Morphological Characteristics and DNA Barcoding of the Rare Blanket Octopus Tremoctopus violaceus (Cephalopoda: Tremoctopodidae) in the Adriatic Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Morphological and Biological Analysis
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification and Sequencing
2.3. Molecular and Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results
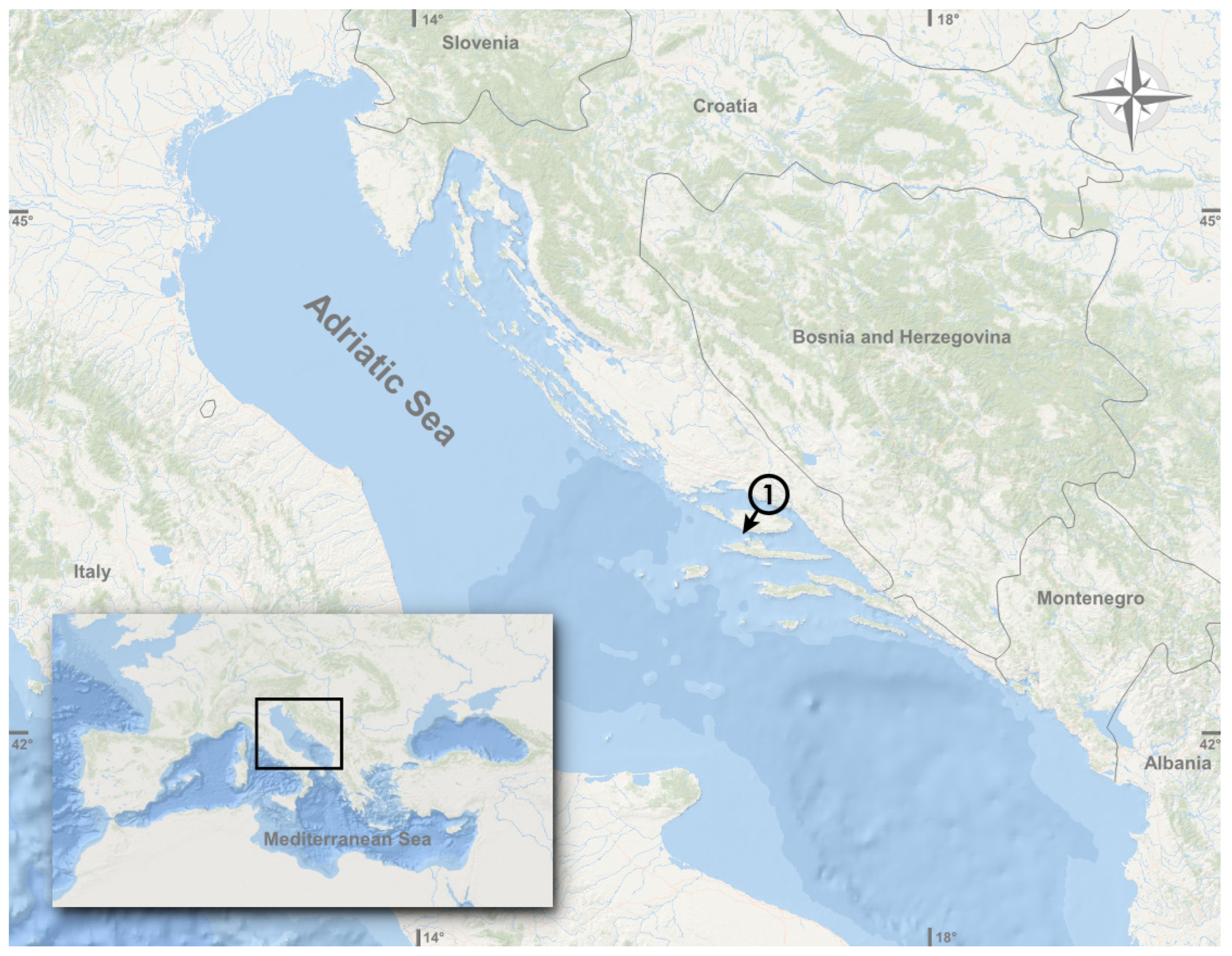
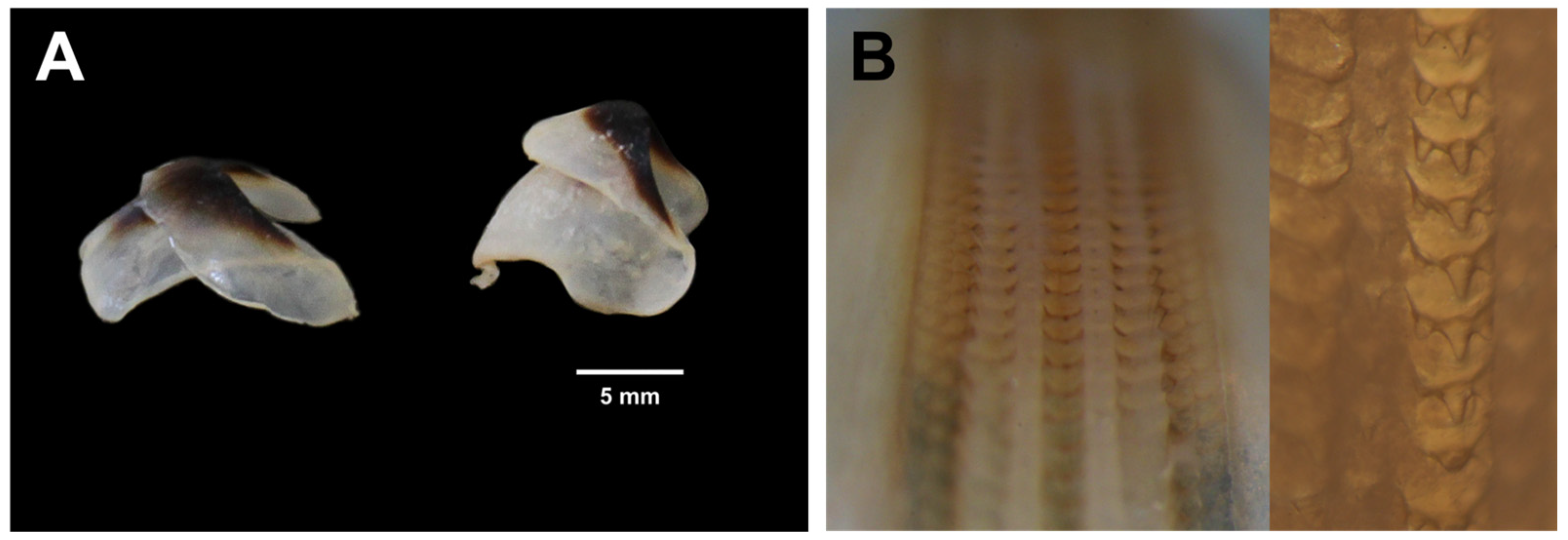
3.1. Morphological and Biological Analysis
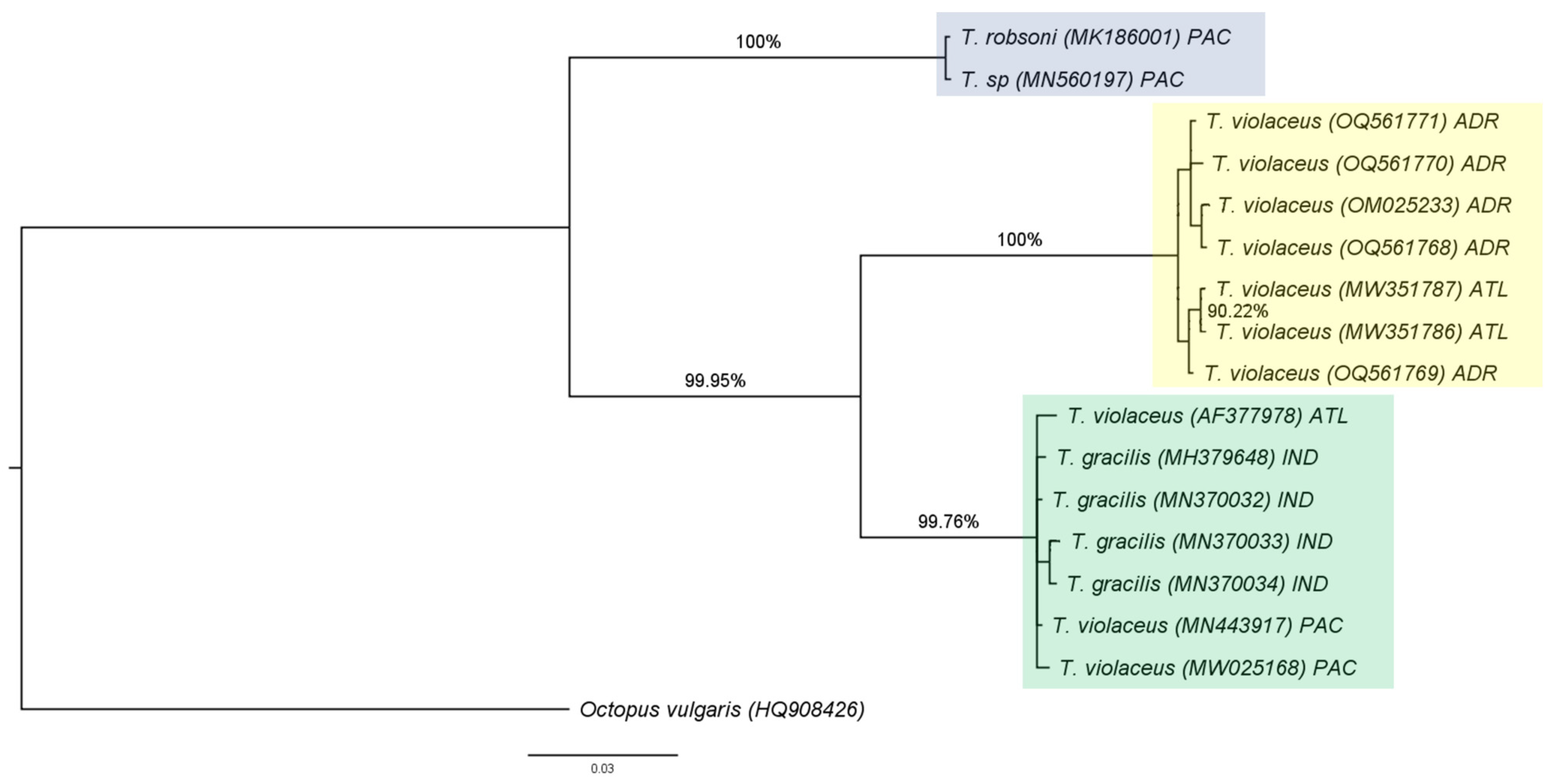
3.2. Molecular and Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Finn, J.K. Family Tremoctopodidae Tryon, 1879. In Cephalopods of the World. An Annotated and Illustrated Catalogue of Cephalopod Species Known to Date. Volume 3. Octopods and Vampire Squids; Jereb, P., Roper, C.F.E., Norman, M.D., Finn, J.K., Eds.; FAO Species Catalogue for Fishery Purposes; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2016; Volume 3, pp. 240–243. [Google Scholar]
- WoRMS Editorial Board World Register of Marine Species. Available online: https://www.Marinespecies.Org (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- Thomas, R. Systematics, Distribution, and Biology of Cephalopods of the Genus Tremoctopus (Octopoda: Tremoctopodidae). Bull. Mar. Sci. 1977, 27, 353–392. [Google Scholar]
- Nesis, K. Cephalopods of the World: Squid, Cuttlefish, Octopuses and Their Allies; T.F.H. Publications Inc. Ltd.: Neptune City, NJ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Orsi Relini, L.; Belluscio, A.; Ardizzone, G. Tracking the Indopacific Pelagic Octopus Tremoctopus gracilis in the Mediterranean. Rapp. Procès Verbaux Comm. Int. Pour L’exploration Sci. Mer Méditerranée 2004, 37, 415. [Google Scholar]
- Rifi, M.; Souissi, J. Première Mention Du Poulpe Palmée Tremoctopus gracilis (Eydoux & Souleyet, 1852) Dans Le Golfe de Tunis. In Proceedings of the 4ème Congrès Franco-Maghrébin et 5èmes Journées Franco-Tunisiennes de Zoologie, Korba, Tunisia, 19 November 2014; p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- Bello, G.; Andaloro, F.; Battaglia, P. Non-Indigenous Cephalopods in the Mediterranean Sea: A Review. Acta Adriat. 2020, 61, 113–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agus, B.; Carbonara, P.; Melis, R.; Cannas, R.; Carugati, L.; Cera, J.; Donnaloia, M.; Mulas, A.; Pais, A.; Ruiu, S.; et al. First Integrative Morphological and Genetic Characterization of Tremoctopus violaceus sensu stricto in the Mediterranean Sea. Animals 2021, 12, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Badillo, M.d.L.; Meiners-Mandujano, C.; Galindo-Cortes, G.; Morillo-Velarde, P.S.; González-Gómez, R.; Barriga-Sosa, I.; de los Angeles Barriga-Sosa, I.; Pliego-Cárdenas, R. The First Record of Tremoctopus violaceus sensu stricto Delle Chiaje,1830 in Southwestern Gulf of Mexico Gives a Hint of the Taxonomic Status of Tremoctopus gracilis. ZooKeys 2021, 1012, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangold, K.; von Boletzky, S. Céphalopodes. In Fiches D’identification des Especes pour les Besoins de la Pêche. (Revision 1) Méditerranée et Mer Noire; Fisher, W., Bauchot, M., Schneider, M., Eds.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1987; Volume 1, pp. 633–714. [Google Scholar]
- Biagi, V.; Bertozzi, A. Presenza Stagionale Di Tremoctopus violaceus Delle Chiaie, 1830 (Cephalopoda: Octopoda) Nel Mare Di Piombino (Li). Boll. Malacol. 1992, 28, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Laptikhovsky, V.; Salman, A. On Reproductive Strategies of the Epipelagic Octopods of the Superfamily Argonautoidea (Cephalopoda: Octopoda). Mar. Biol. 2003, 142, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quetglas, A.; Ordines, F.; Gonzalez, M.; Zaragoza, N.; Mallol, S.; Valls, M.; De Mesa, A. Uncommon Pelagic and Deep-Sea Cephalopods in the Mediterranean: New Data and Literature Review. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2013, 14, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famulari, S.; Savoca, S.; Panarello, G.; Iaria, C.; Spanò, N.; Capillo, G. New Record of a Female Violet Blanket Octopus (Tremoctopus violaceus Delle Chiaje, 1830) in the Strait of Messina, Southern Italy. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardo, G. Prospetto Della Fauna Marina Volgare Del Veneto Estuario Con Cenni Sulle Principali Specie Commestibili Dell’Adriatico, Sulle Venete Pesche, Sulle Valli, Ecc. In Venezia e le sue Lagune; Antonelli, G., Ed.; Nell’ I. R. privil. stabilimento Antonelli: Venezia, Italy, 1847; Volume 2, pp. 113–156. [Google Scholar]
- Kolombatović, G. Cefalopodi Dibranchiati Del Circondario Marittimo Di Spalato. In Glasnik Hrvatskoga Naravoslovnoga Društva; Brusina, S., Ed.; Hrvatsko naravoslovno društvo: Zagreb, Croatia, 1888; pp. 340–342. [Google Scholar]
- Kolombatović, G. Discussioni Su Due Specie Di Cefalopodi Dibranchiati. In Glasnik Hrvatskoga Naravoslovnoga Društva; Kučera, O., Ed.; Hrvatsko naravoslovno društvo: Zagreb, Croatia, 1905; pp. 382–394. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, G. Einige Beobachtungen an Tremoctopus violaceus. Note Ist It-Germ Biol. Mar. Rovigno 1937, 25, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Bello, G. Tremoctopus violaceus (Cephalopoda: Tremoctopodiadae) in the Stomach Contents of a Swordfish from the Adriatic Sea. Boll. Malacol. 1993, 29, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Glavić, N.; Tutman, P.; Kožul, V.; Skaramuca, B. Rare Finding of Palmate Octopus Tremoctopus violaceus violaceus Delle Chiaje, 1829 in Southeastern Adriatic Waters. In Proceedings of the 8th Croatian Biological Congress, Zagreb, Croatia, 27 September–2 October 2003; pp. 325–326. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, M.R. A Handbook for the Identification of Cephalopod Beaks; Oxford University Press: Oxford, NY, USA, 1986; ISBN 978-0-19-857603-7. [Google Scholar]
- Rasero, M.; Gonzalez, A.F.; Castro, B.G.; Guerra, A. Predatory Relationships of Two Sympatric Squid, Todaropsis eblanae And Illex coindetii (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae) in Galician Waters. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 1996, 76, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follesa, M.C.; Carbonara, P. Atlas of the Maturity Stages of Mediterranean Fishery Resources; Food & Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2019; 268p. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, G.; Shaw, E.M.; Carrillo, M.; Zanuy, S. Protein Salting-Out Method Applied to Genomic DNA Isolation from Fish Whole Blood. BioTechniques 1998, 24, 238–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA Primers for Amplification of Mitochondrial Cytochrome c Oxidase Subunit I from Diverse Metazoan Invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Hafner, M.S.; Sudman, P.D.; Villablanca, F.X.; Spradling, T.A.; Demastes, J.W.; Nadler, S.A. Disparate Rates of Molecular Evolution in Cospeciating Hosts and Parasites. Science 1994, 265, 1087–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, C.; Frati, F.; Beckenbach, A.; Crespi, B.; Liu, H.; Flook, P. Evolution, Weighting, and Phylogenetic Utility of Mitochondrial Gene Sequences and a Compilation of Conserved Polymerase Chain Reaction Primers. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1994, 87, 651–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An Integrated and Extendable Desktop Software Platform for the Organization and Analysis of Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA Sequence Polymorphism Analysis of Large Data Sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, M. Molecular Evolutionary Genetics; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987; ISBN 978-0-231-88671-0. [Google Scholar]
- Tajima, F. Statistical Method for Testing the Neutral Mutation Hypothesis by DNA Polymorphism. Genetics 1989, 123, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian Inference of Phylogenetic Trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.-T.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A Fast Online Phylogenetic Tool for Maximum Likelihood Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W232–W235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast Model Selection for Accurate Phylogenetic Estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the Ultrafast Bootstrap Approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. A Simple Method for Estimating Evolutionary Rates of Base Substitutions through Comparative Studies of Nucleotide Sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlini, D.B.; Young, R.E.; Vecchione, M. A Molecular Phylogeny of the Octopoda (Mollusca: Cephalopoda) Evaluated in Light of Morphological Evidence. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2001, 21, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, G. Teuthophagous Predators as Collectors of Oceanic Cephalopods: The Case of the Adriatic Sea. Boll. Malacol. 1996, 32, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Romeo, T.; Battaglia, P.; Pedà, C.; Perzia, P.; Consoli, P.; Esposito, V.; Andaloro, F. Pelagic Cephalopods of the Central Mediterranean Sea Determined by the Analysis of the Stomach Content of Large Fish Predators. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2012, 66, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castriota, L.; Finoia, M.G.; Campagnuolo, S.; Romeo, T.; Potoschi, A.; Andaloro, F. Diet of Tetrapturus belone (Istiophoridae) in the Central Mediterranean Sea. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2008, 88, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida Tubino, R.; De Souza Moraes, L.E.; Rangel, C.A.; Monteiro-Neto, C. A New Record for a Tremoctopus violaceus Chiaie, 1830 (Mollusca, Tremoctopodidae) from Rio de Janeiro Coast, Southeastern Brazil. Pan-Am. J. Aquat. Sci. 2010, 5, 572–576. [Google Scholar]
- Voss, G.L. A Review of the Cephalopods of the Gulf of Mexico. Bull. Mar. Sci. Gulf Caribb. 1956, 6, 85–178. [Google Scholar]
- Eusebi Borzelli, G.L.; Carniel, S. A Reconciling Vision of the Adriatic-Ionian Bimodal Oscillating System. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Civitarese, G.; Gačić, M.; Lipizer, M.; Eusebi Borzelli, G.L. On the Impact of the Bimodal Oscillating System (BiOS) on the Biogeochemistry and Biology of the Adriatic and Ionian Seas (Eastern Mediterranean). Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 3987–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voight, J.R. Cladistic Analysis of the Octopods Based on Anatomical Character. J. Molluscan Stud. 1997, 63, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allcock, A.L.; Strugnell, J.M.; Johnson, M.P. How Useful Are the Recommended Counts and Indices in the Systematics of the Octopodidae (Mollusca: Cephalopoda). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2008, 95, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Álvarez, F.Á.; Sánchez, P.; Villanueva, R. Morphological and Molecular Assessments of Bobtail Squids (Cephalopoda: Sepiolidae) Reveal a Hidden History of Biodiversity. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 7, 632261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, T.A.S.; Sales, J.B.L.; Markaida, U.; Granados-Amores, J.; Gales, S.M.; Sampaio, I.; Vallinoto, M.; Rodrigues-Filho, L.F.S.; Ready, J.S. Revisiting the Phylogeny of the Genus Lolliguncula Steenstrup 1881 Improves Understanding of Their Biogeography and Proves the Validity of Lolliguncula argus Brakoniecki & Roper, 1985. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2021, 154, 106968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsi Relini, L. Notes about Colour Displays Observed in Female Specimens of Tremoctopus (Cephalopoda: Octopoda) and Their Taxonomic Value. Boll. Malacol. 2009, 45, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Stoeckle, M.Y.; Zemlak, T.S.; Francis, C.M. Identification of Birds through DNA Barcodes. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhardt, K.; Knebelsberger, T. Identification of Cephalopod Species from the North and Baltic Seas Using Morphology, COI and 18S RDNA Sequences. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2015, 69, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delghandi, M.; Delghandi, M.P.; Goddard, S. The Significance of PCR Primer Design in Genetic Diversity Studies: Exemplified by Recent Research into the Genetic Structure of Marine Species. In PCR Primer Design; Basu, C., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2022; Volume 2392, pp. 3–15. ISBN 978-1-07-161798-4. [Google Scholar]



| Specimen ID | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Female | Female | Female | Female |
| Body weight (g) | 257.68 | 93.94 | 81.55 | 74.72 |
| Dorsal mantle length (mm) | 113 | 82 | 80 | 78 |
| Total length (mm) | 412 | 267 | 238 | 251 |
| Head length (mm) | 41 | 30 | 27 | 30 |
| Head width (mm) | 36 | 31 | 34 | 27 |
| Stomach weight (g) | 3.60 | 1.51 | 2.35 | 1.59 |
| Stomach fullness index | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| Maturity | mature | developing | developing | developing |
| Reproductive system weight (g) | 11.66 | 0.62 | 0.55 | 0.59 |
| Ovary weight (g) | 8.31 | 0.32 | 0.22 | 0.25 |
| Arm length I (left/right) (mm) | 191/185 | 129/NO | 97/101 | 138/140 |
| Arm length II (left/right) (mm) | 300/292 | 175/172 | NO/146 | 168/165 |
| Arm length III (left/right) (mm) | 139/135 | 97/91 | 76/80 | 76/82 |
| Arm length IV (left/right) (mm) | 143/147 | 105/105 | 95/106 | 130/100 |
| Upper hood length (mm) | 7.30 | 5.62 | 5.48 | 5.06 |
| Upper crest length (mm) | 12.04 | 9.68 | 9.10 | 8.86 |
| Lower hood length (mm) | 5.43 | 3.99 | 3.91 | 3.35 |
| Lower crest length (mm) | 8.68 | 6.25 | 6.05 | 5.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petrić, M.; Dragičević, B.; Stanić, R.; Trumbić, Ž. Morphological Characteristics and DNA Barcoding of the Rare Blanket Octopus Tremoctopus violaceus (Cephalopoda: Tremoctopodidae) in the Adriatic Sea. Diversity 2023, 15, 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15060794
Petrić M, Dragičević B, Stanić R, Trumbić Ž. Morphological Characteristics and DNA Barcoding of the Rare Blanket Octopus Tremoctopus violaceus (Cephalopoda: Tremoctopodidae) in the Adriatic Sea. Diversity. 2023; 15(6):794. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15060794
Chicago/Turabian StylePetrić, Mirela, Branko Dragičević, Rino Stanić, and Željka Trumbić. 2023. "Morphological Characteristics and DNA Barcoding of the Rare Blanket Octopus Tremoctopus violaceus (Cephalopoda: Tremoctopodidae) in the Adriatic Sea" Diversity 15, no. 6: 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15060794
APA StylePetrić, M., Dragičević, B., Stanić, R., & Trumbić, Ž. (2023). Morphological Characteristics and DNA Barcoding of the Rare Blanket Octopus Tremoctopus violaceus (Cephalopoda: Tremoctopodidae) in the Adriatic Sea. Diversity, 15(6), 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15060794








