DNA Barcoding for Species Identification of Moss-Dwelling Invertebrates: Performance of Nanopore Sequencing and Coverage in Reference Database
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and DNA Extraction
2.2. Nanopore Sequencing
2.3. Basecalling of ONT Reads
2.4. Demultiplexing and Generating Consensus Barcodes
2.5. Sanger Sequencing
2.6. Comparison among Sequencing Methods and Reference Database Coverage
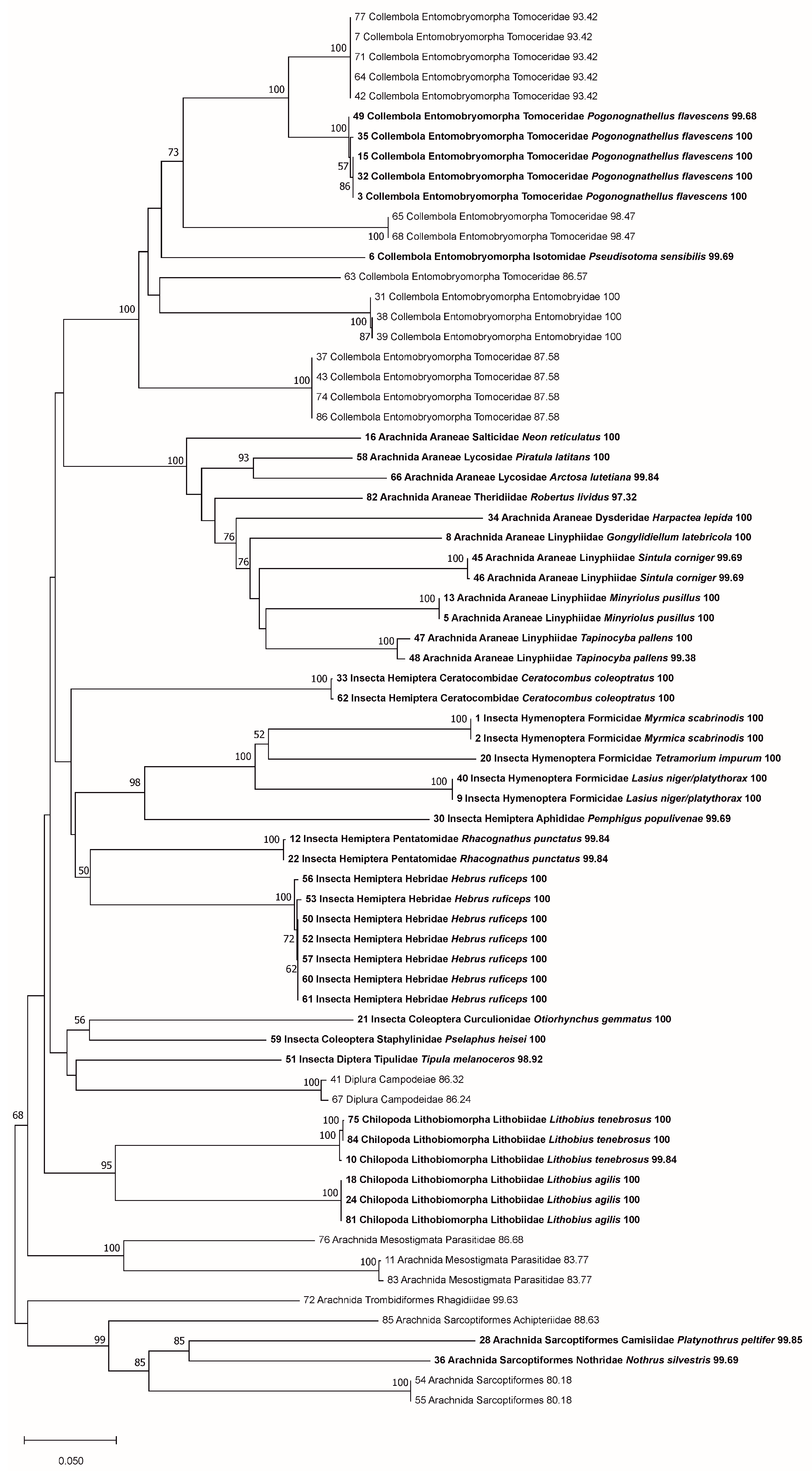
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Sequencing Approaches
3.1.1. Different Nanopore Sequencing Approaches
3.1.2. Nanopore vs. Sanger Sequencing
3.2. Coverage in BOLD
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vernooy, R.; Haribabu, E.; Muller, M.R.; Vogel, J.H.; Hebert, P.D.N.; Schindel, D.E.; Shimura, J.; Singer, G.A.C. Barcoding life to conserve biological diversity: Beyond the taxonomic imperative. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prather, C.M.; Pelini, S.L.; Laws, A.; Rivest, E.; Woltz, M.; Bloch, C.P.; Del Toro, I.; Ho, C.K.; Kominoski, J.; Newbold, T.A.S.; et al. Invertebrates, ecosystem services and climate change. Biol. Rev. 2013, 88, 327–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Isbell, F.; Cowles, J.M. Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2014, 45, 471–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkhofer, K.; Rusch, A.; Andersson, G.K.S.; Bommarco, R.; Dänhardt, J.; Ekbom, B.; Jönsson, A.; Lindborg, R.; Olsson, O.; Rader, R.; et al. A framework to identify indicator species for ecosystem services in agricultural landscapes. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 91, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, K.; van der Heyde, M.; Coghlan, M.; Wardell-Johnson, G.; Bunce, M.; Harris, R.; Nevill, P. Invertebrate DNA metabarcoding reveals changes in communities across mine site restoration chronosequences. Restor. Ecol. 2019, 27, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, J.; Pereira, H.M. Biodiversity: Monitoring trends and implications for ecosystem functioning. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, R1390–R1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losapio, G.; Genes, L.; Knight, C.J.; McFadden, T.N.; Pavan, L. Monitoring and modelling the effects of ecosystem engineers on ecosystem functioning. Funct. Ecol. 2024, 38, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, M.E.; Ceríaco, L.M.P.; Daniel, G.M.; Dellapé, P.M.; Löbl, I.; Marinov, M.; Reis, R.E.; Young, M.T.; Dubois, A.; Agarwal, I.; et al. The taxonomic impediment: A shortage of taxonomists, not the lack of technical approaches. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2021, 193, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, M.A.; Kirwan, G.M.; Lourenço, A.C.C.; Sobral, G.; Bockmann, F.A.; Stopiglia, R. On the notions of taxonomic ‘impediment’, ‘gap’, ‘inflation’ and ‘anarchy’, and their effects on the field of conservation. Syst. Biodivers. 2021, 19, 296–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäffer, S.; Kerschbaumer, M.; Koblmüller, S. Multiple new species: Cryptic diversity in the widespread mite species Cymbaeremaeus cymba (Oribatida, Cymbaeremaeidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019, 135, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäffer, S.; Koblmüller, S. Unexpected diversity in the host-generalist oribatid mite Paraleius leontonychus (Oribatida, Scheloribatidae) phoretic on Palearctic bark beetles. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carapelli, A.; Greenslade, P.; Nardi, F.; Leo, C.; Convey, P.; Frati, F.; Fanciulli, P.P. Evidence for cryptic diversity in the “Pan-Antarctic” springtail Friesea antarctica and the description of two new species. Insects 2020, 11, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfingstl, T.; Lienhard, A.; Baumann, J.; Koblmüller, S. A taxonomist‘s nightmare–cryptic diversity in Caribbean intertidal arthropods (Arachnida, Acari, Oribatida). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2021, 163, 107240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raphalo, E.M.; Cole, M.L.; Daniels, S.R. Barcoding of South African forest-dwelling snails (Mollusca: Gastropoda) reveals widespread cryptic diversity. Invertebr. Biol. 2021, 140, e12348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlebec, D.; Podnar, M.; Kučinić, M.; Harms, D. Molecular analyses of pseudoscorpions in a subterranean biodiversity hotspot reveal cryptic diversity and microendemism. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; deWaard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, D.M.; Brodnicke, O.B.; Evankow, A.M.; Ferreira, A.O.; Fontes, J.T.; Hansen, A.K.; Jensen, M.R.; Kalaycı, T.E.; Leeper, A.; Patil, S.K.; et al. The future of DNA barcoding: Reflections from early career researchers. Diversity 2021, 13, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanger, F.; Nicklen, S.; Coulson, A.R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 5463–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.M.; Sanders, J.Z.; Kaiser, R.J.; Hughes, P.; Dodd, C.; Connell, C.R.; Heiner, C.; Kent, S.B.H.; Hood, L.E. Fluorescence detection in automated DNA sequence analysis. Nature 1986, 321, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuber, P.; Chooneea, D.; Geeves, C.; Salatino, S.; Creedy, T.J.; Griffin, C.; Sivess, L.; Barnes, I.; Price, B.; Misra, R. Comparing the accuracy and efficiency of third generation sequencing technologies, Oxford Nanopore Technologies, and Pacific Biosciences, for DNA barcode sequencing applications. Ecol. Genet. Genom. 2023, 28, 100181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taberlet, P.; Coissac, E.; Pompanon, F.; Brochmann, C.; Willerslev, E. Towards next-generation biodiversity assessment using DNA metabarcoding. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 2045–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruppert, K.M.; Kline, R.J.; Rahman, M.S. Past, present, and future perspectives of environmental DNA (eDNA) metabarcoding: A systematic review in methods, monitoring, and applications of global eDNA. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 17, e00547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñol, J.; Mir, G.; Gomez-Polo, P.; Agustí, N. Universal and blocking primer mismatches limit the use of high-throughput DNA sequencing for the quantitative metabarcoding of arthropods. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajibabaei, M.; Shokralla, S.; Zhou, X.; Singer, G.A.C.; Baird, D.J. Environmental barcoding: A next-generation sequencing approach for biomonitoring applications using river benthos. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenk, J.; Geisen, S.; Kleinbölting, N.; Traunspurger, W. Metabarcoding data allow for reliable biomass estimates in the most abundant animals on Earth. Metabarcoding Metagenom. 2019, 3, e46704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkuil, Y.I.; Nicolaus, M.; Ubels, R.; Dietz, M.W.; Samplonius, J.M.; Galema, A.; Kiekebos, K.; de Knijff, P.; Both, C. DNA metabarcoding quantifies the relative biomass of arthropod taxa in songbird diets: Validation with camera-recorded diets. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e8881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rourke, M.L.; Fowler, A.M.; Hughes, J.M.; Broadhurst, M.K.; DiBattista, J.D.; Fielder, S.; Wilkes Walburn, J.; Furlan, E.M. Environmental DNA (eDNA) as a tool for assessing fish biomass: A review of approaches and future considerations for resource surveys. Environ. DNA 2022, 4, 9–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbrecht, V.; Leese, F. Can DNA-based ecosystem assessments quantify species abundance? Testing primer bias and biomass-sequence relationships with an innovative metabarcoding protocol. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Olsen, H.E.; Paten, B.; Akeson, M. The Oxford Nanopore MinION: Delivery of nanopore sequencing to the genomics community. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delahaye, C.; Nicolas, J. Sequencing DNA with nanopores: Troubles and biases. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlin, K.; Lim, M.C.W.; Prost, S. NGSpeciesID: DNA barcode and amplicon consensus generation from long-read sequencing data. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 1392–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivathsan, A.; Lee, L.; Katoh, K.; Hartop, E.; Kutty, S.N.; Wong, J.; Yeo, D.; Meier, R. ONTbarcoder and MinION barcodes aid biodiversity discovery and identification by everyone, for everyone. BMC Biol. 2021, 19, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vierstraete, A.R.; Braeckman, B.P. Amplicon_sorter: A tool for reference-free amplicon sorting based on sequence similarity and for building consensus sequences. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e8603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidov, K.; Iankelevich-Kounio, E.; Yakovenko, I.; Koucherov, Y.; Rubin-Blum, M.; Oren, M. Identification of plastic-associated species in the Mediterranean Sea using DNA metabarcoding with nanopore MinION. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baloğlu, B.; Chen, Z.; Elbrecht, V.; Braukmann, T.; MacDonald, S.; Steinke, D. A workflow for accurate metabarcoding using nanopore MinION sequencing. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2021, 12, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Reis, A.L.; Beckley, L.E.; Olivar, M.P.; Jeffs, A.G. Nanopore short-read sequencing: A quick, cost-effective and accurate method for DNA metabarcoding. Environ. DNA 2022, 5, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richlen, M.L.; Barber, P.H. A technique for the rapid extraction of microalgal DNA from sngle live and preserved cells. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2005, 5, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pentinsaari, M.; Hebert, P.D.N.; Mutanen, M. Barcoding beetles: A regional survey of 1872 species reveals high identification success and unusually deep interspecific divergences. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-da-Conceicoa, L.; Elbrecht, V.; Hall, A.; Briscoe, A.; Barber-James, H.; Price, B. Metabarcoding unsorted kick-samples facilitates macroinvertebrate-based biomonitoring with increased taxonomic resolution, while outperforming environmental DNA. Environ. DNA 2021, 3, 353–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anđelić Dmitrović, B.; Jelić, M.; Rota, E.; Jelaska, L.Š. DNA barcoding of invertebrates inhabiting olive orchards and vineyards accelerates understudied Mediterranean biodiversity assessment. Diversity 2022, 14, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukowski, B.; Ratnasingham, S.; Hanisch, P.E.; Hebert, P.D.N.; Perez, K.; deWaard, J.; Tubaro, P.L.; Lijtmaer, D.A. DNA barcodes reveal striking arthropod diversity and unveil seasonal patterns of variation in the southern Atlantic Forest. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roslin, T.; Somervuo, P.; Pentinsaari, M.; Hebert, P.D.N.; Agda, J.; Ahlroth, P.; Anttonen, P.; Aspi, J.; Blagoev, G.; Blanco, S.; et al. A molecular-based identification resource for the arthropods of Finland. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2022, 22, 803–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivathsan, A.; Hartop, E.; Puniamoorthy, J.; Lee, W.T.; Kutty, S.N.; Kurina, O.; Meier, R. Rapid, large-scale species discovery in hyperdiverse taxa using 1D MinION sequencing. BMC Biol. 2019, 17, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Bollas, A.; Wang, Y.; Au, K.F. Nanopore sequencing technology, bioinformatics and applications. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 1348–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivathsan, A.; Feng, V.; Suárez, D.; Emerson, B.; Meier, R. ONTbarcoder 2.0: Rapid species discovery and identification with real-time barcoding facilitated by Oxford Nanopore R10.4. Cladistics 2023, 40, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.R.; Proctor, H.C.; deWaard, J.R.; Hebert, P.D.N. DNA barcodes expose unexpected diversity in Canadian mites. Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 5347–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porco, D.; Bedos, A.; Greenslade, P.; Janion, C.; Skarżyński, D.; Stevens, M.I.; Jansen van Vuuren, B.; Deharveng, L. Challenging species delimitation in Collembola: Cryptic diversity among common springtails unveiled by DNA barcoding. Invertebr. Syst. 2012, 26, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Saltzwedel, H.; Scheu, S.; Schaefer, I. Genetic structure and distribution of Parisotoma notabilis (Collembola) in Europe: Cryptic diversity, split of lineages and colonization patterns. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, T.-W.; Mateos, E.; Scheu, S.; Schaefer, I. DNA-based approaches uncover cryptic diversity in the European Lepidocyrtus lanuginosus species group (Collembola: Entomobryidae). Invertebr. Syst. 2019, 22, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. EU Soil Strategy for 2030: Reaping the Benefits of Healthy Soils for People, Food, Nature and Climate; Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Skoracka, A.; Magalhães, S.; Rector, B.G.; Kuczyński, L. Cryptic speciation in the Acari: A function of species lifestyles or our ability to separate species? Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2015, 67, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D.N. A DNA-based registry for all animal species: The Barcode Index Number (BIN) system. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, B. Die Ameisen Mittel-Und Nordeuropas; Lutra: Boxberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Seifert, B. A Taxonomic revision of the Palaearctic members of the subgenus Lasius s.str. (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Soil Org. 2020, 92, 15–86. [Google Scholar]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Penton, E.H.; Burns, J.M.; Janzen, D.H.; Hallwachs, W. Ten species in one: DNA barcoding reveals cryptic species in the Neotropical Skipper Butterfly Astraptes fulgerator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14812–14817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germain, J.-F.; Chatot, C.; Meusnier, I.; Artige, E.; Rasplus, J.-Y.; Cruaud, A. Molecular identification of Epitrix potato flea beetles (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) in Europe and North America. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2013, 103, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, J.; Costa, P.M.; Teixeira, M.A.; Ferreira, M.S.; Costa, M.H.; Costa, F.O. Enhanced primers for amplification of DNA barcodes from a broad range of marine metazoans. BMC Ecol. 2013, 13, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
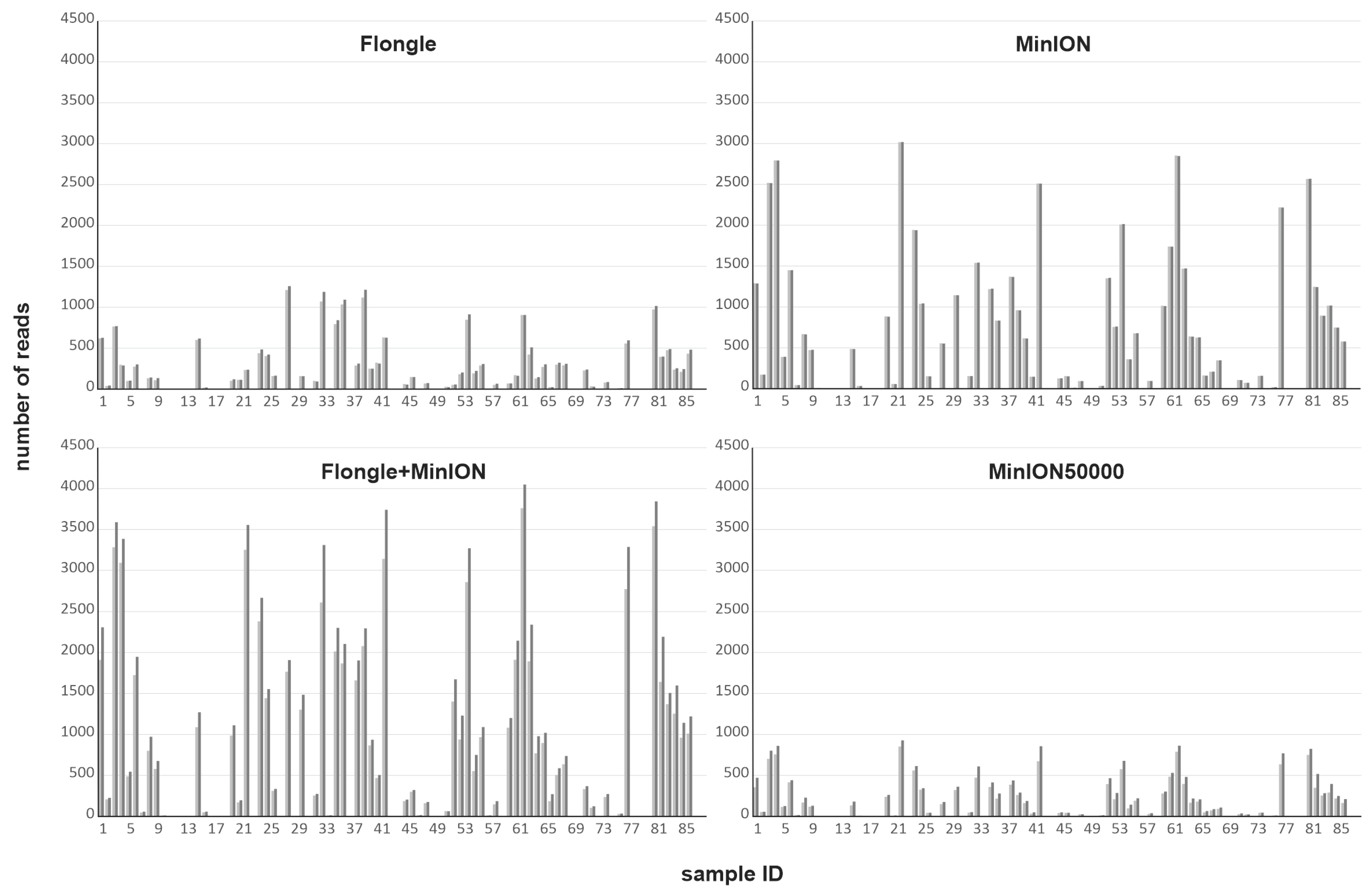
| Flongle hac | Flongle shac | MinION hac | MinION shac | MinION+ Flongle hac | MinION+ Flongle shac | MinION 50000 hac | MinION 50000 shac | Sanger | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of reads in file | 59,638 | 59,185 | 179,488 | 181,252 | 239,126 | 240,437 | 50,000 | 50,000 | |
| Number of reads passing length filter | 43,334 | 43,304 | 126,041 | 127,618 | 169,375 | 170,922 | 35,214 | 35,270 | |
| Number of reads used for demultiplexing | 39,417 | 39,428 | 113,266 | 114,799 | 152,683 | 154,227 | 31,806 | 31,868 | |
| Number of samples in demultiplexing file | 88 | 88 | 88 | 88 | 88 | 88 | 88 | 88 | |
| Number of samples with ≥5× coverage | 60 | 60 | 62 | 63 | 62 | 63 | 58 | 58 | |
| Number of good barcodes obtained after first alignment of up to 200 reads | 28 | 37 | 50 | 56 | 54 | 55 | 45 | 52 | |
| Number of erroneous barcodes obtained after first alignment of up to 200 reads | 28 | 21 | 11 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 10 | 5 | |
| Number of good barcodes obtained after aligning similar reads | 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | |
| Number of erroneous barcodes obtained after aligning similar reads | 23 | 17 | 9 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 3 | |
| Number of barcodes fixed | 25 | 20 | 7 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 8 | 3 | |
| Final number of barcodes | 57 | 59 | 58 | 60 | 59 | 59 | 56 | 56 | 63 |
| Final number of barcodes that cannot be fixed | 3 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | |
| Number of Ns in final barcodes | 94 | 66 | 11 | 23 | 3 | 2 | 49 | 26 | |
| Number of filtered barcodes | 53 | 55 | 57 | 58 | 59 | 58 | 53 | 54 | |
| Number of QC-compliant full-length barcodes * | 32 | 39 | 51 | 58 | 56 | 56 | 48 | 53 | 35 |
| Number of barcodes with 1–5 errors | 21 | 16 | 6 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 1 | |
| Number of barcodes with 6–10 errors | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| Number of barcodes with 11–15 errors | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| Number of barcodes with over 15 errors | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koblmüller, S.; Resl, P.; Klar, N.; Bauer, H.; Zangl, L.; Hahn, C. DNA Barcoding for Species Identification of Moss-Dwelling Invertebrates: Performance of Nanopore Sequencing and Coverage in Reference Database. Diversity 2024, 16, 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16040196
Koblmüller S, Resl P, Klar N, Bauer H, Zangl L, Hahn C. DNA Barcoding for Species Identification of Moss-Dwelling Invertebrates: Performance of Nanopore Sequencing and Coverage in Reference Database. Diversity. 2024; 16(4):196. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16040196
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoblmüller, Stephan, Philipp Resl, Nadine Klar, Hanna Bauer, Lukas Zangl, and Christoph Hahn. 2024. "DNA Barcoding for Species Identification of Moss-Dwelling Invertebrates: Performance of Nanopore Sequencing and Coverage in Reference Database" Diversity 16, no. 4: 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16040196
APA StyleKoblmüller, S., Resl, P., Klar, N., Bauer, H., Zangl, L., & Hahn, C. (2024). DNA Barcoding for Species Identification of Moss-Dwelling Invertebrates: Performance of Nanopore Sequencing and Coverage in Reference Database. Diversity, 16(4), 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16040196








