was applied because the data were partly diametrically bimodal and violated the von Mises distribution assumption [31]. The directionality of movement (a measure of how close the movement resembles a straight path) was analyzed by calculating the D:Wall value [32], where D is the shortest distance from the starting point to the end position of the seastar (after three hours of movement) and Wall is the total distance travelled during one observation, thus, the sum of the distances travelled after one, two, and three hours. Moving in a straight line means displaying perfect directional movement and would, therefore, result in a D:Wall value of 1. The smaller the value gets, the less directional the movement is. A D:Wall value of >0.7 is considered to be ‘highly directional’, a value of >0.5 as ‘partly directional’ and a value of <0.5 is ‘undirected’ movement [32,33]. The data on the duration of stay in shelters violated the normality and homogeneity of variances assumptions. Hence, to test for a general difference between treatments in the duration of stay in shelters a Kruskal-Wallis test was applied. Single treatments were then compared using Mann-Whitney tests.
3. Results
The current produced by the tides in Maharepa was generally weaker than the tide-independent current present in Temae (Table 1 and Table 2). The movement tracks of the seastars in Temae during the 2.5-week period are shown in Figure 1b and the ones in Maharepa, recorded during 3 h, in Figure 1d. Most of the individuals from the fed treatment in Temae stayed for more than three hours in the shelter provided; therefore, no data on movement patterns could be obtained on them during this time. However, their movement patterns could be obtained from the observation for several days (Section 3.3). The mean distances covered by A. cf. solaris during 1 and 3 h of movement, from which the directionality of movement was calculated, are shown in Table 3. The observation of the seastars during all experiments revealed that they always actively moved using their tube feet, even in strong currents, and were not passively transported by them.

Table 1.
Mean movement direction of Acanthaster cf. solaris after one hour and test for a preferred direction (Rao’s spacing test) at two sites with respective water current strengths. Note that the circular mean direction is not very meaningful when there is no preferred direction in the seastars’ movement (when Rao’s spacing test is not significant). * Refers to significant test p < 0.05.

Table 2.
Mean movement direction of Acanthaster cf. solaris after 3 h, test for a preferred direction (Rao’s spacing test) and D:Wall value at two sites with respective water current strengths. Note that the circular mean direction is not very meaningful when there is no preferred direction in the seastars movement (when Rao’s spacing test is not significant). * Refers to significant test p < 0.05.

Table 3.
Mean distance covered after one and three hours of A. cf. solaris.
3.1. Movement Patterns after One Hour
In Temae (strong current, see Table 1) starved A. cf. solaris showed significant preference for a common direction of movement and blinded A. cf. solaris tended towards a common directional preference that approximately resembled the direction of the currents present (255°–270°). For fed individuals a statistical analysis was not possible, as only one individual had left the shelter after 1 h. In Maharepa (weak current, see Table 1) no common preference for a certain direction could be detected in any of the treatments (Table 1). The water currents in Maharepa came from between 320° and 340° and no general rheotactic orientation could be detected in the movement tracks of the seastars.
3.2. Movement Patterns after Three Hours
The directionality of movement of individual A. cf. solaris was high (D:Wall value ≥0.7), regardless of site or treatment. Starved and blinded A. cf. solaris in Temae showed a significant preferred direction of movement that resembled the direction of the currents present (255°–270°). In contrast, no preferred direction could be observed in blinded, starved or fed A. cf. solaris at the location with weaker currents i.e., Maharepa (Table 2).
3.3. Movement Patterns after Several Days in Temae
The analysis of the positions of A. cf. solaris from all treatments after more than 3 h of movement revealed a significant common directional preference (Rao’s spacing test: fed (N = 11): U = 244, p < 0.001, circular mean direction: 245°; starved (N = 8): U = 248.2, p = 0.002, circular mean direction: 235°; blinded (11): U = 208, p = 0.001, circular mean direction: 248°) to move downstream (Figure 1b, Table S1). Only one individual from the blinded treatment and one from the starved treatment had its last recorded position upstream of the release point. The amount of time the movement of single individuals could be tracked was between 3 h and 11 days, however, most individuals could not be followed for longer than six days. Additionally, the tracking time was shortened, as some individuals did not leave the shelter for several hours or days (see Section 3.4). For an overview of release and tracking times, and numbers and distances moved, please see Figure S1.
3.4. Duration of Stay in a Shelter
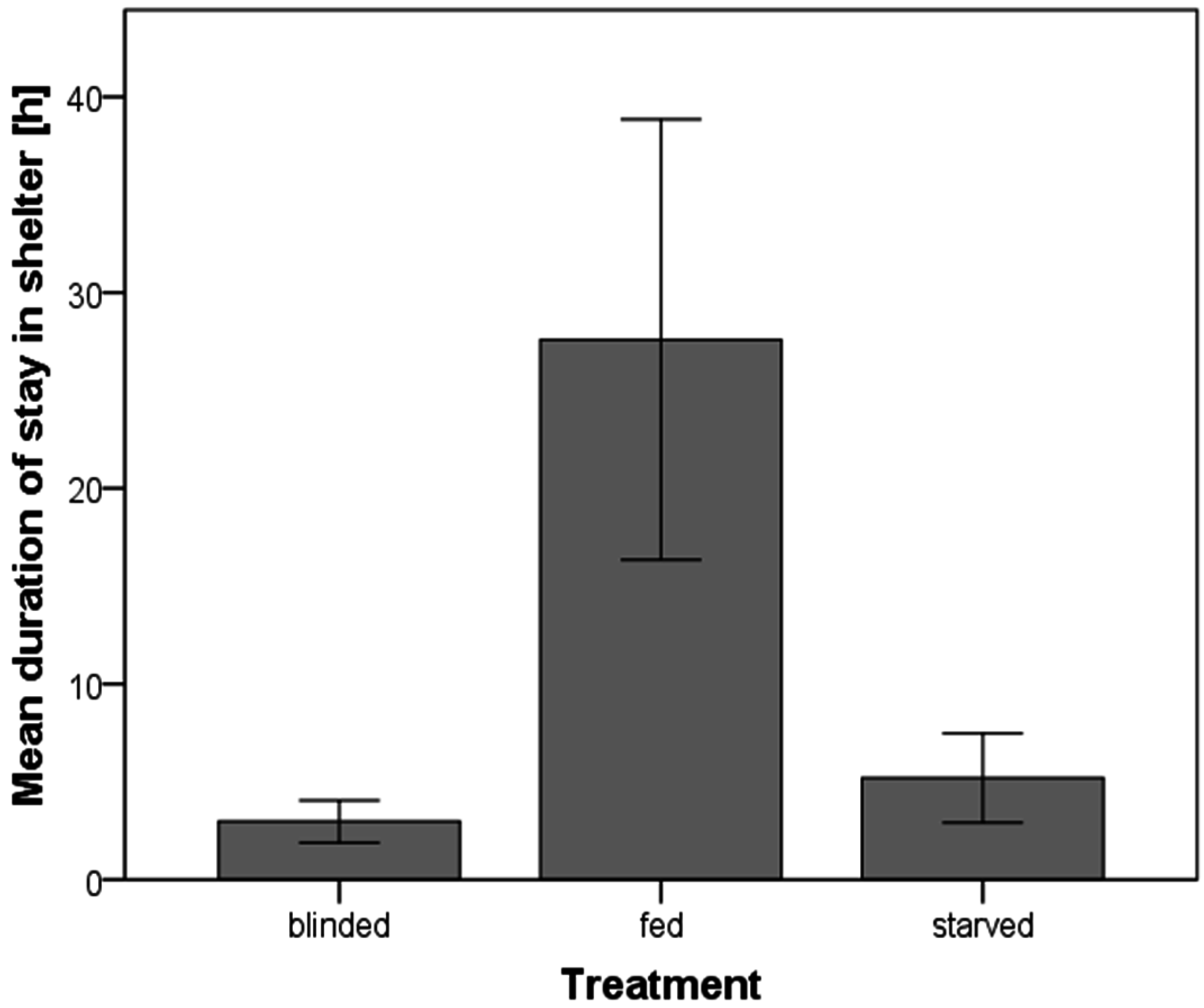
A. cf. solaris from different treatments significantly differed in the time they stayed in the shelter (Kruskal-Wallis test; p = 0.013). Starved A. cf. solaris stayed for a significantly shorter time in the shelter than fed ones (Mann-Whitney-Test; U = 27.5, p = 0.028). Fed individuals remained in the shelter for 28 ± 11 h. All except one fed individual stayed longer than one hour and one fed individual stayed for five days in the shelter. In contrast, the starved individuals left the shelter after 5 ± 2 h and half of the starved A. cf. solaris left the shelter less than one hour after their release. Blinded individuals did not differ in their duration of stay from starved ones (Mann-Whitney-Test; U = 51.0, p > 0.05), but differed significantly from fed ones, too (Mann-Whitney-Test; U = 21.5, p = 0.008, Figure 2).
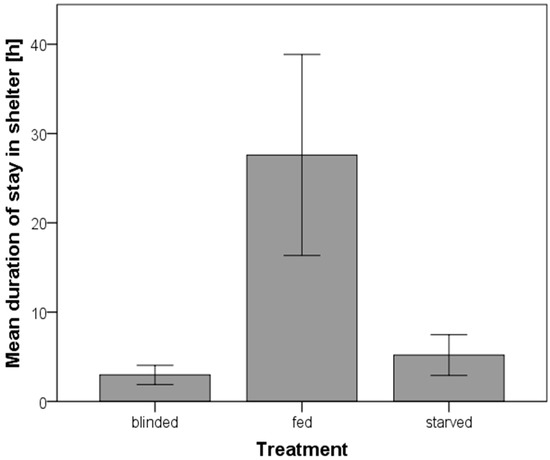
Figure 2.
Mean duration of stay in a shelter of Acanthaster cf. solaris. Error bars represent the standard error.
4. Discussion
A trigger for A. cf. solaris to start its movements between reefs may be its state of nourishment. Our experiment showed that starved individuals left a safe shelter almost immediately after they were placed there, indicating that a poor nutritional state induces migration towards a new food patch. In contrast, fed individuals stayed there, sometimes for days. Blinded individuals were also in a good nutritional state, but started as early as starved individuals, a behavior that contradicts the hypothesis that nourishment induces movement. However, blinded individuals were obviously not behaving like starved or fed individuals. Some of them ended up very close to the shore (in Temae) and when they were recaptured they were often moving on sand, while others had found a small reef block to hide or feed. This supports the finding that vision is playing an important role in the orientation of A. cf. solaris [13,14]. At the same time, the lack of visual information may have caused their early departure, as they may not have recognized being in a safe location, in the shade of a shelter.
The analysis of the movement patterns after the seastars had left the shelter indicate that there is a relationship between the strength of the water current and the direction of A. cf. solaris movements on sand. Surprisingly, in strong current A. cf. solaris followed its direction and showed negative rheotaxis independent of their nutritional state or their ability to see, even after several days of observation. This behavior is uncommon as often seastars show positive rheotaxis [22,34,35,36], even in the absence of chemical cues in the water [24]. Castilla and Crisp [34] found a reversal of the normally observed positive rheotaxis in Asterias rubens in the laboratory to be caused by the following factors: a sudden increase of the sea water temperature, a reduction of the sea water salinity below 25‰ S, a drop in the oxygen tension below 4.18 mL O2/L, a pH of less than 6.9, and long periods of captivity under starvation. Although water parameters were not recorded in the study area, such dramatic changes are highly unlikely to have occurred during the experiments, especially given that no storms, heavy rains or swells took place. In addition, strong surge, which is suggested to alter A. cf. solaris movements [37], can be excluded as an influencing factor, as experiments were only performed during very calm seas. Seastars may show negative rheotaxis in the presence of a cue that indicates potential predators or harmful conditions [34]. However, this is also highly unlikely to have caused the observed movement patterns as such reactions have only been shown as a response to an immediate predator cue present in the water [17,38,39] and, therefore, the immediate presence of a predator, which was not observed during the time of the experiment.
A factor that indeed might have caused the negative rheotaxis observed in the present study was starvation. However, blinded individuals also showed negative rheotaxis in strong currents, which is not directly attributable to their nutritional state. Additionally, instead of showing negative rheotaxis, other seastars even enhance their positive responsiveness to cues when starved [18,27,40]. It might be assumed that the sand did not provide enough gripping surface to the tube feet and the seastars might, therefore, have been passively transported by the current rather than actively moving with it [3]. However, the observations made during the experiments show that the seastars moved actively using their tube feet and could still change their direction of movement to the side and that several individuals could also move against the current. One remaining explanation for the observed downstream movement is that the seastars actively move with the current if it is too strong to save energy. The fact that A. cf. solaris showed movement in random directions and no general downstream movement in weaker currents support this hypothesis. In even weaker currents (mean velocity: 0.054 m·s−1) and on shorter timescales, also, no influence of currents on movement direction in A. cf. solaris was observed [32]. The only other field study that investigated movement patterns of tagged A. cf. solaris was conducted on a solid reef structure, not like the present one on sandy substrate. Movement patterns here were random, as in the present study during weak currents, but no clear measurements of current strengths were made stating only that currents moved strongly in ‘both directions parallel to the shore’ [5]. Such inconsistent movement directions as a response to a constant cue were also often found in chemoreception-studies of other seastars (reviewed by Sloan and Campbell [23]). Still, in the present study, random movement directions were consistently shown over all treatments during weak currents. This suggests that either no cue for orientation could be detected by A. cf. solaris or the cues were detected but the seastars did not react to them.
The probability that chemical cues from coral food were present in the water was very high, as in both experimental sites the water carried towards the seastars first had to pass the reef crest. Although, the water was not tested for chemical traces of corals, the question is why A. cf. solaris was not moving towards the reef in the vicinity at all, considering that especially starved individuals should try to reach feeding grounds. This challenges the ability of A. cf. solaris to successfully navigate between reefs and maybe even the functionality of chemoreception for long distance navigation. At the same time, the fact that blinded seastars followed the same inconsistent movement in weak currents as fed and starved ones implies that visual cues, which have been proven to be important in short-distance navigation [14], were also not responsible for the observed movement patterns at long distances. The observation that some of the individuals in Maharepa had started moving into the deep water of the channel south to the release point, and that others in Temae had moved into shallower water in the direction of the beach, does rather imply that movement on larger scales between reefs may be random. Additionally, directed navigation or orientation seems to be limited to the very presence of a distinct chemical or visual cue only a few meters away. Still, in both experiments, movement of single individuals was generally highly directional, which may prevent re-encountering already traversed areas [33]. Such a high directionality of movement has already been shown for A. cf. solaris, although in shorter time scales and on artificial substrate [32]. For movements between reefs this may be beneficial, as the distance covered is maximized, however, it still needs to move in the right direction to find a reef. A directed movement towards the reef was only shown in one individual from each treatment in Maharepa, which underpins that A. cf. solaris is not efficient in finding reefs from a distance.
5. Conclusions
A. cf. solaris in strong currents showed downstream movement, in contrast to weaker currents where movement was random; however, movement was not directed towards the reef in both experiments. This indicates that the senses of A. cf. solaris are generally not well suited to locate distant reefs. It remains unknown if A. cf. solaris uses specific cues to direct its movement between reefs, although the trigger for the onset of movement may well be a poor nutritional state. Importantly, the negative rheotaxis (movement with the current) shown might protect certain reefs from being invaded by A. cf. solaris, when currents between reefs are strong and consistently flow into one direction causing the seastar to move parallel to, or away from, the reef.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at www.mdpi.com/1424-2818/8/4/25/s1, Table S1: Compass directions after several hours or days of A. cf. solaris in Temae, Figure S1. Overview of release and tracking time and date and distances moved in-between by A. cf. solaris in Temae.
Acknowledgments
Financial support for Robert Sigl by the Cusanuswerk is gratefully acknowledged. We want to thank Maximilian Schweinsberg and the staff of the Richard B. Gump South Pacific Research Station for their help. This publication was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) and the University of Bayreuth in the funding program Open Access Publishing.
Author Contributions
R.S. and C.L. conceived, designed and performed the experiments; R.S. analyzed the data; R.S. and C.L. wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Pratchett, M.S.; Caballes, C.F.; Rivera-Posada, J.; Sweatman, H.P.A. Limits to understanding and managing outbreaks of crown-of-thorns starfish (Acanthaster planci spp.). In Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review; Hughes, R.N., Hughes, D.J., Smith, I.P., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 133–200. [Google Scholar]
- Birkeland, C.; Lucas, J. Acanthaster Planci: Major Management Problem of Coral Reefs; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Chesher, R.H. Destruction of Pacific corals by the sea star Acanthaster planci. Science 1969, 165, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endean, R. Report on Investigations Made into Aspects of the Current Acanthaster planci (crown-of-thorns) Infestations of Certain Reefs of the Great Barrier Reef. Available online: http://trove.nla.gov.au/work/24663525?q&versionId=29777393 (accessed on 29 October 2016).
- Branham, J.M.; Reed, S.; Bailey, J.H.; Caperon, J. Coral-eating sea stars Acanthaster planci in Hawaii. Science 1971, 172, 1155–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, P.J. Preliminary observations of the decomposition of crown-of-thorns starfish, Acanthaster planci (L.). Coral Reefs 1992, 11, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branham, J.M. Crown of thorns on coral reefs. Bioscience 1973, 23, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayal, M.; Vercelloni, J.; Lison de Loma, T.; Bosserelle, P.; Chancerelle, Y.; Geoffroy, S.; Stievenart, C.; Michonneau, F.; Penin, L.; Planes, S.; et al. Predator crown-of-thorns starfish (Acanthaster planci) outbreak, mass mortality of corals, and cascading effects on reef fish and benthic communities. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, P. The Acanthaster phenomenon. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 1986, 24, 379–480. [Google Scholar]
- Ormond, R.F.; Campbell, A.C. Formation and breakdown of Acanthaster planci aggregations in the Red Sea. In Proceedings of the Second International Coral Reef Symposium, Brisbane, Australia, 22 June–2 July 1973; Cameron, A.M., Cambell, B.M., Cribb, A.B., Endean, R., Jell, J.S., Jones, O.A., Mather, P., Talbot, F.H., Eds.; The Great Barrier Reef Committee: Brisbane, Australia; pp. 595–619.
- Barham, E.G.; Gowdy, R.W.; Wolfson, F.H. Acanthaster (Echinodermata, Asteroidea) in the Gulf of California. Fish. Bull. 1973, 71, 927–942. [Google Scholar]
- Garm, A.; Nilsson, D. Visual navigation in starfish: First evidence for the use of vision and eyes in starfish. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petie, R.; Hall, M.R.; Hyldahl, M.; Garm, A. Visual orientation by the crown-of-thorns starfish (Acanthaster planci). Coral Reefs 2016, 35, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigl, R.; Steibl, S.; Laforsch, C. The role of vision for navigation in the crown-of-thorns seastar, Acanthaster planci. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, D.; Brauer, R.; Jordan, M. Locomotory response of Acanthaster planci to various species of coral. Nature 1970, 228, 342–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castilla, J.C.; Crisp, D.J. Responses of Asterias rubens to olfactory stimuli. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 1970, 50, 829–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, A.; Coppard, S.; D’Abreo, C.; Tudor-Thomas, R. Escape and aggregation responses of three echinoderms to conspecific stimuli. Biol. Bull. 2001, 201, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochette, R.; Hamel, J.; Himmelman, J. Foraging strategy of the asteroid Leptasterias polaris: Role of prey odors, current and feeding status. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 106, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormond, R.; Campbell, A.C.; Head, S.H.; Moore, R.J.; Rainbow, P.R.; Saunders, A.P. Formation and breakdown of aggregations of the crown-of-thorns starfish, Acanthaster planci (L.). Nature 1973, 246, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, N. Aspects of the feeding biology of Asteroids. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 1980, 18, 57–124. [Google Scholar]
- Atema, J. Chemoreception in the sea: Adaptations of chemoreceptors and behaviour to aquatic stimulus conditions. Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol. 1985, 39, 387–423. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sloan, N.; Northway, S. Chemoreception by the Asteroid Crossaster papposus (L.). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1982, 61, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, N.; Campbell, A. Perception of food. In Echinoderm Nutrition; Jangoux, M., Lawrence, J., Eds.; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1982; pp. 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- Drolet, D.; Himmelman, J.H. Role of current and prey odour in the displacement behaviour of the sea star Asterias vulgaris. Can. J. Zool. 2004, 82, 1547–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, R.; Jordan, M. Triggering of the stomach eversion reflex of Acanthaster planci by coral extracts. Nature 1970, 228, 344–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentinčič, T. Food finding and stimuli to feeding in the sea star Marthasterias glacialis. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1973, 7, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribi, G.; Jost, P. Feeding rate and duration of daily activity of Astropecten aranciacus (Echinodermata: Asteroidea) in relation to prey density. Mar. Biol. 1978, 45, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClintock, J.B.; Lawrence, J.M. Ingestive conditioning in Luidia clathrata (Say) (Echinodermata: Asteroidea): Effect of nutritional condition on selectivity, teloreception, and rates of ingestion. Mar. Behav. Physiol. 1984, 10, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCurley, R.S.; Kier, W.M. The functional morphology of starfish tube feet: The role of a crossed-fiber helical array in movement. Biol. Bull. 1995, 188, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, J. Movement Ecology Tools for ArcGIS (ArcMET). Available online: www.movementecology.net (accessed on 12 August 2014).
- Jammalamadaka, S.R.; SenGupta, A. Topics in Circular Statistics; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, B.; Bos, A.; Graf, G.; Gumanao, G. Size-specific locomotion rate and movement pattern of four common Indo-Pacific sea stars (Echinodermata; Asteroidea). Aquat. Biol. 2011, 12, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheibling, R. Optimal foraging movements of Oreaster reticulatus (L.) (Echinodermata: Asteroidea). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1981, 51, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla, J.C.; Crisp, D.J. Responses of Asterias rubens to water currents and their modification by certain environmental factors. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1973, 7, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenchel, T. Feeding biology of the sea-star Luidia sarsi Düben & Koren. Ophelia 1965, 2, 223–236. [Google Scholar]
- Nickell, T.D.; Moore, P.G. The behavioural ecology of epibenthic scavenging invertebrates in the Clyde Sea area: Laboratory experiments on attractions to bait in moving water, underwater TV observation in situ and general conclusions. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1992, 159, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goreau, T.F.; Lang, J.C.; Graham, E.A. Structure and ecology of the Saipan Reefs in relation to predation by Acanthaster planci (Linnaeus). Bull. Mar. Sci. 1972, 22, 113–152. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, E.M.; Palmer, A.R. Effects of body size and shape on locomotion in the bat star (Patiria miniata). Biol. Bull. 2012, 222, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Veldhuizen, H.; Oakes, V. Behavioral responses of seven species of Asteroids to the Asteroid predator, Solaster dawsoni. Oecologia 1981, 48, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClintock, J.B.; Lawrence, J. Characteristics of foraging in the soft-bottom benthic starfish Luidia clathrata (Echinodermata: Asteroidea): Prey selectivity, switching behavior, functional responses and movement patterns. Oecologia 1985, 66, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).