Abstract
The ecological restoration of degraded alpine steppe is a critical component of ecological conservation efforts on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. In this study, we investigated the effects of fertilization, reseeding, and combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures on the vegetation community, soil properties and microbial community diversity in degraded alpine steppe through field vegetation surveys, and soil microbial high-throughput sequencing at an experimental site of fertilized and reseeded grassland restoration located in the Yellow River Source area. The results demonstrated the following: (1) both reseeding and combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures significantly affected grassland vegetation community structure and diversity; (2) fertilization and combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures significantly affected soil pH and total phosphorus (TP) content; (3) while fertilization and combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures markedly altered microbial community structure, reseeding alone significantly affected microbial diversity. Co-occurrence network analysis revealed that soil microbial communities were significantly influenced by fertilization restoration measures; redundancy analysis (RDA) showed that microbial communities under fertilization and combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures were primarily governed by soil TP, whereas those in control and reseeding plots were strongly associated with soil pH and organic carbon (SOC). This study explored effective restoration measures suitable for degenerating alpine steppe in the Yellow River Source area, aiming to provide a scientific basis and technical support for the ecological protection and restoration of the Three-River Headwaters.
1. Introduction
The Yellow River Source Region stands as one of the most ecologically sensitive and biodiverse regions within the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau’s natural ecosystems. With an average elevation exceeding 4200 m, the region exhibits a distinct plateau continental climate and supports a unique and representative alpine steppe ecosystem. It plays a vital role in delivering key ecosystem services and functions, including water source conservation, biodiversity preservation, and the development of sustainable livestock husbandry [1]. Affected by global climate change and human activities, particularly multiple stressors including high altitude, low temperatures, drought, freeze–thaw cycles, and overgrazing, alpine grasslands have undergone varying degrees of degradation. This has become one of the most critical ecological and environmental challenges in the Yellow River Source Region [2], significantly impairing the integrity and sustainability of key regional ecological functions such as water conservation [3]. This degradation not only leads to the loss of vegetation community diversity and the deterioration of soil physicochemical properties (e.g., compaction, salinization) but, more crucially, significantly alters the structure and function of soil microbial communities [4,5]. These changes lead to diminished microbial diversity, disrupt nutrient and carbon cycling processes, and destabilize the soil microbiota, ultimately exacerbating the degradation of the alpine steppe ecosystem. Therefore, exploring the restoration effects of different measures on degraded alpine steppe holds significant importance for ecological protection and restoration efforts across the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau.
Restoring degraded alpine steppe ecosystems is a systemic, long-term, and highly challenging endeavor, where the selection of appropriate restoration measures is critical [6]. While common practices such as fencing enclosure, soil aeration techniques, fertilization, reseeding, and tillage have achieved initial success in temperate grassland restoration [7,8,9,10], they exhibit notable limitations. For example, prolonged fencing may restrict species dispersal [11], and mechanical interventions like tillage or root cutting risk damaging soil structure—particularly in the fragile, arid alpine steppes characterized by thin, impoverished soils [12]. Studies indicate that fertilization and reseeding are among the most common and effective measures for restoring degraded alpine grasslands [13]. Reseeding with native grass species improves seedling survival rates and enhances vegetation cover and biomass, while fertilization directly enriches soil nutrients, yielding significant short-term gains in grassland productivity and promoting vegetation growth and development. Studies by Li Xilai et al. [14] on degraded alpine meadows showed that both fertilization and reseeding restoration measures effectively increased above- and belowground communities, but had negligible effects on promoting plant species diversity. Similarly, Yu Hao et al. [15] found that reseeding alone enhanced biomass in the temperate grasslands of Gonghe County, Qinghai, yet significantly reduced species richness. Moreover, their research revealed that reseeding, fertilization, and combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures all decreased the network complexity of bacterial communities while enhancing their stability. Gu et al. [8] demonstrated that the application of organic fertilizer significantly improves soil quality and rhizosphere microbial community health in alpine meadows. However, existing research predominantly focuses on degraded alpine meadow ecosystems [16,17,18], with inconsistent outcomes across different restoration measures [19,20,21]. Given the distinct cold arid habitats and ecological characteristics of alpine steppe compared to alpine meadows, it is imperative to investigate the differential effects of fertilization, reseeding, and combined restoration measures on the restoration of aboveground and belowground biodiversity in this unique grassland type. Such studies are critical for developing targeted ecological rehabilitation strategies in the Yellow River Source region.
Aboveground communities and belowground biodiversity serve not only as critical indicators reflecting grassland growth conditions and ecological environmental assessments [22,23] but also as essential parameters for evaluating ecosystem functions in both macroscopic and microscopic states of alpine steppe. The existing studies on belowground biomass in degraded grasslands primarily analyze soil physicochemical properties and microbial community characteristics, including soil nutrient content, microbial community composition, and intra/intergroup diversity [24,25]. However, advancements in high-throughput sequencing technology have revealed that soil microorganisms exhibit not only high taxonomic diversity but also complex interspecies interactions. Therefore, elucidating the relationship between soil microbial diversity and ecological functions requires moving beyond taxonomic diversity to incorporate microbial co-occurrence networks. These networks can visualize interspecies interactions, reveal underlying mechanisms stabilizing microbial communities, and reflect ecological linkages and processes that cannot be captured by taxonomic diversity alone [26,27]. Compared to single-species microbial community diversity studies, microbial co-occurrence network analysis better captures the diversity, complexity, and stability of soil microorganisms in degraded alpine steppe ecosystems [28]. Wagg et al. [29] experimentally demonstrated that both soil microbial diversity and network complexity positively influence multiple ecosystem functions. Therefore, integrating microbial co-occurrence network analysis with investigations of soil microbial community composition and diversity offers a more comprehensive approach to elucidating the mechanisms underlying belowground biomass dynamics under different restoration measures. This integrated framework enables researchers to move beyond taxonomic diversity and explore functional synergies, competitive interactions, and stability mechanisms shaped by a microbial community structure.
Based on this, our study focused on degraded alpine steppe in the Yellow River Source area of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, establishing experimental sites to implement three restoration measures: fertilization, reseeding, and combined fertilization with reseeding. Through systematic analysis of the response characteristics of vegetation community traits, soil physicochemical properties, as well as microbial community composition, diversity, and co-occurrence networks in degraded alpine steppe under different restoration measures, this study aims to investigate the variations of aboveground and belowground biodiversity under different restoration measures to identify the most effective restoration measures for degraded alpine steppe ecosystems in the Yellow River Source area and to provide evidence-based scientific support for the ecological restoration of degraded alpine steppe in the Yellow River Source region, while offering scientific foundations and technical guidance for conservation and rehabilitation projects in Three-River-Source National Park. To achieve this objective, we proposed the working hypothesis that the combined fertilization with the reseeding restoration measure serves as an effective approach for degraded alpine steppe in the Yellow River Source Region, and this measure directly influences both vegetation communities and microbial diversity in alpine steppe ecosystems.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site Description
The experimental site is located in Zhalinghu Township, Maduo County, Qinghai Province, China (97°1′20″–99°14′57″ E, 33°55′5″–35°28′15″ N), which lies within the core area of the Yellow River Source Park in the Three-River-Source National Park. It is also one of the most typical and severely degraded alpine grassland regions in Maduo County. In May 2024, a permanent monitoring and ecological restoration experimental site was established on a moderately degraded alpine steppe slope (5°), covering an area of 1200 m2. The dominant plant species include Stipa purpurea Griseb., Carex moorcroftii Falc. ex Boott, and Leontopodium leontopodioides (Willd.) Beauverd. A total of 13 alpine steppe plant species belonging to 8 families and 12 genera were recorded within the experimental area (Table S1). The region exhibits a typical plateau continental climate, with an elevation of approximately 4300 m. The mean annual air temperatures are 6.1 °C in spring/summer and −3.6 °C in autumn/winter. The annual precipitation averages 300 mm, peaking from June to August [30].
2.2. Experimental Design
The experiment included three restoration measures and one control group (Figure 1): fertilization, reseeding, combined fertilization with reseeding, and control. Each restoration measure had five randomized replicate quadrats (2 m × 2 m), totaling 20 quadrats enclosed by ropes anchored at four corner stakes. The restoration strategies followed established ecological restoration standards in the region. For the reseeding restoration measure, native grass seeds with germination rates >60% were mixed and sown, including Poa crymophila Keng (3 g/quadrat) and Elymus breviaristatus (Keng) Keng f. (12 g/quadrat). The fertilization restoration measure used a granular organic fertilizer formulated for pasture (N:P2O5:K2O = 18:12:5) at a rate of 30 kg/ha (180 g/quadrat). The control group received no interventions. All quadrats underwent sod-breaking treatments (cutting depth ≈ 3 cm, row spacing 10 cm), were covered with green non-woven fabric post-sowing, and the fabric was removed one month after uniform seedling emergence. To prevent livestock disturbance, the entire experimental site was fenced with wire.
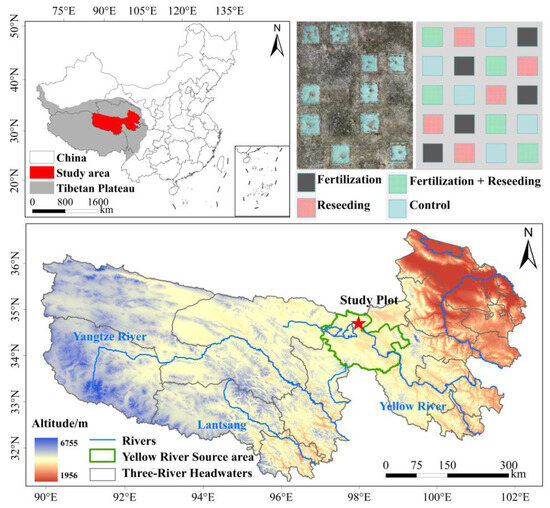
Figure 1.
Design of fixed observation experiment in the study area and ecological restoration.
2.3. Plot Investigation and Sample Collection
During the peak growing season of August 2024, aboveground and belowground biodiversity surveys and sample collection were conducted in the experimental plots. For vegetation surveys, a 1 m × 1 m quadrat sampling method was employed to monitor species abundance, height, cover, biomass, and frequency in each plot. All vegetation within the quadrats was cut at ground level, oven-dried at 85 °C for 24 h, and weighed to determine dry biomass. In the same plots, soil samples were collected using a 7 cm diameter soil auger under sterile conditions. Three random cores were taken from the 0–20 cm soil layer, mixed homogeneously, and divided into two subsamples: One subsample was sieved through a 2 mm mesh, air-dried, and analyzed for total nitrogen (TN), TP, total potassium (TK), SOC, and pH. The other subsample was stored in sterile centrifuge tubes, frozen, and transported to the laboratory for soil microbial sequencing. Five replicates were maintained for each treatment gradient.
2.4. Determination of Soil Physicochemical Properties
Soil pH was measured using the glass electrode method. SOC content was determined by potassium dichromate oxidation with external heat digestion. TN content was measured via digestion with sulfuric acid and accelerant using the Kjeldahl method. TP content was analyzed using alkaline fusion with NaOH followed by the molybdenum-antimony anti-spectrophotometric method. TK content was quantified using the flame photometric method with NaOH fusion.
2.5. Soil Microbial Analysis
Soil microbial DNA was extracted using the Magnetic Soil and Stool DNA Kit (DP712), followed by PCR amplification of the 16S rRNA and ITS rRNA genes. Amplicons were sequenced on the Illumina NovaSeq platform. ASV (Amplicon Sequence Variant) data were taxonomically annotated to analyze bacterial and fungal community diversity at the phylum level. Alpha diversity was evaluated using the Chao 1, Faith’s PD, Shannon, and Simpson indices. Beta diversity was assessed via NMDS (Non-Metric Multidimensional Scaling) based on Unifrac distance matrices, with statistical significance tested using PERMANOVA (Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance). RDA was performed to explore relationships between environmental factors and microbial communities. Co-occurrence networks were constructed using the “WGCNA” package in R, with Spearman correlation coefficients calculated for ASVs. To reduce network complexity, edges with |r| > 0.7 and p < 0.001 were retained for bacteria, while |r| > 0.6 and p < 0.001 were used for fungi. Network parameters were visualized and analyzed using Gephi 0.10.1 software.
2.6. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
Experimental data were organized using Excel 2010. Three community diversity indices—Simpson, Shannon–Wiener, and Pielou evenness—were calculated based on plant species survey data. Statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics 27.0.1. Specifically, one-way ANOVA (analysis of variance) and the LSD (least significant difference) test were employed to assess differences in vegetation communities, soil physicochemical properties, and soil microbial communities among different restoration measures. Each gradient was set up with 5 replicates. The soil samples from each plot were uniformly mixed to test physicochemical properties and extract DNA. All statistical analyses were based on data from the 5 replicate plots. Origin 2024 software and R language 4.2.2 were utilized for data visualization and supplementary statistical analyses.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Different Restoration Measures on Vegetation Communities and Diversity
Vegetation community characteristics under the three restoration measures showed distinct differences (Figure 2). Compared to the control group, the combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures significantly increased grassland vegetation coverage and biomass (p < 0.05), with increases of 31 ± 1.86% in coverage and 111.22 ± 3.71 g·m−2 in biomass. The fertilization restoration measures only significantly improved grassland biomass (p < 0.05), with an increment of 39.54 ± 1.11 g·m−2, but had no significant effect on coverage (p > 0.05). The reseeding restoration measures did not significantly enhance grassland coverage or biomass (p > 0.05).
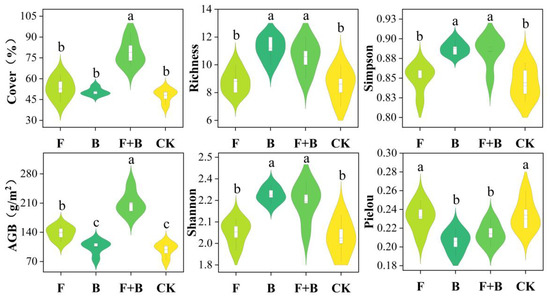
Figure 2.
Effects of different restoration measures on vegetation communities and diversity. Note: F: Fertilization; B: Reseeding; F+B: Combined fertilization with reseeding; CK: Control group, the same below. Different letters indicate significant differences between groups (p < 0.05), the same below.
Regarding grassland vegetation diversity, both reseeding and combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures significantly increased the richness, Simpson index, and Shannon index of grassland vegetation communities compared to the control group, and also significantly decreased the Pielou index (p < 0.05). In contrast, the fertilization restoration measure had no significant effect on vegetation community diversity (p > 0.05).
3.2. Effects of Different Restoration Measures on Soil Physicochemical Properties
Analyses of soil physicochemical properties following different restoration measures showed that fertilization and combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures significantly reduced soil pH (p < 0.05), improved the alkaline soil environment, and significantly increased TP content (p < 0.05). No significant effects on SOC, TN, or TK contents were observed under any of the restoration measures (p > 0.05) (Figure S1).
3.3. Effects of Different Restoration Measures on Soil Microbial Communities
3.3.1. Composition Characteristics of Soil Microbial Communities Under Different Restoration Measures
Based on the OTU (operational taxonomic unit) data obtained, taxonomic annotation was performed to analyze the relative abundances of the top 10% of bacterial and fungal taxa at the phylum level. A total of 14 bacterial phyla and 7 fungal phyla were identified (Figure 3). Actinobacteriota, Proteobacteria, and Acidobacteriota were the dominant bacterial phyla, with average relative abundances of 30.65%, 20.64%, and 18.81%, respectively. Their cumulative abundance exceeded 70%, among which Actinobacteriota exhibited the highest relative abundance. To compare differences in bacterial abundance across different restoration measures, significant variations were observed in the abundances of Actinobacteriota, Chloroflexota, and Firmicutes under the fertilization restoration measure (p < 0.05). Myxococcota exhibited significant differences specifically under the reseeding restoration measure (p < 0.05), whereas no significant differences were observed in Proteobacteria and Acidobacteriota across the four restoration measures (p > 0.05). Additionally, Methylomirabilota were detected in both groups under the fertilization restoration measure. For fungi, Ascomycota, Mortierellomycota, and Basidiomycota were the dominant phyla, accounting for 95.08% of the total fungal abundance—among which Ascomycota (78.43%) had the highest relative abundance. Comparisons across the four restoration measures revealed significant differences in Basidiomycota abundance under the fertilization restoration measure (p < 0.05), while no significant differences were observed in Ascomycota and Mortierellomycota (p > 0.05).
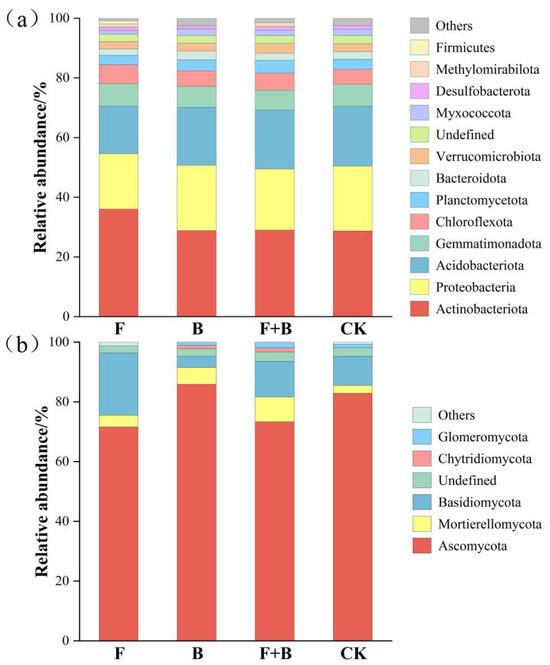
Figure 3.
Composition of soil microbial community under different remediation measures. Note: (a) The relative abundance of bacteria at the phylum level; (b) The relative abundance of fungi at the phylum level.
3.3.2. Diversity Characteristics of Soil Microbial Communities Under Different Restoration Measures
Alpha diversity analysis indicated that the Chao 1 index and Faith’s PD index of both bacterial and fungal communities in soil under reseeding and combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures were relatively high but showed no significant differences. The Simpson index of fungal communities significantly decreased under the reseeding restoration measures (p < 0.05), while no significant changes were observed in the control group, fertilization restoration measures, or combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures (p > 0.05). Additionally, the reseeding restoration measure significantly enhanced the heterogeneity of fungal community alpha diversity (Table 1).

Table 1.
The α diversity of soil microbial communities under different restoration measures. Note: Different letters indicate significant differences between groups (p < 0.05).
NMDS was used to analyze the beta diversity of bacterial and fungal communities (Figure S2). After calculation based on the weighted Unifrac distance, the two-dimensional stress values of bacterial and fungal community compositions ranged between 0.13 and 0.15, indicating certain interpretive significance. Significant differences were observed in the compositional structure of microbial communities among different groups. Specifically, no significant differences were detected between the bacterial community structures of different restoration measures and the control group, but significant differences were found between the fertilization and combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures. Significant differences in fungal community structure were detected between restoration measures (fertilization alone and combined fertilization with reseeding) and the control group.
3.3.3. Soil Microbial Ecological Networks Under Different Restoration Measures
To further investigate the potential interactions between microorganisms under different restoration measures, we constructed co-occurrence networks for bacterial and fungal communities under four conditions (F, B, FB, and CK) (Figure 4) and calculated relevant topological properties (Table S2). Compared to fungal communities, bacteria formed more complex co-occurrence networks with higher numbers of nodes and edges. Compared to the control group, the number of edges, average degree, and network density of co-occurrence networks for both bacterial and fungal communities decreased under the three restoration measures. Notably, the fertilization restoration measure exhibited significantly lower values than the reseeding and combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures. The modularity index of bacterial networks under the three restoration measures was higher than that of the control group, with the highest value (0.967) observed under the fertilization restoration measure. For fungal networks, only the fertilization restoration measure showed a modularity index higher than the control, while the others displayed no significant differences. Under the fertilization, reseeding, and combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures, the number of positive correlations in bacterial and fungal networks significantly outnumbered the negative correlations. Analysis of core species within modules of different networks revealed that the key taxa in bacterial networks were Actinobacteriota, Acidobacteriota, and Proteobacteria, accounting for up to 80.78% of the community under the fertilization restoration measure. In fungal networks, nodes were dominated by Ascomycota, particularly under the fertilization restoration measure, where Ascomycota alone constituted 60.45% of the total community.
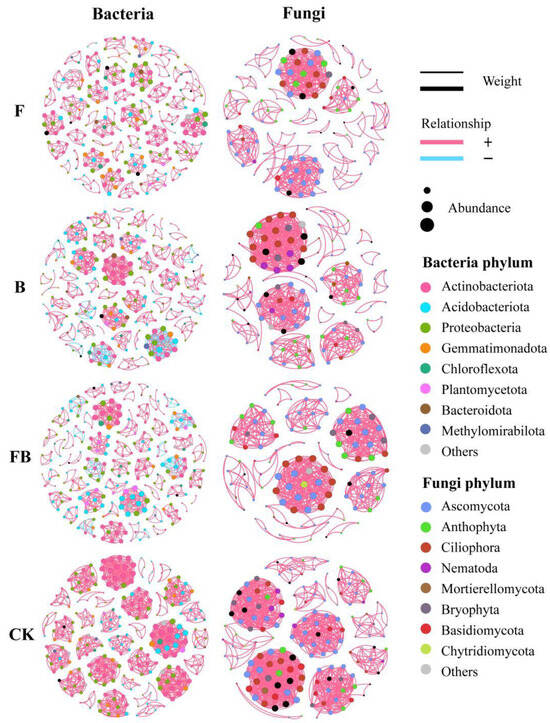
Figure 4.
Microbial co-occurrence networks of soil bacteria and fungi under different remediation measures.
3.3.4. Effects of Environmental Factors on Soil Microbial Communities Under Different Remediation Measures
RDA was further used to investigate the correlations between bacterial and fungal communities and soil physicochemical properties under different restoration measures. The results from the RDA analysis indicated that the sample points of bacterial and fungal communities under the fertilization and combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures were primarily distributed on the right side of the first ordination axis, with their composition mainly driven by TP—particularly showing significant effects on the bacterial community structure. In contrast, sample points under the reseeding and control restoration measures were mostly distributed on the left side of the first ordination axis and were significantly influenced by soil pH and SOC (Figure 5a,b).
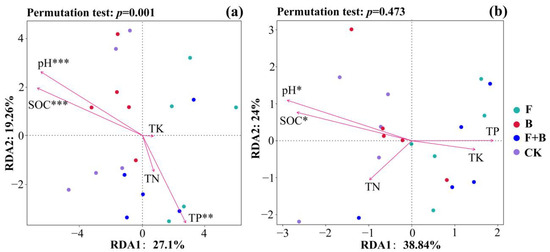
Figure 5.
RDA analysis of microbial communities and soil environmental factors. Note: (a) redundancy analysis of bacterial community; (b) redundancy analysis of fungal community; different colored dots represent sample groups of different restoration measures; arrows represent environmental factors; * means p < 0.05, ** means p < 0.01, *** means p < 0.001.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Different Restoration Measures on Aboveground Vegetation in Degraded Alpine Steppe
The recovery of grassland species diversity and aboveground biomass is a critical indicator for assessing the effectiveness of ecological restoration in degraded alpine grasslands. Changes in vegetation communities under different restoration measures often reflect key drivers of recovery [31]. This study found that the combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures significantly improved vegetation cover and biomass, demonstrating superior efficacy compared to single restoration measures (fertilization or reseeding alone). This suggests that all three restoration measures contributed positively to restoration, but their outcomes varied. This aligns with findings by Li et al. [14] and Hu et al. [16] in alpine meadows, where combined fertilization with reseeding yielded similar restoration outcomes. Soil fertilization rapidly replenishes essential nutrients (e.g., N-P-K) for plant growth in the short term. Concurrently, reseeding with native graminoid species—such as Elymus breviaristatus and Poa crymophila, fills the vacant ecological niches in degraded grasslands. By effectively competing with other species, these introduced grasses preferentially occupy the spatial and resource niches made available by degradation [14,32]. This synergistic approach thereby significantly enhances overall biomass and vegetation coverage. Regarding vegetation community diversity, this study found that reseeding significantly increased the richness, Simpson index, and Shannon index of grassland communities while significantly reducing Pielou’s evenness index. Mi et al. [33] analyzed 1386 datasets from global degraded grasslands and similarly concluded that grass species mixtures significantly enhance diversity indices, with stronger short- and medium-term restoration effects. In contrast, fertilization alone did not significantly enhance vegetation community diversity in this study, consistent with Niu et al.’s [34] findings that fertilization had no significant impact on species diversity. However, it might improve functional richness and functional diversity indices. This outcome may arise from varying responses of different grassland types and species compositions to short-term fertilization and fluctuations in organic fertilizer concentrations, leading to insignificant changes in community species diversity under fertilization restoration measures. This study fully considered climatic conditions in the Yellow River Source region and drew on prior experience to implement a mixed planting strategy using two native grass species, achieving ecological restoration of alpine steppe. This approach not only avoided resource depletion caused by introducing non-dominant species during reseeding but also ensured the stability of dominant species within the community [35].
4.2. Effects of Different Restoration Measures on Soil Physicochemical Properties
As the substrate for plant growth, changes in soil physicochemical properties influence plant growth characteristics and reflect plant–soil interactions. This study found that fertilization and combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures significantly reduced soil pH and increased TP content. In contrast, SOC, TN, and TK showed no significant changes. These results indicate that fertilization plays a dominant role in altering soil physicochemical properties, likely due to the introduction of exogenous chemical elements. Prolonged sunlight exposure in alpine steppe leads to significant water evaporation from the soil, causing salt accumulation at the soil surface. This directly alters soil pH in the short term and affects plant root growth [36]. In contrast, the application of organic fertilizer weakens salt accumulation at the soil surface. It not only enables plants to better utilize water fixed by nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium but also enhances the decomposition of SOC, thereby improving the alkaline soil environment and benefiting the growth and development of alpine steppe vegetation [37]. Additionally, apart from a significant increasing trend in TP content following pH reduction, no significant changes were observed in other indicators. To explain this phenomenon, Robles et al. [38] attributed it to the release of phosphorus, which promoted the dissolution of soil phosphates and thus reduced soil pH. Other indicators, however, were influenced by multiple factors such as restoration duration, soil structure, and grassland type [39], and did not show significant changes.
4.3. Effects of Different Restoration Measures on Soil Microbial Diversity in Degraded Alpine Steppe
The composition, structure, and diversity of microbial communities in soil are closely linked to vegetation growth and development [40]. The sequencing results of this study showed that bacterial communities in alpine steppe soil were dominated by Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria, and Acidobacteria, while fungal communities were dominated by Ascomycota, Mortierellomycota, and Basidiomycota. This aligns with the findings of Li et al. [25], Du et al. [41], and Zhou et al. [42], confirming that these six phyla are the dominant bacterial and fungal lineages in alpine steppe ecosystems. This study found that the relative abundances of the bacterial phylum Actinobacteria and the fungal phylum Basidiomycota both significantly increased under the fertilization restoration measure, indicating that fertilization also influences the composition of bacterial and fungal communities. Additionally, Methylomirabilota were only detected in the two fertilization-treated groups and not found in the reseeding or control groups. Zhang et al. [43] reported that Methylomirabilota are a nitrate/nitrite-dependent anaerobic methane oxidizer commonly found in coastal sediment microorganisms involved in the methane cycle. Their detection under the fertilization restoration measure in this study, however, may be attributed to the enhanced nutrient exchange promoted by the interaction between organic fertilizer and vegetation residues [44]. The occurrence of such microbial communities may also be associated with factors including the climate, topography, altitude, and applied fertilizers in this study area. Under conditions of freeze–thaw cycles in permafrost and intensified surface water evaporation, the grassland is highly susceptible to patchy salinization. Salt ions accumulate around plant roots, and under the promotion of N-P-K compound fertilizers, increased nitrate formation occurs, thereby enriching the abundance of Methylomirabilota.
Alpha diversity analysis of microorganisms indicated that the alpha diversity of bacterial communities did not change significantly under different restoration measures in the short term. However, the Simpson index of fungal communities showed significant differences under the reseeding restoration measure, and reseeding significantly enhanced the heterogeneity of fungal community alpha diversity. This suggests that reseeding to some extent affects the diversity of fungal communities. Su et al. [45] found that after no-tillage reseeding in degraded alpine steppe, the diversity indices of soil fungal communities significantly increased and were notably higher than those of bacterial communities. Similarly, Wang et al. [46] reported that the restoration of degraded alpine meadows affects soil microbial community structure, with fungal communities being more sensitive to meadow changes than bacterial communities, which aligns with the findings of this study. Furthermore, Witt and Setälä [47] proposed that changes in plant species composition alter microbial community composition, thereby affecting microbial diversity—a pattern corroborated by the reseeding restoration measure in this study. NMDS analysis revealed significant differences in the bacterial community structure between the fertilization and combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures, indicating that these restoration measures did not alter overall bacterial community composition. However, under the sole fertilization restoration measures, additional reseeding did alter the bacterial community structure. For fungal communities, both fertilization and combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures showed significant differences from the control group, suggesting that these measures significantly influence the soil fungal community structure in alpine steppe, primarily driven by fertilization. This aligns with findings from Liu et al. [48] and Wen et al. [49], who reported that nitrogen fertilizer application significantly affects soil fungal community structure in alpine meadows.
4.4. Microbial Co-Occurrence Networks Under Different Restoration Measures in Degraded Alpine Steppe
Different restoration measures not only affect the composition of alpine steppe microbial communities in terms of diversity and species composition but also exert a significant influence on the complex interactive relationships among microorganisms. These interactions—including symbiosis, mutualism, and parasitism—form intricate ecological networks, enabling microorganisms to share soil niches and nutrient resources [50,51]. Co-occurrence network analysis in this study revealed that, compared to the control group, the fertilization restoration measure resulted in lower numbers of edges, average degree, and network density in both bacterial and fungal soil communities, while exhibiting a higher modularity index. These findings indicate that fertilization significantly reduces the scale and complexity of species interactions in bacterial and fungal networks of alpine steppe, while enhancing network stability. This conclusion validates the study by Wan et al. [52], which posits a positive correlation between microbial community stability and the modularity index. In contrast, Zhang et al. [53] and Li et al. [54] reported that the reseeding restoration measure had no significant impact on the network structure and diversity of soil microorganisms, which may be attributed to climate, reseeded grass species, and grassland degradation status. Key microbial taxa play critical roles in driving the structure and function of microbial communities. In this study, the co-occurrence network composition of bacterial and fungal communities at the phylum level was consistent with the results of relative abundance analysis at the same taxonomic level, as well as the co-occurrence network patterns observed in Wu et al.’s [55] soil microbial studies. This indicates that Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria, Acidobacteria, and Ascomycota are key contributing taxa to the composition, distribution, and assembly of bacterial and fungal communities, respectively. These phyla exert crucial influences on the modularity, connectivity, and stability of microbial communities in alpine steppe ecosystems.
Additionally, positive correlation edges in co-occurrence networks generally indicate niche consistency or symbiotic relationships between species, while negative correlation edges suggest competitive relationships or predation. Wu et al. [56] and Yang et al. [57], who studied alpine meadows and semi-arid grasslands, respectively, found that nutrient addition altered the complexity of soil bacterial and fungal networks in different grassland types, leading to the speculation that synergistic or competitive relationships may exist among microbial communities. Under fertilization, reseeding, and combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures, this study observed that the proportion of positive correlation edges in bacterial co-occurrence networks exceeded 86%, while that in fungal co-occurrence networks even reached 100%. This indicates widespread cooperative symbiotic relationships among bacterial and fungal communities in degraded alpine steppe soils, with fungal communities exhibiting more advantageous synergistic relationships than bacterial communities—critical for decomposing recalcitrant organic compounds in soil [58]. Such interaction patterns may help microbial communities collectively adapt to microecological changes following soil degradation. Additionally, the increased modularity index under fertilization suggests a greater abundance of functionally similar microbial taxa in the network. Nutrient addition enhances functional redundancy within communities, thereby improving the stability of bacterial and fungal networks to cope with diverse external environmental changes.
4.5. Correlation Between Microbial Communities and Environmental Factors in Degraded Alpine Steppe Under Different Restoration Measures
RDA analysis in this study indicated that changes in bacterial and fungal communities under fertilization and combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures were primarily driven by TP, with particularly significant effects on bacterial community structure—consistent with most previous findings [59]. Ai et al. [60] and Mei et al. [61] similarly observed that under different fertilization conditions, phosphorus and other physicochemical factors influence soil bacterial communities by altering soil nutrients and acidity/alkalinity. Notably, changes in soil phosphorus content following organic fertilizer application significantly affect bacterial community structure, promoting the growth of specific microorganisms by modifying the structure and composition of soil microbial communities [62]. In contrast, under the control and reseeding restoration measures, changes in bacterial and fungal communities in this study were significantly driven by pH and SOC. pH, as one of the best indicators of soil microbial diversity, significantly affects community composition. Zhu et al. [63] analyzed the factors influencing microbial communities under reseeding in degraded meadows and found that pH significantly impacts microbial community structure. Huang et al. [64] similarly concluded that both bacterial and fungal genera in soil are significantly correlated with pH. SOC is the most critical driver of microbial community spatial distribution on the Tibetan Plateau. Studies by Kong et al. [65], Li et al. [66], and Li et al. [67] have shown that under different fertilization methods or reseeding restoration measures, SOC is a key factor influencing microbial community structure. By balancing carbon and nitrogen cycles in degraded grasslands, SOC promotes changes in microbial communities. These results indicate that significant differences in soil microbial communities under different restoration measures are influenced by distinct environmental factors. Changes in these factors directly or indirectly determine the composition, structure, diversity, and spatial distribution of bacterial and fungal communities, thereby affecting the dynamics of belowground biomass in alpine steppe ecosystems.
5. Conclusions
This study conducted restoration trials on degraded alpine steppe in the Yellow River Source region using three restoration measures: fertilization, reseeding, and combined fertilization with reseeding. Short-term restoration monitoring and analysis yielded the following key findings:
(1) For vegetation communities and diversity: The combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures significantly improved grassland vegetation coverage and biomass. Reseeding and combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures had more pronounced effects on the richness, Simpson index, and Shannon index of grassland vegetation communities.
(2) For soil physicochemical properties: Fertilization and combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures significantly reduced soil pH and increased TP content, thereby improving the alkaline soil environment.
(3) For soil microorganisms: Different restoration measures did not significantly alter the dominant bacterial or fungal phyla. Alpha diversity analysis indicated that fungal communities were more sensitive to reseeding, with the Simpson index of fungal communities significantly decreasing under the reseeding restoration measure. Beta diversity analysis showed that the bacterial community structure remained unchanged across restoration measures, while additional reseeding under the sole fertilization background altered the bacterial community structure. Fertilization alone significantly affected the fungal community structure.
(4) Co-occurrence network analysis revealed that bacterial co-occurrence networks exhibited higher complexity, modularity, and keystone species numbers compared to fungal networks under different restoration measures. Compared to the control, fertilization significantly reduced the complexity of soil bacterial and fungal co-occurrence networks while increasing network stability. Under fertilization, reseeding, and combined fertilization with reseeding restoration measures, the co-occurrence networks were dominated by positive correlation relationships. Actinobacteria, Acidobacteria, Proteobacteria, and Ascomycota were identified as keystone species in bacterial and fungal communities of degraded alpine steppe.
(5) Bacterial and fungal communities under fertilization and combined fertilization with reseeding were primarily driven by TP content, which significantly influenced bacterial community structure. Under the control and reseeding restoration measures, soil pH and SOC content were the key drivers.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d17090617/s1, Table S1: Plant community composition in the alpine steppe of the Yellow River Source region; Figure S1: Effects of different remediation measures on soil physicochemical properties; Figure S2: NMDS analysis of soil microbial communities under different restoration measures; Table S2: Topology of bacterial and fungal networks under different remediation practices.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.N. and M.Y.; investigation, Y.K., Y.Z., M.S. and L.Y.; data curation, X.N., M.Y., Y.K., Y.Z., M.S. and L.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, X.N.; writing—review and editing, X.N. and M.Y.; visualization, M.Y.; supervision, M.Y., S.W. and D.H.; project administration, M.Y., S.W. and D.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the China Geological Survey Project (Grant No. DD20242555), Open Project of the Key Laboratory of Coupling Processes and Effects of Natural Resource Elements, Ministry of Natural Resources (Grant No. 2024KFKT009) and Innovation Science and Technology Fund of the Natural Resources Comprehensive Survey Command Center, China Geological Survey (Grant No. KC20240013).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Yang, Y.; Qin, T.; Yan, D.; Liu, S.; Feng, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, H.; Gao, H. Analysis of the evolution of ecosystem service value and its driving factors in the Yellow River Source Area, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Hu, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Change in Alpine Grassland NPP in Response to Climate Variation and Human Activities in the Yellow River Source Zone from 2000 to 2020. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isbell, F.; Gonzalez, A.; Loreau, M.; Cowles, J.; Díaz, S.; Hector, A.; Mace, G.M.; Wardle, D.A.; O‘Connor, M.I.; Duffy, J.E.; et al. Linking the influence and dependence of people on biodiversity across scales. Nature 2017, 546, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coban, O.; De Deyn, G.B.; van der Ploeg, M. Soil microbiota as game-changers in restoration of degraded lands. Science 2022, 375, abe0725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Osborne, B.; Zhou, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, W.; Zou, J. Edaphic factors control microbial biomass and elemental stoichiometry in alpine meadow soils of the Tibet Plateau. Plant Soil 2024, 503, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shang, X.; Yan, H.; Xu, J.; Liang, T.; Zhou, H. Impact of restoration measures on plant and soil characteristics in the degraded alpine grasslands of the Qinghai Tibetan Plateau: A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 347, 108394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, T.; Guo, R.; Li, H.; Zhang, R.; Allan Degen, A.; Huang, K.; Wang, X.; Bai, Y.; Shang, Z. Fencing enclosure alters nitrogen distribution patterns and tradeoff strategies in an alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. CATENA 2021, 197, 104948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Zhou, X.; Yu, H.; Yan, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Feng, K.; Du, X.; Lu, G.; et al. Microbial and chemical fertilizers for restoring degraded alpine grassland. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2023, 59, 911–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Yang, W.; Ji-Shi, A.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Qu, G.; Zhao, J.; Wu, G.-L. Artificial reseeding improves multiple ecosystem functions in an alpine sandy meadow of the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 2052–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, X.; Zhou, C.; Shao, X.; Shi, Z.; Li, H.; Su, H.; Qin, R.; Chang, T.; Hu, X.; et al. Alpine Grassland Degradation and Its Restoration in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Grasses 2023, 2, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liang, E.; Barrio, I.C.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Fu, B. Fences undermine biodiversity targets. Science 2021, 374, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yu, T.; Shan, D.; Yan, R.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Wuren, Q. Investigation into the Effects of Different Restoration Techniques on the Soil Nutrient Status in Degraded Stipa grandis Grassland. Agronomy 2024, 14, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liu, Q.; Deng, Y.; Gu, S.S.; Lu, G.X.; Zhou, X.L. Effects of Reseeding and Fertilization on Bacterial Communities in Rhizosphere Soil of Alpine Degraded Grassland. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 7350–7357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Duan, C.; Chai, Y.; Xu, W. Effects of Fertilization and Reseeding on Biomass and Species Diversity of Patchy Degraded Alpine Meadows with Different Slope Directions. Chin. J. Grassl. 2024, 46, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Lu, G.X.; Yan, H.L.; Wang, Y.C. Effects of the Transformation from Natural Alpine Grassland to Mixed Artificial Grassland on the Characteristics of Soil Microbial Community. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 2928–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, S.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Long, R.; Jin, G.; Zhang, B. Effects of No-Till Seeding and Fertilization on Vegetation Restoration and Soil Physicochemical Properties in Alpine Degraded Grazing Grasslands. Agronomy 2025, 15, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, X.; Qin, W.; Wang, S. Ecological Restoration Enhances the Stability and Associated Organic Carbon of Soil Aggregates in a Tibetan Alpine Meadow. Land Degrad. Dev. 2025, 36, 1206–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, N.; Shi, P.; Zheng, L.; Zhou, T.; Cong, N.; Hou, G.; Song, M.; Tian, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, J. Restoration effects of fertilization and grazing exclusion on different degraded alpine grasslands: Evidence from a 10-year experiment. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 170, 106361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Meng, L.; Fang, H.; Dang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Wu, G.-L. Reseeding improved productivity but not soil functions in the severely degraded alpine meadows on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Restor. Ecol. 2025, 33, e70019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slodowicz, D.; Durbecq, A.; Ladouceur, E.; Eschen, R.; Humbert, J.-Y.; Arlettaz, R. The relative effectiveness of different grassland restoration methods: A systematic literature search and meta-analysis. Ecol. Solut. Evid. 2023, 4, e12221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Xie, L. Fertilization can accelerate the pace of soil microbial community response to rest-grazing duration in the three-river source region of China. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, e10734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, T.; Kawamura, K. Grassland degradation in China: Methods of monitoring, management and restoration. Grassl. Sci. 2007, 53, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Xu, B.; Yang, X.; Jin, Y.; Li, J.; Xia, L.; Chen, S.; Ma, H. Remote Sensing Estimates of Grassland Aboveground Biomass Based on MODIS Net Primary Productivity (NPP): A Case Study in the Xilingol Grassland of Northern China. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 5368–5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Li, J.; Sun, J.; Yang, C. Soil degradation influences soil bacterial and fungal community diversity in overgrazed alpine meadows of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, D.; Xu, G.; Yan, R.; Huang, Y.; Feng, L.; Yi, J.; Xue, X.; Liu, H. Effects of Alpine Grassland Degradation on Soil Microbial Communities in Qilian Mountains of China. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 912–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Q.; Yan, Q.; Deng, Y.; Michaletz, S.T.; Buzzard, V.; Weiser, M.D.; Waide, R.; Ning, D.; Wu, L.; He, Z.; et al. Biogeographic patterns of microbial co-occurrence ecological networks in six American forests. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 107897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Fan, B.; Zhou, G. Soil microbial network complexity predicts soil multifunctionality better than soil microbial diversity during grassland-farmland-shrubland conversion on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 379, 109356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, X.; Li, S.; Tang, R.; Su, J. Microbial network complexity and diversity together drive the soil ecosystem multifunctionality of forests during different woodland use intensity in dry and wet season. For. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 542, 121086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagg, C.; Schlaeppi, K.; Banerjee, S.; Kuramae, E.E.; van der Heijden, M.G.A. Fungal-bacterial diversity and microbiome complexity predict ecosystem functioning. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Huang, Q.; Shen, Q.; Kang, Y.; Shi, M.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, D. Latitudinal gradient and environmental drivers of soil organic carbon in permafrost regions of the Headwater Area of the Yellow River. Carbon Neutrality 2025, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaei, A.; Ali, A.; Chahouki, M.A.Z.; Jafari, M. Plant coverage is a potential ecological indicator for species diversity and aboveground biomass in semi-steppe rangelands. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D. Niche tradeoffs, neutrality, and community structure: A stochastic theory of resource competition, invasion, and community assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10854–10861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, W.; Zheng, H.; Chi, Y.; Ren, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, F. Reseeding inhibits grassland vegetation degradation—Global evidence. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 374, 109144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, K.; Choler, P.; de Bello, F.; Mirotchnick, N.; Du, G.; Sun, S. Fertilization decreases species diversity but increases functional diversity: A three-year experiment in a Tibetan alpine meadow. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 182, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Sobuj, N.; Byun, C. Native plants do not benefit from arriving early, but invasives pay to arrive late. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Senbayram, M.; Zang, H.; Ugurlar, F.; Aydemir, S.; Brüggemann, N.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Bol, R.; Blagodatskaya, E. Effect of biochar origin and soil pH on greenhouse gas emissions from sandy and clay soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 129, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desie, E.; Vancampenhout, K.; van den Berg, L.; Nyssen, B.; Weijters, M.; den Ouden, J.; Muys, B. Litter share and clay content determine soil restoration effects of rich litter tree species in forests on acidified sandy soils. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 474, 118377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Aguilar, A.A.; Pang, J.; Postma, J.A.; Schrey, S.D.; Lambers, H.; Jablonowski, N.D. The effect of pH on morphological and physiological root traits of Lupinus angustifolius treated with struvite as a recycled phosphorus source. Plant Soil 2019, 434, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Zou, J.; Feng, Z.; Wen, T. Effects of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica afforestation on soil physicochemical properties at the southern edge of the Mu Us Sandy Land, China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 545, 121254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Wu, C.; Zou, J.; Zhou, H.; Li, J. Alpine meadow degradation regulates soil microbial diversity via decreasing plant production on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 163, 112097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, S.; Gao, X.; He, X.; Dong, S. Core microbes regulate plant-soil resilience by maintaining network resilience during long-term restoration of alpine grasslands. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, P.; Xiao, H.; Yuxin, W.; Chen, J. Changes in the soil microbial communities of alpine steppe at Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau under different degradation levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2281–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Liang, B.; Li, X.; Lv, H.; Zhou, W.; Wu, X.; Wang, L. Digging deeper to find the effect of long-term greenhouse cultivation with excessive fertilization and irrigation on the structure and assemblage of soil bacterial community. Geoderma 2024, 451, 117087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Peñuelas, J.; Chu, H. Abundance of kinless hubs within soil microbial networks are associated with high functional potential in agricultural ecosystems. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Ma, L.; Chang, T.; Qin, R.; Zhang, Z.; She, Y.; Wei, J.; Zhou, C.; Hu, X.; Shi, Z.; et al. Effects of Main Land-Use Types on Plant and Microbial Diversity and Ecosystem Multifunctionality in Degraded Alpine Grasslands. Land 2023, 12, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhou, H.; Zuo, J.; Chen, P.; She, Y.; Yao, B.; Dong, S.; Wu, J.; Li, F.; Njoroge, D.M.; et al. Responses of Soil Microbial Metabolic Activity and Community Structure to Different Degraded and Restored Grassland Gradients of the Tibetan Plateau. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 770315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, C.; Setälä, H. Do plant species of different resource qualities form dissimilar energy channels below-ground? Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 44, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Huang, M.; Zhou, S. Plant diversity promotes soil fungal pathogen richness under fertilization in an alpine meadow. J. Plant Ecol. 2020, 14, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.-C.; Li, H.-Y.; Lin, Z.-A.; Zhao, B.-Q.; Sun, Z.-B.; Yuan, L.; Xu, J.-K.; Li, Y.-Q. Long-term fertilization alters soil properties and fungal community composition in fluvo-aquic soil of the North China Plain. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, R.; Wen, Y.; Ma, L.; Xu, Z.; Wen, L.; Zhuo, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, L. Composition, Predicted Functions, and Co-occurrence Networks of Bacteria and Fungi in Hummock Wetlands of Northeastern Inner Mongolia, China. Microb. Ecol. 2025, 88, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Liu, W.; Hu, Y.; Xia, L.; Fan, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W. Ecosystem multifunctionality and soil microbial communities in response to ecological restoration in an alpine degraded grassland. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1173962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, K.; Li, Y.; Qin, R.; Yang, J.; Fang, C.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Li, S.; Li, F.-M. Soil warming decreases carbon availability and reduces metabolic functions of bacteria. CATENA 2023, 223, 106913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, R.; Xing, F. Planting grass enhances relations between soil microbes and enzyme activities and restores soil functions in a degraded grassland. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1290849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, M.; Wu, J. Sheep dung addition and reseeding promote ecosystem multifunctionality by mediating soil microbial network complexity in a subtropical grassland. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 211, 106157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yang, J.; Ruan, H.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Naeem, I.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, D. The diversity and co-occurrence network of soil bacterial and fungal communities and their implications for a new indicator of grassland degradation. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Ding, M.; Zhang, H.; Devlin, A.T.; Wang, P.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Wen, J.; Liu, L.; et al. Reduced soil multifunctionality and microbial network complexity in degraded and revegetated alpine meadows. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 343, 118182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Cheng, L.; Che, L.; Su, Y.; Li, Y. Nutrients addition decreases soil fungal diversity and alters fungal guilds and co-occurrence networks in a semi-arid grassland in northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 172100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Zhao, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wu, Y.; Fang, L.; Bing, H. Fungal community determines soil multifunctionality during vegetation restoration in metallic tailing reservoir. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 478, 135438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zuo, Q.; Du, B.; Chen, W.; Wei, D.; Huang, Q. Contrasting responses of bacterial and fungal communities to aggregate-size fractions and long-term fertilizations in soils of northeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Guo, D.; Zhou, W.; Huang, S. Distinct responses of soil bacterial and fungal communities to changes in fertilization regime and crop rotation. Geoderma 2018, 319, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, N.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Peng, C.; Gao, H.; Zhu, P.; Gu, Y. Effects of 40 years applications of inorganic and organic fertilization on soil bacterial community in a maize agroecosystem in northeast China. Eur. J. Agron. 2021, 130, 126332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Barret, M.; Mooij, M.J.; Rice, O.; Morrissey, J.P.; Dobson, A.; Griffiths, B.; O’Gara, F. Long-term phosphorus fertilisation increased the diversity of the total bacterial community and the phoD phosphorus mineraliser group in pasture soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2013, 49, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Han, W.; Shen, Z.; Muraina, T.O.; Chen, J.; Sun, D. Comparison of soil microbial community between reseeding grassland and natural grassland in Songnen Meadow. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; He, Y.; Zhou, L.; Liu, R.; Chen, H.; Du, Z.; Fu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, C.; et al. Opposite effects of soil pH on bacteria and fungi β diversity in forests at a continental scale. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, S.; Wang, W.; Song, X.; Guo, D.; Lawi, A.S. Soil bacterial community characteristics and its effect on organic carbon under different fertilization treatments. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1356171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Chen, L.; Xu, J.; Ma, L.; Olk, D.C.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, J.; Xin, X. Chemical nature of soil organic carbon under different long-term fertilization regimes is coupled with changes in the bacterial community composition in a Calcaric Fluvisol. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2018, 54, 999–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, S.; Chen, H.; Wu, J. Reseeding promotes plant biomass by improving microbial community stability and soil fertility in a degraded subalpine grassland. Geoderma 2025, 453, 117160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).