Changes and Influencing Factors of Carbon Content in Surface Sediments of Different Sedimentary Environments Along the Jiangsu Coast, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Laboratory Analyses
2.4. Research Methods and Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Change Characteristics of Physicochemical Properties of Surface Sediments
3.2. Variation Characteristics of OC and IC Content in Surface Sediments
3.3. Identification of the Importance of Factors Affecting IC and OC
4. Discussion
4.1. Discussion on the Reasons for the Changes in Various Indicators
4.2. Response Mechanism of Organic/Inorganic Carbon Burial in the Vegetation Area to Important Impact Factors
4.3. Response Mechanism of Organic/Inorganic Carbon Burial in the Transition Area to Important Impact Factors
4.4. Response Mechanism of Organic/Inorganic Carbon Burial to Important Impact Factors in the Bare Flat Area
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bai, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, J.; Cui, B.; Liu, X. Depth-distribution patterns and control of soil organic carbon in coastal salt marshes with different plant covers. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Middelburg, J.; Caraco, N. Major role of marine vegetation on the oceanic carbon cycle. Biogeosciences 2005, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernetta, J.C.; Milliman, J.D. Land-Ocean Interactions in the Coastal Zone—Implementation Plan; IGBP Global Change Report No. 33. 215; International Geosphere-Biosphere Programme: Stockholm, Sweden, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, M. Review of “Sustainable development in east china sea evolution of resources and environment in coastal zone and bay area”. Geogr. Res. 2020, 39, 2427–2428. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, H.; Zhu, J. The land and ocean interactions in the coastal zone of china. Mar. Sci. Bull. 1999, 18, 11–17, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Shu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, Z.; Yang, P.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, M. Multi-proxy reconstruction of the Holocene transition from a transgressive to regressive coastal evolution in the northern Jiangsu Plain, East China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2021, 572, 110405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dussaillant, A.; Galdames, P.; Sun, C.L. Water level fluctuations in a coastal lagoon: El Yali Ramsar wetland, Chile. Desalination 2009, 246, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, I.; Spencer, T.; French, J.R.; Leggett, J.; Dixon, M. Wave Transformation Over Salt Marshes: A Field and Numerical Modelling Study from North Norfolk, England. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1999, 49, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouma, T.J.; Vries, M.B.D.; Low, E.; Kusters, L.; Herman, P.M.J.; Tánczos, I.C.; Temmerman, S.; Hesselink, A.; Meire, P.; Regenmortel, S.V. Flow hydrodynamics on a mudflat and in salt marsh vegetation: Identifying general relationships for habitat characterisations. Hydrobiologia 2005, 540, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoutens, K.; Heuner, M.; Minden, V.; Ostermann, T.S.; Silinski, A.; Belliard, J.P.; Temmerman, S. How effective are tidal marshes as nature-based shoreline protection throughout seasons? Limnol. Oceanogr. 2019, 64, 1750–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumeier, U. Velocity and turbulence variations at the edge of saltmarshes. Cont. Shelf Res. 2007, 27, 1046–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carling, P.A. Temporal and spatial variation in intertidal sedimentation rates. Sedimentology 1982, 29, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, J.R.; Spencer, T.; Murray, A.L.; Arnold, N.S. Geostatistical analysis of sediment deposition in two small tidal wetlands, Norfolk, UK. J. Coast. Res. 1995, 11, 308–321. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, D.J.; Spencer, T.; Murray, A.L.; French, J.R.; Leonard, L. Marsh surface sediment deposition and the role of tidal creeks: Implications for created and managed coastal marshes. J. Coast. Conserv. 1999, 5, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.R.L.; Duffy, M.J. Medium-term sedimentation on high intertidal mudflats and salt marshes in the Severn Estuary, SW Britain: The role of wind and tide. Mar. Geol. 1998, 150, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, K.S.; Paterson, D.M.; Cramp, A. Sedimentary Processes in the Intertidal Zone; Geological Society Special Publication; Geological Society: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Yang, S. A review of influences of saltmarsh vegetation on physical processes in intertidal wetlands. Adv. Earth Sci. 2007, 6, 583–592, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Bai, F.; Yang, G.; Ou, W. Distribution characteristics of organic carbon, nitrogen, and phosphor in sediments from different ecologic zones of tidal flats in north Jiangsu province. Quat. Sci. 2007, 27, 756–765, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Yin, A.; Yang, X.; Wu, P.; Fan, M.; Wu, J.; Zhang, M.; Gao, C. Changes in surface soil organic/inorganic carbon concentrations and their driving forces in reclaimed coastal tidal flats. Geoderma 2019, 352, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Shu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Ma, Y. Distribution and factors influencing organic and inorganic carbon in surface sediments of tidal flats in northern Jiangsu, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 126, 107633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Ma, Q.; Lin, J.; Chen, Y.; Shu, Q. Distribution and Sources of Organic Carbon in Surface Intertidal Sediments of the Rudong Coast, Jiangsu Province, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Deng, D.; Zou, C.; Han, R.; Xin, Y.; Shu, Z.; Zhang, L. Spartina alterniflora saltmarsh soil organic carbon properties and sources in coastal wetlands. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 3342–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, G.; Wang, S.; Mao, C.; Tang, Z.; Rao, W. The isotopic composition of organic carbon, nitrogen and provenance of organic matter in surface sediment from the Jiangsu tidal flat, southwestern Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 182, 114010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.; Wen, T.; Jin, C.; Zhao, K.; Su, M. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of soil organic carbon in tidal flat wetland of central Jiangsu, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 34, 2978–2984, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Bai, J.; Zhao, Q.; Jia, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, X. Soil carbon storage and carbon sources under different Spartina alterniflora invasion periods in a salt marsh ecosystem. Catena 2021, 196, 104831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, M.; Wu, H.; Jiang, M. Impacts of Spartina alterniflora invasion on soil carbon contents and stability in the Yellow River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145188. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Wei, S.; Chen, H.; Li, B.; Nie, M. Effects of Spartina invasion on the soil organic carbon content in salt marsh and mangrove ecosystems in China. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 59, 1937–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Luan, Z.; Yan, D.; Li, J.; Xie, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, M.; Wu, C. Effects of Spartina alterniflora Invasion on Soil Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Yancheng Coastal Wetlands. Land 2022, 11, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Wang, W.; Wen, J.; Feng, T.; Peñuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Liang, C. Spartina alterniflora invasion differentially alters microbial residues and their contribution to soil organic C in coastal marsh and mangrove wetlands. Catena 2023, 230, 107246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, H. Soft modelling, the basic design and some extensions. In Systems Under Indirect Observation: Causality-StructurePrediction; Wold, H., Jöreskog, K.G., Eds.; North-Holland Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1982; Part II; pp. 1–54. [Google Scholar]
- Wold, S.; Sjöström, M.; Eriksson, L. PLS-regression: A basic tool of chemometrics. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2001, 58, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, N.; Shi, Z.; Chen, F.; Wang, Y. Partial Least Squares Regression for Determining the Control Factors for Runoff and Suspended Sediment Yield during Rainfall Events. Water 2015, 7, 3925–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Fang, N.; Xiao, H.; Shi, Z. Sediment deposition changes the relationship between soil organic and inorganic carbon: Evidence from the Chinese Loess Plateau. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 302, 107076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Ai, L.; Li, X.; Huang, X.; Wu, G.; Liao, W. Partial least-squares regression for linking land-cover patterns to soil erosion and sediment yield in watersheds. J. Hydrol. 2013, 98, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onderka, M.; Wrede, S.; Rodný, M.; Pfister, L.; Hoffmann, L.; Krein, A. Hydrogeologic and landscape controls of dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) and dissolved silica (DSi) fluxes in heterogeneous catchments. J. Hydrol. 2012, 450–451, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Zhu, K.; Cui, Y.; Du, H.; Chen, J. Spatial distribution of soil carbon and nitrogen in Jiaozhou Bay estuarine wetlands. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2014, 23, 50–60, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Miao, P.; Xie, W.; Yu, D.; Chen, J.; Gong, J. Vertical distribution and seasonal variation of nitrogen, phosphorus elements in Spartina alterniflora wetland of Jiaozhou bay, Shangdong, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 28, 1533–1540, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Pan, S.; Zhang, R.; Li, J.; Bai, F. Spatial distributions of organic carbon and nitrogen and their isotopic compositions in sediments of the Changjiang Estuary and its adjacent sea area. J. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wu, Y.; Kang, Q.; Zhang, J. Spatial variations of carbon, nitrogen, phosphorous and sulfur in the salt marsh sediments of the Yangtze Estuary in China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 71, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xie, W.; Wang, Z.; Yan, Q. Effects of Spartina alterniflora invasion on sulfur content temporal and spatial variation in tidal flat wetland of Jiaozhou Bay. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2019, 39, 870–879, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; An, S.; Deng, Z.; Yin, D.; Zhi, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, L.; Fang, C.; Qian, C. Sulfur storage changed by exotic Spartina alterniflora in coastal saltmarshes of China. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zheng, Z.; Chang, Z.; Luo, Y. Characteristics of anaerobic digestion and physicochemical properties of Spartina alterniflora at different growth stages. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2011, 27, 260–265, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Yan, J.; He, D.; Cai, J.; Wang, R.; You, W.; Xiao, S.; Hou, D.; Li, W. Effects of Spartina alterniflora invasion in eastern Fujian coastal wetland on the physicochemical properties and enzyme activities of mangrove soil. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2017, 39, 70–77, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, Q.; Zhao, L.; Ge, S.; Chen, D.; Dong, Q.; Zhao, X. Land-use effects on organic and inorganic carbon patterns in the topsoil around Qinghai Lake basin, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Catena 2016, 147, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, F.J. Organic form of soil nitrogen. In Nitrogen in Agricultural Soils; Stevenson, F.J., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Xiao, C.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Fu, X.; Le, Y.; Wang, L. Spatial variability of organic carbon in the soil of wetlands in Chongming Dongtan and its influential factors. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2009, 28, 1522–1528, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Mao, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Miao, Z.; Ma, W.; Song, C.; Ren, C.; Jia, M. Soil organic carbon in the Sanjiang Plain of China: Storage, distribution and controlling factors. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 1635–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ying, R.; Shi, J.; Long, T.; Lin, Y. Advancement in study on adsorption of organic matter on soil minerals and its mechanism. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2017, 54, 805–818, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Bughio, M.A.; Wang, P.; Meng, F.; Qing, C.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Wang, X.; Junejo, S.A. Neoformation of pedogenic carbonates by irrigation and fertilization and their contribution to carbon sequestration in soil. Geoderma 2016, 262, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.; Miao, N.; Wang, P.; Ju, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, J.; Kuzyakov, Y. Dramatic loss of inorganic carbon by nitrogen-induced soil acidification in Chinese croplands. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 3738–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


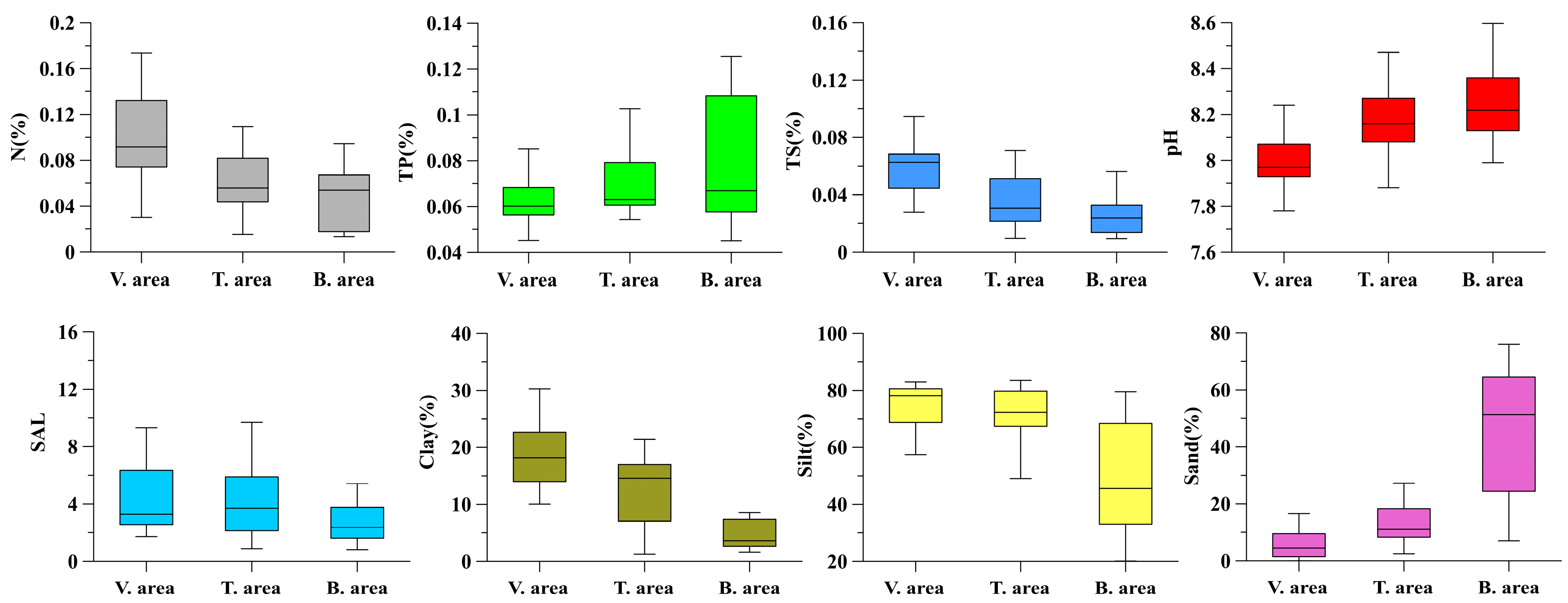
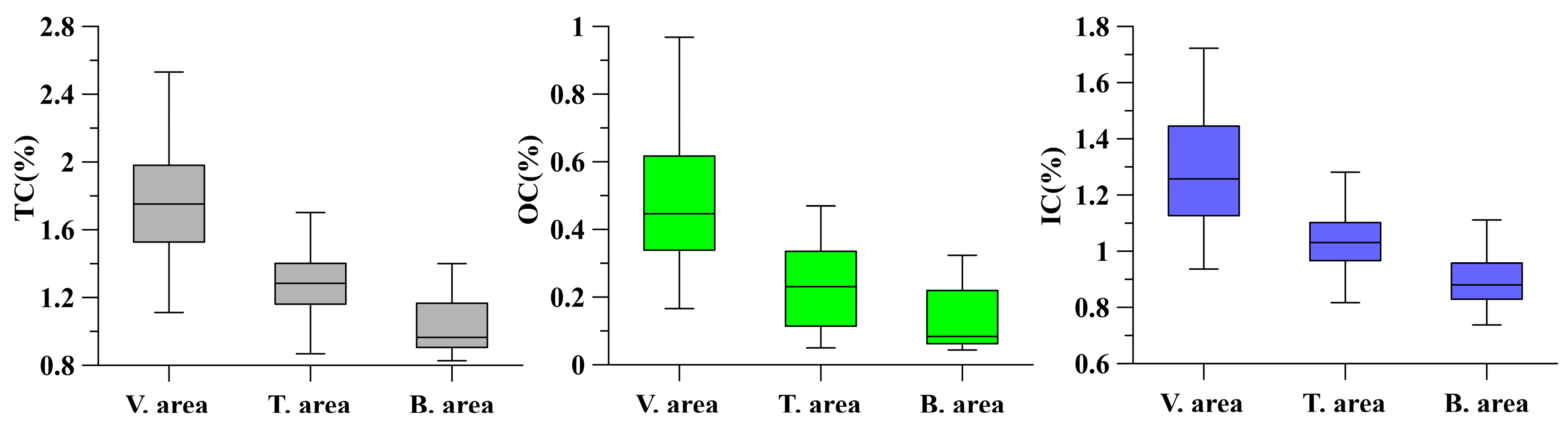

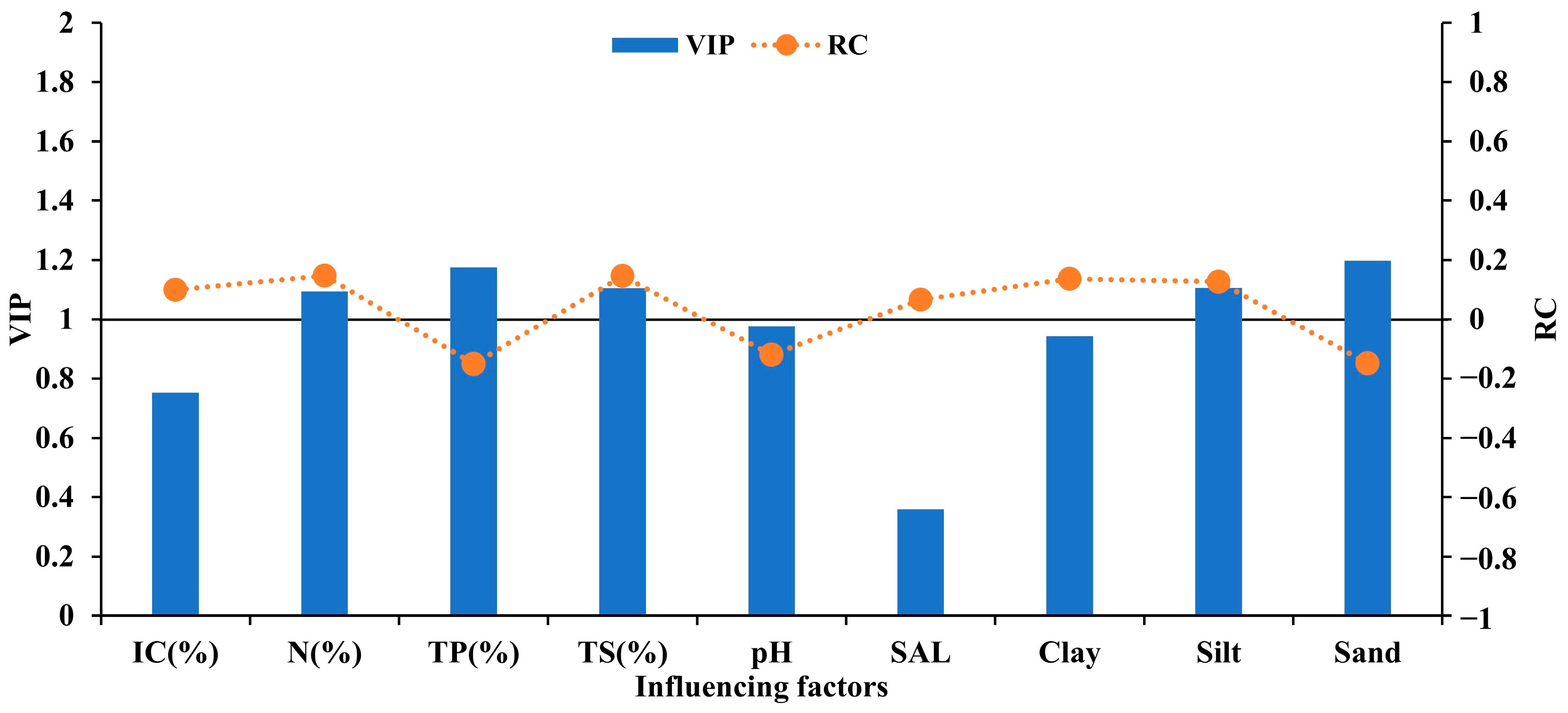

| TC (%) | OC (%) | IC (%) | N (%) | TP (%) | TS (%) | pH | SAL | Clay (%) | Silt (%) | Sand (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetation area | Mean | 1.77 | 0.47 | 1.29 | 0.11 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 7.99 | 4.52 | 18.95 | 74.87 | 6.23 |
| Min. | 1.11 | 0.17 | 0.94 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 7.70 | 1.71 | 10.05 | 57.40 | 0.02 | |
| Max. | 2.53 | 0.97 | 1.72 | 0.44 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 8.24 | 14.40 | 37.91 | 83.02 | 24.73 | |
| CV | 21.14 | 39.72 | 16.73 | 65.29 | 14.47 | 38.02 | 1.41 | 63.40 | 35.37 | 9.37 | 96.62 | |
| Transition area | Mean | 1.29 | 0.24 | 1.06 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 8.18 | 4.74 | 12.53 | 69.97 | 17.50 |
| Min. | 0.87 | 0.05 | 0.82 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 7.88 | 0.88 | 1.25 | 36.94 | 2.47 | |
| Max. | 1.86 | 0.47 | 1.64 | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 8.59 | 21.00 | 21.44 | 83.58 | 60.25 | |
| CV | 18.98 | 51.21 | 15.15 | 47.54 | 28.66 | 49.02 | 1.81 | 87.77 | 50.17 | 17.40 | 92.52 | |
| Bare flat area | Mean | 1.02 | 0.12 | 0.90 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.03 | 8.24 | 2.97 | 5.73 | 49.07 | 45.17 |
| Min. | 0.83 | 0.04 | 0.74 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 7.99 | 0.81 | 1.60 | 20.09 | 6.95 | |
| Max. | 1.40 | 0.32 | 1.11 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.06 | 8.60 | 8.82 | 19.33 | 79.58 | 76.06 | |
| CV | 15.76 | 71.19 | 9.64 | 59.73 | 34.12 | 54.93 | 1.78 | 69.21 | 88.92 | 37.09 | 48.88 |
| Variable | R2 | Q2 | Components | Explained Variation in Y (%) | Cumulative Explained Variation in Y (%) | Q2cum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OC | 0.6421 | 0.5797 | 1 | 64.21 | 64.21 | 0.5797 |
| IC | 0.8037 | 0.7124 | 1 | 53.19 | 53.19 | 0.4907 |
| 2 | 20.91 | 74.10 | 0.6157 | |||
| 3 | 2.58 | 76.68 | 0.6882 | |||
| 4 | 3.69 | 80.37 | 0.7124 |
| Variable | R2 | Q2 | Components | Explained Variation in Y (%) | Cumulative Explained Variation in Y (%) | Q2cum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OC | 0.7941 | 0.7724 | 1 | 79.41 | 79.41 | 0.7724 |
| IC | 0.3800 | 0.2715 | 1 | 28.07 | 28.07 | 0.2555 |
| 2 | 9.93 | 38.00 | 0.2715 |
| Variable | R2 | Q2 | Components | Explained Variation in Y (%) | Cumulative Explained Variation in Y (%) | Q2cum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OC | 0.9057 | 0.8886 | 1 | 89.26 | 89.26 | 0.8782 |
| 2 | 1.31 | 90.57 | 0.8886 | |||
| IC | 0.8339 | 0.7985 | 1 | 73.06 | 73.06 | 0.7057 |
| 2 | 10.33 | 83.39 | 0.7985 |
| Vegetation Area | Transition Area | Bare Flat Area | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation coefficient | 0.701 | 0.521 | 0.735 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, L.; Ye, H.; Yin, J.; Shu, Q.; Fan, Y. Changes and Influencing Factors of Carbon Content in Surface Sediments of Different Sedimentary Environments Along the Jiangsu Coast, China. Diversity 2025, 17, 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17030158
Xu L, Ye H, Yin J, Shu Q, Fan Y. Changes and Influencing Factors of Carbon Content in Surface Sediments of Different Sedimentary Environments Along the Jiangsu Coast, China. Diversity. 2025; 17(3):158. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17030158
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Linlu, Hui Ye, Jianing Yin, Qiang Shu, and Yuxin Fan. 2025. "Changes and Influencing Factors of Carbon Content in Surface Sediments of Different Sedimentary Environments Along the Jiangsu Coast, China" Diversity 17, no. 3: 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17030158
APA StyleXu, L., Ye, H., Yin, J., Shu, Q., & Fan, Y. (2025). Changes and Influencing Factors of Carbon Content in Surface Sediments of Different Sedimentary Environments Along the Jiangsu Coast, China. Diversity, 17(3), 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17030158





