Phytoplankton Communities in Green Bay, Lake Michigan after Invasion by Dreissenid Mussels: Increased Dominance by Cyanobacteria
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
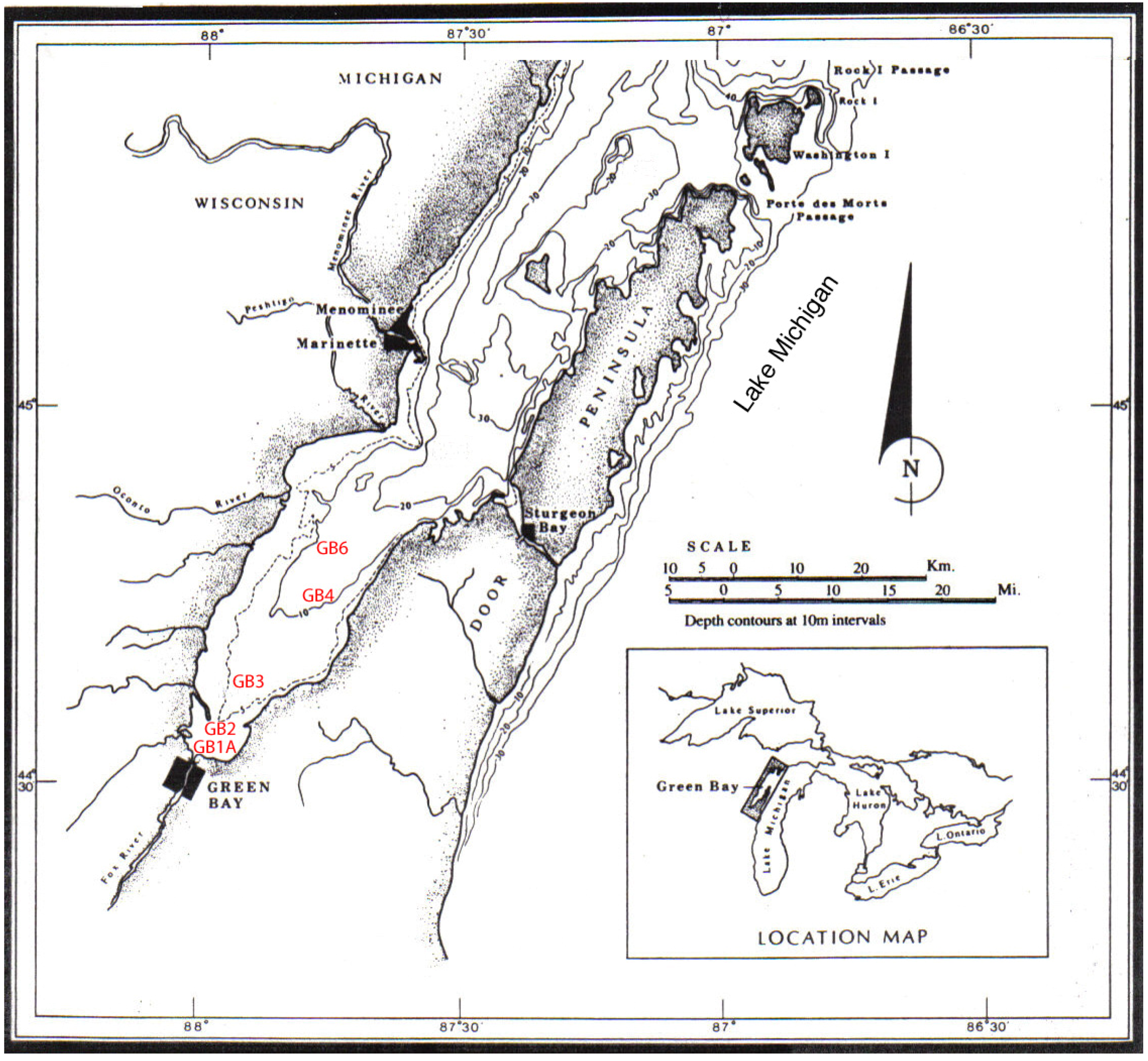
3. Results
3.1. Phytoplankton Biomass
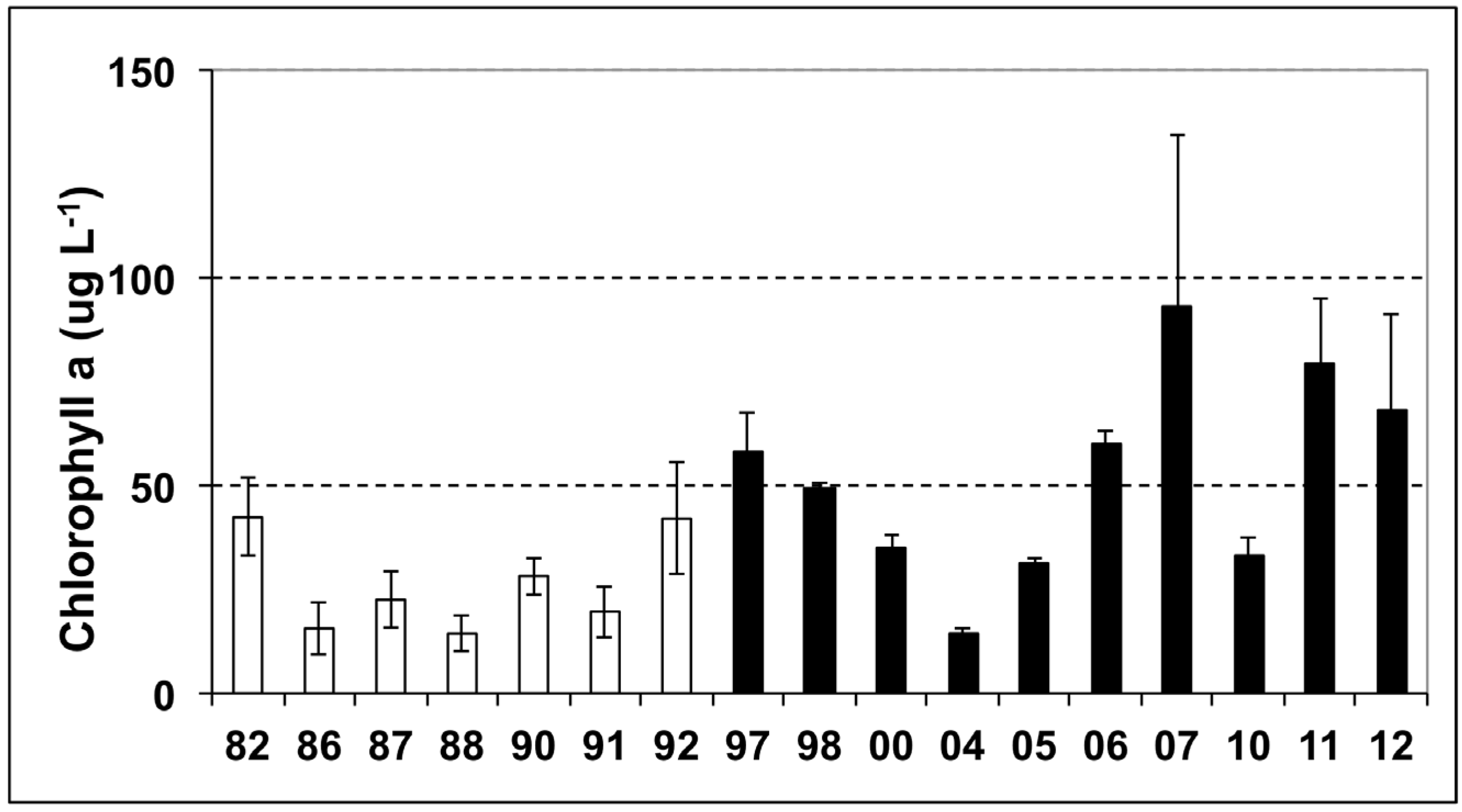
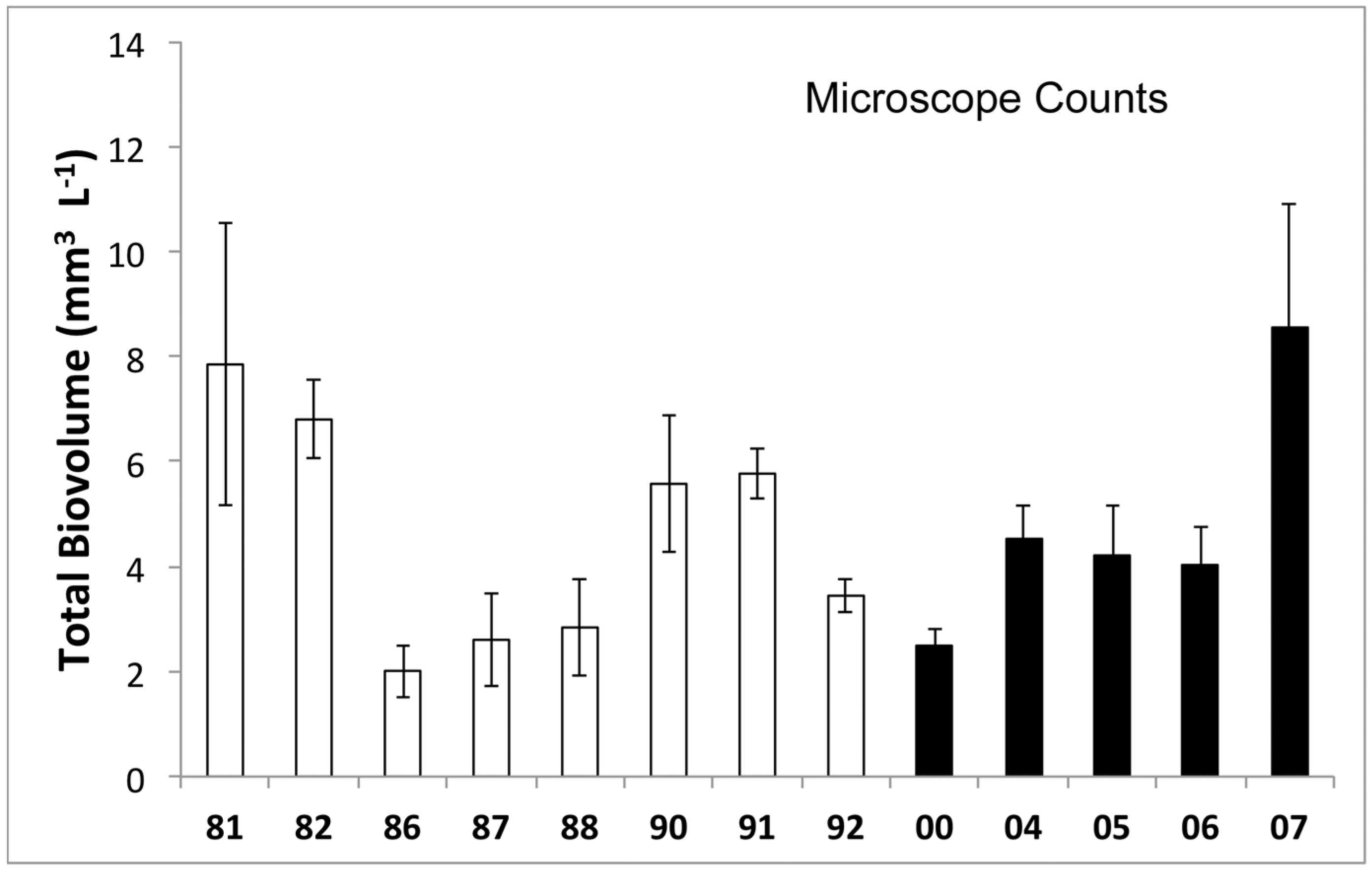
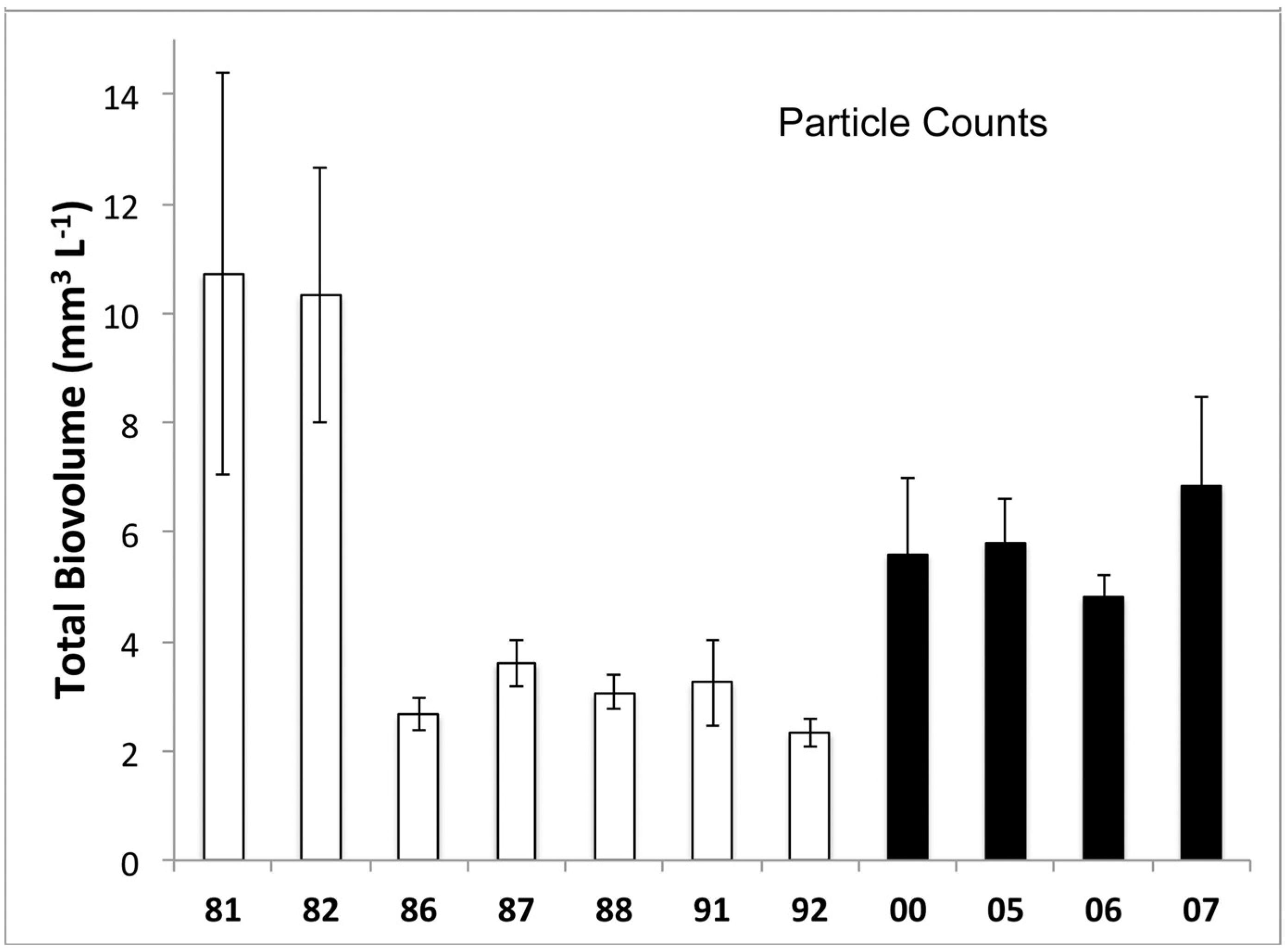
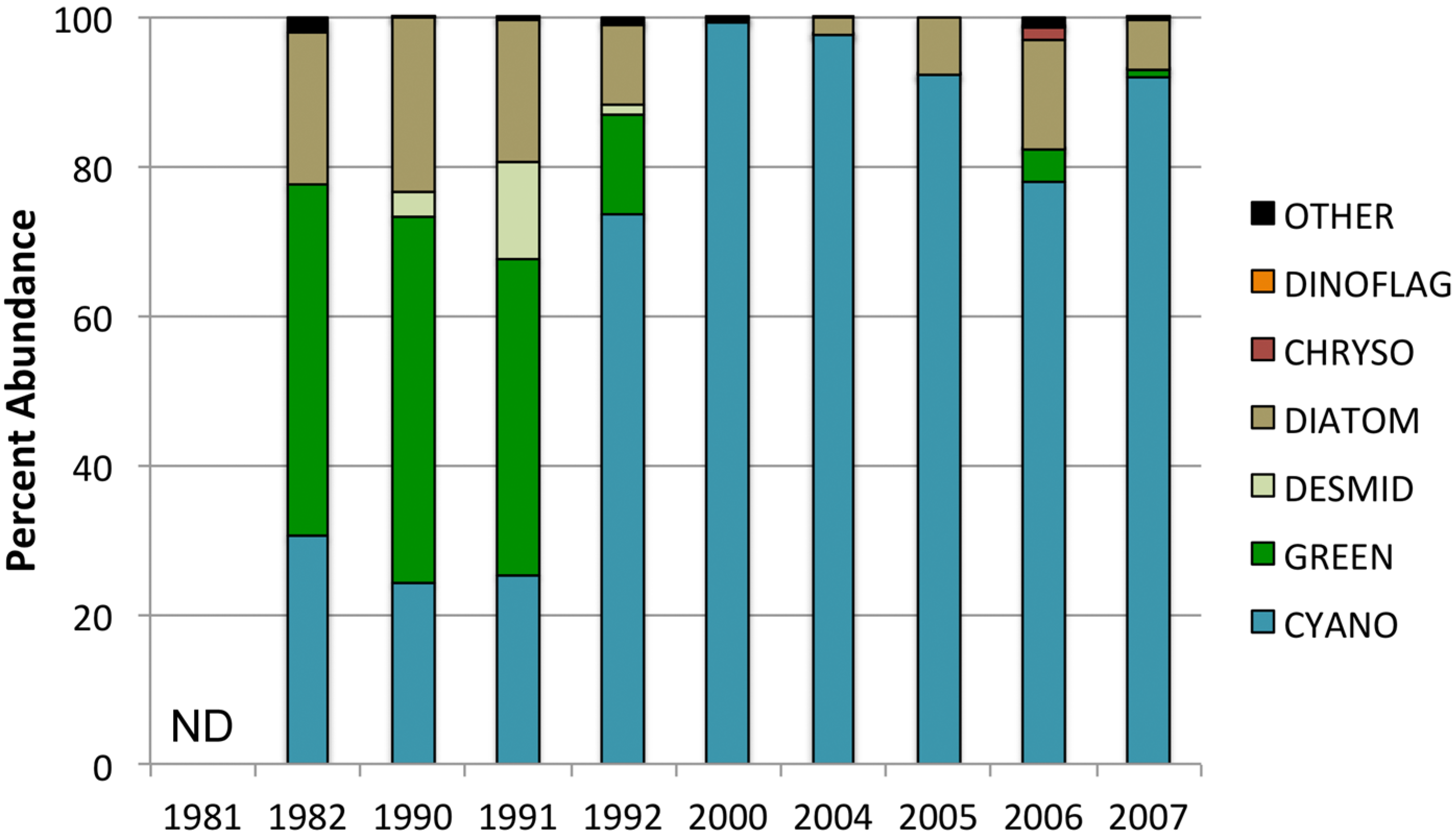
3.2. Phytoplankton Community Composition
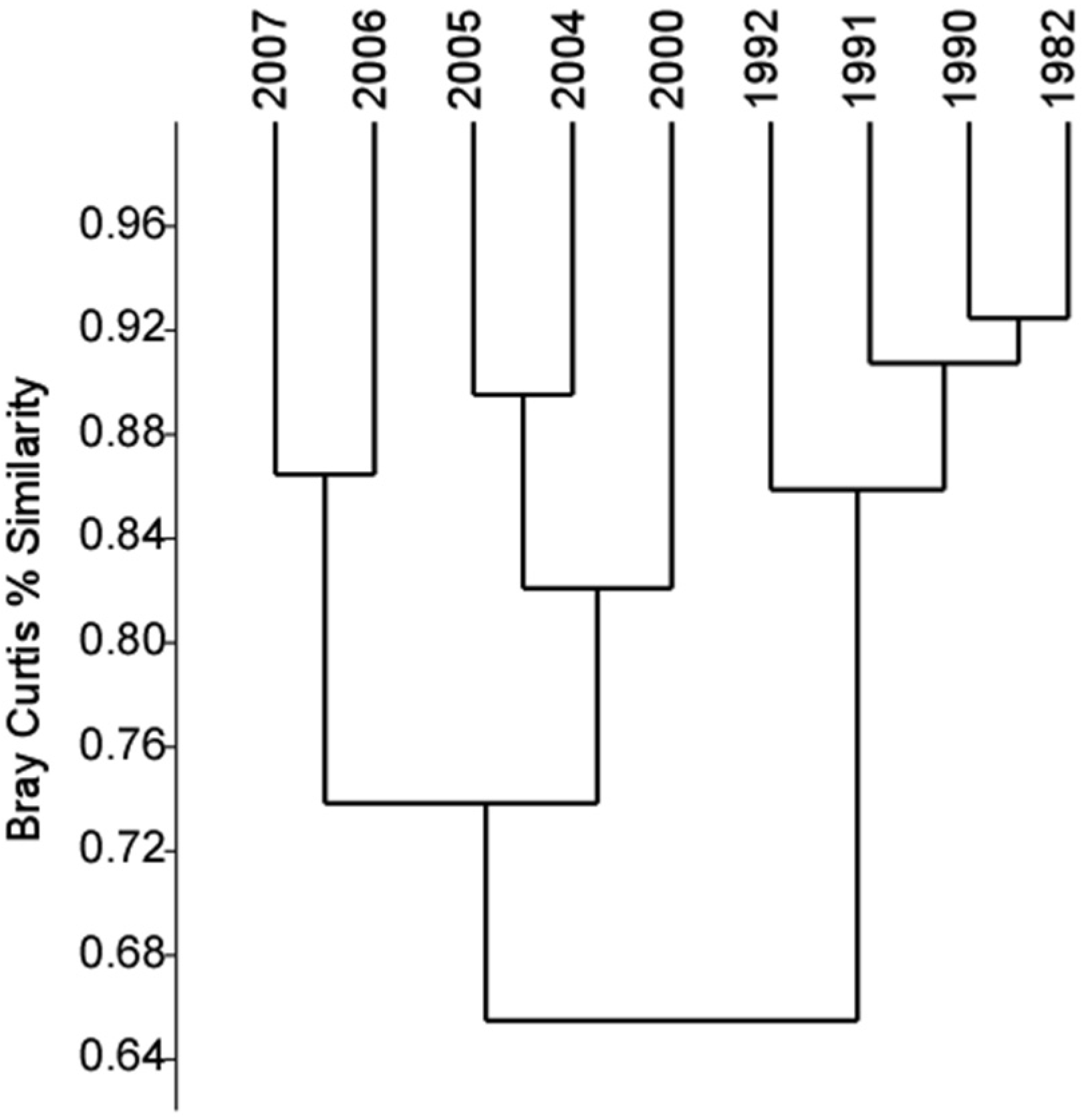
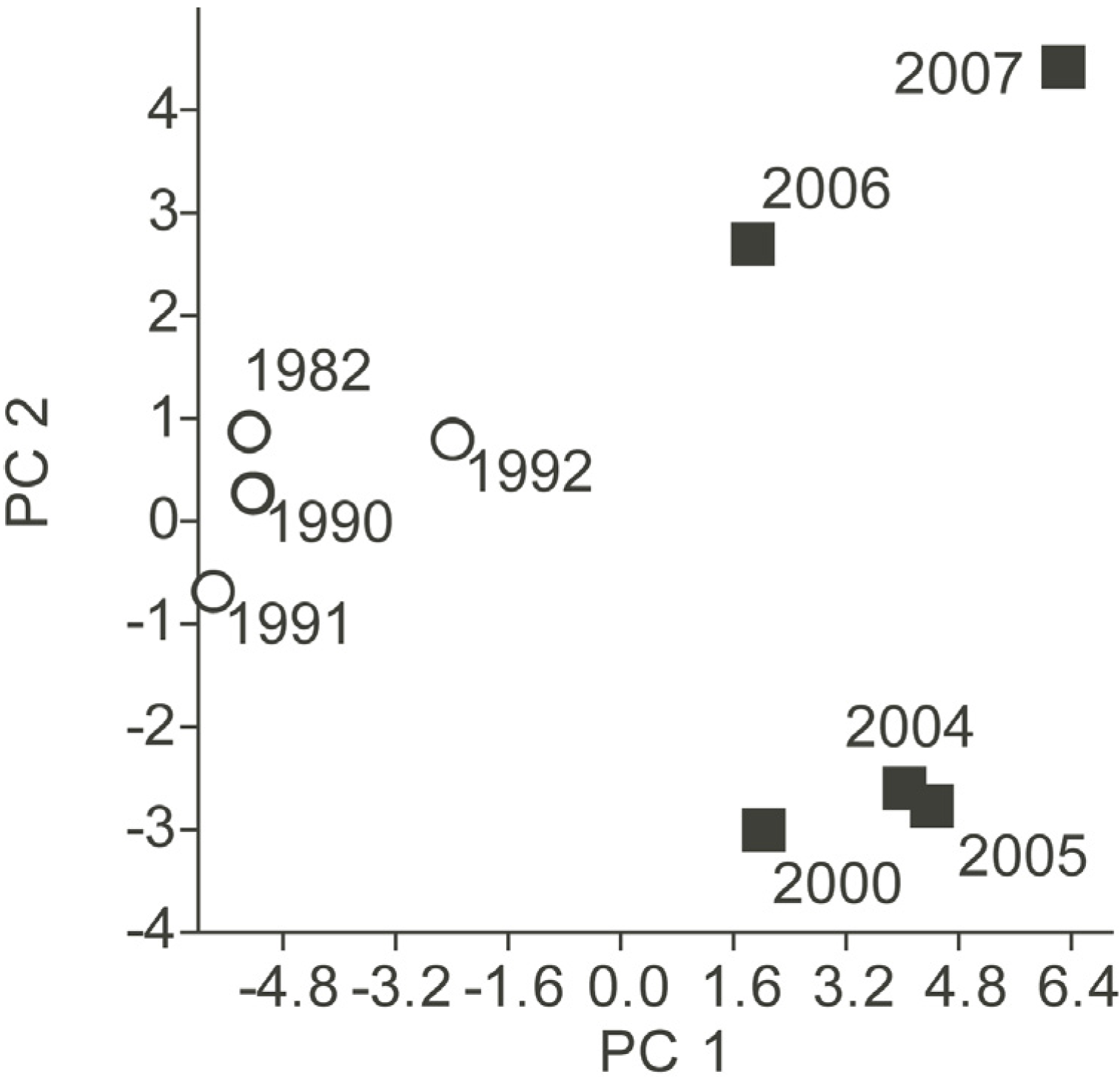
| Taxon | Axis 1 | Axis 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Cyanobacteria | 0.895 | 0.091 |
| Non-desmid green algae | −0.281 | 0.473 |
| Desmids | −0.237 | 0.211 |
| Diatoms | 0.172 | 0.425 |
| Non-diatom Chrysophyta | 0.119 | 0.641 |
| Dinoflagellates | −0.105 | 0.165 |
| Other | −0.094 | 0.326 |

| Year | N | Mean Abundance (Cells mL−1) | Lower 95% Limit | Upper 95% Limit | Significance (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1982 | 6 | 16.9 | 13.1 | 21.9 | - |
| 2000 | 3 | 2,129.6 | 1,925.6 | 2,355.2 | 0.000001 |
| 2004 | 3 | 5,732.1 | 2,974.3 | 11,046.9 | 0.0059 |
| 2006 | 5 | 2,384.1 | 1,223.7 | 4,644.9 | 0.0008 |
| 2007 | 5 | 2,978.8 | 1,753.0 | 5,061.7 | 0.0001 |
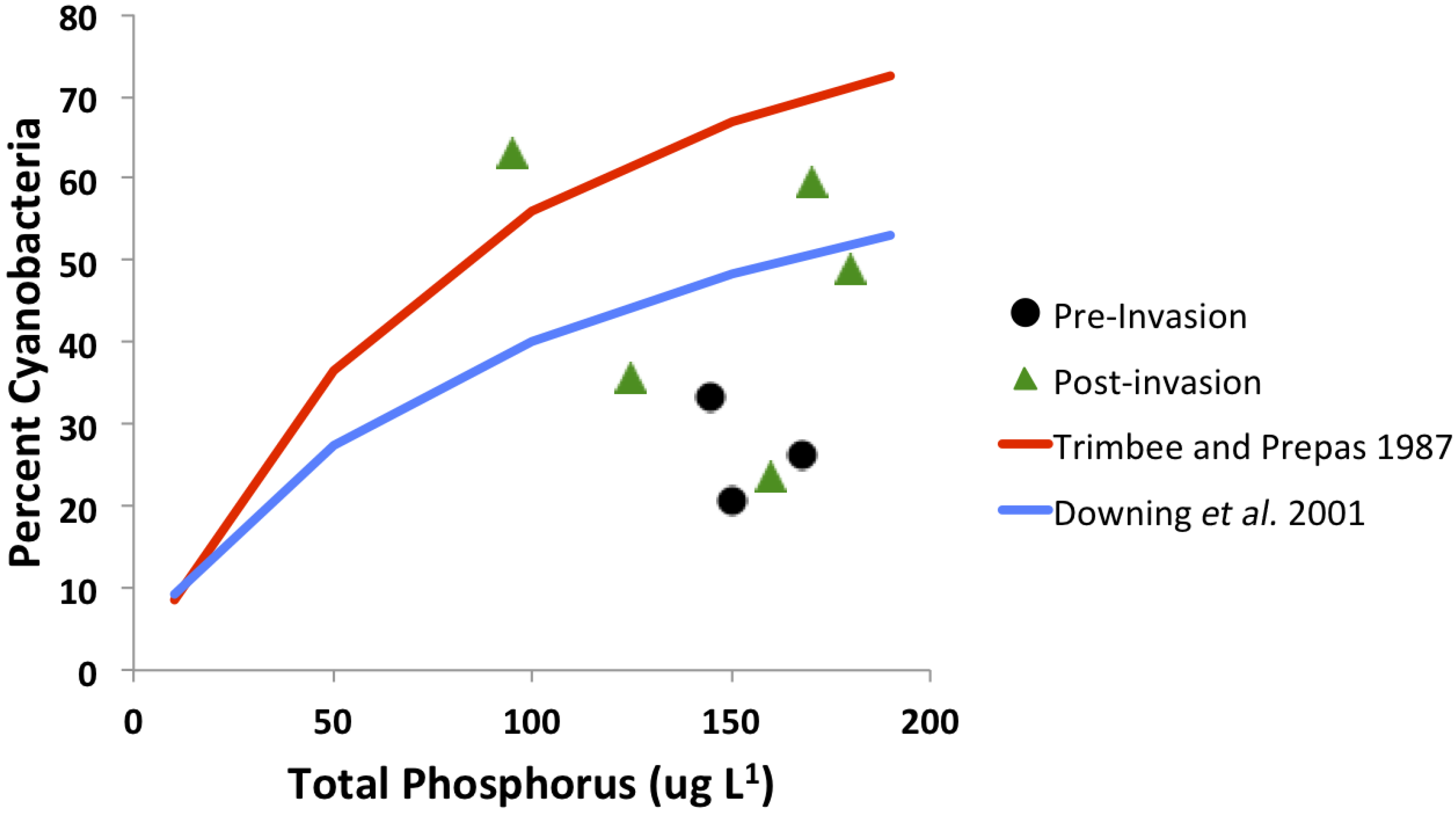
| Year | Cyano | Green | Diatom | Dinoflag | Chryso |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 6 | 20 | 9 | 1 | 2 |
| 1991 | 6 | 19 | 8 | 1 | 0 |
| 1992 | 7 | 21 | 9 | 2 | 2 |
| 2000 | 6 | 16 | 10 | 1 | 1 |
| 2004 | 6 | 11 | 18 | 1 | 0 |
| 2005 | 4 | 3 | 16 | 1 | 0 |
| 2006 | 6 | 16 | 16 | 2 | 1 |
| 2007 | 6 | 12 | 15 | 1 | 2 |
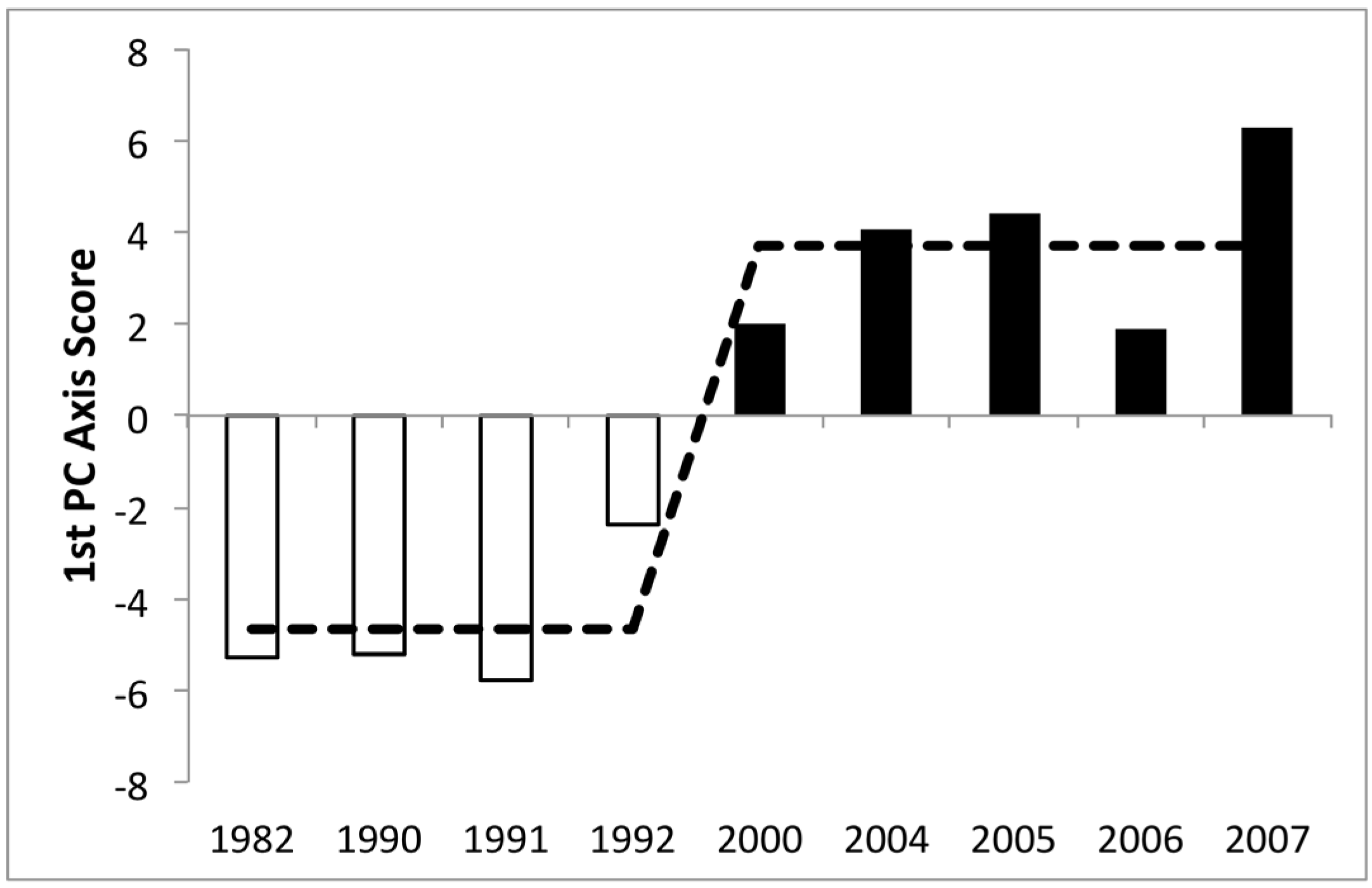
3.3. Changes in Abundance over Time
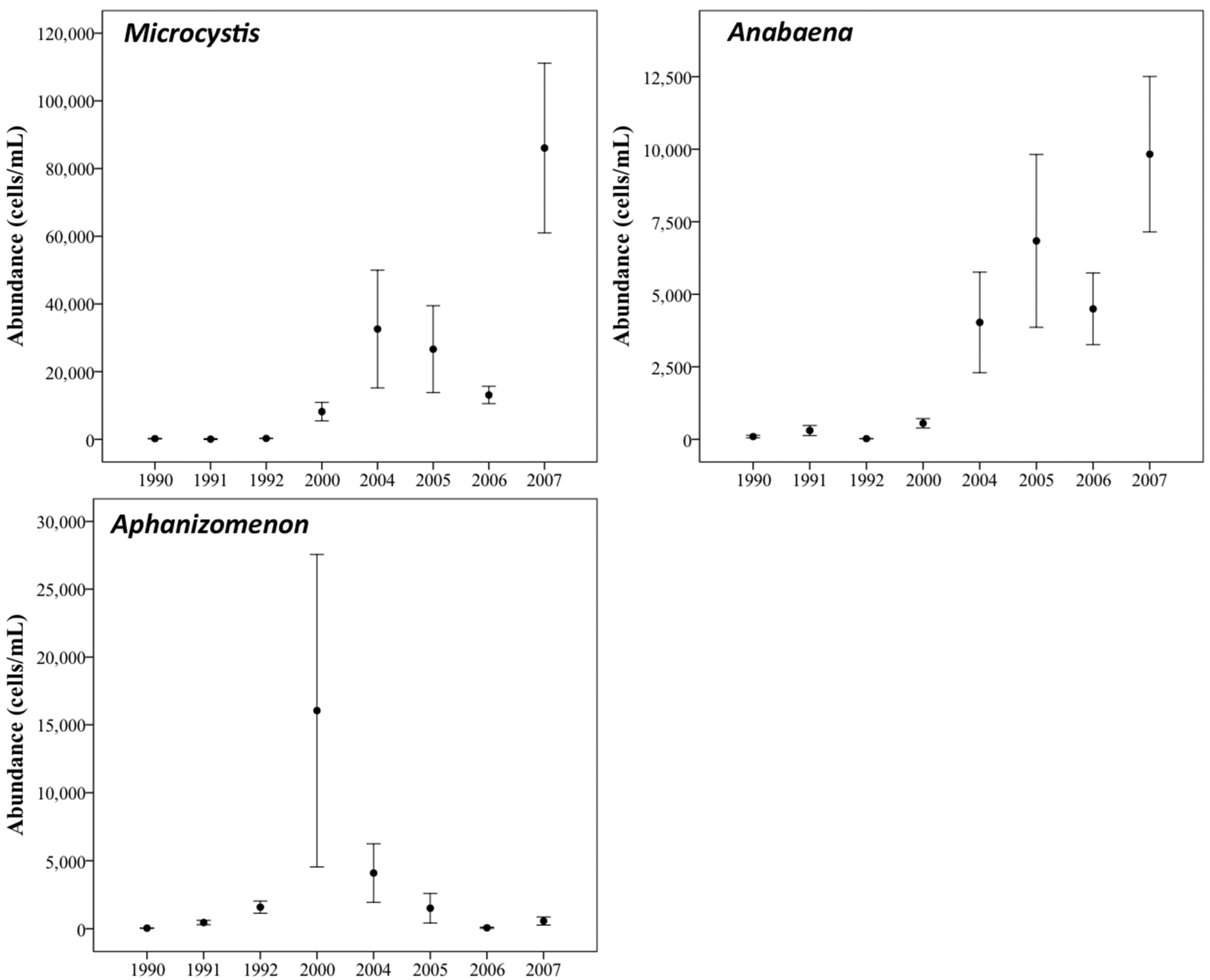
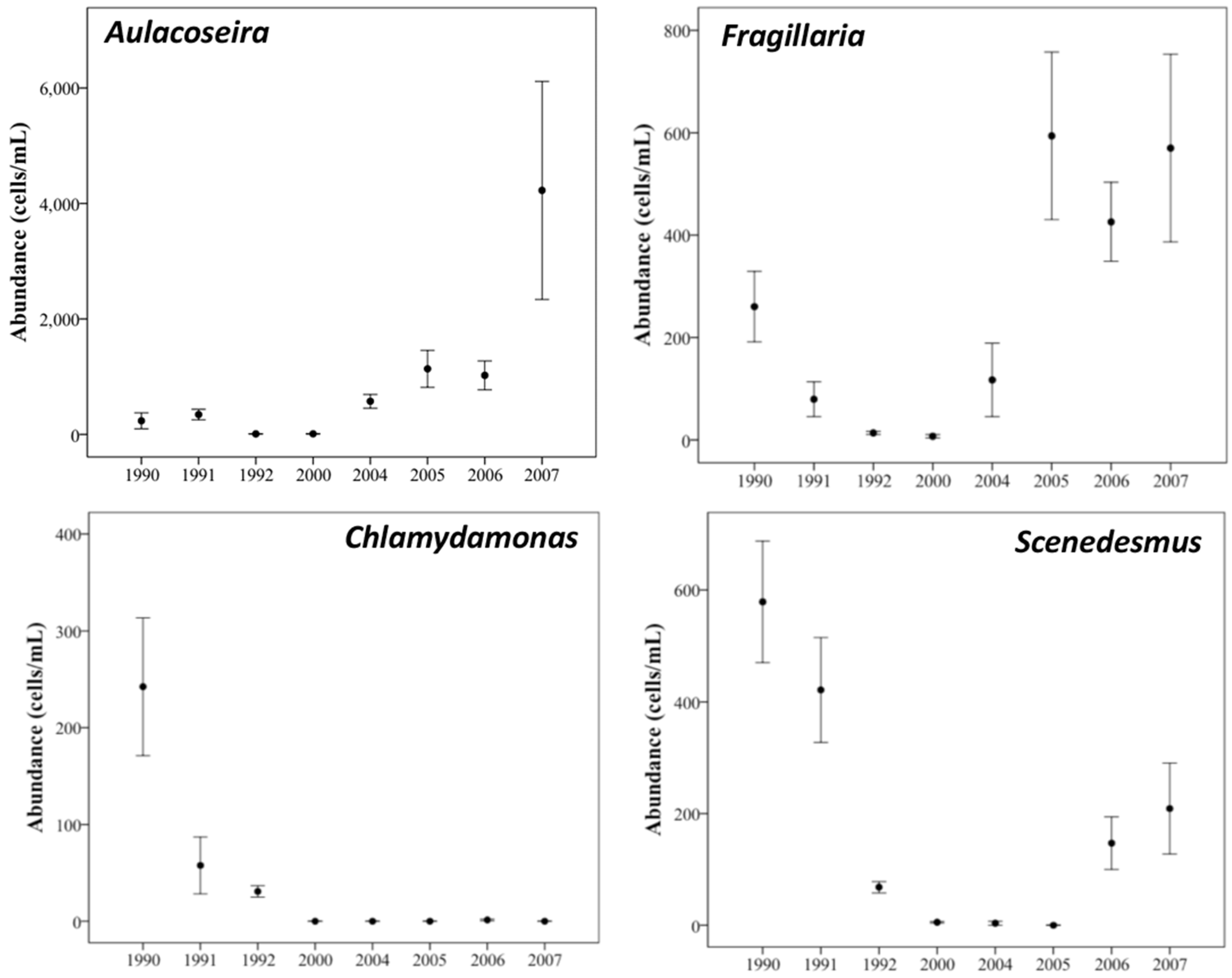
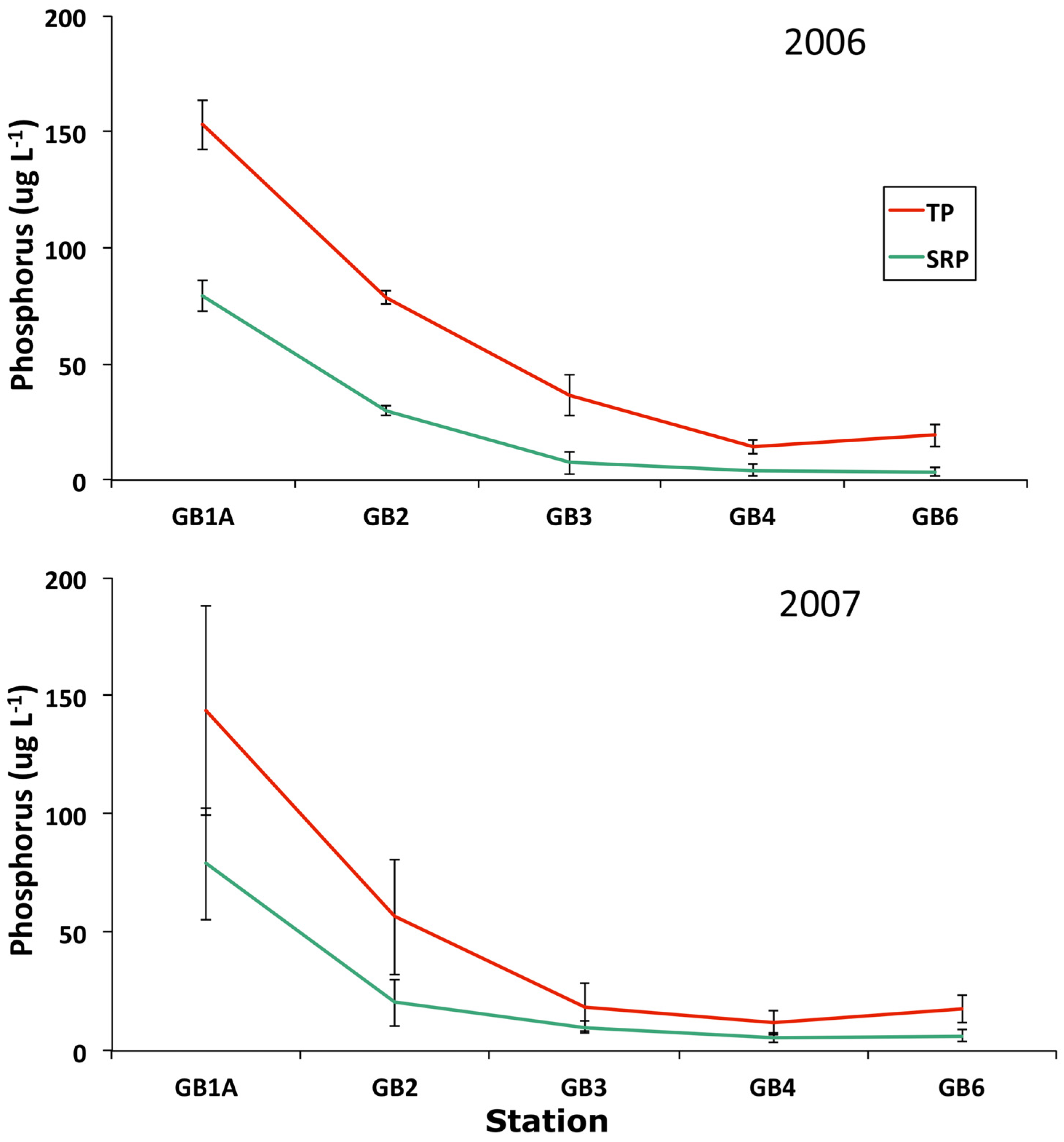
3.4. Trophic Gradient Conditions
| Station | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB1A | GB2 | GB3 | GB4 | GB6 | |
| Total Phosphorus (ug/L) | |||||
| 1980 | 223.7 | 158.3 | 47.8 | 45.3 | 42.3 |
| (23.6) | (40.8) | (17.8) | (14.7) | (8.9) | |
| 2006 | 153.1 | 78.9 | 36.6 | 14.4 | 19.3 |
| (10.7) | (2.9) | (8.8) | (3.2) | (4.8) | |
| 2007 | 143.7 | 56.5 | 18.3 | 11.6 | 17.6 |
| (44.3) | (24.6) | (10.1) | (5.1) | (5.7) | |
| Chlorophyll a (ug/L) | |||||
| 1980 | 53.3 | 63.1 | 18.6 | 9.8 | 9.9 |
| (23.1) | (15.9) | (3.4) | (2.9) | (3.3) | |
| 2006 | 90.3 | 60.2 | 25.3 | 16.8 | 17.0 |
| (9.4) | (8.4) | (7.6) | (2.0) | (4.5) | |
| 2007 | 196.7 | 93.2 | 27.6 | 25.3 | 27.9 |
| (34.4) | (50.4) | (8.8) | (7.0) | (10.0) | |
| Secchi Depth (m) | |||||
| 1980 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 1.3 | 2.4 | 2.4 |
| (0.03) | (0.1) | (0.2) | (0.3) | (0.5) | |
| 2006 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.8 | 2.3 | 2.8 |
| (0.1) | (0.04) | (0.3) | (0.3) | (0.5) | |
| 2007 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 1.7 | 2.2 | 3.0 |
| (0.02) | (0.2) | (0.2) | (0.3) | (0.6) | |
4. Discussion
4.1. Phytoplankton Community Drivers
4.1.1. Grazing Impacts
4.1.2. Selective Grazing
4.1.3. Nutrient Conditions
4.1.4. Physical Habitat Conditions
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lodge, D.M.; Williams, S.; MacIsaac, H.J.; Hayes, K.R.; Leung, B.; Reichard, S.; Mack, R.N.; Moyle, P.B.; Smith, M.; Andow, D.A.; et al. Biological invasions: Recommendations for U.S. Policy and management. Ecol. Appl. 2006, 16, 2035–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strayer, D.L. Twenty years of zebra mussels: Lessons from the mollusk that made headlines. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2009, 7, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, E.L.; Leach, J.H.; Carlton, J.T.; Secor, C.L. Exotic species and the integrity of the Great Lakes - lessons from the past. Bioscience 1994, 44, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, J.M.; Lodge, D.M. Rate of species introductions in the great lakes via ships’ ballast water and sediments. Can. J. Fish. and Aquat. Sci. 2007, 64, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderploeg, H.A.; Nalepa, T.F.; Jude, D.J.; Mills, E.L.; Holeck, K.T.; Liebig, J.R.; Grigorovich, I.A.; Ojaveer, H. Dispersal and emerging ecological impacts of Ponto-Caspian species in the Laurentian Great Lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahnenstiel, G.L.; Lang, G.A.; Nalepa, T.F.; Johengen, T.H. Effects of zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) colonization on water quality parameters in Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron. J. Great Lakes Res. 1995, 21, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacIsaac, H.J.; Sprules, W.G.; Johannsson, O.E.; Leach, J.H. Filtering impacts of larval and sessile zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) in western Lake Erie. Oecologia 1992, 92, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunt, C.M.; Maclsaac, H.J.; Sprules, W.G. Pumping rates and projected filtering impacts of juvenile zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) in western Lake Erie. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1993, 50, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrentyev, P.J.; Gardner, W.S.; Cavaletto, J.F.; Beaver, J.R. Effects of the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha Pallas) on protozoa and phytoplankton from Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron. J. Great Lakes Res. 1995, 21, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrisi, N.; Mills, E.L.; Rudstam, L.G.; Stewart, D.J. Impact of zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) on the pelagic lower trophic levels of Oneida Lake, New York. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 58, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbiero, R.P.; Rockwell, D.C.; Warren, G.J.; Tuchman, M.L. Changes in spring phytoplankton communities and nutrient dynamics in the eastern basin of Lake Erie since the invasion of Dreissena spp. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2006, 63, 1549–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depew, D.C.; Guildford, S.J.; Smith, R.E.H. Nearshore-offshore comparison of Chlorophyll a and phytoplankton production in the dreissenid-colonized eastern basin of Lake Erie. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2006, 63, 1115–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, D.B.; Adlerstein, S.A.; Vanderploeg, H.A.; Fahnenstiel, G.L.; Scavia, D. Phytoplankton community composition of Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron, during the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) invasion: A multivariate analysis. J. Great Lakes Res. 2010, 36, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnott, D.L.; Vanni, M.J. Nitrogen and phosphorus recycling by the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) in the western basin of Lake Erie. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1996, 53, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, J.D.; Edwards, W.J.; Pontius, R.A.; Kane, D.D.; Zhang, H.Y.; Shea, J.F.; Richey, J.N.; Culver, D.A. Soluble nitrogen and phosphorus excretion of exotic freshwater mussels (Dreissena spp.): Potential impacts for nutrient remineralisation in western Lake Erie. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 1146–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, E.L.; Casselman, J.M.; Dermott, R.; Fitzsimons, J.D.; Gal, G.; Holeck, K.T.; Hoyle, J.A.; Johannsson, O.E.; Lantry, B.F.; Makarewicz, J.C.; et al. Lake Ontario: Food web dynamics in a changing ecosystem (1970–2000). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2003, 60, 471–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecky, R.E.; Smith, R.E.H.; Barton, D.R.; Guildford, S.J.; Taylor, W.D.; Charlton, M.N.; Howell, T. The nearshore phosphorus shunt: A consequence of ecosystem engineering by dreissenids in the Laurentian Great Lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2004, 61, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, S.N.; Vander Zanden, M.J. What a difference a species makes: A meta-analysis of dreissenid mussel impacts on freshwater ecosystems. Ecol. Monogr. 2010, 80, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althouse, B.; Higgins, S.; Vander Zanden, M.J. Benthic and planktonic primary production along a nutrient gradient in Green Bay, Lake Michigan, USA. Freshw. Sci. 2014, 33, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, S.N.; Vander Zanden, M.J.; Joppa, L.N.; Vadeboncoeur, Y. The effect of dreissenid invasions on chlorophyll and the chlorophyll: Total phosphorus ratio in north-temperate lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 68, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.; Stow, C.A.; Bernhardt, E.S. Impacts of dreissenid mussel invasions on chlorophyll and total phosphorus in 25 lakes in the USA. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertand, G.; Lang, J.; Ross, J. The Green Bay Watershed: Past, Present, Future; University of Wisconsin Sea Grant Institute: Madison, WI, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Klump, J.V.; Edgington, D.N.; Sager, P.E.; Robertson, D.M. Sedimentary phosphorus cycling and a phosphorus mass balance for the Green Bay (Lake Michigan) ecosystem. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1997, 54, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richman, S.; Sager, P.E.; Banta, G.; Harvey, T.R.; De Stasio, B.T. Phytoplankton standing stocks, size distribution, species composition and productivity along a trophic gradient in Green Bay, Lake Michigan. Internationale Vereinigung fuer Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie Verhandlungen 1984, 22, 460–469. [Google Scholar]
- De Stasio, B.T.; Richman, S. Phytoplankton spatial and temporal distributions in Green Bay, Lake Michigan, prior to colonization by the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha). J. Great Lakes Res. 1998, 24, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sager, P.E.; Richman, S. Functional interaction of phytoplankton and zooplankton along the trophic gradient in Green Bay, Lake Michigan. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1991, 49, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualls, T.M.; Dolan, D.M.; Reed, T.; Zorn, M.E.; Kennedy, J. Analysis of the impacts of the zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha, on nutrients, water clarity, and the chlorophyll-phosphorus relationship in lower Green Bay. J. Great Lakes Res. 2007, 33, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stasio, B.T.; Schrimpf, M.B.; Beranek, A.E.; Daniels, W.C. Increased Chlorophyll a, phytoplankton abundance, and cyanobacteria occurrence following invasion of Green Bay, Lake Michigan by dreissenid mussels. Aquat. Invasions 2008, 3, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stasio, B.T.; Schrimpf, M.B.; Beranek, A.E.; Daniels, W.C.; Hoyer, E. Dreissenid driving tests: Going the “wrong” way in Green Bay, Lake Michigan? Internationale Vereinigung fuer Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie Verhandlungen 2010, 30, 1540–1544. [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel, R.G.; Likens, G.E. Limnological Analyses, 2nd ed.; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 1991; p. 391. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls, K.H.; Hoyle, J.A.; Johannsson, O.E.; Dermott, R. A biological regime shift in the Bay of Quinte ecosystem (Lake Ontario) associated with the establishment of invasive dreissenid mussels. J. Great Lakes Res. 2011, 37, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. Past: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Rodionov, S.N. A sequential algorithm for testing climate regime shifts. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, T.M.; Descy, J.-P.; de Stasio, B.T.; Gerrish, G.A.; Hood, J.M.; Hurley, J.P.; Amand., A.L.S. Evaluations of phytoplankton communities using varied techniques: A multi-media comparison of lakes in northern Wisconsin, USA. Internationale Vereinigung fuer Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie Verhandlungen 2000, 27, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Trimbee, A.M.; Prepas, E.E. Evaluation of total phosphorus as a predictor of the relative biomass of blue-green-algae with emphasis on Alberta lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1987, 44, 1337–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downing, J.A.; Watson, S.B.; McCauley, E. Predicting cyanobacteria dominance in lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 58, 1905–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, R.E. Changes in planktonic diatoms and water transparency in Hatchery Bay, Bass Island area, western Lake Erie since the establishment of the zebra mussel. J. Great Lakes Res. 1993, 19, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, K.H. Detection of regime shifts in multi-species communities: The Bay of Quinte phytoplankton example. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2011, 2, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.E.; Sarnelle, O. Relationship between zebra mussel biomass and total phosphorus in European and North American lakes. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2002, 153, 339–351. [Google Scholar]
- Kryger, J.; Riisgard, H.U. Filtration-rate capacities in 6 species of European fresh-water bivalves. Oecologia 1988, 77, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fettes, A.L. The Bottom of the Bay Then and Now: Investigations into Both the Zebra Mussels Colonizing Green Bay and the Pre-Invasion Macroinvertebrate Community. Master’s Thesis, University of Wisconsin-Green Bay, Green Bay, WI, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Salim, A.Y. Alternative Sampling Method to Determine Factors Affecting Distribution and Ecological Impact of the Zebra Mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) in Lower Green Bay, WI. Master’s Thesis, University of Wisconsin-Green Bay, Green Bay, WI, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Vanderploeg, H.A.; Johengen, T.H.; Fahnenstiel, G.L.; Nalepa, T.F.; Liebig, J.R.; Carmichael, W.W.; Agy, M.A. Zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) selective filtration promoted toxic Microcystis blooms in Saginaw Bay (Lake Huron) and Lake Erie. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 58, 1208–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, K.H.; Hopkins, G.J. Recent changes in Lake Erie (north shore) phytoplankton-cumulative impacts of phosphorus loading reductions and the zebra mussel introduction. J. Great Lakes Res. 1993, 19, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.M.; Levinton, J.S.; Kurdziel, J.P.; Shumway, S.E. Selective feeding and biodeposition by zebra mussels and their relation to changes in phytoplankton composition and seston load. J. Shellfish Res. 1998, 17, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar]
- Bastviken, D.T.E.; Caraco, N.F.; Cole, J.J. Experimental measurements of zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) impacts on phytoplankton community composition. Freshw. Biol. 1998, 39, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionisio Pires, L.M.; Jonker, R.R.; Van Donk, E.; Laanbroek, H.J. Selective grazing by adults and larvae of the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha): Application of flow cytometry to natural seston. Freshw. Biol. 2004, 49, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naddafi, R.; Eklov, P.; Pettersson, K. Non-lethal predator effects on the feeding rate and prey selection of the exotic zebra mussel Dreissena polymorpha. Oikos 2007, 116, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderploeg, H.A.; Johengen, T.H.; Liebig, J.R. Feedback between zebra mussel selective feeding and algal composition affects mussel condition: Did the regime changer pay a price for its success? Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 47–63. [Google Scholar]
- White, J.D.; Sarnelle, O. Size-structured vulnerability of the colonial cyanobacterium, Microcystis aeruginosa, to grazing by zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha). Freshw. Biol. 2014, 59, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionisio Pires, L.M.; Bontes, B.M.; Van Donk, E.; Ibelings, B.W. Grazing on colonial and filamentous, toxic and non-toxic cyanobacteria by the zebra mussel Dreissena polymorpha. J. Plankton Res. 2005, 27, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.M.; Levinton, J.S.; Ward, J.E. Particle transport in the zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha (Pallas). Biol. Bull. 2000, 199, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richman, S.; Sager, P.E. Patterns of phytoplankton-zooplankton interactions along a trophic gradient: II. Biomass and size distribution. Internationale Vereinigung fuer Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie Verhandlungen 1990, 24, 401–405. [Google Scholar]
- Qualls, T.M.; Harris, H.J.; Harris, V. The State of the Bay: The Condition of the Bay of Green Bay/Lake Michigan 2013; University of Wisconsin Sea Grant Institute: Madison, WI, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Culver, D.A.; Boegman, L. Dreissenids in Lake Erie: An algal filter or a fertilizer? Aquat. Invasions 2011, 6, 175–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, D.D.; Conroy, J.D.; Richards, R.P.; Baker, D.B.; Culver, D.A. Re-eutrophication of Lake Erie: Correlations between tributary nutrient loads and phytoplankton biomass. J. Great Lakes Res. 2014, 40, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, R.T.; Fahnenstiel, G.L.; Gardner, W.S.; Cavaletto, J.F.; Hwang, S.J. Ecosystem-level effects of zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha): An enclosure experiment in Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron. J. Great Lakes Res. 1995, 21, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalepa, T.F.; Gardner, W.S.; Malczyk, J.M. Phosphorus cycling by mussels (unionidae, bivalvia) in Lake St. Clair. Hydrobiologia 1991, 219, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellina, E.; Rasmussen, J.B.; Mills, E.L. Impact of zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) on phosphorus cycling and chlorophyll in lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1995, 52, 2553–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderhoef, L.N.; Huang, C.Y.; Musil, R.; Williams, J. Nitrogen-fixation (acetylene-reduction) by phytoplankton in Green Bay, Lake Michigan, in relation to nutrient concentrations. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1974, 19, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sager, P.E.; Banta, G.; Kirk, J. The relation between areal and volumetric expressions of 14C productivity in Green Bay, Lake Michigan. Internationale Vereinigung fuer Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie Verhandlungen 1984, 22, 470–474. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, R.E.; Claflin, L.W. Horizontal distribution of planktonic diatoms in Green Bay, mid-july 1970. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1975, 20, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S.; Huszar, V.; Kruk, C.; Naselli-Flores, L.; Melo, S. Towards a functional classification of the freshwater phytoplankton. J. Plankton Res. 2002, 24, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, P.J.; Rigler, F.H. Phosphorus-chlorophyll relationship in lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1974, 19, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stow, C.A.; Cha, Y. Are Chlorophyll a-total phosphorus correlations useful for inference and prediction? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 3768–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnelle, O.; Raikow, D.F.; Wilson, A.E.; Hamilton, S.K.; Knoll, L.B. Complex interactions between the zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha, and the harmful phytoplankter, Microcystis aeruginosa. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnelle, O.; White, J.D.; Horst, G.P.; Hamilton, S.K. Phosphorus addition reverses the positive effect of zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) on the toxic cyanobacterium, Microcystis aeruginosa. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3471–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacIsaac, H.J.; Johannsson, O.E.; Ye, J.; Sprules, W.G.; Leach, J.H.; McCorquodale, J.A.; Grigorovich, I.A. Filtering impacts of an introduced bivalve (Dreissena polymorpha) in a shallow lake: Application of a hydrodynamic model. Ecosystems 1999, 2, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, D.K.; Adolph, S.C.; Cottingham, K.L.; Schneider, D.W. Predicting the consequences of dreissenid mussels on a pelagic food web. Ecol. Model. 1996, 85, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, D.W.; Madon, S.P.; Stoeckel, J.A.; Sparks, R.E. Seston quality controls zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) energetics in turbid rivers. Oecologia 1998, 117, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penning, W.E.; Pozzato, L.; Vijverberg, T.; Noordhuis, R.; bij de Vaate, A.; van Donk, E.; Dionisio Pires, L.M. Effects of suspended sediments on food uptake for zebra mussels in Lake Markermeer, the Netherlands. Inland Waters 2013, 3, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, T.; Fettes, A.L.; Wielgus, S.J.; Barnes, A.K.; Schiefelbein, J.J. Refugia and local controls: Benthic invertebrate dynamics in lower Green Bay, Lake Michigan following zebra mussel invasion. J. Great Lakes Res. 2004, 30, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Stasio, B.T.; Schrimpf, M.B.; Cornwell, B.H. Phytoplankton Communities in Green Bay, Lake Michigan after Invasion by Dreissenid Mussels: Increased Dominance by Cyanobacteria. Diversity 2014, 6, 681-704. https://doi.org/10.3390/d6040681
De Stasio BT, Schrimpf MB, Cornwell BH. Phytoplankton Communities in Green Bay, Lake Michigan after Invasion by Dreissenid Mussels: Increased Dominance by Cyanobacteria. Diversity. 2014; 6(4):681-704. https://doi.org/10.3390/d6040681
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Stasio, Bart T., Michael B. Schrimpf, and Brendan H. Cornwell. 2014. "Phytoplankton Communities in Green Bay, Lake Michigan after Invasion by Dreissenid Mussels: Increased Dominance by Cyanobacteria" Diversity 6, no. 4: 681-704. https://doi.org/10.3390/d6040681
APA StyleDe Stasio, B. T., Schrimpf, M. B., & Cornwell, B. H. (2014). Phytoplankton Communities in Green Bay, Lake Michigan after Invasion by Dreissenid Mussels: Increased Dominance by Cyanobacteria. Diversity, 6(4), 681-704. https://doi.org/10.3390/d6040681




