Developmental Dynamics of Bacterial Microbiota in Aphis gossypii Revealed Using Full-Length 16S rRNA Sequencing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Aphis gossypii Samples at Different Developmental Stages
2.2. Full-Length 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing Across Developmental Stages
2.3. Data Analysis
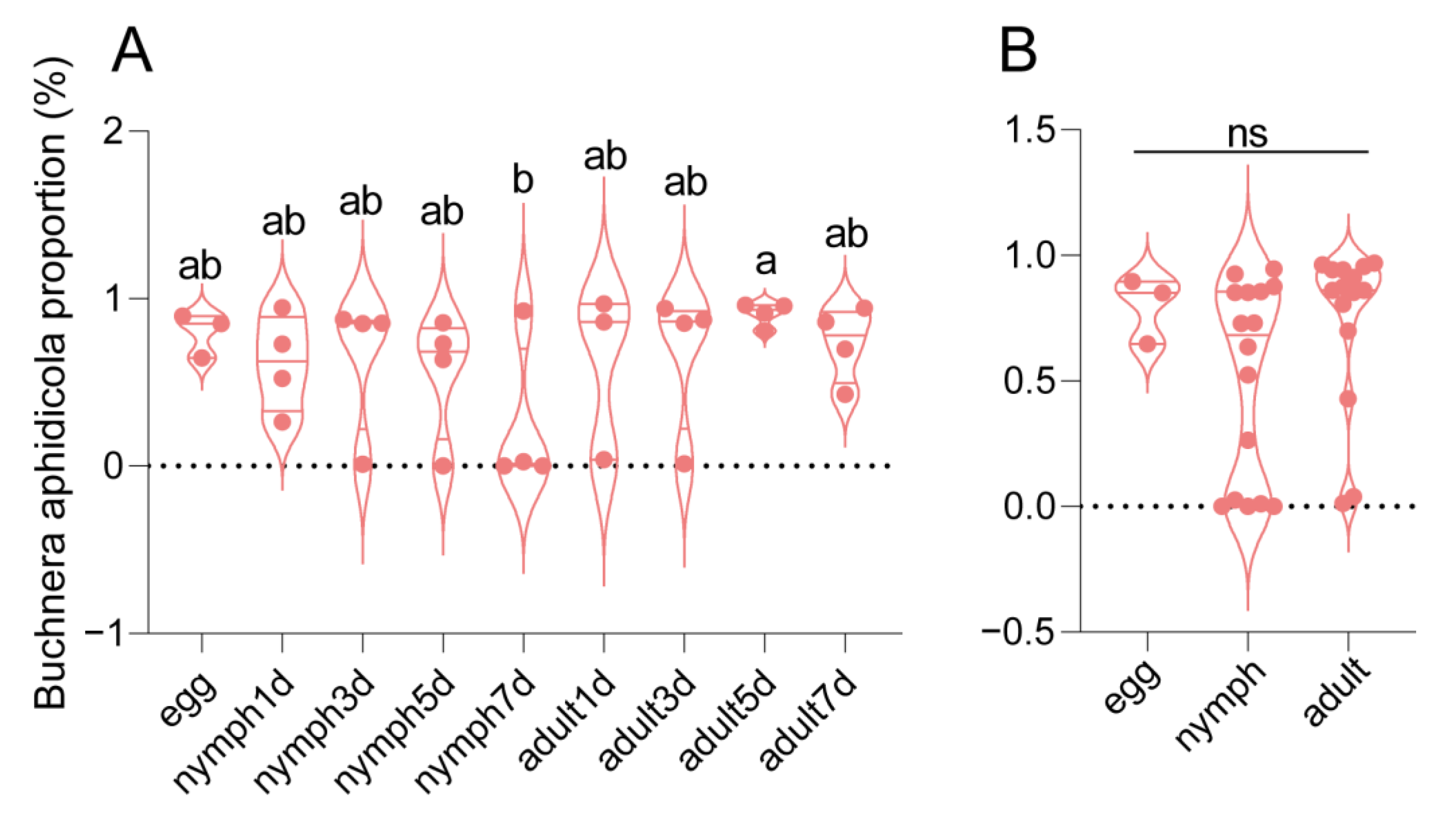
3. Results
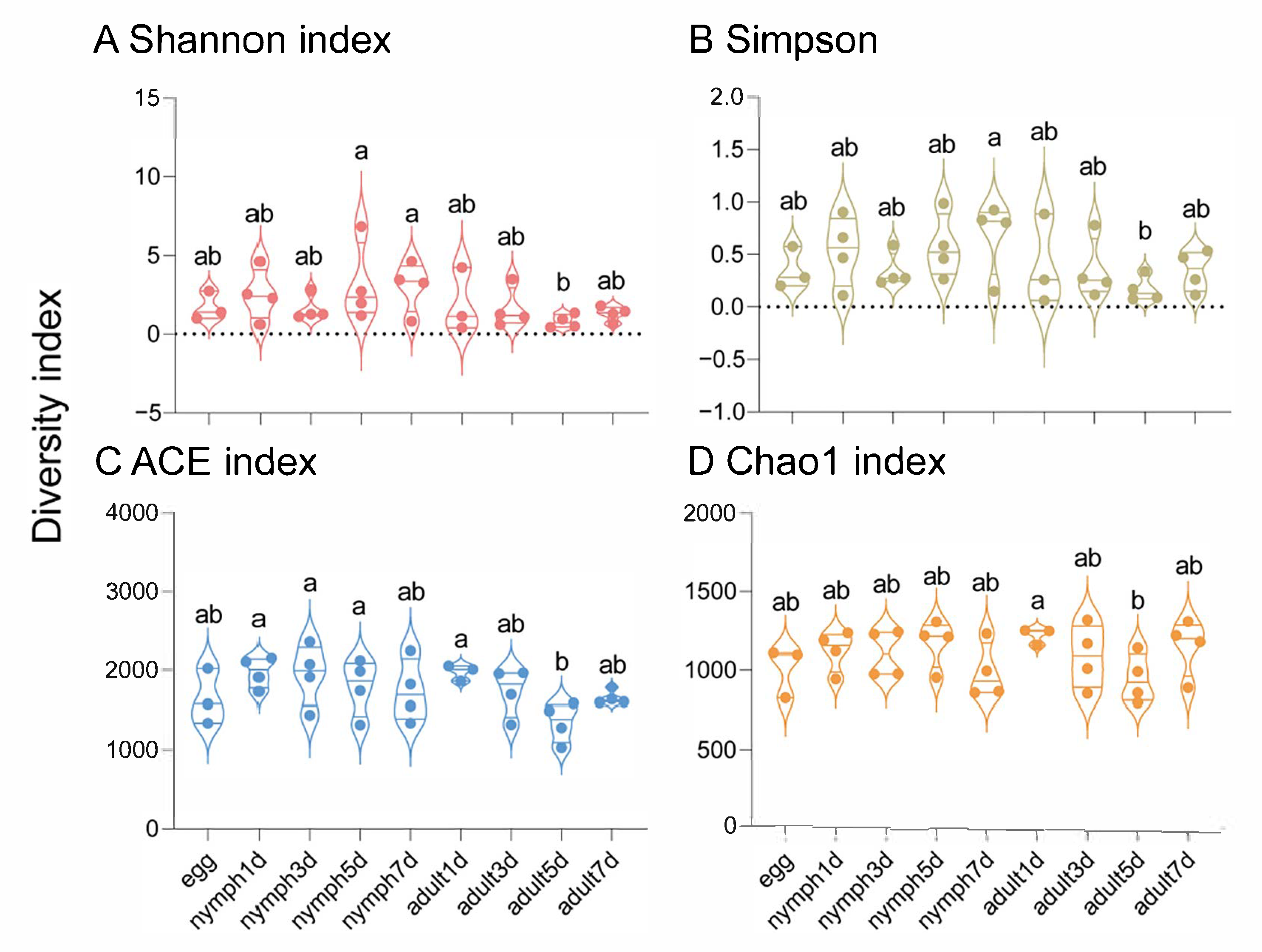
3.1. Sequencing Data of Bacterial Microbiota in Aphis gossypii
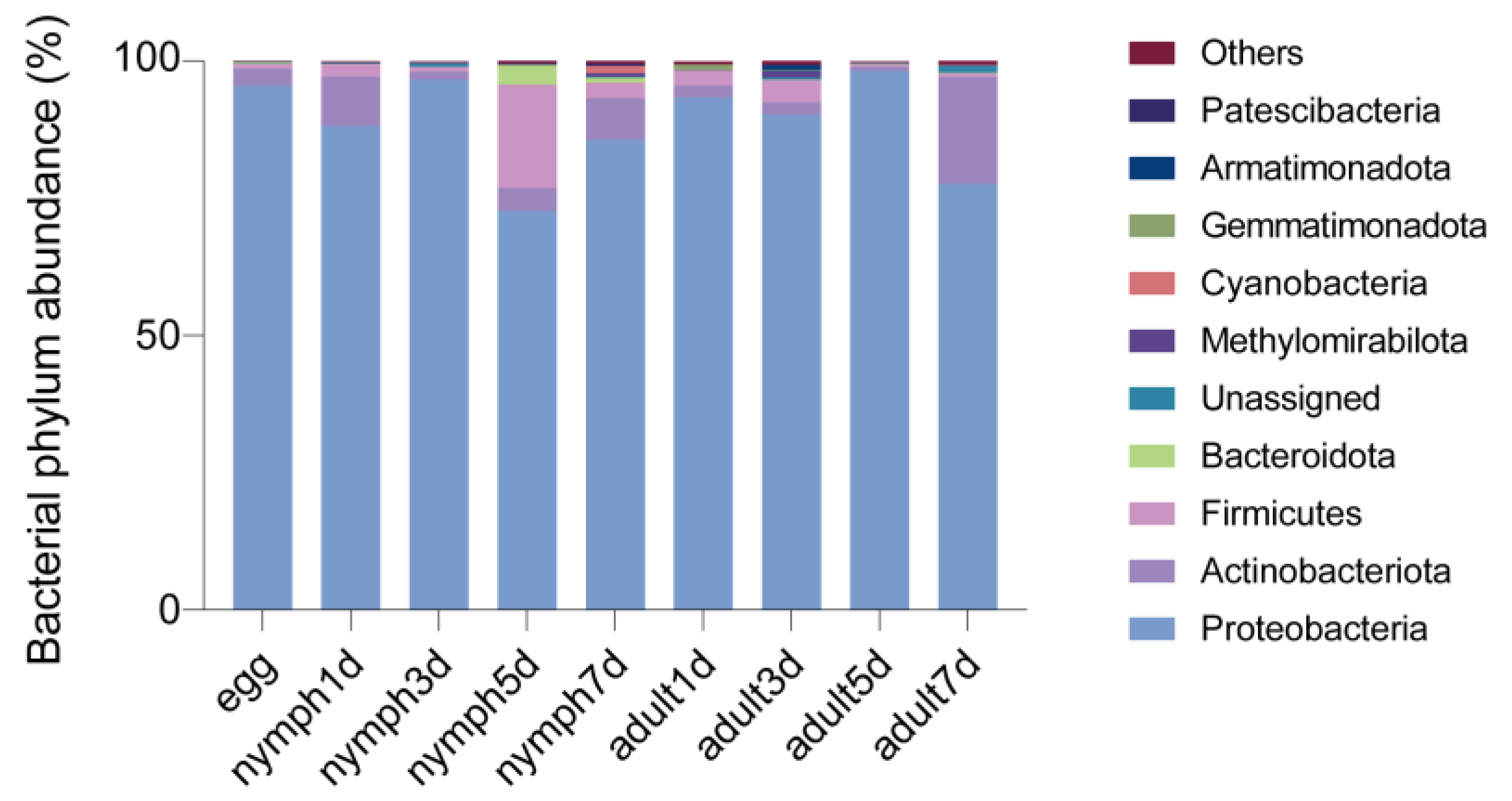
3.2. Bacterial Communities in Different Growth Stages of Aphis gossypii
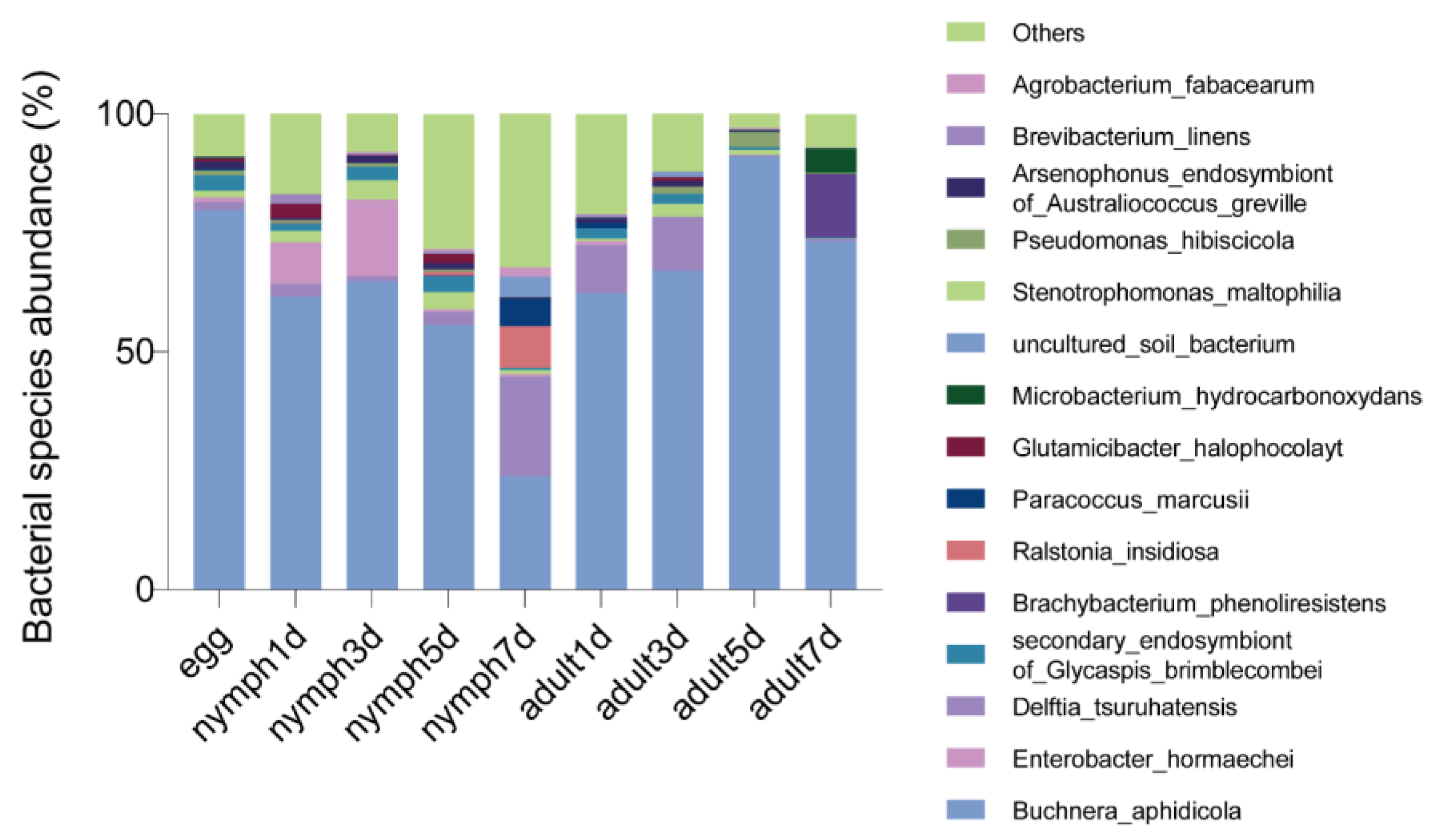
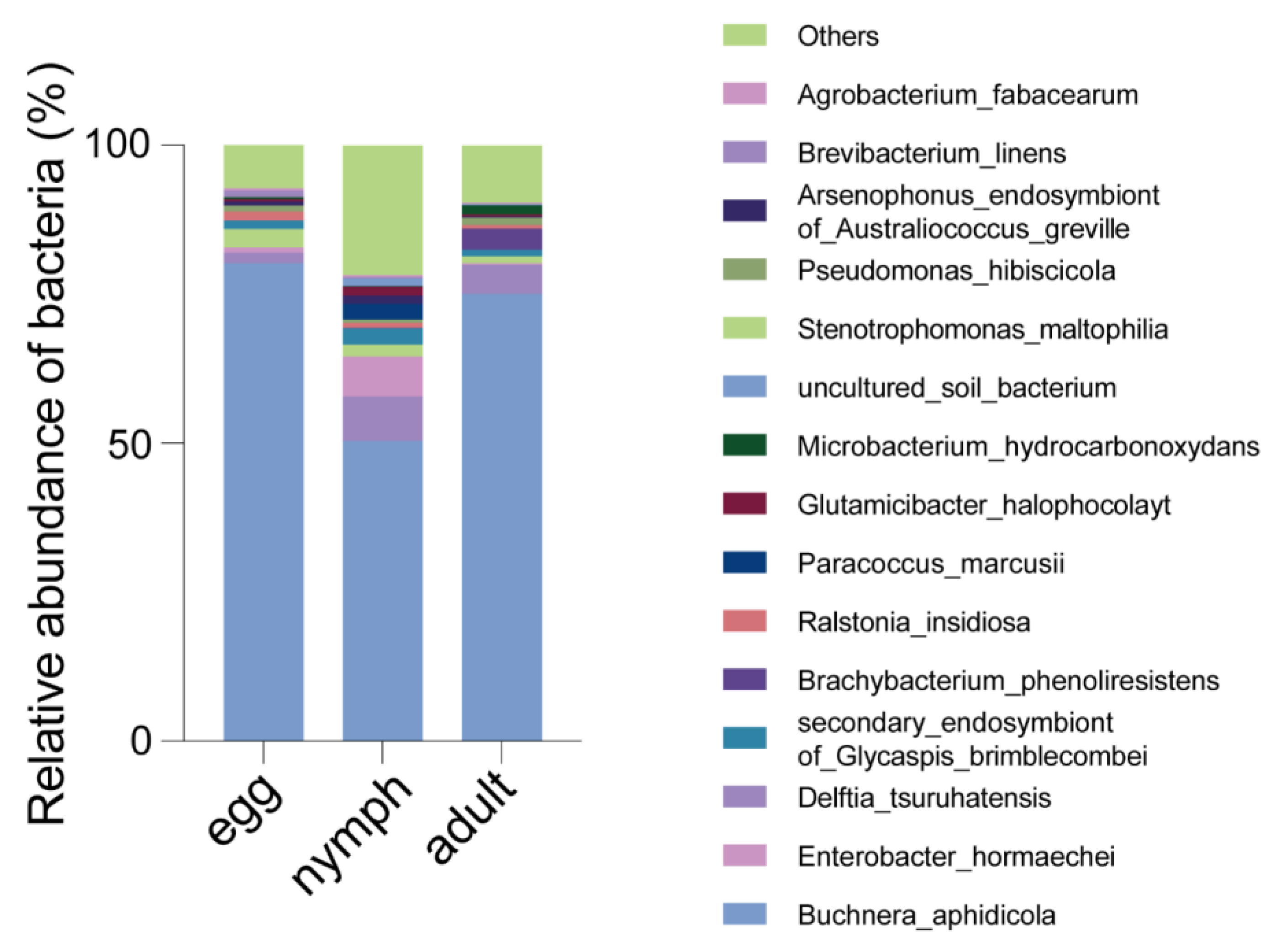
3.3. Bacterial Microbiota Varied in Different Growth Stages of Aphis gossypii
3.4. Functions of Bacterial Microbiota Changed with the Development of Aphis gossypii
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, Z.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, H.; Luo, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; An, H.; et al. GhMYB18 confers Aphis gossypii Glover resistance through regulating the synthesis of salicylic acid and flavonoids in cotton plants. Plant Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Wen, S.; Chen, X.; Gao, X.; Zeng, X.; Liu, X.; Tian, F.; Shang, Q. UDP-glycosyltransferases contribute to spirotetramat resistance in Aphis gossypii Glover. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 166, 104565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, J.; Cui, L.; Wang, Q.; Huang, W.; Ji, X.; Yang, Q.; Rui, C. Overexpression of ATP-binding cassette transporters associated with sulfoxaflor resistance in Aphis gossypii glover. Pest Manag Sci. 2021, 77, 4064–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Yang, Q.; Ji, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Rui, C.; Cui, L. An insecticide phenotypic resistance diagnostic kit for cotton aphid Aphis gossypii Glover (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Pest. Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 5463–5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Yao, Y.; Li, X.; Gao, X.; Li, J.; Ma, K. Characterization, expression, and functional analysis of TRPV genes in cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii Glover. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 267, 109582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, P.; Moran, N.A. The gut microbiota of insects: Diversity in structure and function. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 699–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brune, A.; Dietrich, C. The gut microbiota of termites: Digesting the diversity in the light of ecology and evolution. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 69, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, A.E. Multiorganismal insects: Diversity and function of resident microorganisms. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2015, 60, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, A.K.; Moran, N.A. The impact of microbial symbionts on host plant utilization by herbivorous insects. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 1473–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, F.; Ding, B.Y.; Niu, J.; Lu, J.M.; Xie, X.C.; Li, C.Z.; Zhang, W.; Pan, D.; Jiang, R.X.; Wang, J.J. microRNA maintains nutrient homeostasis in the symbiont-host interaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2406925121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigenobu, S.; Yorimoto, S. Aphid hologenomics: Current status and future challenges. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2022, 50, 100882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smee, M.R.; Hendry, T.A. Context-dependent benefits of aphids for bacteria in the phyllosphere. Am. Nat. 2022, 199, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Chen, J.; Qin, M.; Jiang, L.; Qiao, G. Geography-dependent symbiont communities in two oligophagous aphid species. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2021, 97, fiab132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouari, S.; Ben Halima, M.K.; Reyes-Prieto, M.; Latorre, A.; Gil, R. Natural occurrence of secondary bacterial symbionts in aphids from Tunisia, with a focus on genus Hyalopterus. Environ. Entomol. 2018, 47, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zytynska, S.E. Cohabitation and roommate bias of symbiotic bacteria in insect hosts. Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 5199–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, T.; Ruan, Y.; Ning, Z.; Lu, Y.; Guo, J.; Xiao, Z.; Yang, K. Metagenomic approaches reveal the variations of microbiota structures and functions with the growth of Melanaphis sacchari. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2025, 28, 102402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrato-Salas, J.; Gendrin, M. Involvement of Microbiota in Insect Physiology: Focus on B Vitamins. mBio 2023, 28, e0222522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xu, L. The pivotal roles of gut microbiota in insect-plant interactions for sustainable pest management. Npj Biofilms Microbio. 2023, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wang, J.; Huang, X.; Guan, B.; Feng, Q.; Deng, H. Composition and diversity of gut microbiota across developmental stages of Spodoptera frugiperda and its effect on the reproduction. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1237684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cini, A.; Meriggi, N.; Bacci, G.; Cappa, F.; Vitali, F.; Cavalieri, D.; Cervo, R. Gut microbial composition in different castes and developmental stages of the invasive hornet Vespa velutina nigrithorax. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 140873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, K.D.; Wang, Q.; Nute, M.G.; Tyshaieva, A.; Reeves, E.; Soriano, S.; Wu, Q.; Graeber, E.; Finzer, P.; Mendling, W.; et al. Emu: Species-level microbial community profiling of full-length 16S rRNA Oxford Nanopore sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Yuan, M.Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, C.L.; Liu, T.X.; Zhang, Y.J.; Chu, D. First evidence for thermal tolerance benefits of the bacterial symbiont Cardinium in an invasive whitefly, Bemisia tabaci. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 5021–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosher, J.J.; Bowman, B.; Bernberg, E.L.; Shevchenko, O.; Kan, J.; Korlach, J. Improved performance of the PacBio SMRT technology for 16S rDNA sequencing. J. Microbiol. Methods 2014, 104, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.Y.; Chen, X.Y.L.; Yang, H.; Cernava, T. Microbiome structure of the aphid Myzus persicae (Sulzer) is shaped by different Solanaceae plant diets. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 667257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Chen, J.; Xu, S.F.; Jiang, L.Y.; Qiao, G.X. Microbiota associated with Mollitrichosiphum aphids (Hemiptera: Aphididae: Greenideinae): Diversity, host species specificity and phylosymbiosis. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 2184–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.T.; Chen, J.; Jiang, L.Y.; Qiao, G.X. Diversity of bacteria associated with Hormaphidinae aphids (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Insect Sci. 2021, 28, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Luo, J.-Y.; Wang, C.-Y.; Lv, L.-M.; Cui, J.-J. Bacterial communities of the cotton aphid Aphis gossypii associated with Bt cotton in northern China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordenstein, S.R.; Theis, K.R. Host biology in light of the microbiome: Ten principles of holobionts and hologenomes. PLoS Biol. 2015, 13, e1002226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Dikow, R.B.; Su, X.; Wen, J.; Ren, Z. Comparative genomics of the primary endosymbiont Buchnera aphidicola in aphid hosts and their coevolutionary relationships. BMC Biol. 2024, 22, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Leonard, S.P.; Li, Y.; Moran, N.A. Obligate bacterial endosymbionts limit thermal tolerance of insect host species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24712–24718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, A.E. Nutritional interactions in insect-microbial symbioses: Aphids and their symbiotic bacteria Buchnera. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1998, 43, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, N.A.; McLaughlin, H.J.; Sorek, R. The dynamics and time scale of ongoing genomic erosion in symbiotic bacteria. Science 2009, 323, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo-Franco, J.J.; Duque-Gamboa, D.N.; Toro-Perea, N. Bacterial communities of Aphis gossypii and Myzus persicae (Hemiptera: Aphididae) from pepper crops (Capsicum sp.). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, J.A.; Weldon, S.; Smith, A.H.; Kim, K.L.; Hu, Y.; Łukasik, P.; Doll, S.; Anastopoulos, I.; Novin, M.; Oliver, K.M. Uncovering symbiont-driven genetic diversity across North American pea aphids. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 2045–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twayana, M.; Girija, A.M.; Mohan, V.; Shah, J. Phloem: At the center of action in plant defense against aphids. J. Plant Physiol. 2022, 273, 153695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriyanov, P.A.; Kashina, D.D.; Menshikova, A.N. Genomic analysis of multidrug-resistant Delftia tsuruhatensis isolated from raw bovine milk. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1321122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranc, A.; Dubourg, G.; Fournier, P.E.; Raoult, D.; Fenollar, F. Delftia tsuruhatensis, an emergent opportunistic healthcare-associated pathogen. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 594–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Mishra, A.; Jha, B. Anti-quorum sensing and anti-biofilm activity of Delftia tsuruhatensis extract by attenuating the quorum sensing-controlled virulence factor production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Rodrigues, J.; Bilgo, E.; Tormo, J.R.; Challenger, J.D.; De Cozar-Gallardo, C.; Pérez-Victoria, I.; Reyes, F.; Castañeda-Casado, P.; Gnambani, E.J.; et al. Delftia tsuruhatensis TC1 symbiont suppresses malaria transmission by anopheline mosquitoes. Science 2023, 381, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agergaard, C.N.; Porsbo, L.J.; Sydenham, T.V.; Hansen, S.G.K.; Steinke, K.; Larsen, S.L.; Helgason, K.O.; Hansen, F.; Karstensen, K.T.; Henius, A.E.; et al. Contaminated dicloxacillin capsules as the source of an NDM-5/OXA-48-producing Enterobacter hormaechei ST79 outbreak, Denmark and Iceland, 2022 and 2023. Euro Surveill. 2023, 28, 2300108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, M.; Hassan, B.; Khan, A.U.; Ali, A.; Swedberg, G.; Hasan, B. Genomic characterization of high-risk Escherichia coli and Enterobacter hormaechei clones recovered from a single tertiary-care hospital in Pakistan. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 3907–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Duan, L.; Liu, F.; Hu, Y.; Leng, C.; Kan, Y.; Yao, L.; Shi, H. First report of Enterobacter hormaechei with respiratory disease in calves. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, K.; Liu, W.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z. Enterobacter hormaechei in the intestines of housefly larvae promotes host growth by inhibiting harmful intestinal bacteria. Parasit Vectors 2021, 14, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, C.-H.; Jang, H.A.; Kim, J.K.; Kotaki, T.; Shinada, T.; Yoo, J.-W.; Lee, B.L. Burkholderia gut symbiont modulates titer of specific juvenile hormone in the bean bug Riptortus pedestris. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 99, 103399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werren, J.H.; Baldo, L.; Clark, M.E. Wolbachia: Master manipulators of invertebrate biology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Xie, K.; Zhu, Y.X.; Huo, S.M.; Hoffmann, A.; Hong, X.Y. Wolbachia dominate Spiroplasma in the co-infected spider mite Tetranychus truncatus. Insect Mol. Biol. 2020, 29, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’aglio, E.; Lacotte, V.; Peignier, S.; Rahioui, I.; Benzaoui, F.; Vallier, A.; Da Silva, P.; Desouhant, E.; Heddi, A.; Rebollo, R. Weevil carbohydrate intake triggers endosymbiont proliferation: A trade-off between host benefit and endosymbiont burden. mBio 2023, 14, e03333-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, K.J.; Moran, N.A. Effect of host genotype on symbiont titer in the aphid-Buchnera symbiosis. Insects 2011, 2, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zug, R.; Hammerstein, P. Bad guys turned nice? A critical assessment of Wolbachia mutualisms in arthropod hosts. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2015, 90, 89–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, E.V.S.; Moran, N.A. The honeybee microbiota and its impact on health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matchado, M.S.; Rühlemann, M.; Reitmeier, S.; Kacprowski, T.; Frost, F.; Haller, D.; Baumbach, J.; List, M. On the limits of 16S rRNA gene-based metagenome prediction and functional profiling. Microb. Genom. 2024, 10, 001203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Xie, X.; Hou, Q.; Wei, C.; Chen, Z.; Fan, L.; Liang, E.; Li, Z.; Yang, K. Developmental Dynamics of Bacterial Microbiota in Aphis gossypii Revealed Using Full-Length 16S rRNA Sequencing. Diversity 2025, 17, 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17060404
Wang Y, Xie X, Hou Q, Wei C, Chen Z, Fan L, Liang E, Li Z, Yang K. Developmental Dynamics of Bacterial Microbiota in Aphis gossypii Revealed Using Full-Length 16S rRNA Sequencing. Diversity. 2025; 17(6):404. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17060404
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yunchao, Xingmei Xie, Qiuli Hou, Chuying Wei, Zhan Chen, Leilei Fan, E Liang, Zhuo Li, and Kun Yang. 2025. "Developmental Dynamics of Bacterial Microbiota in Aphis gossypii Revealed Using Full-Length 16S rRNA Sequencing" Diversity 17, no. 6: 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17060404
APA StyleWang, Y., Xie, X., Hou, Q., Wei, C., Chen, Z., Fan, L., Liang, E., Li, Z., & Yang, K. (2025). Developmental Dynamics of Bacterial Microbiota in Aphis gossypii Revealed Using Full-Length 16S rRNA Sequencing. Diversity, 17(6), 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17060404





