Research Trends and Hotspots in eDNA-Based Surveys of Macroinvertebrates: A Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Search Strategies
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
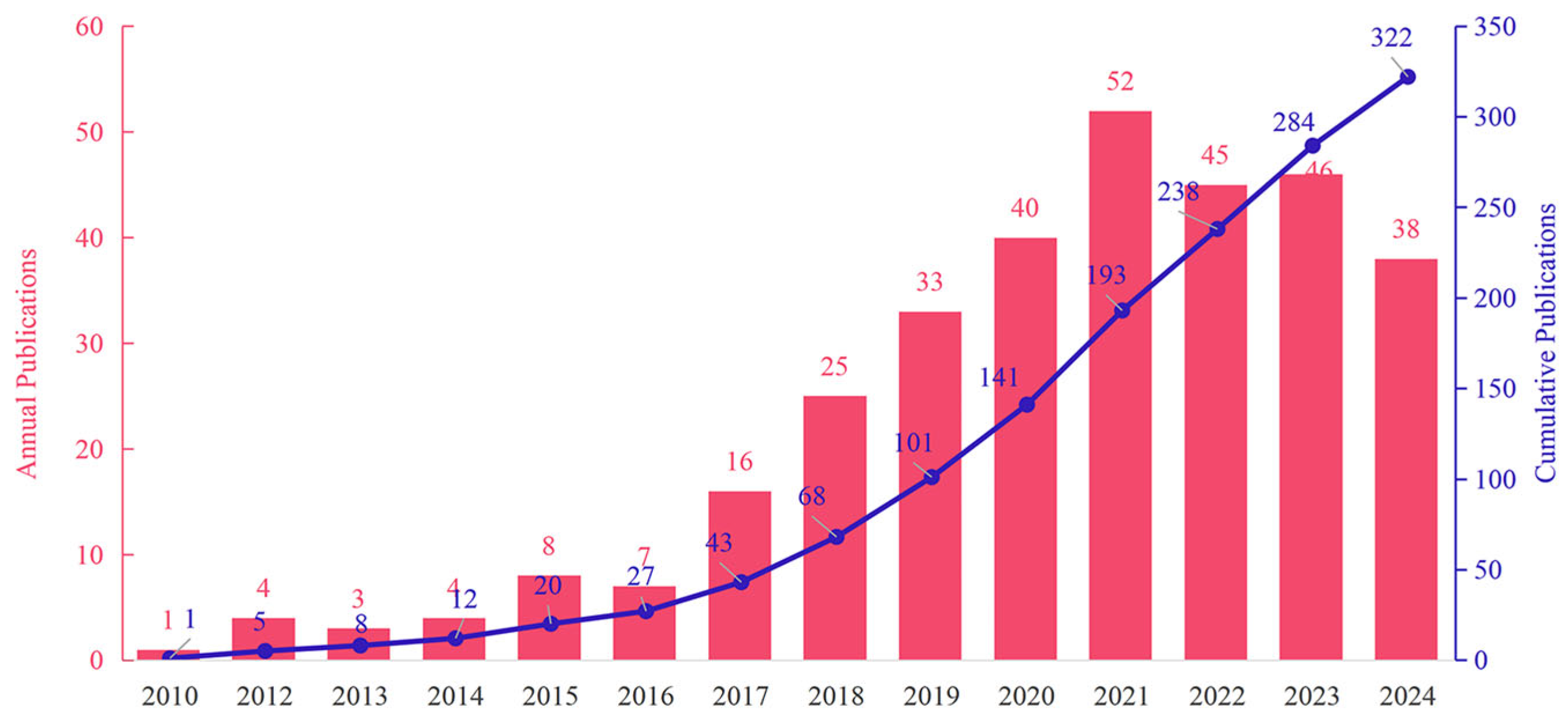
3.1. Publication Model
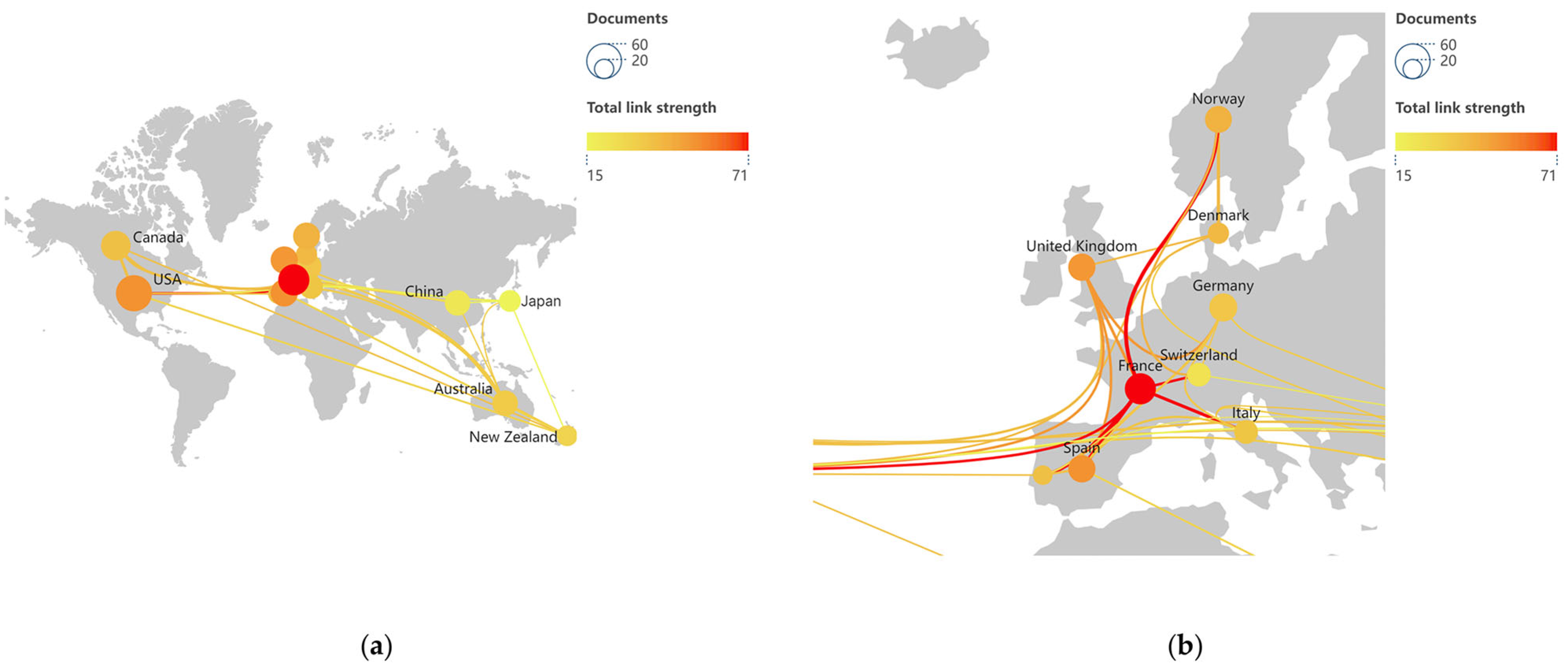
3.2. Cooperation of Countries
3.3. High-Impact Journals, Productive Authors, and Highly Cited Articles
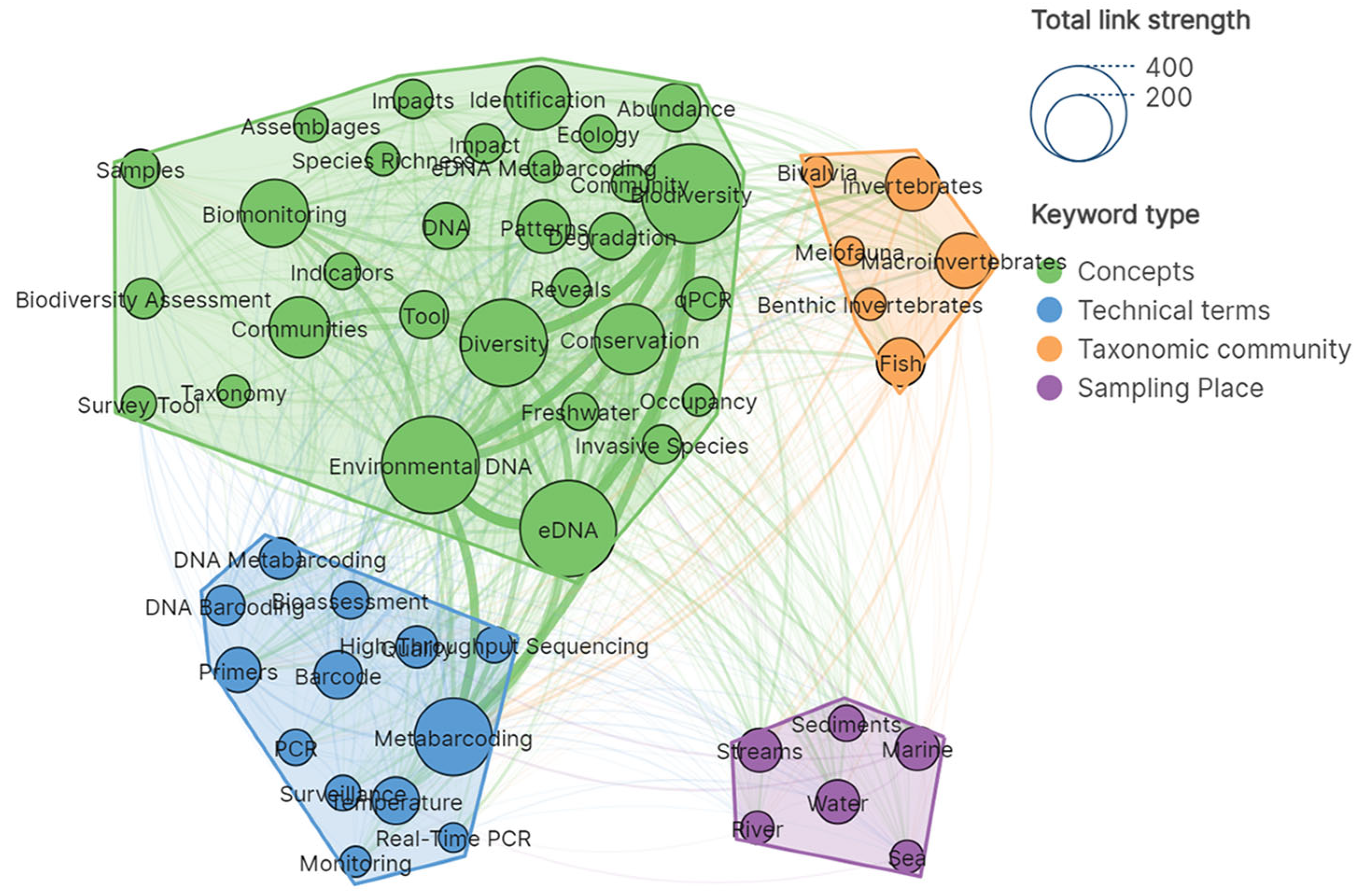
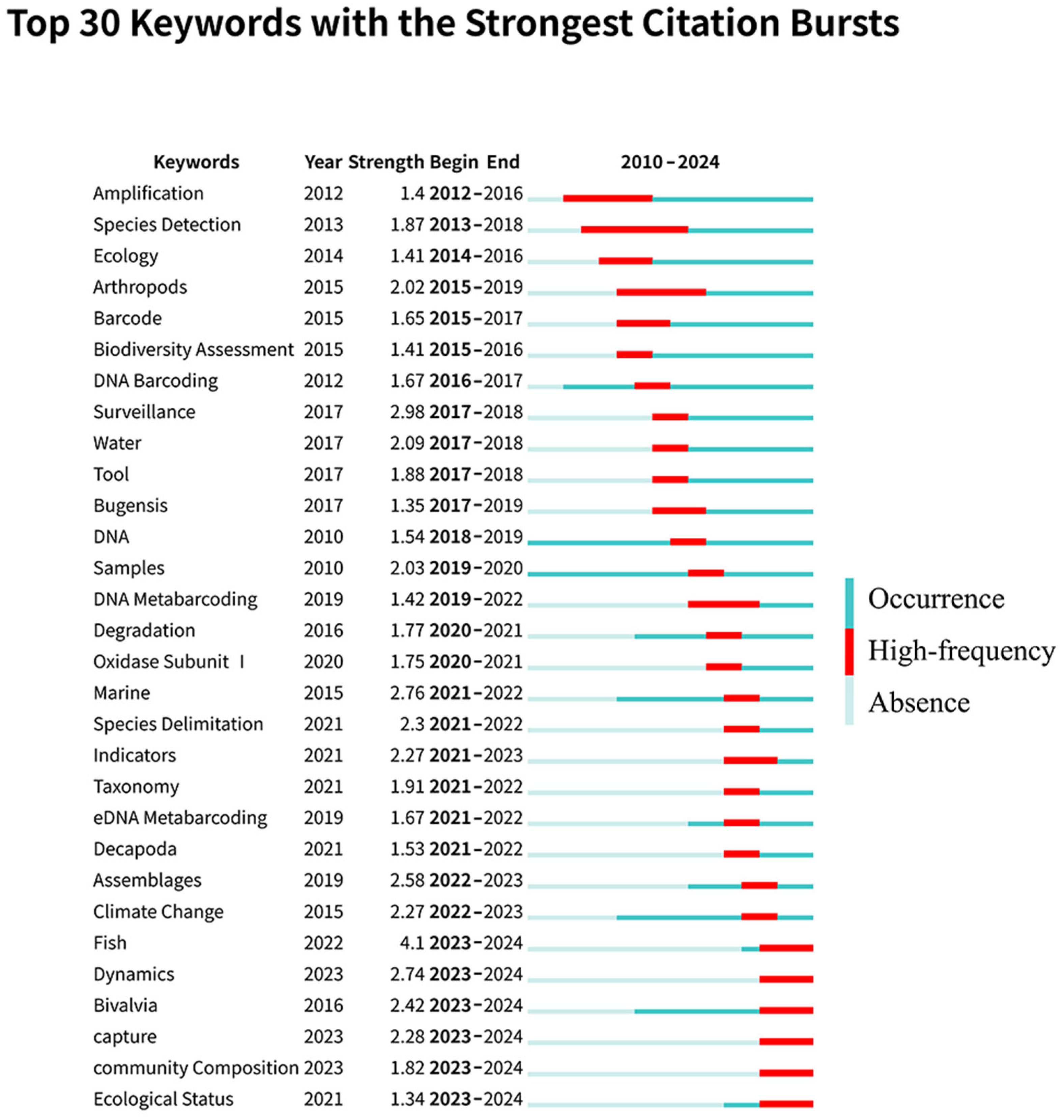
3.4. Keyword Network Analysis
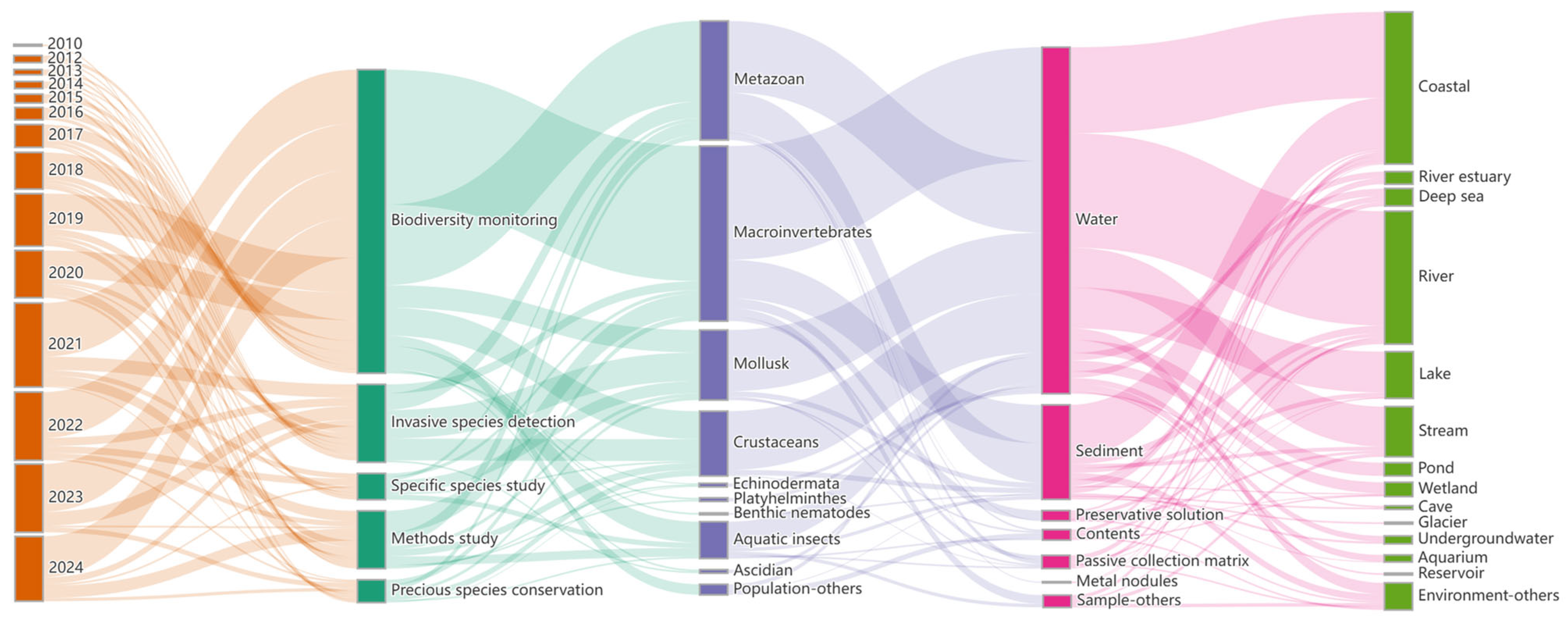
3.5. Analysis of Research Directions
3.6. The Main Research Directions of Monitoring Articles
3.6.1. Diversity Studies
3.6.2. Invasive Species Detection
3.6.3. Protection of Rare Species
3.7. Research and Technological Advances
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carter, J.L.; Resh, V.H.; Hannaford, M.J. Macroinvertebrates as Biotic Indicators of Environmental Quality. In Methods in Stream Ecology, 3rd ed.; Lamberti, G.A., Hauer, F.R., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2017; Volume 3, pp. 293–318. ISBN 978-0-12-813047-6. [Google Scholar]
- Birk, S.; Bonne, W.; Borja, A.; Brucet, S.; Courrat, A.; Poikane, S.; Solimini, A.; van de Bund, W.; Zampoukas, N.; Hering, D. Three Hundred Ways to Assess Europe’s Surface Waters: An Almost Complete Overview of Biological Methods to Implement the Water Framework Directive. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 18, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.-I.; Knowler, D.J.; Lévêque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.-H.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L.J.; et al. Freshwater Biodiversity: Importance, Threats, Status and Conservation Challenges. Biol. Rev. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, M.J.; Uzarski, D.G.; Burton, T.M. Macroinvertebrate Community Composition in Relation to Anthropogenic Disturbance, Vegetation, and Organic Sediment Depth in Four Lake Michigan Drowned River-Mouth Wetlands. Wetlands 2007, 27, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-Ulloa, R.; Umaña-Villalobos, G.; Springer, M. Downstream Effects of Hydropower Production on Aquatic macroinvertebrate Assemblages in Two Rivers in Costa Rica. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2014, 62 (Suppl. S2), 179–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C.K.; Whiles, M.R. macroinvertebrate Communities in Restored and Natural Platte River Slough Wetlands. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2008, 27, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfrender, M.E.; Hawkins, C.P.; Bagley, M.; Courtney, G.W.; Creutzburg, B.R.; Epler, J.H.; Fend, S.; Schindel, D.; Ferrington, L.C.; Hartzell, P.L.; et al. Assessing macroinvertebrate Biodiversity in Freshwater Ecosystems: Advances and Challenges in DNA-Based Approaches. Q. Rev. Biol. 2010, 85, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beng, K.C.; Corlett, R.T. Applications of Environmental DNA (eDNA) in Ecology and Conservation: Opportunities, Challenges and Prospects. Biodivers. Conserv. 2020, 29, 2089–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.A.; Chadderton, W.L.; Jerde, C.L.; Mahon, A.R.; Turner, C.R.; Lodge, D.M. Environmental Conditions Influence eDNA Particle Size Distribution in Aquatic Systems. Environ. DNA 2021, 3, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, D.C.; Leal, C.G. Steps Forward in Biomonitoring 2.0: eDNA Metabarcoding and Community-Level Modelling Allow the Assessment of Complex Drivers of Neotropical Fish Diversity. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 1688–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, S.; Takahara, T.; Doi, H.; Shibata, N.; Yamanaka, H. The Detection of Aquatic Macroorganisms Using Environmental DNA Analysis—A Review of Methods for Collection, Extraction, and Detection. Environ. DNA 2019, 1, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficetola, G.F.; Miaud, C.; Pompanon, F.; Taberlet, P. Species Detection Using Environmental DNA from Water Samples. Biol. Lett. 2008, 4, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.H.; Lee, J.; Noh, J.; Lee, C.; Hong, S.; Kwon, B.-O.; Kim, J.-J.; Khim, J.S. Characteristics of Long-Term Changes in Microbial Communities from Contaminated Sediments along the West Coast of South Korea: Ecological Assessment with eDNA and Physicochemical Analyses. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprilia, M.; Effendi, H.; Hariyadi, S.; Permatasari, P.A. Aquatic eDNA Metabarcoding Reveals Biodiversity and Plankton Composition in River Ecosystems. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2023, 32, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brantschen, J.; Fopp, F.; Adde, A.; Keck, F.; Guisan, A.; Pellissier, L.; Altermatt, F. Habitat Suitability Models Reveal the Spatial Signal of Environmental DNA in Riverine Networks. Ecography 2024, 2024, e07267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa Prieto, A.; Hardion, L.; Debortoli, N.; Bournonville, T.; Mathot, T.; Marescaux, J.; Chanez, E.; Staentzel, C.; Beisel, J.-N. A Comparative Analysis of eDNA Metabarcoding and Field Surveys: Exploring Freshwater Plant Communities in Rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vautier, M.; Chardon, C.; Goulon, C.; Guillard, J.; Domaizon, I. A Quantitative eDNA-Based Approach to Monitor Fish Spawning in Lakes: Application to European Perch and Whitefish. Fish. Res. 2023, 264, 106708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Métris, K.L.; Métris, J. Aircraft Surveys for Air eDNA: Probing Biodiversity in the Sky. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariza, M.; Engelstad, M.; Lieungh, E.; Laux, M.; Ready, J.; Mauvisseau, Q.; Halvorsen, R.; de Boer, H.J. Evaluating the Feasibility of Using Plant-Specific Metabarcoding to Assess Forest Types from Soil eDNA. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2024, 27, e12806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhu, C.; Cheng, Y.; Lei, Y.; Nan, Y.; Ouyang, S.; Wu, X. Exploring Freshwater Snail Diversity and Community Structure in China’s Largest Lake Using eDNA Technology. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Long, H.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, F.; Jin, W.; Wang, G.; Chang, W.; Pi, Y.; Gao, L.; et al. eDNA Assessment of Pelagic Fish Diversity, Distribution, and Abundance in the Central Pacific Ocean. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2022, 56, 102661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamoto, T.; Miya, M.; Sado, T.; Seino, S.; Doi, H.; Kondoh, M.; Nakamura, K.; Takahara, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Yamanaka, H.; et al. An Illustrated Manual for Environmental DNA Research: Water Sampling Guidelines and Experimental Protocols. Environ. DNA 2021, 3, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.P.; Lodge, D.M.; Lee, K.N.; Theroux, S.; Sepulveda, A.J.; Scholin, C.A.; Craine, J.M.; Andruszkiewicz Allan, E.; Nichols, K.M.; Parsons, K.M.; et al. Toward a National eDNA Strategy for the United States. Environ. DNA 2024, 6, e432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Willerslev, E. Environmental DNA—An Emerging Tool in Conservation for Monitoring Past and Present Biodiversity. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, E.M.; Gleeson, D.; Wisniewski, C.; Yick, J.; Duncan, R.P. eDNA Surveys to Detect Species at Very Low Densities: A Case Study of European Carp Eradication in Tasmania, Australia. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 56, 2505–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Guo, N.; Gao, J.; Xiao, N. Using eDNA to Survey Amphibians: Methods, Applications, and Challenges. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2024, 121, 456–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlapati, D.; Charankumar, B.; Ramu, K.; Madeswaran, P.; Murthy, M.V.R. A Review on the Applications and Recent Advances in Environmental DNA (eDNA) Metagenomics. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio-Technol. 2019, 18, 389–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VOSviewer. Available online: https://www.vosviewer.com/ (accessed on 6 November 2024).
- Hirsch, J.E. An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 16569–16572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Llimos, F. Differences and Similarities between Journal Impact Factor and CiteScore. Pharm. Pract. 2018, 16, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SCImago Graphica. Available online: https://www.graphica.app/ (accessed on 6 November 2024).
- Pajek. Available online: http://mrvar.fdv.uni-lj.si/pajek/ (accessed on 6 November 2024).
- CiteSpace. Available online: https://citespace.podia.com/ (accessed on 6 November 2024).
- Sankey. Available online: https://gallery.pyecharts.org/#/Sankey/ (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Deiner, K.; Altermatt, F. Transport Distance of Invertebrate Environmental DNA in a Natural River. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, D.; Borja, A.; Jones, J.I.; Pont, D.; Boets, P.; Bouchez, A.; Bruce, K.; Drakare, S.; Hanfling, B.; Kahlert, M.; et al. Implementation Options for DNA-Based Identification into Ecological Status Assessment under the European Water Framework Directive. Water Res. 2018, 138, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treguier, A.; Paillisson, J.-M.; Dejean, T.; Valentini, A.; Schlaepfer, M.A.; Roussel, J.-M. Environmental DNA Surveillance for Invertebrate Species: Advantages and Technical Limitations to Detect Invasive Crayfish Procambarus Clarkii in Freshwater Ponds. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 51, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajibabaei, M.; Spall, J.L.; Shokralla, S.; van Konynenburg, S. Assessing Biodiversity of a Freshwater benthic macroinvertebrate Community through Non-Destructive Environmental Barcoding of DNA from Preservative Ethanol. BMC Ecol. 2012, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordier, T.; Esling, P.; Lejzerowicz, F.; Visco, J.; Ouadahi, A.; Martins, C.; Cedhagen, T.; Pawlowski, J. Predicting the Ecological Quality Status of Marine Environments from eDNA Metabarcoding Data Using Supervised Machine Learning. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9118–9126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshobane, M.C.; Khoza, T.T.; Niassy, S. The Period of Insect Research in the Tropics: A Bibliometric Analysis. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2022, 42, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-J.; Chien, T.-W.; Liao, K.-W.; Lai, F.-J. Using the Sankey Diagram to Visualize Article Features on the Topics of Whole-Exome Sequencing (WES) and Whole-Genome Sequencing (WGS) since 2012: Bibliometric Analysis. Medicine 2022, 101, e30682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardiola, M.; Uriz, M.J.; Taberlet, P.; Coissac, E.; Wangensteen, O.S.; Turon, X. Correction: Deep-Sea, Deep-Sequencing: Metabarcoding Extracellular DNA from Sediments of Marine Canyons. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, L.; Harford, A.J.; Hose, G.C.; Humphrey, C.L.; Chariton, A.; Greenfield, P.; Davis, J. Saline Mine Water Influences Eukaryote Life in Shallow Groundwater of a Tropical Sandy Stream. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chown, S.L.; Hodgins, K.A.; Griffin, P.C.; Oakeshott, J.G.; Byrne, M.; Hoffmann, A.A. Biological Invasions, Climate Change and Genomics. Evol. Appl. 2015, 8, 23–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, C.S.; Sepulveda, A.; Ray, A.; Baumgardt, J.; Waits, L.P. Environmental DNA as a New Method for Early Detection of New Zealand Mudsnails (Potamopyrgus Antipodarum). Freshw. Sci. 2013, 32, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clusa, L.; Garcia-Vazquez, E.; Fernandez, S.; Meyer, A.; Machado-Schiaffino, G. Nuisance Species in Lake Constance Revealed through eDNA. Biol. Invasions 2021, 23, 1619–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, T.; Cattapan, F.; Falautano, M.; Julian, D.; Malinverni, R.; Poloni, E.; Sanseverino, W.; Todesco, S.; Castriota, L. eDNA Metabarcoding Analysis as Tool to Assess the Presence of Non-Indigenous Species (NIS): A Case Study in the Bilge Water. Diversity 2023, 15, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerde, C.L.; Mahon, A.R.; Chadderton, W.L.; Lodge, D.M. “Sight-Unseen” Detection of Rare Aquatic Species Using Environmental DNA. Conserv. Lett. 2011, 4, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lor, Y.; Schreier, T.M.; Waller, D.L.; Merkes, C.M. Using Environmental DNA (eDNA) to Detect the Endangered Spectaclecase Mussel (Margaritifera Monodonta). Freshw. Sci. 2020, 39, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthicke, S.; Doyle, J.R.; Cabrera, M.G.; Patel, F.; Mclatchie, M.J.; Doll, P.C.; Chandler, J.F.; Pratchett, M.S. eDNA Monitoring Detects New Outbreak Wave of Corallivorous Seastar (Acanthaster Cf. Solaris) at Lizard Island, Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 2024, 43, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chucholl, F.; Fiolka, F.; Segelbacher, G.; Epp, L.S. eDNA Detection of Native and Invasive Crayfish Species Allows for Year-Round Monitoring and Large-Scale Screening of Lotic Systems. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 639380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, Z.T.; Lim, C.S.; Tay, Y.C.; Tan, Y.; Beng, S.; Tun, K.; Teo, S.; Huang, D. Environmental DNA Detection of the Invasive Mussel Mytella Strigata as a Surveillance Tool. Manag. Biol. Invasion 2021, 12, 578–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Du, Y.; Zeng, X.; Ni, G. Development and Testing of Species-Specific Primers for Detecting the Presence of the Northern Pacific Sea Star (Asterias Amurensis) from Environmental DNA. Mar. Biotechnol. 2024, 26, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coissac, E.; Riaz, T.; Puillandre, N. Bioinformatic Challenges for DNA Metabarcoding of Plants and Animals. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1834–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jonge, D.S.W.; Merten, V.; Bayer, T.; Puebla, O.; Reusch, T.B.H.; Hoving, H.-J.T. A Novel Metabarcoding Primer Pair for Environmental DNA Analysis of Cephalopoda (Mollusca) Targeting the Nuclear 18S rRNA Region. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 8, 201388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clusa, L.; Ardura, A.; Gower, F.; Miralles, L.; Tsartsianidou, V.; Zaiko, A.; Garcia-Vazquez, E. An Easy Phylogenetically Informative Method to Trace the Globally Invasive Potamopyrgus Mud Snail from River’s eDNA. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahara, T.; Ikebuchi, T.; Doi, H.; Minamoto, T. Using Environmental DNA to Estimate the Seasonal Distribution and Habitat Preferences of a Japanese Basket Clam in Lake Shinji, Japan. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 221, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, K.M.; Stat, M.; Harvey, E.S.; Skepper, C.L.; DiBattista, J.D.; Richards, Z.T.; Travers, M.J.; Newman, S.J.; Bunce, M. eDNA Metabarcoding Survey Reveals Fine-Scale Coral Reef Community Variation across a Remote, Tropical Island Ecosystem. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 1069–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, F.M.S.; Feio, M.J.; Porto, M.; Filipe, A.F.; Bonin, A.; Serra, S.R.Q.; Alves, P.C.; Taberlet, P.; Beja, P. Assessing Changes in Stream macroinvertebrate Communities across Ecological Gradients Using Morphological versus DNA Metabarcoding Approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 149030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiner, K.; Bik, H.M.; Machler, E.; Seymour, M.; Lacoursiere-Roussel, A.; Altermatt, F.; Creer, S.; Bista, I.; Lodge, D.M.; de Vere, N.; et al. Environmental DNA Metabarcoding: Transforming How We Survey Animal and Plant Communities. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 5872–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamperti, L.; Sanchez, T.; Si Moussi, S.; Mouillot, D.; Albouy, C.; Flück, B.; Bruno, M.; Valentini, A.; Pellissier, L.; Manel, S. New Deep Learning-Based Methods for Visualizing Ecosystem Properties Using Environmental DNA Metabarcoding Data. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2023, 23, 1946–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Organism Group | Order | Family | Major Taxonomic Group | Collection Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aquatic Beetle | Actiniaria | Actiniidae, etc. | Annelida | Benthic dredge |
| Aquatic Insect | Alcyoniacea | Xeniidae, etc. | Anthozoa | benthic grab |
| Benthic | Amphipoda | Gammaridae, etc. | Asteroidea | Benthic sampler |
| Benthos | Apodida | Synaptidae, etc. | Bivalvia | Benthic sediment sampler |
| Caddisfly | Archaeogastropoda | Trochidae, etc. | Bryozoa | benthic survey |
| Clam | Arcoida | Arcidae, etc. | Calcarea | benthic trawl |
| Corals | Arhynchobdellida | Hirudinidae, etc. | Cnidaria | Benthic trawl net |
| Crabs | Basommatophora | Ancylidae, etc. | Crustacea | Box corer |
| Crustaceans | Blattaria | Blattidae, etc. | Ctenophora | D-frame net |
| Lobsters | Coleoptera | Psephenidae, etc. | Cubozoa | D-shaped net |
| Macrobenthos | Decapoda | Potamidae, etc. | Demospongiae | kicking net |
| Macroinvertebrate | Dendroceratida | Darwinellidae, etc. | Echinodermata | Multi-corer |
| Mayfly | Dendrochirotida | Phyllophoridae, etc. | Echinoidea | Sediment core |
| Mussel | Diptera | Chaoboridae, etc. | Gastropoda | |
| Mussels | Ephemeroptera | Ephemeridae, etc. | Hexactinellida | |
| Oyster | Errantia | Nereidae, etc. | Hirudinea | |
| EPT | Forcipulatida | Asteriidae, etc. | Holothuroidea | |
| Polychaete | Halichondrida | Axinellidae, etc. | Hydrozoa | |
| Sea anemones | Hemiptera | Aphelocheiridae, etc. | Insecta | |
| Sea cucumbers | Hexactinosida | Euretidae, etc. | Mollusca | |
| Sea urchins | Isopoda | Anthuridae, etc. | Nemertea | |
| Shrimps | Lepidoptera | Pyralidae, etc. | Oligochaeta | |
| Snail | Megaloptera | Corydalidae, etc. | Ophiuroidea | |
| Sponge | Mesogastropoda | Ampullariidae, etc. | Platyhelminthes | |
| Starfish | Myoida | Corbulidae, etc. | Polychaeta | |
| Stonefly | Mytiloida | Mytilidae, etc. | Polyplacophora | |
| Worm | Neogastropoda | Muricidae, etc. | Porifera | |
| Nereidida | Hesionidae, etc. | Scaphopoda | ||
| Neuroptera | Sisyridae, etc. | Scyphozoa | ||
| Odonata | Calopterygidae, etc. | Staurozoa | ||
| Ophiurida | Oreasteridae, etc. | Trematoda | ||
| Phyllodocida | Acoetidae, etc. | Turbellaria | ||
| Plecoptera | Perlidae, etc. | Urochordata | ||
| Poecilosclerida | Esperiopsidae, etc. | |||
| Pterioida | Limidae, etc. | |||
| Scleractinia | Oculinidae, etc. | |||
| Trichoptera | Rhyacophilidae, etc. | |||
| Unionoida | Unionidae, etc. | |||
| Veneroida | Sphaeriidae, etc. |
| Rank | Publication | First Address Country | First Address Participating Institutions | Citations | Publication Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Monitoring endangered freshwater biodiversity using environmental DNA | Denmark | University of Copenhagen | 783 | 2012 |
| 2 | Can DNA-Based Ecosystem Assessments Quantify Species Abundance? Testing Primer Bias and Biomass-Sequence Relationships with an Innovative Metabarcoding Protocol | Germany | Ruhr-Universität Bochum | 461 | 2015 |
| 3 | Transport Distance of Invertebrate Environmental DNA in a Natural River | Switzerland | Eawag Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology | 420 | 2014 |
| 4 | DNA barcoding and metabarcoding of standardized samples reveal patterns of marine benthic diversity | USA | Smithsonian Institution | 368 | 2015 |
| 5 | Environmental DNA as a new method for early detection of New Zealand mudsnails (Potamopyrgus antipodarum) | USA | University of Idaho | 288 | 2013 |
| 6 | Second-generation environmental sequencing unmasks marine metazoan biodiversity | Wales | Bangor University | 271 | 2010 |
| 7 | Implementation options for DNA-based identification into ecological status assessment under the European Water Framework Directive | Germany | University of Duisburg-Essen | 244 | 2018 |
| 8 | Environmental DNA surveillance for invertebrate species: advantages and technical limitations to detect invasive crayfish Procambarus clarkii in freshwater ponds | France | Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique | 202 | 2014 |
| 9 | Annual time-series analysis of aqueous eDNA reveals ecologically relevant dynamics of lake ecosystem biodiversity | Wales | Bangor University | 192 | 2017 |
| 10 | Environmental DNA reveals seasonal shifts and potential interactions in a marine community | USA | University of South Florida | 170 | 2020 |
| 11 | Assessing biodiversity of a freshwater benthic macroinvertebrate community through non-destructive environmental barcoding of DNA from preservative ethanol | Canada | University of Guelph | 148 | 2012 |
| 12 | eDNA metabarcoding survey reveals fine-scale coral reef community variation across a remote, tropical island ecosystem | Australia | Curtin University | 146 | 2020 |
| 13 | Deep-Sea, Deep-Sequencing: Metabarcoding Extracellular DNA from Sediments of Marine Canyons | Spain | Centre for Advanced Studies of Blanes—CEAB-CSIC | 143 | 2015 |
| 14 | Predicting the Ecological Quality Status of Marine Environments from eDNA Metabarcoding Data Using Supervised Machine Learning | Switzerland | University of Geneva | 134 | 2017 |
| 15 | The downside of eDNA as a survey tool in water bodies | France | Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique | 132 | 2015 |
| Rank | Kit Name | Manufacturer | Documents |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit | Qiagen | 94 |
| 2 | DNeasy PowerSoil Kit | Qiagen | 33 |
| 3 | DNeasy PowerWater Kit | Qiagen | 26 |
| 4 | DNeasy PowerMax Soil kit | Qiagen | 21 |
| 5 | FastDNA™ Spin kit for Soil | MP Biomedicals | 7 |
| 6 | DNeasy PowerWater Sterivex kit | Qiagen | 5 |
| 7 | NucleoSpin Soil, Mini kit for DNA from soil | Macherey-Nagel | 5 |
| 8 | NucleoSpin Tissue, Mini kit for DNA from cells and tissue | Macherey-Nagel | 5 |
| 9 | QIAamp® DNA Mini Kit | Qiagen | 4 |
| 10 | E.Z.N.A.® Mollusc DNA Kit | Omega Bio-tek | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, X.; Zhang, J.; Shao, Z.; Chai, L.; Nie, J.; Yin, D.; Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Yan, C. Research Trends and Hotspots in eDNA-Based Surveys of Macroinvertebrates: A Bibliometric Analysis. Diversity 2025, 17, 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17060402
Ge X, Zhang J, Shao Z, Chai L, Nie J, Yin D, Zhang H, Liu W, Yan C. Research Trends and Hotspots in eDNA-Based Surveys of Macroinvertebrates: A Bibliometric Analysis. Diversity. 2025; 17(6):402. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17060402
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Xinyu, Junyu Zhang, Ziming Shao, Lu Chai, Jiaxin Nie, Dan Yin, Haoran Zhang, Wenbin Liu, and Chuncai Yan. 2025. "Research Trends and Hotspots in eDNA-Based Surveys of Macroinvertebrates: A Bibliometric Analysis" Diversity 17, no. 6: 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17060402
APA StyleGe, X., Zhang, J., Shao, Z., Chai, L., Nie, J., Yin, D., Zhang, H., Liu, W., & Yan, C. (2025). Research Trends and Hotspots in eDNA-Based Surveys of Macroinvertebrates: A Bibliometric Analysis. Diversity, 17(6), 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17060402







