Effect of Abiotic Factors on Nectar Quality and Secretion of Two Early Spring Species, Galanthus nivalis L. and Helleborus niger L.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
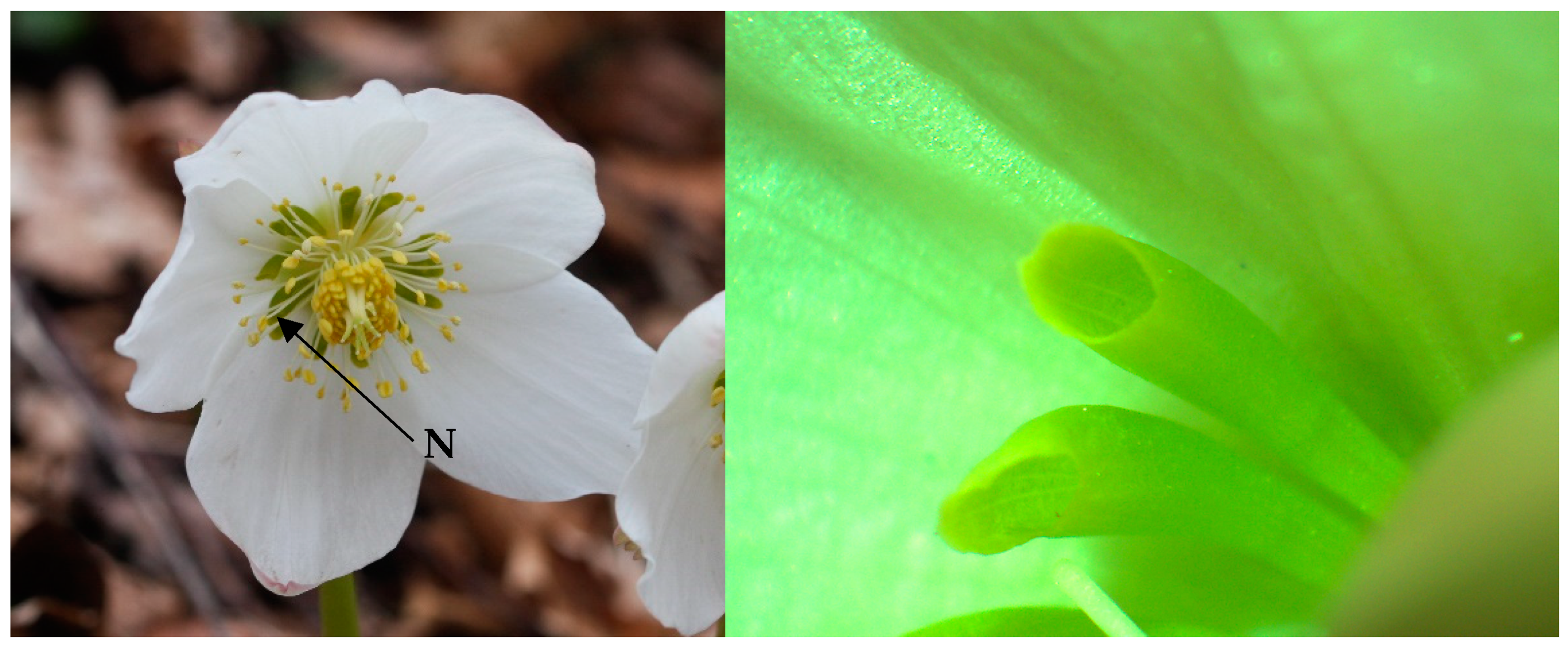
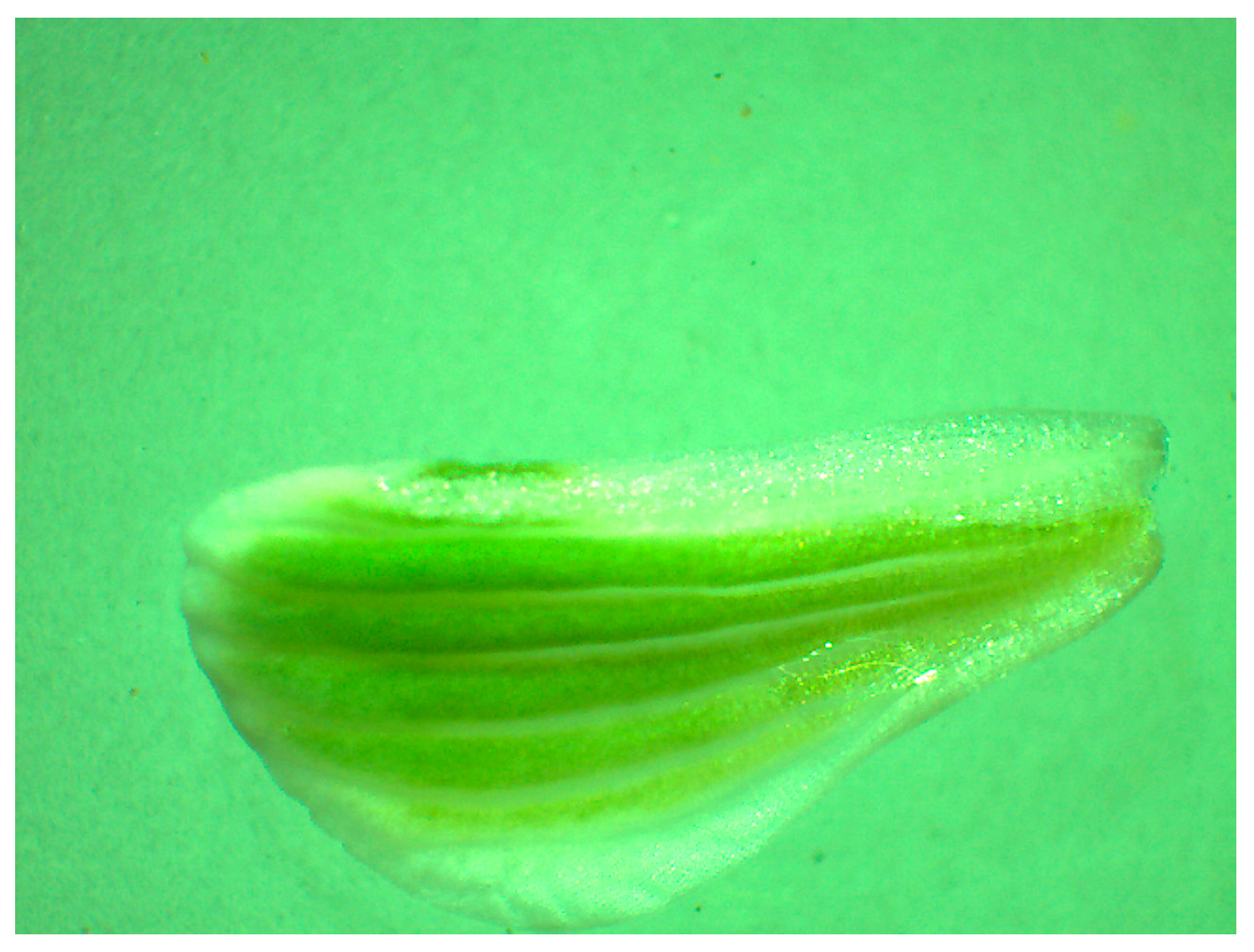
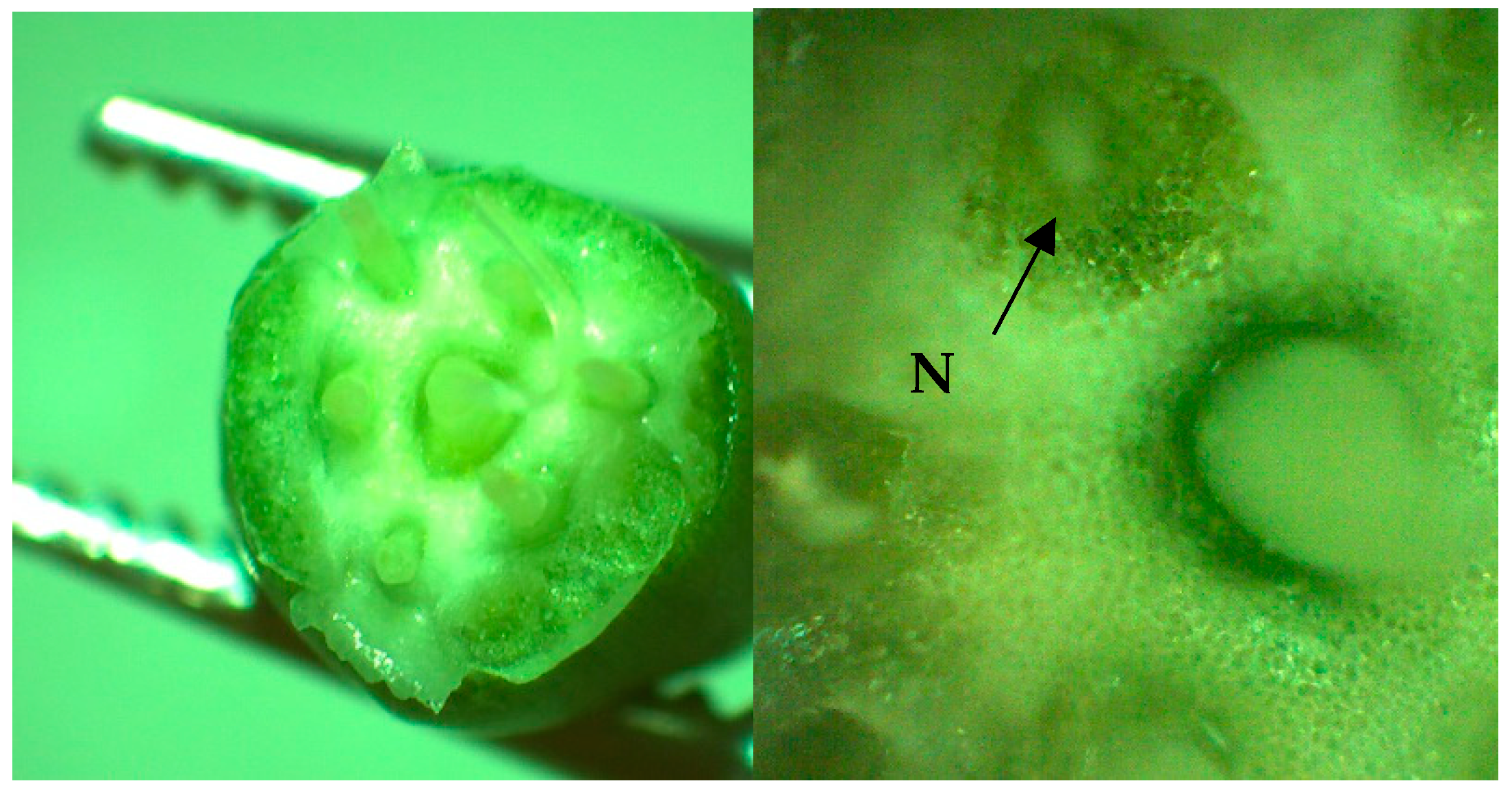
2.1. Researched Plant Species
2.2. Sampling Locations
2.3. Nectar Sampling
2.4. Abiotic Factors Measurements
2.5. Nectar Analysis
2.5.1. Sugar Analysis
2.5.2. Phenolic Compound Analysis
2.5.3. Amino Acid Analysis
2.6. Statistics Analysis
3. Results
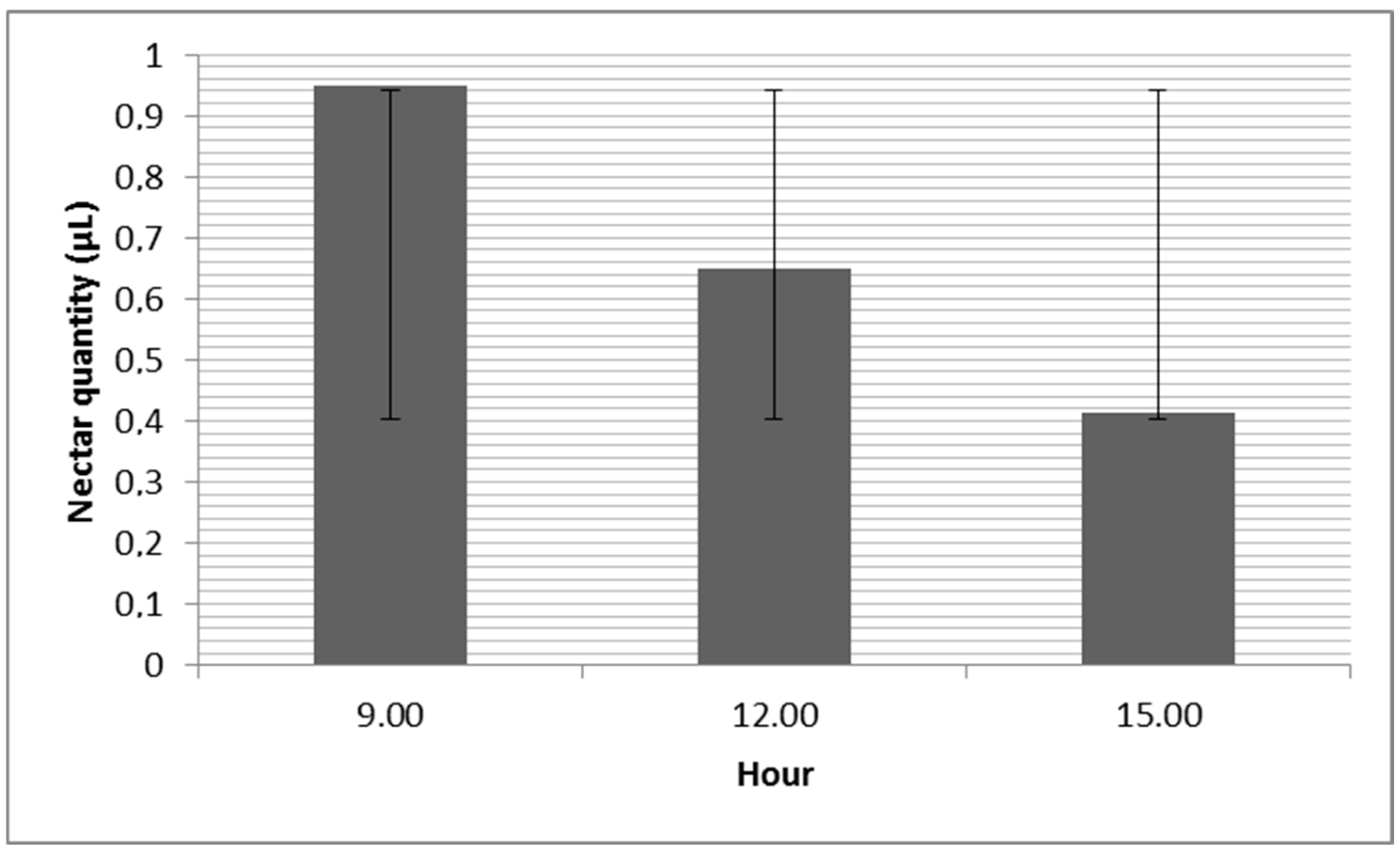
3.1. G. nivalis and H. niger Nectar Secretion through the Day
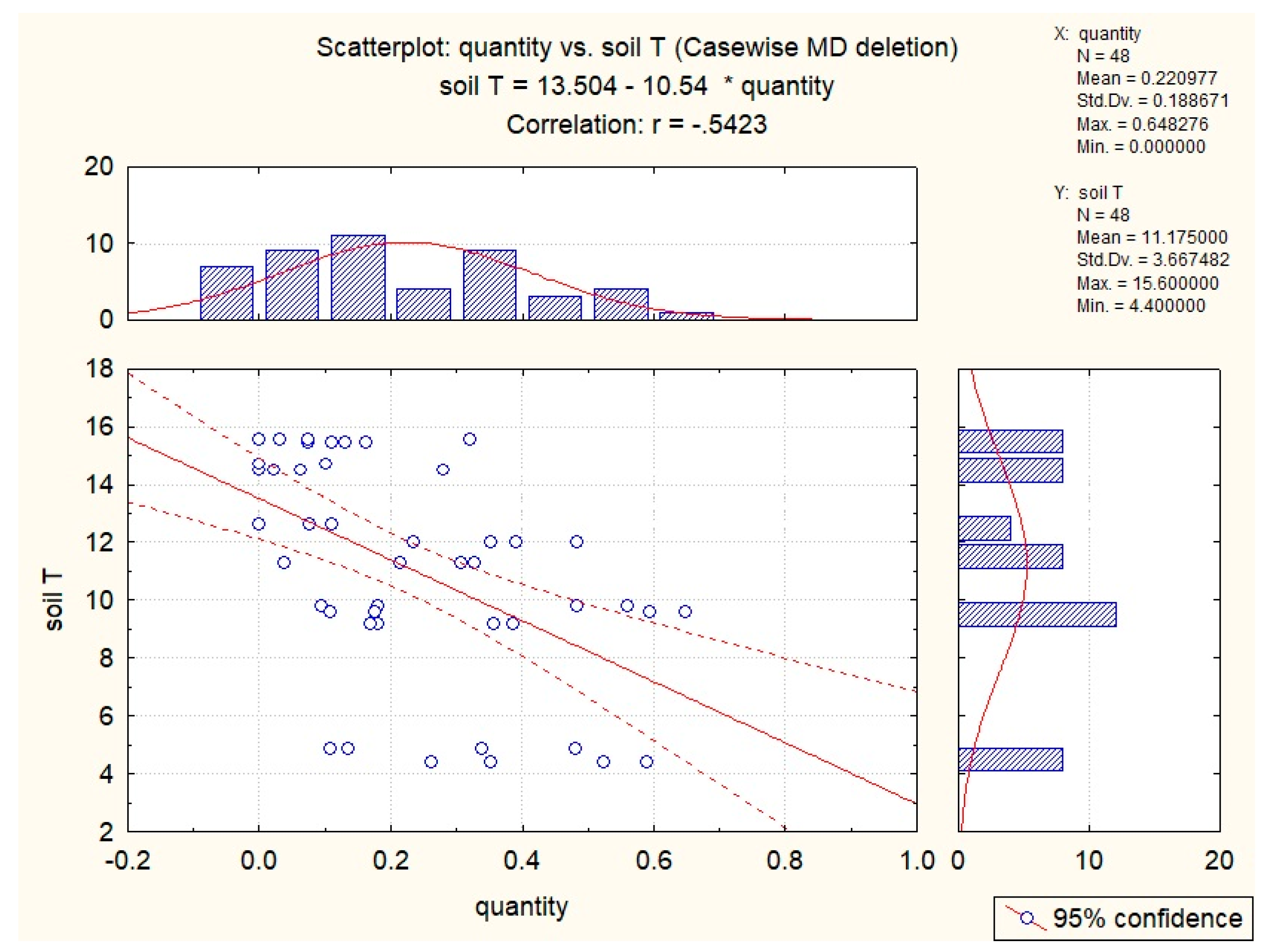
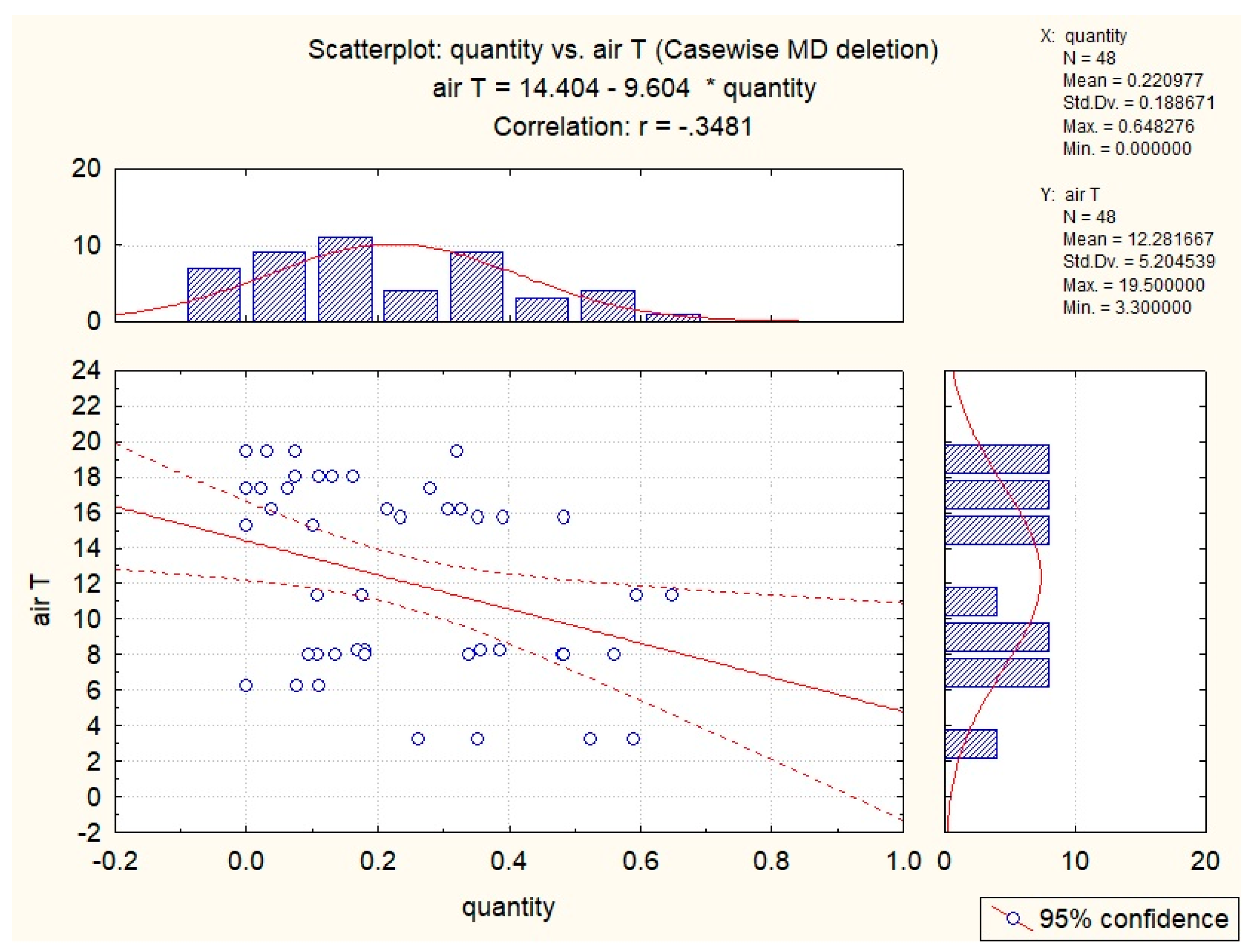
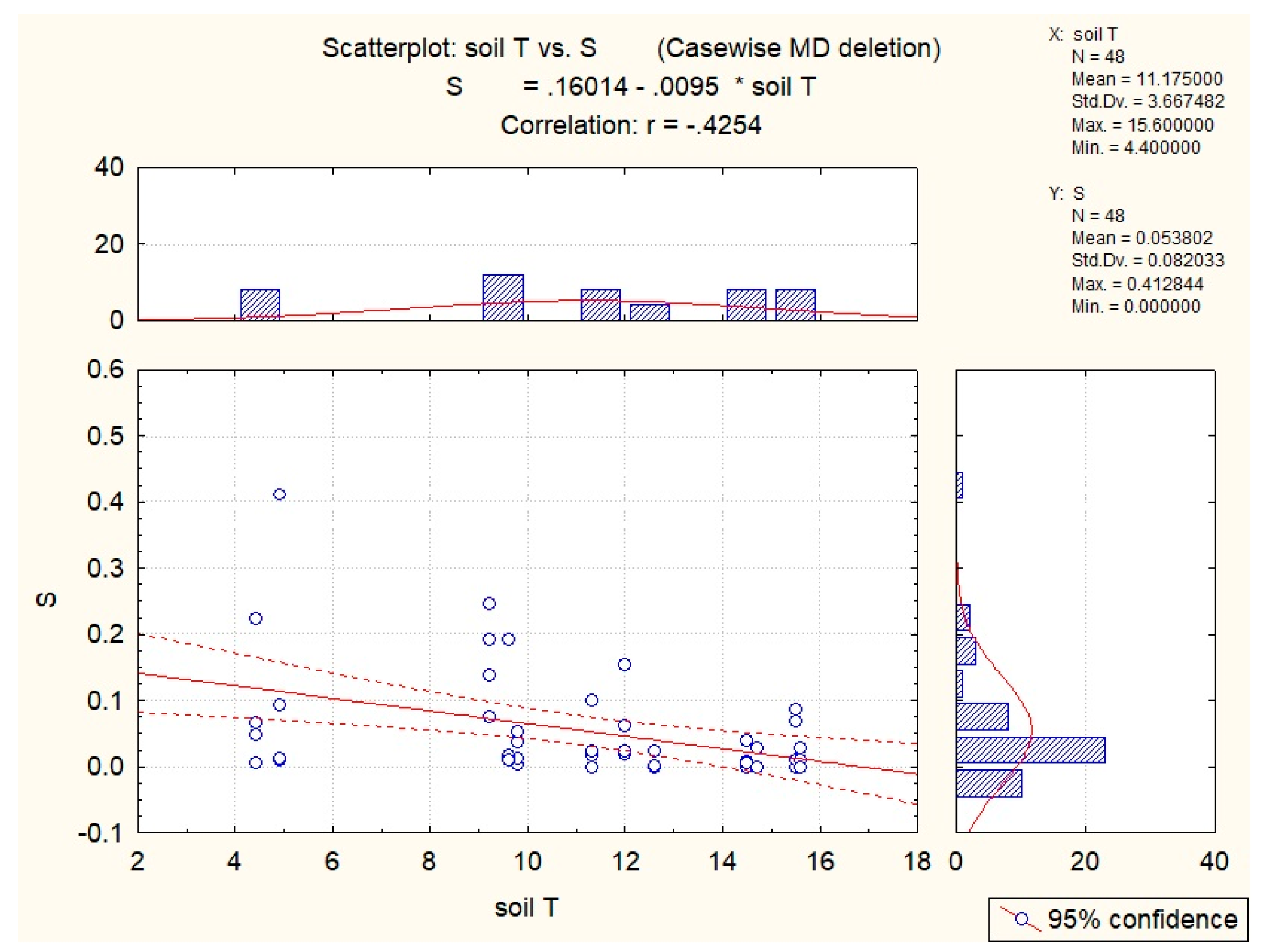
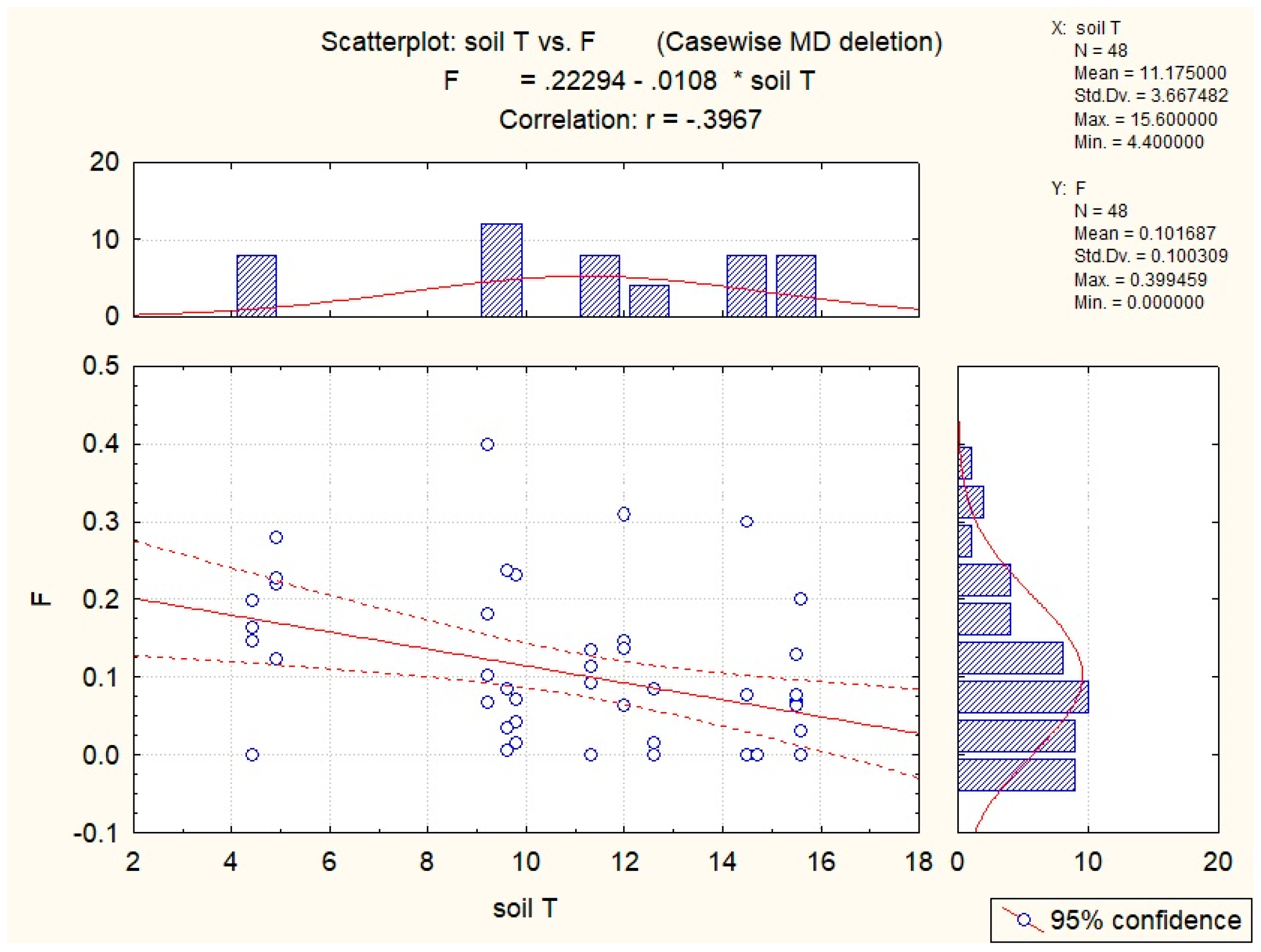
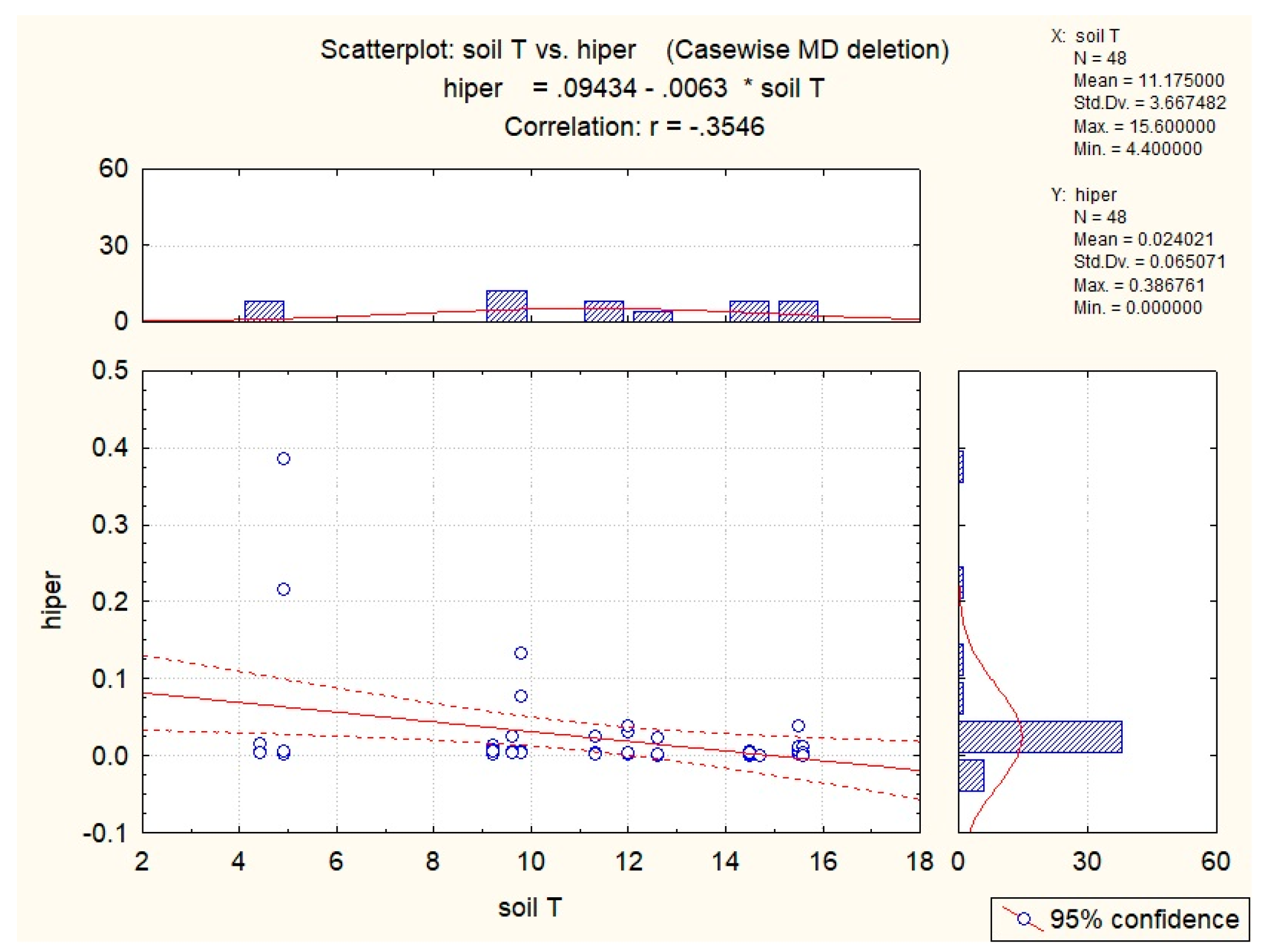
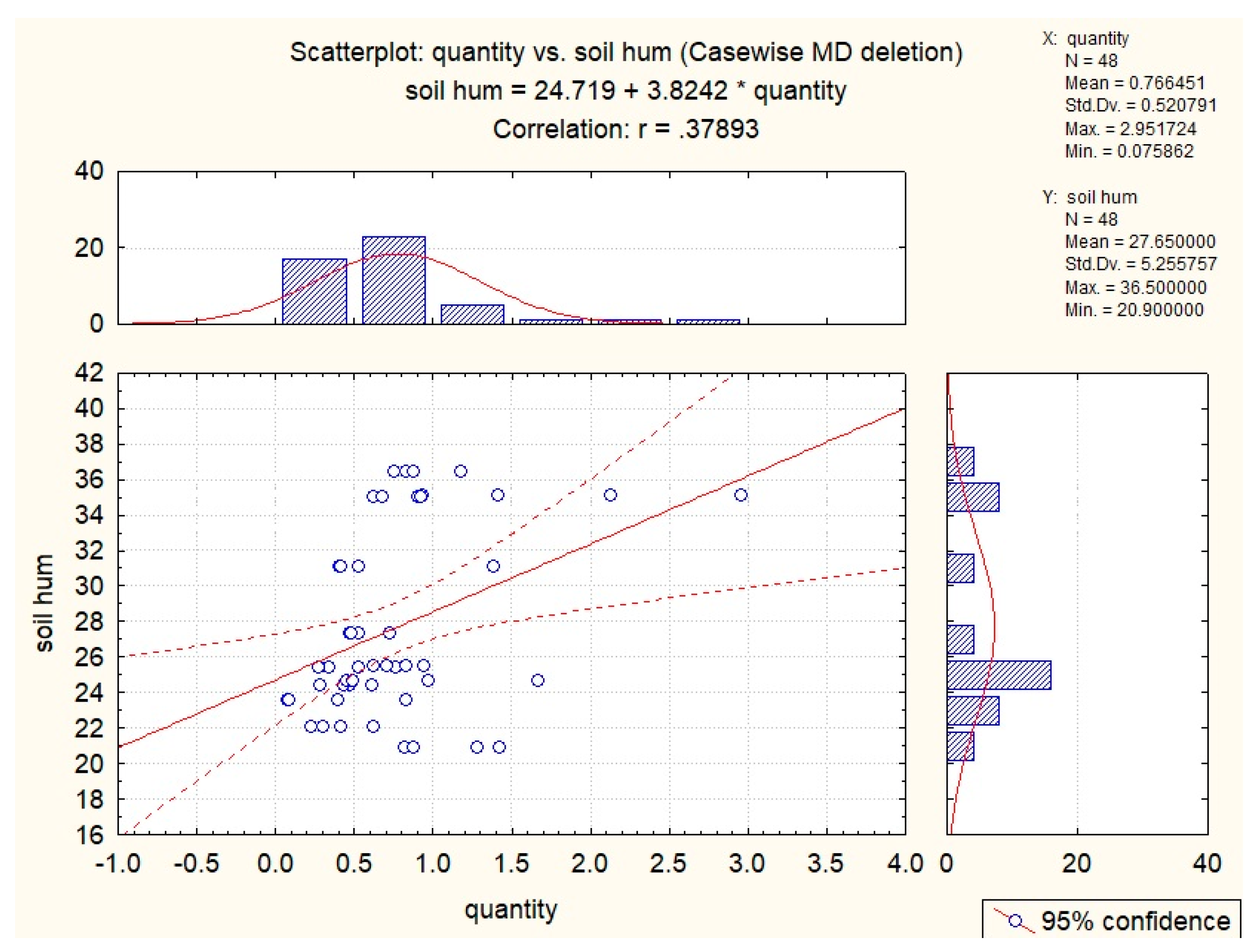
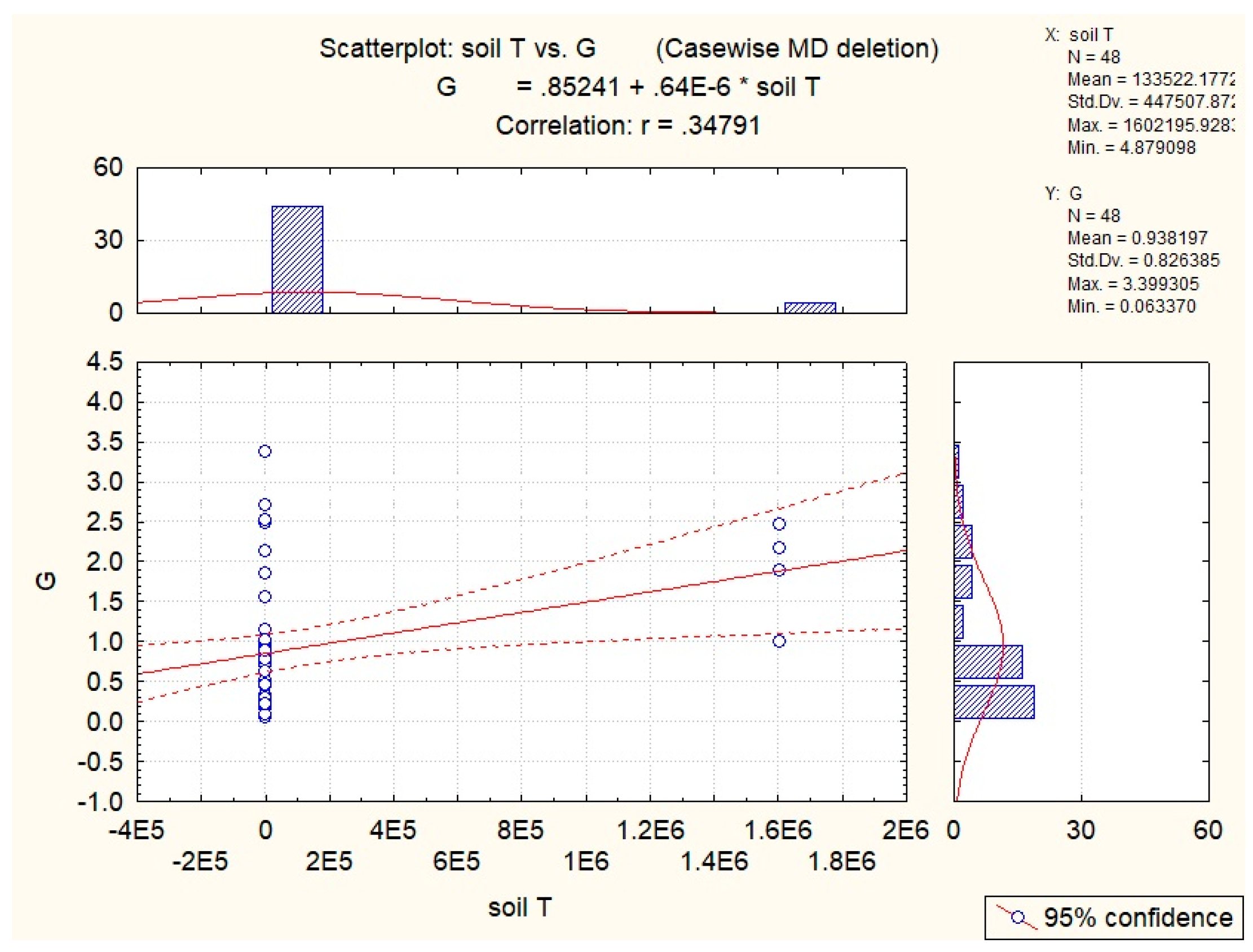
3.2. Abiotic Factors’ Influence on Nectar in G. nivalis and H.niger
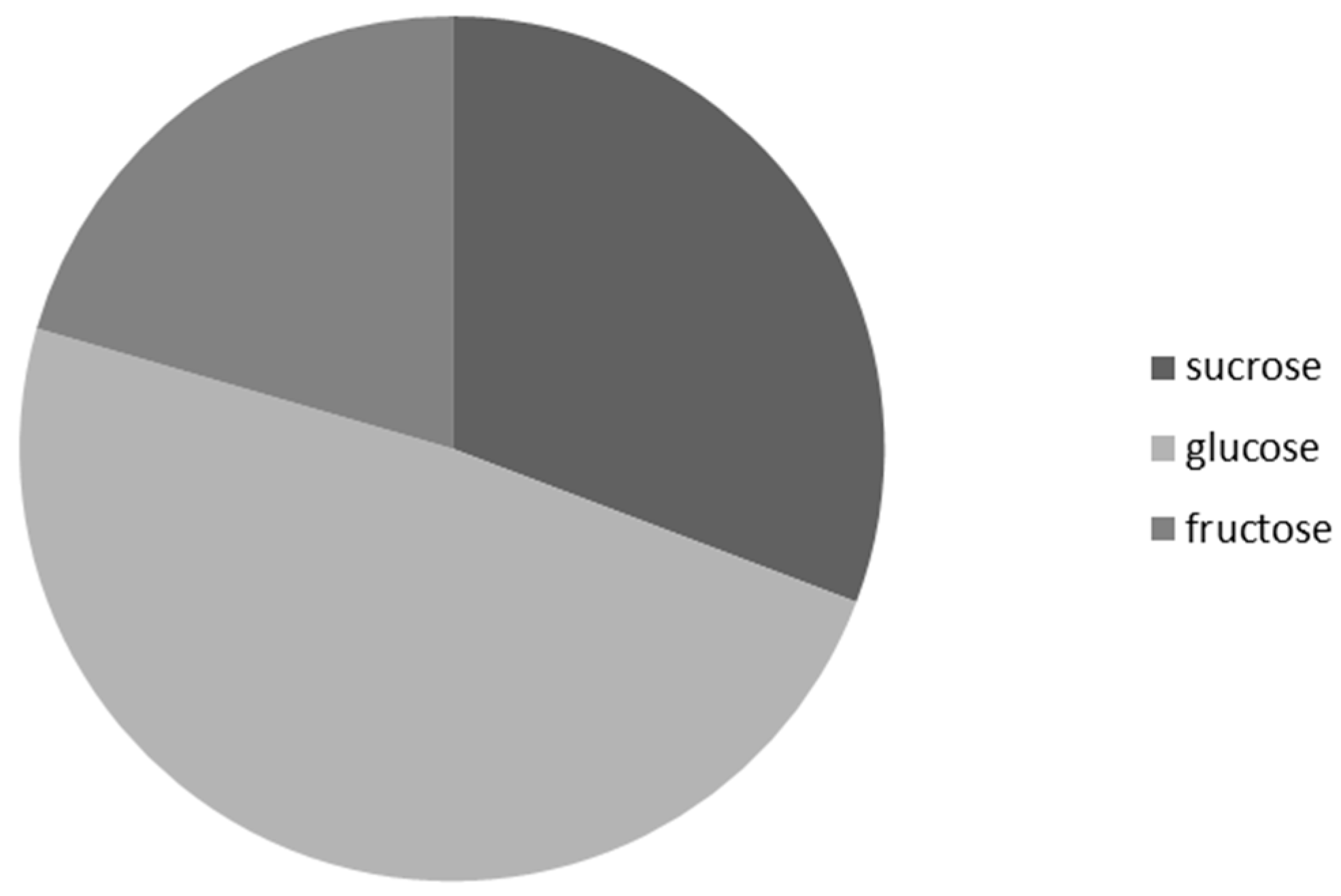
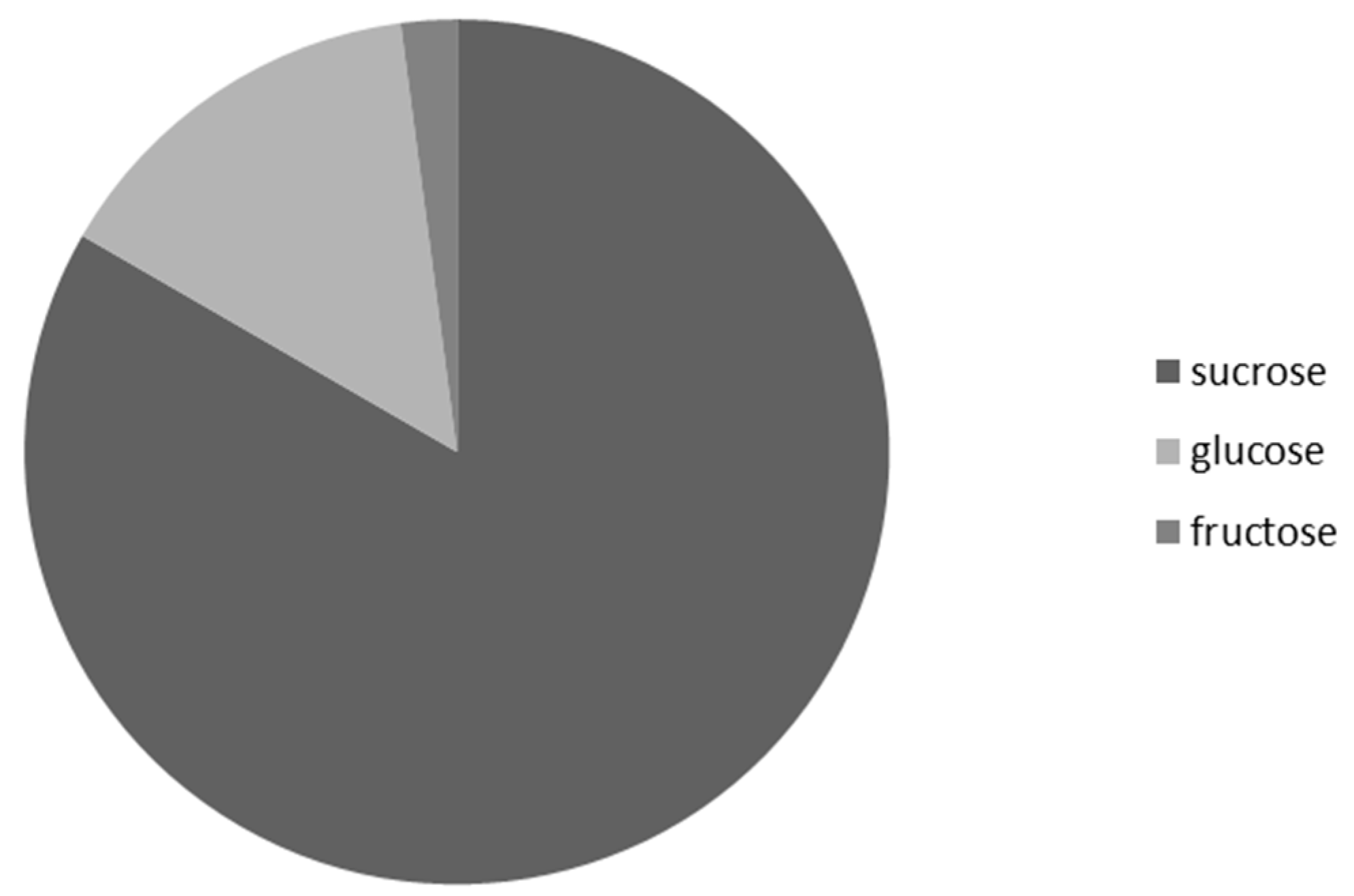
3.3. Frequency of Occurrence of the Most Represented Sugar in Nectar Samples of G. nivalis and H. niger
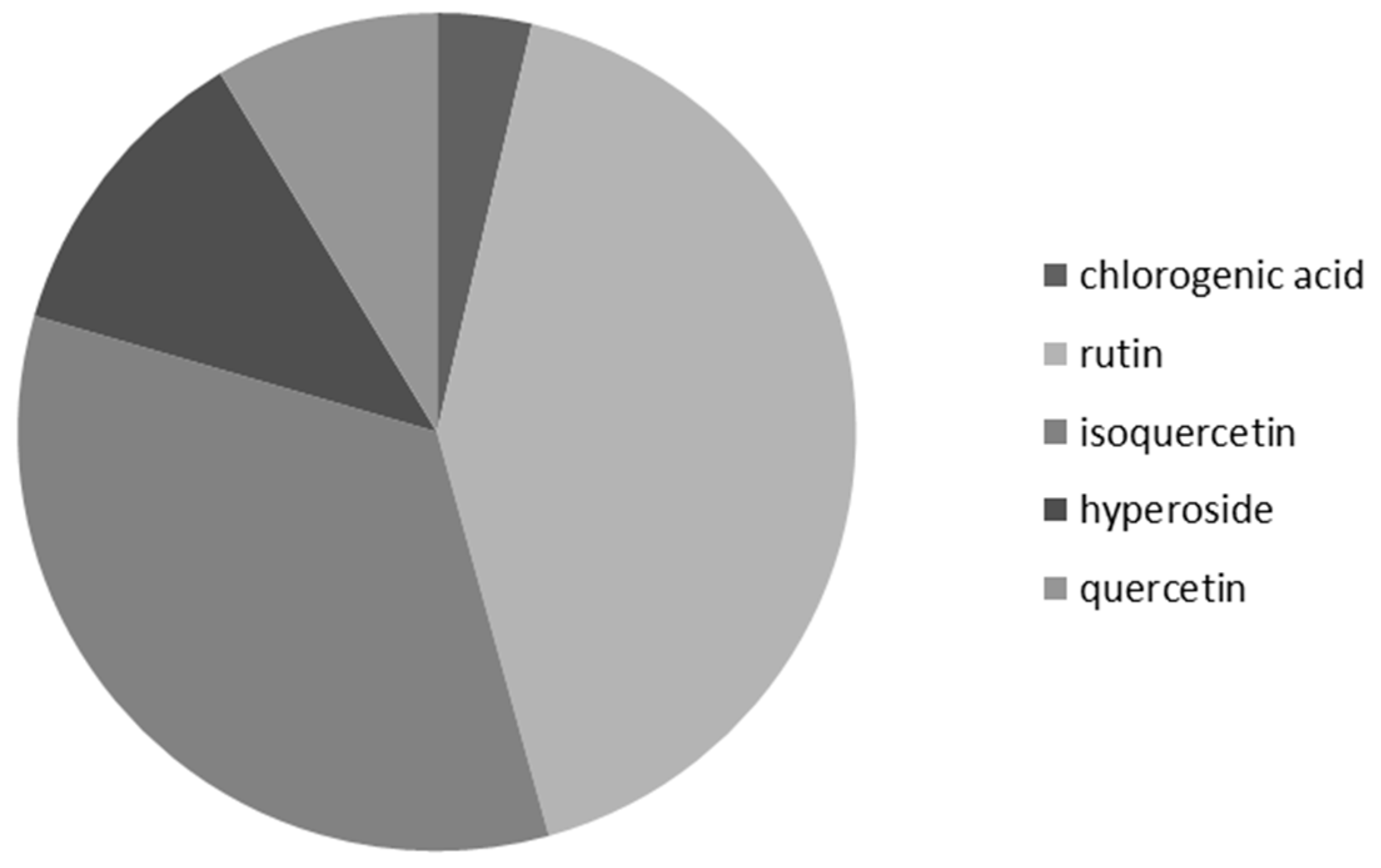
3.4. Frequency of Occurrence of Selected Phenolic Compounds in Nectar Samples of G. nivalis and H. niger
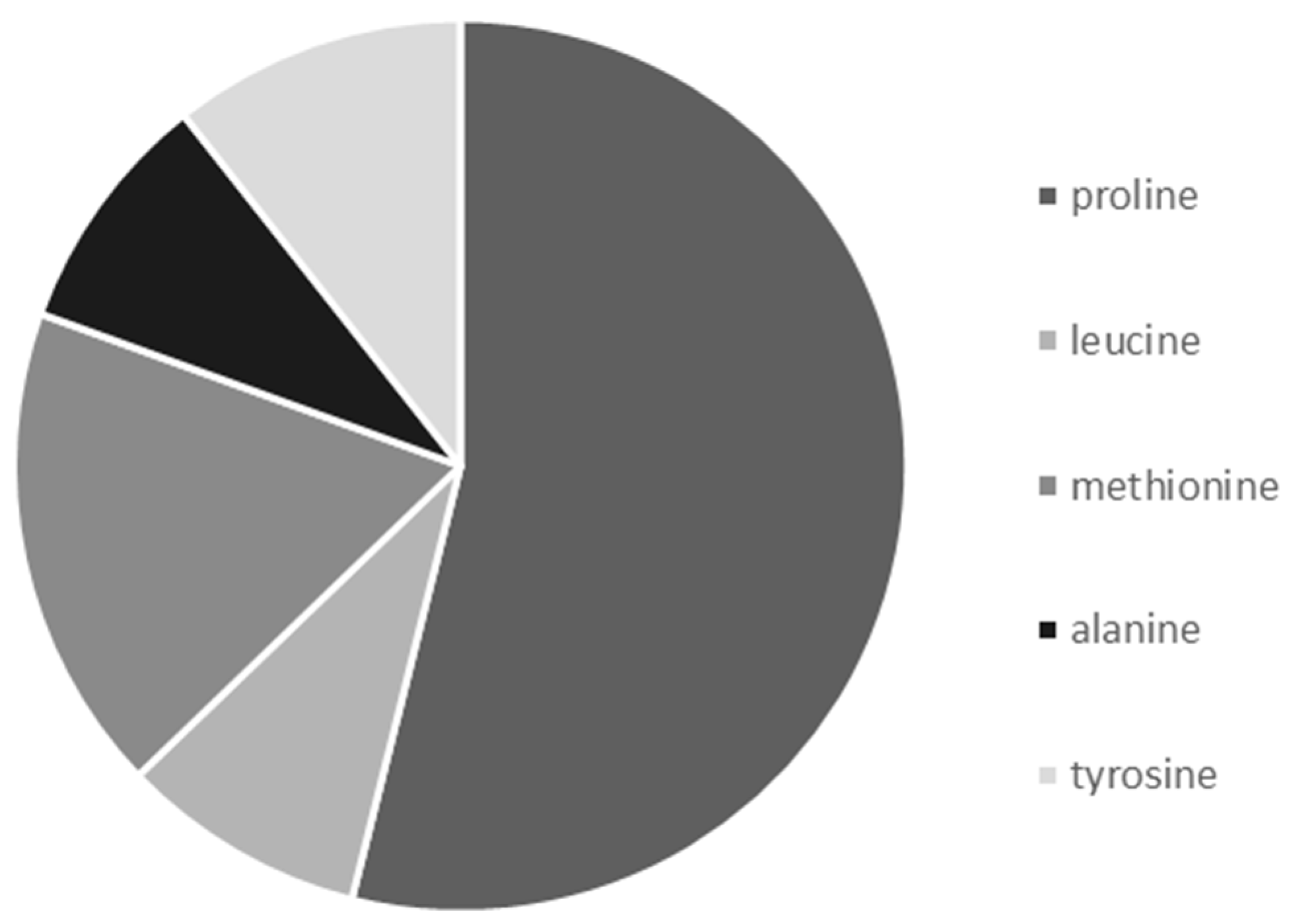
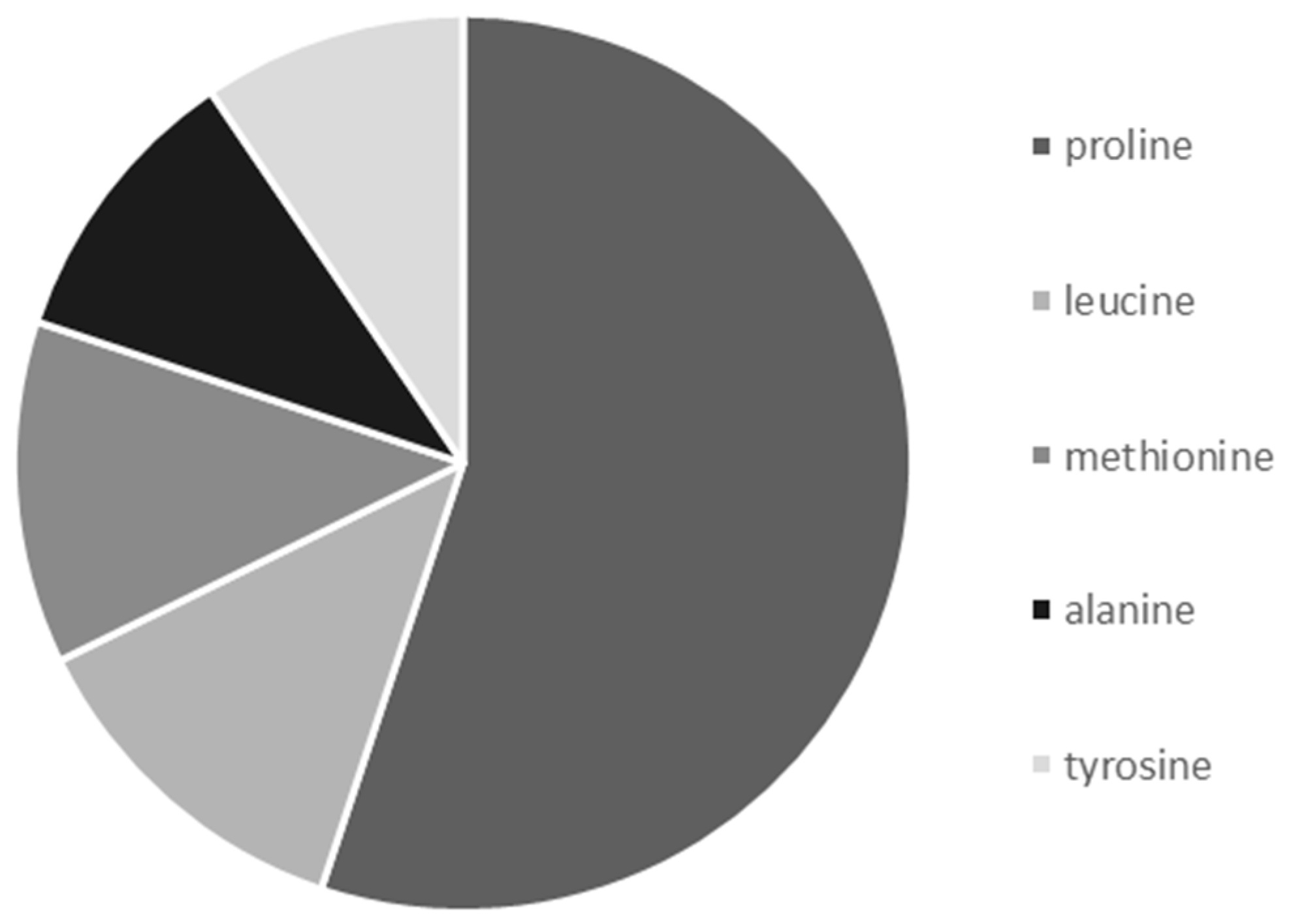
3.5. Frequency of Occurrence of Selected Amino acids in Nectar Samples of G. nivalis and H. niger
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knuth, P. Handbook of Flower Pollination Based upon Herman’s Muller Work, the Fertilisation of Flowers by Insects; The Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1906; 383p. [Google Scholar]
- Kulloli, S.K.; Chandore, A.; Aitawade, M.M. Nectar dynamics and pollination studies in three species of Lamiaceae. Curr. Sci. 2011, 100, 509–516. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, R.; Schmitt, A.J.; Thomas, J.B.; Carter, C.J. Rewiew: Nectar biology: From molecules to ecosystems. Plant Sci. 2017, 262, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepi, M.; Grasso, D.A.; Mancuso, S. Nectar in plant–insect mutualistic relationships: From food reward to partner manipulation. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 10–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, G.; Baker, I. Amino-acids in nectar and their evolutionary significance. Nature 1973, 241, 543–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravnjak, B.; Bavcon, J.; Božič, J. Avtohtone Medovite Rastline; Botanični vrt Univerze v Ljubljani, Oddelek za biologijo, Biotehniška fakulteta = University Botanic Gardens Ljubljana, Department of Biology, Biotechnical Faculty: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2020; 285p. [Google Scholar]
- Vesprini, J.L.; Nepi, M.; Pacini, E. Nectary structure, nectar secretion patterns and nectar composition in two Helleborus species. Plant Biol. 2008, 1, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, F.; Obratov-Petković, D.; Macukanović-Jocić, M. Nectar production in species of the Genus galanthus L. (Amaryllidaceae) from Serbia. Glas. Sumar. Fak. 2014, 109, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šušek, A.; Ivančič, A. Pollinators of Helleborus niger in Slovenian naturally occurring populations. Acta Agric. Slov. 2006, 87, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepi, M. Nectary structure and ultrastructure. In Nectaries and Nectar; Nicolson, S., Nepi, M., Pacini, E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pacini, E.; Nicolson, S.W. Introduction. In Nectaries and Nectar; Nicolson, S., Nepi, M., Pacini, E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Irwin, R.E.; Cook, D.; Richardson, L.L.; Manson, J.S.; Gardner, D.R. Secondary compounds in floral rewards of toxic rangeland plants: Impacts on pollinators. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 7335–7344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantyne, G.; Wilmer, P. Nectar theft and floral ant-repellence: A link between nectar volume and ant-repellent traits? PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrant, D.S.; Schumann, R.; Petit, S. Field methods for sampling and storing nectar from flowers with low nectar volumes. Ann. Bot. 2008, 103, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mačukanović-Jocić, M.; Djurdjević, L. Influence of microclimatic conditions on nectar exudation in Glechoma hirsuta. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2005, 57, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mačukanović Jocić, M.; Duletić-Laušević, S.; Jocic, G. Nectar production in three melliferous species of Lamiaceae in natural and experimental conditions. Acta Vet. 2004, 54, 475–487. [Google Scholar]
- Chalcoff, V.R.; Aizen, M.A.; Galetto, L. Nectar concentration and composition of 26 species from the temperate forest of South America. Ann. Bot. 2006, 97, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, J.; Smith, G.C.; Sack, S.; Cash, A. Variation in nectar volume and composition of Impatiens capensis at the individual, plant, and population levels. Oecologia 1995, 102, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer-Young, E.C.; Farrell, I.W.; Adler, L.S.; Milano, N.J.; Egan, P.A.; Junker, R.R.; Irwin, R.E.; Stevenson, P.C. Chemistry of floral rewards: Intra- and interspecific variability of nectar and pollen secondary metabolites across taxa. Ecol. Monogr. 2019, 89, e01335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kradolfer, U.; Erhardt, A. Nectar secretion patterns in Salvia pratensis L. (Lamiaceae). Flora 1995, 190, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolson, S.W. Nectar consumers. In Nectaries and Nectar; Nicolson, S., Nepi, M., Pacini, E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Petanidou, T. Sugars in Mediterranean Floral Nectars: An Ecological and Evolutionary Approach. J. Chem. Ecol. 2005, 31, 1065–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, H.G.; Baker, I. Floral nectar sugar constituents in relation to pollinator type. In Handbook of Experimental Pollination Ecology; Jones, C.E., Little, R.J., Van Nostrand, R., Eds.; Scientific and Academic Editions: Rosemead, CA, USA, 1983; pp. 117–141. [Google Scholar]
- Scheiner, R.; Page, R.E.; Erber, J. Sucrose responsiveness and behavioral plasticity in honey bees (Apis mellifera). Apidologie 2004, 35, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Gilet, T.; Bush, J.W.M. Optimal concentrations in nectar feeding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16618–16621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petanidou, T. Ecological and evolutionary aspects of oral nectars in Mediterranean habitats. In Nectaries and Nectar; Nicolson, S.W., Nepi, M., Pacini, E., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 343–377. [Google Scholar]
- Adler, L.S. The ecological significance of toxic nectar. Oikos 2000, 91, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertazzini, M.; Forlani, G. Intraspecific variability of floral nectar volume and composition in rapeseed (Brassica napus L. var. oleifera). Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roguz, K.; Bajguz, A.; Chmur, M.; Golebiewska, A.; Roguz, A.; Zych, M. Diverstiy of nectar amino acids in the Fritillaria (Liliaceae) genus: Ecological and evolutionary implications. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagler, J.R.; Buchmann, S.L. Honeybee (Hymenoptera: Apidae) foraging responses to phenolic-rich nectars. J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 1993, 66, 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Bavcon, J.; Eler, K.; Šušek, A. Telohi v Sloveniji; Biotehniška fakulteta: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2012; 201p. [Google Scholar]
- McLewin, W. Helleborus and the Helleborastrum Problem; Wellesley-Cambridge Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019; 309p. [Google Scholar]
- Martinčič, A.; Wraber, T.; Jogan, N.; Podobnik, A.; Turk, B.; Vreš, B.; Ravnik, V.; Frajman, B.; Strgulc Krajšek, S.; Trčak, B.; et al. Mala Flora Slovenije: Ključ za Določanje Praprotnic in Semenk; Tehniška Založba Slovenije: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2007; 967p. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, M.; Davis, A.; Grimshaw, J. Snowdrops; The Griffin Press: Barnet, UK, 2001; 361p. [Google Scholar]
- Bavcon, J. Navadni mali zvončki (Galanthus nivalis L.) v Sloveniji; Biotehniška fakulteta: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2014; 308p. [Google Scholar]
- Weryszko-Chmielewska, E.; Chwil, M. Flowering biology and structure of floral nectaries in Galanthus nivalis L. Acta Soc. Bot. Pol. 2016, 85, 3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ARSO [Agencija Republike Slovenije za Okolje]. Available online: https://www.arso.gov.si/ (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Bernadelo, G. A systmetaic survey of floral nectaries. In Nectaries and Nectar; Nicolson, S., Nepi, M., Pacini, E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolić, T. Morfologija biljaka—Razvoj, Građa i Uloga Biljnih Tkiva, Organa i Organskih Sustava; Alfa d.d.: Zagreb, Croatia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Corbet, S.A. Pollination and the weather. Isr. J. Bot. 1990, 39, 13–30. [Google Scholar]
- Malovrh, K.; Ravnjak, B.; Bavcon, J.; Križman, M. Nectar Production and Three Main Sugars in Nectar of Salvia pratensis and Salvia glutinosa in Correlation with Abiotic Factors. Agriculture 2024, 14, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbassioon, A.; Stanley, D.A. Exploring relationships between time of day and pollinator activity in the context of pesticide use. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2023, 72, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, B.J.; Cane, J.H. Impact of enhanced ultraviolet-B radiation on flower, pollen, and nectar production. Am. J. Bot. 1999, 86, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petanidou, T.; Goethals, V.; Smets, E. Nectary structure of Labiatae in relation to their nectar secretion and characteristics in a Mediterranean shrub community: Does flowering time matter? Plant Syst. Evol. 2000, 225, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percival, M.S. Types of nectar in angiosperms. New Phytol. 1961, 60, 235–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, C.M.; Garcia, I.M.; Perez, R. Invisible floral larcenies: Microbial communities degrade floral nectar of bumble bee-pollinated plants. Ecology 2008, 89, 2369–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotirić Akšoć, M.; Tosti, T.; Nedić, N.; Marković, M.; Ličina, V.; Milojković-Opsenica, D.; Tešić, Ž. Influence of frost damage on the sugars and sugar alcohol composition in quince (Cydonia oblonga Mill.) floral nectar. Acta Physiol. Plantarium 2015, 37, 1701. [Google Scholar]
- Dapper, H. Wesen und Vorkommen der Psychroklinie. Baumschulpraxis 1981, 3, 122–123. [Google Scholar]
- Blüthgen, N.; Fiedler, K. Preferences for sugars and amino acids and their conditionality in a diverse nectar-feeding ant community. J. Anim. Ecol. 2004, 73, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhao, G.; Yu, Y.; Liu, F. High Concentration of Nectar Quercetin Enhances Worker Resistance to Queen’s Signals in Bees. Chem. Ecol. 2010, 36, 1241–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolson, S. Sweet solutions: Nectar chemistry and quality. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2022, 377, 20210163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riveros, A.J.; Gronenberg, W. The flavonoid rutin protects the bumble bee Bombus impatiens against cognitive impairment by imidacloprid and fipronil. J. Exp. Biol. 2022, 225, jeb244526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, V.C.; Fernandez, M.; Galmarini, C.R.; Silva, M.F. Analysis of phenolic compounds in onion nectar by miniaturized off-line solid phase extraction-capillary zone electrophoresis. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 4878. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.; Taine, E.; Meng, D.; Cui, T.; Tan, W. Chlorogenic Acid: A Systematic Review on the Biological Functions, Mechanistic Actions, and Therapeutic Potentials. Nutrients 2024, 16, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nešović, M.; Gasič, U.; Tosti, T.; Horvacki, N.; Šikoparija, B.; Nedić, N.; Blagojević, S.; Ignjatović, L.; Tešić, Ž. Polyphenol profile of buckwheat honey, nectar and pollen. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 201576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaudo, A.D.; Tooker, J.F.; Grozinger, C.M.; Patch, H.M. Bee nutrition and floral resource restoration. Curr. Opin. Insect. Sci. 2015, 10, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostryco, M.; Chwil, M. Nectar abundance and nectar composition in selected Rubus idaeus L. varieties. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Analyte | Repeatability (% RSD; n = 5) | Reproducibility (% RSD; n = 3) | LOD (μg) * | LOQ (μg) * | Linearity Range (μg *; r) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sucrose | 2.24 | 3.63 | 0.17 | 0.56 | 0.6–15; 0.9999 |
| Glucose | 3.07 | 4.73 | 0.22 | 0.72 | 0.7–15; 0.9998 |
| Fructose | 3.46 | 4.02 | 0.25 | 0.82 | 0.8–15; 0.9994 |
| Analyte | Repeatability (% RSD; n = 5) | Reproducibility (% RSD; n = 3) | LOD (ng) * | LOQ (ng) * | Linearity Range (ng *; r) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorogenic acid | 0.45 | 0.72 | 1.1 | 3.6 | 3.6–250; 0.9999 |
| Rutin | 0.29 | 1.64 | 1.4 | 4.9 | 4.9–250; 0.9999 |
| Quercitrin/isoquercitrin | 1.38 | 4.94 | 1.9 | 6.6 | 6.6–250; 0.9998 |
| Hyperoside | 1.47 | 4.21 | 2.2 | 7.2 | 7.2–250; 0.9995 |
| Quercetin | 0.76 | 3.27 | 3.7 | 12.2 | 12.2–250; 0.9997 |
| Analyte | Repeatability (% RSD; n = 5) | Reproducibility (% RSD; n = 3) | LOD (ng) * | LOQ (ng) * | Linearity Range (ng *; r) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proline | 2.82 | 5.37 | 0.7 | 2.3 | 2.3–200; 0.9993 |
| Leucine/Isoleucine | 2.07 | 3.71 | 0.9 | 3.0 | 3.0–200; 0.9995 |
| Methionine | 4.74 | 6.39 | 1.9 | 6.4 | 6.4–200; 0.9988 |
| Alanine | 0.58 | 4.38 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.5–200; 0.9958 |
| Tyrosine | 1.96 | 2.53 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.5–200; 0.9992 |
| Abiotic Factor | Quantity | Sucrose | Glucose | Fructose | Hyperoside |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UVB | |||||
| Soil T | −0.54 | −0.43 | −0.36 | −0.40 | −0.35 |
| Soil hum | |||||
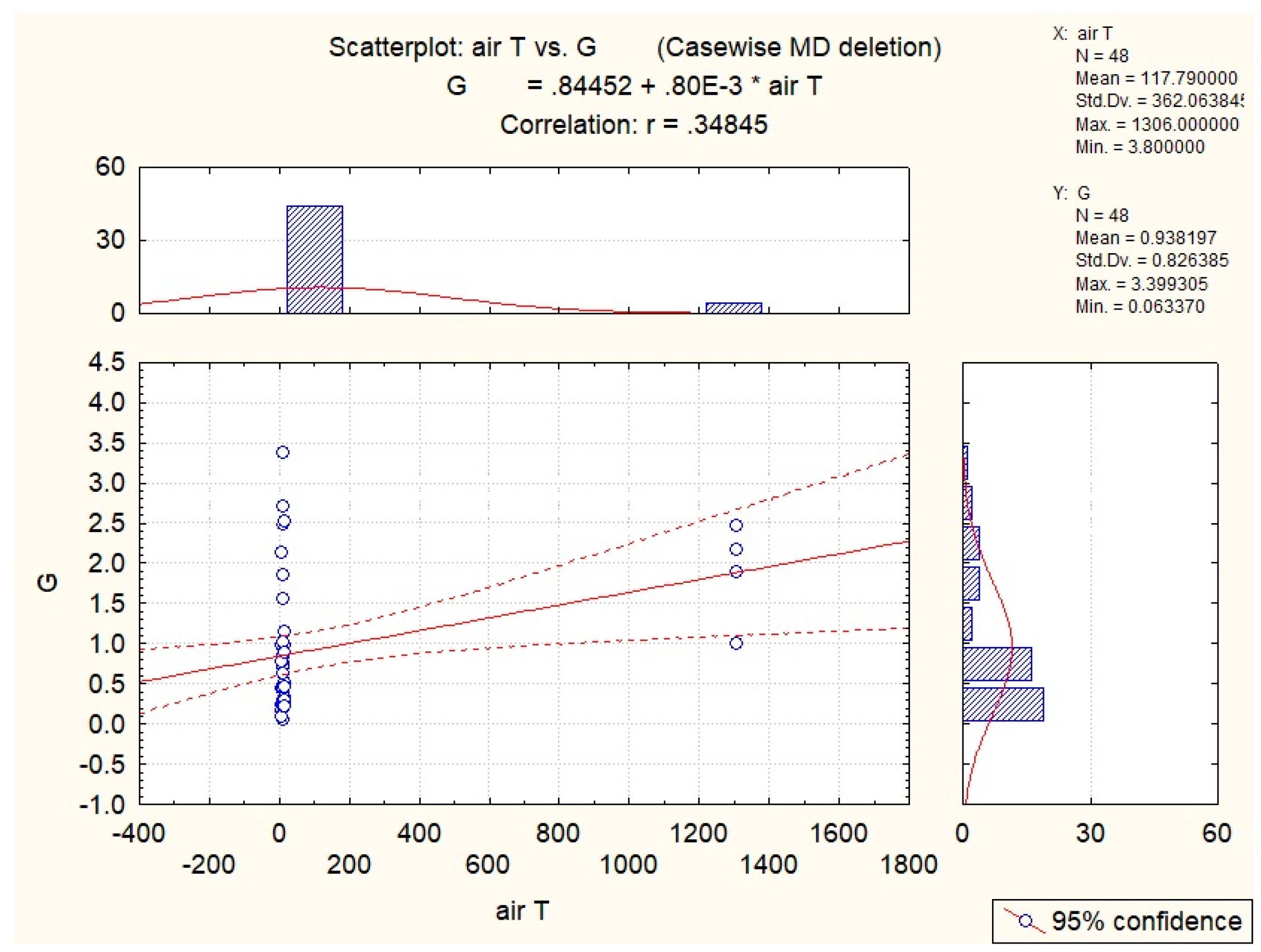
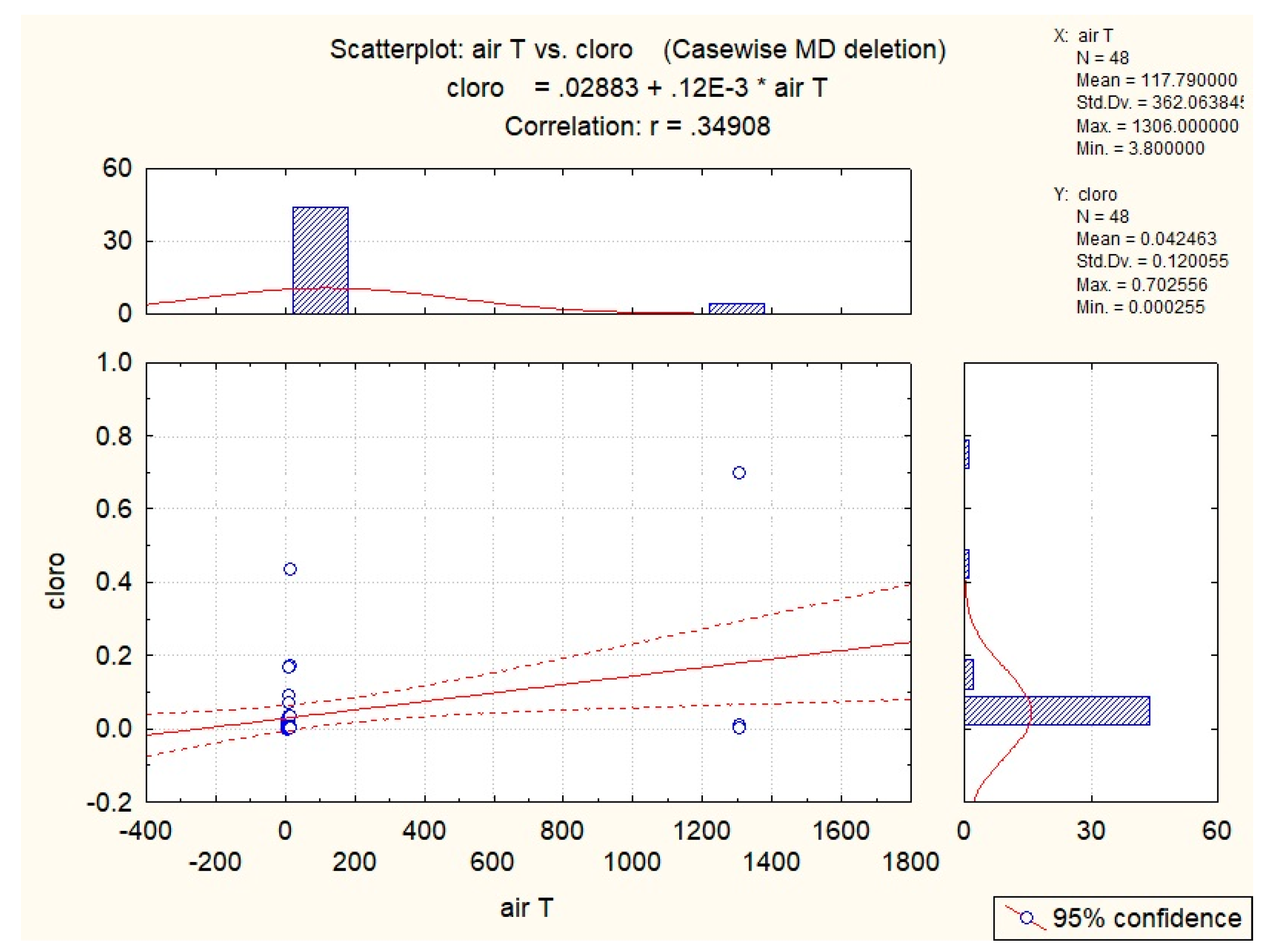
| Air T | −0.35 | −0.29 | |||
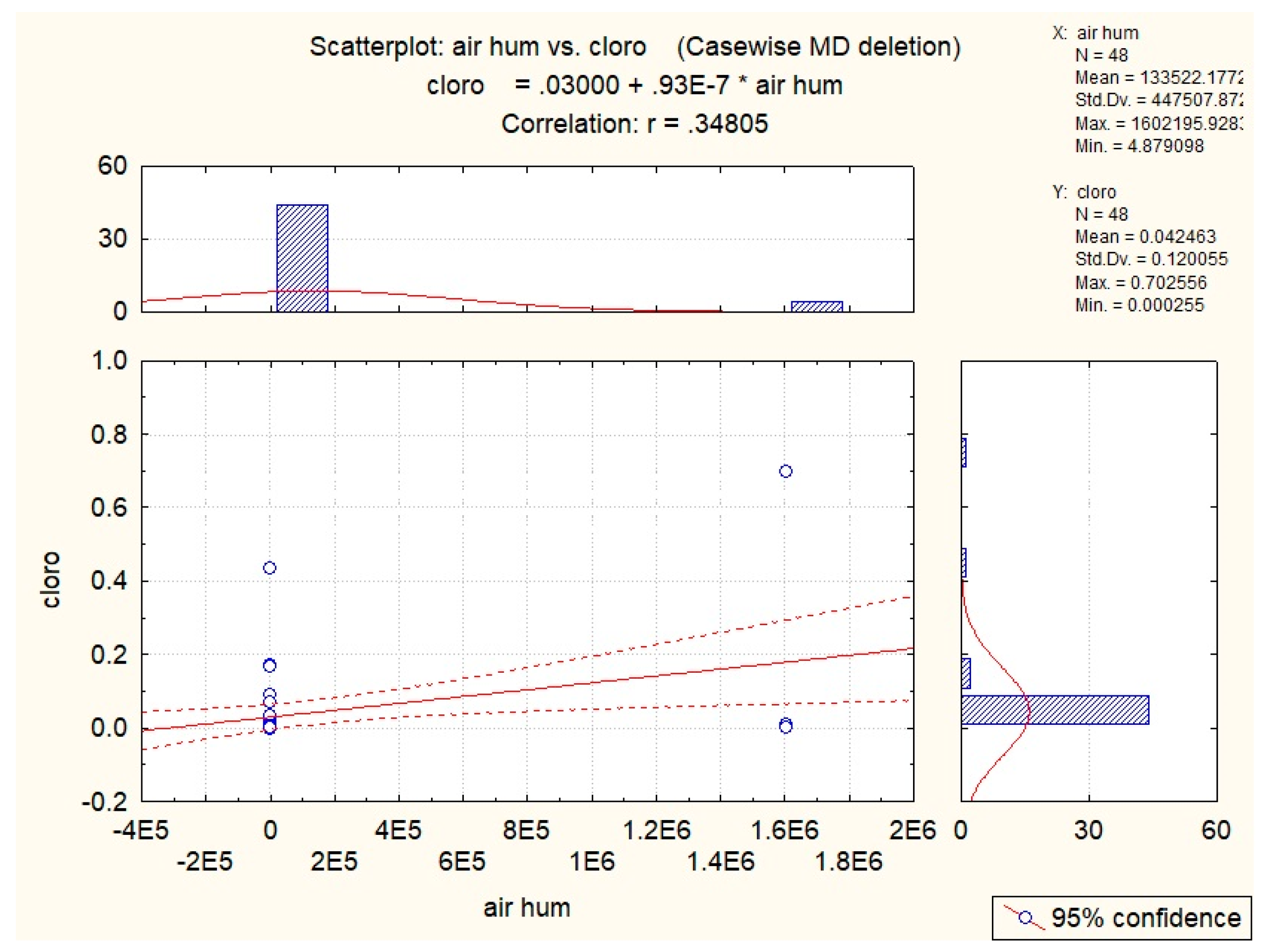
| Air hum |
| Abiotic Factor | Quantity | Glucose | Chlorogenic Acid | Hyperoside |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UVB | 0.34 | |||
| Soil T | 0.35 | |||
| Soil hum | 0.38 | |||
| Air T | 0.35 | 0.35 | ||
| Air hum | 0.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malovrh, K.; Bavcon, J.; Križman, M.; Ravnjak, B. Effect of Abiotic Factors on Nectar Quality and Secretion of Two Early Spring Species, Galanthus nivalis L. and Helleborus niger L. Diversity 2024, 16, 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16080469
Malovrh K, Bavcon J, Križman M, Ravnjak B. Effect of Abiotic Factors on Nectar Quality and Secretion of Two Early Spring Species, Galanthus nivalis L. and Helleborus niger L. Diversity. 2024; 16(8):469. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16080469
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalovrh, Katja, Jože Bavcon, Mitja Križman, and Blanka Ravnjak. 2024. "Effect of Abiotic Factors on Nectar Quality and Secretion of Two Early Spring Species, Galanthus nivalis L. and Helleborus niger L." Diversity 16, no. 8: 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16080469
APA StyleMalovrh, K., Bavcon, J., Križman, M., & Ravnjak, B. (2024). Effect of Abiotic Factors on Nectar Quality and Secretion of Two Early Spring Species, Galanthus nivalis L. and Helleborus niger L. Diversity, 16(8), 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16080469






