Climate-Niche Evolution in Leaf-Warblers (Aves: Phylloscopidae): A Matter of Phylogeny
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Phylogenies
2.2. Ecological Niche Modelling
2.3. Predicted Niche Occupancy Profiles and Niche Overlap
2.4. Evolution of Predicted Niche Occupancy and Disparity
3. Results
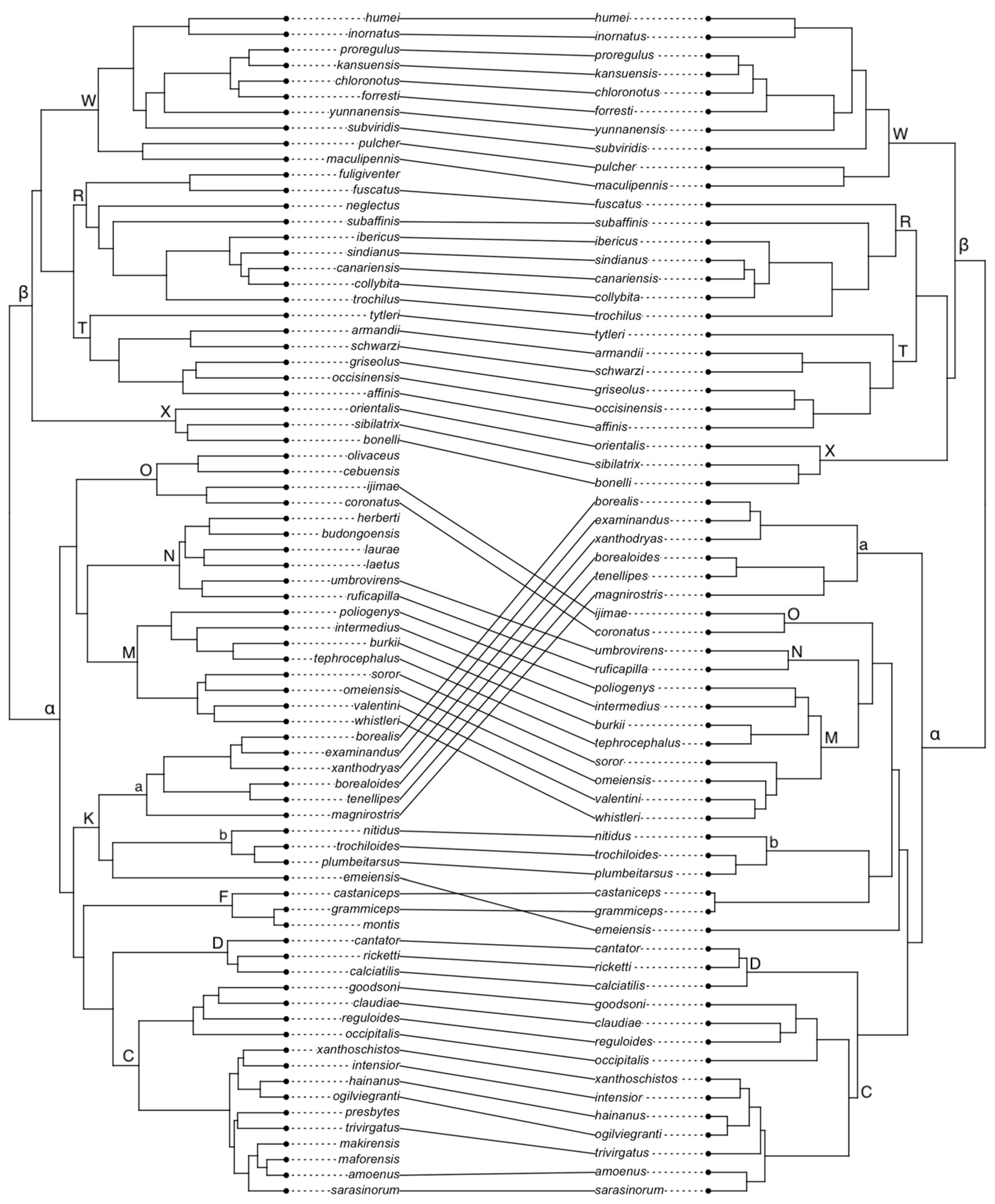
3.1. Phylogenetic Trees
3.2. Predicted Niche Occupancy and Niche Overlap
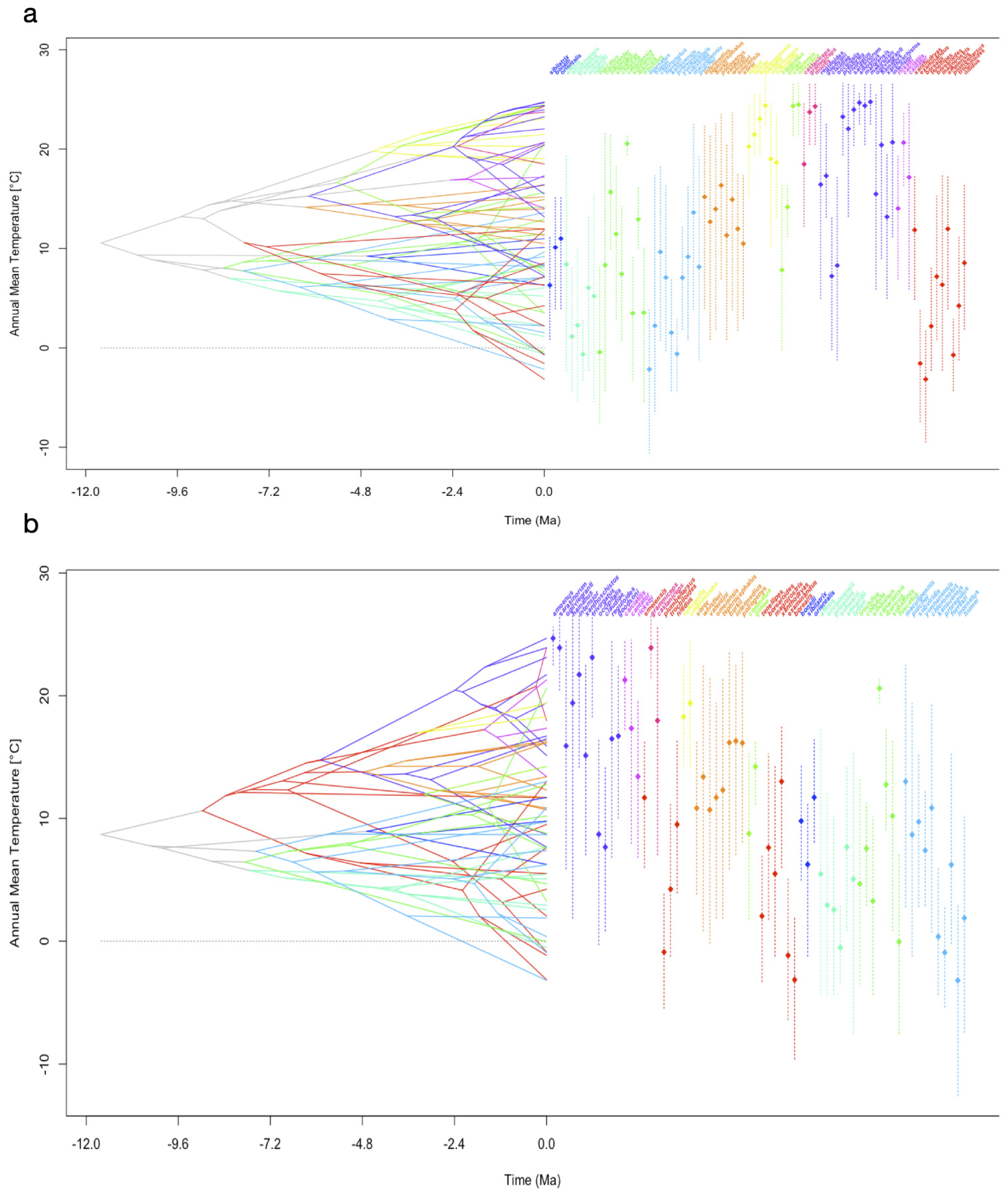
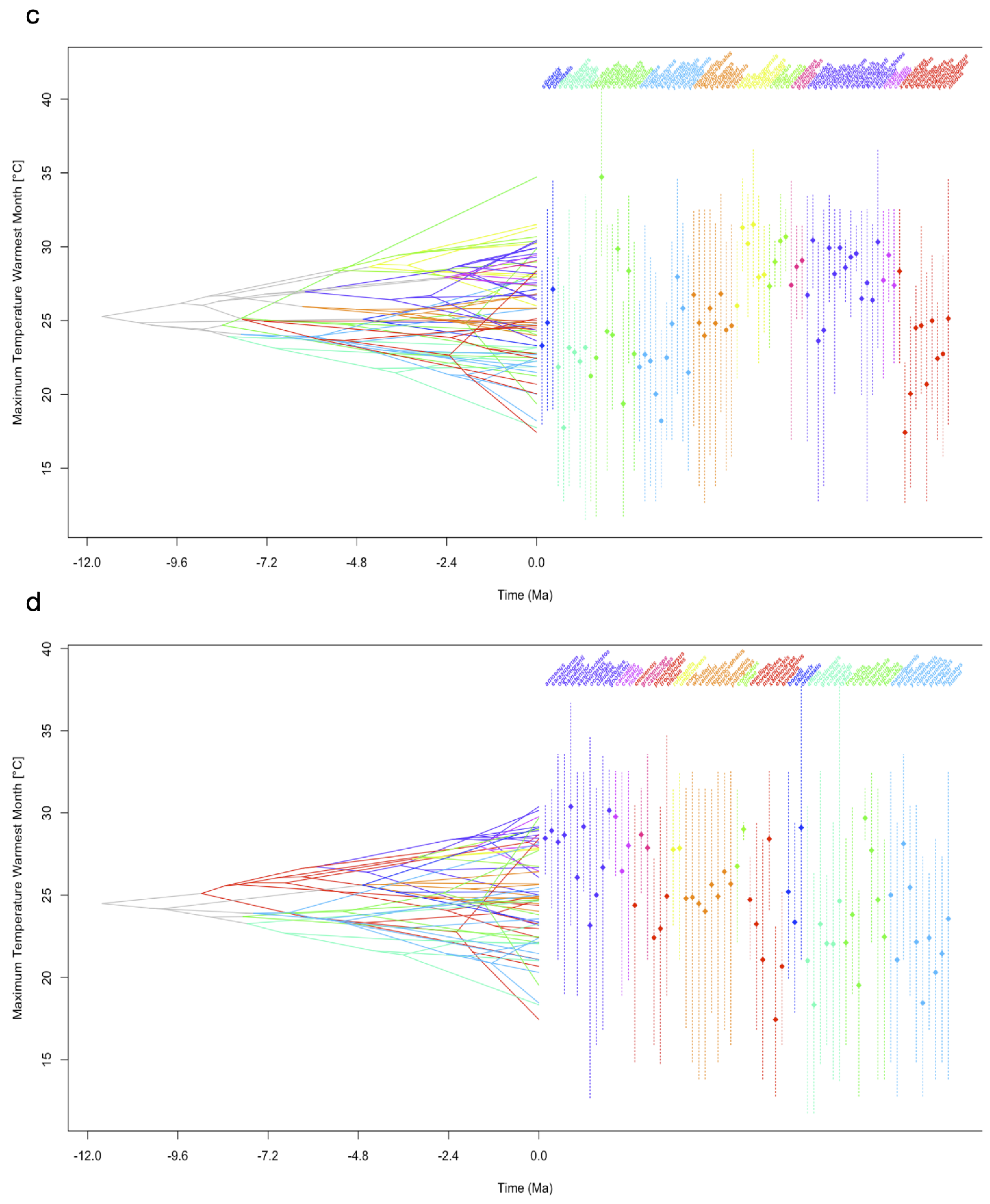
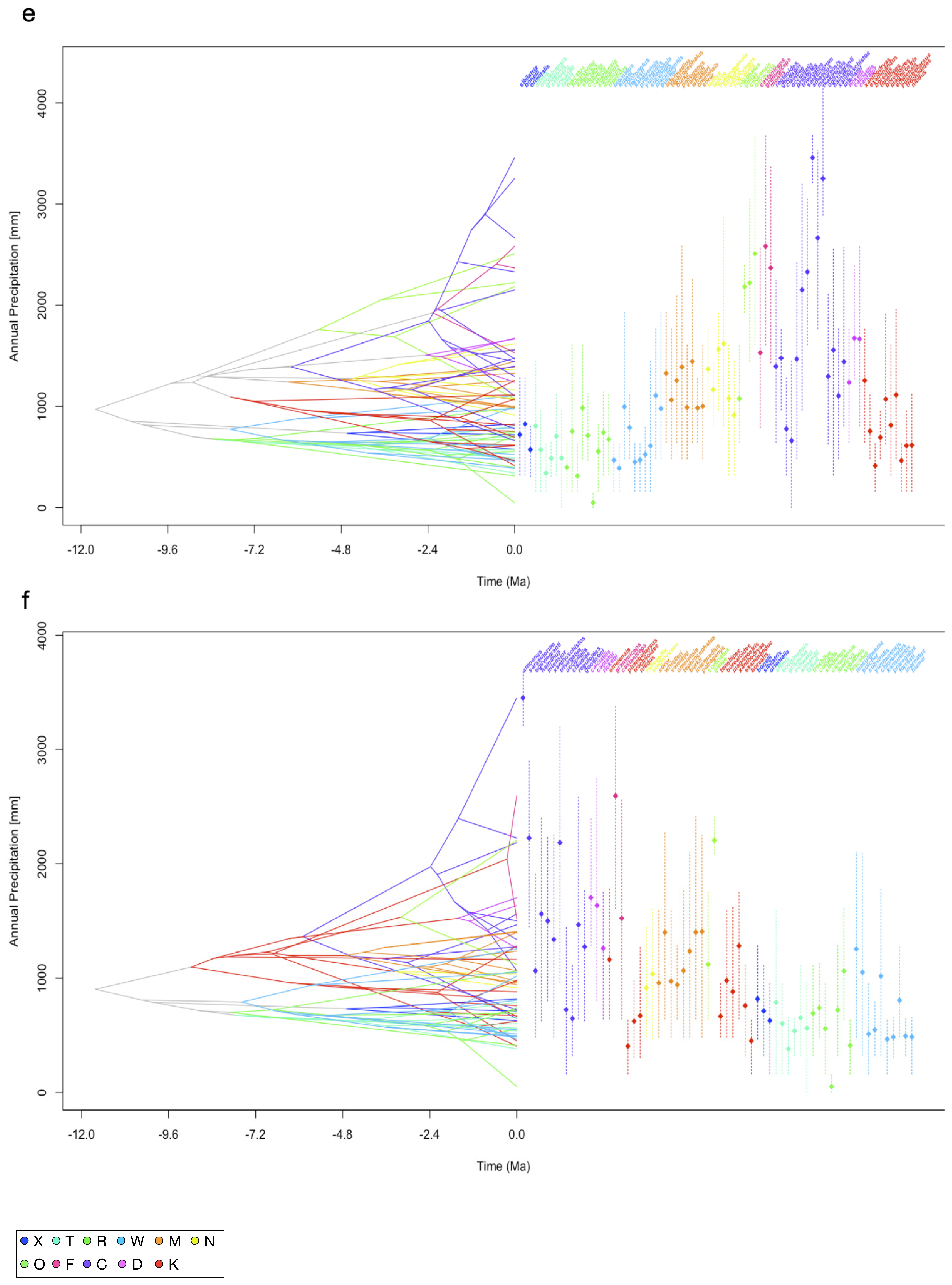
3.3. Evolutionary History of PNO
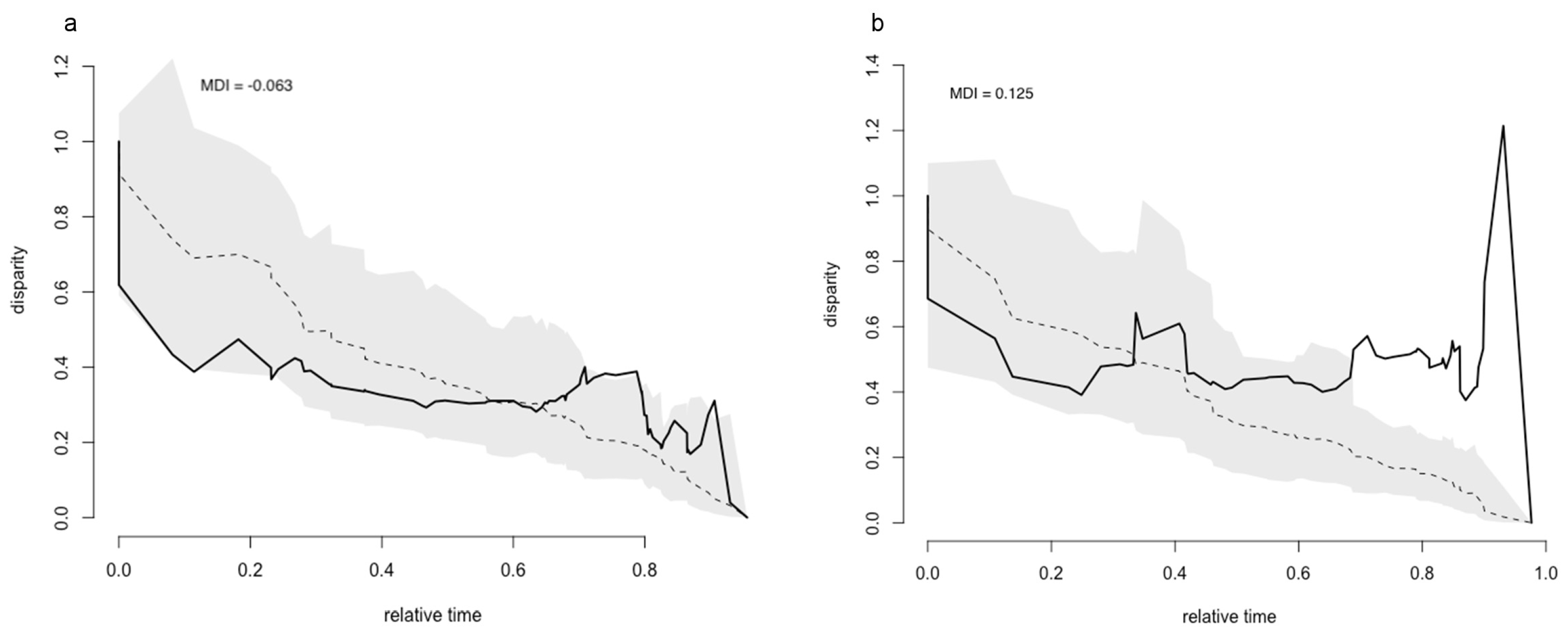
3.4. Disparity Through Time
3.5. Phylogenetic Signal and Evolutionary Models
4. Discussion
4.1. Shortcomings to Modelling Climatic Tolerances and Their Evolution in Extant Leaf-Warbler Species
4.2. Differing Phylogenetic Trees Impact the Evolutionary History of PNOs
4.3. DTT, MDI, Deviations from BM Evolution and Completeness of the Phylogenetic Tree
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evans, M.E.K.; Smith, S.A.; Flynn, R.S.; Donoghue, M.J. Climate, niche evolution, and diversification of the “Bird-Cage” Evening Primroses (Oenothera, sections Anogra and Kleinia). Am. Nat. 2009, 173, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyári, Á.S.; Reddy, S. Comparative phyloclimatic analysis and evolution of ecological niches in the Scimitar Babblers (Aves: Timaliidae: Pomatorhinus). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, L.B.; Davies, T.J.; Ackerly, D.D.; Kraft, N.J.B.; Harrison, S.P.; Anacker, B.L.; Cornell, H.V.; Damschen, E.I.; Grytnes, J.-A.; Hawkins, B.A.; et al. Phylogeny, niche conservatism and the latitudinal diversity gradient in mammals. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 2131–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, D.L.; Glor, R.E.; Turelli, M. Environmental niche equivalency versus conservatism: Quantitative approaches to niche evolution. Evolution 2008, 62, 2868–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.J.; Dudík, M.; Schapire, R.E. Maxent Software for Modeling Species Niches and Distributions (3.4.1). 2020. Available online: http://biodiversityinformatics.amnh.org/open_source/maxent/ (accessed on 13 October 2020).
- Saupe, E.E.; Barve, N.; Owens, H.L.; Cooper, J.C.; Hosner, P.A.; Peterson, T. Reconstructing ecological niche evolution when niches are incompletely characterized. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, H.L.; Ribeiro, V.; Saupe, E.E.; Cobos, M.E.; Hosner, P.A.; Cooper, J.C.; Samy, A.M.; Barve, V.; Barve, N.; Muñoz, R.C.J.; et al. Acknowledging uncertainty in evolutionary reconstructions of ecological niches. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 6967–6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapli, P.; Flouri, T.; Telford, M.J. Systematic errors in phylogenetic trees. Curr. Biol. 2020, 31, R51–R66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenwyk, J.L.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Shen, X.-X.; Rokas, A. Incongruence in the phylogenomic era. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2023, 14, 834–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gastauer, M.; Meira-Neto, J.A.A. Avoiding inaccuracies in tree calibration and phylogenetic community analysis using Phylocom 4.2. Ecol. Inform. 2013, 15, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, D.E.; Alström, P.; Olsson, U.; Benowitz-Fredericks, Z.M. Cryptic species in the genus Phylloscopus (Old World leaf-warblers). Ibis 2001, 143, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Hoyo, J.; Collar, N.J. HBW and BirdLife International Illustrated Checklist of the Birds of the World. Volume 2: Passerines; Lynx Editions: Barcelona, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, J.H. Taxonomy in Flux Checklist 3.08. 2017. Available online: http://jboyd.net/Taxo/List.html (accessed on 14 February 2022).
- Gill, F.; Donsker, D.; Rasmussen, P. IOC World Bird List (v12.1). 2022. Available online: https://www.worldbirdnames.org/ioc-lists/crossref/ (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- del Hoyo, J.; Elliott, A.; Christie, D.A. (Eds.) Handbook of the Birds of the World. Volume 11. Old World Flycatchers to Old World Warblers; Lynx Editions: Barcelona, Spain, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Alström, P.; Olsson, U.; Lei, F. A review of the recent advances in the systematics of the avian superfamily Sylvioidea. Chin. Birds 2013, 4, 99–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, S.E.; Hijmans, R.J. WorldClim 2: New 1-km spatial resolution climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4302–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietze, D.T.; Martens, J.; Fischer, B.S.; Sun, Y.; Klussmann-Kolb, A.; Päckert, M. Evolution of leaf-warbler songs (Aves: Phylloscopidae). Ecol. Evol. 2015, 5, 781–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alström, P.; Rheindt, F.E.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, M.; Wang, J.; Zhu, X.; Gwee, C.Y.; Hao, Y.; Ohlson, J.; Jia, C.; et al. Complete species-level phylogeny of the leaf-warbler (Aves: Phylloscopidae) radiation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 126, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heled, J.; Drummond, A.J. Bayesian inference of species trees from multilocus data. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoener, T.W. The Anolis lizards of Bimini: Resource partitioning in a complex fauna. Ecology 1968, 49, 704–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heibl, C.; Calenge, C. Phyloclim: Integrating Phylogenetics and Climatic Niche Modeling. R Package Version 0.9.5. 2018. Available online: https://github.com/heibl/phyloclim/ (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Rödder, D.; Lötters, S. Niche shift versus niche conservatism? Climatic characteristics of the native and invasive ranges of the Mediterranean house gecko (Hemidactylus turcicus). Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2009, 18, 674–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakob, S.S.; Heibl, C.; Rödder, D.; Blattner, F.R. Population demography influences climatic niche evolution: Evidence from diploid American Hordeum species (Poaceae). Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 1423–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennell, M.W.; Eastman, J.M.; Slater, G.J.; Brown, J.W.; Uyeda, J.C.; FitzJohn, R.G.; Alfaro, M.E.; Harmon, L.J. Geiger v2.0: An expanded suite of methods for fitting macroevolutionary models to phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2216–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagel, M. Inferring the historical patterns of biological evolution. Nature 1999, 401, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomberg, S.P.; Garland, T.; Ives, A.R. Testing for phylogenetic signal in comparative data: Behavioral traits are more labile. Evolution 2003, 57, 717–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münkemüller, T.; Lavergne, S.; Bzeznik, B.; Dray, S.; Jombart, T.; Schiffers, K.; Thuiller, W. How to measure and test phylogenetic signal. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2012, 3, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamilar, J.M.; Cooper, N. Phylogenetic signal in primate behaviour, ecology and life history. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20120341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, J. Maximum-likelihood estimation of evolutionary trees from continuous characters. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1973, 25, 471–492. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Butler, M.A.; King, A.A. Phylogenetic comparative analysis: A modeling approach for adaptive evolution. Am. Nat. 2004, 164, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmon, L.J.; Losos, J.B.; Davies, T.J.; Gillespie, R.G.; Gittleman, J.L.; Jennings, W.B.; Kozak, K.H.; A McPeek, M.; Moreno-Roark, F.; Near, T.J.; et al. Early bursts of body size and shape evolution are rare in comparative data. Evolution 2010, 64, 2385–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, F.C.; Thuiller, W.; Davies, T.J.; Lavergne, S. Neutral biogeography and the evolution of climatic niches. Am. Nat. 2014, 183, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, L.J.; Schulte, J.A.; Larson, A.; Losos, J.B. Tempo and mode of evolutionary radiation in Iguanian lizards. Science 2003, 301, 961–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rödder, D.; Engler, J.O. Quantitative metrics of overlaps in Grinnellian niches: Advances and possible drawbacks. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2011, 20, 915–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyres, A.; Böhning-Gaese, K.; Orme, C.D.L.; Rahbek, C.; Fritz, S.A. A tale of two seasons: The link between seasonal migration and climatic niches in passerine birds. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 11983–11997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.C. Ecological niche divergence or ecological niche partitioning in a widespread Neotropical bird lineage. PeerJ 2024, 12, e17345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmon, L.J. Phylogenetic Comparative Methods: Learning from Trees; Open Textbook Library: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Freckleton, R.P.; Harvey, P.H. Detecting non-Brownian trait evolution in adaptive radiations. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestro, D.; Kostikova, A.; Litsios, G.; Pearman, P.B.; Salamin, N. Measurement errors should always be incorporated in phylogenetic comparative analysis. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.D.; Gillung, J.P. Phylogenomics—Principles, opportunities and pitfalls of big-data phylogenetics. Syst. Entomol. 2019, 45, 225–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Label | Variable | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| bio1 | annual mean temperature | °C |
| bio2 | mean diurnal range | °C |
| bio3 | isothermality | % |
| bio4 | temperature seasonality (SD of monthly temperature) | °C |
| bio5 | maximum temperature of the warmest month | °C |
| bio6 | minimum temperature of the coldest month | °C |
| bio7 | annual temperature range | °C |
| bio8 | mean temperature of the wettest quarter | °C |
| bio9 | mean temperature of the driest quarter | °C |
| bio10 | mean temperature of the warmest quarter | °C |
| bio11 | mean temperature of the coldest quarter | °C |
| bio12 | annual precipitation | mm |
| bio13 | precipitation of the wettest month | mm |
| bio14 | precipitation of the driest month | mm |
| bio15 | precipitation seasonality (coefficient of variation) | % |
| bio16 | precipitation of the wettest quarter | mm |
| bio17 | precipitation of the driest quarter | mm |
| bio18 | precipitation of the warmest quarter | mm |
| bio19 | precipitation of the coldest quarter | mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gräf, L.; Griebeler, E.M.; Oldeland, J.; Tietze, D.T. Climate-Niche Evolution in Leaf-Warblers (Aves: Phylloscopidae): A Matter of Phylogeny. Diversity 2025, 17, 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17120844
Gräf L, Griebeler EM, Oldeland J, Tietze DT. Climate-Niche Evolution in Leaf-Warblers (Aves: Phylloscopidae): A Matter of Phylogeny. Diversity. 2025; 17(12):844. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17120844
Chicago/Turabian StyleGräf, Luisa, Eva Maria Griebeler, Jens Oldeland, and Dieter Thomas Tietze. 2025. "Climate-Niche Evolution in Leaf-Warblers (Aves: Phylloscopidae): A Matter of Phylogeny" Diversity 17, no. 12: 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17120844
APA StyleGräf, L., Griebeler, E. M., Oldeland, J., & Tietze, D. T. (2025). Climate-Niche Evolution in Leaf-Warblers (Aves: Phylloscopidae): A Matter of Phylogeny. Diversity, 17(12), 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17120844






