Returners and New Arrivals After the Crash: Intermediate Hosts and Global Invaders Dominate Gastropod Fauna of Lake Naivasha, Kenya
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material & Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Field Sampling
2.3. DNA-Barcoding
3. Results
3.1. Species Diversity and Distribution

| Family | Species | Specimen Image | Voucher No. | Location | BLAST Results 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ampullariidae | Pomacea canaliculata (Lamarck, 1822) |  | UGSB 31089 * | LN02 | Pomacea canaliculata (MYS) MG230745 [100%] Pomacea canaliculata (MYS) MG230743 [100%] |
| UGSB 31090 | LN02 | Pomacea canaliculata (MYS) MG230745 [100%] Pomacea canaliculata (MYS) MG230743 [100%] | |||
| Bulinidae | Bulinus forskalii (Ehrenberg, 1831) |  | UGSB 31085 | LN01 | Bulinus forskalii (ZWE) PP468526 [99.8%] Bulinus forskalii (KEN) OP233129 [99.7%] |
| UGSB 31086 * | LN01 | Bulinus forskalii (ZWE) PP468526 [99.8%] Bulinus forskalii (KEN) OP233129 [99.7%] | |||
| Bulinus cf. tropicus |  | UGSB 31093 * | LN03 | Bulinus tropicus (KEN) ON112314 [100%] Bulinus tropicus (KEN) OP233128 [99.7%] | |
| UGSB 31094 | LN03 | Bulinus tropicus (KEN) ON112314 [100%] Bulinus tropicus (KEN) OP233128 [99.7%] | |||
| Lymnaeidae | Pseudosuccinea columella (Say, 1817) |  | UGSB 31083 * | LN01 | Pseudosuccinea columella (AUS) MG976151 [100%] Pseudosuccinea columella (ARG) MW830999 [100%] |
| UGSB 31084 | LN01 | Pseudosuccinea columella (AUS) MG976151 [100%] Pseudosuccinea columella (ARG) MW830999 [100%] | |||
| Physidae | Physella acuta (Draparnaud, 1805) |  | UGSB 31091 * | LN02 | Physella aff. acuta (AUS) MG976187 [100%] Physella acuta (GRC) KF737936 [100%] |
| Planorbidae | Biomphalaria cf. sudanica |  | USGB 31087 * | LN01 | Biomphalaria sp. (TZA) KY745885 [99.7%] Biomphalaria cf. sudanica (UGA) HM768904 [99.7%] |
| UGSB 31088 | LN01 | Biomphalaria sp. (?) HM769143 [99.8%] Biomphalaria sp. (TZA) KY745885 [99.7%] |
3.2. Mollusk Faunal Change
| Publication | Time of Collection | Species Found * |
|---|---|---|
| [19] | 1929 | Radix natalensis, Bulinus tropicus, Afrogyrorbis natalensis |
| [30] | 1971–1973 | Sphaeriidae |
| [20] | 1982 | Bulinus tropicus, Radix natalensis, Biomphalaria sp. |
| [31] | 1987/88 | Bulinus truncatus |
| [21] | 1982/1983 1984 | Radix natalensis, Afrogyrorbis natalensis, Physella acuta, Ferrissia sp. Physella acuta, Ferrissia sp. |
| [32] | N/A | Bulinus tropicus |
| [13] | 1970s 1984/85 | Physella acuta, Bulinus tropicus, Radix natalensis, Biomphalaria sudanica, Afrogyrorbis natalensis Physella acuta |
| [22] | 2010 | Physella acuta |
4. Discussion
4.1. Drivers of Decline
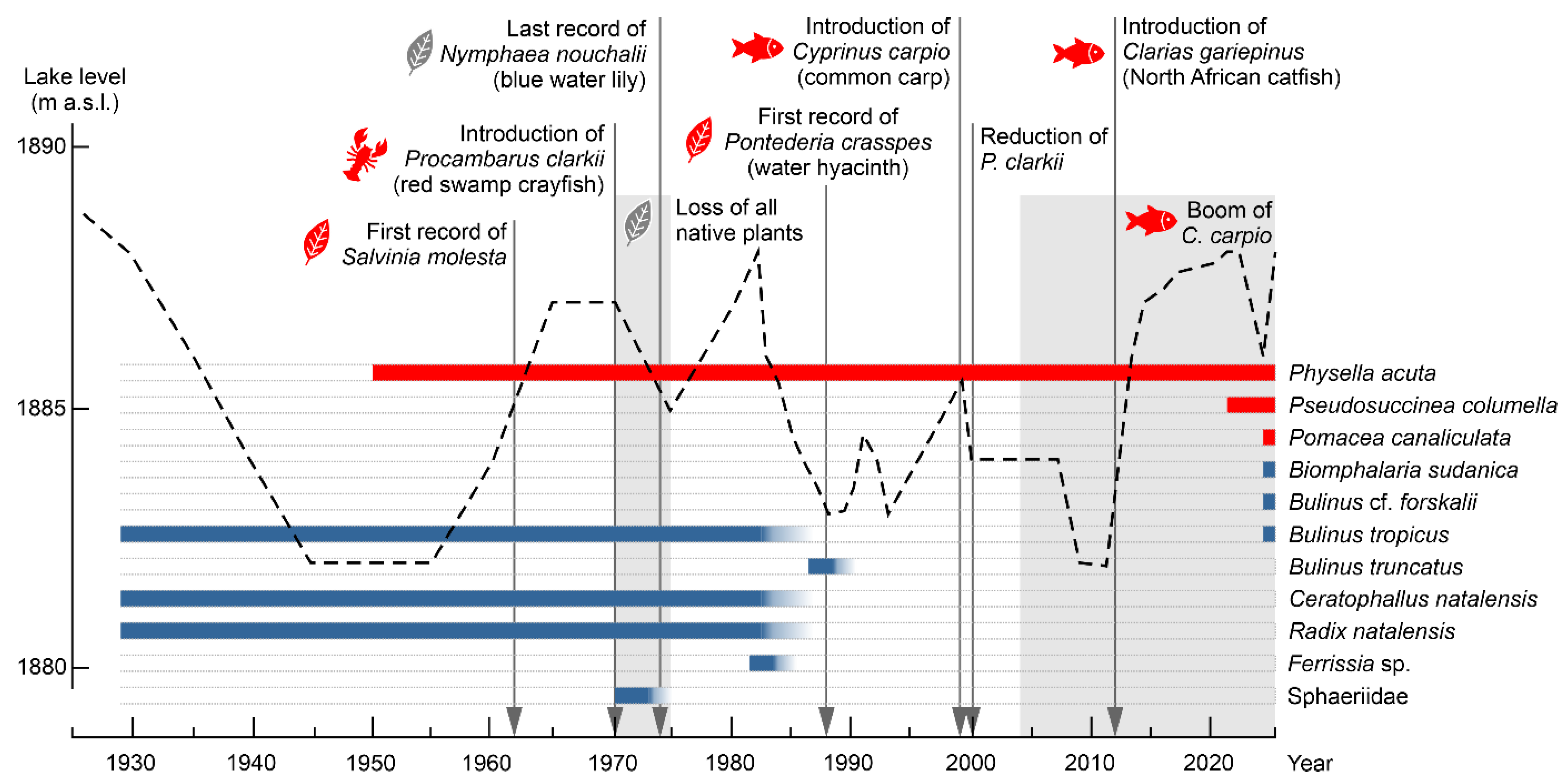
4.2. Drivers of Revival of Mollusc Fauna
4.3. Implications for and Lessons Learnt from Mollusks
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Havel, J.E.; Kovalenko, K.E.; Thomaz, S.M.; Amalfitano, S.; Kats, L.B. Aquatic invasive species: Challenges for the future. Hydrobiologia 2015, 750, 147–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, D.M.; Morrison, E.H.J.; Macharia, M.M.; Mavuti, K.M.; Upton, C. Lake Naivasha, Kenya: Ecology, society and future. Freshw. Rev. 2011, 4, 89–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, D.; Pacini, N.; Morrison, E.; Kimani, D.; Mwinami, T.; Upton, C. The unique natural resources of Lake Naivasha; Can they survive? In Agricultural Intensification, Environmental Conservation, Conflict and Co-Existence at Lake Naivasha, Kenya; Kuiper, G., Kioko, E.M., Bollig, M., Eds.; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 93–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherardi, F.; Robert Britton, J.; Mavuti, K.M.; Pacini, N.; Grey, J.; Tricarico, E.; Harper, D.M. A review of allodiversity in Lake Naivasha, Kenya: Developing conservation actions to protect East African lakes from the negative impacts of alien species. Biol. Conserv. 2011, 144, 2585–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, C.S.; Boar, R.R.; Hubble, D.S.; Gikungu, M.; Harper, D.M.; Hickley, P.; Tarras-Wahlberg, N. The dynamics and ecology of exotic tropical species in floating plant mats: Lake Naivasha, Kenya. Hydrobiologia 2002, 488, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschuren, D. Reconstructing fluctuations of a shallow East African lake during the past 1800 yrs from sediment stratigraphy in a submerged crater basin. J. Paleolimnol. 2001, 25, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoof-Leichsenring, K.R.; Junginger, A.; Olaka, L.A.; Tiedemann, R.; Trauth, M.H. Environmental variability in Lake Naivasha, Kenya, over the last two centuries. J. Paleolimnol. 2011, 45, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meeren, T.; Verschuren, D. Zoobenthos community turnover in a 1650-yr lake-sediment record of climate-driven hydrological change. Ecosphere 2021, 12, e03333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongo, E.; Agembe, S.W.; Manyala, J.O.; Mutethya, E. Assessment of the current trophic state and water quality of Lake Naivasha, Kenya using multivariate techniques. Lakes Reserv. 2023, 28, e12422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosca, C.; Junginger, A.; Kübler, S.; Babechuk, M.G.; Olaka, L.A.; Schoenberg, R. Isotopic and trace element record of changing metal source contributions to tropical freshwater Lake Naivasha (Kenya). Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oel, P.R.; Mulatu, D.W.; Odongo, V.O.; Meins, F.M.; Hogeboom, R.J.; Becht, R.; Stein, A.; Onyando, J.O.; Van Der Veen, A. The effects of groundwater and surface water use on total water availability and implications for water management: The case of Lake Naivasha, Kenya. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 3477–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otiang’a-Owiti, G.E.; Oswe, I.A. Human impact on lake ecosystems: The case of Lake Naivasha, Kenya. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2007, 32, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D. Freshwater Snails of Africa and Their Medical Importance; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- West, K.; Michel, E. The dynamics of endemic diversification: Molecular phylogeny suggests an explosive origin of the thiarid gastropods of Lake Tanganyika. Adv. Ecol. Res. 2000, 31, 331–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaubrecht, M. Adaptive radiation of thalassoid gastropods in Lake Tanganyika, East Africa: Morphology and systematization of a paludomid species flock in an ancient lake. Zoosyst. Evol. 2008, 84, 71–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultheiß, R.; Van Bocxlaer, B.; Wilke, T.; Albrecht, C. Old fossils–young species: Evolutionary history of an endemic gastropod assemblage in Lake Malawi. Proc. R. Soc. B. 2009, 276, 2837–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahulu, A.; Stelbrink, B.; Van Bocxlaer, B.; Riedel, F.; Albrecht, C. Going with the flow? Diversification of gastropods reflects drainage evolution in Africa. J. Biogeogr. 2021, 48, 1579–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzburger, W.; Van Bocxlaer, B.; Cohen, A.S. Ecology and evolution of the African Great Lakes and their faunas. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2014, 45, 519–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkin, P.M. Reports on the Percy Sladen expedition to some rift valley Lakes in Kenya in 1929. VII. Summary of the ecological results, with special reference to the alkaline lakes. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 1936, 18, 161–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouma, J.H.; Waithaka, F.T. Bulinus tropicus (Krauss, 1848) from Kenya found naturally infected with Schistosoma bovis. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1984, 78, 341–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, F.; Beeby, A.; Kirby, P. A study of the macro-invertebrates of Lake Naivasha, Oloidien and Sonachi, Kenya. Rev. Hydrobiol. Trop. 1989, 22, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht, C.; Clewing, C.; Seebens, H.; Chibwana, F.D.; Da Silva, E.L.; Leal, M.F.; Lingofo Bolaya, R.; Marwoto, R.M.; Odaibo, A.; Pinheiro, T.G.; et al. When one global invasion hides another—Cryptic interspecific invasion in freshwater gastropods. Divers. Distrib. 2025, 31, e13958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, A.; Norris, K.; Chadwick, M.A.; Avery, S.; Olaka, L.; Tebbs, E.J. Rising lake levels in central East Africa are driven by increasing rainfall and land-use intensification. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 56, 101999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrnegger, M.; Kray, P.; Stecher, G.; Cherono Kiplangat, N.; Otieno, D.; Olang, L.; Nicholson, S.E. Paleohydrology repeating? Regional hydrological change may lead to an overflow and cross-mixing of an alkaline and a freshwater lake in East Africa. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 55, 101951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes-Lima, M.; Lopes-Lima, A.; Burlakova, L.; Douda, K.; Alonso, Á.; Karatayev, A.; Ng, T.H.; Vinarski, M.; Zieritz, A.; Sousa, R. Non-native freshwater molluscs: A brief global review of species, pathways, impacts and management strategies. Hydrobiologia 2025, 852, 1005–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaut, R.W.; Owen, R.B. Lake Naivasha. In The Kenya Rift Lakes: Modern and Aancient; Renaut, R.W., Owen, R.B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 417–461. [Google Scholar]
- Wilke, T.; Davis, G.M.; Qiu, D.; Spear, R.C. Extreme mitochondrial sequence diversity in the intermediate schistosomiasis host Oncomelania hupensis robertsoni: Another case of ancestral polymorphism? Malacologia 2006, 48, 143–157. [Google Scholar]
- Dusabe, M.C.; Kalinda, C.; Clewing, C.; Hyangya, B.L.; Van Bocxlaer, B.; Albrecht, C. Environmental perturbations and anthropogenic disturbances determine mollusc biodiversity of Africa’s explosive Lake Kivu. J. Great Lakes Res. 2024, 50, 102339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Schwartz, S.; Wagner, L.; Miller, W. A greedy algorithm for aligning DNA sequences. J. Comput. Biol. 2000, 7, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milbrink, G. On the limnology of two alkaline lakes (Nakuru and Naivasha) in the East Rift Valley System in Kenya. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 1977, 62, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.S.; Shaw, K.M. Freshwater snails of the Bulinus truncatus/tropicus complex in Kenya: Tetraploid species. J. Molluscan Stud. 1989, 55, 509–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.S.; Shaw, K.M.; Rollinson, D. Freshwater snails of the Bulinus truncatus/tropicus complex (Basommatophora: Planorbidae) in Kenya: Diploid populations. J. Molluscan Stud. 1991, 57, 143–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.; Harper, D. The alien Louisianan red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii Girard in Lake Naivasha, Kenya 1999–2003. Freshw. Crayfish 2006, 15, 195–202. [Google Scholar]
- Triest, L.; Sierens, T.; Njambuya, J.; Terer, T.; Stiers, I. Within-lake isolation and reproductive strategy of Stuckenia pectinata (L.) Börner at Lake Naivasha (Kenya): About water level fluctuations and alien species. Aquat. Bot. 2025, 197, 103840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, K.A.; Cowie, R.H.; Thiengo, S.C.; Strong, E.E. Comparing apples with apples: Clarifying the identities of two highly invasive Neotropical Ampullariidae (Caenogastropoda). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2012, 166, 723–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lounnas, M.; Correa, A.C.; Vázquez, A.A.; Dia, A.; Escobar, J.S.; Nicot, A.; Arenas, J.; Ayaqui, R.; Dubois, M.P.; Gimenez, T.; et al. Self-fertilization, long-distance flash invasion and biogeography shape the population structure of Pseudosuccinea columella at the worldwide scale. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 887–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngcamphalala, P.I.; Malatji, M.P.; Mukaratirwa, S. Geography and ecology of invasive Pseudosuccinea columella (Gastropoda: Lymnaeidae) and implications in the transmission of Fasciola species (Digenea: Fasciolidae)—A review. J. Helminthol. 2022, 96, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alba, A.; Vázquez, A.A.; Sánchez, J.; Gourbal, B. Immunological resistance of Pseudosuccinea columella snails from Cuba to Fasciola hepatica (Trematoda) infection: What we know and where we go on comparative molecular and mechanistic immunobiology, ecology and evolution. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 794186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrus, P.S.; Stothard, J.R.; Wade, C.M. Seasonal patterns of Schistosoma mansoni infection within Biomphalaria snails at the Ugandan shorelines of Lake Albert and Lake Victoria. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamba, H.O.; Roberts, J.M.D. Schistosomiasis in and around Lake Naivasha, Kenya: Seven years surveillance. East Afr. Med. J. 1979, 56, 255–262. [Google Scholar]
- Tabo, Z.; Breuer, L.; Fabia, C.; Samuel, G.; Albrecht, C. A machine learning approach for modeling the occurrence of the major intermediate hosts for Schistosomiasis in East Africa. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumwebaze, I.; Clewing, C.; Dusabe, M.C.; Tumusiime, J.; Kagoro-Rugunda, G.; Hammoud, C.; Albrecht, C. Molecular identification of Bulinus spp. intermediate host snails of Schistosoma spp. in crater lakes of Western Uganda with implications for the transmission of the Schistosoma haematobium group parasites. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumwebaze, I.; Clewing, C.; Chibwana, F.D.; Kipyegon, J.K.; Albrecht, C. Evolution and biogeography of freshwater snails of the genus Bulinus (Gastropoda) in afromontane extreme environments. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 902900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowie, R.H. Apple snails (Ampullariidae) as agricultural pests: Their biology, impacts and management. In Molluscs as Crop Pests; Barker, G.M., Ed.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2002; pp. 145–192. [Google Scholar]
- Cowie, R.H.; Hayes, K.A. Apple snails. In A Handbook of Global Freshwater Invasive Species; Francis, R.G., Ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2012; pp. 207–221. [Google Scholar]
- Buddie, A.G.; Rwomushana, I.; Offord, L.C.; Kibet, S.; Makale, F.; Djeddour, D.; Cafa, G.; Vincent, K.K.; Muvea, A.M.; Chacha, D.; et al. First report of the invasive snail Pomacea canaliculata in Kenya. CABI Agric. Biosci. 2021, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantine, K.L.; Makale, F.; Mugambi, I.; Chacha, D.; Rware, H.; Muvea, A.; Kipngetich, V.K.; Tambo, J.; Ogunmodede, A.; Djeddour, D.; et al. Assessment of the socio-economic impacts associated with the arrival of apple snail (Pomacea canaliculata) in Mwea irrigation scheme, Kenya. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 4343–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makale, F.; Muvea, A.M.; Mugambi, I.; Chacha, D.; Finch, E.A.; Rwomushana, I. Current and potential distribution of the invasive apple snail, Pomacea canaliculata in Eastern Africa: Evidence from delimiting surveys and modelling studies. CABI Agric. Biosci. 2024, 5, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, M.A.; Martín, P.R. Dealing with a hyper-successful neighbor: Effects of the invasive apple snail Pomacea canaliculata on exotic and native snails in South America. Curr. Zool. 2019, 65, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bocxlaer, B.; Albrecht, C. Ecosystem change and establishment of an invasive snail alter gastropod communities in long-lived Lake Malawi. Hydrobiologia 2015, 744, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
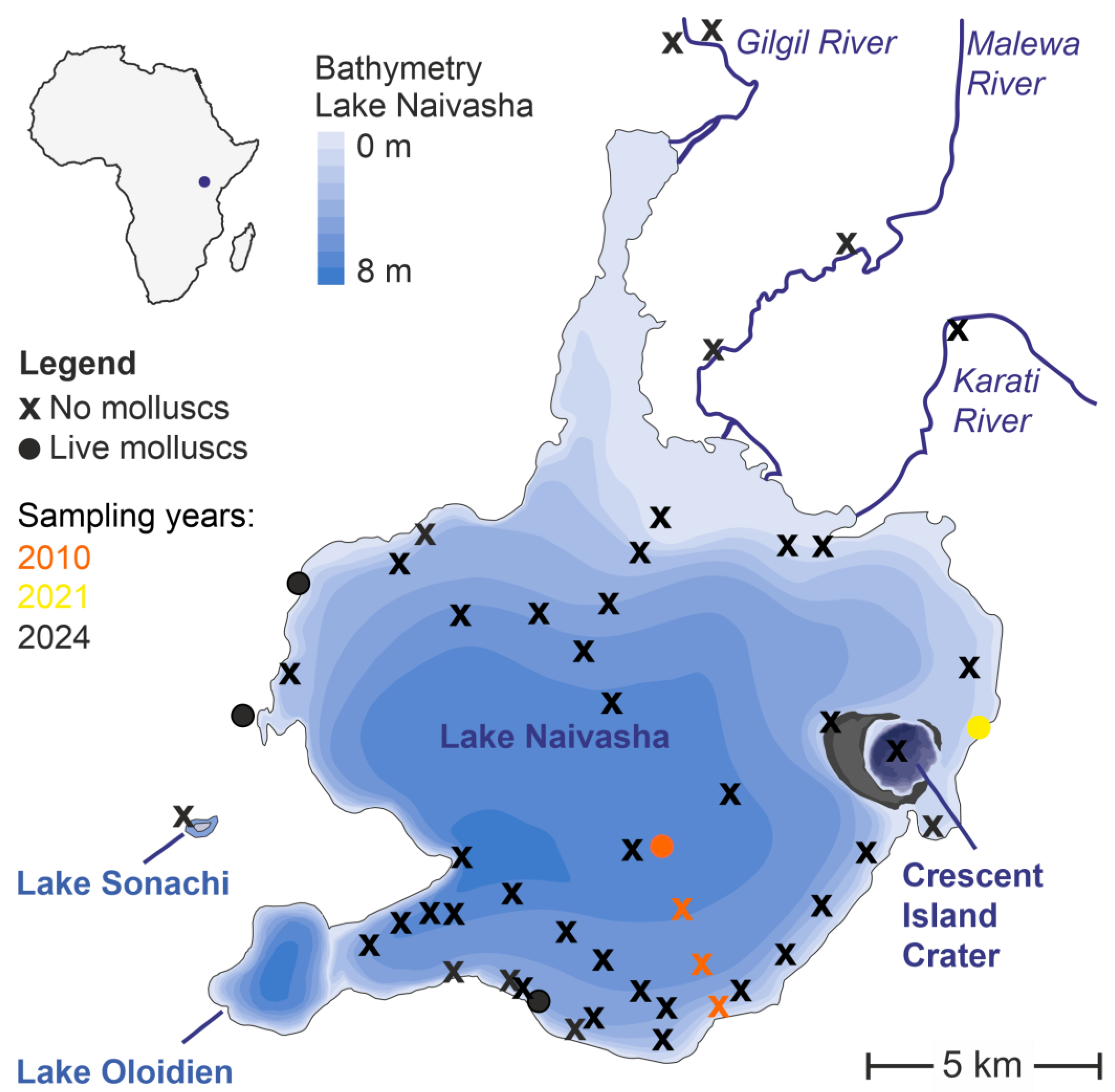
| Locality | Loc. Code | Coordinates | Ecological Conditions | Species Found |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lake Naivasha, Olsurwa water pump | LN01 | −0.73191° N/36.283763° E | Shoreline with spring inflow, macrophytes and muddy substrates; water parameters: pH 7.34, conductivity 534 yS/cm, TDS 267, PSU 0.26, oxygen 86.5%, temp. 20.6 °C | Pseudosuccinea columella Bulinus forskalii Biomphalaria cf. sudanica |
| Lake Naivasha, Kwamoya beach | LN02 | −0.82738° N/36.34021° E | Shoreline, macrophytes, muddy substrate, water parameters: pH 7.45, conductivity 426 yS/cm, TDS 213, PSU 0.20, oxygen 87.8%, temp. 24.4 °C | Physella acuta Pomacea canaliculata |
| Huruma stream, Lake Naivasha tributary, western shore near Hurumua | LN03 | −0.74626° N/36.27507° E | Fast flowing stream with few macrophytes, very turbid, water level high, water parameters: pH 7.74, conductivity 753 yS/cm, TDS 377, PSU 0.37, oxygen 76.3%, temp. 20.75 | Bulinus tropicus |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albrecht, C.; Kipyegon, J.K.; Junginger, A.; Clewing, C. Returners and New Arrivals After the Crash: Intermediate Hosts and Global Invaders Dominate Gastropod Fauna of Lake Naivasha, Kenya. Diversity 2025, 17, 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17040265
Albrecht C, Kipyegon JK, Junginger A, Clewing C. Returners and New Arrivals After the Crash: Intermediate Hosts and Global Invaders Dominate Gastropod Fauna of Lake Naivasha, Kenya. Diversity. 2025; 17(4):265. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17040265
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbrecht, Christian, John Kochey Kipyegon, Annett Junginger, and Catharina Clewing. 2025. "Returners and New Arrivals After the Crash: Intermediate Hosts and Global Invaders Dominate Gastropod Fauna of Lake Naivasha, Kenya" Diversity 17, no. 4: 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17040265
APA StyleAlbrecht, C., Kipyegon, J. K., Junginger, A., & Clewing, C. (2025). Returners and New Arrivals After the Crash: Intermediate Hosts and Global Invaders Dominate Gastropod Fauna of Lake Naivasha, Kenya. Diversity, 17(4), 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17040265








