A New Species of Gammanema (Nematoda: Chromadorida: Selachinematidae) from Jeju Island, South Korea †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Morphological Analysis
2.2. DNA Extraction and Amplification
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
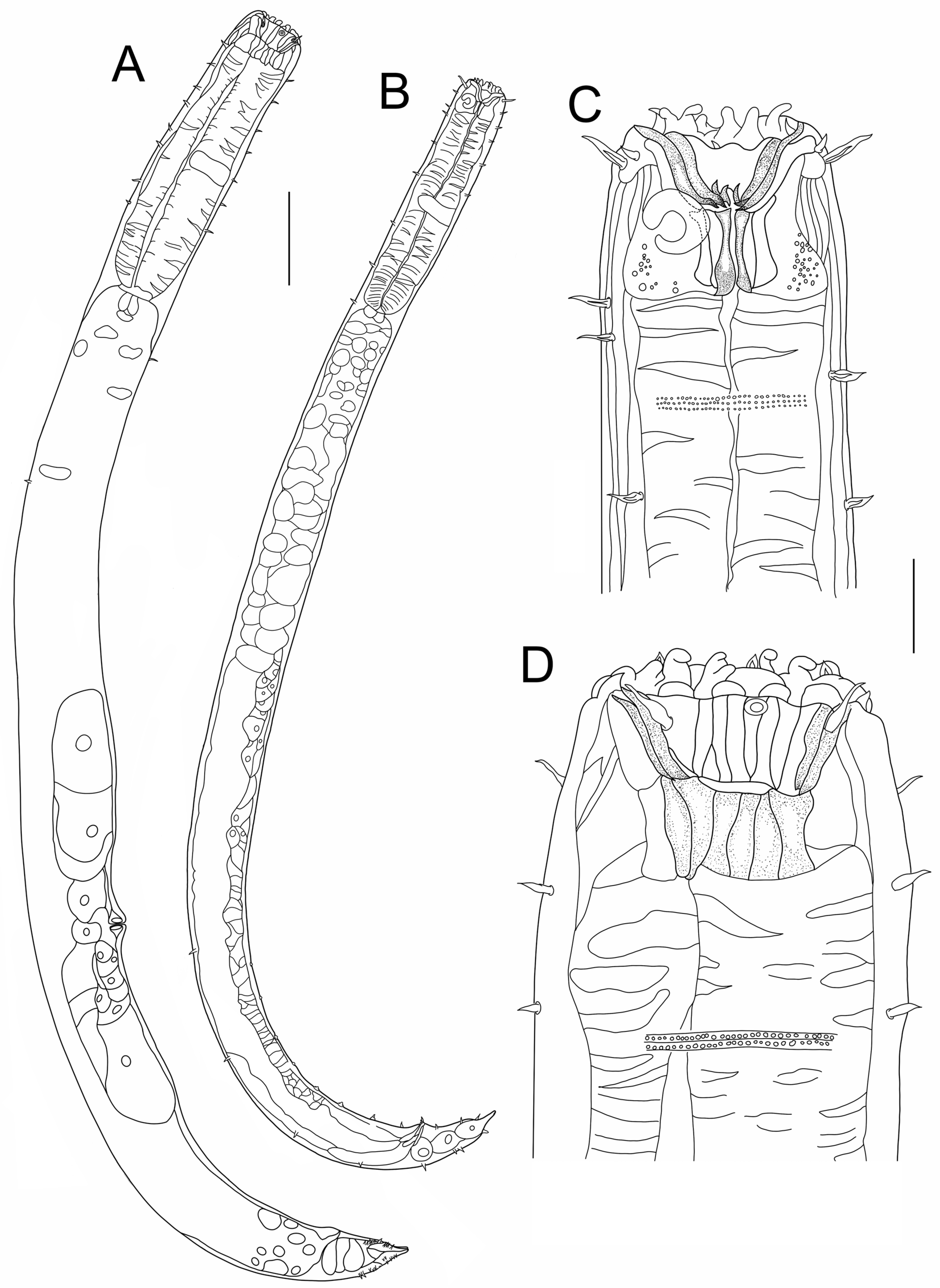
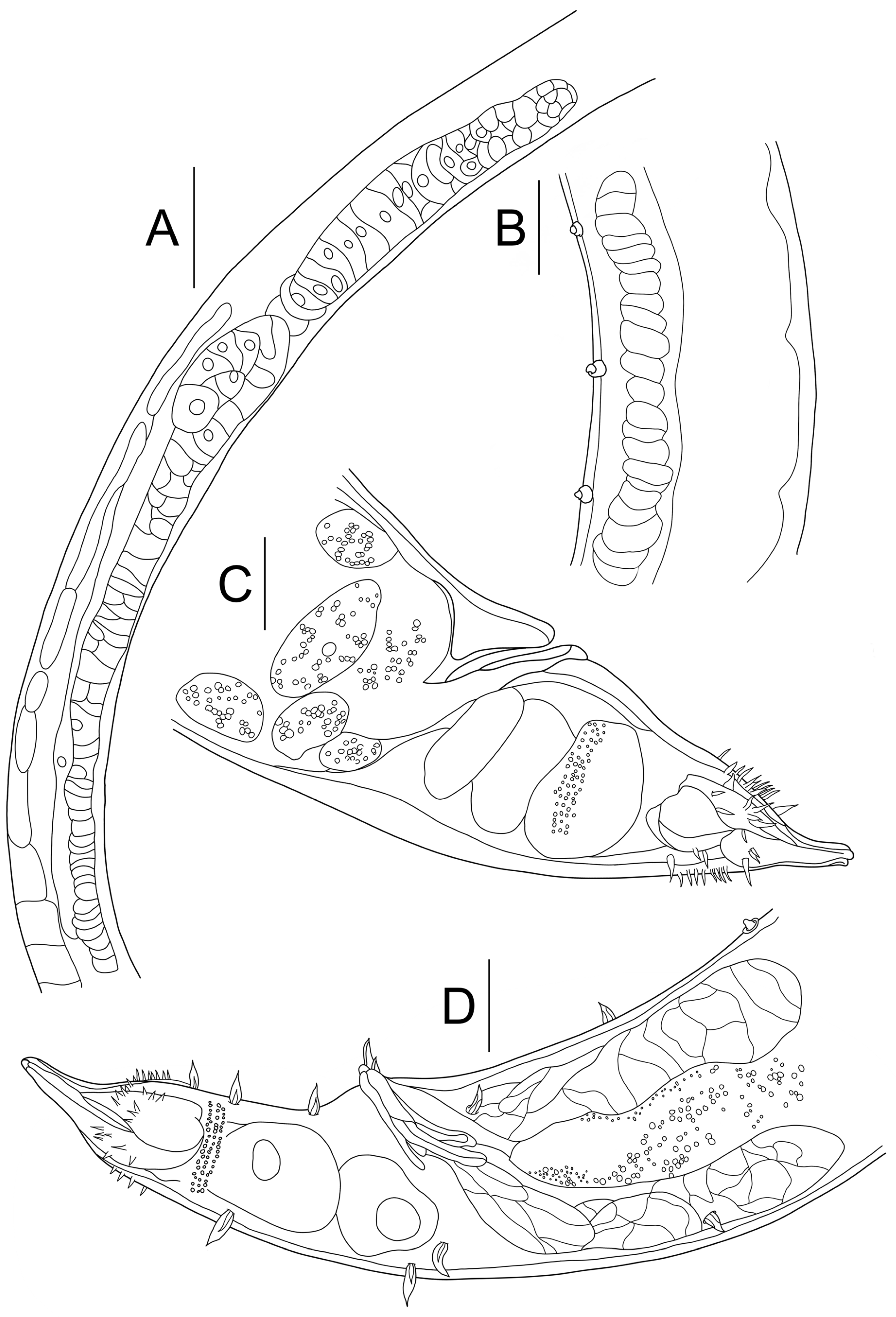
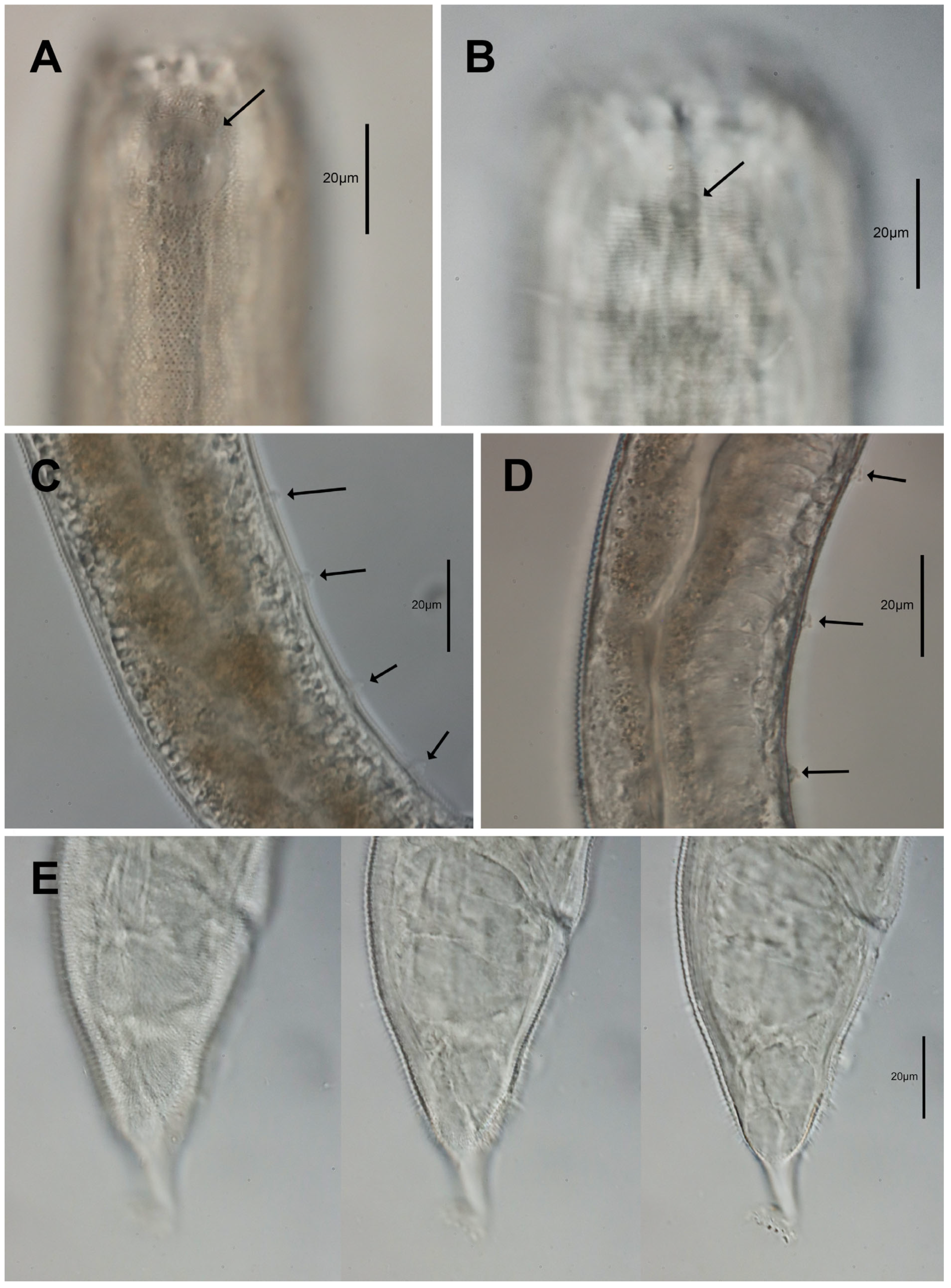
3.1. Morphological Analysis
- Gammanema agglutinans Leduc, 2013 (Leduc 2013: 21–25, Figures 11–13, Table 2; Continental slope of New Zealand, Chatham Rise, 350–1238 m depth) [29].
- Gammanema anthostoma Okhlopkov, 2002 (Okhlopkov 2002: 42–45, Figures 2 and 3; Russia, White Sea, Kandalaksha Bay) [1].
- Gammanema cancellatum Gerlach, 1955 (Gerlach 1955: 271–272, Figure 10; Libertad, coastal groundwater, San Salvador, El Salvador) [30].
- Gammanema conicauda Gerlach, 1953 (Gerlach, 1953: 553–555, Figure 17; Tyrrhenian Sea, area of Naples, surf zone; North Sea coast) [31].
- Gammanema curvata Gagarin & Klerman, 2007: 780, Figure 2, Table 2; Mediterranean coast of Israel) [32].
- Gammanema kosswigi Gerlach, 1964 (Gerlach 1964: 38–39, Figure 11; Maldive Islands) [7].
- Gammanema lunatum Leduc & Zhao, 2025 (Leduc & Zhao 2025: 133–138, Figures 6–9; New Zealand, Upper continental slope, 680 m depth) [3].
- Gammanema magnum Shi & Xu, 2018 (Shi & Xu 2018: 3–9, Figures 1–4, Table 1; East China Sea, Nanji Islands, Dasha’ao Beach) [34].
- Gammanema mediterraneum Vitiello, 1970 (Vitiello 1970: 491–493, Figure XV 30 a–e; West Mediterranean) [35].
- Gammanema okhlopkovi Tchesunov, Jeong & Lee, 2020 (Tchesunov, Jeong & Lee 2020: 8–13, Figure 4–7, Table 3; Jeju Island, South Korea) [6].
- Gammanema polydonta Murphy, 1965 (Murphy 1965: 176–170, Figures 3A–C, 4A–H; Chilean coast) [8].
- Gammanema smithi Murphy, 1964 (Murphy 1964: 194–198, Figures 3A,B,D,E, 4, 5B; Puget Sound [36].
- Gammanema tchesunovi Gagarin & Klerman, 2007 (Gagarin & Klerman 2007: 782–785, Figure 3, Table 3; Mediterranean coast of Israel) [32].
- Locality: collected from a sandy subtidal zone of Gwangchigi Beach (33°27′24.35″ N 126°55′31.34″ E), Goseong-ri, Seongsan-eup, Seogwipo-si, Jeju Island, Republic of Korea.
- Materials examined: Holotype (NIBRIV0000927420), allotype (NIBRIV0000927421), two paratype males (one sequenced after digital micrograph for measurements, NIBRIV0000927422) and two paratype females (NIBRIV0000927423–NIBRIV0000927424) deposited to the National Institute of Biological Resources (Republic of Korea). All specimens were collected on 29 April 2025.
- Description:
- Diagnosis and relationships:
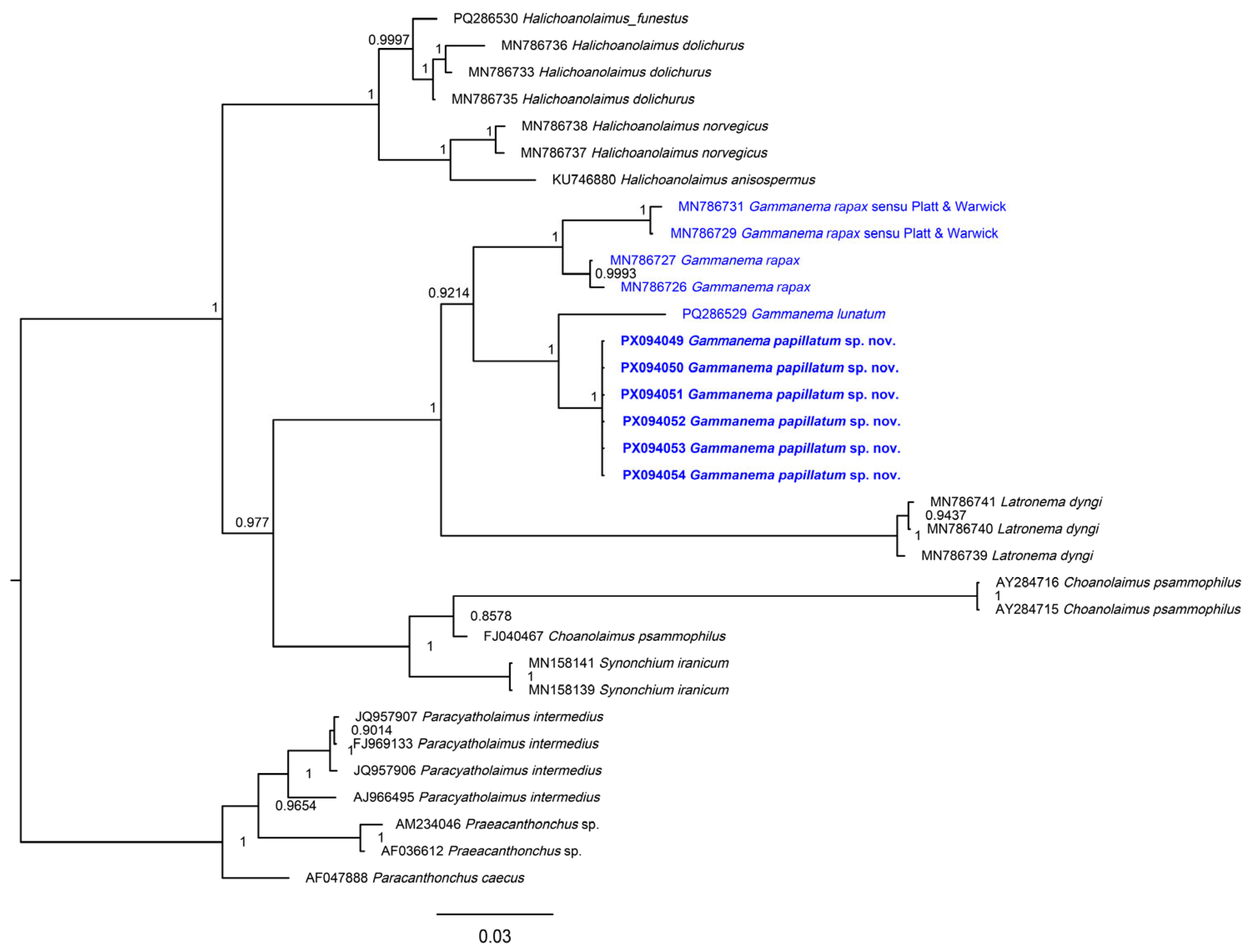
3.2. Molecular Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| L | Whole body length |
| a | Body length divided by maximum body diameter |
| b | Body length divided by pharynx length |
| c | Body length divided by tail length |
| c’ | Tail length divided by anal body diameter |
| cbd | Corresponding body diameter |
References
- Okhlopkov, J.R. Free-living nematodes of the families Selachinematidae and Richtersiidae in the White Sea (Nematoda, Chromadoria). Zoosystematica Rossa 2002, 11, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchesunov, A.V.; Okhlopkov, J.R. On some selachinematid nematodes (Chromadorida: Selachinematidae) deposited in the collection of the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History. Nematology 2006, 8, 21–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leduc, D.; Zhao, Z.Q. Three new nematode species (Chromadorida: Selachinematidae) from the continental slope of New Zealand. Eur. J. Taxon. 2025, 989, 119–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miljutin, D.M.; Gad, G.; Miljutina, M.M.; Mokievsky, V.; Fonseca-Genevois, V.; Esteves, A.M. The state of knowledge on deep-sea nematode taxonomy: How many valid species are known down there? Mar. Biodivers. 2010, 40, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moens, T.; Braeckman, U.; Derycke, S.; Fonseca, G.; Gallucci, F.; Gingold, R.; Guilini, K.; Ingels, J.; Leduc, D.; Vanaverbeke, J. Ecology of free-living marine nematodes. In Handbook of Zoology: Gastrotricha, Cycloneuralia and Gnathifera; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2013; Volume 2, pp. 109–152. [Google Scholar]
- Tchesunov, A.; Jeong, R.; Lee, W. Two New Marine Free-Living Nematodes from Jeju Island Together with a Review of the Genus Gammanema Cobb 1920 (Nematoda, Chromadorida, Selachinematidae). Diversity 2020, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, S.A. Revision der Choniolaiminae und Selachinematinae (freilebende Meeres-Nematoden). In Mitteilungen aus dem Hamburgischen Zoologischen Museum und Institut (Kosswig-Festschrift); Lütcke & Wulff: Hamburg, Germany, 1964; pp. 23–49. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, D.G. Chilean marine nematodes. Veröffentlichungen Inst. Meeresforsch. Bremerhav. 1965, 9, 173–203. [Google Scholar]
- Platt, H.; Warwick, R. Free-Living Marine Nematodes; Part 2: British Chromadorids; Brill, E.J., Backhuys, W., Eds.; Linnean Society of London: London, UK, 1988; p. 502. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.; Boström, S.; Holovachov, O. Revision of the genus Cobbionema Filipjev, 1922 (Nematoda, Chromadorida, Selachinematidae. Eur. J. Taxon. 2020, 702, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemys (Ed.) Nemys: World Database of Nematodes. Available online: https://nemys.ugent.be (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Son, K.; Jeong, R. The Discovery and Delimitation of a New Cryptic Species of Spirinia (Nematoda: Desmodoridae) Using SSU and LSU rDNA Divergence. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.J.; Fonseca, G.; Mundo-Ocampo, M.; Guilherme, B.C.; Rocha-Olivares, A. Diversity of free-living marine nematodes (Enoplida) from Baja California assessed by integrative taxonomy. Mar. Biol. 2010, 157, 1665–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leduc, D.; Zhao, Z.Q. Morphological and molecular characterisation of Spirinia antipodea Leduc n. sp.(Nematoda: Desmodoridae), a cryptic species related to S. parasitifera, from the coast of New Zealand. Nematology 2019, 21, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopper, D. Drawing and measuring nematodes. In Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food; Her Majesty’s Stationery Office: London, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Meeker, N.D.; Hutchinson, S.A.; Ho, L.; Trede, N.S. Method for isolation of PCR-ready genomic DNA from zebrafish tissues. Biotechniques 2007, 43, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holterman, M.; van der Wurff, A.; van den Elsen, S.; van Megen, H.; Bongers, T.; Holovachov, O.; Bakker, J.; Helder, J. Phylum-wide analysis of SSU rDNA reveals deep phylogenetic relationships among nematodes and accelerated evolution toward crown clades. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 1792–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ley, P.; De Ley, I.T.; Morris, K.; Abebe, E.; Mundo-Ocampo, M.; Yoder, M.; Heras, J.; Waumann, D.; Rocha-Olivares, A.; Jay Burr, A.H.; et al. An integrated approach to fast and informative morphological vouchering of nematodes for applications in molecular barcoding. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2005, 360, 1945–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. Clustal-W—Improving the Sensitivity of Progressive Multiple Sequence Alignment through Sequence Weighting, Position-Specific Gap Penalties and Weight Matrix Choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. A Simple Method for Estimating Evolutionary Rates of Base Substitutions through Comparative Studies of Nucleotide-Sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. Mrbayes: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and high-performance computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A. Figtree, Version 1.4.4; Institute of Evolutionary Biology, University of Edinburgh: Edinburgh, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Inglis, W.G. An Outline Classification of the Phylum Nematoda. Aust. J. Zool. 1983, 31, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitwood, B.G. A revised classification of the Nematoda. J. Parasitol. Pap. Helminthol. Ninth Annu. Meet. 1933, 20, 115–148. [Google Scholar]
- Cobb, N.A. Selachinema, a new nematode genus with remarkable mandibles. In Contributions to a Science of Nematology; University of Nebraska–Lincoln: Lincoln, NE, USA, 1914; Volume 4, pp. 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Cobb, N.A. One hundred new nemas (type species of 100 new genera). In Contributions to a Science of Nematology; University of Nebraska–Lincoln: Lincoln, NE, USA, 1914; Volume 9, pp. 217–343. [Google Scholar]
- Leduc, D. Two new genera and five new species of Selachinematidae (Nematoda, Chromadorida) from the continental slope of New Zealand. Eur. J. Taxon. 2013, 63, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, S.A. Zur Kenntnis der freilebenden marinen Nematoden von San Salvador. Z. Wiss. Zool. 1955, 158, 249–303. [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach, S.A. Die Nematodenbesiedlung des Sandstrandes und des Küstengrundwassers an der italienischen Küste I. Systematischer Teil. Arch. Zool. Ital. 1953, 37, 417–640. [Google Scholar]
- Gagarin, V.G.; Klerman, A.K. New species of predatory chromadorids (Nematoda, Chromadorida) from the Mediterranean Sea. Zool. Zhurnal 2007, 86, 778–786. [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach, S.A. Die Nematodenfauna der Uferzonen und des Küstengrundwassers am finnischen Meeresbusen. Acta Zool. Fenn. 1953, 73, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, B.Z.; Xu, K.D. Two new rapacious nematodes from intertidal sediments, Gammanema magnum sp. nov. and Synonchium caudatubatum sp. nov. (Nematoda, Selachinematidae). Eur. J. Taxon. 2018, 405, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitiello, P. Nématodes libres marins des vases profondes du Golfe du Lion. II. Chromadorida. Téthys 1970, 2, 449–500. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, D.G. Free-living marine nematodes, I. Southerniella youngi, Dagda phinneyi, and Gammanema smithi, new species. Proc. Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 1964, 31, 190–198. [Google Scholar]
- Wieser, W. Free-living marine nematodes II. Chromadoroidea. Acta Univ. Lund. NF 1954, 50, 1–148. [Google Scholar]
- de Man, J.G. Sur quelques nématodes libres de la mer du Nord, nouveaux ou peu connus. Mémoires Société Zool. Fr. 1888, 1, 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- de Man, J.G. Die Einheimischen, Frei In Der Reinen Erde Und Im Süssen Wasser Lebenden Nematoden. Monographisch Bearbeitet. Vorläufiger Bericht und descriptiv-systematischer Theil. Tijdschr. Ned. Dierkd. Ver. 1879, 5, 1–104. [Google Scholar]


| Characters | Male | Female | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Holotype | Males (n = 3) Mean ± sd (Range) | Allotype | Females (n = 3) Mean ± sd (Range) | |
| L | 1366 | 1247 ± 99.7 (1122–1366) | 1574 | 1539 ± 35.5 (1503–1574) |
| a (L/gbd) | 23.6 | 22 ± 1 (21.2–23.6) | 16.7 | 20 ± 0.5 (19.7–20.6) |
| b (L/pharynx length) | 5.2 | 5 ± 0.2 (4.8–5.2) | 4.7 | 5 ± 0.1 (4.8–5) |
| c (L/tail length) | 16.1 | 17 ± 1 (16.1–18.4) | 19.7 | 19 ± 1.1 (18.3–20.6) |
| c’ (tail length/anal body diameter) | 2.1 | 2 ± 0.2 (1.7–2.1) | 1.5 | 2 ± 0.2 (1.6–2) |
| Inner labial/Outer labial setae length | 3 | 2 ± 0.5 (2–3) | 3 | 3 ± 0.5 (2–3) |
| Cephalic setae length | 11 | 12 ± 1.9 (11–15) | 13 | 19 ± 0.5 (18–19) |
| Cephalic setae cbd | 42 | 39 ± 2.1 (37–42) | 66 | 57 ± 0.5 (56–57) |
| Amphid (at center) cbd | 47 | 44 ± 2.9 (40–47) | 70 | 61 ± 1.5 (59–62) |
| Amphid height | 13 | 14 ± 1.9 (13–17) | 7 | 6 ± 0 (6–6) |
| Amphid width | 11 | 13 ± 3.1 (10–17) | 7 | 6 ± 0 (6–6) |
| Amphid width/body width (%) | 0.23 | 0 ± 0.1 (0.2–0.4) | 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0 (0.1–0.1) |
| Amphid (at center) distance to anterior | 17 | 15 ± 1.7 (13–17) | 22 | 26 ± 1 (25–27) |
| Buccal cavity (pharyngostome) distance to the anterior | 37 | 35 ± 2.2 (32–37) | 47 | 51 ± 2 (49–53) |
| Anterior (gymnostome) depth | 19 | 18 ± 1.9 (15–19) | 27 | 26 ± 1 (25–27) |
| Anterior rhabdion length | 21 | 20 ± 0.8 (19–21) | 26 | 26 ± 1 (25–27) |
| Posterior rhabdion length | 17 | 16 ± 1.2 (14–17) | 22 | 21 ± 2 (19–23) |
| Nerve ring distance to the anterior | 125 | 121 ± 5.2 (114–125) | 186 | 163 ± 2 (161–165) |
| Nerve ring cbd (corresponding body diameter) | 53 | 50 ± 5 (43–54) | 83 | 66 ± 2 (64–68) |
| Pharynx length | 263 | 249 ± 11 (236–263) | 335 | 313 ± 2 (311–315) |
| Pharyngeal base width | 37 | 34 ± 2.5 (31–37) | 69 | 57 ± 6 (51–63) |
| Pharynx cbd | 50 | 49 ± 0.9 (48–50) | 76 | 56 ± 4.5 (51–60) |
| Max body diameter | 58 | 55 ± 2.1 (53–58) | 94 | 77 ± 3.5 (73–80) |
| Spicule length (as arc) | 43 | 38 ± 4.1 (33–43) | n/a | n/a |
| Gubernaculum length | 24 | 25 ± 2.9 (22–29) | n/a | n/a |
| Supplementary organs | 7 | 8 ± 0.5 (7–8) | n/a | n/a |
| Posterior-most supplement distance to the anterior to the cloacal opening | 58 | 61 ± 2.2 (58–63) | n/a | n/a |
| Distance between supplementary organs | 28–42 | 27–36, 20–26 | n/a | n/a |
| Cloacal/anal body diameter | 41 | 39 ± 2.8 (35–41) | 53 | 44 ± 1 (43–45) |
| Tail length | 85 | 72 ± 9.9 (61–85) | 80 | 80 ± 6.5 (73–86) |
| Terminal cone portion (smooth) | 17 | 16 ± 0.9 (15–17) | 16 | 19 ± 6 (13–25) |
| Vulva distance to anterior | n/a | n/a | 1018 | 965 ± 27 (938–992) |
| Vulva body diam. | n/a | n/a | 92 | 81 ± 1.5 (79–82) |
| Vulva distance to anterior/total body length | n/a | n/a | 0.65 | 0.6 ± 0 (0.6–0.6) |
| Characteristic | G. papillatum sp. nov. | G. lunatum | G. agglutinans | G. conicauda | Other Gammanema spp. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male amphidial fovea shape | Loop-shaped (¾ turn) | Loop-shaped (¾ turn) | Loop-shaped (½ turn) | Unispiral | Multispiral |
| Female amphidial fovea shape | Unispiral (1.0 turn) | Unispiral (1.0 turn) | Spiral (1.5 turns) | Unispiral | Multispiral |
| Male amphid width/cbd (%) | 23–38 | 27–46 | 28–29 | 36 (calc) | – |
| Female amphid width/cbd (%) | 10 | 30 (error?) 10 (calc) | 10–12 | 11 (calc) | – |
| Cuticular spines | Present (minute) | Present (minute) | Present (minute) | Not specified | Absent |
| Precloacal supplements (number and shape) | 7–8 papillae | 6–10 cup-shaped | <6 tubular | 22 papillae | – |
| Posterior-most supplement distance to the anterior to the cloacal opening | 58–63 | 18–32 | – | – | – |
| Distance between precloacal supplements | 18–35 | 5–17 | – | – | – |
| Body length (µm) | 1122–1366 | 754–1196 | 544–696 | 1985–2419 | – |
| a ratio (L/gbd) | 21–23 | 13–15 | 10–11 | 41–48 | – |
| b | 5 | 5–6 | 4–5 | 7.3–7.7 | – |
| c | 16–18 | 13–20 | 12–13 | 33–38 | – |
| c’ | 1.7–2 | 1.3–1.6 | 1.2–1.3 | 1.1–1.4 | – |
| Outer labial setae length (µm) | 2–3 | 2–4 | 2 | 16 | – |
| Cephalic setae length (µm) | 11–15 | 8–20 | 10–11 | 30–33 | – |
| # | Species Name | Isolate Number | GenBank Accession Number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18S | 28S | |||
| 988F, 1813F | D2A | |||
| /1912R, 2646R | /D3B | |||
| (~1600 bp) | (~750 bp) | |||
| 1 | Gammanema papillatum sp. nov. | K1 | PX094049 | PX094055 |
| 2 | Gammanema papillatum sp. nov. | K2 | PX094050 | PX094056 |
| 3 | Gammanema papillatum sp. nov. | K3 | PX094051 | PX094057 |
| 4 | Gammanema papillatum sp. nov. | K6 | PX094052 | PX094058 |
| 5 | Gammanema papillatum sp. nov. | K8 | PX094053 | PX094059 |
| 6 | Gammanema papillatum sp. nov. | K9 | PX094054 | PX094060 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Son, K.; Jeong, R. A New Species of Gammanema (Nematoda: Chromadorida: Selachinematidae) from Jeju Island, South Korea. Diversity 2025, 17, 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17090639
Son K, Jeong R. A New Species of Gammanema (Nematoda: Chromadorida: Selachinematidae) from Jeju Island, South Korea. Diversity. 2025; 17(9):639. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17090639
Chicago/Turabian StyleSon, Kyeongmoon, and Raehyuk Jeong. 2025. "A New Species of Gammanema (Nematoda: Chromadorida: Selachinematidae) from Jeju Island, South Korea" Diversity 17, no. 9: 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17090639
APA StyleSon, K., & Jeong, R. (2025). A New Species of Gammanema (Nematoda: Chromadorida: Selachinematidae) from Jeju Island, South Korea. Diversity, 17(9), 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17090639






