Impact of Different Sources of Anthropogenic Pollution on the Structure and Distribution of Antarctic Marine Meiofauna Communities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Study Area
2.3. Preparation and Identification of Meiofauna
2.4. Environmental Variables and Contaminants
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Meiofauna Community
3.1.1. Density and Diversity Parameters
3.1.2. Spatial Structure
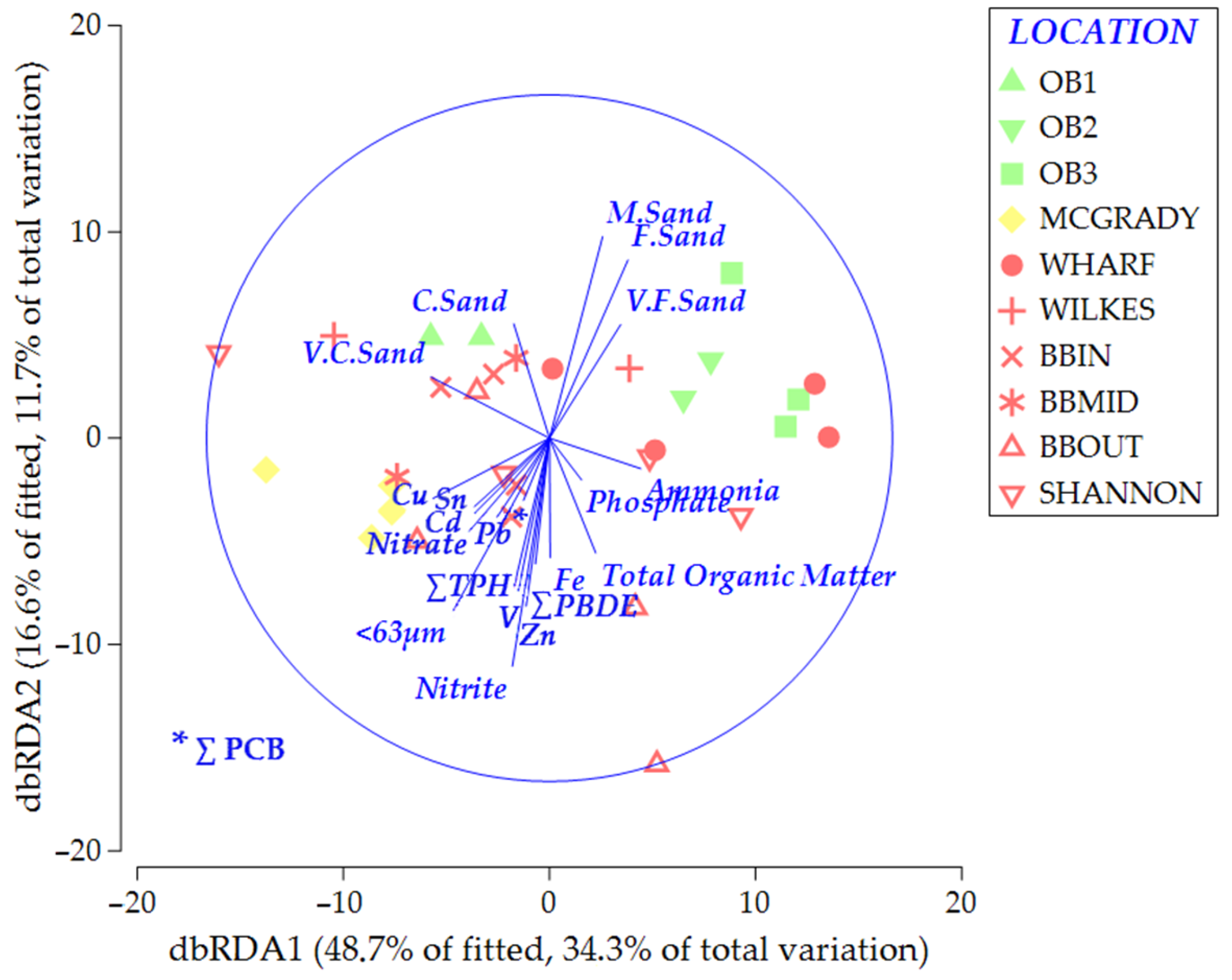
3.2. Environmental Variables and Contaminants Influences on Meiofauna Community
Correlation between Meiofauna and Environmental Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Benthic Contamination in East Antarctic Bays
4.2. Density, Biodiversity, and Spatial Variation in Meiofaunal Communities
4.3. Environmental Variables and Contaminant Influences on Meiofaunal Communities
4.4. Meiofauna as Environmental Indicators in Antarctica
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McKinley, E.; Acott, T.; Yates, K.L. Marine Social Sciences: Looking towards a Sustainable Future. Environ. Sci. Policy 2020, 108, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, R.B.; Thatje, S.; Mcclintock, J.B.; Hughes, K.A. Anthropogenic Impacts on Marine Ecosystems in Antarctica. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 2011, 1223, 82–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louati, H.; Said, O.B.; Soltani, A.; Got, P.; Cravo-Laureau, C.; Duran, R.; Aissa, P.; Pringault, O.; Mahmoudi, E. Biostimulation as an Attractive Technique to Reduce Phenanthrene Toxicity for Meiofauna and Bacteria in Lagoon Sediment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 3670–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeppilli, D.; Sarrazin, J.; Leduc, D.; Arbizu, P.M.; Fontaneto, D.; Fontanier, C.; Gooday, A.J.; Kristensen, R.M.; Ivanenko, V.N.; Sørensen, M.V.; et al. Is the Meiofauna a Good Indicator for Climate Change and Anthropogenic Impacts? Mar. Biodivers. 2015, 45, 505–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schratzberger, M.; Ingels, J. Meiofauna Matters: The Roles of Meiofauna in Benthic Ecosystems. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2018, 502, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giere, O. Meiobenthology: The Microscopic Motile Fauna of Aquatic Sediments; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Balsamo, M.; Semprucci, F.; Frontalini, F.; Coccioni, R. Meiofauna as a Tool for Marine Ecosystem Biomonitoring. Mar. Ecosyst. 2012, 4, 77–104. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, S.; Kennedy, J.P. Synthesis, Characterization and Properties of Octa-Arm Polyisobutylene-Based Star Polymers. Polym. Synth. Complexation 1999, 146, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Vanaverbeke, J.; Steyaert, M.; Vanreusel, A.; Vincx, M. Nematode Biomass Spectra as Descriptors of Functional Changes Due to Human and Natural Impact. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 249, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingels, J.; Zeppilli, D.; Giere, O. Meiofauna—Adapted to Life at the Limits. In New Horizons in Meiobenthos Research: Profiles, Patterns and Potentials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 363–400. [Google Scholar]
- Walton, D.W.H. Antarctica: Global Science from a Frozen Continent; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mcminn, A.; Hodgson, D. Summer Phytoplankton Succession in Ellis Fjord, Eastern Antarctica. J. Plankton Res. 1993, 15, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, E.; Eisenman, I.; Wagner, T.J.W. Polar Amplification Due to Enhanced Heat Flux Across the Halocline. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, 86706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.S.; Kim, S.L.; Oliver, J.S. Anthropogenic Disturbance and Biodiversity of Marine Benthic Communities in Antarctica: A Regional Comparison. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.S.; Johnstone, G.J.; King, C.; Raymond, T.; Rutter, A.; Stark, S.C.; Townsend, A.T. Contamination of the Marine Environment by Antarctic Research Stations: Monitoring Marine Pollution at Casey Station from 1997 to 2015. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.S. The Distribution and Abundance of Soft-Sediment Macrobenthos around Casey Station, East Antarctica. Polar Biol. 2000, 23, 840–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, B.A.W.; Goldsworthy, P.M.; Riddle, M.J.; Snape, I.; Stark, J.S. Contamination Effects by a ‘Conventional’and a ‘Biodegradable’Lubricant Oil on Infaunal Recruitment to Antarctic Sediments: A Field Experiment. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2007, 340, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.S.; Riddle, M.J.; Snape, I.; Scouller, R.C. Human Impacts in Antartic Marine Soft-Sediment Assemblages: Correlations between Multivariate Biological Patterns and Environmental Variables at Casey Station. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 56, 717–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danovaro, R.; Gambi, C.; Luna, G.M.; Mirto, S. Sustainable Impact of Mussel Farming in the Adriatic Sea (Mediterranean Sea): Evidence from Biochemical, Microbial and Meiofaunal Indicators. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 49, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.S.; Mohammad, M.; McMinn, A.; Ingels, J. Diversity, Abundance, Spatial Variation, and Human Impacts in Marine Meiobenthic Nematode and Copepod Communities at Casey Station, East Antarctica. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.S.; Riddle, M.J.; Simpson, R.D. Human Impacts in Soft-sediment Assemblages at Casey Station, East Antarctica: Spatial Variation, Taxonomic Resolution and Data Transformation. Austral. Ecol. 2003, 28, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.S.; Snape, I.; Riddle, M.J. Abandoned Antarctic Waste Disposal Sites: Monitoring Remediation Outcomes and Limitations at Casey Station. In Ecological Management & Restoration; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Heip, C.H.R.; Vincx, M.; Vranken, G. The Ecology of Marine Nematodes; Aberdeen University Press: Aberdeen, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Pfannkuche, O.; Thiel, H. Sample Processing. Introd. Study Meiofauna 1988, 9, 134–145. [Google Scholar]
- Witthöft-Mühlmann, A.; Traunspurger, W.; Rothhaupt, K.O. Meiobenthic Response to River-borne Benthic Particulate Matter–a Microcosm Experiment. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 1548–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, R.P.; Thiel, H. Introduction to the Study of Meiofauna; Smithsonian Institution Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Heiri, O.; Lotter, A.F.; Lemcke, G. Loss on Ignition as a Method for Estimating Organic and Carbonate Content in Sediments: Reproducibility and Comparability of Results. J. Paleolimnol. 2001, 25, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snape, I.; Scouller, R.C.; Stark, S.C.; Stark, J.; Riddle, M.J.; Gore, D.B. Characterisation of the Dilute HCl Extraction Method for the Identification of Metal Contamination in Antarctic Marine Sediments. Chemosphere 2004, 57, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.; Gorley, R.; Clarke, K.P. For PRIMER: Guide to Software and Statistical Methods. Primer-E Ltd. 2008, 32, 57–79. [Google Scholar]
- Danovaro, R.; Gambi, C.; Mirto, S.; Sandulli, R.; Ceccherelli, V. Meiofauna. In Mediterranean Marine Benthos: A Manual of Methods for Its Sampling and Study. Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2004, 11, 55–97. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, M.; Vezzulli, L.; Marin, V.; Laconi, P.; Albertelli, G.; Fabiano, M. The Use of Meiofauna Diversity as an Indicator of Pollution in Harbours. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 1428–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.R.M.C.; Bergami, E.; Gomes, V.; Corsi, I. Occurrence and Distribution of Legacy and Emerging Pollutants Including Plastic Debris in Antarctica: Sources, Distribution and Impact on Marine Biodiversity. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 186, 114353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snape, I.; Riddle, M.J.; Stark, J.S.; Cole, C.M.; King, C.K.; Duquesne, S.; Gore, D.B. Management and Remediation of Contaminated Sites at Casey Station, Antarctica. Polar Rec. 2001, 37, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scouller, R.C.; Snape, I.; Stark, J.S.; Gore, D.B. Evaluation of Geochemical Methods for Discrimination of Metal Contamination in Antarctic Marine Sediments: A Case Study from Casey Station. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antarctic Station Catalogue. Council of Managers of National Antarctic Programs; COMNAP: Christchurch, New Zealand, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Green, G.; Skerratt, J.H.; Leeming, R.; Nichols, P.D. Hydrocarbon and Coprostanol Levels in Seawater, Sea-Ice Algae and Sediments near Davis Station in Eastern Antarctica: A Regional Survey and Preliminary Results for a Field Fuel Spill Experiment. Mar. Pollut. Bull 1992, 25, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.S.; Corbett, P.A.; Dunshea, G.; Johnstone, G.; King, C.; Mondon, J.A.; Power, M.L.; Samuel, A.; Snape, I.; Riddle, M. The Environmental Impact of Sewage and Wastewater Outfalls in Antarctica: An Example from Davis Station, East Antarctica. Water Res. 2016, 105, 602–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, A.; Lannuzel, D.; Rodemann, T.; Meiners, K.M.; Auman, H.J. Microplastic Contamination in East Antarctic Sea Ice. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 154, 111130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennicutt, M.C.; Klein, A.; Montagna, P.; Sweet, S.; Wade, T.; Palmer, T.; Sericano, J.; Denoux, G. Temporal and Spatial Patterns of Anthropogenic Disturbance at McMurdo Station, Antarctica. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 34010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheller, P.F.; Corbisier, T.N. Monitoring the Anthropogenic Impacts in Admiralty Bay Using Meiofauna Community as Indicators (King George Island, Antarctica). An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2022, 94, e20210616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhove, S.; Lee, H.J.; Beghyn, M.; Van Gansbeke, D.; Brockington, S.; Vincx, M. The Metazoan Meiofauna in Its Biogeochemical Environment: The Case of an Antarctic Coastal Sediment. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. 1998, 78, 411–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.-H.; Kim, K.-C.; Lee, S.-H.; Back, J.-W.; Lee, D.-J.; Lee, W.-C. The Community Structure of Meiofauna in Marian Cove, King George Island, Antarctica. Ocean Polar Res. 2011, 33, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoshou, L.I.U.; Xiaoxiao, W.; Lu, W.; Zhinan, Z. A Preliminary Study of Intertidal Meiofauna in Fildes Peninsula, Antarctica. Chin. J. Polar Res. 2020, 32, 281. [Google Scholar]
- Säring, F.; Veit-Köhler, G.; Seifert, D.; Liskow, I.; Link, H. Sea-Ice-Related Environmental Drivers Affect Meiofauna and Macrofauna Communities Differently at Large Scales (Southern Ocean, Antarctic). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2022, 700, 13–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.; Yoo, K.-C.; Kim, D. Meiofauna and Nematode Community Composition in Maxwell Bay, King George Island, Antarctica. Ocean Sci. J. 2022, 57, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.S.; Raymond, T.; Deppeler, S.L.; Morrison, A.K. Antarctic Seas. In World Seas: An Environmental Evaluation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Ingels, J.; Hasemann, C.; Soltwedel, T.; Vanreusel, A. Polar Meiofauna—Antipoles or Parallels? In New Horizons in Meiobenthos Research: Profiles, Patterns and Potentials; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 285–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolosa, I.; Mesa-Albernas, M.; Alonso-Hernandez, C.M. Inputs and Sources of Hydrocarbons in Sediments from Cienfuegos Bay, Cuba. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1624–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, D.C.; de Souza, J.R.B.; Taniguchi, S.; Bícego, M.C.; Zanardi-Lamardo, E. Sources and Distribution of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in a an Urbanized Tropical Estuary and Adjacent Shelf, Northeast of Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egres, A.G.; Hatje, V.; Miranda, D.A.; Gallucci, F.; Barros, F. Functional Response of Tropical Estuarine Benthic Assemblages to Perturbation by Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, R.B.; Dos Santos, G.A.P.; de Farias, A.L.L.; França, D.A.A.; Cavalcante, R.A.; Zanardi-Lamardo, E.; de Souza, J.R.B.; Esteves, A.M. Effects of PAHs on Meiofauna from Three Estuaries with Different Levels of Urbanization in the South Atlantic. PeerJ 2022, 10, e14407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losi, V.; Grassi, E.; Balsamo, M.; Rocchi, M.; Gaozza, L.; Semprucci, F. Changes in Taxonomic Structure and Functional Traits of Nematodes as Tools in the Assessment of Port Impact. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 260, 107524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Arruda-Santos, R.H.; Schettini, C.A.F.; Yogui, G.T.; Maciel, D.C.; Zanardi-Lamardo, E. Sources and Distribution of Aromatic Hydrocarbons in a Tropical Marine Protected Area Estuary under Influence of Sugarcane Cultivation. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stogiannidis, E.; Laane, R. Source Characterization of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons by Using Their Molecular Indices: An Overview of Possibilities. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 234, 49–133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coull, B.C. Role of Meiofauna in Estuarine Soft-bottom Habitats. Aust. J. Ecol. 1999, 24, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Skowronski, R.S.; Corbisier, T.N. Meiofauna Distribution in Martel Inlet, King George Island (Antarctica): Sediment Features versus Food Availability. Polar Biol. 2002, 25, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, D.J.; Tsui, T.K.N. Ammonia Toxicity in Fish. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 45, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shailaja, M.S.; Narvekar, P.V.; Alagarsamy, R.; Naqvi, S.W.A. Nitrogen Transformations as Inferred from the Activities of Key Enzymes in the Arabian Sea Oxygen Minimum Zone. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2006, 53, 960–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, S. Marine Eutrophication: A Growing International Problem. Ambio 1990, 19, 101. [Google Scholar]
- Shailaja, M.S.; Rodrigues, A. Nitrite-Induced Enhancement of Toxicity of Phenanthrene in Fish and Its Implications for Coastal Waters. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 56, 1107–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenihan, H.S. Benthic Marine Pollution around McMurdo Station, Antarctica: A Summary of Findings. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1992, 25, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenihan, H.S.; Oliver, J.S. Anthropogenic and Natural Disturbances to Marine Benthic Communities in Antarctica. Ecol. Appl. 1995, 5, 311–326. [Google Scholar]
- Stark, J.S.; Smith, J.; King, C.K.; Lindsay, M.; Stark, S.; Palmer, A.S.; Snape, I.; Bridgen, P.; Riddle, M. Physical, Chemical, Biological and Ecotoxicological Properties of Wastewater Discharged from Davis Station, Antarctica. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2015, 113, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majer, A.P.; Petti, M.A.V.; Corbisier, T.N.; Ribeiro, A.P.; Theophilo, C.Y.S.; de Lima Ferreira, P.A.; Figueira, R.C.L. Bioaccumulation of Potentially Toxic Trace Elements in Benthic Organisms of Admiralty Bay (King George Island, Antarctica). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 79, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucuksezgin, F.; Kontas, A.; Altay, O.; Uluturhan, E.; Darılmaz, E. Assessment of Marine Pollution in Izmir Bay: Nutrient, Heavy Metal and Total Hydrocarbon Concentrations. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryan, G.W.; Langston, W.J. Bioavailability, Accumulation and Effects of Heavy Metals in Sediments with Special Reference to United Kingdom Estuaries: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 1992, 76, 89–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenihan, H.S.; Peterson, C.H.; Kim, S.L.; Conlan, K.E.; Fairey, R.; McDonald, C.; Grabowski, J.H.; Oliver, J.S. Variation in Marine Benthic Community Composition Allows Discrimination of Multiple Stressors. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 261, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okereafor, U.; Makhatha, M.; Mekuto, L.; Uche-Okereafor, N.; Sebola, T.; Mavumengwana, V. Toxic Metal Implications on Agricultural Soils, Plants, Animals, Aquatic Life and Human Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfiligoj, B. Sensitivity of Antarctic Marine Invertebrates and Microalgae to Metal Exposure. Doctoral Dissertation, Deakin University, Geelong, VIC, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kefford, B.J.; King, C.K.; Wasley, J.; Riddle, M.J.; Nugegoda, D. Sensitivity of a Large and Representative Sample of Antarctic Marine Invertebrates to Metals. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2019, 38, 1560–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, A.; Sharman, T. Copper Toxicity. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra, N.; Ger, T.-R.; Uapipatanakul, B.; Huang, J.-C.; Chen, K.H.-C.; Hsiao, C.-D. Review of Copper and Copper Nanoparticle Toxicity in Fish. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahrgang, J.; Brooks, S.J.; Evenset, A.; Camus, L.; Jonsson, M.; Smith, T.J.; Lukina, J.; Frantzen, M.; Giarratano, E.; Renaud, P.E. Seasonal Variation in Biomarkers in Blue Mussel (Mytilus Edulis), Icelandic Scallop (Chlamys Islandica) and Atlantic Cod (Gadus Morhua)—Implications for Environmental Monitoring in the Barents Sea. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 127, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Pan, L.; Wang, L. The Detoxification Process, Bioaccumulation and Damage Effect in Juvenile White Shrimp Litopenaeus Vannamei Exposed to Chrysene. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 114, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.N.; Mariz Junior, C.F.; de Paulo, D.V.; Carvalho, P.S.M. Toxicity of Effluents from Gasoline Stations Oil-Water Separators to Early Life Stages of Zebrafish Danio Rerio. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.S.; Mohammad, M.; McMinn, A.; Ingels, J. The Effects of Hydrocarbons on Meiofauna in Marine Sediments in Antarctica. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2017, 496, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.S. Patterns of Higher Taxon Colonisation and Development in Sessile Marine Benthic Assemblages at Casey Station, Antarctica, and Their Use in Environmental Monitoring. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 365, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, S.; McLagan, D.; Schlabach, M.; Bossi, R.; Hawker, D.; Cropp, R.; King, C.K.; Stark, J.S.; Mondon, J.; Nash, S.B. An Antarctic Research Station as a Source of Brominated and Perfluorinated Persistent Organic Pollutants to the Local Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coull, B.C.; Chandler, G.T. Pollution and Meiofauna: Field, Laboratory, and Mesocosm Studies. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 1992, 30, 191–271. [Google Scholar]
- Fair, P.A.; Houde, M. Environmental Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals and Their Effects in Marine Mammals. In Environmental Contaminants and Endocrine Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 283–306. [Google Scholar]
- Vonderheide, A.P.; Mueller, K.E.; Meija, J.; Welsh, G.L. Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers: Causes for Concern and Knowledge Gaps Regarding Environmental Distribution, Fate and Toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 400, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covaci, A.; Harrad, S.; Abdallah, M.A.-E.; Ali, N.; Law, R.J.; Herzke, D.; de Wit, C.A. Novel Brominated Flame Retardants: A Review of Their Analysis, Environmental Fate and Behaviour. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 532–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, R.C.; Kim, S.L.; Harvey, E.; La Guardia, M.J.; Mainor, T.M.; Bush, E.O.; Jacobs, E.M. Antarctic Research Bases: Local Sources of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ether (PBDE) Flame Retardants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 1452–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauvin, J.-C. Evolution à Long Terme (1978–1986) Des Populations d’Amphipodes Des Sables Fins de La Pierre Noire (Baie de Morlaix, Manche Occidentale) Aprss La Catastrophe de l’Amoco Cadiz. Mar. Environ. Res 1987, 21, 247–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauvin, J.-C. The Fine Sand Abra Alba Community of the Bay of Morlaix Twenty Years after the Amoco Cadiz Oil Spill. Mar. Pollut. Bull. Great Br. 1998, 36, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, F.; Abad, M.; Bodergat, A.-M.; Carbonel, P.; Rodríguez-Lázaro, J.; Yasuhara, M. Marine and Brackish-Water Ostracods as Sentinels of Anthropogenic Impacts. Earth Sci. Rev. 2005, 72, 89–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorri, J.; Veit-Köhler, G.; Boufahja, F.; Abd-Elkader, O.H.; Plavan, G.; Mahmoudi, E.; Aïssa, P. Assessing Metallic Pollution Using Taxonomic Diversity of Offshore Meiobenthic Copepods. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbisier, T.N.; Bícego, M.C.; Bromberg, S.; Dalto, A.G.; Figueira, R.C.L.; Gheller, P.F.; de Castro Martins, C.; Montone, R.C.; Nakayama, C.R.; Pellizari, V.H.; et al. Influence of Sediment Quality on the Benthic Communities of Admiralty Bay, King George Island, Antarctica. Annu. Act. Rep. 2014, 8, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nipper, M.; Scott Carr, R. Recent Advances in the Use of Meiofaunal Polychaetes for Ecotoxicological Assessments. Hydrobiologia 2003, 496, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinke, M.; Ristau, K.; Bergtold, M.; Höss, S.; Claus, E.; Heininger, P.; Traunspurger, W. Using Meiofauna to Assess Pollutants in Freshwater Sediments: A Microcosm Study with Cadmium. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louati, H.; Said, O.B.; Soltani, A.; Got, P.; Mahmoudi, E.; Cravo-Laureau, C.; Duran, R.; Aissa, P.; Pringault, O. The Roles of Biological Interactions and Pollutant Contamination in Shaping Microbial Benthic Community Structure. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2535–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauvin, J.-C.; Andrade, H.; de-la-Ossa-Carretero, J.A.; Del-Pilar-Ruso, Y.; Riera, R. Polychaete/Amphipod Ratios: An Approach to Validating Simple Benthic Indicators. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 63, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whomersley, P.; Huxham, M.; Schratzberger, M.; Bolam, S. Differential Response of Meio- and Macrofauna to in Situ Burial. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. 2009, 89, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen Gupta, B.K.; Yanko, V.; Arnold, A.J.; Parker, W.C. Effects of Marine Pollution on Benthic Foraminifera. Mod. Foraminifera 2003, 13, 217–235. [Google Scholar]
- Pertama, S.; Kedua, P.; Akhir, P. Water Quality Study Based on Meiofauna Abundance and Pollution Index in The Coastal Zone of Losari Beach, Makassar. J. Ilmu Lingkung 2019, 17, 172–180. [Google Scholar]
- Lynn, D.H. Ciliophora. eLS 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, K.M.; Gill, R.A.; Robotham, P.W.J. The PAH and Organic Content of Sediment Particle Size Fractions. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1990, 51, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraschetti, S.; Gambi, C.; Giangrande, A.; Musco, L.; Terlizzi, A.; Danovaro, R. Structural and Functional Response of Meiofauna Rocky Assemblages to Sewage Pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 52, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corinaldesi, C.; Canensi, S.; Carugati, L.; Martire, M.L.; Marcellini, F.; Nepote, E.; Sabbatini, S.; Danovaro, R. Organic Enrichment Can Increase the Impact of Microplastics on Meiofaunal Assemblages in Tropical Beach Systems. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damasio, B.V.; Timoszczuk, C.T.; Kim, B.S.M.; de Mello e Sousa, S.H.; Bícego, M.C.; Siegle, E.; Figueira, R.C.L. Impacts of Hydrodynamics and Pollutants on Foraminiferal Fauna Distribution in the Santos Estuary (SE Brazil). J. Sediment. Environ. 2020, 5, 61–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janakiraman, A.; Naveed, M.S.; Sheriff, M.A.; Altaff, K. Ecological Restoration Assessment of Adyar Creek and Estuary Using Meiofaunal Communities as Ecological Indicators for Aquatic Pollution. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2017, 9, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingels, J.; Kiriakoulakis, K.; Wolff, G.A.; Vanreusel, A. Nematode Diversity and Its Relation to the Quantity and Quality of Sedimentary Organic Matter in the Deep Nazaré Canyon, Western Iberian Margin. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2009, 56, 1521–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusceddu, A.; Fraschetti, S.; Mirto, S.; Holmer, M.; Danovaro, R. Effects of Intensive Mariculture on Sediment Biochemistry. Ecol. Appl. 2007, 17, 1366–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semprucci, F.; Balsamo, M.; Sandulli, R. Assessment of the Ecological Quality (EcoQ) of the Venice Lagoon Using the Structure and Biodiversity of the Meiofaunal Assemblages. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 ) represent sampling points in impacted locations belonging to Newcomb Bay, green circles (
) represent sampling points in impacted locations belonging to Newcomb Bay, green circles ( ) in non-impacted locations belonging to O’Brien Bay, and yellow circles (
) in non-impacted locations belonging to O’Brien Bay, and yellow circles ( ) in non-impacted locations belonging to Newcomb Bay. The approximate location of Casey Station is indicated by the “star” symbol.
) in non-impacted locations belonging to Newcomb Bay. The approximate location of Casey Station is indicated by the “star” symbol.
 ) represent sampling points in impacted locations belonging to Newcomb Bay, green circles (
) represent sampling points in impacted locations belonging to Newcomb Bay, green circles ( ) in non-impacted locations belonging to O’Brien Bay, and yellow circles (
) in non-impacted locations belonging to O’Brien Bay, and yellow circles ( ) in non-impacted locations belonging to Newcomb Bay. The approximate location of Casey Station is indicated by the “star” symbol.
) in non-impacted locations belonging to Newcomb Bay. The approximate location of Casey Station is indicated by the “star” symbol.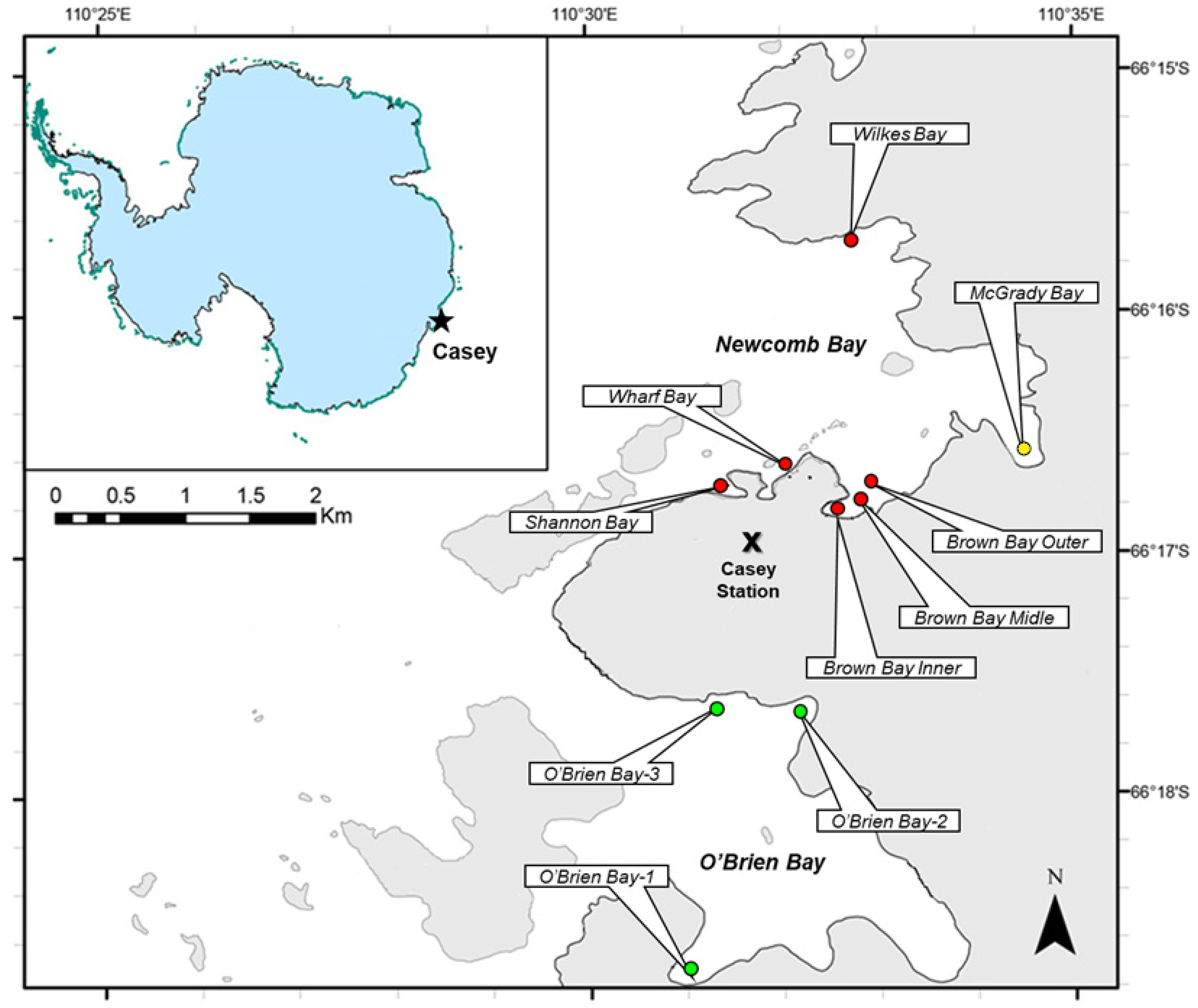
 ) are impacted locations, belonging to Newcomb Bay, yellow (
) are impacted locations, belonging to Newcomb Bay, yellow ( ) is the reference location belonging to Newcomb Bay, and green (
) is the reference location belonging to Newcomb Bay, and green ( ) are reference locations belonging to O’Brien Bay. Circle-shaped symbols (●) indicate outliers.
) are reference locations belonging to O’Brien Bay. Circle-shaped symbols (●) indicate outliers.
 ) are impacted locations, belonging to Newcomb Bay, yellow (
) are impacted locations, belonging to Newcomb Bay, yellow ( ) is the reference location belonging to Newcomb Bay, and green (
) is the reference location belonging to Newcomb Bay, and green ( ) are reference locations belonging to O’Brien Bay. Circle-shaped symbols (●) indicate outliers.
) are reference locations belonging to O’Brien Bay. Circle-shaped symbols (●) indicate outliers.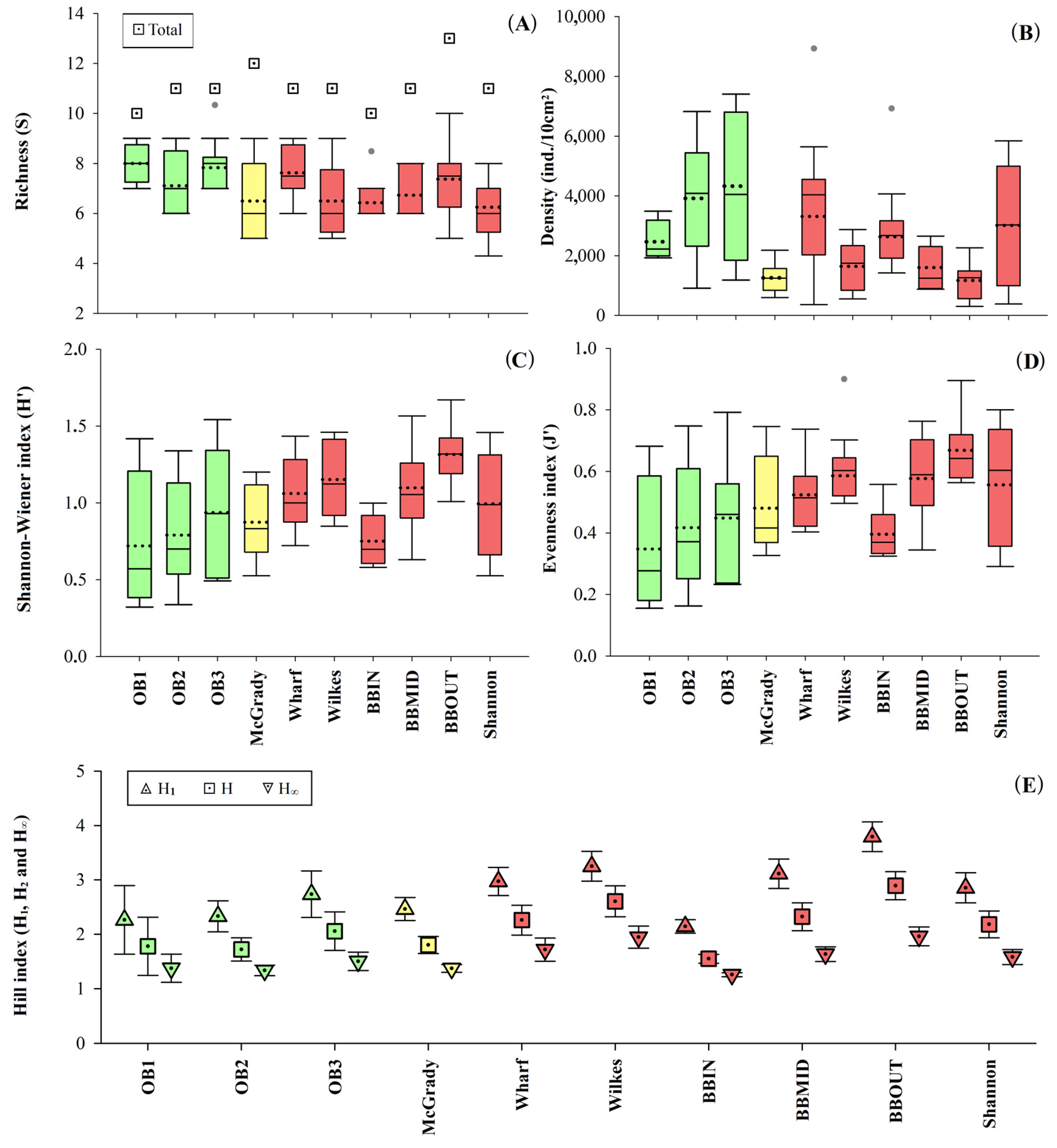
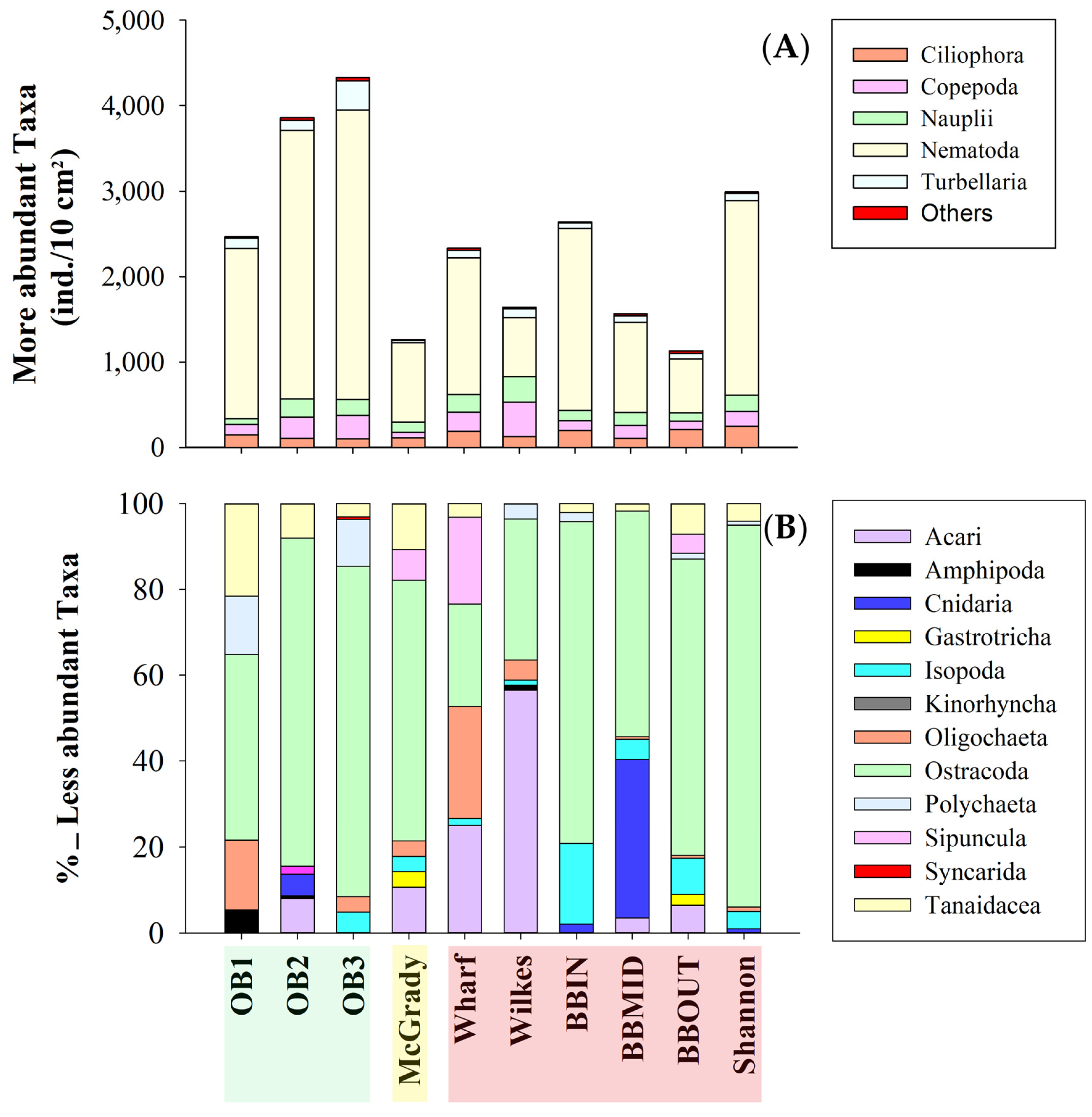
 ) are impacted locations, belonging to Newcomb Bay, yellow (
) are impacted locations, belonging to Newcomb Bay, yellow ( ) is the reference location belonging to Newcomb Bay, and green (
) is the reference location belonging to Newcomb Bay, and green ( ) are reference locations belonging to O’Brien Bay. The vertical lines extending from each box represent the minimum and maximum value. Star-shaped symbols (●) indicate outliers. (A) Ciliophora, (B) Copepoda, (C) Nauplii, (D) Nematoda, (E) Turbellaria, and (F) others taxa.
) are reference locations belonging to O’Brien Bay. The vertical lines extending from each box represent the minimum and maximum value. Star-shaped symbols (●) indicate outliers. (A) Ciliophora, (B) Copepoda, (C) Nauplii, (D) Nematoda, (E) Turbellaria, and (F) others taxa.
 ) are impacted locations, belonging to Newcomb Bay, yellow (
) are impacted locations, belonging to Newcomb Bay, yellow ( ) is the reference location belonging to Newcomb Bay, and green (
) is the reference location belonging to Newcomb Bay, and green ( ) are reference locations belonging to O’Brien Bay. The vertical lines extending from each box represent the minimum and maximum value. Star-shaped symbols (●) indicate outliers. (A) Ciliophora, (B) Copepoda, (C) Nauplii, (D) Nematoda, (E) Turbellaria, and (F) others taxa.
) are reference locations belonging to O’Brien Bay. The vertical lines extending from each box represent the minimum and maximum value. Star-shaped symbols (●) indicate outliers. (A) Ciliophora, (B) Copepoda, (C) Nauplii, (D) Nematoda, (E) Turbellaria, and (F) others taxa.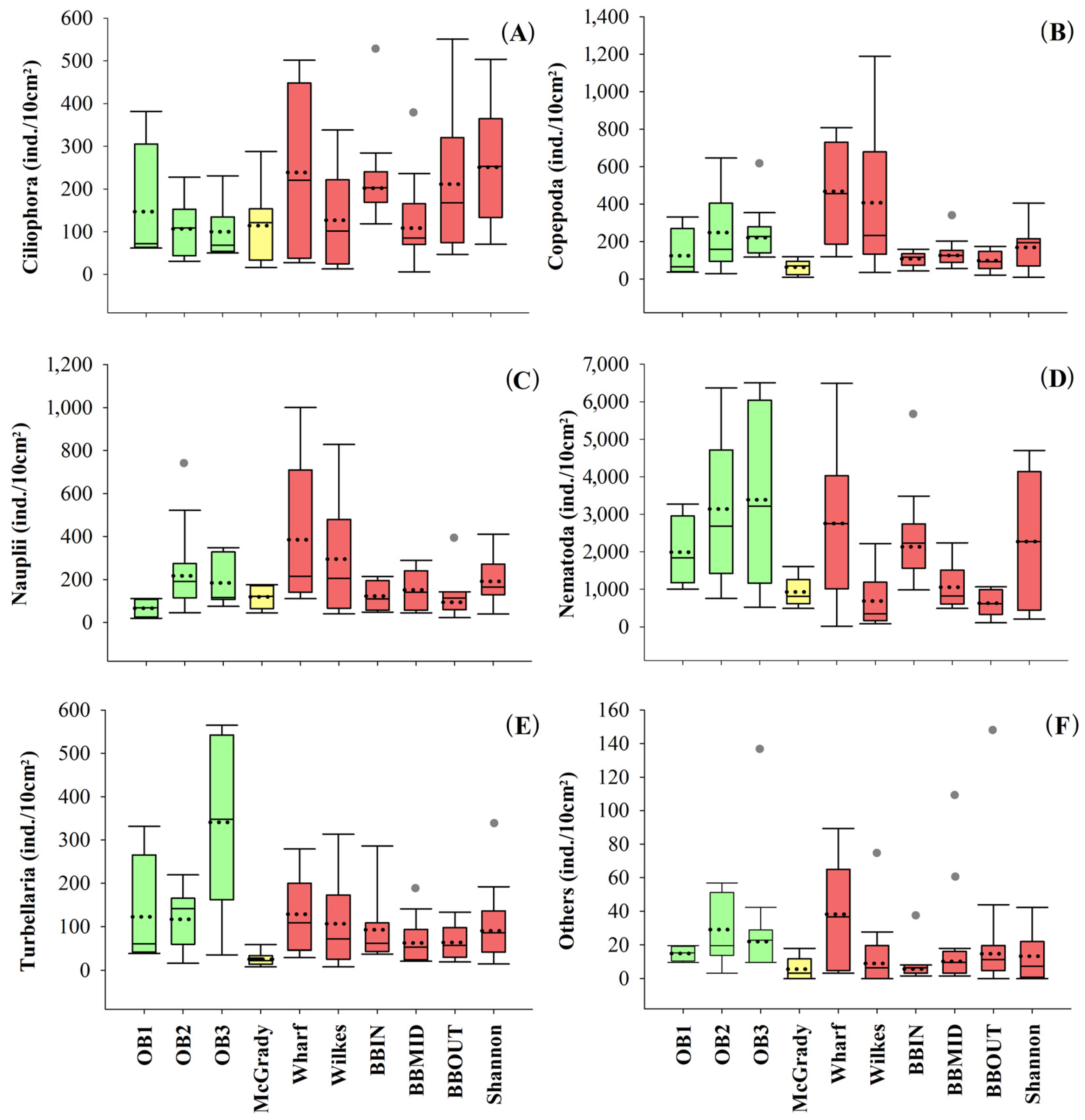
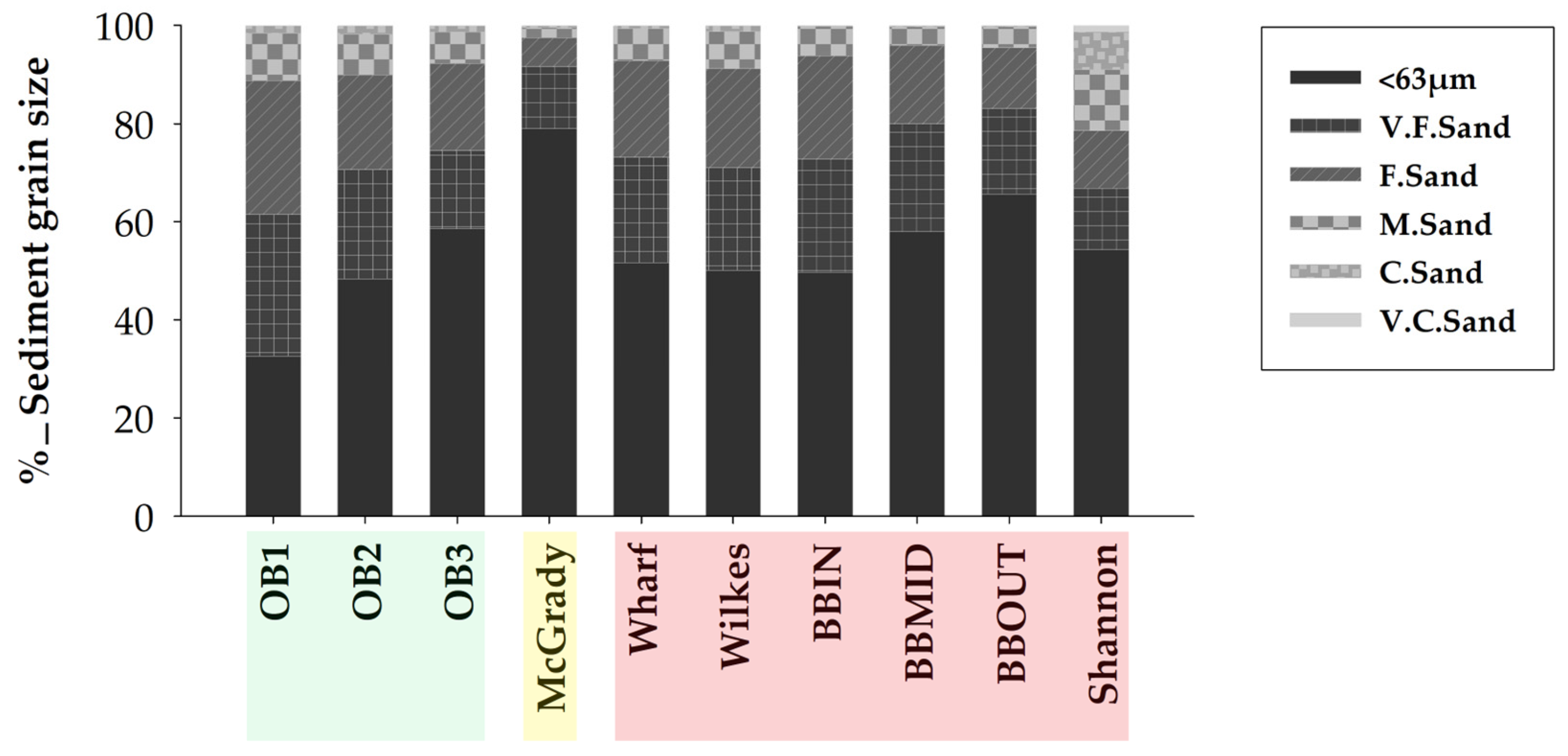

| Location | Med. (±SE) | EcoQ |
|---|---|---|
| OB1 | 8.00 ± 0.40 | Moderate |
| OB2 | 7.11 ± 0.42 | Poor |
| OB3 | 8.28 ± 0.52 | Moderate |
| McGrady | 6.50 ± 0.56 | Poor |
| Wharf | 7.62 ± 0.37 | Poor |
| Wilkes | 6.50 ± 0.50 | Poor |
| BBIN | 6.75 ± 0.36 | Poor |
| BBMID | 6.72 ± 0.27 | Poor |
| BBOUT | 7.37 ± 0.53 | Poor |
| Shannon | 6.25 ± 0.35 | Poor |
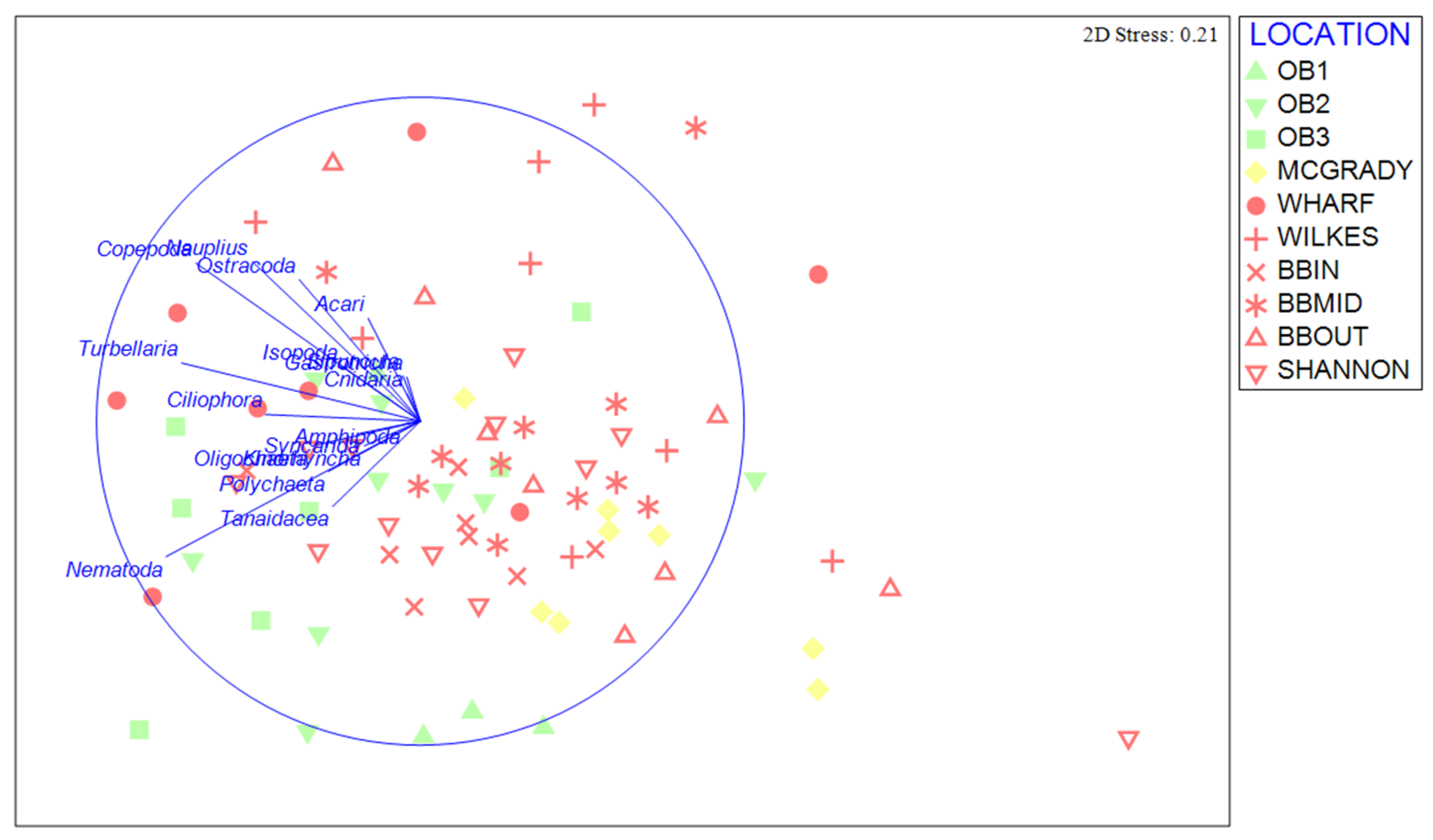
| Meiofauna Structure | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | PERMANOVA Results | |||
| df | MS | Pseudo-F | p (perm) | |
| Bay | 1 | 1183.10 | 2.37 | 0.50 |
| Location [Bay] | 8 | 511.77 | 2.27 | <0.01 |
| Site [Location [Bay]] | 12 | 217.47 | 0.99 | 0.51 |
| Plot [Site [Location [Bay]]] | 21 | 218.78 | 1.30 | 0.07 |
| Residual | 40 | 167.99 | ||
| Total | 82 | |||
| Source | PERMANOVA Results | |||
| df | MS | Pseudo-F | p (perm) | |
| Location | 9 | 586.36 | 3.07 | <0.01 |
| O’Brien vs. McGrady * | 1 | 1358.90 | 7.33 | <0.01 |
| O’Brien vs. Wharf * | 1 | 517.46 | 2.35 | 0.03 |
| O’Brien vs. Wilkes * | 1 | 984.40 | 4.40 | <0.01 |
| O’Brien vs. BBIN * | 1 | 494.36 | 2.96 | 0.01 |
| O’Brien vs. BBMID * | 1 | 658.11 | 3.75 | <0.01 |
| O’Brien vs. BBOUT * | 1 | 1011.10 | 4.93 | <0.01 |
| O’Brien vs. Shannon * | 1 | 573.25 | 2.76 | 0.02 |
| Reference locations vs. Wharf * | 1 | 698.49 | 2.91 | 0.01 |
| Reference locations vs. Wilkes * | 1 | 745.50 | 3.07 | 0.01 |
| Reference locations vs. BBIN * | 1 | 362.82 | 1.82 | 0.10 |
| Reference locations vs. BBMID * | 1 | 344.14 | 1.69 | 0.14 |
| Reference locations vs. BBOUT * | 1 | 631.75 | 2.76 | 0.02 |
| Reference locations vs. Shannon * | 1 | 332.51 | 1.45 | 0.19 |
| Residual | 73 | 190.73 | ||
| Total | 82 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
França, D.A.A.; Ingels, J.; Stark, J.S.; da Silva, R.B.; de França, F.J.L.; dos Santos, G.A.P. Impact of Different Sources of Anthropogenic Pollution on the Structure and Distribution of Antarctic Marine Meiofauna Communities. Diversity 2024, 16, 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16080464
França DAA, Ingels J, Stark JS, da Silva RB, de França FJL, dos Santos GAP. Impact of Different Sources of Anthropogenic Pollution on the Structure and Distribution of Antarctic Marine Meiofauna Communities. Diversity. 2024; 16(8):464. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16080464
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrança, Débora A.A., Jeroen Ingels, Jonathan S. Stark, Renan B. da Silva, Flávia J.L. de França, and Giovanni A.P. dos Santos. 2024. "Impact of Different Sources of Anthropogenic Pollution on the Structure and Distribution of Antarctic Marine Meiofauna Communities" Diversity 16, no. 8: 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16080464
APA StyleFrança, D. A. A., Ingels, J., Stark, J. S., da Silva, R. B., de França, F. J. L., & dos Santos, G. A. P. (2024). Impact of Different Sources of Anthropogenic Pollution on the Structure and Distribution of Antarctic Marine Meiofauna Communities. Diversity, 16(8), 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16080464






