Abstract
The results of a review of the chelonian remains retrieved in the excavations carried out in Mealhada (Coimbra, central Portugal) are presented here. Mealhada is a Portuguese Middle Palaeolithic classical site, discovered at the end of the 19th century, and chronologically ascribed to the interglacial Riss-Würm (ca. 120 ka BP). This study has allowed the identification, justification, and figuration of remains attributed to three Iberian chelonian taxa, Testudinidae indet., Mauremys leprosa, and Emys orbicularis, the last one being recognized for the first time in this site. Thus, an update on the data concerning the chelonian record from Mealhada has been achieved, offering new justified taxonomic evidence regarding Iberian chelonian taxa distribution during the Upper Pleistocene. Furthermore, chelonian consumption amongst pre-Upper Palaeolithic hunter-gatherer groups has been documented worldwide. Frequently a locally captured resource, archaeological turtle remains offer relevant information concerning the role that small prey has played in hominid nutritional choices. The potential presence of anthropic alterations (e.g., cutmarks) in some of the chelonian remains from Mealhada is here analysed and the human consumption hypothesis assessed.
1. Introduction
The study of tortoise remains (e.g., Chersine hermanni, Testudo graeca) recovered in the Iberian Peninsula and other Middle Palaeolithic sites worldwide as a dietary resource has been a subject of debate [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. Framed within a broader discussion regarding the consumption of small prey (e.g., leporids, birds) in the pre-Upper Palaeolithic contexts, tortoises have provided relevant data that has proved its significance in the Neanderthal palaeodiet, not being an exclusive resource for the anatomically modern humans [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13] (see Blasco et al. [13] for an extended lecture on the topic). In contrast the potential role of terrapins (e.g., Mauremys leprosa, Emys orbicularis) as a dietary resource has not been assessed in Iberian Peninsula Middle Palaeolithic contexts, mainly due to its low incidence and scarce number of remains.
The Middle Palaeolithic (ca. 120 ka BP) site of Mealhada is located 14 km north of the city of Coimbra, in Portugal (Western Europe), in the alluvial deposits of the lower terrace of the Cértima River (Figure 1). It was first excavated in the late 19th century and presented by C. Ribeiro to the scientific community at the International Congress of Geology held in Paris in 1878, emphasizing the presence of mammal remains identified as Elephas antiquus. Soon after, Ribeiro [14] reported the presence of faunal remnants and lithic artefacts similar to those recovered in the classical Lower Palaeolithic site of Saint-Acheul (Northern France). Mealhada was studied, among others, by Fontes [15], and Zbyszewski [16,17] (see Cunha-Ribeiro [18] for a summary of the investigations performed there).
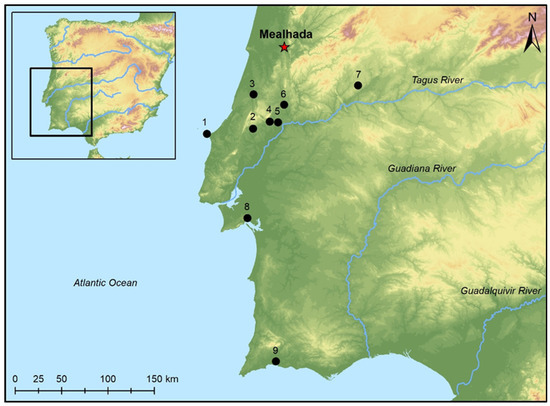
Figure 1.
Mealhada Middle Palaeolithic site location on the Iberian Atlantic Coast (Coimbra, central Portugal). Other Portuguese Palaeolithic archaeological turtle records mentioned in the text are: (1) Gruta da Furninha (Peniche); (2) Lapa do Picareiro (Alcanede); (3) Gruta Nova da Columbeira (Bombarral); (4) Galeria Pesada (Almonda); (5) Gruta da Oliveira/Gruta da Aroeira (Torres Novas); (6) Gruta do Caldeirão I/ Gruta do Morgado Superior (Tomar); (7) Foz do Enxarrique (Vila Velha de Ródão); (8) Gruta da Figueira Brava (Arrábida); (9) Gruta Ibn Amar (Lagoa) (Map: Pablo Paniego Díaz).
Zbyszewski [19] made a recapitulation of all the previous studies and a description of the stratigraphy, fauna, flora, and lithic industries recovered in Mealhada. The author also reported the presence of Upper Acheulean industries, which led him to date the deposits as belonging to the Riss glaciation. However, the presence of certain taxa, such as, Hippopotamus incognitus (as well as Elephas antiquus, Homotherium latidens, and large individuals of Equus caballus) forced him to exclude the colder periods, which led to the relative assignment of the deposit to the interglacial Riss-Würm (ca. 120 ka BP) [20,21,22]. Pioneering studies of plant remains and pollens were carried out, and, together with the faunal assemblage, reinforced the proposed chronology [23]. The relative dating was also supported by a U date (80,886 + 42,423 − 31,265 BP) [24] (p. 112), although no stratigraphic association was provided for the sample. The climatic conditions inferred from the fauna ensemble are temperate with warm temperatures, although humid, and closely related to lake or river plain areas [25] (pp. 135–136).
The first reference of turtle remains recovered at the site of Mealhada was provided by Zbyszewski [19], who cited the presence of Testudo sp. and included a figure showing some remains [19] (p. 22). The author mentioned the existence of 77 shell plates deposited in the Museu dos Serviços Geológicos (Museu Geológico de Lisboa—MG), indicating the size of the largest and smallest remain, as well as its stratigraphical location in level 4 [19] (p. 26). Antunes and colleagues [21] (p. 166) referred again to the aforementioned remains, being cited as Chélonien indet. (sic) by them, noting that, although previously cited as Testudo sp. (see Zbyszewski [19]), an accurate systematic attribution required detailed future study. Jiménez Fuentes and colleagues [25] collected the data described above in their study of turtle remains from Gruta Nova da Columbeira site. They suggested that if it was confirmed that the remains of Mealhada were A. (Agrionemys) hermanni (sic), their presence on the Portuguese Atlantic coast would go back at least until −80,000 to −150,000 years, and its northern distribution limit would rise considerably [25] (p. 137). Crespo [26] updated the published information on Portuguese paleoherpetofauna including the turtle remains of Mealhada and identifying the taxa Agrionemys sp. (sic) and Mauremys leprosa in the site. Crespo [26] (p. 28) cited the presence of M. leprosa for the first time at the site and suggested that the record was the oldest one in the Iberian Peninsula, doubting the identification of the species in the Pliocene/Lower Pleistocene of Barranco León 5 (Guadix-Baza basin, south-eastern Spain) [27]. Regarding the specimens attributed to Agrionemys (sic), the author stated that the remains probably belonged to A. hermanni (sic) since there were no reliable records of the presence of A. graeca (sic) in Portugal [26] (p. 28).
The aim of this study is to review the turtle remains recovered in the Mealhada site during the excavations performed in the 19th century, and deposited in the MG, in order to confirm or update the taxonomic identification and to perform an archaezoological and taphonomical traditional analysis. The results of our study have provided new justified taxonomic identifications including the identification of three forms, Testudinidae indet., Mauremys leprosa (Geoemydidae), and Emys orbicularis (Emydidae) (identified here for the first time). Also, possible anthropic modifications are characterized whereas the dubious material contextualization leads to caution in developing related hypotheses.
2. Materials and Methods
The material studied here are turtle remains from Mealhada deposited in MG (Lisbon, Portugal). The site presents the museum registration number 788. Remains are placed in two boxes labelled 42-A-1 and numbered MG 8217.1 and MG 8217.2. In addition, they present a note indicating ‘Galeria Sul do Plaça de Augusto Ferreira. A 6.0 m prof. 1880′. In box MG 8217.1 the material is marked as ‘Cam. 4′ (meaning ‘camada’ or level 4).
The applied methodology is the standard for archaeozoological traditional analysis. The material was first-hand revised, figurated, and photographed (using a camera Canon Ixus 107), providing here an illustrative selection of the identified genera and species (Figure 2 and Figure 3). Potential human taphonomical evidence was examined with a hand loupe with 10×, 15×, and 20× magnifications. All the figures presented here have been elaborated with the software Adobe Photoshop® and CorelDRAW®. In the material figurations (Figure 2 and Figure 3), plates are drawn in black, and scutes in grey. Discontinuous lines in these figures indicate fractured margins. Striped fill represents suture areas or ligamentous union areas in Figure 2, and fractured surfaces in Figure 3.

Figure 2.
MG 8217.1/MG 8217.2 Carapacial turtle plates selection from the Middle Palaeolithic site of Mealhada (Coimbra, central Portugal) in dorsal (left) and ventral (right) views. Mauremys leprosa plates selection (A,D,F,H): (A), nuchal; (D), left 3 peripheral; (F), suprapygal 2; (H), pygal. Emys orbicularis plates selection (B,E,G): (B), nuchal; (E), left 3 peripheral; (G), pygal. (C), left 7 peripheral of Testudinidae indet. (A’–H’), plates figuration. Red rectangle indicates a burned area.
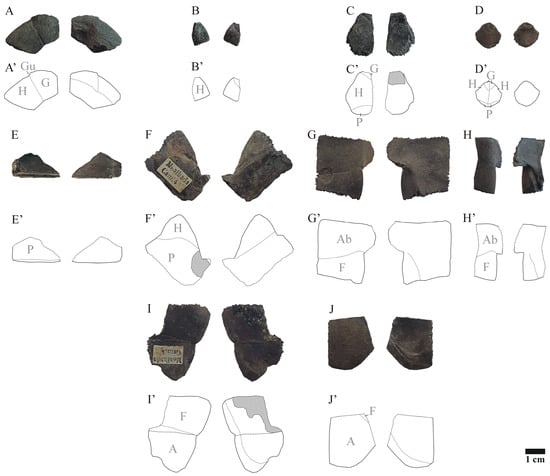

Figure 3.
MG 8217.1/MG 8217.2 Plastral turtle plates selection from the Middle Palaeolithic site of Mealhada (Coimbra, central Portugal) in dorsal (left) and ventral (right) views. Mauremys leprosa plates selection (A,C,F,G,I): (A), right epiplastron; (C), entoplastron; (F), left hyoplastron; (G), left hypoplastron; (I), left xiphiplastron. Emys orbicularis plates selection (B,D,E,H,J): (B), left epiplastron; (D), entoplastron; (E), left hyoplastron; (H), left hypoplastron; (J), left xiphiplastron. (A’–J’), plates figuration.
The diagnostic criteria used for the taxonomical identification of the remains was selected from various works [27,28,29,30,31,32,33]. The quantification of the remains performed here includes the number of remains (NR), the number of identified specimens (NISP) and the minimum number of individuals (MNI) [34,35]; all percentages are from the NR total (see Table 1). The relative age determination (defining its ontogenetic stage as juvenile or adult) is based on the straight carapace length (SCL) [36,37,38,39], the shell plates size and/or the ossification degree. The sex determination is based on the criteria proposed by various authors for the taxa identified here [36,37,38,39].

Table 1.
Turtle remains from the Middle Paleolithic site of Mealhada (Coimbra, central Portugal) identified in the Museu Geológico de Lisboa (Lisbon, Portugal). The number of shell skeletal elements identified (and indeterminate) by taxon, NISP and percentage are indicated.
Human and natural taphonomic evidences have been defined following different publications [40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47]. Incisions, scratches, and fractures are characterized and defined following various works [40,41]. Possible carnivore and other predator actions and alterations have been analysed following Pérez-Ripoll and Sampson [41,42]. Burning damage degree is described based on coloration [44,45], and its location within the turtle shell [46]. The potential confusion of alterations origin with postdeposicional processes was assessed following Fernández-Jalvo and Andrews [47].
3. Results
The first-hand review of the Mealhada material deposited in MG has yielded the identification of 129 turtle remains (NR), which conceded a NISP of 65 (50.5%), 64 remaining unidentified (49.6%) (see Table 1). All the specimens correspond to carapacial and plastral plates. The total MNI is 11 specimens, one specimen assigned to Testudinidae indet., six to Mauremys leprosa, and four to Emys orbicularis. Within the Mauremys leprosa specimens, three are identified as males, and only one as a female. Both ontogenetic stages, juvenile and adult, have been recognised in the ensemble.
The set shows a substantial fragmentation value (76.7%) (complete/incomplete), the majority of which corresponds to a postdepositional origin. Potential anthropogenic alterations have been recognized in a very low percentage (13.2%). Seven remains present incisions and scratches groups (5.4%) (Table 2, Figure 4 and Figure 5), at least eight burning traces (6.2%), and two fractures (1.5%). Most of the documented incisions and scratches are characterized by being very slight and by their location in the carapace ventral side and in the plastron dorsal side (except those from the right hyoplastron, located on the ventral side, see 7 in Table 2). Black burned traces have been here found mainly on peripheral Emys orbicularis plates in its posterior/lateral side. Fresh fractures are identified in the dorsal part of two right hyoplastra, one of them with a short and slight incision in the ventral side (Figure 5E). No carnivore or other predator activity has been identified.

Table 2.
Potential anthropic alterations description and location on turtle remains from the Middle Paleolithic site of Mealhada (Coimbra, central Portugal).
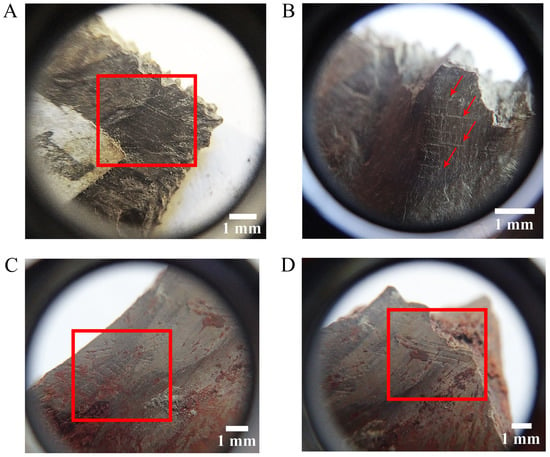
Figure 4.
Details of incisions and scratches groups in turtle remains from the Middle Palaeolithic site of Mealhada (Coimbra, central Portugal). Arrows and boxes mark the identified alterations. For each specimen alteration type, see Table 2. Mauremys leprosa right peripheral 10 detail (A) and left xiphiplastron detail (B). Emys orbicularis right epiplastron detail (C,D).
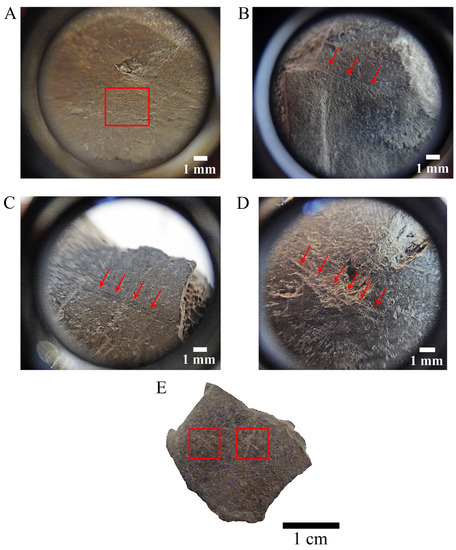
Figure 5.
Details of incisions and scratches groups in turtle remains from the Middle Palaeolithic site of Mealhada (Coimbra, central Portugal). Arrows and boxes mark the identified alterations. For each specimen alteration type, see Table 2. Testudinidae indet. left peripheral 7 detail (A). Freshwater terrapin indet. peripheral indet. Detail (B). Mauremys leprosa left hyoplastron detail (C,D) and right hyoplastron (E).
In the ensemble, two nuchal plate morphologies are identified (Figure 2A,B). Among the four preserved nuchal plates, three have a long cervical scute that medially overlaps the plate anterior half and lack of sulcus on their lateral regions (Figure 2A). In contrast, the remaining nuchal has a short cervical scute and shows the sulcus between vertebral 1 and left pleural 1 on its left lateral edge (Figure 2B).
Within the peripheral plates, three differentiated morphologies are observed (Figure 2C–E). Some of them have the pleuro-marginal sulcus close or next to the costal–peripheral suture (Figure 2C,D), while others present this sulcus on the plate lateral margin (Figure 2E). In addition, some bridge peripheral plates (3 to 7) show a sutured contact with the plastron (Figure 2C,D), the connection being ligamentous in others (Figure 2E). In contrast, a left peripheral plate 7 is relatively high and thin, and the pleuro-marginal sulcus overlaps the region corresponding to the costal–peripheral suture (Figure 2C). In ventral view, it shows the suture with the left hyoplastral process. The suprapygal plates present both the sulcus between the vertebral scute 5 and the marginals 12, as well as the medial sulcus present between this last pair of scutes (Figure 2F). Two morphotypes of pygal plates are observed (Figure 2G,H). One displays the sulcus between the vertebral scute 5 and the marginal scutes 12, as well as the medial sulcus between the latter (Figure 2G). The other, only displays the medial sulcus between marginals 12 (Figure 2H).
Two epiplastra morphologies are noted (Figure 3A,B). Some have a well-developed gular notch and the epi-hyoplastron suture is anteriorly directed at its lateral end (Figure 3A). Others have this suture straight (Figure 3B). One entoplastron (Figure 3C) is rhomboid shaped; the other (Figure 3D) is hexagonal. Some hyoplastra have a contact surface with a hinge in its posterior end (Figure 3E), but others have well-developed osseous bridges (Figure 3F). Some hypoplastra present well-developed bridges (Figure 3G), but others show a hinge at their anterior end (Figure 3H). The xiphiplastra present a pointed posterior end in some cases (Figure 3I), that region being rounded in others (Figure 3J).
4. Discussion
4.1. Systematic Discussion
The presence of Testudinidae in Mealhada is justified by several criteria observed in one of the identified peripheral plates (see Figure 2C). These are: the plate greater thickness in relation to the rest of the turtle shell remains from the site, the comparatively deeper sulcus, its considerably greater length than width, and the position of its pleuro-marginal sulcus on the costal–peripheral suture. These character states are shared, among other members of the lineage, between the Iberian taxa Chersine hermanni and Testudo graeca [30,31,32,33]. No diagnostic criteria for an identification at species level are present in the analysed plate, being recognized as Testudinidae indet. Therefore, the previously proposed attribution as Testudo sp. (sic) [19] and Agrionemys sp. (sic), even A. hermanni (sic) [25,26], is not justified and cannot be substantiated. The tortoise remain probably belongs to the taxon Chersine hermanni, as previously proposed [25,26], hence considering the Iberian record as there is no justified evidence of Testudo graeca until the first/second century AD [48]. Therefore, due to the lack of sufficient anatomical criteria to support the species identification, it is only considered justified to confirm the presence of Testudinidae indet.
The presence of Mauremys leprosa in the Mealhada site, previously proposed but not justified by Crespo [26], is confirmed by certain characters observed in the remains. These are: a cervical scute that medially overlaps the nuchal plate anterior half; peripheral plates with the pleuro-marginal sulcus situated in the plate’s upper half, without overlapping the costal–peripheral sutures; peripheral plates displaying an osseous contact with the plastron; the presence of the medial sulcus between the marginals 12 on the pygal plate; a rhomboid entoplastron; a well-developed gular notch in the epiplastra and an anteriorly directed epi-hyoplastron suture; well-developed osseous hyoplastral and hypoplastral buttresses; a suture joint between carapace and plastron; and a pointed posterior end in the xiphiplastra. An exclusive character combination for Emys orbicularis within the European record of turtles allows us its identification for the first time in the site: a relatively short cervical scute, being wider than higher; the presence of the sulcus between the first vertebral and first pleural scutes on the nuchal plate left edge; the pleuro-marginal sulcus on the peripheral plate’s anterior half; a ligamentous contact between the carapace and the plastron; a hexagonal entoplastron; a hyo-hypoplastra connection by hinge; and xiphiplastra with a rounded posterior end.
All these aspects allow us to recognize the identification of three different Iberian turtle taxa in the Mealhada site (Coimbra, central Portugal). Two forms correspond to freshwater terrapins, Mauremys leprosa and Emys orbicularis, and the third is attributable to a terrestrial tortoise (Testudinidae indet.). Regarding the Iberian turtle taxa record during the Upper Pleistocene, Mealhada is identified here as the oldest Iberian Peninsula archaeological site in which three turtle forms are recognized. Even though the presence of the species Chersine hermanni cannot be substantiated, the identified presence of tortoises raises the northern limit of the Testudinidae distribution for the Upper Pleistocene (ca. 120 ka BP) as previously noted [25] (p. 137). In this context, Chersine hermanni has been identified in central Portugal in the following archaeological sites (see Figure 1): Gruta da Aroeira (Torres Novas) (ca. 428–362 ka BP) [49]; Galeria Pesada (Almonda) (241 ± 30/22 ka BP) [50]; Gruta da Figueira Brava (Arrábida) (ca. 80–110 ka BP) [6]; Gruta da Oliveira (Torres Novas) (ca. 100–35 ka BP) [4,6]; Foz do Enxarrique (Vila Velha de Ródão) (44 ± 3 ka BP) [3]; Lapa do Picareiro (Alcanede) (45 ka BP) [51]; Gruta Nova da Columbeira (Bombarral) (35.9–101.5 ka BP) [25]; and Gruta da Furninha (Peniche) (31,265 ka BP) [52,53]. One more reference of the species can be found on the southern Iberian Atlantic coast in Gruta Ibn Amar (Lagoa, southern Portugal) (ca. 80 ka BP) [54,55].
Concerning the freshwater terrapins, Mealhada also offers the oldest and farthest northern archaeological reference for both Mauremys leprosa and Emys orbicularis on the Iberian Atlantic coast for the Upper Pleistocene. Emys orbicularis is also identified in Gruta Nova da Columbeira (Bombarral, central Portugal) (35.9–101.5 ka BP) [25] and in Gruta da Figueira Brava (Arrábida, central Portugal), although the recovered remain in this last site is considered as a Holocene intrusion [4]. The Mealhada archaeological record of Mauremys leprosa is the oldest for Portugal and the Iberian Atlantic coast, with no other reference of the species in that area until the Upper Palaeolithic, in two sites located in Tomar (Santarém, central Portugal): Gruta do Caldeirão I (ca. 40–26.5 ka BP) [4,26,56] and Gruta do Morgado Superior [51]. The scepticism regarding the identification of Mauremys leprosa remains in Barranco León 5 (Guadix-Baza basin, south-eastern Spain) expressed by Crespo [26] was already cleared by Bailón [27]. In this last study, which includes the remains figuration and systematic justification, the author proposed the identification of Mauremys cf. M. leprosa, waiting for more evidence to confirm certain characteristics whose differences could be justified by population variability [27] (p. 189).
4.2. Archaeozoological Discussion
The Middle Paleolithic site of Mealhada offers an exceptional turtle record, considering the presence of three Iberian turtle taxa. However, as recovered in an early dig, the contextualization of these remains is problematic. Thanks to the information gathered by Zbyszewski [19], together with the material notes and labels at MG, we recognize that the turtle remains studied here were yielded on the interventions made before 1880. Level 4, from which the material probably comes, is described as clayey grey sandstone of medium to thick grain with bones [19] (p. 9). However, there is no mention of the remains association with the lithic material. The bone and lithic industry described by Zbyszewski [19] belongs to interventions made after 1897, although some worked bone and flakes come from the mentioned Level 4.
At a taphonomic level, cutmarks located inside the turtle shell, as in this case, have been associated in other sites to a secondary processing (i.e., defleshing) for consumption [1,2,4,5,6,46,51]. These evidence locations (see 1–6 in Table 2) may correspond to actions related to skinning, eviscerating, and defleshing (Figure 4 and Figure 5). In contrast, one of these alterations groups is located in the ventral side of a hyoplastron (Table 2; Figure 5E). The group is formed by two parallel, short, and slight incisions, and a third short and slight incision of unknown origin, that perhaps may be associated to postdepositional processes. Burning damage location corresponds with that documented in experimental roasting [46,51]. These evidences could indicate that a particular specimen was roasted by contacting coals for consumption, as documented in other Middle Palaeolithic Iberian sites [1,2,4,5,6]. Fresh fractures located in two hyoplastra could be related to shell opening [38]. It also should be noted that all the material has a homogeneous dark grey colour scheme (Figure 2 and Figure 3), as described for Level 4. In contrast, a single plate has red ochre sediment residues (Figure 4C,D). This could probably indicate a different stratigraphic origin for this plate, or, perhaps, the presence of a pigment associated with an unknown concrete functionality that resulted in the groups of scratches observed on the plate.
Human consumption of tortoises is relatively well documented in the Middle Palaeolithic Iberian Peninsula [1,2,4,5,6]. In these sites, anthropic evidence (e.g., cutmarks, burning, or fractures) identification and characterization has been proved as relevant in supporting the consumption hypothesis as its specific location within the turtle shell, and its association to precise butchering and cooking actions [1,2,4,5,6,51]. Regarding Mealhada, the low percentage of potential anthropic evidence is similar to that documented in other sites [6,51]. Only cutmarks (or incisions), fractures, and burning marks have been recognised by the analysis of the remains studied here, but its location can be clearly associated with specific butchery and cooking actions.
Even though the taphonomic analysis performed here suggests the presence of anthropic alterations in turtle remains found in Mealhada, these evidences should be considered with caution. As recognised in other archaeological sites (e.g., Gruta Nova da Columbeira, see [57]), the remains here examined have the information constraints associated with antique excavation methodologies (e.g., destructive dig methods, uncertain stratigraphic association, relative site dating, lack of absolute dating, selective material collection). The absence of appendicular bones may perhaps be indicative of selective material collection, or the intervention of birds [42]. Consequently, the studied ensemble may be biased or may not be analogous, belonging to different chronological moments. The identified incisions could also have been the result of other taphonomic processes (e.g., trampling) [47]. Although trampling and anthropic origin hypotheses cannot be assessed here due to the lack, at the time of the study, of better analysis instruments (e.g., microscopes, ESEM), the location of some of the identified marks may reinforce the anthropic origin. Even so, it is considered that the human consumption hypothesis should be contemplated with the appropriate caution.
Among small prey, tortoises are relatively easy-to-catch animals that do not require a particular technology, compared to fast prey (such as leporids or birds [58,59]), and can be caught circumstantially [60]. In contrast, terrapins are more elusive. On the one hand, Mauremys leprosa escapes from a human observer at an average distance of 19 m. This distance may be larger if the observer is on the opposite shore, and smaller on shores without vegetation [61]. On the other hand, Emys orbicularis avoids shores to sunbathe [39], therefore, their capture requires relatively elaborate techniques. The Iberian Peninsula Middle Palaeolithic record offers a clear predominance of tortoise versus terrapin remains [1,2,4,5,6,51]. This prevalence may be indicative of a Neanderthal preference for tortoise capture and consumption due to its low energy investment. It may also reflect a relative abundance of tortoise versus a scarce terrapin presence, making the development of capture techniques for the latter unnecessary. In this sense, the possible presence of anthropic alterations in terrapin remains found in Mealhada constitutes a novelty in the Iberian Peninsula Middle Palaeolithic record. Possible Neanderthal interest in this type of resource may also be indicative of a greater presence of terrapins in the area.
4.3. Paleoenvironmental Discussion
Although turtles are less favourable paleoenvironmental and climatic indicators [27,62] compared to other reptiles, and especially to amphibians, its presence may imply certain climatic conditions. Currently, two forms of Testudinidae live in the Iberian Peninsula, Chersine hermanni (sensu [63]; i.e., the Hermann’s Tortoise), and Testudo graeca (i.e., the Greek Tortoise or Spur-thighed Tortoise) [64]. These forms inhabit a great diversity of habitats in areas of Mediterranean and sub-Mediterranean climate, preferably in areas of clarified Mediterranean forest: holm oak, cork oak, steppe, and brush, very often inhabiting the garrigue [36,37]. Two forms of freshwater terrapins currently inhabit the Iberian Peninsula. Mauremys leprosa inhabits large and permanent wet areas with fresh water or with low salinity, preferring stagnant or low-current rivers, with abundant perimeter and aquatic vegetation, and high insolation [65]. Emys orbicularis occupies all types of clean water bodies, both fresh and brackish, temporary, or not, although it prefers those with little or no current and abundant perimetral and aquatic vegetation cover [39,66].
On the one hand, tortoises (Testudinidae) and Mauremys leprosa are Mediterranean forms with a marked thermophilic character [27,62]. On the other hand, Emys orbicularis needs warm summers with an average temperature in July above 18 °C for the successful development of egg-laying [67]. Freshwater terrapins (Mauremys leprosa and Emys orbicularis) are also indicative of nearby large, permanent, or temporary stagnant, or low-current, wet areas with fresh water, or with low salinity, and abundant perimeter and aquatic vegetation [39,65,66]. The nearby wet areas were formerly inferred from the presence of freshwater molluscs remains in the site [19].
5. Conclusions
The presence of three Iberian turtle forms in the Middle Palaeolithic (ca. 120 ka BP) archaeological Mealhada site (Coimbra, central Portugal) is here recognized: two freshwater terrapins (Mauremys leprosa and Emys orbicularis) and an indeterminate terrestrial tortoise (Testudinidae indet.). The previous reference of Mauremys leprosa [26] in the site is now verified and justified; the hitherto presence of Emys orbicularis is here stated and justified, and, while the formerly suggested identification of Chersine hermanni [19,25,26] in the site cannot be supported, the presence of Testudinidae indet. is recognized. The Mealhada record is here established as the oldest Iberian Peninsula archaeological site in which three turtle forms are identified. The northern limit of the Testudinidae distribution on the Iberian Atlantic coast for the Upper Pleistocene (ca. 120 ka BP) has been considerably increased. Mealhada shows also the oldest and farthest northern archaeological reference for both terrapin species (Mauremys leprosa and Emys orbicularis) on the Iberian Atlantic coast for the Upper Pleistocene. Thus, an update of the data concerning the archaeological turtle record from Mealhada has been achieved, offering new justified taxonomic evidence regarding the Iberian turtle taxa distribution on the Portuguese Atlantic coast during the Upper Pleistocene.
Additionally, the presence of possible anthropic manipulation evidence on terrapin remains has been assessed for the first time here and related to human consumption. However, the absence of reliable stratigraphic information, and the lack, at the time of the study, of better analysis instruments (e.g., microscopes, ESEM), should lead to caution in reaching this conclusion.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.B.J., A.P.-G. and C.L.v.L.-V.; Methodology, I.B.J., A.P.-G. and C.L.v.L.-V.; Software, I.B.J.; Validation, I.B.J., A.P.-G. and C.L.v.L.-V.; Formal analysis, I.B.J.; Investigation, I.B.J.; Resources, I.B.J.; Data curation, I.B.J.; Writing—original draft preparation, I.B.J.; Writing—review and editing, I.B.J., A.P.-G. and C.L.v.L.-V.; Visualization, I.B.J., A.P.-G. and C.L.v.L.-V.; Supervision, A.P.-G. and C.L.v.L.-V.; Project administration, C.L.v.L.-V.; Funding acquisition, C.L.v.L.-V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, Gobierno de España, grant number: Plan Nacional I+D+i PID2019-111210GB-I00.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We kindly acknowledge the assistance of Miguel Ramalho and José António Anacleto of the Museu Geológico de Lisboa during this research. We thank Pablo Paniego Díaz for the Figure 1 elaboration.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
Ab: abdominal scute; A: anal scute; C: cervical scute; F: femoral scute; G: gular scute; Gu: gular notch; H: humeral scute; M: marginal scute; P: pectoral scute; Pl: pleural scute; V: vertebral scute.
References
- Blasco, R. Human consumption of tortoises at Level IV of Bolomor Cave (Valencia, Spain). J. Archaeol. Sci. 2008, 35, 2839–2848. [Google Scholar]
- Blasco, R.; Blain, H.-A.; Rosell, J.; Díez, J.C.; Huguet, R.; Rodríguez, J.; Arsuaga, J.L.; Bermúdez de Castro, J.M.; Carbonell, E. Earliest evidence for human consumption of tortoises in the European Early Pleistocene from Sima del Elefante, Sierra de Atapuerca, Spain. J. Hum. Evol. 2011, 61, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, J.; Sanchis, A. The Quaternary fossil record of the genus Testudo in the Iberian Peninsula. Archaeological implications and diachronic distribution in the western Mediterranean. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2009, 36, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar]
- Nabais, M. Middle Palaeolithic Tortoise Use at Gruta da Oliveira (Torres Novas, Portugal). In Actas das IV Jornadas de Jovens em Investigação Arqueológica—JIA 2011; Universidade do Algarve: Faro, Portugal, 2012; Volume 1, pp. 251–258. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchis, A.; Morales, J.; Pérez, L.; Hernández, C.; Galván, B. La tortuga mediterránea en yacimientos valencianos del Paleolítico medio: Distribución, origen de las acumulaciones y nuevos datos procedentes del Abric del Pastor (Alcoi, Alacant). In Preses petites i grups humans en el passat; Sanchis, A., Pascual, J., Eds.; Museu de Prehistòria de València: Valencia, Spain, 2015; pp. 97–120. [Google Scholar]
- Nabais, M.; Zilhão, J. The consumption of tortoise among Last Interglacial Iberian Neanderthals. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2019, 217, 225–246. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, R.; Cruz-Uribe, K. Large Mammals and Tortoise Bones from Eland’s Bay Cave and Nearby sites, western Cape Province, South Africa. In Papers in the Prehistory of the Western Cape, South Africa; BAR International Series, 332; Parkington, J., Hall, M., Eds.; BAR Publishing: Oxford, UK, 1987; pp. 132–163. [Google Scholar]
- Stiner, M.C. Small animal exploitation and its relation to hunting, scavenging, and gathering in the Italian Mousterian. Archaeol. Pap. Am. Anthropol. Assoc. 1993, 4, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speth, J.; Tchernov, E. Middle Paleolithic Tortoise Use at Kebara Cave (Israel). J. Archaeol. Sci. 2002, 29, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiner, M.C. The Faunas of the Hayonim Cave, Israel. A 20.000-Year Record of Paleolithic Diet, Demography and Society; Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnology, Harvard University: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, J. Taphonomic analysis of the Middle Stone Age faunal assemblage from Pinnacle Point Cave 13B, Western Cape, South Africa. J. Hum. Evol. 2010, 59, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.; Henshilwood, C. Tortoise taphonomy and tortoise butchery patterns at Blombos Cave, South Africa. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2014, 41, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, R.; Rosell, J.; Smith, K.; Maul, L.; Sañudo, P.; Barkai, R.; Gopher, A. Tortoises as a dietary supplement: A view from the Middle Pleistocene site of Qesem Cave, Israel. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 133, 165–182. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, C. Discours du Secrétaire-général. In Congrès International d’Anthropologie et d’Archéologie Préhistorique, Rapport sur la Session de Lisbonne; Cartailhac, E., Ed.; Eugène Boban: Paris, France, 1880; pp. 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Fontes, J. Station paléolithique de Mealhada. Comun. Serv. Geól. Port. 1915, 11, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zbyszewski, G. Contribution à l’étude du littoral quaternaire au Portugal. Publ. Museu Lab. Mineral. Geol. Faculdade Ciên. Pôrto 1940, 15, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Zbyszewski, G. La classification du Paléotithique ancien et la chronologie da Quaternaire de Portugal en 1942. Bol. Soc. Geol. Port. 1943, 2, 3–111. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha-Ribeiro, J.P. A estação paleolítica da Mealhada nos 120 anos de estudo do Acheulense em Portugal. Arqu. Port. 1995, IV, 35–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zbyszewski, G. Nova contribuição para o conhecimento da jazida quaternária da Mealhada. Mem. Not. Publ. Museu Lab. Mineral. Geol. Univ. Coimbra 1977, 84, 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Antunes, M. Acerca de um osso do Pleistocénico de Mealhada: Presença de um “tigre dentes de sabre”, Homotherium latidens (Owen, 1846). Ciências da Terra (UNL) 1986, 8, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Antunes, M.; Cardoso, J.L.; Faure, M. Présence de Hippopotamus incognitus au Portugal et remarques sur les sites qûaternaires de Mealhada. Comun. Serv. Geól. Port. 1988, 74, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Antunes, M.; Cardoso, J.L. Quaternary elephants in Portugal: New data. Ciências da Terra (UNL) 1992, 11, 17–37. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, C. A estação arqueológica de Mealhada e sua cronologia. Trab. Soc. Port. Antrop. Etnol. 1944, X, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Lapparent de Broin, F.; Antunes, M. Pleistocene chelonians from Gruta da Figueira Brava (Arrábida, Portugal). In Last Neanderthals in Portugal. Odontologic and Other Evidence; Antunes, M., Ed.; Academia das Ciências de Lisboa: Lisboa, Portugal, 2000; Volume Tomo XXXVIII, pp. 105–116. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez Fuentes, E.; Cardoso, J.L.; Crespo, E. Presencia De Agrionemys (=Testudo) Hermanni (Gmelin, 1789) En El Paleolítico Medio De La Gruta Nova Da Columbeira (Bombarral, Provincia De Estremadura, Portugal). Stvd. Geol. Salmant. 1998, 34, 123–139. [Google Scholar]
- Crespo, E. Paleoherpetofauna portuguesa. Rev. Esp. Herpetol. 2002, Volumen Especial, 17–35. [Google Scholar]
- Bailón, S. Quelonios fósiles del yacimiento de Barranco León (Pleistoceno Inferior, Orce, Granada, España). In Ocupaciones humanas en el Pleistoceno Inferior y Medio de la Cuenca de Guadix-Baza; Toro, I., Martínez-Navarro, B., Agustí, J., Eds.; Junta de Andalucía. Consejería de Cultura: Sevilla, Spain, 2010; pp. 185–195. [Google Scholar]
- Hervet, S. Tortues du Quaternaire de France: Critères de détermination, répartition chronologique et géographique. Mésogée 2000, 58, 3–47. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-Fuentes, E. Los quelonios del sitio de ocupación achelense de Aridos-1 (Arganda, Madrid). In Ocupaciones Achelenses en el Valle del Jarama. Geología, Paleontología, Paleoecología y Prehistoria; Santoja, M., López-Martínez, L., Pérez-González, A., Eds.; Publicaciones de la Excelentísima Diputación Provincial de Madrid: Madrid, Spain, 1980; pp. 139–143. [Google Scholar]
- de Lapparent de Broin, F.; Bour, R.; Parham, J.F.; Perälä, J. Eurotestudo, a new genus for the species Testudo hermanni Gmelin, 1789 (Chelonii, Testudinidae). C. R. Palevol 2006, 5, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lapparent de Broin, F.; Bour, R.; Perälä, J. Morphological definition of Eurotestudo (Testudinidae, Chelonii): First part. Ann. Paléontol. 2006, 92, 255–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lapparent de Broin, F.; Bour, R.; Perälä, J. Morphological definition of Eurotestudo (Testudinidae, Chelonii): Second part. Ann. Paléontol. 2006, 92, 325–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-García, A.; Murelaga, X.; Mancheño, M.A.; Aberasturi Rodríguez, A.; Romero, G. The tortoises from the Lower Pleistocene paleontological site of Quibas (Región de Murcia, Spain). C. R. Palevol 2015, 14, 598–603. [Google Scholar]
- Clason, A.T. Some remarks on the use and presentation of archaezoological data. Helinium 1972, 12, 139–153. [Google Scholar]
- Grayson, D.K. Quantitative Zooarchaeology: Topics in the Analysis of Archaeological Faunas; Academic press: Orlando, FL, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Bertolero, A. Tortuga mediterránea—Testudo hermanni Gmelin, 1789. In Enciclopedia Virtual de los Vertebrados Españoles; Salvador, A., Marco, A., Eds.; Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales: Madrid, Spain, 2015; Available online: http://www.vertebradosibericos.org/reptiles/tesher.html (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Díaz-Paniagua, C.; Andreu, A.C. Tortuga mora—Testudo graeca Linnaeus, 1758. In Enciclopedia Virtual de los Vertebrados Españoles; Salvador, A., Marco, A., Eds.; Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales: Madrid, Spain, 2015; Available online: http://www.vertebradosibericos.org/reptiles/tesgra.html (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Díaz-Paniagua, C.; Andreu, A.C.; Keller, C. Galápago leproso—Mauremys leprosa (Schweigger, 1812). In Enciclopedia Virtual de los Vertebrados Españoles; Salvador, A., Marco, A., Eds.; Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales: Madrid, Spain, 2015; Available online: http://www.vertebradosibericos.org/reptiles/maulep.html (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Ayres, C. Galápago europeo—Emys orbicularis (Linnaeus, 1758). In Enciclopedia Virtual de los Vertebrados Españoles; Salvador, A., Marco, A., Eds.; Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales: Madrid, Spain, 2015; Available online: http://www.vertebradosibericos.org/reptiles/emyorb.html (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Liesau von Lettow-Vorbeck, C. El Soto de Medinilla: Faunas de Mamíferos de la Edad del Hierro en el Valle del Duero (Valladolid, España). Archaeofauna 1998, 7, 11–210. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez Ripoll, M. Marcas de Carnicería, Fracturas Intencionadas y Mordeduras de Carnívoros en Huesos Prehistóricos del Mediterráneo Español; Instituto de Cultura “Juan-Gil Albert”: Alicante, Spain, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Sampson, C. Taphonomy of Tortoises Deposited by Birds and Bushmen. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2000, 27, 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Lyman, R.L. Vertebrate Taphonomy; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Albizuri, S.; Colomer, S.; Buisan, C. Experimentación sobre la exposición del tejido óseo a focos de calor. Estud. Antig. 1993, 6, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, R. A morphological investigation of burnt animal bone and an evaluation of its utility in archaeology. J. Archaeol. Sci. 1993, 20, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, A.; Laroulandie, V.; Cochard, D.; Binder, D. Les brulures, des traces ambiguës aux origines multiples. Application aux vestiges des tortues de l’Abri du Mourre de Seve (Sorges, Vaucluse). In Taphonomie des Petits Vertébrés: Référentiels et Transferts aux Fossiles; British Archaeological Reports, International Series; Laroulandie, V., Mallye, J.-B., Denys, C., Eds.; BAR Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2011; Volume 2269, pp. 181–194. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Jalvo, Y.; Andrews, P. Atlas of Taphonomic Identifications. 1001+ Images of Fossil and Recent Mammal Bone Modification; Springer: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Boneta Jiménez, I.; Pérez-García, A.; Liesau von Lettow-Vorbeck, C. The oldest evidence of Testudo graeca (Testudinidae) in the Iberian Peninsula. Anat. Rec. 2022, Special Issue, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daura, J.; Sanz, M.; Arsuaga, J.-L.; Hoffman, D.L.; Quam, R.M.; Ortega, M.C.; Santos, E.; Gómez, S.; Rubio, A.; Villaescusa, L.; et al. New Middle Pleistocene hominin cranium from Gruta da Aroeira (Portugal). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 3397–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, A.; Brugal, J.; Chabai, V.; Monigal, K.; Goldberg, P.; Hockett, B.; Peman, E.; Elorza, M.; Mallol, C. Le gisement pléistocène moyen de Galeria Pesada (Estrémadure, Portugal): Premiers résultats. Paleo 2002, 14, 77–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boneta Jiménez, I. Los quelonios en el registro arqueológico de la península ibérica: Aproximación a su estudio a través del conjunto del yacimiento calcolítico de Camino de las Yeseras. Doctoral Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Madrid, Spain, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado, J.F.N. La grotte de Furninha a Peniche. In Congrès International d’Anthropologie et d’Archéologie Préhistoriques. Compte-Rendu de la neuvième Session à Lisbonne, 1880; Typographie de l’Académie Royale des Sciences: Lisboa, Portugal, 1884; pp. 207–278. [Google Scholar]
- Harlé, E. Les mammifères et oiseaux quaternaires connus jusqu’ici en Portugal. Comun. Serv. Geól. Port 1910, 8, 22–85. [Google Scholar]
- Bicho, N.F. The Middle Paleolithic Occupation of Southern Portugal. In Settlement Dynamics of the Middle Paleolithic and Middle Stone Age II; Conard, N., Ed.; Kerns Verlog: Tübingen, Germany, 2004; pp. 513–531. [Google Scholar]
- Bicho, N.F. As comunidades humanas de caçadores-recolectores do Algarve Ocidental. Perspectiva ecológica. In Evolução Geohistórica do Litoral Portugês e Fenómenos Correlativos. Geologia, Historia, Arqueologia e Climatologia. Actas; Tavares, A.A., Tavares, M.J.F., Cardoso, J.L., Eds.; Universidade Aberta: Lisboa, Portugal, 2004; pp. 359–396. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, S.J.M. The mammals and birds from the Gruta do Caldeirão, Portugal. Rev. Port. Arqueol. 2002, 5, 29–98. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Laso, M.C.; Brugal, J.-P.; Raposo, L. Gruta Nova da Columbeira (Bombarral, Portugal): Un modelo de ocupación en cueva durante el Paleolítico Medio. Resultados del estudio del registro de macromamíferos. Trab. Prehist. 2015, 72, 304–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiner, M.C. Thirty years on the “Broad Spectrum Revolution” and paleolithic demography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 6993–6996. [Google Scholar]
- Stiner, M.C.; Kuhn, S.L. Changes in the ‘connectedness’ and resilience of Paleolithic societies in the Mediterranean ecosystems. Hum. Ecol. 2006, 34, 693–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, P. Etnografía y Alimentación Entre los Tobas Ñachilamoleek y Wichi-Lhukutas del Chaco Central (Argentina); Pastor Arenas Editor: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- López, P.; Marcos, I.; Martín, J. Effects of habitat-related visibility on escape decisions of the Spanish terrapin Mauremys leprosa. Amphib.-Reptil. 2005, 26, 557–561. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez Fuentes, E.; Gil, S.; Pollos, S. Quelonios del Pleistoceno Medio de las Grajas (Archidona: Málaga). Stvd. Geol. Salmant. 1995, 31, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-García, A.; Martín-Jiménez, M.; Vlachos, E.; Codrea, V. The most complete extinct species of Testudo (Testudines, Testudinidae) defined by several well-preserved skeletons from the late Miocene of Romania. J. Syst. Palaeontol. 2022, 19–18, 1237–1270. [Google Scholar]
- Fauna de Vertebrados: Anfibios y Reptiles. Available online: https://www.miteco.gob.es/es/biodiversidad/temas/inventarios-nacionales/inventario-especies-terrestres/ieet_anfib_reptl.aspx (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Keller, C. Ecología de las poblaciones de Mauremys Leprosa y Emys orbicularis en el Parque Nacional de Doñana. Doctoral Thesis, Universidad de Sevilla, Sevilla, Spain, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, C.; Andreu, A.C. Emys orbicularis Galápago europeo. In Atlas y Libro Rojo de los Anfibios y Reptiles de España, 2nd ed.; Pleguezuelos, J.M., Márquez, R., Lizana, M., Eds.; Dirección General de Conservación de la Naturaleza-Asociación Herpetológica Española: Madrid, Spain, 2002; pp. 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Stuart, A.J. Pleistocene occurrences of the European pond tortoise (Emys orbicularis L.) in Britain. Boreas 1979, 8, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).