The Role of Cymodocea nodosa and Caulerpa prolifera Meadows as Nitrogen Sinks in Temperate Coastal Lagoons
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
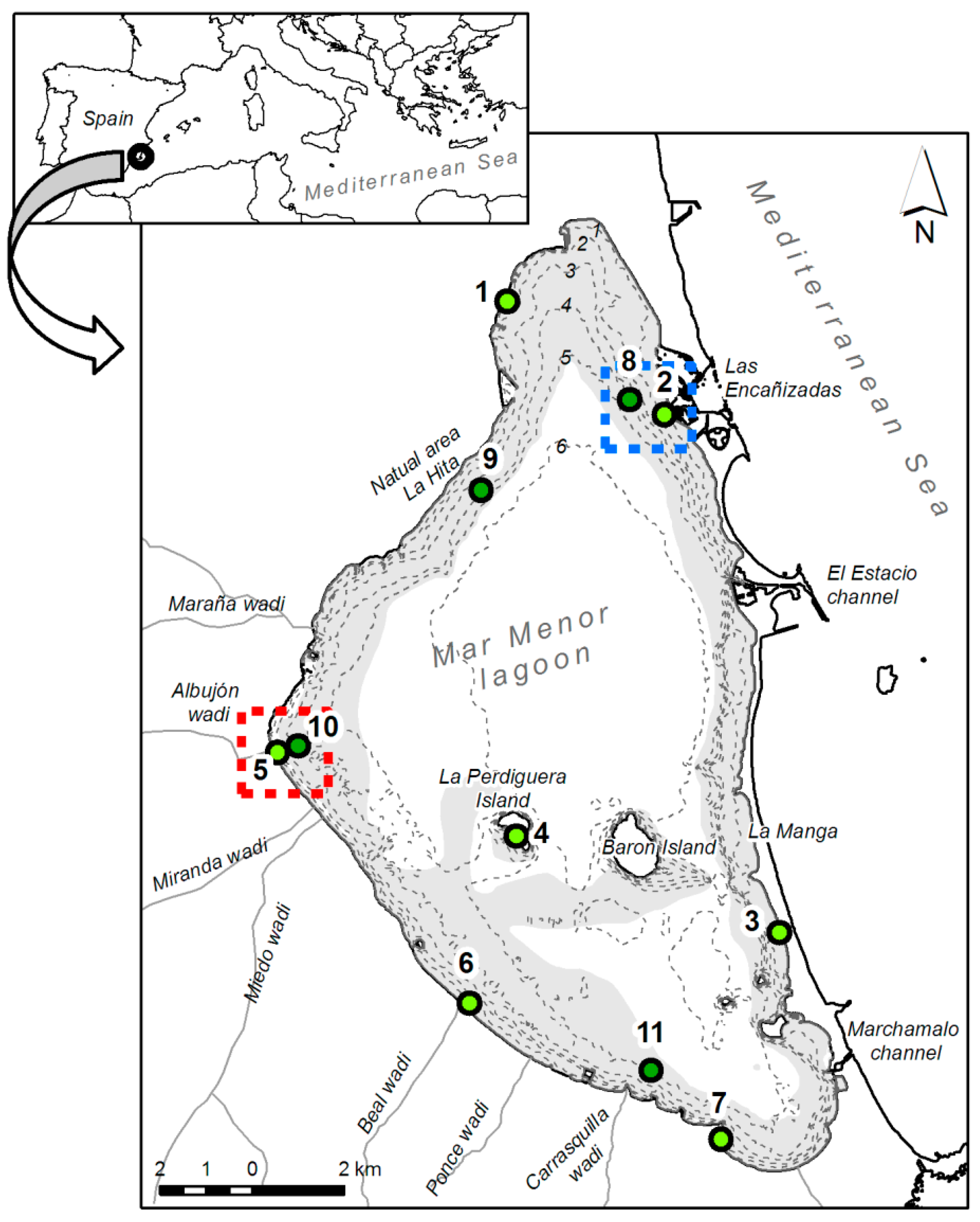
2.1. Study Area
2.2. DIN Uptake Kinetics
2.3. Biomass, N Content in Macrophyte Tissues, and N Stock and N Demand Estimations of Meadows
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
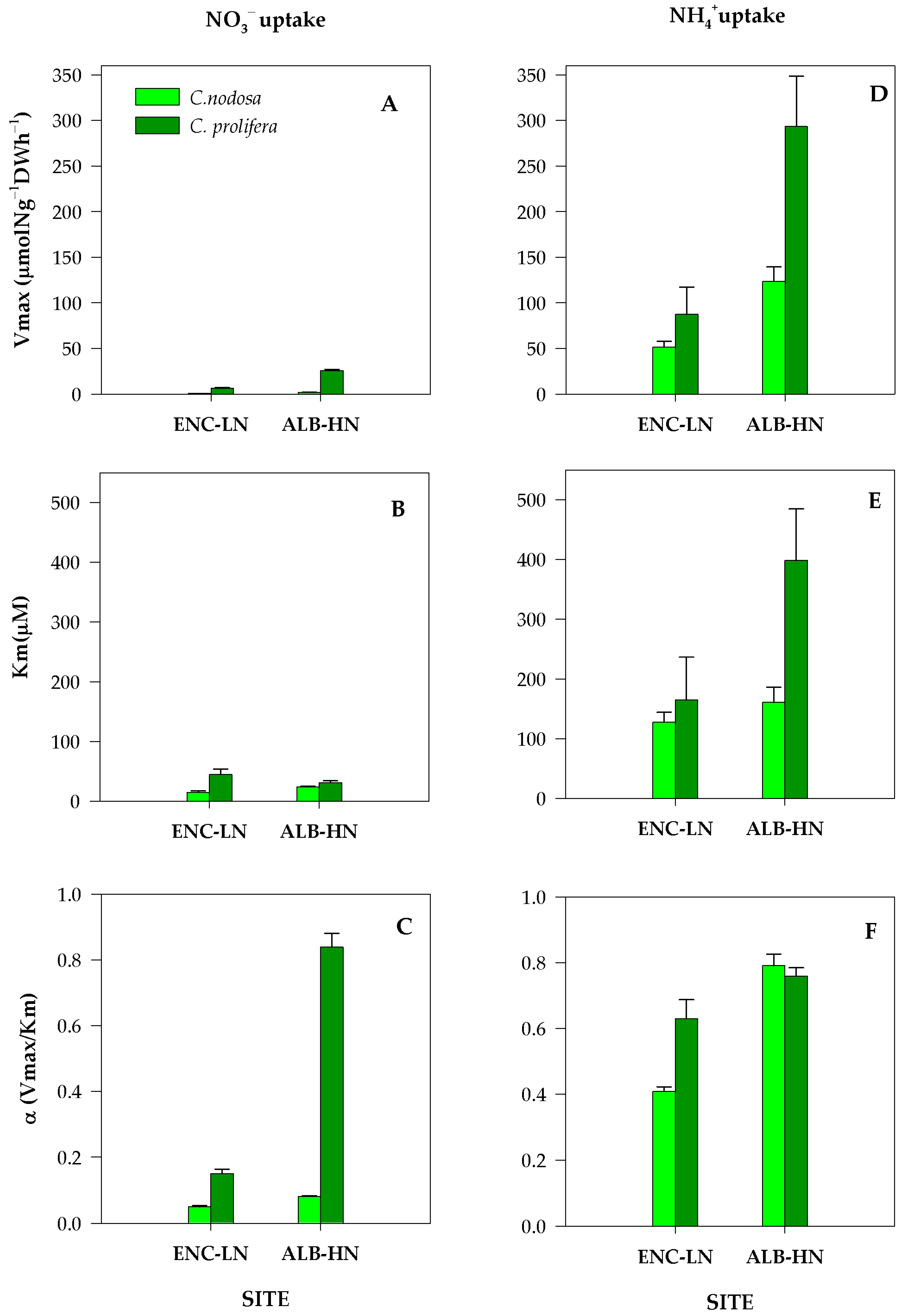
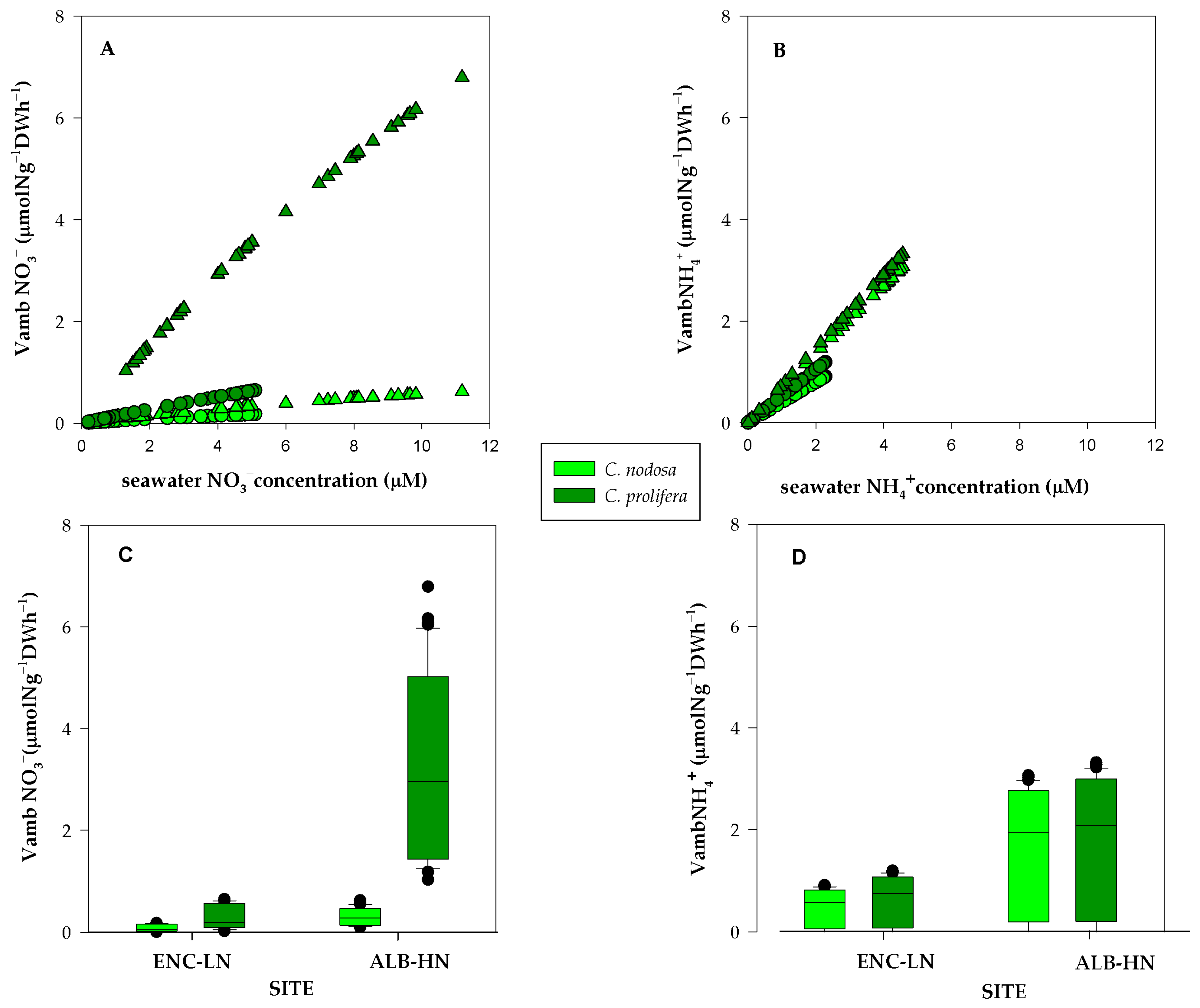
3.1. Experimental Uptake Kinetics
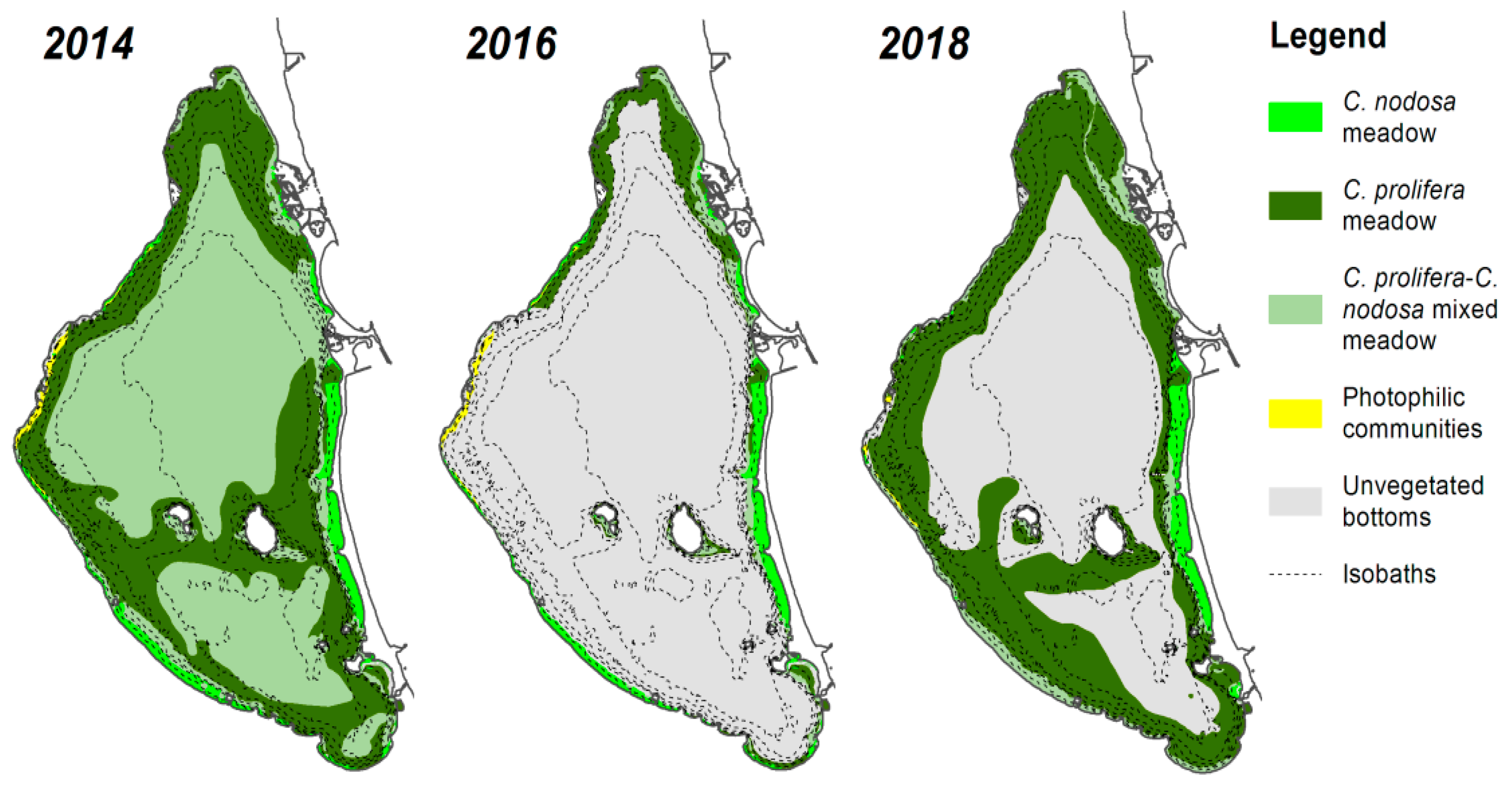
3.2. Biomass, N Content, C/N Ratios, and N Stocks and Annual N Demands of Meadows
4. Discussion
4.1. DIN Acquistion by Aboveground Tissues of C. nodosa and C. prolifera from the Mar Menor
4.2. Nitrogen Pools in C. nodosa and C. prolifera Meadows of the Mar Menor
4.3. Control of Nitrogen Inputs by Dominant Perennial Macrophytes of the Mar Menor
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barnes, R.S.K. Coastal Lagoons; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1980; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; De Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.O.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, A.; Brito, A.C.; Icely, J.D.; Derolez, V.; Clara, I.; Angus, S.; Schernewski, G.; Inácio, M.; Lillebø, A.I.; Sousa, A.I.; et al. Assessing, quantifying and valuing the ecosystem services of coastal lagoons. J. Nat. Conserv. 2018, 44, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjerfve, B. Coastal lagoons. In Elsevier Oceanography Series; Elsevier, Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 60, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Nixon, S.; Buckley, B.; Granger, S.; Bintz, J. Responses of very shallow marine ecosystems to nutrient enrichment. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2001, 7, 1457–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryther, J.H.; Dunstan, W.M. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and eutrophication in the coastal marine environment. Science 1971, 171, 1008–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howarth, R.W.; Marino, R. Nitrogen as the limiting nutrient for eutrophication in coastal marine ecosystems: Evolving views over three decades. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viaroli, P.; Naldi, M.; Bondavalli, C.; Bencivelli, S. Growth of the seaweed Ulva rigida C. Agardh in relation to biomass densities, internal nutrient pools and external nutrient supply in the Sacca di Goro lagoon (Northern Italy). Hydrobiologia 1996, 329, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Human, L.R.; Snow, G.C.; Adams, J.B.; Bate, G.C.; Yang, S.C. The role of submerged macrophytes and macroalgae in nutrient cycling: A budget approach. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 154, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapel, J.; Hemminga, M.A.; Bogert, C.G.; Maas, Y.E. Nitrogen (15N) retention in small Thalassia hemprichii seagrass plots in an offshore meadow in South Sulawesi, Indonesia. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGlathery, K.J.; Sundbäck, K.; Anderson, I.C. Eutrophication in shallow coastal bays and lagoons: The role of plants in the coastal filter. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 348, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, B.J.; Gahnström, A.M.; Walker, D.I. The role of benthic vegetation as a sink for elevated inputs of ammonium and nitrate in a mesotrophic estuary. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 219, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saderne, V.; Cusack, M.; Serrano, O.; Almahasheer, H.; Krishnakumar, P.K.; Rabaoui, L.; Duarte, C.M. Role of vegetated coastal ecosystems as nitrogen and phosphorous filters and sinks in the coasts of Saudi Arabia. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 034058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGlathery, K.J.; Sundbäck, K.; Anderson, I.C. The importance of primary producers for benthic nitrogen and phosphorus cycling. In Estuarine Nutrient Cycling: The Influence of Primary Producers; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherland, 2004; pp. 231–261. [Google Scholar]
- Viana, I.G.; Saavedra-Hortúa, D.A.; Mtolera, M.; Teichberg, M. Different strategies of nitrogen acquisition in two tropical seagrasses under nitrogen enrichment. New Phytol. 2019, 223, 1217–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, R.M. The role of nitrogen status in regulating transient ammonium uptake and nitrogen storage by macroalgae. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1985, 92, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touchette, B.W.; Burkholder, J.M. Review of nitrogen and phosphorus metabolism in seagrasses. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2000, 250, 133–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, F.I.; Cornelisen, C.D.; Zande, J.M. Effects of water velocity and canopy morphology on ammonium uptake by seagrass communities. Ecology 2000, 81, 2704–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, A.J. Nitrogen uptake by Gracilaria gracilis (Rhodophyta): Adaptations to a temporally variable nitrogen environment. Bot. Mar. 2002, 45, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurd, C.L.; Harrison, P.J.; Bischof, K.; Lobban, C.S. Nutrients. In Seaweed Ecology and Physiology, 2nd ed; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 238–290. [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer, G.P.; Mazzella, L. Nitrogen acquisition, storage, and use by the co-occurring Mediterranean seagrasses Cymodocea nodosa and Zostera noltii. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 183, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malta, E.J.; Ferreira, D.G.; Vergara, J.J.; Pérez-Lloréns, J.L. Nitrogen load and irradiance affect morphology, photosynthesis and growth of Caulerpa prolifera (Bryopsidales: Chlorophyta). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 298, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessner, F.; Hammer, L. Die Primärproduktion in mediterranen Caulerpa-Cymodocea-Wiesen Aus der Station Zoologique Villefranche sur mer. Bot. Mar. 1960, 2, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrados, J.; Ros, J.D. Production dynamics in a macrophyte-dominated ecosystem: The Mar Menor coastal lagoon (SE Spain). Oecologia Aquat. 1991, 10, 255–270. [Google Scholar]
- Agostini, S.; Pergent, G.; Marchand, B. Growth and primary production of Cymodocea nodosa in a coastal lagoon. Aquat. Bot. 2003, 76, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, E.P.; Peralta, G.; Benavente, J.; Freitas, R.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Quintino, V.; Pérez-Lloréns, J.L. Caulerpa prolifera stable isotope ratios reveal anthropogenic nutrients within a tidal lagoon. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 390, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, A.H.; Paulo, D.S.; Sousa, I.; Serrão, E. The rediscovery of Caulerpa prolifera in Ria Formosa, Portugal, 60 years after the previous record. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2013, 54, 359–364. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, M.; Romero, J. Growth dynamics, production, and nutrient status of the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa in a Mediterranean semi-estuarine environment. Mar. Ecol. 1994, 15, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemminga, M.A.; Duarte, C.M. Seagrass Ecology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Marbà, N.; Hemminga, M.A.; Mateo, M.A.; Duarte, C.M.; Mass, Y.E.; Terrados, J.; Gacia, E. Carbon and nitrogen translocation between seagrass ramets. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 226, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara, J.J.; García-Sánchez, M.P.; Olivé, I.; García-Marín, P.; Brun, F.G.; Pérez-Lloréns, J.L.; Hernández, I. Seasonal functioning and dynamics of Caulerpa prolifera meadows in shallow areas: An integrated approach in Cadiz Bay Natural Park. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 112, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennaro, P.; Piazzi, L.; Persia, E.; Porrello, S. Nutrient exploitation and competition strategies of the invasive seaweed Caulerpa cylindracea. Eur. J. Phycol. 2015, 50, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Engeland, T.; Bouma, T.J.; Morris, E.P.; Brun, F.G.; Peralta, G.; Lara, M.; Middelburg, J.J. Potential uptake of dissolved organic matter by seagrasses and macroalgae. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 427, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, A.; Santos, R. Competition for nitrogen between the seaweed Caulerpa prolifera and the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2020, 648, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, A.; Santos, R. Nutrition of the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa: Pulses of ammonium but not of phosphate are crucial to sustain the species growth. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 158, 104954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, A.; Santos, R. High nitrogen and phosphorous acquisition by belowground parts of Caulerpa prolifera (Chlorophyta) contribute to the species’ rapid spread in Ria Formosa lagoon, southern Portugal. J. Phycol. 2020, 56, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Fernández, J.; Esteve-Selma, M.A.; Martínez-Paz, J.M.; Carreño, M.F.; Martínez-López, J.; Robledano, F.; Farinós, P. Trade-Offs between biodiversity conservation and nutrients removal in wetlands of arid intensive agricultural Basins: The mar menor case, Spain. In Developments in Environmental Modelling; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 26, pp. 275–310. [Google Scholar]
- Lloret, J.; Marín, A.; Marín-Guirao, L. Is coastal lagoon eutrophication likely to be aggravated by global climate change? Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 78, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Ruzafa, A.; Campillo, S.; Fernández-Palacios, J.M.; Garcia-Lacunza, A.; Garcia-Oliva, M.; Ibanez, H.; Marcos, C. Long-term dynamic in nutrients, chlorophyll a, and water quality parameters in a coastal lagoon during a process of eutrophication for decades, a sudden break and a relatively rapid recovery. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.M.; Belando-Torrentes, M.D.; Bernardeau-Esteller, J.; Mercado-Carmona, J.M. Mar Menor lagoon: An iconic case of ecosystem collapse. Harmful Algae News 2022, 70. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, J.M.; Albentsosa, M.; Aldeguer, B.; Alvarez-Rogel, J.; Yebra, L. Informe de Evolución y Estado Actual del Mar Menor en Relación al Proceso de Eutrofización y Sus Causas; Technical Report Instituto Español de Oceanografía (IEO); Spanish Institute of Oceanography: Madrid, Spain, 2020; p. 165. Available online: https://www.miteco.gob.es/es/prensa/informe-ieo-mar-menor.aspx (accessed on 11 December 2022).
- Garcia-Pintado, J.; Martínez-Mena, M.; Barberá, G.G.; Albaladejo, J.; Castillo, V.M. Anthropogenic nutrient sources and loads from a Mediterranean catchment into a coastal lagoon: Mar Menor, Spain. Sci. Total. Environ. 2007, 373, 220–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Rogel, J.; Jiménez-Cárceles, F.J.; Nicolás, C.E. Phosphorus and nitrogen content in the water of a coastal wetland in the Mar Menor lagoon (SE Spain): Relationships with effluents from urban and agricultural areas. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2006, 173, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TRAGSA. Cuantificación, control de la calidad y seguimiento piezométrico de la descarga de agua subterránea del acuífero cuaternario del campo de Cartagena al Mar Menor. In Technical Report Ministerio Para la Transición Ecológica y el Reto Demográfico; Gobierno de España: Madrid, Spain, 2020; p. 97. [Google Scholar]
- Forja, J.M. Estudio Biogeoquímico de Los Fondos del Mar Menor—Estudio de Flujos Bentónicos; Technical Report; Univesidad de Cadiz-Gobierno Regional de Murcia: Cádiz, Spain, 2019; p. 128. [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval-Gil, J.M.; Camacho-Ibar, V.F.; del Carmen Ávila-López, M.; Hernández-López, J.; Zertuche-González, J.A.; Cabello-Pasini, A. Dissolved inorganic nitrogen uptake kinetics and δ15N of Zostera marina L.(eelgrass) in a coastal lagoon with oyster aquaculture and upwelling influence. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2015, 472, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belando, M.D.; Bernardeau-Esteller, J.; Paradinas, I.; Ramos-Segura, A.; García-Muñoz, R.; García-Moreno, P.; Ruiz, J.M. Long-term coexistence between the macroalga Caulerpa prolifera and the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa in a Mediterranean lagoon. Aquat. Bot. 2021, 173, 103415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.; Lee, K.S.; Pérez, M.; Mateo, M.A.; Alcoverro, T. Nutrient dynamics in seagrass ecosystems. In Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 227–254. [Google Scholar]
- Cornelisen, C.D.; Thomas, F.I. Ammonium and nitrate uptake by leaves of the seagrass Thalassia testudinum: Impact of hydrodynamic regime and epiphyte cover on uptake rates. J. Mar. Syst. 2004, 49, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teichberg, M.; Fox, S.E.; Aguila, C.; Olsen, Y.S.; Valiela, I. Macroalgal responses to experimental nutrient enrichment in shallow coastal waters: Growth, internal nutrient pools, and isotopic signatures. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 368, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallentinus, I. Comparisons of nutrient uptake rates for Baltic macroalgae with different thallus morphologies. Mar. Biol. 1984, 80, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naldi, M.; Viaroli, P. Nitrate uptake and storage in the seaweed Ulva rigida C. Agardh in relation to nitrate availability and thallus nitrate content in a eutrophic coastal lagoon (Sacca di Goro, Po River Delta, Italy). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2002, 269, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lei, A.; Zhou, K.; Hu, Z.; Hao, W.; Yang, J. Growth and nitrogen uptake characteristics reveal outbreak mechanism of the opportunistic macroalga Gracilaria tenuistipitata. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, N.; Iizumi, H.; Mukai, H. Nitrogen dynamics of the surfgrass Phyllospadix iwatensis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 293, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquer-Sunyer, R.; Duarte, C.M.; Jordà, G.; Ruiz-Halpern, S. Temperature dependence of oxygen dynamics and community metabolism in a shallow Mediterranean macroalgal meadow (Caulerpa prolifera). Estuaries Coasts 2012, 35, 1182–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, M.; Nizzoli, D.; Castaldelli, G.; Viaroli, P. Community metabolism and buffering capacity of nitrogen in a Ruppia cirrhosa meadow. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 360, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viaroli, P.; Azzoni, R.; Bartoli, M.; Giordani, G.; Tajé, L. Evolution of the trophic conditions and dystrophic outbreaks in the Sacca di Goro lagoon (Northern Adriatic Sea). In Mediterranean Ecosystems; Springer: Milan, Italy, 2001; pp. 467–475. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, S.L.; Banta, G.T.; Pedersen, M.F. Decomposition of marine primary producers: Consequences for nutrient recycling and retention in coastal ecosystems. In Estuarine Nutrient Cycling: The Influence of Primary Producers; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 187–216. [Google Scholar]
- Mercado, J.M.; Cortés, D.; Gómez-Jakobsen, F.; García-Gómez, C.; Ouaissa, S.; Yebra, L.; Ruíz, J.M. Role of small-sized phytoplankton in triggering an ecosystem disruptive algal bloom in a Mediterranean hypersaline coastal lagoon. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 164, 111989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| 2014 | Biomass (t) | N Stock (t) | N Demand (t y−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | max | min | max | min | |
| C. nodosa | |||||
| Aboveground tissues | 6512.9 | 257.9 | 197.3 | 515.8 | 394.7 |
| Belowground tissues | 12,588.5 | 333.3 | 124.8 | 80.0 | 30.0 |
| Total | 19,101.4 | 591.2 | 322.2 | 595.8 | 424.6 |
| C. prolifera | 13,328.4 | 597.1 | 399.9 | 2388.4 | 1599.4 |
| TOTAL MACROPHYTES | 25,014.2 | 1188.4 | 722.0 | 2984.3 | 2024.1 |
| 2016 | Biomass (t) | N Stock (t) | N Demand (t y−1) | ||
| Species | max | min | max | min | |
| C. nodosa | |||||
| Aboveground tissues | 1335.3 | 52.9 | 40.5 | 105.8 | 80.9 |
| Belowground tissues | 3425.2 | 90.6 | 34.0 | 21.7 | 8.2 |
| Total | 4760.5 | 143.5 | 74.4 | 127.5 | 89.1 |
| C. prolifera | 1428.9 | 64.0 | 42.9 | 256.1 | 171.5 |
| TOTAL MACROPHYTES | 5469.9 | 207.5 | 117.3 | 383.6 | 260.5 |
| 2018 | Biomass (t) | N Stock (t) | N Demand (t y−1) | ||
| Species | max | min | max | min | |
| C. nodosa | |||||
| Aboveground tissues | 1335.3 | 52.9 | 40.5 | 105.8 | 80.9 |
| Belowground tissues | 3425.2 | 90.6 | 34.0 | 21.7 | 8.2 |
| Total | 4760.5 | 143.5 | 74.4 | 127.5 | 89.1 |
| C. prolifera | 6236.2 | 279.4 | 187.1 | 1117.5 | 748.3 |
| TOTAL MACROPHYTES | 10,996.7 | 422.8 | 261.5 | 1245.0 | 837.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernardeau-Esteller, J.; Sandoval-Gil, J.M.; Belando, M.D.; Ramos-Segura, A.; García-Muñoz, R.; Marín-Guirao, L.; Ruiz, J.M. The Role of Cymodocea nodosa and Caulerpa prolifera Meadows as Nitrogen Sinks in Temperate Coastal Lagoons. Diversity 2023, 15, 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020172
Bernardeau-Esteller J, Sandoval-Gil JM, Belando MD, Ramos-Segura A, García-Muñoz R, Marín-Guirao L, Ruiz JM. The Role of Cymodocea nodosa and Caulerpa prolifera Meadows as Nitrogen Sinks in Temperate Coastal Lagoons. Diversity. 2023; 15(2):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020172
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernardeau-Esteller, Jaime, José Miguel Sandoval-Gil, María Dolores Belando, Aranzazu Ramos-Segura, Rocío García-Muñoz, Lazaro Marín-Guirao, and Juan Manuel Ruiz. 2023. "The Role of Cymodocea nodosa and Caulerpa prolifera Meadows as Nitrogen Sinks in Temperate Coastal Lagoons" Diversity 15, no. 2: 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020172
APA StyleBernardeau-Esteller, J., Sandoval-Gil, J. M., Belando, M. D., Ramos-Segura, A., García-Muñoz, R., Marín-Guirao, L., & Ruiz, J. M. (2023). The Role of Cymodocea nodosa and Caulerpa prolifera Meadows as Nitrogen Sinks in Temperate Coastal Lagoons. Diversity, 15(2), 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020172









