Reassessing the Diversity of the Arthropod-Pathogenic Genus Pandora Batko (Entomophthoromycotina; Erynioideae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Fungal Collection
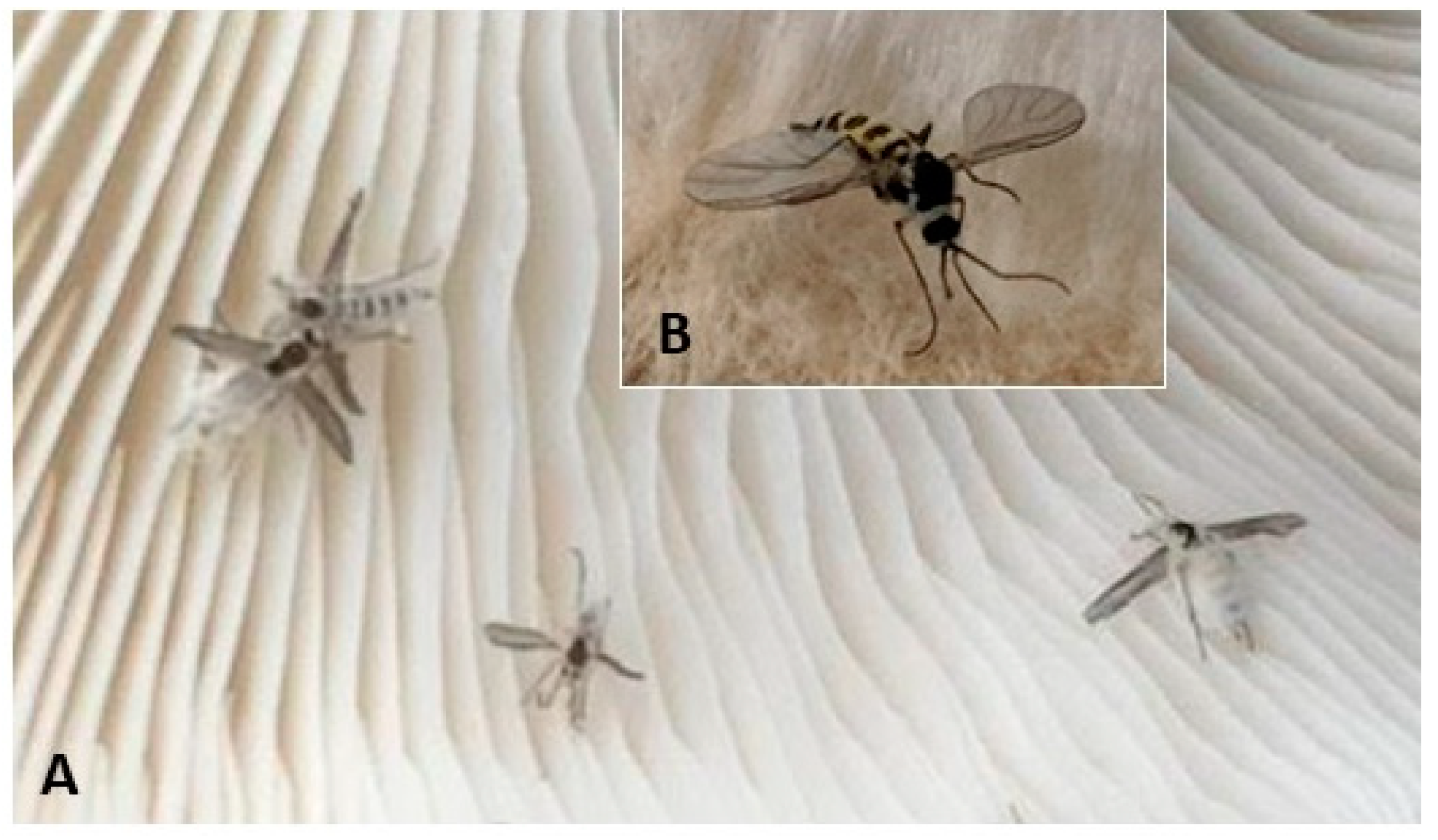
2.1.1. Pandora gloeospora from Mushroom Flies
2.1.2. Fungus from Lophocampa caryae Larvae
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification and Sequencing
2.2.1. Kennett Square, Pennsylvania Sample from Lycoriella mali
2.2.2. Michigan Sample from Lophocampa caryae
2.2.3. Vermont Sample from Lophocampa caryae
2.3. Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Phylogenetic Reconstruction
Taxonomy
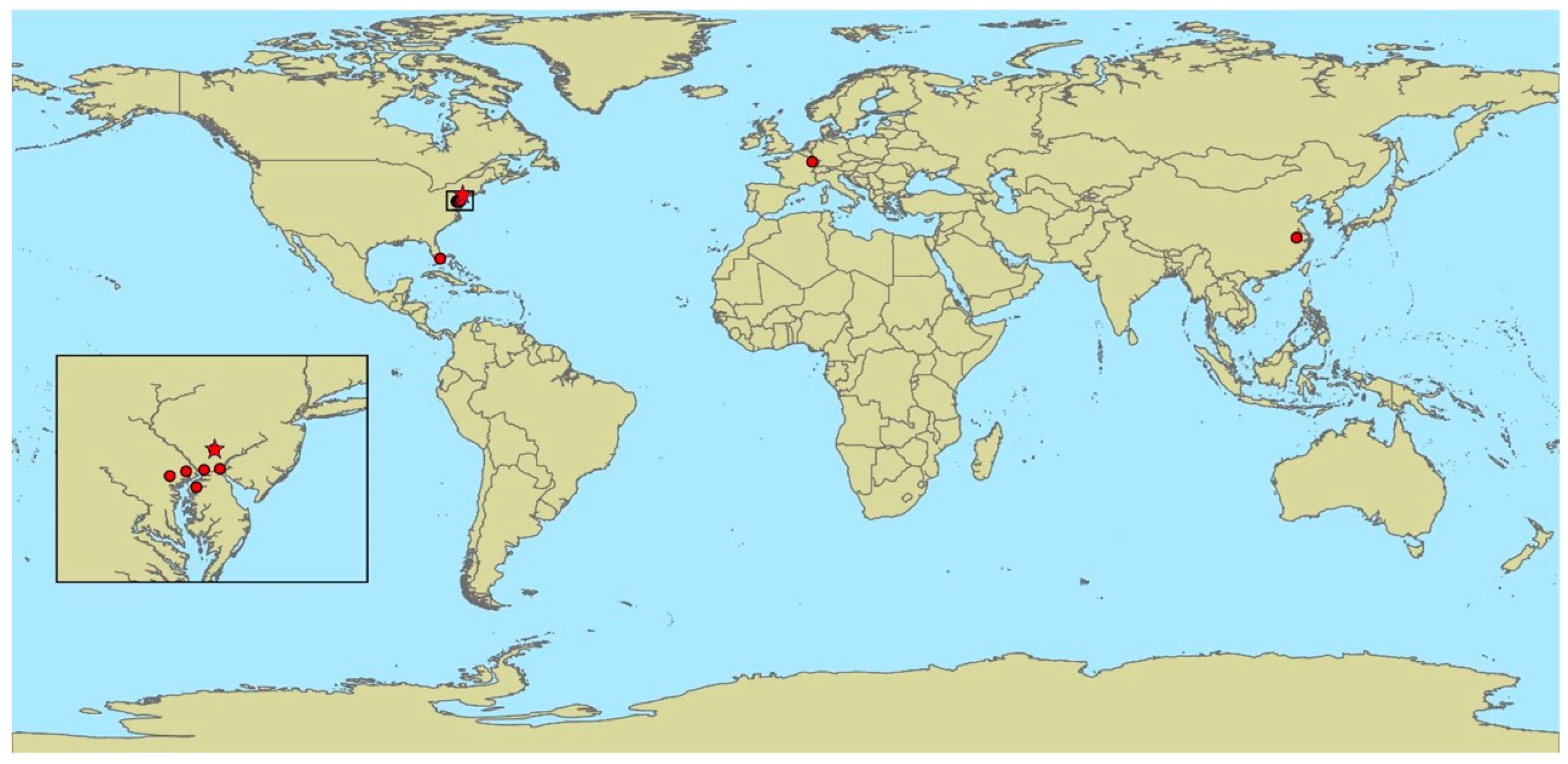
3.2. Pandora gloeospora Biology and Distribution
3.3. New Species Description
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pell, J.; Eilenberg, J.; Hajek, A.E.; Steinkraus, D.C. Biology, ecology and pest management potential of Entomophthorales. In Fungi as Biocontrol Agents: Progress, Problems and Potential; Butt, T.M., Jackson, C.W., Magan, N., Eds.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2001; pp. 71–153. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, H.E.; Steinkraus, D.C.; Eilenberg, J.; Hajek, A.E.; Pell, J.K. Bizarre interactions and endgames: Entomopathogenic fungi and their arthropod hosts. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2006, 51, 331–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, S.; Petrini, O. Keys to the identification of the arthropod pathogenic genera of the families Entomophthoraceae and Neozygitaceae (Zygomycetes), with descriptions of three new subfamilies and a new genus. Sydowia 2005, 57, 23–53. [Google Scholar]
- Batko, A. On the new genera: Zoophthora gen. nov., Triplosporium (Thaxter) gen. nov., and Entomophaga gen. nov. (Phycomycetes: Entomophthoraceae). Bull. Acad. Pol. Sci. Cl II 1964, 12, 323–326. [Google Scholar]
- Batko, A. On the subgenera of the fungus genus Zoophthora Batko 1964 (Entomophthoraceae). Acta Mycol. 1966, 2, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ze’ev, I.; Kenneth, R.G. Features criteria of taxonomic value in the Entomophthorales. 1. A revision of the Batkoan classification. 2. A revision of the genus Erynia Nowakowski 1881 (Zoophthora Batko 1965). Mycotaxon 1982, 14, 393–475. [Google Scholar]
- Bałazy, S. Flora Polska, Grzyby (Mycota). Vol. 24. Owadomorkowe, Entomophthorales; Polish Academy of Sciences: Kraków, Poland, 1993; 356p. [Google Scholar]
- Humber, R.A. Synopsis of a revised classification for the Entomophthorales (Zygomycotina). Mycotaxon 1989, 34, 441–460. [Google Scholar]
- Gryganskyi, A.P.; Humber, R.A.; Smith, M.E.; Hodge, K.; Huang, B.; Voigt, K.; Vilgalys, R. Phylogenetic lineages in Entomophthoromycota. Persoonia 2013, 30, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryganskyi, A.P.; Hajek, A.E.; Voloshchuk, N.; Idnurm, A.; Eilenberg, J.; Manfrino, R.G.; Bushley, K.E.; Kava, L.; Kutovenko, B.; Anike, F.; et al. Potential for use of species in the subfamily Erynioideae for biological control and biotechnology. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, A.H.; Lindquist, O.H. Insects of eastern hardwood trees. Canad. For. Serv., For. Tech. Rpt. 1982, 29, 212. [Google Scholar]
- Hajek, A.E.; Papierok, B.; Eilenberg, J. Methods for study of the Entomophthorales, In Manual of Techniques in Invertebrate Pathology, 2nd ed.; Lacey, L., Ed.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 285–316. [Google Scholar]
- Bosso, L.; Senatore, M.; Varlese, R.; Ruocco, M.; Garonna, A.P.; Bonanomi, G.; Mazzoleni, S.; Cristinzio, G. Severe outbreak of Fusarium solani on Quercus ilex vectored by Xylosandrus compactus. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 94 4 Supplement, S4.99. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta, R.I.T.; Humber, R.A.; Sánchez-Peña, S.R. Zoophthora radicans (Entomophthorales), a fungal pathogen of Bagrada hilaris and Bactericera cockerelli (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae and Triozidae): Prevalence, pathogenicity, and interplay of environmental influence, morphology, and sequence data on fungal identification. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016, 139, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryganskyi, A.P.; Golan, J.; Dolatabadi, S.; Mondo, S.; Robb, S.; Idnurm, A.; Muszewska, A.; Steczkiewicz, K.; Masonjones, S.; Liao, H.L.; et al. Phylogenetic and phylogenomic definition of Rhizopus species. G3 (Bethesda) 2018, 8, 2007–2018, Erratum in G3 (Bethesda) 2019, 9, 2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauff, F.; Lutzoni, F. Phylogeny of the Gyalectales and Ostropales (Ascomycota, Fungi): Among and within order relationships based on nuclear ribosomal RNA small and large subunits. Molec. Phylogen. Evol. 2002, 25, 138–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardes, M.; Bruns, T.D. ITS primers with enhanced specificity for basidiomycetes—Application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Mol. Ecol. 1993, 2, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications (I); Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Hajek, A.E.; Gryganskyi, A.; Bittner, T.; Liebherr, J.K.; Liebherr, J.H.; Moulton, J.K.; Jensen, A.B.; Humber, R.A. Phylogenetic placement of two species known only from resting spores: Zoophthora independentia sp. nov. and Z. porteri comb nov. (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016, 140, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A.B.; Eilenberg, J. Genetic variation within the insect-pathogenic genus Entomophthora, focusing on the E. muscae complex, using PCR-RFLP of the ITS II and the LSU rDNA. Mycol. Res. 2001, 105, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjøller, R.; Rosendahl, S. Detection of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (Glomales) in roots by nested PCR and SSCP (Single Stranded Confirmation Polymorphism). Plant Soil 2000, 226, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilgalys, R.; Hester, M. Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 4238–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddison, W.P.; Maddison, D.R. Mesquite: A modular system for evolutionary analysis, Version 3.81. 2023. Available online: https://www.mesquiteproject.org/ (accessed on 23 July 2024).
- Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. MODELTEST: Testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 1988, 14, 817–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwickl, D.J. Genetic Algorithm Approaches for the Phylogenetic Analysis of Large Biological Sequence Datasets under the Maximum Likelihood Criterion. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, USA, 2006; 125 p. [Google Scholar]
- Vuillemin, P. Études biologiques sur les champignons. Soc. Sci. (Nancy) Bull. Soc. Sci. Nancy 1886, 8 (année 19), 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Remaudière, G.; Hennebert, G.L. Révision systématique de Entomophthora aphidis Hoffm. in Fres. Description de deux nouveaux pathogènes d’Aphides. Mycotaxon 1980, 11, 269–321. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Huang, B.; Fan, M. New species, new record, new combinations and emendation of entomophthoralean fungi pathogenic to dipteran insects. Mycosystema 1997, 16, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.W.; Keil, C.B. Redescription of Pandora gloeospora (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) from Lycoriella mali (Diptera: Sciaridae). Mycotaxon 1990, 38, 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, L.-S.; Wen, T.-C.; Hyde, K.D.; Kang, J.-C. An updated checklist of fungal species in Entomophthorales and their host insects from China. Mycosystema 2016, 35, 666–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorsetti, A.C.; Jensen, A.B.; López Lastra, C.; Humber, R.A. First report of Pandora neoaphidis resting spore formation in vivo in aphid hosts. Fung. Biol. 2012, 116, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodge, K.; Hajek, A.E.; Gryganskyi, A. The first entomophthoralean killing millipedes, Arthrophaga myriapodina n. gen. n. sp., causes climbing before host death. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2017, 149, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Yu, D.-S.; Wang, C.-F.; Liu, X.-Y.; Huang, B. A taxonomic revision of the genus Conidiobolus (Ancylistaceae, Entomophthorales): Four clades including three new genera. MycoKeys 2020, 66, 55–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, S.; Hülsewig, T.; Jensen, A.B. Fungi attacking springtails (Sminthuridae, Collembola) with a description of Pandora batallata, sp. nov. (Entomophthoraceae). Sydowia 2022, 75, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Species, # of Specimens | 18S Accession # | 28S Accession # |
|---|---|---|
| Arthrophaga myriapodina (2) | MF544092, MF544093 | MF544094, NG058604 |
| Entomophaga aulicae | U35394 | EF392372 |
| Ent. maimaiga | EF392556 | EF392395 |
| Entomophthora muscae (2) | AY635820, D29948 | DQ273772, DQ481224 |
| En. planchoniana | AF353723 | MH366738 |
| En. schizophorae | AF052402 | DQ481228 |
| Erynia conica | AF368513 | EF392396 |
| E. ovispora | JX242620 | JX242601 |
| E. rhizospora | AF368514 | EF392397 |
| Eryniopsis caroliniana | AF368517 | EF392387 |
| Furia americana | EF392554 | EF392389 |
| F. gastropachae | EF392562 | EF392407 |
| F. ithacensis | AF351134 | EF392388 |
| F. pieris | AF368519 | EF392390 |
| F. sciarae | AF368515 | EF392399 |
| F. virescens | EF392555 | EF392393 |
| Massospora levispora (2) | MH483020, MN706559 | MH483016, MN706591 |
| M. tettigatis | MN706562 | MN706593 |
| Neoconidiobolus thromboides (2) | AF052401, JX242616 | JF816214, JX242597 |
| Pandora batallata | - | ON176196 |
| P. blunckii | JX242621 | JX242602 |
| P. bullata | HQ677592 | - |
| P. delphacis | AF368521, EF392551 | EF392384, EF392386 |
| P. dipterigena | AF368522 | EF392380 |
| P. gammae | OM732268 | OM732269 |
| P. gloeospora | PQ038061 | PQ062133 |
| P. kondoiensis (2) | AF351133, JX242622 | EF392391, JX242603 |
| P. neoaphidis (3) | EU267188, EU267192, EU267193 | EF392405, MH366634, MH366734 |
| P. neopyralidarum | AF368518 | EF392394 |
| P. sylvestris | PQ038062 | PQ062134 |
| Strongwellsea castrans | AF052406 | - |
| Zoophthora anglica | AF368524 | EF392379 |
| Z. lanceolata | EF392550 | EF392385 |
| Z. occidentalis | AF368525 | EF392402 |
| Z. phalloides | EF392558 | EF392400 |
| Z. radicans (2) | D61381, JX242624 | MK970712, MK970714 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hajek, A.E.; Gryganskyi, A.P.; Gouli, S.Y.; Bittner, T.D.; Sullivan, C.F.; Parker, B.L. Reassessing the Diversity of the Arthropod-Pathogenic Genus Pandora Batko (Entomophthoromycotina; Erynioideae). Diversity 2024, 16, 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16100603
Hajek AE, Gryganskyi AP, Gouli SY, Bittner TD, Sullivan CF, Parker BL. Reassessing the Diversity of the Arthropod-Pathogenic Genus Pandora Batko (Entomophthoromycotina; Erynioideae). Diversity. 2024; 16(10):603. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16100603
Chicago/Turabian StyleHajek, Ann E., Andrii P. Gryganskyi, Svetlana Y. Gouli, Tonya D. Bittner, Cheryl F. Sullivan, and Bruce L. Parker. 2024. "Reassessing the Diversity of the Arthropod-Pathogenic Genus Pandora Batko (Entomophthoromycotina; Erynioideae)" Diversity 16, no. 10: 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16100603
APA StyleHajek, A. E., Gryganskyi, A. P., Gouli, S. Y., Bittner, T. D., Sullivan, C. F., & Parker, B. L. (2024). Reassessing the Diversity of the Arthropod-Pathogenic Genus Pandora Batko (Entomophthoromycotina; Erynioideae). Diversity, 16(10), 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16100603






