Lipid Profile of the Freshwater Pearl Mussel Margaritifera margaritifera Inhabiting Different Biotopes of the Lake-River System of the Kem River, White Sea Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Lipid Analysis
2.3. Determination of Size and Age Parameters of the Freshwater Pearl Mussel
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
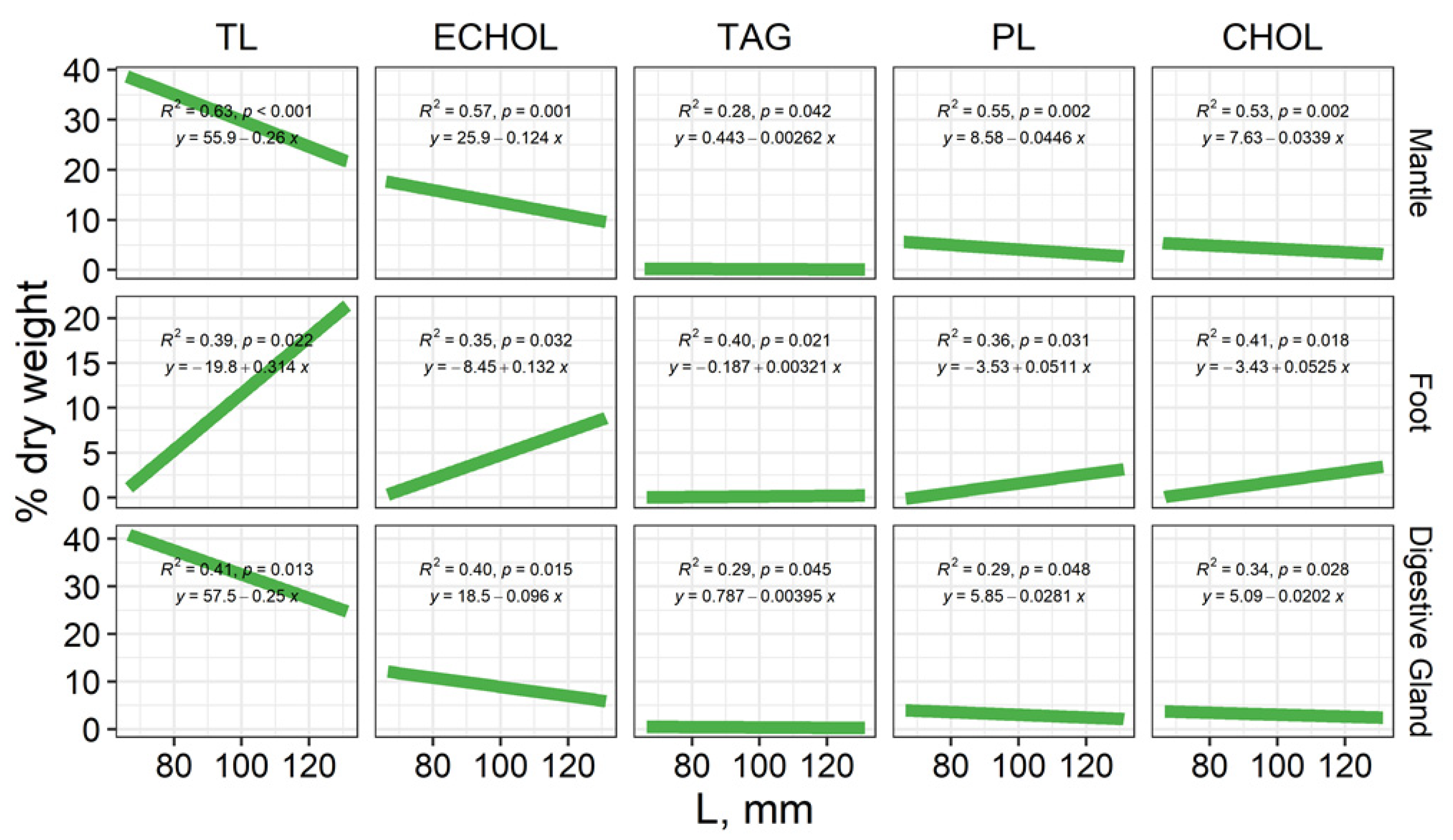
3.1. The Total Lipid Content and Levels of Individual Lipid Classes
3.1.1. Mantle
3.1.2. Foot (Muscle Tissue)
3.1.3. Digestive Gland
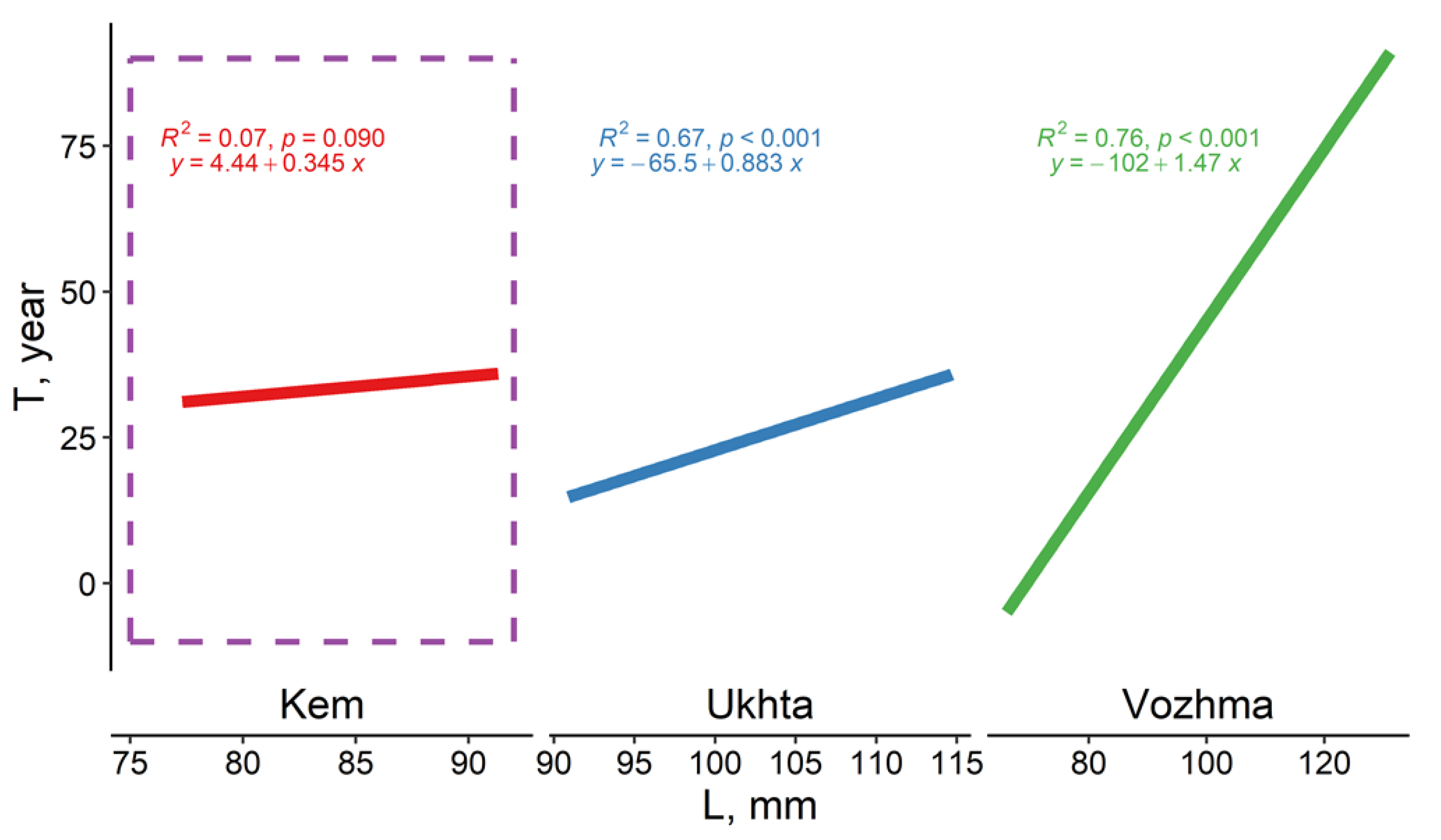
3.2. Individual Size, Age, and Growth Characteristics of M. margaritifera
3.2.1. Vozhma River
3.2.2. Ukhta River
3.2.3. Kem River
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bauer, G. Variation in the life span and size of the freshwater pearl mussel. J. Anim. Ecol. 1992, 61, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyuganov, V.V.; Zotin, A.A.; Tretyakov, V.A. Pearl Oysters and Their Relationship with Salmonids; Koltzov Institute of Developmental Biology RAN: Moscow, Russia, 1993; 133p. [Google Scholar]
- Zyuganov, V.; San Miguel, E.; Neves, R.J.; Longa, A.; Fernández, C.; Amaro, R.; Beletsky, V.; Popkovitch, E.; Kaliuzhin, S.; Johnson, T. Life span variation of the freshwater pearl shell: A model species for testing longevity mechanisms in animals. Ambio 2000, 29, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geist, J. Strategies for the conservation of endangered freshwater pearl mussels (Margaritifera margaritifera L.): A synthesis of conservation genetics and ecology. Hydrobiologia 2010, 644, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hassel, J.H.; Farris, J.L. A review of the use of unionid mussels as biological indicators of ecosystem health. In Freshwater Bivalve Ecotoxicology; Van Hassel, J.H., Farris, J.L., Eds.; SETAC; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA; Webster: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 19–49. [Google Scholar]
- Natural Resources; Species Survival Commission; IUCN Species Survival Commission. IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- FGBU “VNII Ecology”. Red Book of the Russian Federation, Volume “Animals”, 2nd ed.; FGBU “VNII Ecology”: Moscow, Russia, 2021; p. 1128. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes-Lima, M.; Teixeira, A.; Froufe, E.; Lopes, A.; Varandas, S.; Sousa, R. Biology and conservation of freshwater bivalves: Past, present and future perspectives. Hydrobiologia 2014, 735, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes-Lima, M.; Sousa, R.; Geist, J.; Aldridge, D.C.; Araujo, R.; Bergengren, J.; Bespalaya, Y.; Bódis, E.; Burlakova, L.; Van Damme, D.; et al. Conservation status of freshwater mussels in Europe: State of the art and future challenges. Biol. Rev. 2017, 92, 572–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machordom, A.; Araujo, R.; Erpenbeck, D.; Ramos, M.Á. Phylogeography and conservation genetics of endangered European Margaritiferidae (Bivalvia: Unionoidea). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2003, 78, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungbluth, J.H.; Coomans (Henry), H.E.; Grohs, H. Bibliographie der Flussperlmuschel Margaritifera Margaritifera (Linnaeus, 1758) [Mollusca: Pelecypoda]. Versl. Tech. Gegevens 1985, 41, 1–220. [Google Scholar]
- Zyuganov, V.A.; Zotin, L.; Nezlin, V.; Tretiakov, V. The Freshwater Pearl Mussels and Their Relationships with Salmonid Fish; VNIRO, Russian Federal Research Institute of Fisheries and Oceanography: Moscow, Russia, 1994; 104p. [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson, P. Regional monitoring of freshwater pearl mussel Margaritifera margaritifera in the County of Norrbotten, Sweden. Biol. Bull. 2017, 44, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulasvirta, P.; Leinikki, J.; Syväranta, J. Freshwater pearl mussel in Finland - current status and future prospects. Biol. Bull. 2017, 44, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, R.; Ramos, M.A. Status and conservation of the giant European freshwater pearl mussel (Margaritifera auricularia) (Spengler, 1793) (Bivalvia: Unionoidea). Biol. Conserv. 2000, 96, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.R.; Cosgrove, P.J.; Hastie, L.C. The extent of, and causes for, the decline of a highly threatened naiad: Margaritifera margaritifera. In Ecology and Evolution of the Freshwater Mussels Unionoida; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 337–357. [Google Scholar]
- Bolotov, I.N.; Bespalaya, Y.V.; Vikhrev, I.V.; Aksenova, O.V.; Aspholm, P.E.; Gofarov, M.Y.; Klishko, O.K.; Kolosova, Y.S.; Kondakov, A.V.; Lyubas, A.A.; et al. Taxonomy and distribution of freshwater pearl mussels (Unionoida: Margaritiferidae) of the Russian Far East. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makhrov, A.; Bespalaya, J.; Bolotov, I.; Vikhrev, I.; Gofarov, M.; Alekseeva, Y.; Zotin, A. Historical geography of pearl harvesting and current status of populations of freshwater pearl mussel Margaritifera margaritifera (L.) in the western part of Northern European Russia. Hydrobiologia 2014, 735, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuttelod, A.; Seddon, M.; Neubert, E. European Red List of Non-Marine Molluscs; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2011; p. 97. [Google Scholar]
- Bolotov, I.N.; Bespalaya, Y.V.; Makhrov, A.A.; Aspholm, P.E.; Aksenov, A.S.; Gofarov, M.Y.; Dvoryankin, G.A.; Usacheva, O.V.; Vikhrev, I.V.; Sokolova, S.E.; et al. Influence of historical exploitation and recovery of biological resources on contemporary status of Margaritifera margaritifera L. and Salmo salar L. populations in Northwestern Russia. Biol. Bull. Rev. 2012, 2, 460–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhrov, A.A.; Ieshko, E.P.; Shchurov, I.L.; Barskaya, Y.Y.; Lebedeva, D.I.; Novokhatskaya, O.V.; Shirokov, V.A. Evaluation of the state of populations of the European pearl mussel (Margaritifera margaritifera) in North Karelia using data on the abundance and infection of host fish. Zool. J. 2009, 88, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar]
- Cosgrove, P.J.; Young, M.R.; Hastie, L.C.; Gaywood, M.; Boon, P.J. The status of the freshwater pearl mussel Margaritifera margaritifera Linn. in Scotland. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2000, 10, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, P.J.; Hastie, L.C. Conservation of threatened freshwater pearl mussel populations: River management, mussel translocation and conflict resolution. Biol. Conserv. 2001, 99, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheder, C.; Lerchegger, B.; Flödl, P.; Csar, D.; Gumpinger, C.; Hauer, C. River bed stability versus clogged interstitial: Depth-dependent accumulations of substances in freshwater pearl mussel (Margaritifera margaritifera L.) habitats in Austrian streams as a function of hydromorphological parameters. Limnologica 2015, 50, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, G. Threats to the freshwater pearl mussel Margaritifera margaritifera L. in central Europe. Biol. Conserv. 1988, 45, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ieshko, E.P.; Larson, B.M.; Pavlov, Y.L.; Barskaya, Y.Y.; Lebedeva, D.I.; Novokhatskaya, O.V. Population dynamics of the number of glochidia of the freshwater pearl mussel Margaritifera margaritifera L., parasitizing on juvenile salmon fish of northern water bodies. Izv. Akad. Nauk. Seriia Biol. 2009, 6, 734–739. [Google Scholar]
- Ieshko, E.P.; Lebedeva, D.I.; Barskaya, Y.Y.; Shulman, B.S.; Shchurov, I.L.; Shirokov, V.A. Features of infection of juvenile Atlantic salmon during joint parasitism of European pearl mussel glochidia and monogenean Gyrodactylus salaris Malmberg. Proc. Karelian Sci. Cent. Russ. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Ieshko, E.P.; Veselov, A.E.; Murzina, S.A.; Jorgen, G.; Lebedeva, D.I.; Efremov, D.A.; Ruch’ev, M.A.; Zotin, A.A. Freshwater pearl mussel Margaritifera margaritifera L. in the Syuskyuyanjoki River (Lake Ladoga basin). Proc. Karelian Sci. Cent. Russ. Acad. Sci. 2014, 6, 123–133. [Google Scholar]
- Murzina, S.A.; Ieshko, E.P.; Zotin, A.A. Freshwater pearl mussel Margaritifera margaritifera L.: Metamorphosis, growth and development dynamics of encysted glochidia. Izv. Akad. Nauk. Seriia Biol. 2017, 1, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murzina, S.A.; Nefedova, Z.A.; Ieshko, E.P.; Nemova, N.N. Comparative characteristics of the lipid status of gills of juvenile Atlantic salmon infected with glochidia of the freshwater pearl mussel living in rivers of the European North. Izv. Akad. Nauk. Seriia Biol. 2017, 1, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taeubert, J.E.; Geist, J. The relationship between the freshwater pearl mussel (Margaritifera margaritifera) and its hosts. Biol Bull 2017, 44, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwaha, J.; Aase, H.; Geist, J.; Stoeckle, B.C.; Kuehn, R.; Jakobsen, P.J. Host (Salmo trutta) age influences resistance to infestation by freshwater pearl mussel (Margaritifera margaritifera) glochidia. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 1519–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castrillo, P.A.; Varela-Dopico, C.; Bermúdez, R.; Quiroga, M.I.; Ondina, P. The parasitic travel of Margaritifera margaritifera in Atlantic salmon gills: From glochidium to post-larva. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 27, 101340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.; Williams, J. The reproductive biology of the freshwater pearl mussel Margaritifera margaritifera (Linn.) in Scotland. I. Field studies. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1984, 99, 405–422. [Google Scholar]
- Geist, J.; Porkka, M.; Kuehn, R. The status of host fish populations and fish species richness in European freshwater pearl mussel (Margaritifera margaritifera L.) streams. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshwat. Ecosyst. 2006, 16, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taeubert, J.E.; Denic, M.; Gum, B.; Lange, M.; Geist, J. Suitability of different salmonid strains as hosts for the endangered freshwater pearl mussel (Margaritifera margaritifera). Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshwat. Ecosyst. 2010, 20, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonen, J.K.; Luhta, P.L.; Moilanen, E.; Oulasvirta, P.; Turunen, J.; Taskinen, J. Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and brown trout (Salmo trutta) differ in their suitability as hosts for the endangered freshwater pearl mussel (Margaritifera margaritifera) in north-ern Fennoscandian rivers. Freshw. Biol. 2017, 62, 1346–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes-Lima, M.; Burlakova, L.E.; Karatayev, A.Y.; Mehler, K.; Seddon, M.; Sousa, R. Conservation of freshwater bivalves at the global scale: Diversity, threats and research needs. Hydrobiologia 2018, 810, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyuganov, V.V. Monitoring of the biosystem "Pearl-salmon" in the Karelian River Keret over the past 17 years. Successes Mod. Biol. 2008, 128, 424–430. [Google Scholar]
- Makhrov, A.A.; Bolotov, I.N. Does the European pearl mussel (Margaritifera margaritifera) affect the life cycle of the Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar)? Adv. Gerontol. 2010, 23, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vikhrev, I.V. Distribution and Current State of Populations of the European Pearl Oyster (Margaritifera margaritifera L.) on the Eastern Border of the Range. Ph.D. Thesis, Syktyvkar State University, Syktyvkar, Russia, 2013; p. 123. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.L.; Cox, M.M. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry, 5th ed.; W.H. Freeman & Company: New York, NY, USA, 2008; 1294p. [Google Scholar]
- Dyatlovitskaya, E.V.; Bezuglov, V.V. Lipids as bioeffectors. Biochemistry 1998, 63, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sergeeva, M.G.; Varfolomeeva, A.T. Cascade of Arachidonic Acid; National Education: Moscow, Russia, 2006; 256p. [Google Scholar]
- Lagarde, M.; Guichardant, M.; Luquain, C.; Bernoud-Hubac, N.; Calzada, C.; Véricel, E. Structural and Mediator Lipidomics: A Functional View; EPFL Press: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2016; 100p. [Google Scholar]
- Pollero, R.J.; Brenner, R.R.; Gros, E.G. Seasonal changes in lipid and fatty acid composition of the freshwater mollusk, Diplodom patagonicus. Lipids 1981, 16, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagar, A.F.; Dietz, T.H. Seasonal changes in the lipid composition of gill tissue from the freshwater mussel Carunculina texasensis. Physiol. Zool. 1986, 59, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaletto, J.F.; Gardner, W.S. Seasonal dynamics of lipids in freshwater benthic invertebrates. In Lipids in Freshwater Ecosystems; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 109–131. [Google Scholar]
- Capuzzo, J.M.; Leavitt, D.F. Lipid composition of the digestive glands of Mytilus edulis and Carcinus maenas in response to pollutant gradients. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1988, 46, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokina, N.N.; Nefedova, Z.A.; Nemova, N.N. Lipid composition of mussels Mytilus edulis L. from the White Sea. In Influence of Some Environmental Factors; Karelian Scientific Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences: Petrozavodsk, Russia, 2010; p. 243. [Google Scholar]
- Perrat, E.; Couzinet-Mossion, A.; Tankoua, O.F.; Amiard-Triquet, C.; Wielgosz-Collin, G. Variation of content of lipid classes, sterols and fatty acids in gonads and digestive glands of Scrobicularia plana in relation to environment pollution levels. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 90, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabakaeva, O.V.; Tabakaev, A.V. Lipids from soft tissues of the bivalve mollusk Anadara broughtonii. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2015, 51, 946–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes-Dos-Santos, A.; Lopes-Lima, M.; Machado, A.M.; Marcos Ramos, A.; Usié, A.; Bolotov, I.N.; Vikhrev, I.V.; Breton, S.; Castro, L.F.C.; da Fonseca, R.R.; et al. The Crown Pearl: A draft genome assembly of the European freshwater pearl mussel Margaritifera margaritifera (Linnaeus, 1758). DNA Res. 2021, 28, dsab002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, L.C.; Young, M.R. Timing of spawning and glochidial release in Scottish freshwater pearl mussel (Margaritifera margaritifera) populations. Freshw. Biol. 2003, 48, 2107–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolland, J.D.; Bracken, L.J.; Martin, R.; Lucas, M.C. A protocol for stocking hatchery reared freshwater pearl mussel Margaritifera Margaritifera. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2010, 20, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstikov, A.V.; Galakhina, N.E.; Zdorovennov, R.E. Hydrophysical and hydrochemical studies in the estuary of the Kem River in September 2019. Proc. Karelian Sci. Cent. Russ. Acad. Sci. 2020, 4, 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murzina, S.A.; Nefedova, Z.A.; Ruokolainen, T.R.; Vasil’eva, O.B.; Nemova, N.N. Dynamics of lipid content during early development of freshwater salmon Salmo salar L. Russ. J. Dev. Biol. 2009, 40, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekkoeva, S.N.; Murzina, S.A.; Nefedova, Z.A.; Ripatti, P.O.; Falk-Petersen, S.; Berge, J.; Lonne, O.L.; Nemova, N.N. Ecological role of lipids and fatty acids in the early postembryonic development of the daubed shanny, Leptoclinus maculatus (Fries, 1838) from Kongsfjorden, West Spitsbergen in winter. Russ. J. Ecol. 2017, 48, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronin, V.P.; Murzina, S.A.; Nefedova, Z.A.; Pekkoeva, S.N.; Ruokolainen, T.R.; Ruch’ev, M.A.; Nemova, N.N. A comparative study of lipids and it’s dynamic during embryogenesis and early post-embryonic development of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) and brown trout (Salmo trutta L.). Russ. J. Dev. Biol. 2021, 52, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotin, A.A.; Ieshko, E.P. Growth Biorhythms of the Freshwater Pearl Mussel Margaritifera margaritifera (Bivalvia, Margaritifer-idae), Nemina River Population (Karelia). Biol. Bull. 2021, 48, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotin, A.A.; Murzina, S.A.; Filippova, K.A.; Efremov, D.A.; Oulasvirta, P.; Ieshko, E.P. Ecology of the freshwater pearl mussel Margartifera margaritifera (Linnaeus, 1758) in the Kamennaya river (the Kem’ River catchment, White Sea basin). Nat. Conserv. Research. Reserv. Sci. 2021, 6 (Suppl. S1). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotin, A.A.; Murzina, S.A.; Filippova, K.A.; Ieshko, E.P. Growth parameters of the freshwater pearl mussel Margaritifera mar-garitifera (Bivalvia, Margaritiferidae). Vuokinjoki river population (Karelia). Malacologia 2020, 63, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandee, D.I.; Kluytmans, J.H.; Zurburg, W.; Pieters, H. Seasonal variations in biochemical composition of Mytilus edulis with reference to energy metabolism and gametogenesis. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1980, 14, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenne, R.; Polak, L. Lipid composition and storage in the tissues of the bivalve, Macoma balthica. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1989, 17, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caers, M.; Coutteau, P.; Cure, K.; Morales, V.; Gajardo, G.; Sorgeloos, P. The Chilean scallop Argopecten purpuratus (Lamarck, 1819): I. Fatty acid composition and lipid content of six organs. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B: Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1999, 123, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.X.; Huang, X.H.; Zheng, J.; Dong, L.; Chen, J.N.; Dong, X.P.; Zhou, D.-Y.; Zhu, B.-W.; Qin, L. Free amino acids, 5′-Nucleotide, and lipid distribution in different tissues of blue mussel (Mytilis edulis L.) determined by mass spec-trometry based metabolomics. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapin, V.I.; Shatunovsky, M.I. Features of the composition, physiological and ecological significance of fish lipids. Modern success. Biology 1981, 2, 380–394. [Google Scholar]
- Boldyrev, A.A.; Kyyvyaryaynen, E.I.; Ilyukha, V.A. Biomembranology: A Textbook; Publishing House of the Kar Scientific Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences: Petrozavodsk, Russia, 2006; p. 226. [Google Scholar]
- Sukumaran, S.; Pittman, K.B.; Patterson, W.K.; Dickson, J.; Yeend, S.; Townsend, A.; Broadbridge, V.; Price, T.J. A phase I study to determine the safety, tolerability and maximum tolerated dose of green-lipped mussel (Perna canaliculus) lipid extract, in patients with advanced prostate and breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakelova, E.S. The composition of total lipids and the rate of energy metabolism in gastropods. J. Gen. Biol. 2008, 69, 471–478. [Google Scholar]
- Fokina, N.N. Lipid composition of mussels Mytilus edulis L. of the White Sea. Ph.D. Thesis, The Karelian State Pedagogical Academy, Petrozavodsk, Russia, 2007; p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Pita, I.; Sánchez-Lazo, C.; Ruíz-Jarabo, I.; Herrera, M.; Mancera, J.-M. Biochemical composition, lipid classes, fatty acids and sexual hormones in the mussel M. galloprovincialis from cultivated populations in south Spain. Aquaculture 2012, 358, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez–Pita, I.; Sánchez–Lazo, C.; García, F.J. Influence of microalga lipid composition on the sexual maturation of M. galloprovincialis: A hatchery study. Aquac. Nutr. 2016, 22, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finagin, L.K. Cholesterol Metabolism and Its Regulation; Publishing House at Kyiv State University: Kiev, Ukraine, 1980; 166p. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, G.A. Molecular changes in membrane lipids during cold stress. In Environmental Stress in Plants; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989; pp. 249–257. [Google Scholar]
- Veselov, A.E.; Ieshko, E.P.; Zotin, A.A.; Efremov, D.A.; Ruchev, M.A.; Nemova, N.N. Ecology of freshwater form of Atlantic salmon Salmo salar L., brown trout Salmo trutta L. and freshwater pearl mussel Margaritifera margaritifera L. in the Syuskyuyanjoki River (Ladoga Lake basin). Izv. Akad. Nauk. Seriia Biol. 2017, 1, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapranova, L.L.; Nekhoroshev, M.V.; Malakhova, L.V.; Ryabushko, V.I.; Kapranov, S.V.; Kuznetsova, T.V. Fatty acid composition of gonads and gametes in the Black Sea bivalve mollusk Mytilus galloprovincialis Lam. at different stages of sexual maturation. J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 55, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapranova, L.L. Ecological and Biochemical Studies of the Bivalve Mollusc Mytilus Galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819 during the Breeding Season. Ph.D. Thesis, A. O. Kovalevsky Institute of Biology of the Southern Seas of RAS, Sevastopol, Russia, 2022; p. 188. [Google Scholar]
- Duinker, A.; Torstensen, B.E.; Lie, O. Lipid classes and fatty acid composition in female gonads of great scallops—A selective field study. J. Shellfish Res. 2004, 23, 507–515. [Google Scholar]
- Gallager, S.M.; Mann, R.; Sasaki, G.C. Lipid as an index of growth and viability in three species of bivalve larvae. Aquaculture 1986, 56, 81–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollero, R.J.; Ré, M.E.; Brenner, R.R. Seasonal changes of the lipids of the mollusk Chlamys tehuelcha. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Physiol. 1979, 64, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farris, J.L.; Van Hassel, J.H. Freshwater Bivalve Ecotoxicology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor and Francis Group: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007; p. 257. [Google Scholar]
- Neves, R.J.; Weaver, L.R.; Zale, A.V. An evaluation of fish host suitability for glochidia of Villosa vanuxemi and V. nebulosa (Pelec-ypoda: Unionidae). Amer. Midl. Nat. 1981, 113, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
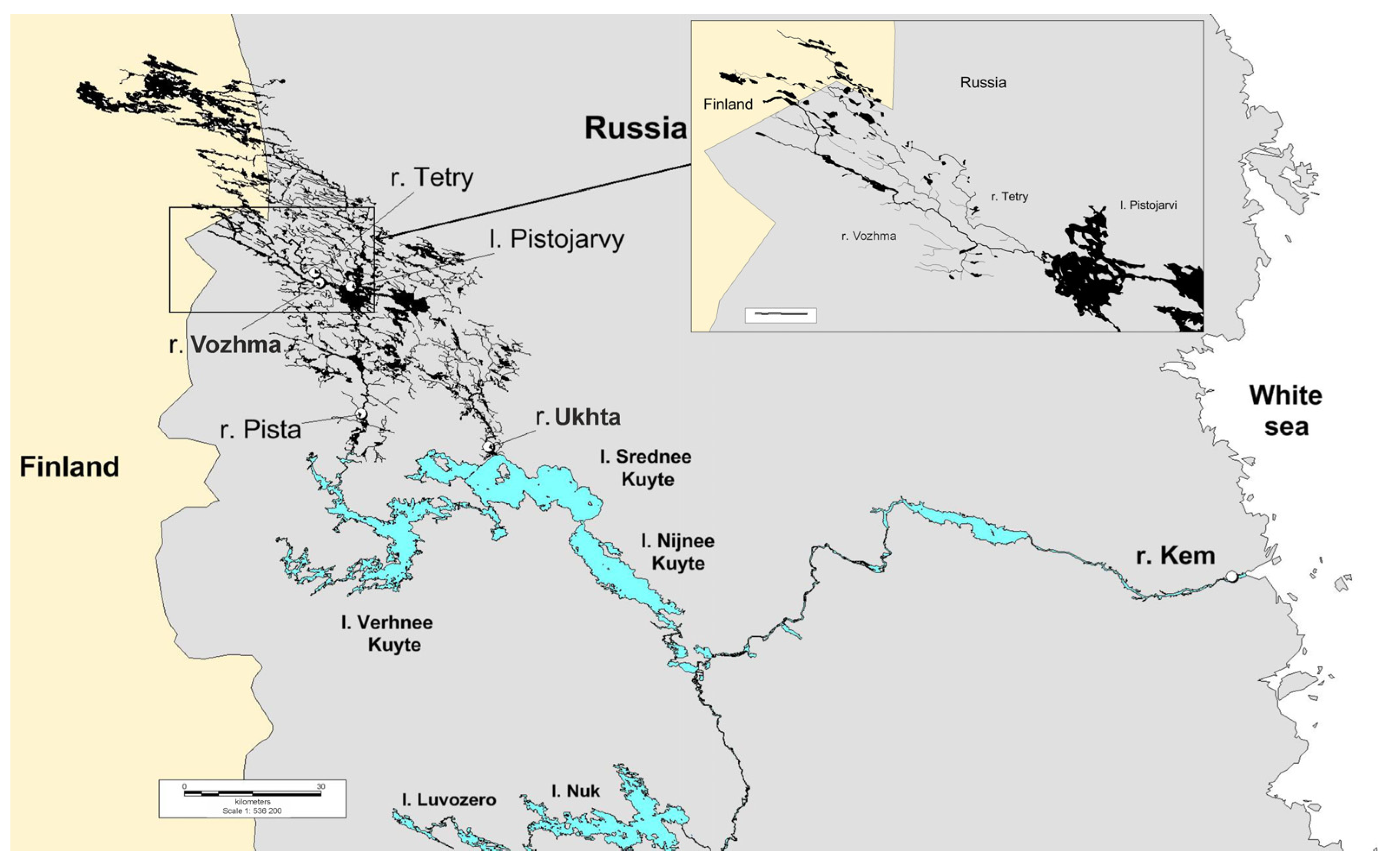
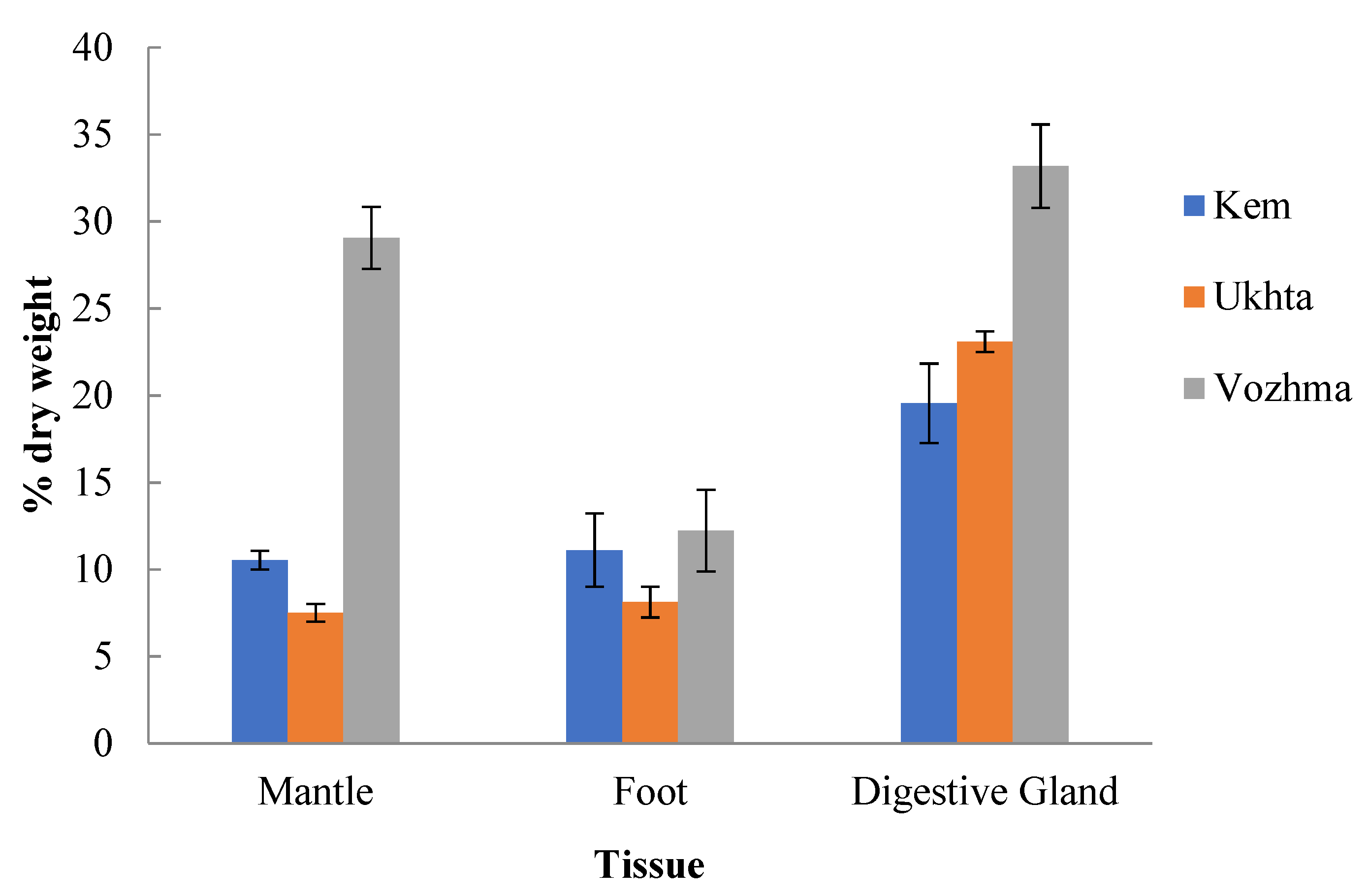
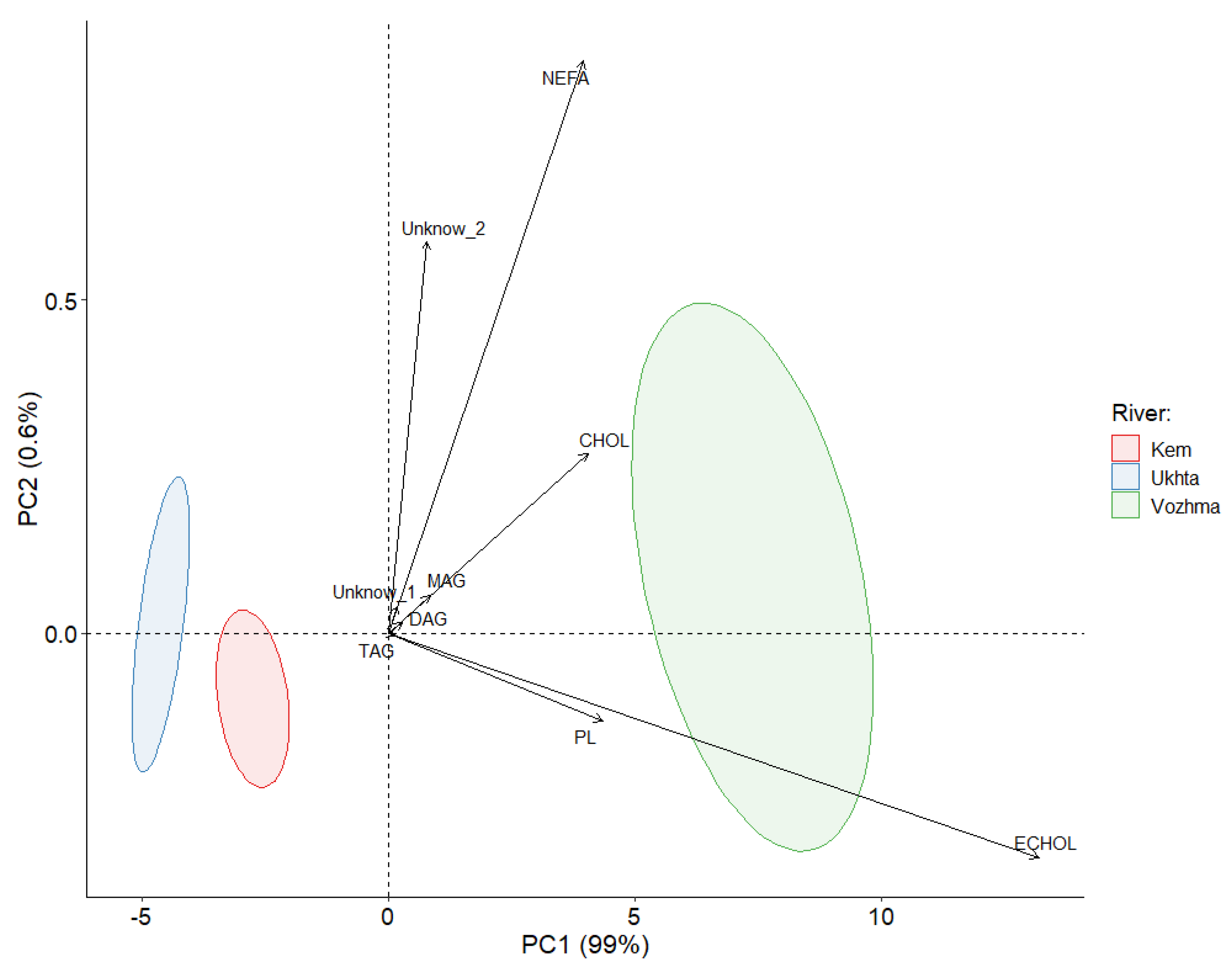
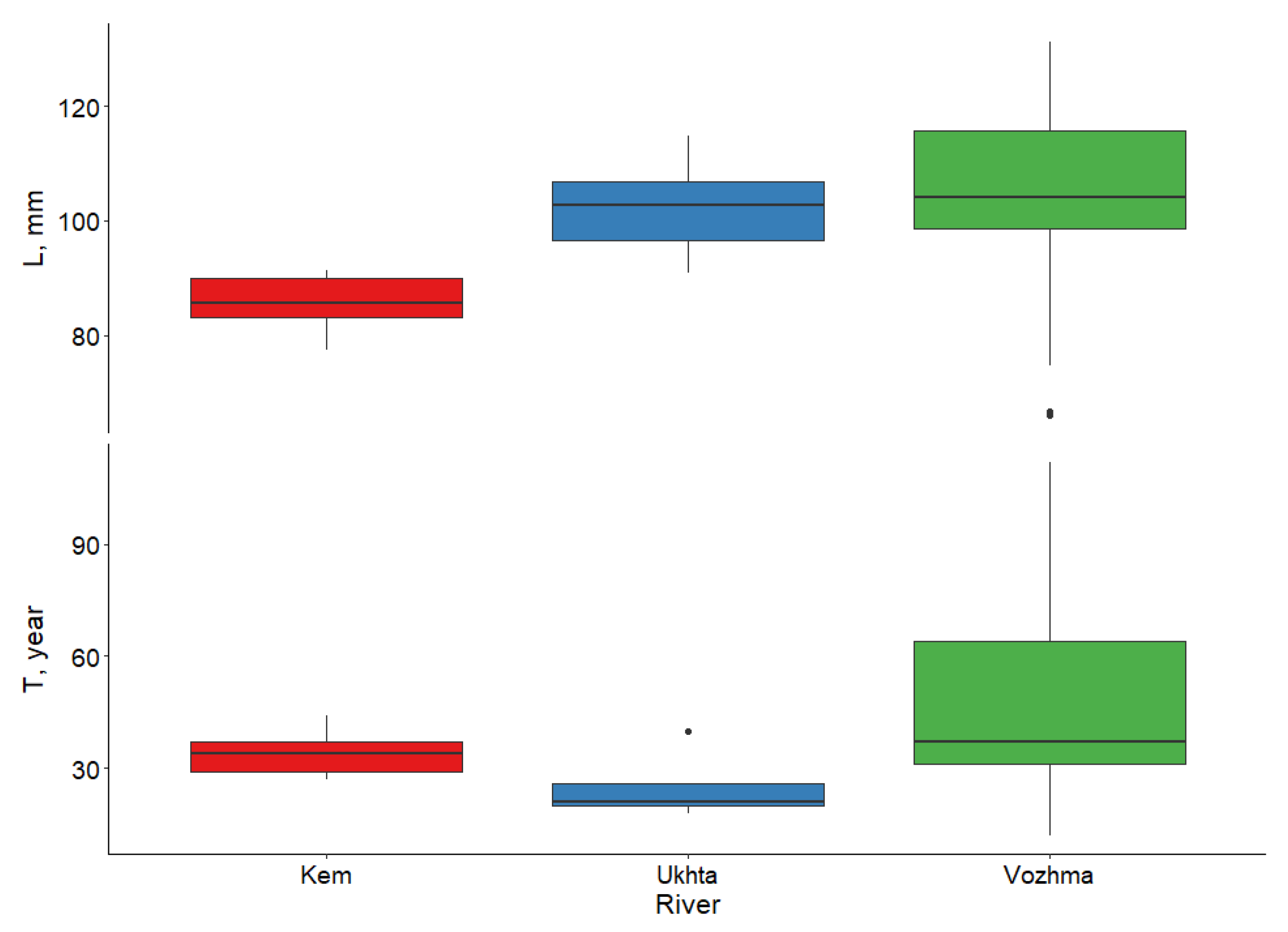

| River | Sampling Date | Water Temperature | Number of Samples (n) | Water System | Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kem (stream of the estuary zone) | 27 September 19 | 5 °C | 15 | White Sea (mouth) | A young colony of the freshwater pearl mussel, recovered after construction of the Kem hydroelectric power station cascade. Oil products and heavy metals as pollutants were determined in the estuary of the Kem River [56]. Close proximity to the city of Kem. |
| Ukhta | 27 September 19 | 5 °C | 15 | Middle Kuito (mouth) Lake → Luusalmi strait → Lower Kuito Lake → Kem River → White Sea | A young colony of the freshwater pearl mussel, recovered after construction of the dam 47 years ago. Close proximity to the city of Kalevala. |
| Vozhma | 3 October 19 | 3 °C | 15 | Pistarvi Lake (mouth) → Pista River → Uper Kuito Lake → Elman River → Middle Kuito Lake → Luusalmi strait → Lower Kuito Lake → Kem’ River → White Sea | Individuals over 100 years old are found in the colony. |
| Tetri | 3 October 19 | 3 °C | 2 | Vozhma River (mouth) → Pistarvi Lake → Pista River → Upper Kuito Lake → Elmane River → Middle Kuito Lake → Luusalmi → Lower Kuito Lake → Kem River → White Sea | A young colony of the freshwater pearl mussel. |
| Kem (Estuary) | Ukhta | Vozhma | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TL | 10.54 ± 0.53 | 7.5 ± 0.51 a | 29.6 ± 1.78 ab |
| PL | 1.11 ± 0.08 | 0.7 ± 0.05 a | 4.08 ± 0.33 ab |
| CHOL | 1.29 ± 0.07 | 1.01 ± 0.07 a | 4.21 ± 0.25 ab |
| ECHOL | 4.59 ± 0.28 | 2.83 ± 0.2 a | 13.37 ± 0.9 ab |
| TAG | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.18 ± 0.03 ab |
| DAG | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 0.16 ± 0.02 | 0.38 ± 0.02 ab |
| MAG | 0.41 ± 0.03 | 0.31 ± 0.03 a | 0.99 ± 0.05 ab |
| NEFA | 2.03 ± 0.08 | 1.57 ± 0.12 a | 4.82 ± 0.24 ab |
| Unknown 1 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.11 ± 0.01 a | 0.22 ± 0.02 ab |
| Unknown 2 | 0.81 ± 0.05 | 0.72 ± 0.07 | 1.35 ± 0.12 ab |
| CHOL/PL | 1.16 ± 0.05 | 1.44 ± 0.06 | 1.03 ± 0.09 |
| Kem (Estuary) | Ukhta | Vozhma | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TL | 11.11 ± 2.11 | 8.13 ± 0.89 | 12.23 ± 2.35 |
| PL | 1.26 ± 0.23 | 0.76 ± 0.08 a | 1.68 ± 0.4 |
| CHOL | 1.6 ± 0.32 | 1.1 ± 0.12 a | 1.93 ± 0.38 |
| ECHOL | 4.94 ± 0.91 | 2.85 ± 0.27 a | 5.01 ± 1.04 |
| TAG | 0.24 ± 0.14 | 0.15 ± 0.04 | 0.14 ± 0.02 |
| DAG | 0.18 ± 0.04 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 0.17 ± 0.03 |
| MAG | 0.45 ± 0.06 | 0.38 ± 0.04 | 0.47 ± 0.08 |
| NEFA | 1.69 ± 0.34 | 1.64 ± 0.22 | 1.9 ± 0.31 |
| Unknown 1 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.03 a | 0.13 ± 0.06 |
| Unknown 2 | 0.71 ± 0.09 | 0.99 ± 0.15 a | 0.81 ± 0.1 |
| CHOL/PL | 1.28 ± 0.35 | 1.45 ± 0.1 | 1.15 ± 0.08 |
| Kem (Estuary) | Ukhta | Vozhma | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TL | 19.56 ± 2.28 | 23.09 ± 0.6 | 33.18 ± 2.4 ab |
| PL | 1.98 ± 0.34 | 1.66 ± 0.06 | 3.18 ± 0.35 ab |
| CHOL | 1.95 ± 0.25 | 1.96 ± 0.05 | 3.16 ± 0.23 ab |
| ECHOL | 5.59 ± 0.72 | 5.77 ± 0.17 | 9.1 ± 0.9 ab |
| TAG | 0.28 ± 0.03 | 0.21 ± 0.02 | 0.41 ± 0.05 ab |
| DAG | 0.28 ± 0.03 | 0.38 ± 0.01 | 0.5 ± 0.04 ab |
| MAG | 0.68 ± 0.06 | 1.01 ± 0.05 | 1.11 ± 0.05 ab |
| NEFA | 3.51 ± 0.37 | 4.5 ± 0.16 | 5.68 ± 0.3 ab |
| Unknown 1 | 0.45 ± 0.04 | 1.1 ± 0.02 | 0.86 ± 0.06 ab |
| Unknown 2 | 4.84 ± 0.48 | 6.49 ± 0.19 | 9.07 ± 0.59 ab |
| CHOL/PL | 0.98 ± 0.12 | 1.18 ± 0.05 | 0.99 ± 0.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pekkoeva, S.N.; Voronin, V.P.; Ieshko, E.P.; Fokina, N.N.; Efremov, D.A.; Murzina, S.A. Lipid Profile of the Freshwater Pearl Mussel Margaritifera margaritifera Inhabiting Different Biotopes of the Lake-River System of the Kem River, White Sea Basin. Diversity 2023, 15, 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020293
Pekkoeva SN, Voronin VP, Ieshko EP, Fokina NN, Efremov DA, Murzina SA. Lipid Profile of the Freshwater Pearl Mussel Margaritifera margaritifera Inhabiting Different Biotopes of the Lake-River System of the Kem River, White Sea Basin. Diversity. 2023; 15(2):293. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020293
Chicago/Turabian StylePekkoeva, Svetlana N., Viktor P. Voronin, Evgeny P. Ieshko, Natalia N. Fokina, Denis A. Efremov, and Svetlana A. Murzina. 2023. "Lipid Profile of the Freshwater Pearl Mussel Margaritifera margaritifera Inhabiting Different Biotopes of the Lake-River System of the Kem River, White Sea Basin" Diversity 15, no. 2: 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020293
APA StylePekkoeva, S. N., Voronin, V. P., Ieshko, E. P., Fokina, N. N., Efremov, D. A., & Murzina, S. A. (2023). Lipid Profile of the Freshwater Pearl Mussel Margaritifera margaritifera Inhabiting Different Biotopes of the Lake-River System of the Kem River, White Sea Basin. Diversity, 15(2), 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020293







