Land Use Effects on the Space Use and Dispersal of an Apex Predator in an Ecotone Between Tropical Biodiversity Hotspots
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
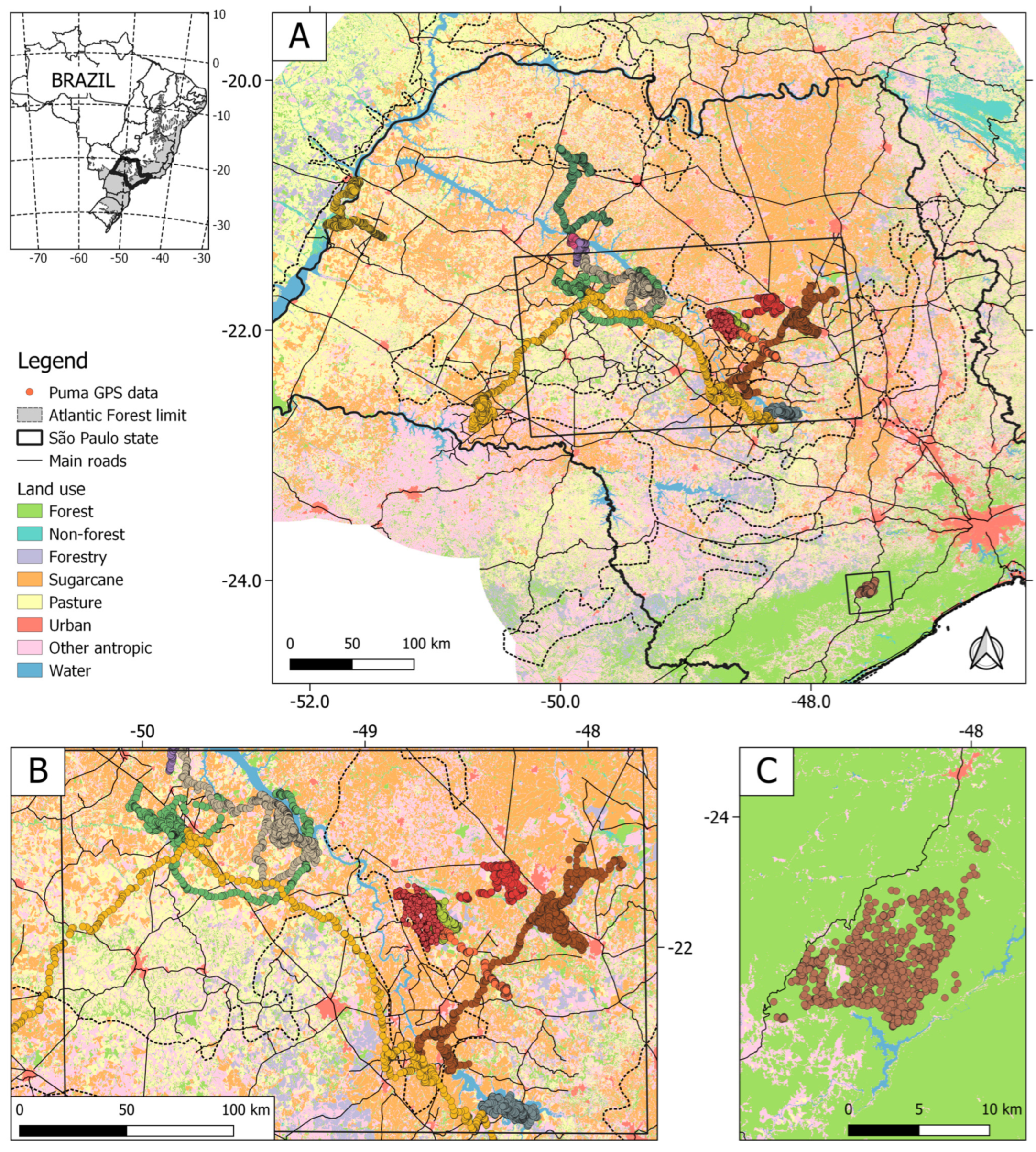
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Puma GPS Data
2.3. Environmental Data
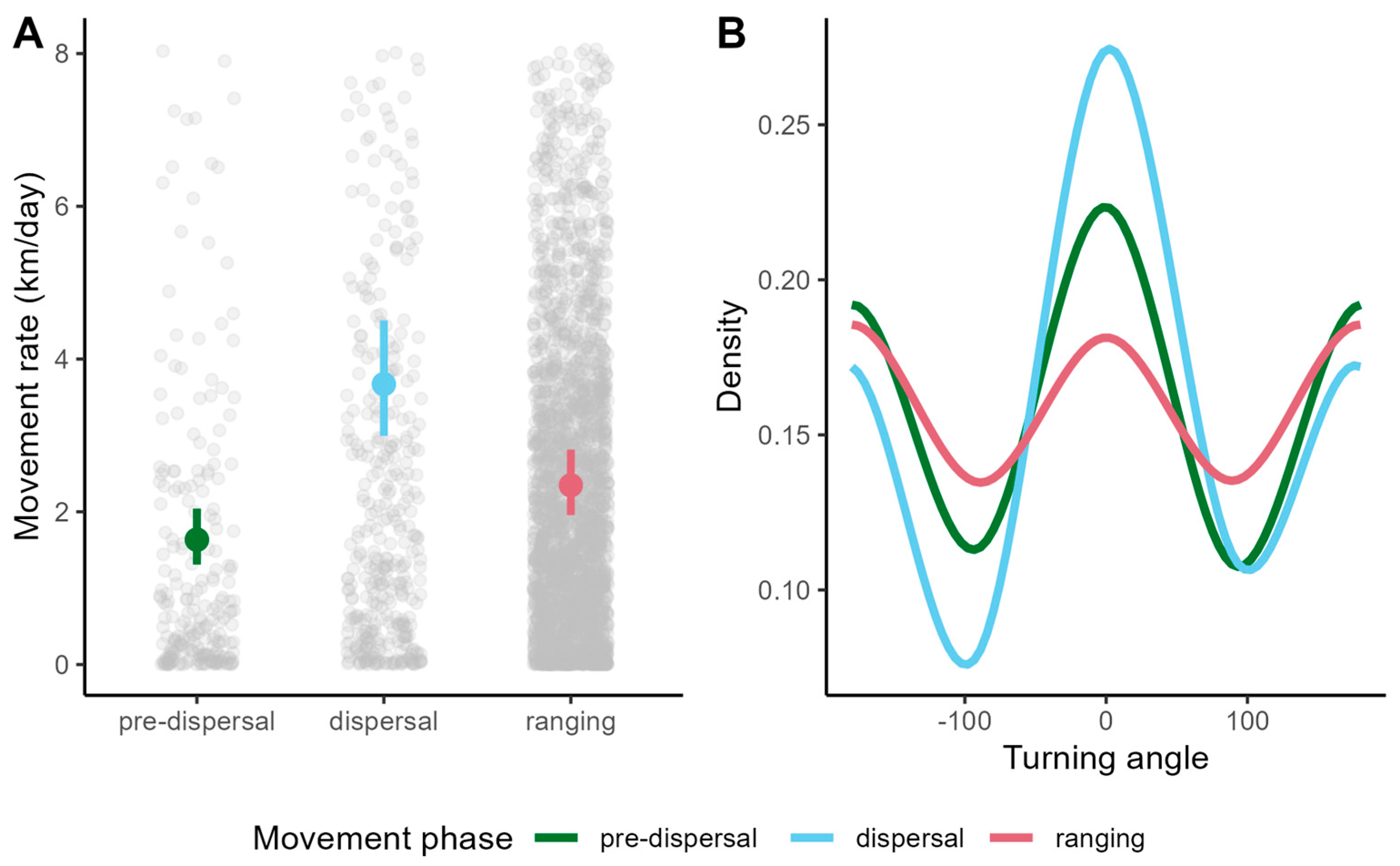
2.4. Identifying and Characterizing Ranging and Dispersal
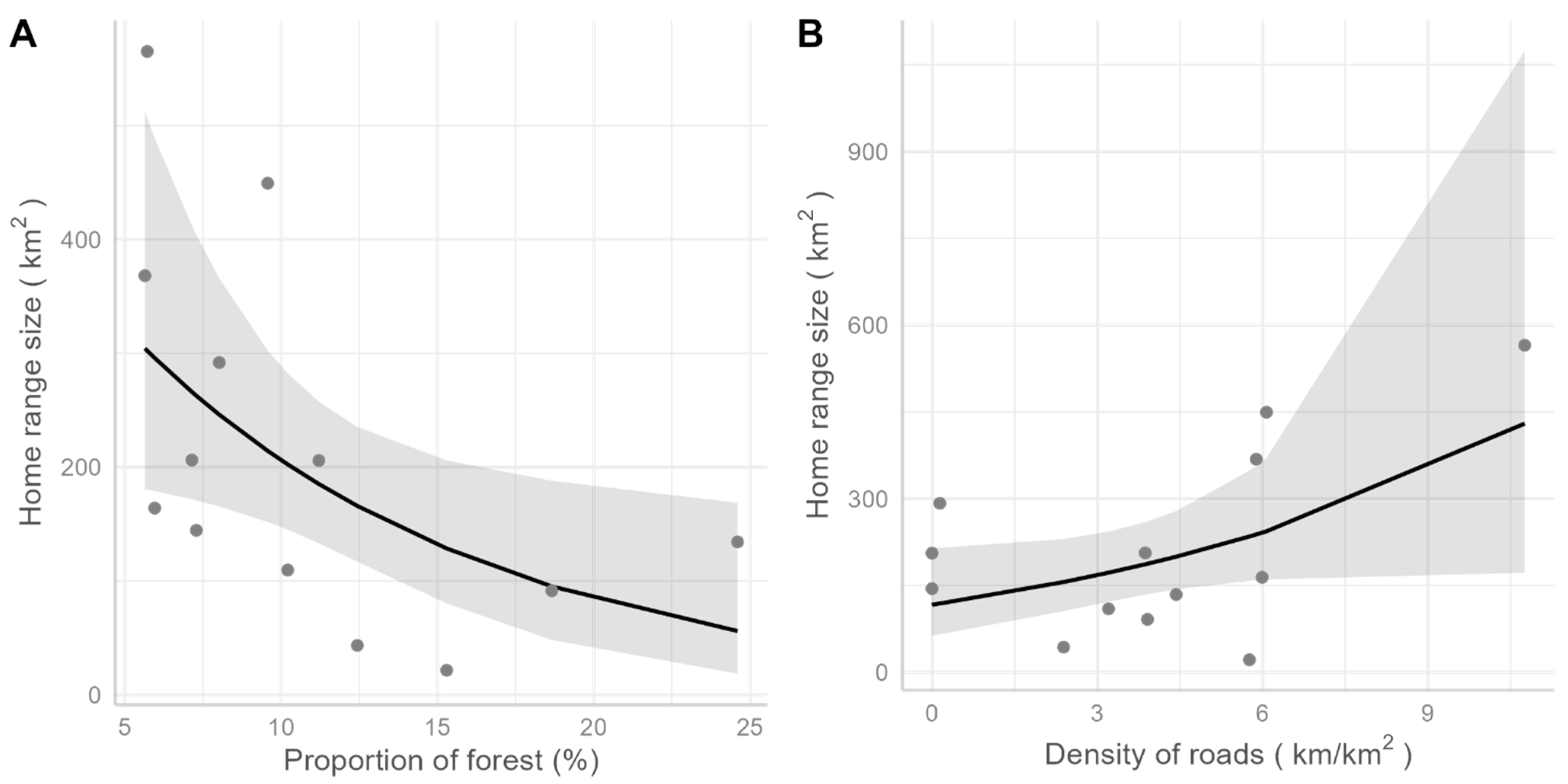
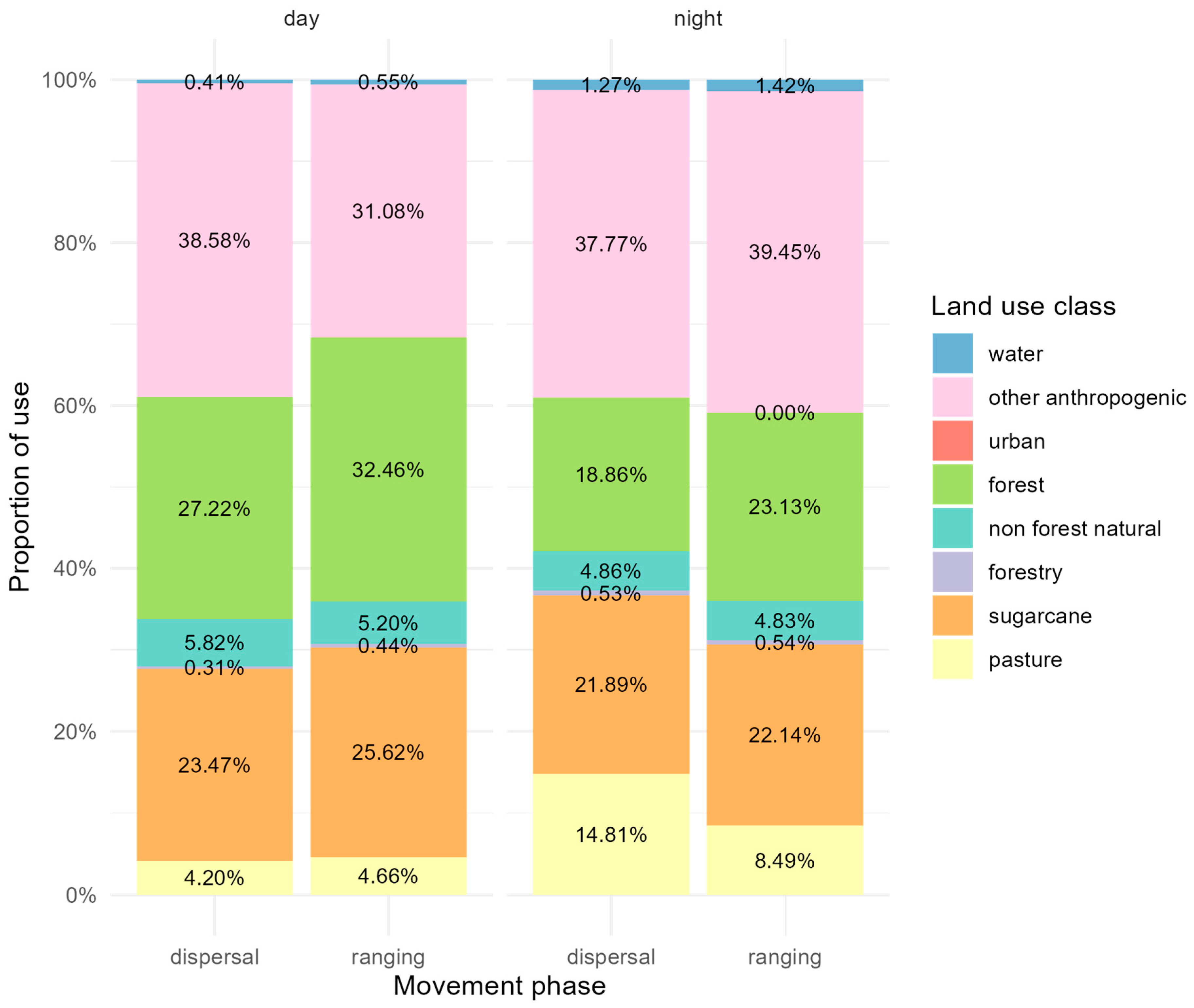
2.5. Effects of the Landscape on Ranging and Dispersal
2.6. Literature Review
3. Results
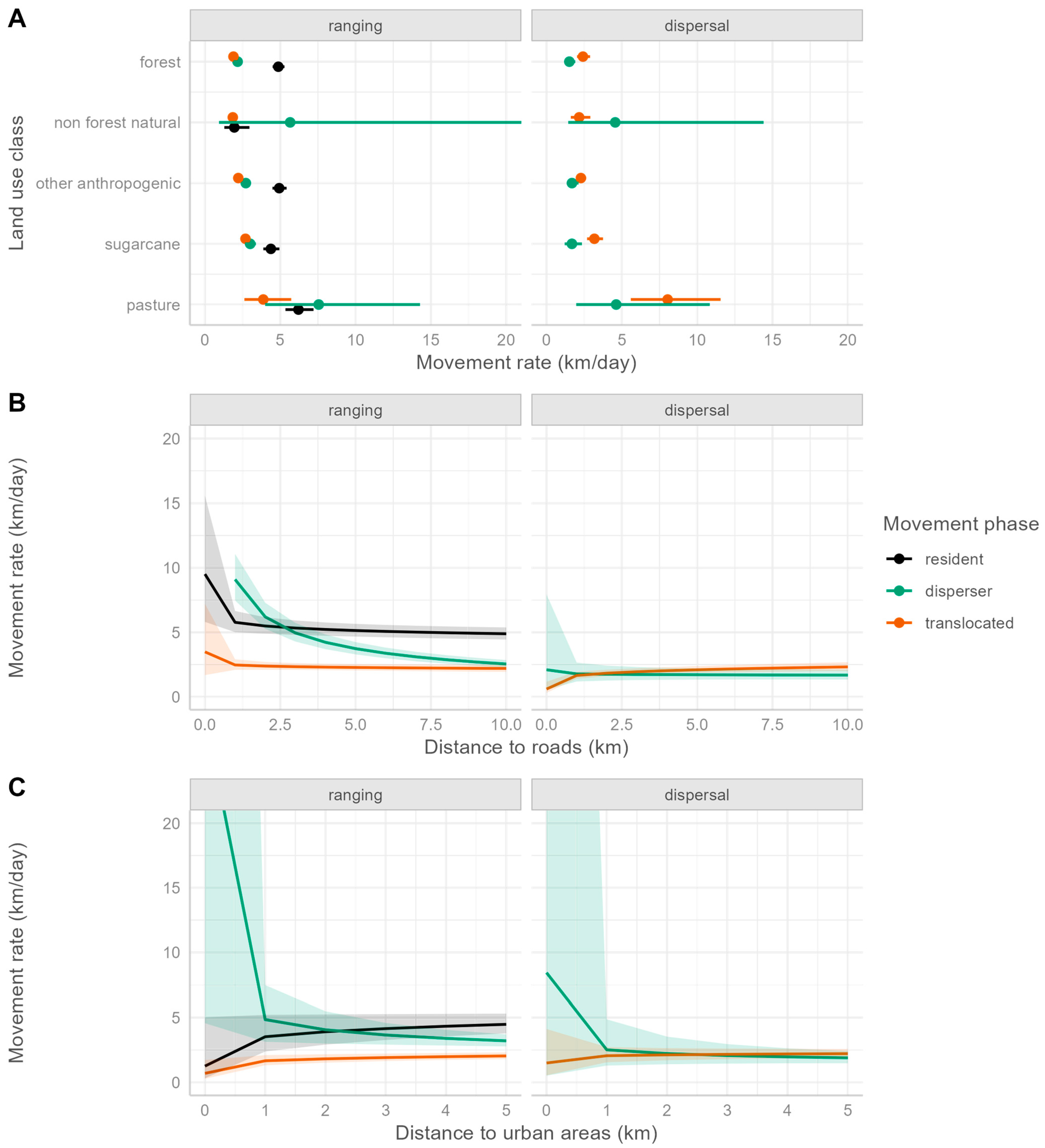
3.1. Pumas in Southeastern Brazil
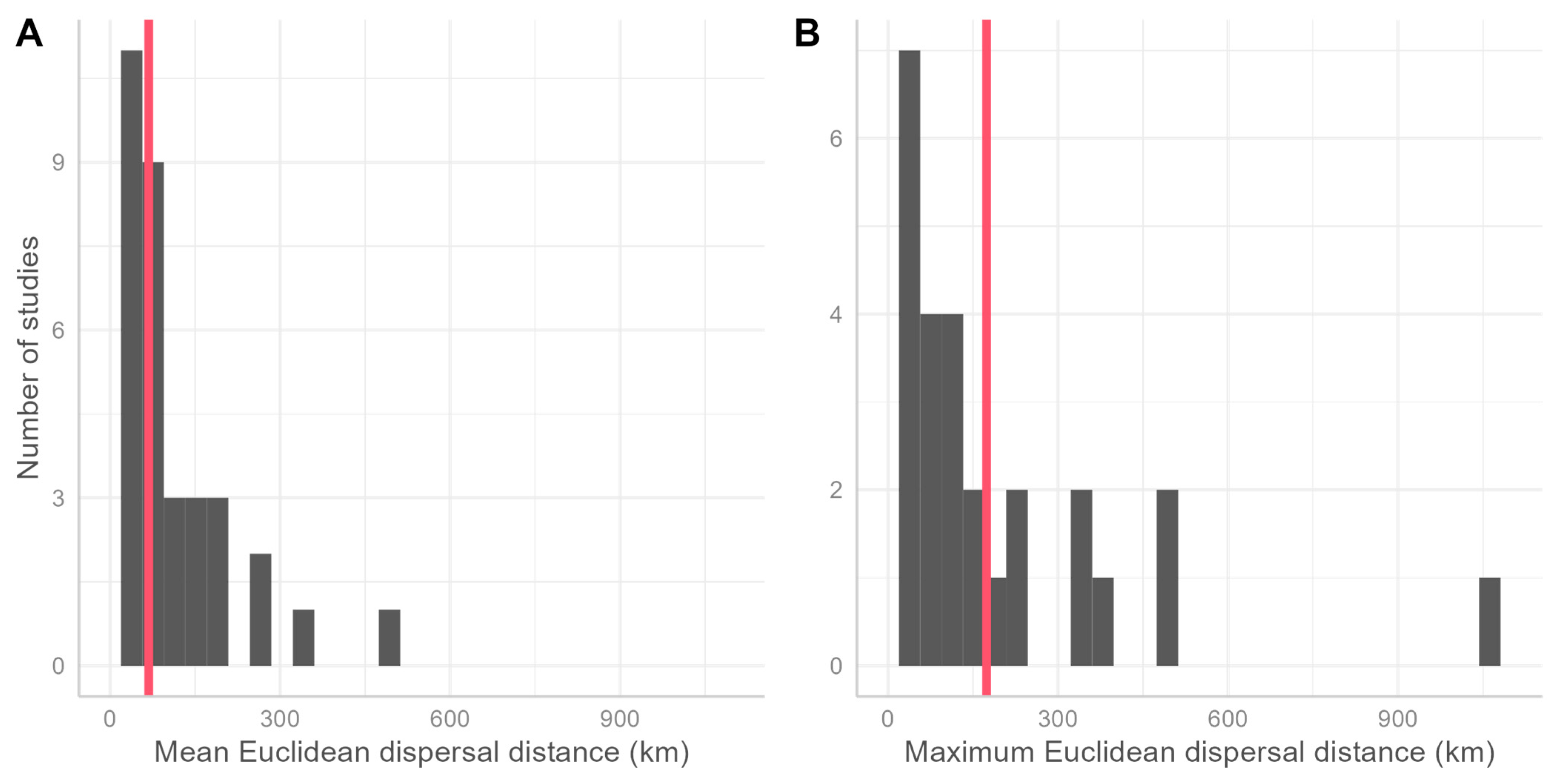
3.2. Summary from the Literature Review
4. Discussion
Conservation and Management Implications
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GPS | Global positioning system |
| MCP | Minimum convex polygon |
| KDE | Kernel density estimation |
| AKDE | Autocorrelated kernel density estimation |
| OUF | Ornstein–Uhlenbeck–Fleming model |
| OU | Ornstein–Uhlenbeck model |
| CVM | Continuous velocity model |
| ARIMA | Autoregressive integrated moving average model |
| IID | Independent identically distributed process |
| AICc | Akaike information criterion corrected for small samples |
References
- da Silveira, N.S.; Niebuhr, B.B.S.; Muylaert, R.d.L.; Ribeiro, M.C.; Pizo, M.A. Effects of Land Cover on the Movement of Frugivorous Birds in a Heterogeneous Landscape. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Moorter, B.; Kivimäki, I.; Panzacchi, M.; Saura, S.; Niebuhr, B.B.; Strand, O.; Saerens, M. Habitat Functionality: Integrating Environmental and Geographic Space in Niche Modeling for Conservation Planning. Ecology 2023, 104, e4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves-Souza, T.; Chase, J.M.; Haddad, N.M.; Vancine, M.H.; Didham, R.K.; Melo, F.L.P.; Aizen, M.A.; Bernard, E.; Chiarello, A.G.; Faria, D.; et al. Species Turnover Does Not Rescue Biodiversity in Fragmented Landscapes. Nature 2025, 640, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, J.M.; Moorcroft, P.R.; Matthiopoulos, J.; Frair, J.L.; Kie, J.G.; Powell, R.A.; Merrill, E.H.; Haydon, D.T. Building the Bridge between Animal Movement and Population Dynamics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2010, 365, 2289–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niebuhr, B.B.S.; Wosniack, M.E.; Santos, M.C.; Raposo, E.P.; Viswanathan, G.M.; da Luz, M.G.E.; Pie, M.R. Survival in Patchy Landscapes: The Interplay between Dispersal, Habitat Loss and Fragmentation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeltsch, F.; Bonte, D.; Pe’er, G.; Reineking, B.; Leimgruber, P.; Balkenhol, N.; Schröder, B.; Buchmann, C.M.; Mueller, T.; Blaum, N.; et al. Integrating Movement Ecology with Biodiversity Research—Exploring New Avenues to Address Spatiotemporal Biodiversity Dynamics. Mov. Ecol. 2013, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, R.; Getz, W.M.; Revilla, E.; Holyoak, M.; Kadmon, R.; Saltz, D.; Smouse, P.E. A Movement Ecology Paradigm for Unifying Organismal Movement Research. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19052–19059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börger, L.; Dalziel, B.D.; Fryxell, J.M. Are There General Mechanisms of Animal Home Range Behaviour? A Review and Prospects for Future Research. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronce, O. How Does It Feel to Be like a Rolling Stone? Ten Questions about Dispersal Evolution. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2007, 38, 231–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, A.M.; Ruiz-Miranda, C.R.; Galetti, P.M., Jr.; Niebuhr, B.B.; Alexandre, B.R.; Muylaert, R.L.; Grativol, A.D.; Ribeiro, J.W.; Ferreira, A.N.; Ribeiro, M.C. Landscape Resistance Influences Effective Dispersal of Endangered Golden Lion Tamarins within the Atlantic Forest. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 224, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Borrajo, N.; López-Bao, J.V.; Palomares, F. Spatial Ecology of Jaguars, Pumas, and Ocelots: A Review of the State of Knowledge. Mammal Rev. 2017, 47, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.E.; Saranholi, B.H.; Dirzo, R.; Galetti, P.M. A Review of Philopatry and Dispersal in Felids Living in an Anthropised World. Mammal Rev. 2022, 52, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilho, C.S.; Marins-Sá, L.G.; Benedet, R.C.; Freitas, T.O. Landscape Genetics of Mountain Lions (Puma concolor) in Southern Brazil. Mamm. Biol. 2011, 76, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, K.R.; Burdett, C.L.; Theobald, D.M.; Rondinini, C.; Boitani, L. Global Patterns of Fragmentation and Connectivity of Mammalian Carnivore Habitat. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2011, 366, 2642–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, K.L.; Bouchet, P.J.; Caley, M.J.; Mengersen, K.; Randin, C.F.; Parnell, S.; Fielding, A.H.; Bamford, A.J.; Ban, S.; Barbosa, A.M.; et al. Outstanding Challenges in the Transferability of Ecological Models. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2018, 33, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, S.; English, H.M.; Bejarano Alegre, V.; Blackwell, P.G.; Bracken, A.M.; Bray, E.; Evans, L.C.; Gan, J.L.; Grecian, W.J.; Gutmann Roberts, C.; et al. Understanding and Predicting Animal Movements and Distributions in the Anthropocene. J. Anim. Ecol. 2025, 94, 1146–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magioli, M.; Moreira, M.Z.; Fonseca, R.C.B.; Ribeiro, M.C.; Rodrigues, M.G.; De Barros Ferraz, K.M.P.M. Human-Modified Landscapes Alter Mammal Resource and Habitat Use and Trophic Structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 18466–18472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magioli, M.; Moreira, M.Z.; Ferraz, K.M.B.; Miotto, R.A.; de Camargo, P.B.; Rodrigues, M.G.; da Silva Canhoto, M.C.; Setz, E.F. Stable Isotope Evidence of Puma concolor (Felidae) Feeding Patterns in Agricultural Landscapes in Southeastern Brazil. Biotropica 2014, 46, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, M.A.; Böhning-Gaese, K.; Fagan, W.F.; Fryxell, J.M.; Van Moorter, B.; Alberts, S.C.; Ali, A.H.; Allen, A.M.; Attias, N.; Avgar, T.; et al. Moving in the Anthropocene: Global Reductions in Terrestrial Mammalian Movements. Science 2018, 359, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lino, A.; Fonseca, C.; Rojas, D.; Fischer, E.; Ramos Pereira, M.J. A Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Habitat Loss and Fragmentation on Genetic Diversity in Mammals. Mamm. Biol. 2019, 94, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida-Rocha, J.M.; Soares, L.A.S.S.; de Andrade, E.R.; Gaiotto, F.A.; Cazetta, E. The Impact of Anthropogenic Disturbances on the Genetic Diversity of Terrestrial Species: A Global Meta-analysis. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 4812–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IPBES. Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services; IPBES secretariat: Bonn, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, J.J.; Morato, R.G.; Niebuhr, B.B.; Alegre, V.B.; Oshima, J.E.F.; de Barros, A.E.; Paviolo, A.; de la Torre, J.A.; Lima, F.; McBride, R.T.; et al. Environmental and Anthropogenic Factors Synergistically Affect Space Use of Jaguars. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 3457–3466.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuijper, D.P.J.; Sahlén, E.; Elmhagen, B.; Chamaillé-Jammes, S.; Sand, H.; Lone, K.; Cromsigt, J.P.G.M. Paws without Claws? Ecological Effects of Large Carnivores in Anthropogenic Landscapes. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20161625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaBarge, L.R.; Evans, M.J.; Miller, J.R.B.; Cannataro, G.; Hunt, C.; Elbroch, L.M. Pumas Puma concolor as Ecological Brokers: A Review of Their Biotic Relationships. Mammal Rev. 2022, 52, 360–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, E.G.; Johnson, C.N. Predator Interactions, Mesopredator Release and Biodiversity Conservation. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 982–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, M.L.S.P.; Galetti, M.; Ribeiro, M.C.; Ferraz, K.M.P.M.B. Mammal Defaunation as Surrogate of Trophic Cascades in a Biodiversity Hotspot. Biol. Conserv. 2013, 163, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunquist, M.E.; Sunquist, F. Wild Cats of the World; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-0-226-77999-7. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, C.; Thompson, D.; Kelly, M.; López-González, C.A. Puma Concolor. In The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015; International Union for Conservation of Nature: Gland, Switzerland, 2015; p. e.T18868A97216466. [Google Scholar]
- BRASIL. Portaria M.M.A. de 7 de Junho de 2022. Altera Os Anexos Da Portaria No 443, de 17 de Dezembro de 2014, Da Portaria No 444, de 17 de Dezembro de 2014, e Da Portaria No 445, de 17 de Dezembro de 2014, Referentes à Atualização Da Lista Nacional de Espécies Ameaçadas de Extinção; Ministério do Meio Ambiente: Brasília, Brazil, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hemker, T.P.; Lindzey, F.G.; Ackerman, B.B. Population Characteristics and Movement Patterns of Cougars in Southern Utah. J. Wildl. Manag. 1984, 48, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, P. Dispersal of Juvenile Cougars in Fragmented Habitat. J. Wildl. Manag. 1995, 59, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-González, C.A.; González-Romero, A. A Synthesis of Current Literature and Knowledge about the Ecology of the Puma (Puma concolor Linnaeus). Acta Zool. Mex. 1998, 75, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maehr, D.S.; Land, E.D.; Shindle, D.B.; Bass, O.L.; Hoctor, T.S. Florida Panther Dispersal and Conservation. Biol. Conserv. 2002, 106, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, K.A.; Vickers, T.W.; Ernest, H.B.; Boyce, W.M. Multi-Level, Multi-Scale Resource Selection Functions and Resistance Surfaces for Conservation Planning: Pumas as a Case Study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, F.C.; Lemos, F.G.; Freitas-Junior, M.C.; Arrais, R.C.; Morato, R.G.; Azevedo, F.C.C. The Importance of Forests for an Apex Predator: Spatial Ecology and Habitat Selection by Pumas in an Agroecosystem. Anim. Conserv. 2021, 24, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyra-Jorge, M.C.; Ribeiro, M.C.; Ciocheti, G.; Tambosi, L.R.; Pivello, V.R. Influence of Multi-Scale Landscape Structure on the Occurrence of Carnivorous Mammals in a Human-Modified Savanna, Brazil. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2010, 56, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magioli, M.; Ferraz, K.M.P.M. Deforestation Leads to Prey Shrinkage for an Apex Predator in a Biodiversity Hotspot. Mammal Res. 2021, 66, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miotto, R.A.; Cervini, M.; Figueiredo, M.G.; Begotti, R.A.; Galetti, P.M. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Pumas (Puma Concolor) in Southeastern Brazil: Implications for Conservation in a Human-Dominated Landscape. Conserv. Genet. 2011, 12, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miotto, R.A.; Cervini, M.; Kajin, M.; Begotti, R.A.; Galetti, P.M. Estimating Puma Puma concolor Population Size in a Human-Disturbed Landscape in Brazil, Using DNA Mark–Recapture Data. Oryx 2014, 48, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paula, T.A.R.; Araujo, G.R.; Deco-Souza, T.; Csermak, A.C., Jr.; Bergo, L.C.F.; Mantovani, J.E.; Silva, L.C.; Magaldi, R.C.F.; Trece, A.S.; Caliman, J.P. Aspectos do uso territorial por onça parda (Puma concolor), através de monitoramento via satélite, na região do Parque Estadual da Serra do Brigadeiro, MG. Arq. Bras. Med. Veterinária Zootec. 2015, 67, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adania, C.H.; de Carvalho, W.D.; Rosalino, L.M.; de Cassio Pereira, J.; Crawshaw, P.G. First Soft-Release of a Relocated Puma in South America. Mammal Res. 2017, 62, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, F.C.; Lemos, F.G.; Freitas-Junior, M.C.; Rocha, D.G.; Azevedo, F.C.C. Puma Activity Patterns and Temporal Overlap with Prey in a Human-modified Landscape at Southeastern Brazil. J. Zool. 2018, 305, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbroch, M.; Wittmer, H.U.; Saucedo, C.; Corti, P. Long-Distance Dispersal of a Male Puma (Puma concolor puma) in Patagonia. Rev. Chil. Hist. Nat. 2009, 82, 459–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoner, D.C.; Wolfe, M.L.; Mecham, C.; Mecham, M.B.; Durham, S.L.; Choate, D.M. Dispersal Behaviour of a Polygynous Carnivore: Do Cougars Puma concolor Follow Source-Sink Predictions? Wildl. Biol. 2013, 19, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweanor, L.L.; Logan, K.A.; Hornocker, M.G. Cougar Dispersal Patterns, Metapopulation Dynamics, and Conservation. Conserv. Biol. 2000, 14, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, J.L.; Paquet, P.C.; Ruggiero, L.F. Resilience and Conservation of Large Carnivores in the Rocky Mountains. Conserv. Biol. 1996, 10, 964–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanin, M.; Palomares, F.; Brito, D. What We (Don’t) Know about the Effects of Habitat Loss and Fragmentation on Felids. Oryx 2015, 49, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, C.M.; Shimbo, J.Z.; Rosa, M.R.; Parente, L.L.; Alencar, A.A.; Rudorff, B.F.T.; Hasenack, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Ferreira, L.G.; Souza-Filho, P.W.M.; et al. Reconstructing Three Decades of Land Use and Land Cover Changes in Brazilian Biomes with Landsat Archive and Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranholi, B.H.; Chávez-Congrains, K.; Galetti, P.M. Evidence of Recent Fine-Scale Population Structuring in South American Puma Concolor. Diversity 2017, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRue, M.A.; Nielsen, C.K. Modelling Potential Dispersal Corridors for Cougars in Midwestern North America Using Least-Cost Path Methods. Ecol. Model. 2008, 212, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, T.; Gurarie, E.; Cheraghi, F.; Kojola, I.; Fagan, W.F. Does Dispersal Make the Heart Grow Bolder? Avoidance of Anthropogenic Habitat Elements across Wolf Life History. Anim. Behav. 2020, 166, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, C.D.; Boyce, M.S.; Nielsen, S.E. Space-Use, Movement and Dispersal of Sub-Adult Cougars in a Geographically Isolated Population. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidinger, I.M.M.; Poethke, H.-J.; Bonte, D.; Hein, S. The Effect of Translocation on Movement Behaviour—A Test of the Assumptions of Behavioural Studies. Behav. Process. 2009, 82, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuka, A.B.; Nafus, M.G.; Yackel Adams, A.A.; Bailey, L.L.; Hooten, M.B. Individual Heterogeneity Influences the Effects of Translocation on Urban Dispersal of an Invasive Reptile. Mov. Ecol. 2022, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancine, M.H.; Muylaert, R.L.; Niebuhr, B.B.; Oshima, J.E.d.F.; Tonetti, V.; Bernardo, R.; De Angelo, C.; Rosa, M.R.; Grohmann, C.H.; Ribeiro, M.C. The Atlantic Forest of South America: Spatiotemporal Dynamics of the Vegetation and Implications for Conservation. Biol. Conserv. 2024, 291, 110499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Project MapBiomas. Project MapBiomas—Collection 5 of Brazilian Land Cover & Use Map Series. Available online: http://mapbiomas.org (accessed on 20 October 2020).
- Alencar, A.Z.; Shimbo, J.; Lenti, F.; Balzani Marques, C.; Zimbres, B.; Rosa, M.; Arruda, V.; Castro, I.; Fernandes Márcico Ribeiro, J.; Varela, V.; et al. Mapping Three Decades of Changes in the Brazilian Savanna Native Vegetation Using Landsat Data Processed in the Google Earth Engine Platform. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, G.R.d.; Deco-Souza, T.d.; Morato, R.G.; Crawshaw, P.G., Jr.; Silva, L.C.d.; Jorge-Neto, P.N.; Csermak-Jr, A.C.; Bergo, L.C.F.; Kantek, D.L.Z.; Miyazaki, S.S.; et al. Use of Foot Snares to Capture Large Felids. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2021, 12, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashman, D.; Christensen, G.C.; Hess, M.L.; Tsukamoto, G.K.; Wickersham, M.S. The Mountain Lion in Nevada; Nevada Fish and Game Department: Reno, NV, USA, 1983; p. 75. [Google Scholar]
- Gay, S.W.; Best, T.L. Age-Related Variation in Skulls of the Puma (Puma concolor). J. Mammal. 1996, 77, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- FBDS. Mapeamento Do Uso Do Solo Dos Biomas Cerrado e Mata Atlântica Na Escala 1:20.000, Projeto de Apoio à Implantação Do CAR; Fundação Brasileira Para o Desenvolvimento Sustentável: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rudorff, B.F.T.; de Aguiar, D.A.; da Silva, W.F.; Sugawara, L.M.; Adami, M.; Moreira, M.A. Studies on the Rapid Expansion of Sugarcane for Ethanol Production in São Paulo State (Brazil) Using Landsat Data. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 1057–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parente, L.; Ferreira, L.; Faria, A.; Nogueira, S.; Araújo, F.; Teixeira, L.; Hagen, S. Monitoring the Brazilian Pasturelands: A New Mapping Approach Based on the Landsat 8 Spectral and Temporal Domains. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 62, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DNIT. Rodovias Georreferenciadas Que Compõem o Subsistema Rodoviário Federal Do Sistema Federal de Viação (SFV) Do Brasil—DNIT (2013); Departamento Nacional de Infraestrutura de Transportes: Brasilia, Brazil, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- GRASS Development Team. Geographic Resources Analysis Support System (GRASS) Software, Version 7.8; Open Source Geospatial Foundation OSGEO: Beaverton, OR, USA, 2020. Available online: https://grass.osgeo.org (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Calabrese, J.M.; Fleming, C.H.; Gurarie, E. ctmm: An R Package for Analyzing Animal Relocation Data As a Continuous-Time Stochastic Process. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 1124–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, C.H.; Calabrese, J.M.; Mueller, T.; Olson, K.A.; Leimgruber, P.; Fagan, W.F. Non-Markovian Maximum Likelihood Estimation of Autocorrelated Movement Processes. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2014, 5, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurarie, E.; Fleming, C.H.; Fagan, W.F.; Laidre, K.L.; Hernández-Pliego, J.; Ovaskainen, O. Correlated Velocity Models as a Fundamental Unit of Animal Movement: Synthesis and Applications. Mov. Ecol. 2017, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, C.H.; Calabrese, J.M. ctmm: Continuous-Time Movement Modeling. R Package Version 0.4.1. Available online: https://doi.org/10.32614/CRAN.package.ctmm (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Fleming, C.H.; Fagan, W.F.; Mueller, T.; Olson, K.A.; Leimgruber, P.; Calabrese, J.M. Rigorous Home Range Estimation with Movement Data: A New Autocorrelated Kernel Density Estimator. Ecology 2015, 96, 1182–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, C.H.; Calabrese, J.M. A New Kernel Density Estimator for Accurate Home-range and Species-range Area Estimation. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morato, R.G.; Stabach, J.A.; Fleming, C.H.; Calabrese, J.M.; De Paula, R.C.; Ferraz, K.M.P.M.; Kantek, D.L.Z.; Miyazaki, S.S.; Pereira, T.D.C.; Araujo, G.R.; et al. Space Use and Movement of a Neotropical Top Predator: The Endangered Jaguar. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noonan, M.J.; Tucker, M.A.; Fleming, C.H.; Akre, T.S.; Alberts, S.C.; Ali, A.H.; Altmann, J.; Antunes, P.C.; Belant, J.L.; Beyer, D.; et al. A Comprehensive Analysis of Autocorrelation and Bias in Home Range Estimation. Ecol. Monogr. 2019, 89, e01344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.J.; Jenks, J.A. Dispersal Movements of Subadult Cougars from the Black Hills: The Notions of Range Expansion and Recolonization. Ecosphere 2010, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-González, C.A. Implicaciones Para la Conservación y el Manejo de Pumas (Puma concolor) Utilizando Como Modelo una Población Suejta a Caceria Deportiva. Ph.D. Dissertation, Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico, Mexico, Mexico, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zeller, K.A.; Jennings, M.K.; Vickers, T.W.; Ernest, H.B.; Cushman, S.A.; Boyce, W.M. Are All Data Types and Connectivity Models Created Equal? Validating Common Connectivity Approaches with Dispersal Data. Divers. Distrib. 2018, 24, 868–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teitelbaum, C.S.; Mueller, T. Beyond Migration: Causes and Consequences of Nomadic Animal Movements. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2019, 34, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunell, A.M.; Deem, V.; Bankovich, B.; Bled, F.; Mazzotti, F.J. Effects of Translocation on American Crocodile Movements and Habitat Use in South Florida. J. Wildl. Manag. 2023, 87, e22427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Moorter, B.; Kivimäki, I.; Panzacchi, M.; Saerens, M. Defining and Quantifying Effective Connectivity of Landscapes for Species’ Movements. Ecography 2021, 44, 870–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choate, D.M.; Longshore, K.M.; Thompson, D.B. Cougar Dispersal and Natal Homing in a Desert Environment. West. North Am. Nat. 2018, 78, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolino, R.M.; Royle, J.A.; Versiani, N.F.; Rodrigues, T.F.; Pasqualotto, N.; Krepschi, V.G.; Chiarello, A.G. Importance of Riparian Forest Corridors for the Ocelot in Agricultural Landscapes. J. Mammal. 2018, 99, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morato, R.G.; Connette, G.M.; Stabach, J.A.; De Paula, R.C.; Ferraz, K.M.P.M.; Kantek, D.L.Z.; Miyazaki, S.S.; Pereira, T.D.C.; Silva, L.C.; Paviolo, A.; et al. Resource Selection in an Apex Predator and Variation in Response to Local Landscape Characteristics. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 228, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miotto, R.A.; Cervini, M.; Begotti, R.A.; Galetti, P.M., Jr. Monitoring a Puma (Puma concolor) Population in a Fragmented Landscape in Southeast Brazil: Pumas in Southeast Brazil. Biotropica 2012, 44, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnell, J.D.C.; Aanes, R.; Swenson, J.E.; Odden, J.; Smith, M.E. Translocation of Carnivores as a Method for Managing Problem Animals: A Review. Biodivers. Conserv. 1997, 6, 1245–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivimäki, I.; Van Moorter, B.; Saerens, M. Sensitivity to Network Perturbations in the Randomized Shortest Paths Framework: Theory and Applications in Ecological Connectivity. J. Phys. Complex. 2024, 5, 025017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio-Maior, H.; Nakamura, M.; Álvares, F.; Beja, P. Designing the Landscape of Coexistence: Integrating Risk Avoidance, Habitat Selection and Functional Connectivity to Inform Large Carnivore Conservation. Biol. Conserv. 2019, 235, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegre, V.B.; Rio-Maior, H.; Oshima, J.E.d.F.; Niebuhr, B.B.; Morato, R.G.; Ribeiro, M.C. The Effect of Anthropogenic Features on the Habitat Selection of a Large Carnivore Is Conditional on Sex and Circadian Period, Suggesting a Landscape of Coexistence. J. Nat. Conserv. 2023, 73, 126412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-González, C.E.; López-González, C.A. Jaguar Interactions with Pumas and Prey at the Northern Edge of Jaguars’ Range. PeerJ 2017, 5, e2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, O.; Castillo, D.F.; Godinho, R.; Mac Allister, M.E.; Fernández, G.P.; Failla, M.; Casanave, E.B. Molecular Data Reveal a Structured Puma (Puma Concolor) Population in Northern Patagonia, Argentina. Mamm. Biol. 2021, 101, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Torre, J.A.; Núñez, J.M.; Medellín, R.A. Spatial Requirements of Jaguars and Pumas in Southern Mexico. Mamm. Biol. 2017, 84, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niebuhr, B.B.; Cavalcanti, S.M.C.; Vilalba, E.A.; Alberico, V.V.; Gebin, J.C.Z.; Santos, D.d.C.; Barban, A.d.B.; Oliveira, R.d.; Gurarie, E.; Morato, R.G. Land Use Effects on the Space Use and Dispersal of an Apex Predator in an Ecotone Between Tropical Biodiversity Hotspots. Diversity 2025, 17, 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17060435
Niebuhr BB, Cavalcanti SMC, Vilalba EA, Alberico VV, Gebin JCZ, Santos DdC, Barban AdB, Oliveira Rd, Gurarie E, Morato RG. Land Use Effects on the Space Use and Dispersal of an Apex Predator in an Ecotone Between Tropical Biodiversity Hotspots. Diversity. 2025; 17(6):435. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17060435
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiebuhr, Bernardo Brandão, Sandra M. C. Cavalcanti, Ermeson A. Vilalba, Vanessa V. Alberico, João Carlos Zecchini Gebin, Danilo da Costa Santos, Ananda de Barros Barban, Raphael de Oliveira, Eliezer Gurarie, and Ronaldo G. Morato. 2025. "Land Use Effects on the Space Use and Dispersal of an Apex Predator in an Ecotone Between Tropical Biodiversity Hotspots" Diversity 17, no. 6: 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17060435
APA StyleNiebuhr, B. B., Cavalcanti, S. M. C., Vilalba, E. A., Alberico, V. V., Gebin, J. C. Z., Santos, D. d. C., Barban, A. d. B., Oliveira, R. d., Gurarie, E., & Morato, R. G. (2025). Land Use Effects on the Space Use and Dispersal of an Apex Predator in an Ecotone Between Tropical Biodiversity Hotspots. Diversity, 17(6), 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17060435





