Ecological Characteristics of Temperate Seagrass Beds in Qingdao Coastal Waters and Ecological Response Relationships with Benthic Macrofauna Communities and Environmental Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
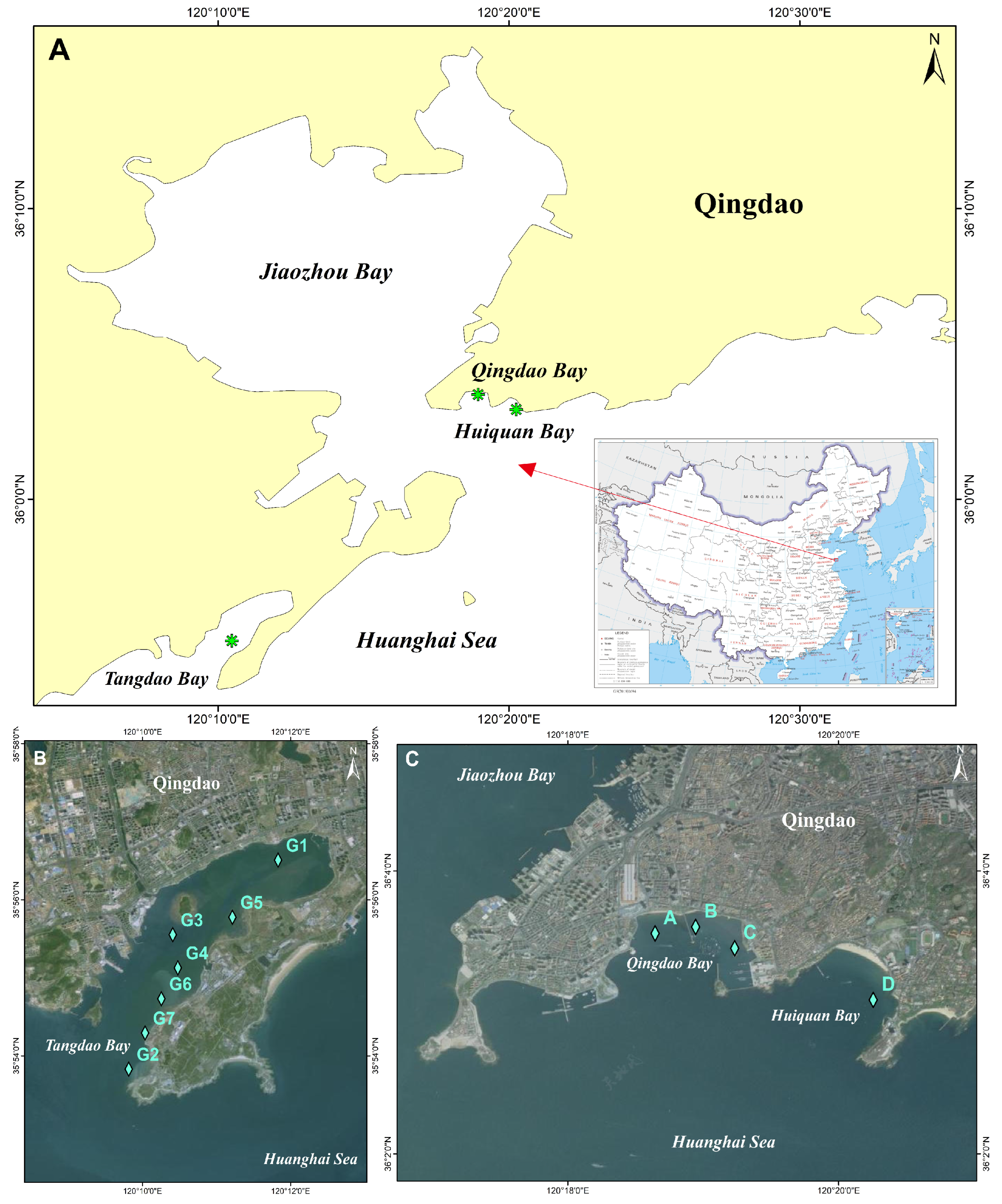
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Design
2.2. Field Sampling and Laboratory Measurements
2.2.1. Seagrass Community Parameters
2.2.2. Environmental Factors
2.2.3. Benthic Macrofauna Community
2.3. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
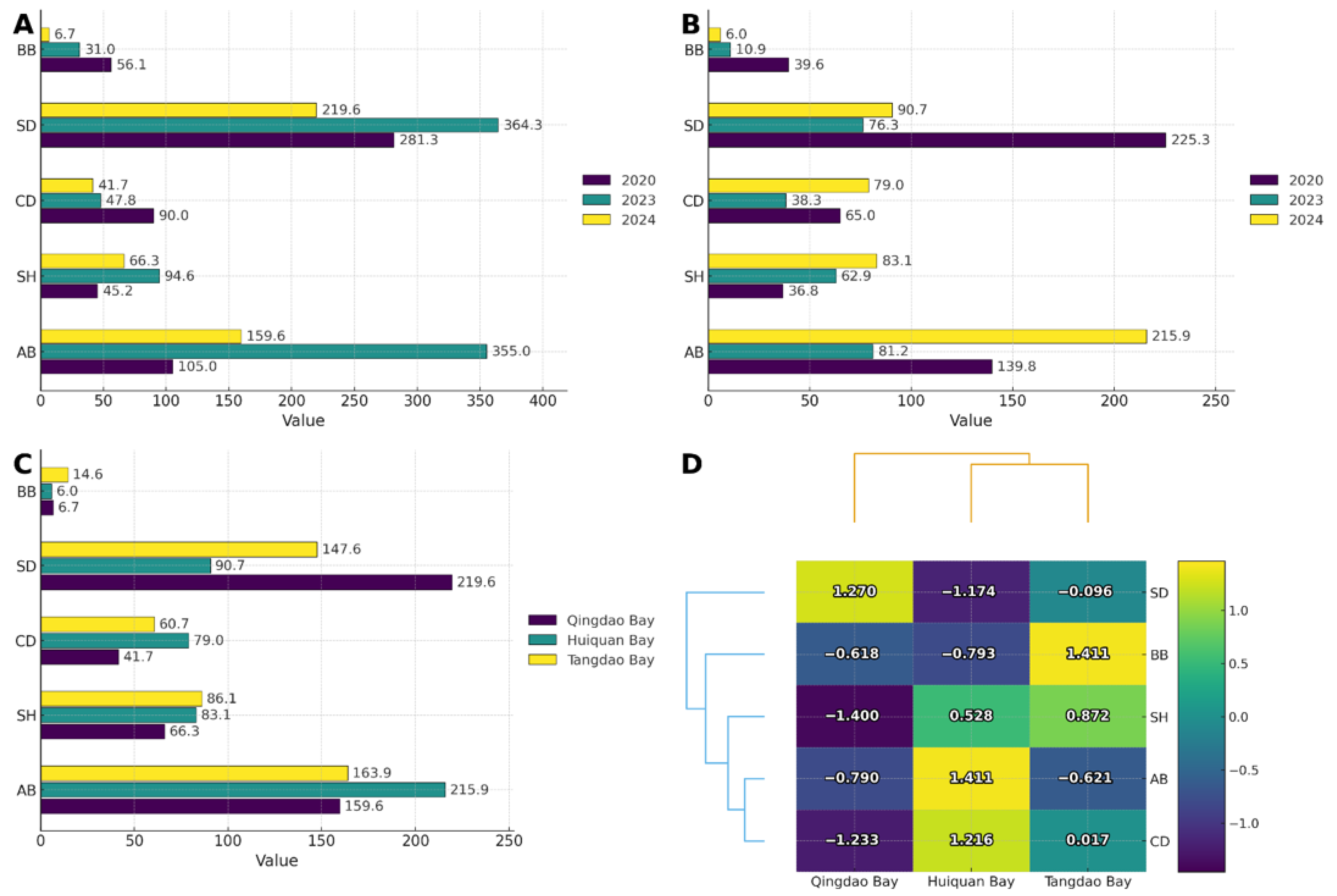
3.1. Seagrass Community Status and Interannual Dynamic Changes
3.2. Benthic Macrofauna Community Structure and Diversity Characteristics in Seagrass Beds
3.2.1. Benthic Macrofauna Community Composition
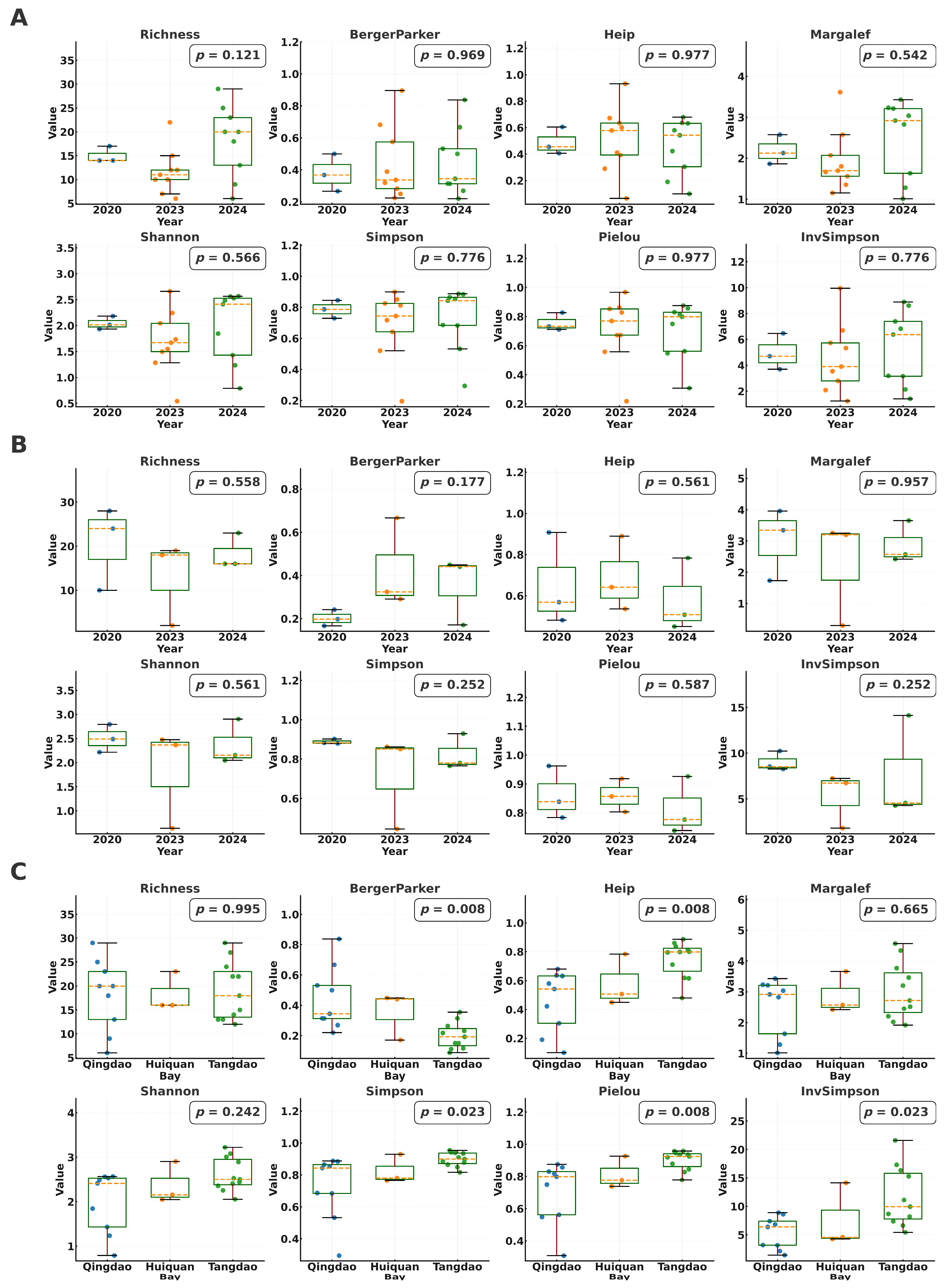
3.2.2. α Diversity Characteristics
3.2.3. β Diversity Characteristics
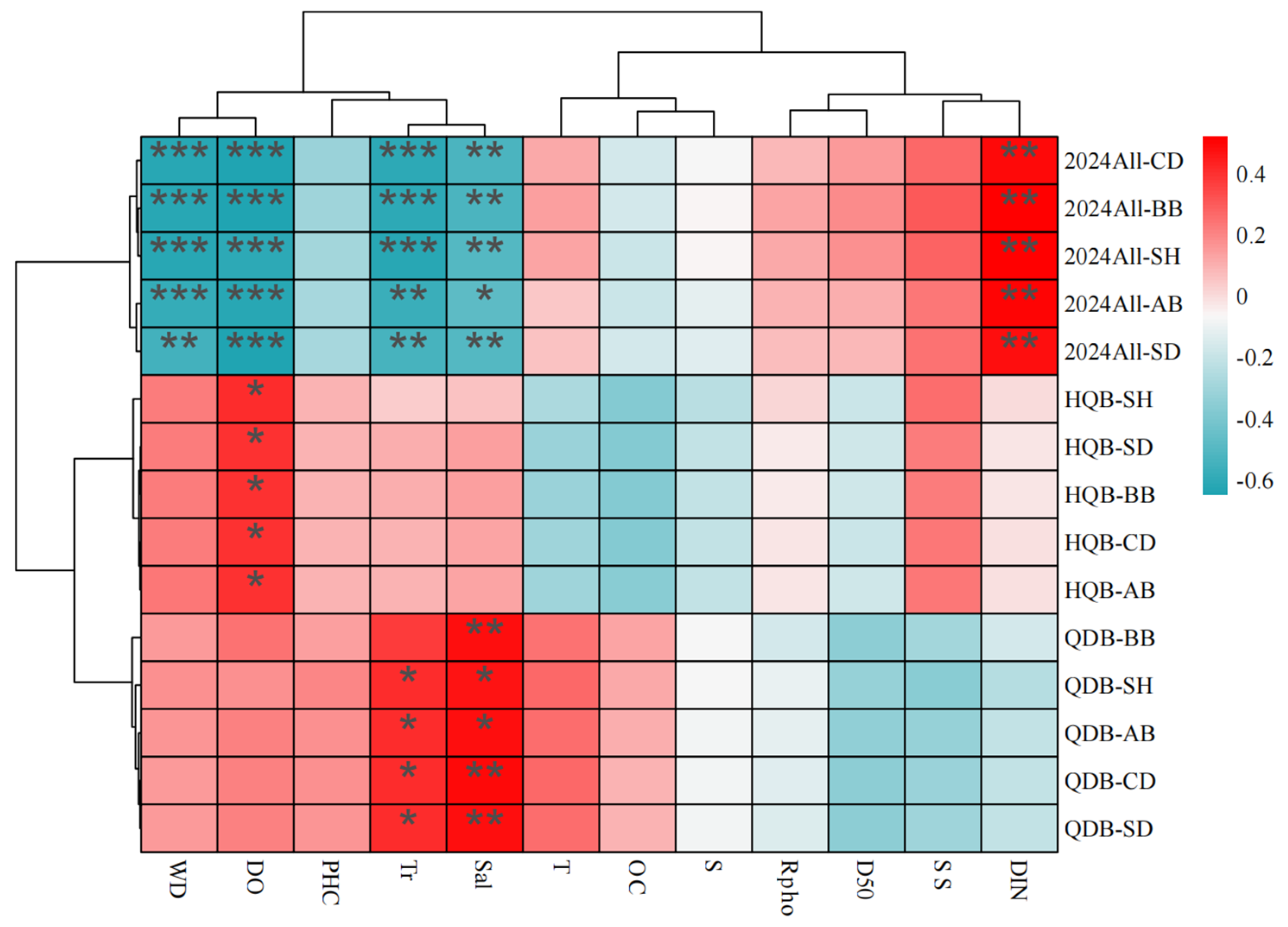
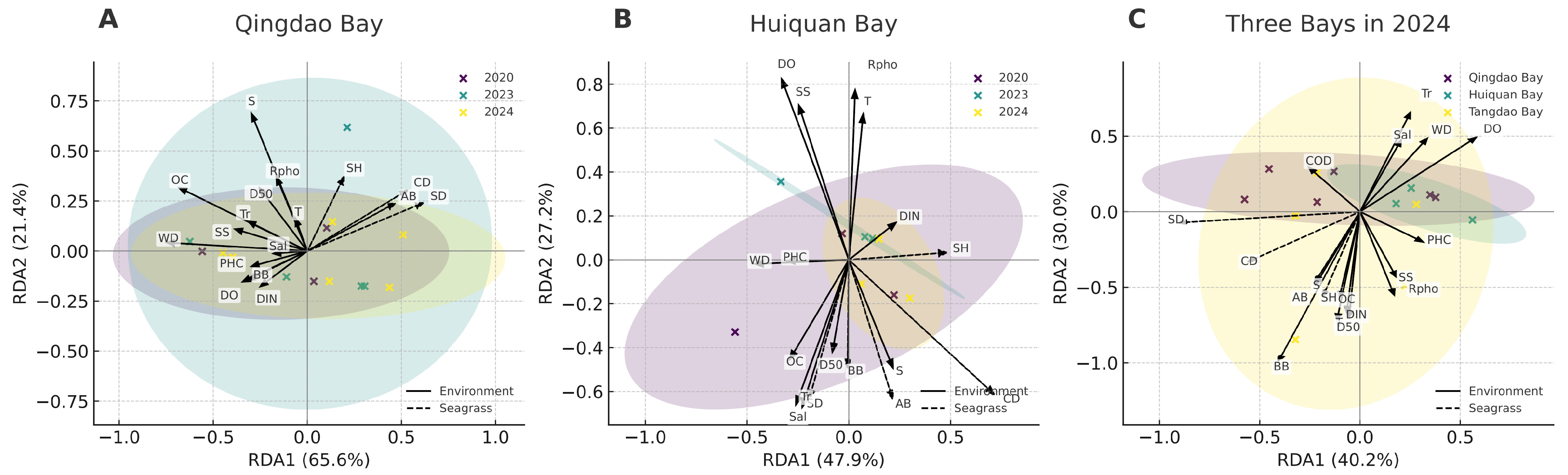
3.3. Response Relationships Between Seagrass Communities and Environmental Factors
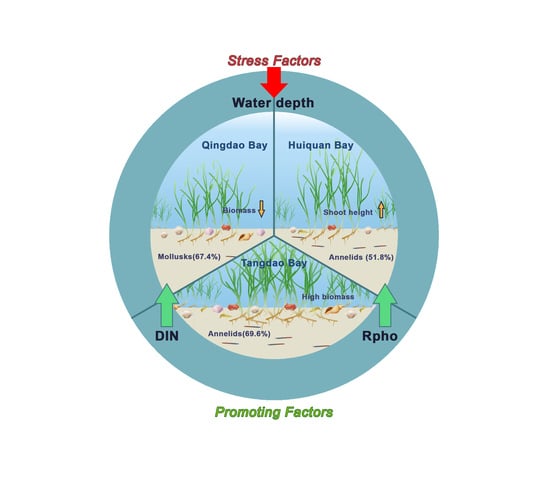
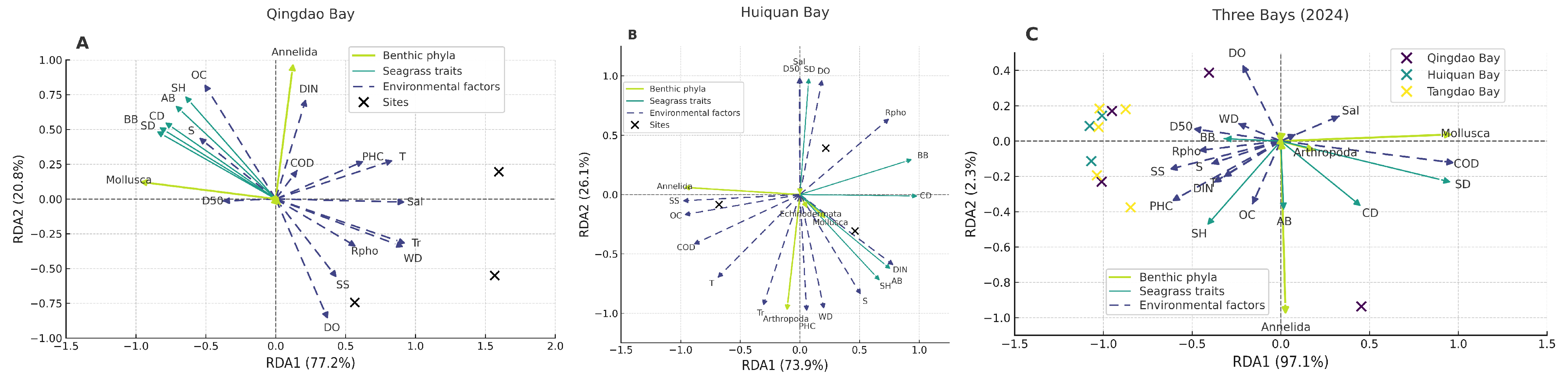
3.4. Coupling Effects of Benthic Animal Communities with Seagrass and Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Seagrass Community Dynamics and Environmental Adaptation Mechanisms
4.2. Ecological Drivers of Macro-Benthic Community Differentiation
4.3. Multiple Coupling Relationships Among Seagrass, Benthic Animals, and Environmental Factors
4.4. Global Implications for Temperate Seagrass Ecosystems
4.5. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nordlund, L.M.; Unsworth, R.K.; Gullström, M.; Cullen-Unsworth, L.C. Global significance of seagrass fishery activity. Fish Fish. 2018, 19, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochida, K.; Hano, T.; Onduka, T.; Ito, K.; Yoshida, G. Physiological responses of eelgrass (Zostera marina) to ambient stresses such as herbicide, insufficient light, and high water temperature. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 208, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, M.d.A.C.; Ward, R.D.; Joyce, C.B.; Kauer, K.; Sepp, K. Carbon stocks in southern England’s intertidal seagrass meadows. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 275, 107947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsworth, R.K.F.; Nordlund, L.M.; Cullen-Unsworth, L.C. Seagrass meadows support global fisheries production. Conserv. Lett. 2019, 12, e12566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, J.E.; Reynolds, P.L.; Boström, C.; Coyer, J.A.; Cusson, M.; Donadi, S.; Douglass, J.G.; Eklöf, J.S.; Engelen, A.H.; Eriksson, B.K.; et al. Biodiversity mediates top–down control in eelgrass ecosystems: A global comparative-experimental approach. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, R.; Hamylton, S. On the very edge: Faunal and functional responses to the interface between benthic seagrass and unvegetated sand assemblages. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 553, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, A.C. Benthic macro-invertebrate community composition within a mangrove/seagrass estuary in northern New Zealand. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 66, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaya, T.; Watanabe, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Hongo, C.; Kayanne, H.; Kuwae, T. Contributions of the direct supply of belowground seagrass detritus and trapping of suspended organic matter to the sedimentary organic carbon stock in seagrass meadows. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 4033–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräfnings, M.L.; Grimm, I.; Valdez, S.R.; Findji, I.; Van Der Heide, T.; Heusinkveld, J.H.; Meijer, K.J.; Eriksson, B.K.; Smeele, Q.; Govers, L.L. Restored intertidal eelgrass (Z. Marina) supports benthic communities taxonomically and functionally similar to natural seagrasses in the Wadden Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 10, 1294845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharlamenko, V.I.; Kiyashko, S.I.; Imbs, A.B.; Vyshkvartzev, D.I. Identification of food sources of invertebrates from the seagrass Zostera marina community using carbon and sulfur stable isotope ratio and fatty acid analyses. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 220, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsworth, R.K.F.; Van Keulen, M.; Coles, R.G. Seagrass meadows in a globally changing environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 83, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, D.; Staveley, T.; Deyanova, D.; Baden, S.; Dupont, S.; Hernroth, B.; Wood, H.; Björk, M.; Gullström, M. Global environmental changes negatively impact temperate seagrass ecosystems. Ecosphere 2019, 10, e02986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen-Unsworth, L.C.; Unsworth, R.K. Strategies to enhance the resilience of the world’s seagrass meadows. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 53, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christianen, M.J.; Smulders, F.O.; Vonk, J.A.; Becking, L.E.; Bouma, T.J.; Engel, S.M.; James, R.K.; Nava, M.I.; De Smit, J.C.; Van Der Zee, J.P.; et al. Seagrass ecosystem multifunctionality under the rise of a flagship marine megaherbivore. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, P.S.; Eklöf, J.S.; Van Katwijk, M.M.; O’brien, K.R.; De La Torre-Castro, M.; Boström, C.; Bouma, T.J.; Krause-Jensen, D.; Unsworth, R.K.; Van Tussenbroek, B.I.; et al. The fundamental role of ecological feedback mechanisms for the adaptive management of seagrass ecosystems—A review. Biol. Rev. 2017, 92, 1521–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unsworth, R.K.F.; Cullen-Unsworth, L.C.; Jones, B.L.H.; Lilley, R.J. The planetary role of seagrass conservation. Science 2022, 377, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.G.; Chen, B.; Nagelkerken, I.; Chen, S.Q.; Hu, W.J. Protect seagrass meadows in China’s waters. Science 2023, 379, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, J.J.; Liu, X.D.; Wang, H.; Song, X.L.; Bao, M.M.; Yu, Q.Y.; Wen, G.Y.; Wei, M. Status and habitat suitability evaluation: A case study of the typical temperate seagrass beds in the Bohai Sea, China. Mar. Environ. Res. 2025, 204, 106873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Ortiz, A.; Serrano, O.; Masqué, P.; Lavery, P.S.; Mueller, U.; Kendrick, G.A.; Rozaimi, M.; Esteban, A.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Marbà, N.; et al. A marine heatwave drives massive losses from the world’s largest seagrass carbon stocks. Nat. Clim. Change 2018, 8, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, S.; Yue, S.D.; Liu, M.J.; Zhang, X.M. Warming northward shifting southern limits of the iconic temperate seagrass (Zostera marina). Iscience 2022, 25, 104755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, D.J. Research progress on degradation factors and restoration technologies of seagrass beds. OAJRC Environ. Sci. 2023, 4, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P. Study on the Population Supplement Mechanism of Zostera marina in Typical Seagrass Beds of Shandong Peninsula. Master’s Thesis, Graduate School, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, China, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.D.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Sun, Q.; Yue, H.W.; Zhang, Z.K. Grain size of intertidal deposits in Tangdao Bay of Qingdao and its hydrodynamic significance. Mar. Geol. Front. 2015, 31, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Cui, Z.; Pan, C.; Xia, M.; Tang, G.; Song, T.; Zhou, J.; Cao, B. Tidal observation and characteristic analysis in Tangdao Bay. China Water Transp. 2016, 16, 130–132. [Google Scholar]
- Short, F.T.; Mckenzie, L.J.; Coles, R.G.; Vidler, K.P.; Gaeckle, J.L. SeagrassNet Manual for Scientific Monitoring of Seagrass Habitat; worldwide edition; University of New Hampshire: Durham, NH, USA, 2006; 73p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, F.T.; Davis, R.C.; Kopp, B.; Short, C.A.; Burdick, D.M. Site-selection model for optimal transplantation of eelgrass Zostera marina in the northeastern US. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 227, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, C.; Hunter, S.; Reel, J.; Parham, T.; Naylor, M.; Karrh, L.; Busch, K.; Golden, R.R.; Lewandowski, M.; Rybicki, N.; et al. Evaluating a large-scale eelgrass restoration project in the Chesapeake Bay. Restor. Ecol. 2010, 18, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 17378.4—2007; China National Standardization Management Committee. The Specification of Oceanographic Survey—Part 4: Seawater Analysis. China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2007.
- GB 17378.5—2007; China National Standardization Management Committee. The Specification of Oceanographic Survey—Part 5: Sediment Analysis. China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Gray, J.S.; Elliott, M. Ecology of Marine Sediments: From Science to Management; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.H. Measurement of diversity. Nature 1949, 163, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasution, M.A.; Hermi, R.; Lubis, F.; Saputra, F.; Ammar, E.E.; Akbar, H. Seagrass biodiversity and its drivers in the Kepulauan Banyak marine nature park, indonesia. Ilmu Kelaut. Indones. J. Mar. Sci. 2024, 29, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P.; Anderson, M.J. Distance-based redundancy analysis: Testing multispecies responses in multifactorial ecological experiments. Ecol. Monogr. 1999, 69, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.Q.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Han, Q.X.; Yan, H.X.; Ji, B.; Chai, Y.T.; Li, S.Y.; Liu, K. Insights into autotrophic carbon fixation strategies through metagonomics in the sediments of seagrass beds. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 188, 106002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Jiang, J.Y.; Wang, D.C.; Fu, G.W.; Song, Y.W.; Wang, H.B.; Zhang, D.H. Assessment of the community status of seagrass bed and its relationship with environmental characteristics in Wenchang, Hainan Island, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1433104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsworth, R.K.F.; Mckenzie, L.J.; Collier, C.J.; Cullen-Unsworth, L.C.; Duarte, C.M.; Eklöf, J.S.; Jarvis, J.C.; Jones, B.L.; Nordlund, L.M. Global challenges for seagrass conservation. Ambio 2019, 48, 801–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabarte-Maeztu, I.; Matheson, F.E.; Manley-Harris, M.; Davies-Colley, R.J.; Oliver, M.; Hawes, I. Effects of fine sediment on seagrass meadows: A case study of Zostera muelleri in pāuatahanui inlet, NewZealand. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, C.J.; Stevens, T.; Lee, S.Y.; Gilby, B.L.; Schlacher, T.A.; Connolly, R.M.; Warnken, J.; Maxwell, P.S.; Olds, A.D. Optimising seagrass conservation for ecological functions. Ecosystems 2019, 22, 1368–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundquist, C.J.; Jones, T.C.; Parkes, S.M.; Bulmer, R.H. Changes in benthic community structure and sediment characteristics after natural recolonisation of the seagrass Zostera muelleri. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, C.M. Quantifying direct and indirect linkages between seagrasses, environment and associated macrofauna in a temperate lagoon. Mar. Ecol. 2024, 45, e12804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, J.E. Biodiversity and the functioning of seagrass ecosystems. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 311, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, B.; Zuschin, M.; Stachowitsch, M. Tolerance of benthic macrofauna to hypoxia and anoxia in shallow coastal seas: A realistic scenario. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 458, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.Z.; Fu, Y.Z.; Song, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.H.; Hu, W.; Guo, J.R. Suitability evaluation of the water environment for seagrass growth areas in the Changshan Archipelago. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.J.; Rosenberg, R. Marine benthic hypoxia: A review of its ecological effects and the behavioural responses of benthic macrofauna. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 1995, 33, 03. [Google Scholar]
- Bulmer, R.H.; Townsend, M.; Drylie, T.; Lohrer, A.M. Elevated turbidity and the nutrient removal capacity of seagrass. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Chen, S.Q.; Chen, B.; Wu, Z.J.; An, W.S.; Luo, L.Z.; Wang, J.; Xie, L.M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, G.C. Implication of macroalgal bloom to soil organic carbon stock in seagrass meadows-a case study in South Hainan, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 870228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Katwijk, M.M.; Van Beusekom, J.E.; Folmer, E.O.; Kolbe, K.; De Jong, D.J.; Dolch, T. Seagrass recovery trajectories and recovery potential in relation to nutrient reduction. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 61, 1784–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubiano-Rincon, S.; Larkin, P.D.; Kim, I.-N. An assessment of hydrogen sulfide intrusion in the seagrass Halodule wrightii. Exp. Results 2022, 3, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fouw, J.; Madden, C.J.; Furman, B.T.; Hall, M.O.; Verstijnen, Y.; Holthuijsen, S.; Frankovich, T.A.; Strazisar, T.; Blaha, M.; Van Der Heide, T. Reduced seagrass resilience due to environmental and anthropogenic effects may lead to future die-off events in Forida Bay. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1366939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, B.J.; Matulich, K.L.; Hooper, D.U.; Byrnes, J.E.; Duffy, E.; Gamfeldt, L.; Balvanera, P.; O’connor, M.I.; Gonzalez, A. The functional role of producer diversity in ecosystems. Am. J. Bot. 2011, 98, 572–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvin, T.J.; Snelgrove, P.V.R. Role of seagrass physical structure in macrofaunal biodiversity-ecosystem functioning relationships. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2025, 754, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staveley, T.A.B.; Perry, D.; Lindborg, R.; Gullström, M. Seascape structure and complexity influence temperate seagrass fish assemblage composition. Ecography 2017, 40, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindeberg, T.; Attard, K.M.; Hüller, J.; Müller, J.; Quintana, C.O.; Infantes, E. Structural complexity and benthic metabolism: Resolving the links between carbon cycling and biodiversity in restored seagrass meadows. Biogeosciences 2024, 21, 1685–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, A.; Dubois, S.F.; Boyé, A.; Becheler, R.; Droual, G.; Chevalier, M.; Pasquier, M.; Roudaut, L.; Fournier-Sowinski, J.; Auby, I.; et al. Environmental filtering and biotic interactions act on different facets of the diversity of benthic assemblages associated with eelgrass. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, e10159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodil, I.F.; Lohrer, A.M.; Attard, K.M.; Thrush, S.F.; Norkko, A. Positive contribution of macrofaunal biodiversity to secondary production and seagrass carbon metabolism. Ecology 2022, 103, e3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millot, J.; Grall, J.; Toumi, C.; Maguer, M.; Boyé, A. Quantifying the direct and indirect relationships linking the environment, seagrass, and their associated fauna. Ecosphere 2024, 15, e4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonk, J.A.; Christianen, M.J.; Stapel, J.; O’brien, K.R. What lies beneath: Why knowledge of belowground biomass dynamics is crucial to effective seagrass management. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 57, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Carlo, G.; Kenworthy, W.J. Evaluation of aboveground and belowground biomass recovery in physically disturbed seagrass beds. Oecologia 2008, 158, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesselbarth, M.H.; Allgeier, J.E. High fish biomass and low nutrient enrichment synergistically enhance stability in a seagrass meta-ecosystem. Conserv. Lett. 2024, 17, e13071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, B.E.; Herren, L.W.; Brewton, R.A.; Alderman, P.K. Nutrient over-enrichment and light limitation of seagrass communities in the indian river lagoon, an urbanized subtropical estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaubert-Boussarie, J.; Altieri, A.H.; Duffy, J.E.; Campbell, J.E. Seagrass structural and elemental indicators reveal high nutrient availability within a tropical lagoon in Panama. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zieman, J.C.; Zieman, R.T. The Ecology of the Seagrass Meadows of the West Coast of Florida: A Community Profile; U.S. Department of the Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service, Research and Development: Falls Church, VA, USA, 1989.
- Bulmer, R.H.; Kelly, S.; Jeffs, A.G. Light requirements of the seagrass, Zostera muelleri, determined by observations at the maximum depth limit in a temperate estuary, New Zealand. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2016, 50, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boström, C.; Jackson, E.L.; Simenstad, C.A. Seagrass landscapes and their effects on associated fauna: A review. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 68, 383–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, J.E.; Cardinale, B.J.; France, K.E.; Mcintyre, P.B.; Thébault, E.; Loreau, M. The functional role of biodiversity in ecosystems: Incorporating trophic complexity. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 522–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodil, I.F.; Lohrer, A.M.; Attard, K.M.; Hewitt, J.E.; Thrush, S.F.; Norkko, A. Macrofauna communities across a seascape of seagrass meadows: Environmental drivers, biodiversity patterns and conservation implications. Biodivers. Conserv. 2021, 30, 3023–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sha, J.; Song, X.; Sun, P.; Yang, Z.; Bao, M.; Wang, H.; Wen, R.; Yu, Q.; Wei, M. Ecological Characteristics of Temperate Seagrass Beds in Qingdao Coastal Waters and Ecological Response Relationships with Benthic Macrofauna Communities and Environmental Factors. Diversity 2025, 17, 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17120816
Sha J, Song X, Sun P, Yang Z, Bao M, Wang H, Wen R, Yu Q, Wei M. Ecological Characteristics of Temperate Seagrass Beds in Qingdao Coastal Waters and Ecological Response Relationships with Benthic Macrofauna Communities and Environmental Factors. Diversity. 2025; 17(12):816. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17120816
Chicago/Turabian StyleSha, Jingjing, Xiaoli Song, Peiyan Sun, Zhibo Yang, Mengmeng Bao, Hui Wang, Ruobing Wen, Qingyun Yu, and Miao Wei. 2025. "Ecological Characteristics of Temperate Seagrass Beds in Qingdao Coastal Waters and Ecological Response Relationships with Benthic Macrofauna Communities and Environmental Factors" Diversity 17, no. 12: 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17120816
APA StyleSha, J., Song, X., Sun, P., Yang, Z., Bao, M., Wang, H., Wen, R., Yu, Q., & Wei, M. (2025). Ecological Characteristics of Temperate Seagrass Beds in Qingdao Coastal Waters and Ecological Response Relationships with Benthic Macrofauna Communities and Environmental Factors. Diversity, 17(12), 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17120816