Effects of Organic Enrichment on Bioturbation Attributes: How Does the Macrofauna Community Respond in Two Different Sedimentary Impacted Areas?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
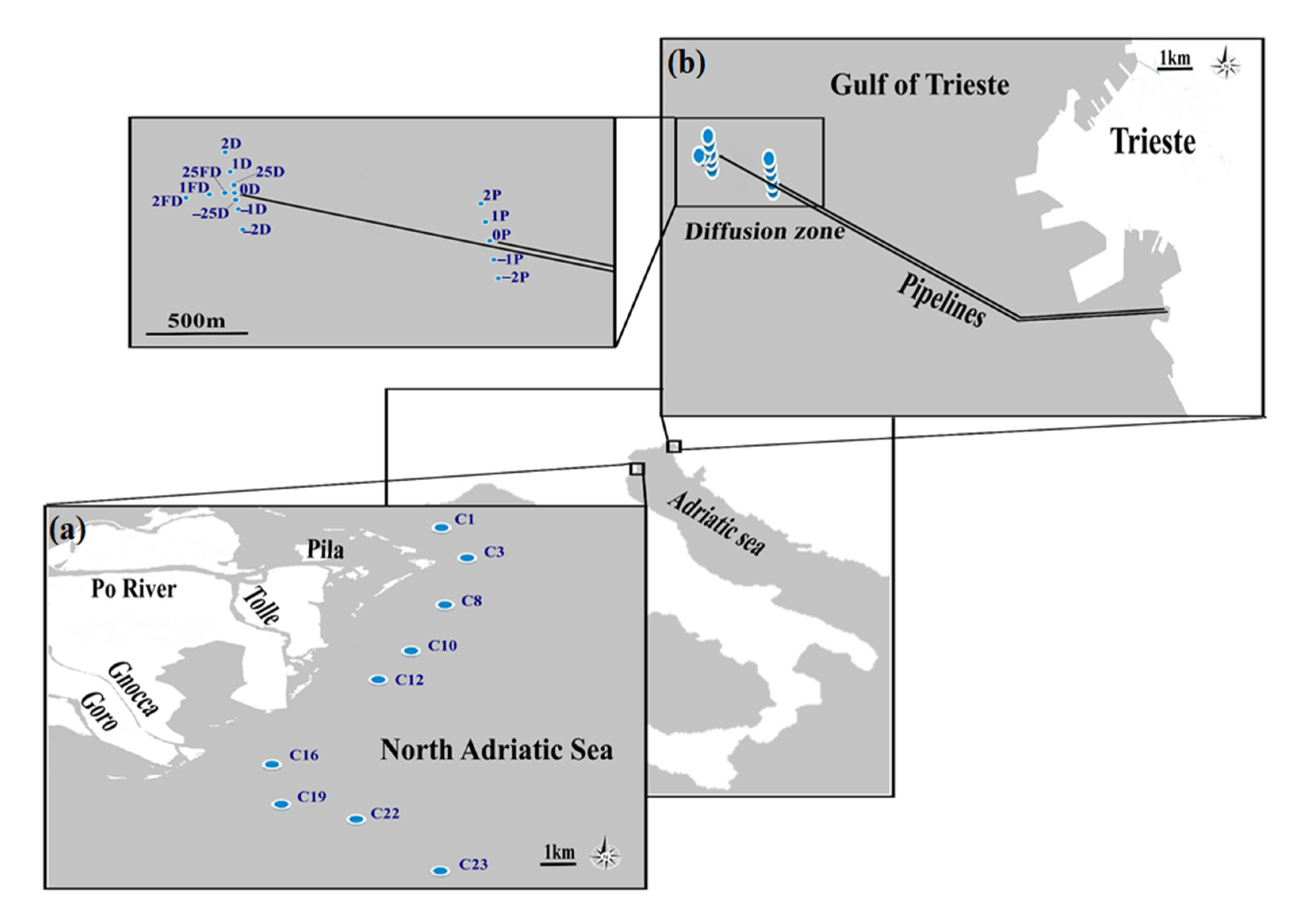
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Design and Samples Processing
2.3. Estimation of the Bioturbation Potential (BP) and Irrigation Potential (IP)
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
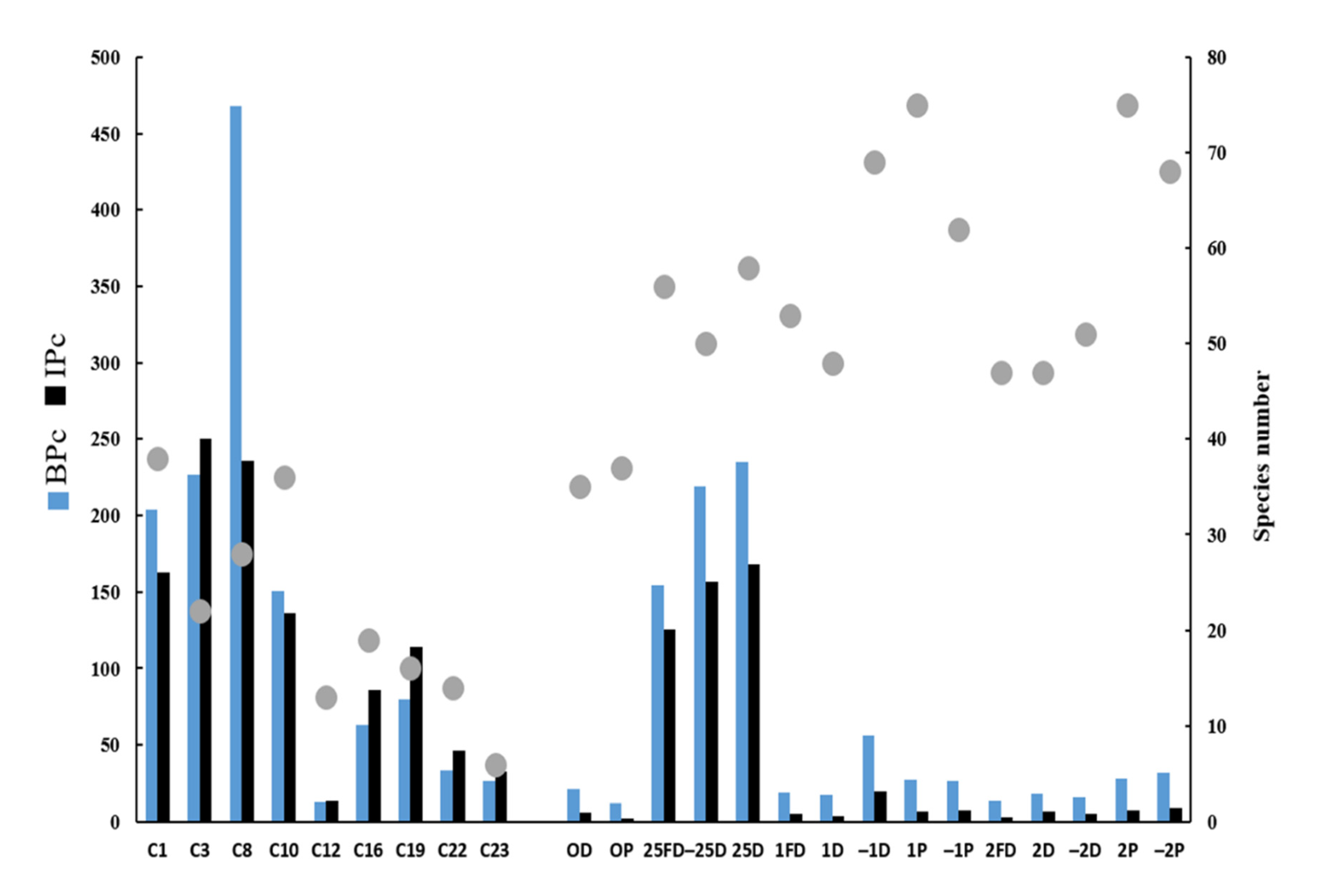
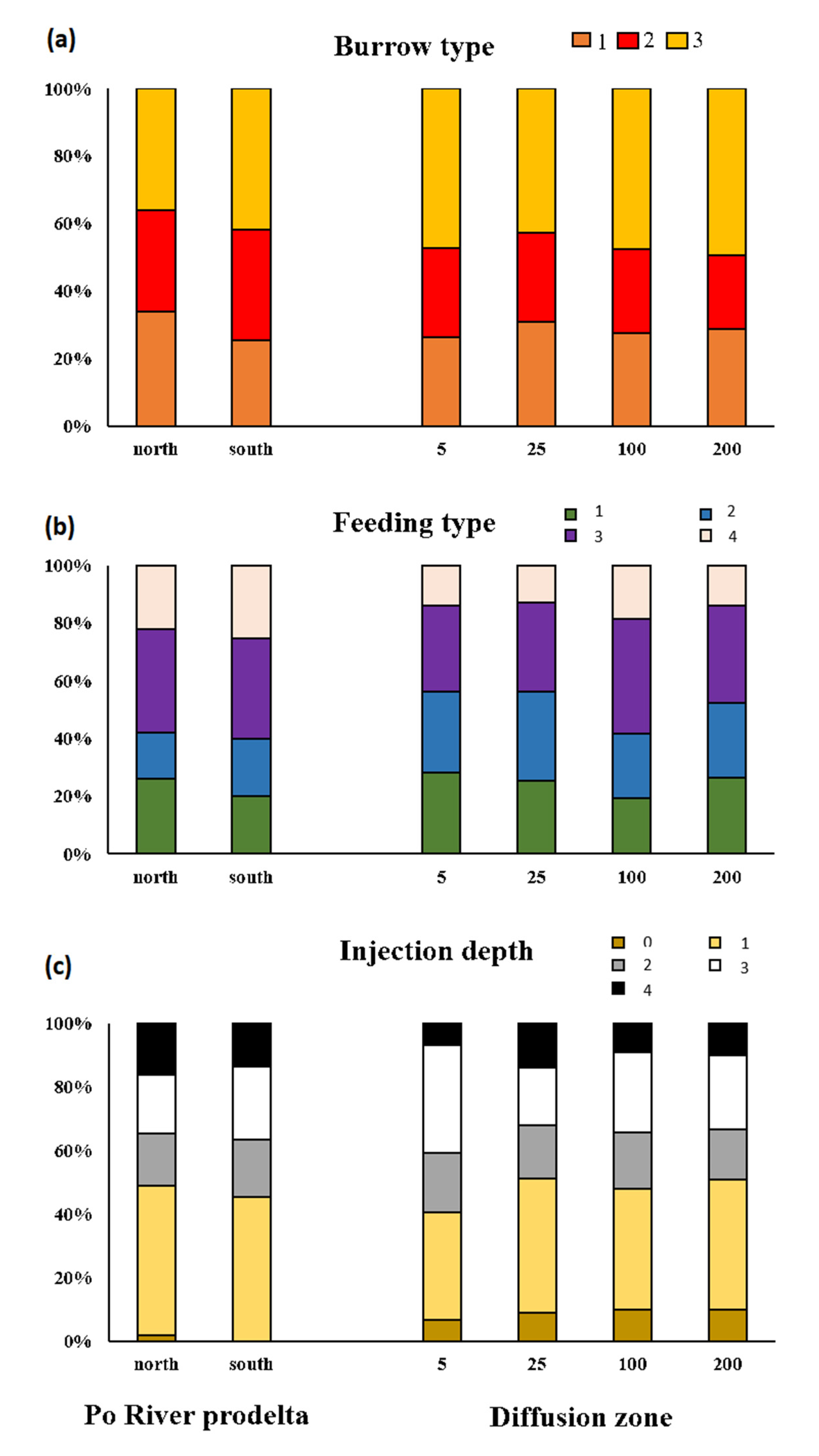
3.1. Taxonomic Composition of the Macrobenthic Community
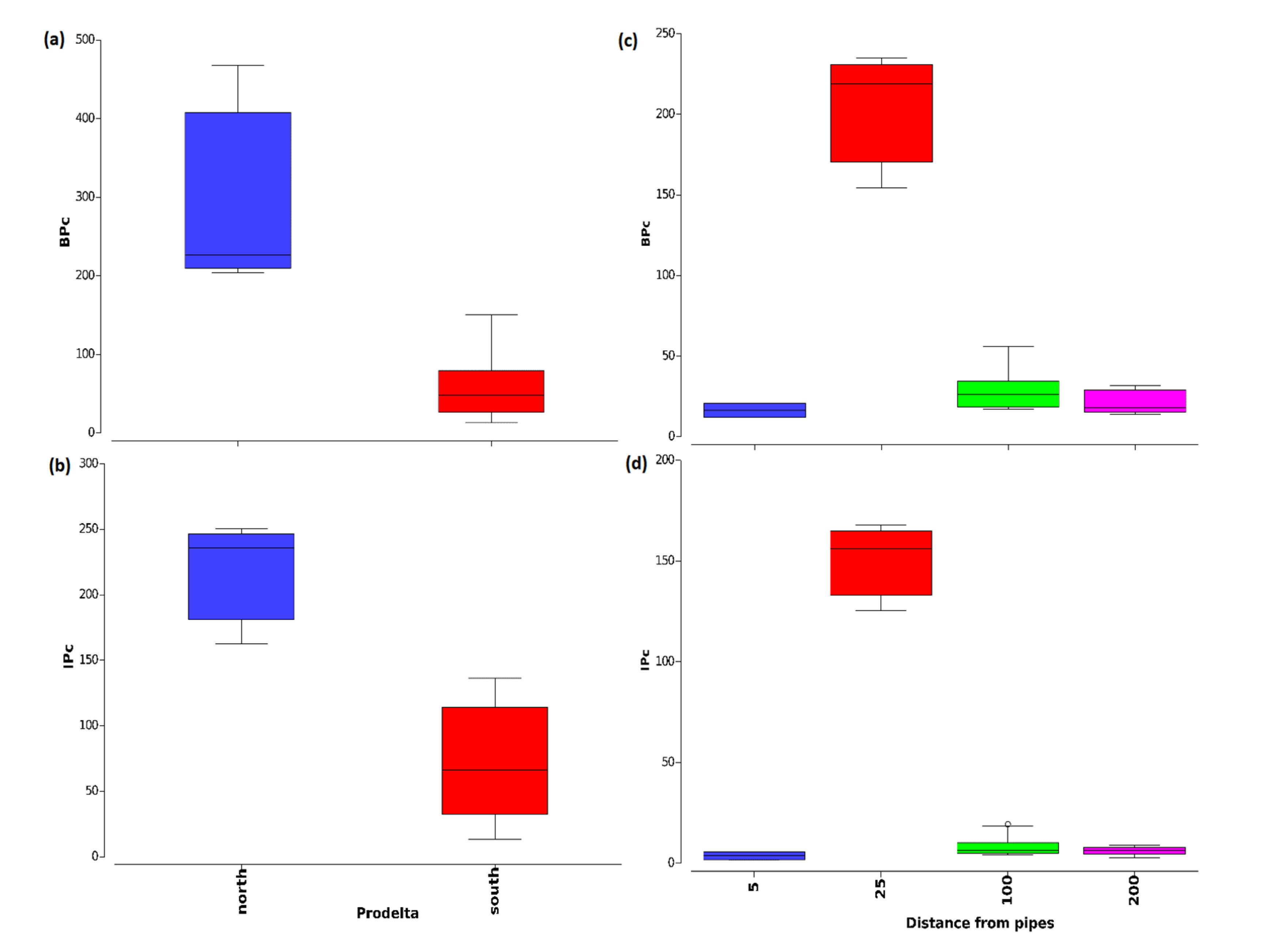
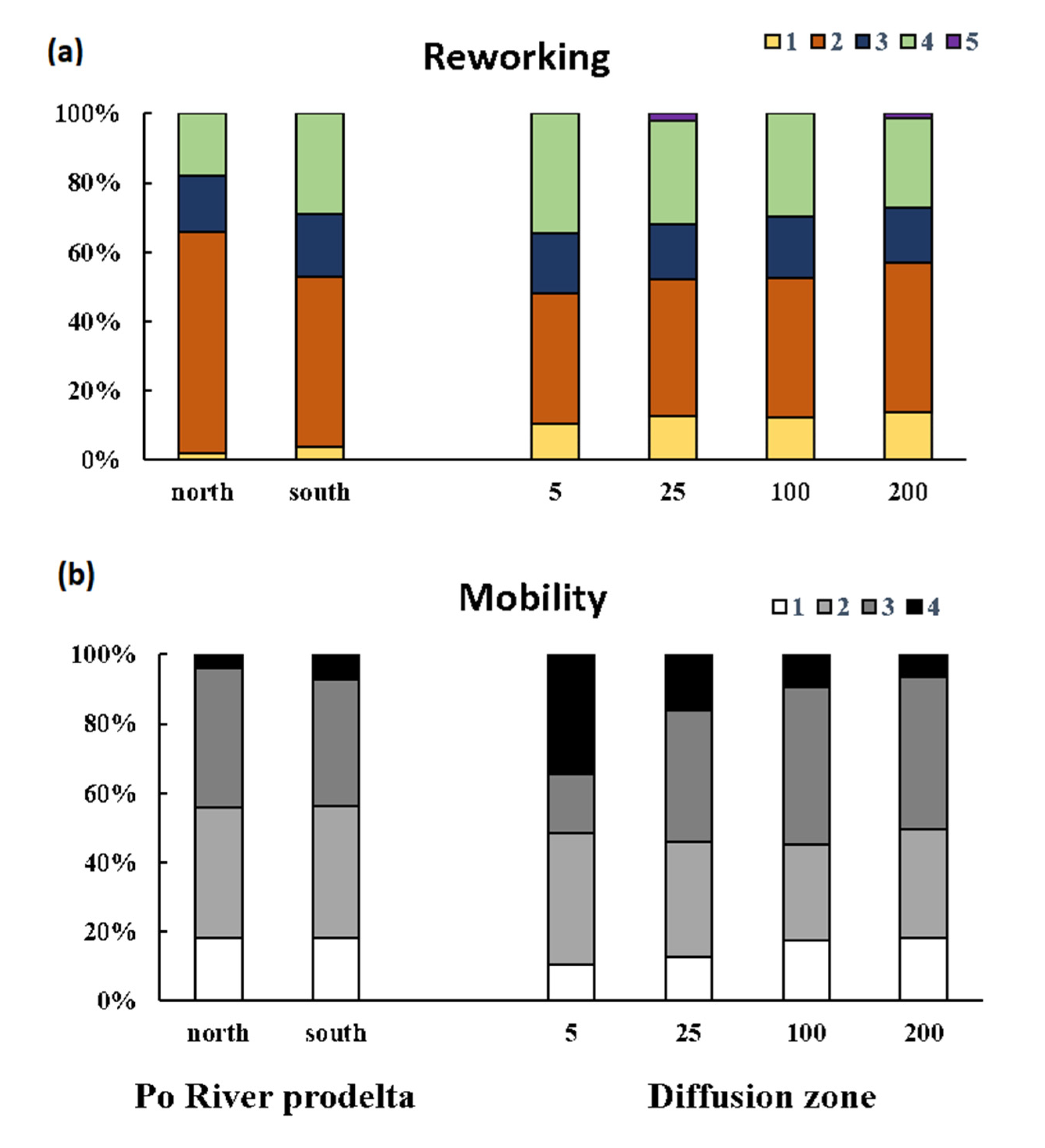
3.2. Macrofauna Bioturbation Attributes
3.3. Relation between Bioturbation Indices and Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Snelgrove, P.V. The biodiversity of macrofaunal organisms in marine sediments. Biodivers. Conserv. 1998, 7, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2Ferraro, S.P.; Cole, F.A. Taxonomic level sufficient for assessing pollution impacts on the Southern California bight macrobenthos—Revisited. Environ. Toxicol. 1995, 14, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancellotti, D.A.; Stotz, W.B. Effects of shoreline discharge of iron mine tailings on a marine softbottom community in northern Chile. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 48, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bremner, J.; Rogers, S.I.; Frid, C.L.J. Methods for describing ecological functioning of marine benthic assemblages using biological traits analysis (BTA). Ecol. Indic. 2006, 6, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoads, D.C.; Boyer, L.F. The effects of marine benthos on physical properties of sediments. In Animal-Sediment Relations; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1982; pp. 3–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffner, L. Small-scale organism distributions and patterns of species diversity: Evidence for positive interactions in an estuarine benthic community. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1990, 61, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meysman, F.J.; Middelburg, J.J.; Heip, C.H. Bioturbation: A fresh look at Darwin’s last idea. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2006, 21, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remaili, T.A.; Simpson, S.L.; Amato, E.D.; Spadaro, D.A.; Jarolimek, C.V.; Jolley, D.F. The impact of sediment bioturbation by secondary organisms on metal bioavailability, bioaccumulation and toxicity to target organisms in benthic bioassays: Implications for sediment quality assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remaili, T.M.; Simpson, S.L.; Jolley, D.E.F. Effects of enhanced bioturbation intensities on the toxicity assessment of legacy-contaminated sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 226, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermillod-Blondin, F. The functional significance of bioturbation and biodeposition on biogeochemical processes at the water-sediment interface in freshwater and marine ecosystems. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2011, 30, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, R.; Grémare, A.; Ducheme, J.C.; Davey, E.; Frank, M. 3D visualization and quantification of marine benthic biogenic structures and particle transport utilizing computer-aided tomography. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 363, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birchenough, S.; Parker, R.; McManus, E.; Barry, J. Combining bioturbation and redox metrics: Potential tools for assessing seabed function. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 12, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giani, M.; Berto, D.; Rampazzo, F.; Savelli, F.; Alvisi, F.; Giordano, P.; Ravaioli, M.; Frascari, F. Origin of sedimentary organic matter in the north-western Adriatic Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 84, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiorni, L.; Nasi, F.; Fiorentino, F.; Auriemma, R.; Rampazzo, F.; Nordström, M.C.; Berto, D. Contribution of deltaic wetland food sources to coastal macrobenthic consumers (Po River Delta, north Adriatic Sea). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1373–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koop, K.; Hutchins, P. Disposal of sewage to the ocean—A sustainable solution? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1996, 33, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasi, F.; Vesal, S.E.; Relitti, F.; Bazzaro, M.; Teixidó, N.; Auriemma, R.; Cibic, T. Taxonomic and functional macrofaunal diversity along a gradient of sewage contamination: A three-year study. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.-B.; Yoon, S.-P.; Jung, R.-H.; Choi, M. Wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) as a source of sediment contamination by toxic organic pollutants and fecal sterols in a semi-enclosed bay in Korea. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, G.M.; Besterman, A.; Buelo, C.; Gephart, J.; Pace, M.L. A synthesis of modern organic carbon accumulation rates in coastal and aquatic inland ecosystems. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnaude, A.M.; Salen-Picard, C.; Polunin, N.V.C.; HarmelinVivien, M.L. Trophodynamic linkage between river runoff and coastal fishery yield elucidated by stable isotope data in the Gulf of Lions (NW Mediterranean). Oecologia 2004, 138, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, C.; Thrush, S.F.; Lohrer, A.M.; Hewitt, J.E. Ecosystem services transcend boundaries: Estuaries provide resource subsidies and influence functional diversity in coastal benthic communities. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotze, H.K.; Lenihan, H.S.; Bourque, B.J.; Bradbury, R.H.; Cooke, R.G.; Kay, M.C.; Kidwell, S.M.; Kirby, M.X.; Peterson, C.H.; Jackson, J.B.C. Depletion, Degradation, and Recovery Potential of Estuaries and Coastal Seas. Science 2006, 312, 1806–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airoldi, L.; Balata, D.; Beck, M.W. The Gray Zone: Relationships between habitat loss and marine diversity and their applications in conservation. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. 2008, 366, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crain, C.M.; Halpern, B.S.; Beck, M.W.; Kappel, C.V. Understanding and managing human threats to the coastal marine environment. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1162, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, M.J.; Clarke, K.R.; Hinz, H.; Austen, M.C.V.; Somerfield, P.J.; Karakassis, I. Global analysis of response and recovery of benthic biota to fishing. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 311, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, A.; Galparsoro, I.; Solaun, O.; Muxika, I.; Tello, E.M.; Uriarte, A.; Valencia, V. The European Water Framework Directive and the DPSIR, a methodological approach to assess the risk of failing to achieve good ecological status. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 66, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, A.; Dauer, D.M.; Elliott, M.; Simenstad, C. Medium and long-term recovery of estuarine and coastal ecosystems: Patterns, rates and restoration effectiveness. Estuaries Coast. 2010, 33, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, A.J.; Skjoldal, H.R.; Engelhard, G.H.; Kershaw, P.J.; Reid, J.B. An integrated approach for assessing the relative significance of human pressures and environmental forcing on the status of Large Marine Ecosystems. Prog. Oceanogr. 2009, 81, 132–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, A.J.; Jenkins, C.; Wood, D.; Bolam, S.G.; Mitchell, P.; Scougal, C.; Judd, A. Assessing cumulative human activities, pressures, and impacts on North Sea benthic habitats using a biological traits approach. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2018, 75, 1080–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lissner, A.L.; Taghorn, G.L.; Diener, D.R.; Schroeter, S.C.; Dixon, D. Recolonization of deep-water hard substrate communities: Potential impacts from oil and gas development. Ecol. Appl. 1991, 1, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, T.H.; Rosenberg, R. Macrobenthic succession in relation to organic enrichment and pollution of the marine environment. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Ann. Rev. 1978, 16, 229–311. [Google Scholar]
- Nasi, F.; Ferrante, L.; Alvisi, F.; Bonsdorff, E.; Auriemma, R.; Cibic, T. Macrofaunal bioturbation attributes in relation to riverine influence: What can we learn from the Po River lagoonal system (Adriatic Sea)? Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 232, 106405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashtgard, S.E.; Gingras, M.K.; Pemberton, S.G. Grain-size controls on the occurrence of bioturbation. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2008, 257, 224–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingras, M.K.; Pemberton, S.G.; Saunders, T.; Clifton, H.E. The ichnology of modern and Pleistocene brackish-water deposits at Willapa Bay, Washington: Variability in estuarine settings. Palaios 1999, 14, 352–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Garcia, E.; Sanchez-Jerez, P.; Aguado-Giménez, F.; Ávila, P.; Guerrero, A.; Sánchez-Lizaso, J.L.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, V.; González, N.; Gairin, J.I.; Carballeira, C.; et al. A meta-analysis approach to the effects of fish farming on soft bottom polychaeta assemblages in temperate regions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 69, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, N.; Ioanna Kalantzi, I.; Karakassis, I. Effects of fish farming on the biological and geochemical properties of muddy and sandy sediments in the mediterranean sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2010, 69, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solan, M.; Cardinale, B.J.; Downing, A.L.; Engelhardt, K.A.; Ruesink, J.L.; Srivastava, D.S. Extinction and ecosystem function in the marine benthos. Science 2004, 306, 1177–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrede, A.; Beermann, J.; Dannheim, J.; Gutow, L.; Brey, T. Organism functional traits and ecosystem supporting services. A novel approach to predict bioirrigation. Ecol. Indicat. 2018, 91, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunker, D.E.; DeClerck, F.; Bradford, J.C.; Colwell, R.K.; Perfecto, I.; Phillips, O.L.; Naeem, S. Species loss and aboveground carbon storage in a tropical forest. Science 2005, 310, 1029–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solan, M.; Wigham, B.D.; Hudson, I.R.; Kennedy, R.; Coulon, C.H.; Norling, K.; Rosenberg, R. In situ quantification of bioturbation using time-lapse fluorescent sediment profile imaging (f-SPI), luminophore tracers and model simulation. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 271, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohrer, A.; Halliday, N.; Thrush, S.; Hewitt, J.; Rodil, I. Ecosystem functioning in a disturbance-recovery context: Contribution of macrofauna to primary production and nutrient release on intertidal sandflats. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2010, 390, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teal, L.; Parker, E.; Solan, M. Coupling bioturbation activity to metal (Fe and Mn) profiles in situ. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 2365–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queirós, A.M.; Hiddink, J.G.; Johnson, G.; Cabral, H.N.; Kaiser, M.J. Context dependence of marine ecosystem engineer invasion impacts on benthic ecosystem functioning. Biol. Invasions 2011, 13, 1059–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solan, M.; Scott, F.; Dulvy, N.K.; Godbold, J.A.; Parker, R. Incorporating extinction risk and realistic biodiversity futures: Implementation of trait-based extinction scenarios. In Marine Biodiversity and Ecosystem Functioning: Frameworks, Methodologies, and Integration; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 127–148. [Google Scholar]
- Van Colen, C.; Rossi, F.; Montserrat, F.; Andersson, M.G.I.; Gribsholt, B.; Herman, P.M.J.; Degraer, S.; Vincx, M.; Ysebaert, T.; Middelburg, J.J. Organism-sediment interactions govern post-hypoxia recovery of ecosystem functioning. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villnäs, A.; Norkko, J.; Lukkari, K.; Hewitt, J.; Norkko, A. Consequences of increasing hypoxic disturbance on benthic communities and ecosystem functioning. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josefson, A.B.; Norkko, J.; Norkko, A. Burial and decomposition of plant pigments in surface sediments of the Baltic Sea: Role of oxygen and benthic fauna. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 455, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, E.; Penha-Lopes, G.; Delefosse, M.; Valdemarsen, T.; Quintana, C.O.; Banta, G.T. What is bioturbation? The need for a precise definition for fauna in aquatic sciences. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 446, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aller, R.C. The effects of macrobenthos on chemical properties of marine sediment and overlying water. In Animal Sediment Relations; McCall, P.L., Tevesz, M.J.S., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1982; pp. 53–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, B.; Vedel, A.; Kristensen, E. Carbon and nitrogen fluxes in sediment inhabited by suspension-feeding (Nereis diversicolor) and non-suspension feeding (N. virens) polychaetes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 192, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painting, S.J.; Van der Molen, J.; Parker, E.; Coughlan, C.; Birchenough, S.; Bolam, S.; Aldridge, J.N.; Forster, R.M.; Greenwood, N. Development of indicators of ecosystem functioning in a temperate shelf sea: A combined fieldwork and modelling approach. Biogeochemistry 2012, 113, 237–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hoey, G.; Permuy, D.C.; Vandendriessche, S.; Vincx, M.; Hostens, K. An ecological quality status assessment procedure for soft-sediment benthic habitats: Weighing alternative approaches. Ecol. Ind. 2013, 25, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renz, J.R.; Powilleit, M.; Gogina, M.; Zettler, M.L.; Morys, C.; Forster, S. Community bioirrigation potential (BIPc), an index to quantify the potential for solute exchange at the sediment-water interface. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 181, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S. Nitrogen and phosphorus budget in coastal and marine cage aquaculture and impacts of effluent loading on ecosystem: Review and analysis towards model development. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweetman, A.K.; Norling, K.; Gunderstad, C.; Haugland, B.T.; Dale, T. Benthic ecosystem functioning beneath fish farms in different hydrodynamic environments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2014, 59, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, J.I.; Keil, R.G. Sedimentary organic matter preservation: An assessment and speculative synthesis. Mar. Chem. 1995, 49, 81–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchini, A.; Munari, C.; Mistri, M. Functions and ecological status of eight Italian lagoons examined using biological traits analysis (BTA). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 1076–1085. Available online: https://www.marlin.ac.uk/biotic (accessed on 1 April 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesi, T.; Miserocchi, S.; Goñi, M.A.; Turchetto, M.; Langone, L.; De Lazzari, A.; Albertazzi, S.; Correggiari, A. Influence of distributary channels on sediment and organic matter supply in event-dominated coastal margins: The Po prodelta as a study case. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldrin, A.; Langone, L.; Miserocchi, S.; Turchetto, M.; Acri, F. Po River plume on the Adriatic continental shelf: Dispersion and sedimentation of dissolved and suspended matter during different river discharge rates. Mar. Geol. 2005, 222, 135–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frignani, M.; Langone, L.; Ravaioli, M.; Sorgente, D.; Alvisi, F.; Albertazzi, S. Fine-sediment mass balance in the western Adriatic continental shelf over a century time scale. Mar. Geol. 2005, 222, 113–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourafalou, V.H. Process studies on the Po River plume, North Adriatic Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 29963–29985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirazzoli, P.A.; Tomasin, A. Recent evolution of surge-related events in the northern Adriatic area. J. Coast. Res. 2002, 18, 537–554. [Google Scholar]
- Lipizer, M.; De Vittor, C.; Falconi, C.; Comici, C.; Tamberlich, F.; Giani, M. Effects of intense physical and biological forcing factors on CNP pools in coastal waters (Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic Sea). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 115, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesal, S.E.; Nasi, F.; Pazzaglia, J.; Ferrante, L.; Auriemma, R.; Relitti, F.; Bazzaro, M.; Del Negro, P. Assessing the sewage discharge effects on soft-bottom macrofauna through traits-based approach. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 173, 113003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesal, S.E.; Auriemma, R.; Libralato, S.; Nasi, F.; Del Negro, P. Impacts of organic enrichment on macrobenthic production, productivity, and transfer efficiency: What can we learn from a gradient of sewage effluents? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 182, 113972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis-Weis, V.; Aleffi, I.F.; Bettoso, N.; Rossini, P.; Orel, G. The benthic macrofauna at the outfalls of the underwater sewage discharges in the Gulf of Trieste (Northern Adriatic Sea, Italy). Ann. Ser. Hist. Nat. 2007, 17, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Novelli, G. Gli Scarichi a Mare Nell’alto Adriatico; Rassegna Tecnica del Friuli Venezia Giulia: Udine, Italy, 1996; Volume 3, pp. 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel, M.A.; Leuchs, H.; Koop, J.H.E. PRESERVATION effects on wet weight, dry weight, and ash-free dry weight biomass estimates of four common estuarine macro-invertebrates: No difference between ethanol and formalin. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2005, 59, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solan, M. The Concerted Use of ‘Traditional’ and Sediment Profile Imagery (SPI) Methodologies in Marine Benthic Characterisation and Monitoring. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Zoology, National University of Ireland, Galway, Ireland, 2000. (Unpublished work). [Google Scholar]
- Queirós, A.M.; Birchenough, S.N.; Bremner, J.; Godbold, J.A.; Parker, R.E.; Romero-Ramirez, A.; Reiss, H.; Solan, M.; Somerfield, P.J.; Van Colen, C.; et al. A bioturbation classification of European marine infaunal invertebrates. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 3958–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogina, M.; Morys, C.; Forster, S.; Gräwe, U.; Friedland, R.; Zettler, M.L. Towards benthic ecosystem functioning maps: Quantifying bioturbation potential in the German part of the Baltic Sea. Ecol. Indicat. 2017, 73, 574–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasi, F.; Nordstr¨om, M.C.; Bonsdorff, E.; Auriemma, R.; Cibic, T.; Del Negro, P. Functional biodiversity of marine soft-sediment polychaetes from two Mediterranean coastal areas in relation to environmental stress. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 137, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-la-Ossa-Carretero, J.A.; Del-Pilar-Ruso, Y.; Giménez-Casalduero, F.; Sánchez-Lizaso, J.L. Assessing reliable indicators to sewage pollution in coastal soft-bottom communities. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 2133–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumars, P.A.; Dorgan, K.M.; Lindsay, S.M. Diet of worms emended: An update of polychaete feeding guilds. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2015, 7, 497–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, L.; Blair, N.; DeMaster, D.; Plaia, G.; Fornes, W.; Martin, C.; Thomas, C. Rapid subduction of organic matter by maldanid polychaetes on the North Carolina slope. J. Mar. Res. 1997, 55, 595–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R.J.A.; Froglia, C.; Arneri, E.; Antolini, B. Observations on the burrows and burrowing behaviour of Brachynotus gemmellari and on the burrows of several other species occurring on Squilla grounds off Ancona, Central Adriatic. Sci. Mar. 1998, 62, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morys, C.; Powilleit, M.; Forster, S. Bioturbation in relation to the depth distribution of macrozoobenthos in the southwestern Baltic Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 579, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuur, A.F.; Ieno, E.N.; Elphick, C.S. A protocol for data exploration to avoid common statistical problems. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2010, 1, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magni, P.; Vesal, S.E.; Giampaoletti, J.; Como, S.; Gravina, M.F. Joint use of biological traits, diversity and biotic indices to assess the ecological quality status of a Mediterranean transitional system. Ecol. Ind. 2023, 147, 109939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, E.; Kostka, J.E. Macrofaunal burrows and irrigation in marine sediment: Microbiological and biogeochemical interactions. In Interactions between Macro- and Microorganisms in Marine Sediments; Kristensen, E., Haese, R.R., Kostka, J.E., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 125–157. [Google Scholar]
- Breine, N.T.; De Backer, A.; Van Colen, C.; Moens, T.; Hostens, K.; Van Hoey, G. Structural and functional diversity of soft–bottom macrobenthic communities in the Southern North Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 214, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrush, S.F.; Hewitt, J.E.; Cummings, V.J.; Ellis, J.I.; Hatton, C.; Lohrer, A.; Norkko, A. Muddy waters: Elevating sediment input to coastal and estuarine habitats. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2004, 2, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, F.; Zaggia, L.; Bellafiore, D.; Bresciani, M.; Giardino, C.; Lorenzetti, G.; Maicu, F.; Manzo, C.; Riminucci, F.; Ravaioli, M.; et al. Mapping turbidity patterns in the Po river prodelta using multi-temporal Landsat 8 imagery. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 198, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maicu, F.; De Pascalis, F.; Ferrarin, C.; Umgiesser, G. Hydrodynamics of the Po River-Delta-Sea system. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 6349–6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queirós, A.M.; Fernandes, J.A.; Faulwetter, S.; Nunes, J.; Rastrick, S.P.; Mieszkowska, N.; Artioli, Y.; Yool, A.; Calosi, P.; Arvanitidis, C.; et al. Scaling up experimental ocean acidification and warming research: From individuals to the ecosystem. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, G.R.; Levinton, J.S. Ecology of deposit feeding animals in marine sediments. Q. Rev. Biol. 1987, 62, 235–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Töornroos, A.; Bonsdorff, E. Developing the multitrait concept for functional diversity: Lessons from a system rich in functions but poor in species. Ecol. Appl. 2012, 22, 2221–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salen-Picard, C.; Arlhac, D.; Alliot, E. Responses of a Mediterranean soft bottom community to short-term (1993–1996) hydrological changes in the Rhone river. Mar. Environ. Res. 2003, 55, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, E. Impact of polychaetes (Nereis spp. and Arenicola marina) on carbon biogeochemistry in coastal marine sediments. Geochem. Trans. 2001, 2, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shull, D.H.; Benoit, J.M.; Wojcik, C.; Senning, J.R. Infaunal burrow ventilation and pore-water transport in muddy sediments. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci 2009, 83, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, E.; Delefosse, M.; Quintana, C.O.; Flindt, M.R.; Valdemarsen, T. Influence of benthic macrofauna community shifts on ecosystem functioning in shallow estuaries. Front. Mar. Sci. 2014, 1, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermillod-Blondin, F.; Rosenberg, R. Ecosystem engineering: The impact of bioturbation on biogeochemical processes in marine and freshwater benthic habitats. Aquat. Sci. 2006, 68, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chareopanich, C.; Montani, S.; Tsutsumi, H.; Matsuoka, S. Modification of chemical characteristics of organically enriched sediment by Capitella sp. I. Mar. Poll. Bull. 1993, 26, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauwe, B.P.H.J.; Herman, P.M.J.; Heip, C.H.R. Community structure and bioturbation potential of macrofauna at four North Sea stations with contrasting food supply. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1998, 173, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, K.; Wada, M.; Kogure, K.; Furota, T. Microbial activity and accumulation of organic matter in the burrow of the mud shrimp, Upogebia major (Crustacea: Thalassinidea). Mar. Biol. 2008, 153, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braeckman, U.; Foshtomi, M.Y.; Van Gansbeke, D.; Meysman, F.; Soetaert, K.; Vincx, M.; Vanaverbeke, J. Variable importance of macrofaunal functional biodiversity for biogeochemical cycling in temperate coastal sediments. Ecosystems 2014, 17, 720–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aller, R.C. Interactions between bioturbation and Mn cycling in marine sediments. EOS Transact. Am. Geophys. Union 1988, 69, 1106. [Google Scholar]


| Area | Response Variables | Predictor Variables | R2 | df | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Po River prodelta | BPc | Clay | 0.74 | 1.7 | 20.71 | <0.01 |
| IPc | Sand | 0.75 | 1.7 | 21.12 | <0.01 | |
| Clay | 0.79 | 1.7 | 26.65 | <0.01 | ||
| C:N | 0.49 | 1.7 | 6.77 | 0.03 | ||
| Diffusion zone | BPc | Sand | 0.56 | 1.13 | 17.07 | <0.01 |
| Silt | 0.57 | 1.13 | 17.28 | <0.01 | ||
| Clay | 0.53 | 1.13 | 14.94 | <0.01 | ||
| TOC | 0.29 | 1.13 | 5.44 | 0.03 | ||
| IPc | Clay | 0.55 | 1.13 | 16.3 | <0.01 | |
| TOC | 0.31 | 1.13 | 5.96 | 0.02 | ||
| Silt | 0.61 | 1.13 | 20.78 | <0.01 | ||
| Sand | 0.6 | 1.13 | 19.62 | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vesal, S.E.; Nasi, F.; Auriemma, R.; Del Negro, P. Effects of Organic Enrichment on Bioturbation Attributes: How Does the Macrofauna Community Respond in Two Different Sedimentary Impacted Areas? Diversity 2023, 15, 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030449
Vesal SE, Nasi F, Auriemma R, Del Negro P. Effects of Organic Enrichment on Bioturbation Attributes: How Does the Macrofauna Community Respond in Two Different Sedimentary Impacted Areas? Diversity. 2023; 15(3):449. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030449
Chicago/Turabian StyleVesal, Seyed Ehsan, Federica Nasi, Rocco Auriemma, and Paola Del Negro. 2023. "Effects of Organic Enrichment on Bioturbation Attributes: How Does the Macrofauna Community Respond in Two Different Sedimentary Impacted Areas?" Diversity 15, no. 3: 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030449
APA StyleVesal, S. E., Nasi, F., Auriemma, R., & Del Negro, P. (2023). Effects of Organic Enrichment on Bioturbation Attributes: How Does the Macrofauna Community Respond in Two Different Sedimentary Impacted Areas? Diversity, 15(3), 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030449






