Microbial Diversity, Selective Isolation and Bioactivity Characterization of Bacterial Populations in Eutrophic Seawater of Coastal East China Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampler Collection
2.2. 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing and Data Analysis
2.3. CECS-Based Selective Isolation of Cultivable Bacterial Strains
2.4. Molecular Identification of Bacterial Strains
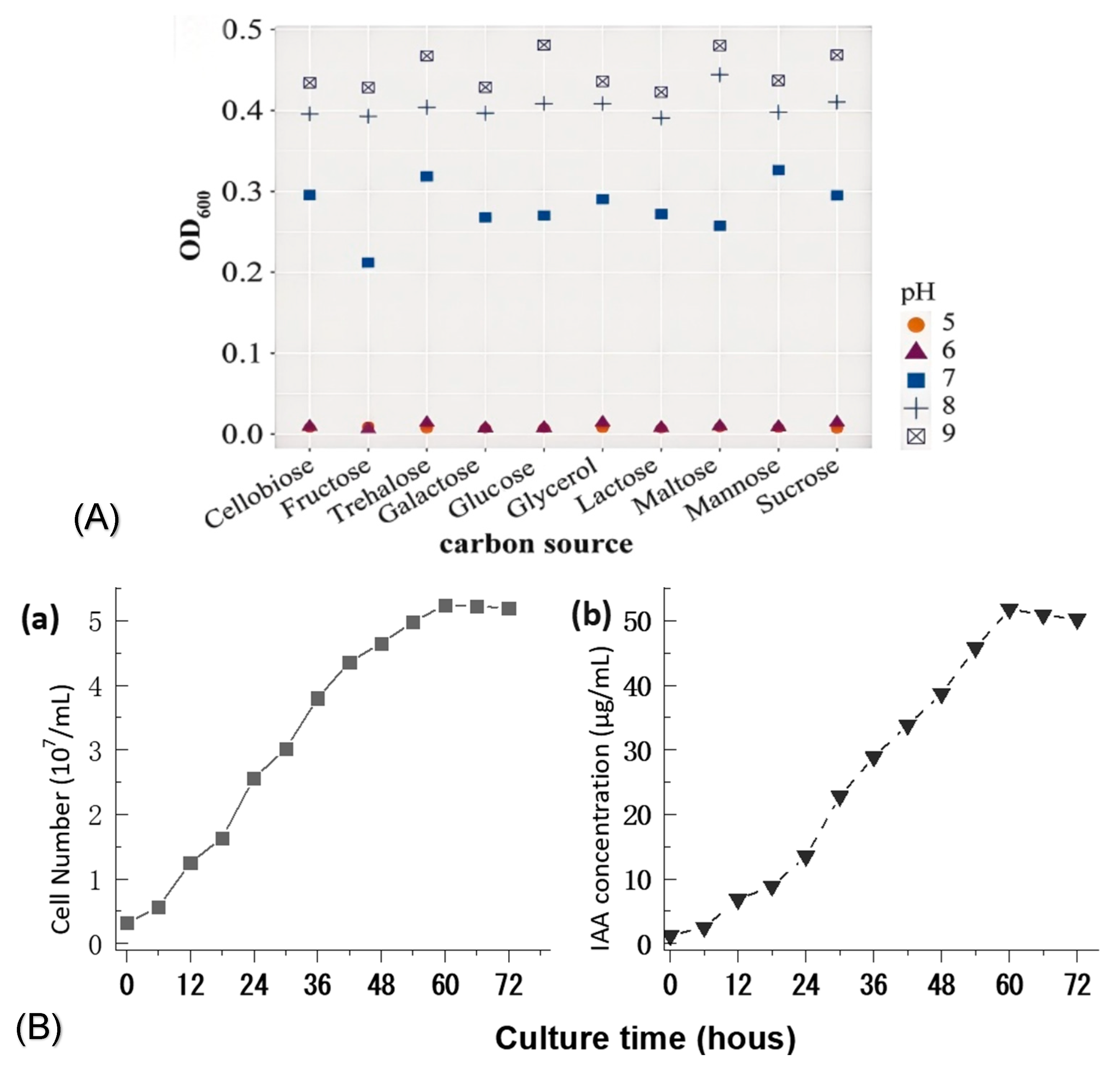
2.5. Culture Optimization of Bacterial Strain
2.6. Bioactivity Measurements
2.6.1. Antibacterial Bioactivity Measurements
2.6.2. Evaluation of Microalgae Growth-Promoting Bioactivity
2.6.3. Screening for IAA-Producing Bacterial Strains
3. Results and Discussions
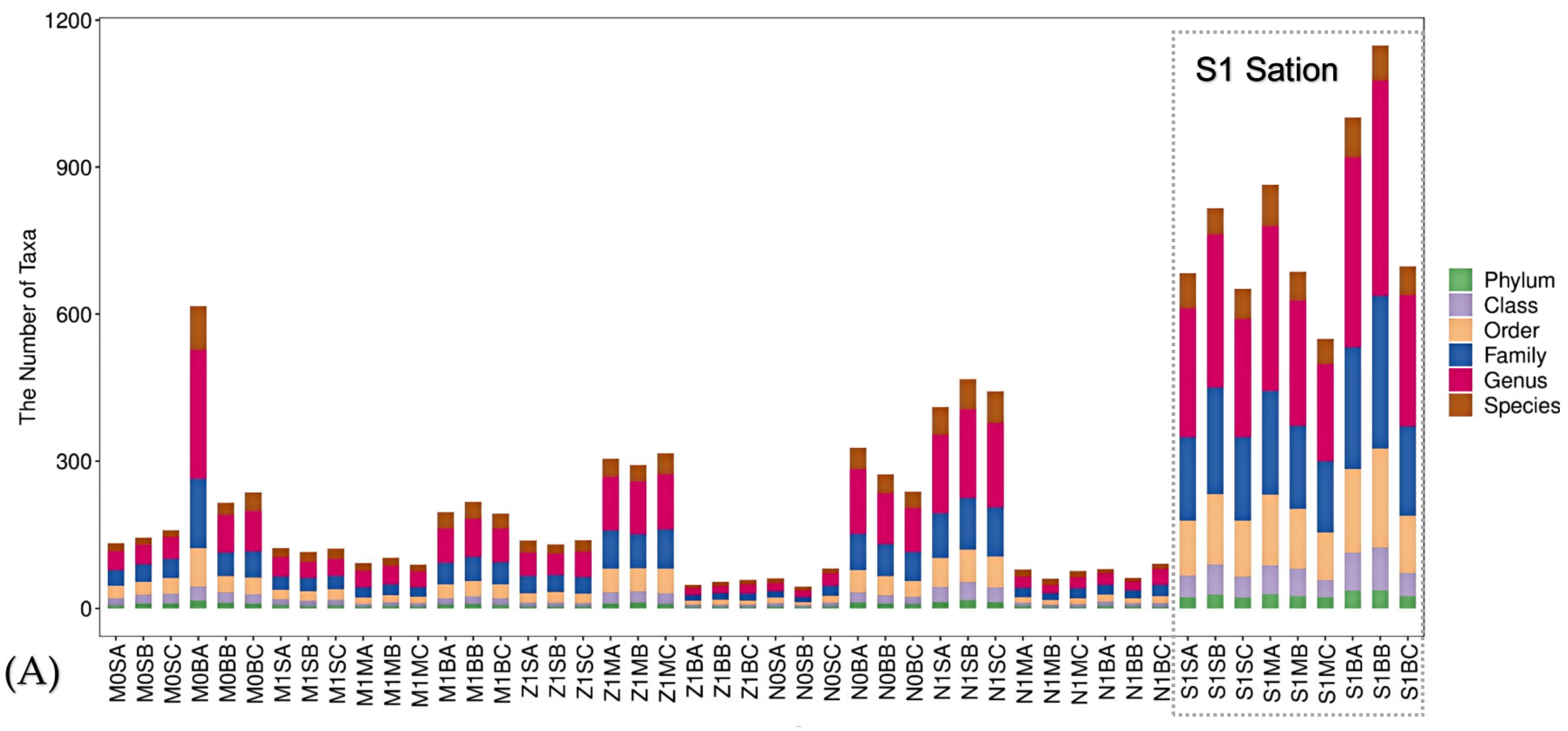
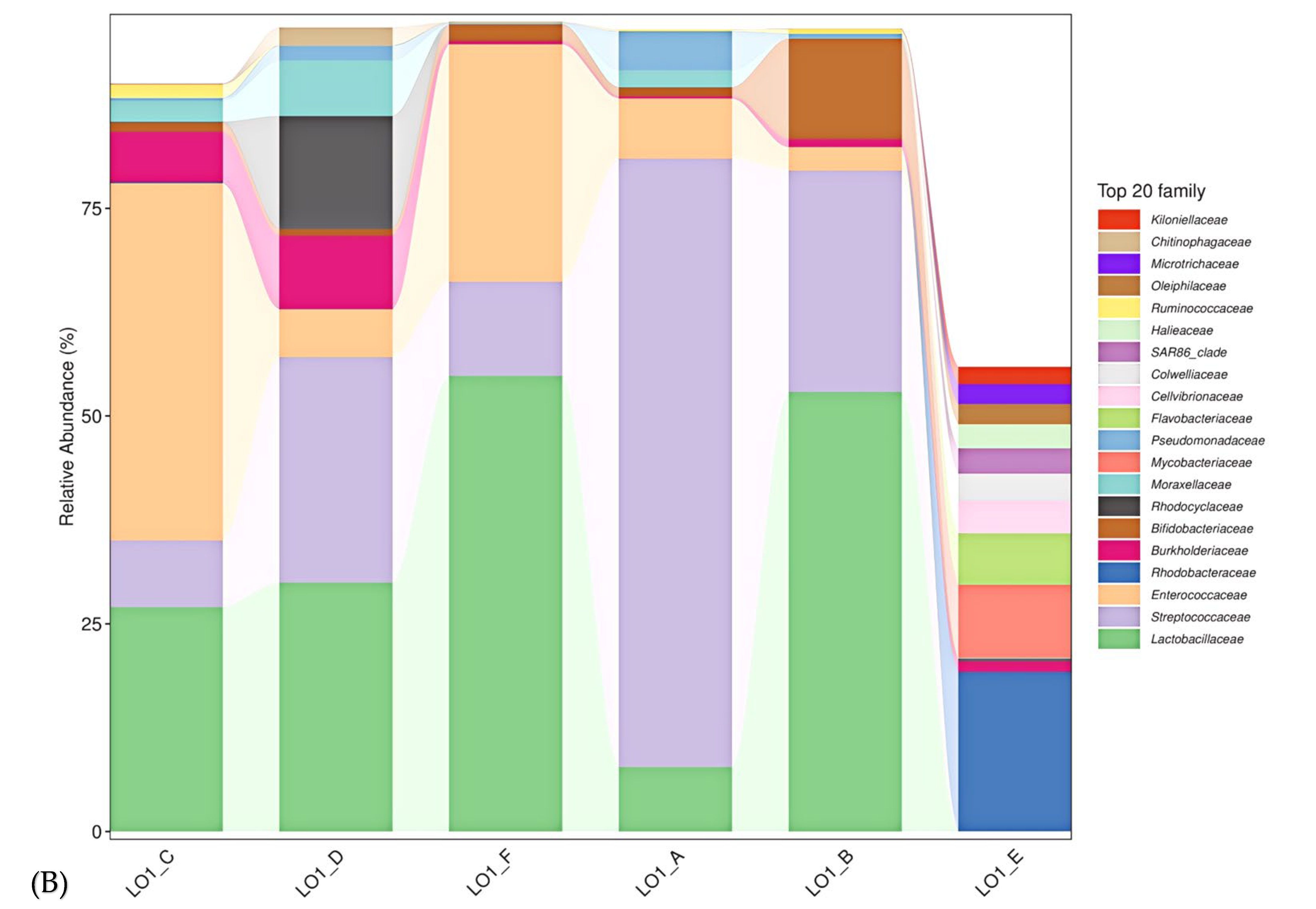
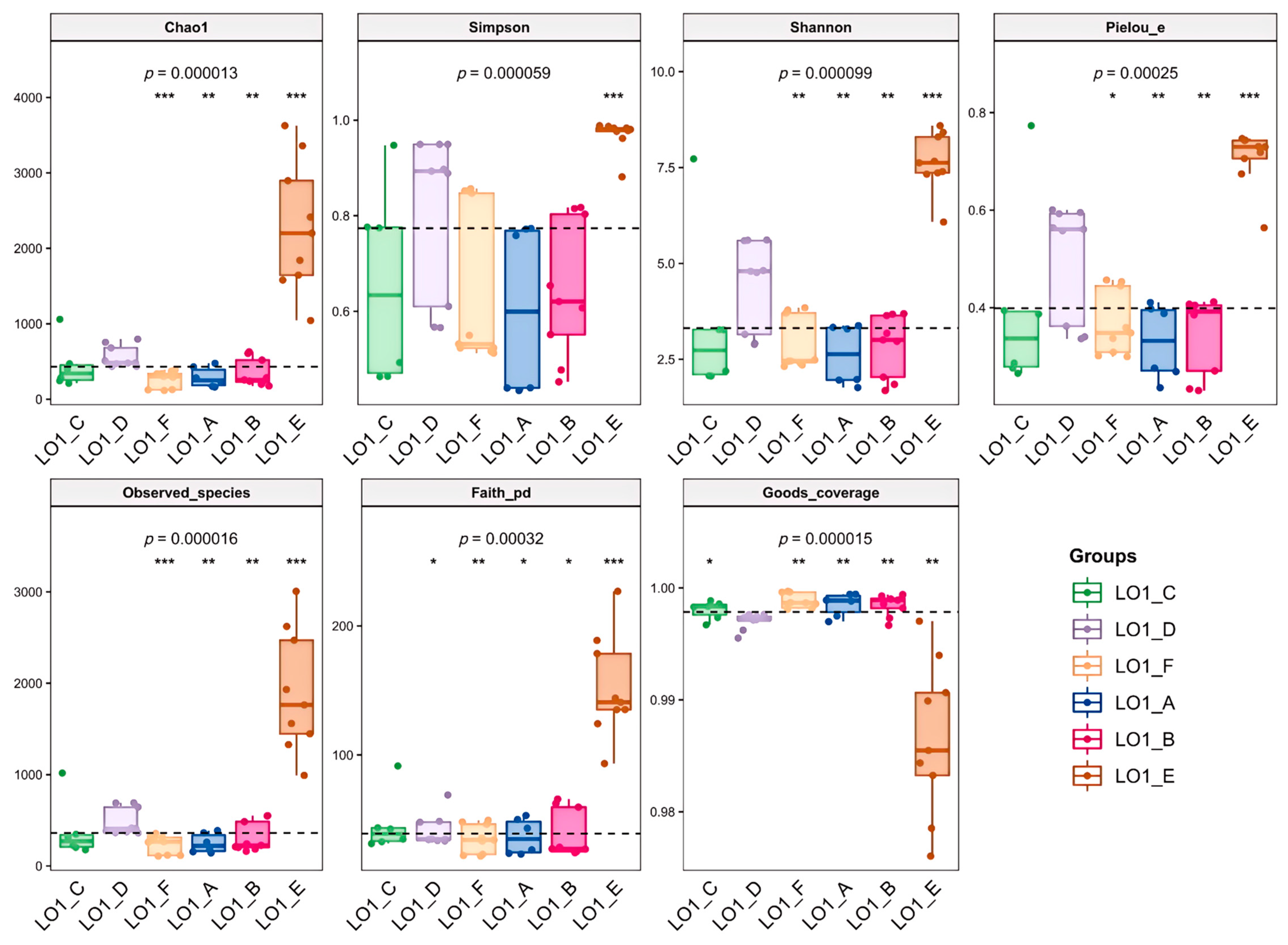
3.1. Comparison of Diversity of Marine Bacterial Populations
3.2. Functional Prediction of Bacterial Populations
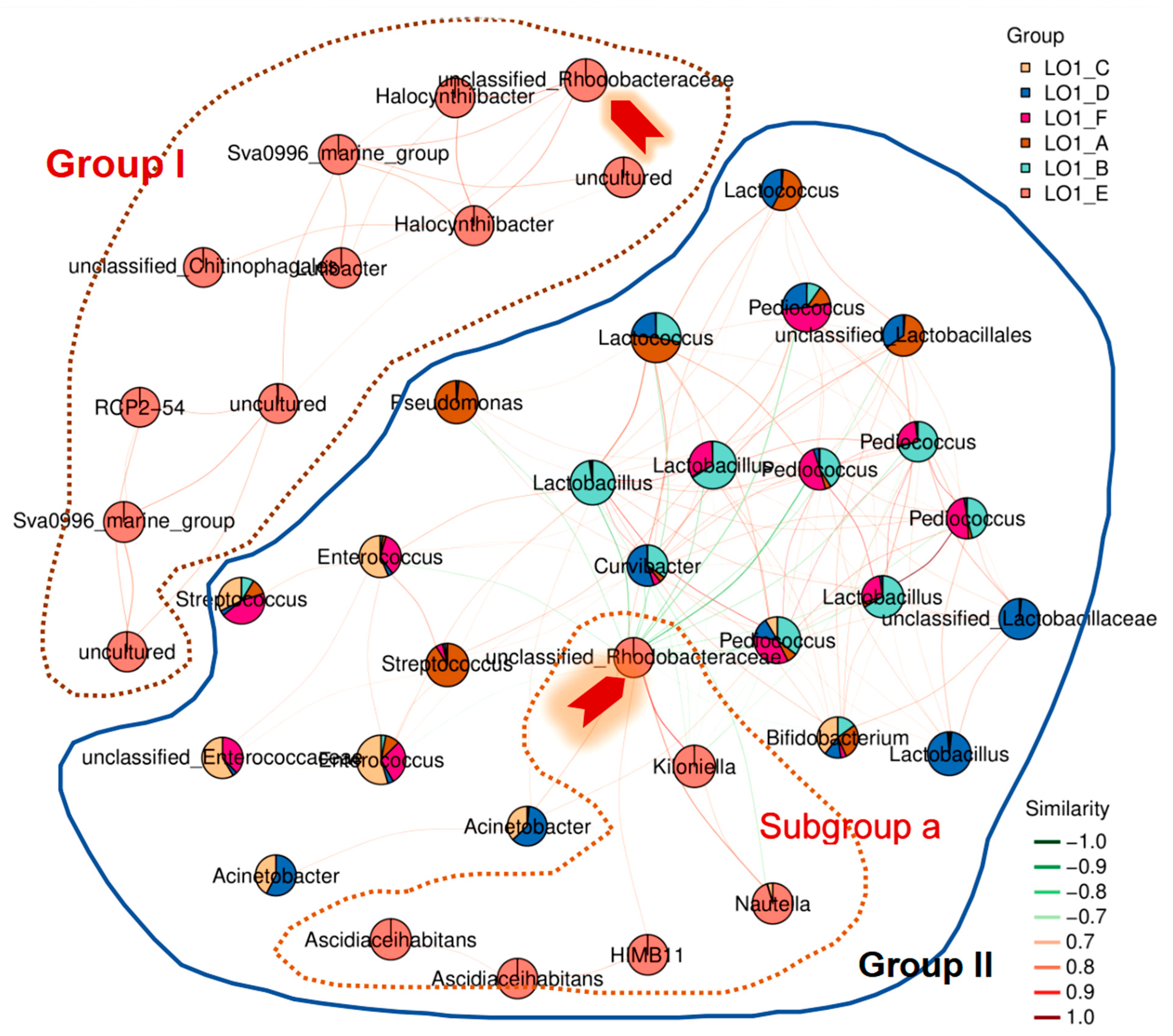
3.3. Characterization of the Keystone Species in the Microbial Populations in S1 Station
3.4. Phylogenetic Characterization of Cultivable Bacterial Strains of S1 Station
3.5. Bioactivity Measurement of Isolated Bacterial Strains
3.6. Culture Optimization of IAA Production by Strain S1-TA-50
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABI | Algae-Bacteria Interactions |
| ASV | Amplicon Sequence Variant |
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| CECS | Combinational Enhanced Cultivation Strategy |
| CTD | Conductivity, Temperature and Depth |
| DMSO | Dimethyl Sulfoxide |
| ECS | East China Sea |
| HABs | Harmful Algal Blooms |
| HPLC | High Performance Liquid Chromatograph |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| MA | Marine Agar |
| MB | Marine Broth |
| MGP | Microalgae Growth-Promoting |
| MIC | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration |
| IAA | Indole-3-Acetic Acid |
| OD | Optical Density |
| OPLS-DA | Orthogonal Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PHA | Polyhydroxyalkanoate |
| PM | Phycosphere Microbiota |
| SD | Stand Deviation |
References
- Landry, Z.C.; Vergin, K.; Mannenbach, C.; Block, S.; Yang, Q.; Blainey, P.; Carlson, C.; Giovannoni, S. Optofluidic Single-Cell Genome Amplification of Sub-micron Bacteria in the Ocean Subsurface. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigo, K.R. Marine microorganisms and global nutrient cycles. Nature 2005, 437, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietra, F. Secondary metabolites from marine microorganisms: Bacteria, protozoa, algae and fungi. achievements and prospects. NatProd. Rep. 1997, 14, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunagawa, S.; Coelho, L.P.; Chaffron, S.; Kultima, J.R.; Labadie, K.; Salazar, G.; Djahanschiri, B.; Zeller, G.; Mende, D.R.; Alberti, A. Structure and function of the global ocean microbiome. Science 2015, 348, 1261359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, G.M.; Kehraus, S.; Seibert, S.F.; Abdel-Lateff, A.; Müller, D. Natural products from marine organisms and their associated microbes. Chembiochem. 2006, 7, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wasserstrom, H.; Kublik, S.; Wasserstrom, R.; Schulz, S.; Schloter, M.; Steinberger, Y. Bacterial populations composition in costal dunes of the Mediterranean along a gradient from the sea shore to the inland. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Juarez, D.L.; Pan, J.F.; Blinebry, S.K.; Gronniger, J.; Clark, J.S.; Johnson, Z.I.; Hunt, D.E. Microbial communities across nearshore to offshore coastal transects are primarily shaped by distance and temperature. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 3862–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, K.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C.; McMinn, A.; Wang, M.; Wang, H. Environmental gradients shape microbiome assembly and stability in the East China sea. Environ. Res. 2023, 238, 117197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, S.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, C.; Li, S. High Throughput Sequencing Reveals Distinct bacterial populations and Functional Diversity in Two Typical Coastal Bays. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1878. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Jiang, R.; Zhang, J.; Li, K.; Zhang, J.; Shao, L.; He, W.; He, P. The impact of IMTA on the spatial and temporal distribution of the surface planktonic bacteria populations in the surrounding sea area of Xiasanhengshan Island of the East China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xie, P.; Dai, J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X. Variation in Structure and Functional Diversity of Surface Bacterioplankton populations in the Eastern East China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.A.; Hmelo, L.R.; van Tol, H.M.; Durham, B.P.; Carlson, L.T.; Heal, K.R.; Morales, R.L.; Berthiaume, C.T.; Parker, M.S.; Djunaedi, B. Interaction and signalling between a cosmopolitan phytoplankton and associated bacteria. Nature 2015, 522, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Tian, X.Q.; Ma, L.Y.; Feng, B.; Liu, Q.H.; Yuan, L.D. Biodiversity of the symbiotic bacteria associated with toxic marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. J. Biosci. Med. 2015, 3, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Moran, M.A. Evolutionary ecology of the marine Roseobacter clade. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2014, 78, 573–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steichen, S.A.; Gao, S.; Waller, P.; Brown, J.K. Association between algal productivity and phycosphere composition in an outdoor Chlorella sorokiniana reactor based on multiple longitudinal analyses. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 1546–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Chen, B.; Yang, Y.; Yi, X.; Wei, M.; Ecklu-Mensah, G.; Buschmann, M.M.; Liu, H.; Gao, J.; Liang, W.; et al. Multi-omics analyses of airway host-microbe interactions in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease identify potential therapeutic interventions. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 1361–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, W.H.; Tahon, G.; Geesink, P.; Sousa, D.Z.; Ettema, T.J.G. Innovations to culturing the uncultured microbial majority. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappé, M.S.; Connon, S.A.; Vergin, K.L.; Giovannoni, S.J. Cultivation of the ubiquitous SAR11 marine bacterioplankton clade. Nature 2002, 418, 630–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Dai, J.; Zhang, L.; Feng, L.; Tian, X.; Yang, Q. Taxonomic, Phylogenomic and Bioactivity Profiling of Novel Phycosphere Bacterium from Model Cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus PCC7942. Marine Drugs 2024, 22, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Pan, Z.K.; Zhang, J.K.; Liu, B.Q.; Yang, Q. Phycobacteria Biodiversity, Selected Isolation, and Bioactivity Elucidation of New Bacterial Species of Highly Toxic Marine Dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum amtk4. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Ge, Y.M.; Iqbal, N.M.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.L. Sulfitobacter alexandrii sp. nov., a new microalgae growth-promoting bacterium with exopolysaccharides bioflocculanting potential isolated from marine phycosphere. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2021, 114, 1091–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, R.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, X. Haliea alexandrii sp. nov.; isolated from phycosphere microbiota of the toxin-producing dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, B.P.; Gao, J.J.; Sheng, Z.; Xue, Q.P.; Zhang, X.L. Marinobacter alexandrii sp. nov.; a novel yellow-pigmented and algae growth-promoting bacterium isolated from marine phycosphere microbiota. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2021, 114, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.Z.; Gao, H.M.; Dai, J.; Zhu, W.Z.; Xu, F.F.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Yang, Q. Taxonomic and Bioactivity Characterizations of Mameliella alba Strain LZ-28 Isolated from Highly Toxic Marine Dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella LZT09. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Li, G.X.; Ge, Y.M.; Iqbal, N.M.; Yang, X.; Cui, Z.D.; Yang, Q. Sphingopyxis microcysteis sp. nov., a novel bioactive exopolysaccharides-bearing Sphingomonadaceae isolated from the Microcystis phycosphere. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2021, 114, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, A.; Mohamed, A.R.; Amin, S.A. Rhodobacteraceae are key players in microbiome assembly of the diatom Asterionellopsis glacialis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 90, e0057024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roager, L.; Kempen, P.J.; Bentzon-Tilia, M.; Sonnenschein, E.C.; Gram, L. Impact of host species on assembly, composition, and functional profiles of phycosphere microbiomes. Msystems 2024, 9, e0058324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zang, Y.; Fan, S.; Miao, X.; Fu, M.; Ma, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, J. Changes in the structure of the microbial community within the phycospheric microenvironment and potential biogeochemical effects induced in the demise stage of green tides caused by Ulva prolifera. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1507660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; He, J.; Yan, H.; Hou, D.; Zhang, D.; Liu, L.; Wang, K. Seasonality in spatial turnover of Bacterioplankton along an ecological gradient in the East China Sea: Biogeographic patterns, processes and drivers. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Bao, Y.; Li, K.; Yang, N.; He, P.; He, C.; Liu, J. The diversity of planktonic bacteria driven by environmental factors in different mariculture areas in the East China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 201, 116136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunagawa, S.; Acinas, S.G.; Bork, P.; Bowler, C.; Tara Oceans Coordinators; Eveillard, D.; Gorsky, G.; Guidi, L.; Iudicone, D.; Karsenti, E.; et al. Tara Oceans: Towards global ocean ecosystems biology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 428–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, M.; Beiko, R.G. 16S rRNA Gene Analysis with QIIME2. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1849, 113–129. [Google Scholar]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustavsson, E.K.; Zhang, D.; Reynolds, R.H.; Garcia-Ruiz, S.; Ryten, M. ggtranscript: An R package for the visualization and interpretation of transcript isoforms using ggplot2. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 3844–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Xu, S.; Wu, Q.; Wu, D.; Zhan, L.; Liao, Y.; Mai, Y.; Zheng, M.; Wang, S.; et al. EasyMultiProfiler: An efficient multi-omics data integration and analysis workflow for microbiome research. Sci. China Life Sci. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bylesjö, M.; Rantalainen, M.; Cloarec, O.; Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Trygg, J. OPLS discriminant analysis: Combining the strengths of PLS-DA and SIMCA classification. J. Chemom. 2006, 20, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2011, 3, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of pathways and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D587–D592. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caspi, R.; Billington, R.; Keseler, I.M.; Kothari, A.; Krummenacker, M.; Midford, P.E.; Ong, W.K.; Paley, S.; Subhraveti, P.; Karp, P.D. The MetaCyc database of metabolic pathways and enzymes—A 2019 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D445–D453. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Xue, Y.; Yang, Q.; Xing, W.; Zhu, S.; Jiang, W.; Liu, J. Benzalkonium chloride disinfection increases the difficulty of controlling foodborne pathogens identified in aquatic product processing. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 488, 137140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, B.; Debode, F.; Hautier, L.; Hulin, J.; Martin, G.S.; Delvaux, A.; Janssen, E.; Mingeot, D. A detailed workflow to develop QIIME2-formatted reference databases for taxonomic analysis of DNA metabarcoding data. BMC Genom. Data 2022, 23, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.Z.; Wang, S.H.; Gao, H.M.; Ge, Y.M.; Dai, J.; Zhang, X.L.; Yang, Q. Characterization of Bioactivities and Biosynthesis of Angucycline/Angucyclinone Derivatives Derived from Gephyromycinifex aptenodytis gen. nov., sp. nov. Mar. Drugs 2021, 20, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.M. Determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2001, 48, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathom-Aree, W.; Sattayawat, P.; Inwongwan, S.; Cheirsilp, B.; Liewtrakula, N.; Maneechote, W.; Rangseekaew, P.; Ahmad, F.; Mehmood, M.A.; Gao, F.; et al. Microalgae growth-promoting bacteria for cultivation strategies: Recent updates and progress. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 286, 127813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szkop, M.; Bielawski, W. A simple method for simultaneous RP-HPLC determination of indolic compounds related to bacterial biosynthesis of indole-3-acetic acid. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2013, 103, 683–691. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, W.; Yang, W.; Zhang, H.; Qian, X.; Sun, K.; Yang, Q.; Shen, X.; Zhang, L. Autoinducer-2 enhances defence of Vibrio furnissii against oxidative stress and DNA damage by modulation of c-di-GMP signaling via a two-component system. mBio 2025, 16, e0292224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duca, D.R.; Glick, B.R. Indole-3-acetic acid biosynthesis and its regulation in plant-associated bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 8607–8619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, T.M.; Bui, X.D.; Trang, L.V.K.; Le, T.M.; Nguyen, M.L.; Trinh, D.M.; Phuong, N.T.D.; Khoo, K.S.; Chew, K.W.; Show, P.L. Isolation of indole-3-acetic acid-producing Azospirillum brasilense from Vietnamese wet rice: Co-immobilization of isolate and microalgae as a sustainable biorefinery. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 349, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duca, D.; Lorv, J.; Patten, C.L.; Rose, D.; Glick, B.R. Indole-3-acetic acid in plant-microbe interactions. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2014, 106, 85–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, D.M.; Sachdeva, R.; Fuhrman, J.A. Ecological dynamics and co-occurrence among marine phytoplankton, bacteria and myoviruses shows microdiversity matters. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1614–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, Y.; Abe, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Shimada, Y.; Saito, H.; Oikawa, H.; Yano, Y.; Satomi, M. Sulfitobacter porphyrae sp. nov., isolated from the red alga Porphyra yezoensis. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbir, H. Updating the Relationship Between the Threshold Value of Average Nucleotide Identity and Digital DNA-DNA Hybridization for Reliable Taxonomy of Corynebacterium. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.N.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Du, Z.J.; Wang, M.Y. Sulfitobacter algicola sp. nov.; isolated from green algae. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 2351–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Lai, Q.; Luo, Q.; Jiang, S.; Zhu, R.; Liang, J.; Gao, Y. Sulfitobacter pseudonitzschiae sp. nov., isolated from the toxic marine diatom Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Jung, Y.T.; Won, S.M.; Park, J.M.; Yoon, J.H. Sulfitobacter undariae sp. nov., isolated from a brown algae reservoir. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 1672–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, Y.; Abe, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Satomi, M. Sulfitobacter pacificus sp. nov., isolated from the red alga Pyropia yezoensis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2015, 107, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chen, S.; Bai, X.; Ma, X.; Xie, Z.; Xu, H. Effect and mechanism of the algicidal bacterium Sulfitobacter porphyrae ZFX1 on the mitigation of harmful algal blooms caused by Prorocentrum donghaiense. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, T.; Hou, C.; Zhao, X.; Zhong, Y.; Guan, C.; Lin, Z.; Tang, X.; Wang, Y. Bacteria associated with Ulva prolifera: A vital role in green tide formation and migration. Harmful Algae 2021, 108, 102104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiralas, R.; Ozer, N.; Segev, E. Abundant Sulfitobacter marine bacteria protect Emiliania huxleyi algae from pathogenic bacteria. ISME Commun. 2023, 3, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, N.E.; Kimbrel, J.A.; Samo, T.J.; Siccardi, A.J.; Stuart, R.K.; Mayali, X. A bloom of a single bacterium shapes the microbiome during outdoor diatom cultivation collapse. MSystems 2025, 10, e0037525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Liu, Q.; Duan, C.; Li, J.; Sun, H.; Xu, L.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Shen, X.; Zhang, L. c-di-GMP inhibits the DNA binding activity of H-NS in Salmonella. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, M.; Rahbar, M.R.; Negahdaripour, M. Interaction of indole-3-acetic acid with horseradish peroxidase as a potential anticancer agent: From docking to molecular dynamics simulation. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 4188–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Li, X.; Tong, M.; Tong, M.; Wu, J.; Chan, L.L.; Cai, Z.; Zhou, J. Indole-3-acetic acid as a cross-talking molecule in algal-bacterial interactions and a potential driving force in algal bloom formation. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 4, 1236925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Tested Strains | Antibacterial Activity (MIC, µg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. subtilis | S. aureus | C. albicans | E. coli | |
| S1-TA-3 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| S1-TA-41 | 25.4 | 15.6 | 12.8 | 10.7 |
| S1-TA-44 | 22.1 | 16.7 | 10.5 | 9.8 |
| S1-TA-50 | 12.3 | 3.3 | 5.4 | 3.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Q.; Ouyang, B.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X. Microbial Diversity, Selective Isolation and Bioactivity Characterization of Bacterial Populations in Eutrophic Seawater of Coastal East China Sea. Diversity 2025, 17, 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17100727
Yang Q, Ouyang B, Liu B, Zhang X. Microbial Diversity, Selective Isolation and Bioactivity Characterization of Bacterial Populations in Eutrophic Seawater of Coastal East China Sea. Diversity. 2025; 17(10):727. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17100727
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Qiao, Bowen Ouyang, Bingqian Liu, and Xiaoling Zhang. 2025. "Microbial Diversity, Selective Isolation and Bioactivity Characterization of Bacterial Populations in Eutrophic Seawater of Coastal East China Sea" Diversity 17, no. 10: 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17100727
APA StyleYang, Q., Ouyang, B., Liu, B., & Zhang, X. (2025). Microbial Diversity, Selective Isolation and Bioactivity Characterization of Bacterial Populations in Eutrophic Seawater of Coastal East China Sea. Diversity, 17(10), 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17100727







