Abstract
Centroscymnus coelolepis is a deep-water sleeper shark and, like most sharks, it is covered in placoid scales, or dermal denticles. The morphological diversity of the dermal denticles in this species, however, has not been described in detail, and ontogenetic changes in denticle morphology are poorly understood in sharks. Combining scanning-electron microscopy and micro-CT imaging, we demonstrate the presence of eleven dermal-denticle morphotypes across the ontogeny and different regions of the body of Centroscymnus coelolepis. The snout, interspiracular, and trunk/tail regions have similar changes in denticle morphotype during development. For example, on the trunks and tails of juveniles (~350 mm TL), denticle crowns have two to three longitudinal ridges and three posterior cusps that are gradually replaced by ridgeless and cuspless crowns in adults (>800 mm TL). Sixteen measurements were obtained from the 3D models generated. A principal component analysis demonstrated that the eleven distinct dermal-denticle morphotypes observed were located in different regions of the morphospace. The denticle volume and surface area showed negative allometry with respect to body length throughout the ontogeny. The results reflect the considerable diversity within the denticle multiverse (ontogenetic and intraspecific variations), and much of this diversity remains to be explored to fully understand the role of dermal denticles in shark taxonomy, ecology, and biomechanics.
1. Introduction
Somniosidae, commonly known as sleeper sharks, are a small family of dogfish sharks from the order Squaliformes [1,2]. This family currently has six accepted genera and seventeen nominal species [3,4,5,6,7], although the status of some nominal species of Scymnodalatias and Somniosus are questionable [8]. These sharks live in deep water and are distributed worldwide [5,7,9,10]. Several aspects of the basic biology of these sharks are poorly understood, including their age at maturity, reproductive behavior, and dispersal and movement patterns [4,11]. We also know little about the intraspecific and ontogenetic variation of the dermal denticles covering the body surfaces of sleeper sharks, despite the importance of denticle shapes for identifying species and understanding their evolution and ecology.
Dermal denticles, or placoid scales, are present in the skin of most extant chondricthyans in various degrees, from entire-body coverage in mako sharks to very few denticles in specific organs of chimeras, or even the complete absence of scales in, for example, electric rays [4,12,13]. Dermal denticles are also present in the fossil record of stem-gnathostomes, such as “thelodonts” (e.g., Heterostraci, Anaspida), Galeaspida, Osteotraci, and “placoderms (e.g., Arthrodira), and crown-gnathostomes, such as “acanthodians” [14]. These tooth-like structures are made up of enameloid and dentine outer layers, with an inner pulp cavity [15]. These characteristics ensure that denticles persist throughout the fossil record [16]. Denticles also have a characteristic structure, with an outer crown that can vary in the presence of certain surface features (e.g., ridges, posterior cusps, or the lack thereof), a neck, and a basal root that is embedded in the dermis [7,17,18,19,20]. Dermal denticles most likely have multiple functions, such as altering the water flow on the body during swimming [21,22,23] and protection from predators [24,25]. Denticles are replaced throughout the life of an elasmobranch [26], with different species having distinct rates of replacement i.e., shedding [27]. Despite the numerous studies on variations in denticle morphology across shark species, only a small number document patterns of morphological variation on the body within a singular species e.g., [15,28]. Even fewer studies exist on the ontogenetic changes observed in the denticle morphology in any shark species e.g., [7,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35].
The dermal-denticle variability in Somniosidae has been sparsely described in the literature, with results mainly focusing on the use of denticle morphology for taxonomic identification [9,10,18,29,32,36,37,38,39]. These studies usually analyzed a single sample, often from a single location. The most detailed accounts on the ontogenetic and topological variation of dermal denticles for species of Somniosidae are those by [7,30,31,40,41]. Garrick’s accounts, however, were limited by the low availability of materials and two-dimensional techniques. Vaz [7] was the first to provide a high-definition scanning-electron microscopy of the variation of dermal denticles across the ontogeny and topology of Scymnodon macracanthus.
Among the Somniosidae, Centroscymnus coelolepis [42] has one of the most striking patterns of ontogenetic variation in dermal-denticle morphology. The denticles of the juveniles of this species are so distinct from those in adults that Bigelow et al. [43] described juveniles of C. coelolepis as a new species, allocating it to a distinct genus (i.e., Scymnodon melas). A year later, Bigelow and Schroeder [29] had access to additional specimens and were able to recognize that the newly described species, Scymnodon melas, was a junior synonym of Centroscymnus coelolepis. Bigelow and Schroeder [29] also provided a brief description of the ontogenetic variation of the dermal denticles in C. coelolepis, but these accounts were limited by their small sample size and examination of single locations on the bodies of the specimens.
The overall goal of this study is to contribute new quantitative data on the ontogeny of shark denticles to better understand the extent of developmental variation in placoid scales. First, we describe in detail the ontogenetic variation in dermal denticles across the body of the sleeper shark, Centroscymnus coelolepis. We used both scanning-electron microscopic images and micro-CT scanning to allow the three-dimensional measurement of denticle shapes. Second, we analyze these data to document the diversity of denticle shapes in multivariate ontogenetic space and then assess the scaling relationships to document denticle parameters, such as surface and volume changes with body size. Third, we compare these data from Centroscymnus coelolepis to available data on other species of the Somniosidae family and consider the taxonomic implications of ontogenetic variation, building on the recent research by Vaz [7,8].
2. Materials and Methods
Terminology for dermal denticles follows Reif [17], Atkinson and Collin [44], Atkinson et al. [45], and Vaz [7]. Scanning-electron-microscopy images were obtained using the Zeiss DSM 940 available in the Instituto de Biociências, Universidade de São Paulo. Skin samples were scanned with a Bruker Skyscan 1173 (µCT-scan) with voxel resolution between 5.77 µm and 6.13 µm, voltage of 30 kV, current of 150 µA, rotation step between 0.35° and 0.4°, and frame average of 3.0 or 4.0. The raw images from the µCT were reconstructed using the software NRecon 2.0 (Bruker).
2.1. Examined Specimens and Skin Samples
A series of 178 specimens of Centroscymnus coelolepis and a total of 526 specimens of the family Somniosidae had their dermal denticles examined under a stereomicroscope. The complete list is attached in Appendix A. Institutional abbreviations follow Sabaj [46]. A subsample of specimens (Table 1) had skin samples of 10 × 10 mm removed from five body locations (Figure 1): dorsal snout, the dorsal surface of the head between the nostril and the anterior edge of the eye; interspiracular region, skin surface between each spiracle; first gill region, surface of the skin dorsal to the first gill aperture; trunk, vertical middle of the trunk ventral to the first dorsal spine; and tail, vertical middle of the tail ventral to the second dorsal spine. The specimens of Centroscymnus coelolepis examined with µCT-scan had an additional sample extracted from the ventral snout, ventral surface of the head between the nostril and the mouth.

Table 1.
Subsample of specimens examined with micro-computed tomography (µCT-scan) and scanning-electron microscopy (SEM).
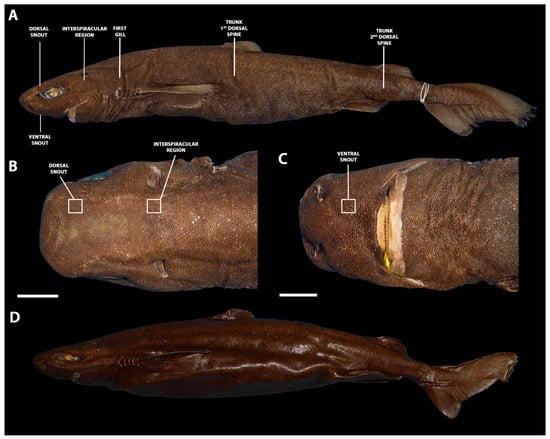
Figure 1.
Denticle-sampling locations on the body of Centroscymnus coelolepis in (A), higher magnification of the dorsal region of the head (B), and ventral region of the head (C) in a juvenile specimen of C. coelolepis (MNRJ 30220, 517 mm TL). (D) Adult specimen of C. coelolepis (ZMH 26039, 885 mm TL). Dorsal snout, the dorsal surface of the head between the nostril and the anterior edge of the eye; ventral snout, ventral surface of the head between the nostril and the mouth; interspiracular region, skin surface between each spiracle; first gill, surface of the skin dorsal to the first gill aperture; trunk first dorsal spine, vertical middle of the trunk ventral to the first dorsal spine; trunk second dorsal spine, vertical middle of the tail ventral to the second dorsal spine. Scale bar: 20 mm.
2.2. µCT Scanning Analysis and Dermal-Denticle Measurements
Materialize Mimics software (version 22.0) was used to segment individual denticles from each µCT scan. A total of 205 individual dermal denticles from across the six locations and five specimens of Centroscymnus coelolepis were segmented for imaging and measurements. Eleven measurements (Figure 2) were taken from each denticle using the “measurement tools” in Mimics: Crown length: largest distance from anterior margin to posterior margin of the crown. Crown width: largest distance between lateral margins of crown. Base width: direct distance between lateral edges of basal root. Base length: direct distance between anterior and posterior edges of basal root. Crown angle: the angle of the crown in relation to the basal root. Central cusp length: the height of the central cusp. Central cusp width: the distance between lateral edges at the base of the cusp. Lateral cusp length: the height of the lateral cusp. Lateral cusp width: the distance between the lateral edges at the base of the cusp (denticles without posterior cusps were scored as zero). Number of longitudinal ridges: the number of ridges arranged longitudinally in the dorsal surface of the crown, both extending partially or entirely across the crown. Surface area and volume of each denticle were calculated by exporting an STL file of a segmented denticle from Mimics and importing it in Materialize 3-Matic software (version 14.0). In the latter, the denticles had their pulp cavity and foramina closed, to make them watertight. The updated STL files were then exported to the MeshLab software (version 2022.02) for calculating surface area and volume. The raw data of individual denticles are provided on a table in Supplementary Materials S1.
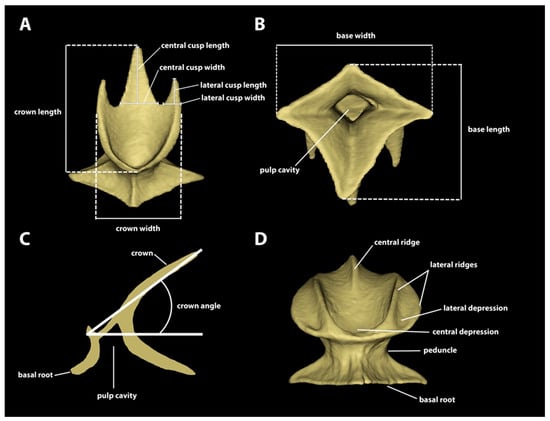
Figure 2.
Measurements and denticle terminology. (A) Frontal-crown view of a single denticle from the trunk (second dorsal spine) of Centroscymnus coelolepis (350 mm TL). Positions of measurements of crown length, crown width, central cusp length and width, and lateral cusp length and width are shown. (B) Ventral view with measurements for base length and base width, as well as terminology for the pulp cavity in the basal root. (C) Lateral cross section showing crown-angle measurement. (D) Anterior view of a single denticle from the spiracle region of a specimen of Centroscymnus coelolepis (650 mm TL). Labels show denticle terminology from Reif [17], Atkinson and Collin [44], Atkinson et al. [45], and Vaz [7] that is used in this manuscript.
2.3. Statistics
Denticles around the body and through ontogeny showed considerable variation, and for the purposes of describing this variation, we initially assigned denticles to general “morphotypes” that represent relatively distinct denticle shapes and sizes, based on their locations on the body and the measurements above. Morphotypes were defined by discrete and continuous characters, such as the number and the development of lateral ridges, presence or absence of posterior cusps in the crown, presence or absence of lateral depressions, central cusp aspect ratio, and the position of the anterolateral edge of the crown in relation to the lateral posterior cusp. Table 2 presents the summary of the diagnostic characters for each morphotype. Subsequent statistical classification using principal components analysis demonstrated the validity of these morphotype assignments.

Table 2.
Summary of the diagnostic characters for defining dermal denticle morphotypes in Centroscymnus coelolepis. The condition “reduced” in “Development of external lateral ridges” means the lateral ridge does not extend past the anterior region of the crown. The condition “complete” means the external lateral ridge reaches the posterior margin of the crown. Abbreviations: lpc, lateral posterior cusp; n/a, not applicable.
To understand how body length affects size differences within the same morphotype, a simple linear regression was fitted using the base R stats package in R (version 4.2.2) to compare crown-length measurements across body length in each morphotype. Additionally, to determine whether denticles in the ventral snout and dorsal snout differed in size, a hypothesis test statistic (t-test) was used within each snout morphotype to determine whether the mean crown length differed significantly between dorsal and ventral denticles. Scaling relationships were analyzed for surface area, volume, crown length, crown width, basal root length, and basal root width versus body length using the slope of the linear regression line of the common logarithm of each measurement plotted against the common logarithm of body length.
A principal component analysis (PCA) was analyzed using the FactoMineR package (version 2.7) in R (version 4.2.2) to collapse the multidimensional measurement data into principal components to visualize denticle-shape transformation through ontogeny. Data were divided into snout denticles (dorsal and ventral snout), spiracle denticles (interspiracular region), and trunk denticles (first gill, trunk by first dorsal spine, and trunk by second dorsal spine). Each point on the PCA plots corresponds to a single denticle and overlaid on top of the PCA is a variable correlation plot and cos2 value, showing the direction and how much each individual measurement contributed to shape space. The R scripts of all statistics performed are available in Supplementary Materials S2. Note: this PCA function uses the mean for the group in cells with null values.
3. Results
3.1. Denticle Morphotypes
Dermal denticles cover most of the body, except for the mouth margins, the posterior margins of the fins, and the dorsal surfaces of the claspers. Our examination of the specimens of Centroscymnus coelolepis demonstrated three main regions where the denticles share similar changes across the ontogeny: the snout, spiracular, and trunk regions (which include the surface around the branchial apertures and caudal regions), similar to those described for C. owstonii [47]. Sexual dimorphism in the morphology of the dermal denticles was not observed. The summary used to distinguish the denticle morphotypes is presented in Table 2. The range of variation observed in each morphotype is presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Range of variation within each variable from the dermal denticles of Centroscymnus coelolepis.
3.1.1. Snout
Morphotype snout one. The dermal denticles classified as morphotype snout one have surface areas ranging from 1.48 mm2 to 2.6 mm2 and volume areas from 0.03 to 0.09 mm3 (Figure 3). The crowns of morphotype snout one are rounded and drop-shaped, without any posterior cusps. The anterior margin is convex and has wide, rounded anterolateral edges. The lateral margins are convex, projecting posteriorly in the anterior region of the margin and posteromedially in the posterior portion. The crown has a wide, blunt, and angular posterior edge. The angle between the crown and the basal root is highly variable, ranging from 19.6 to 58.4 degrees. The dorsal surface of the crown is concave, with a rounded anteromedial central depression, anteriorly surrounded by the inner pair of longitudinal lateral margins. A pair of lateral depressions is also present, one on each side of the anterolateral regions of the crown. The number of longitudinal ridges in this morphotype varies from two to five. The innermost pair of longitudinal lateral ridges surround anteriorly the central depression and project posteriorly, reaching the posterior margin of the crown. The second (outer) pair of lateral ridges in this morphotype, when present, is small, restricted to the anterolateral edges of the crown. The outer pair of lateral ridges delineates the lateral depressions and extends posteriorly only to the anterior region of the lateral margins of the crown. The presence and extent of the central ridge is variable: in some denticles, the central ridge is short, restricted to the posterior edge of the crown (Figure 3A); in others, the central ridge extend from the posterior margin of the central depression to the posterior edge of the crown (Figure 3B); and in some denticles, the central ridge extends throughout the crown, from the anterior to the posterior margin (Figure 3C). The ventral surface is smooth and slightly concave.
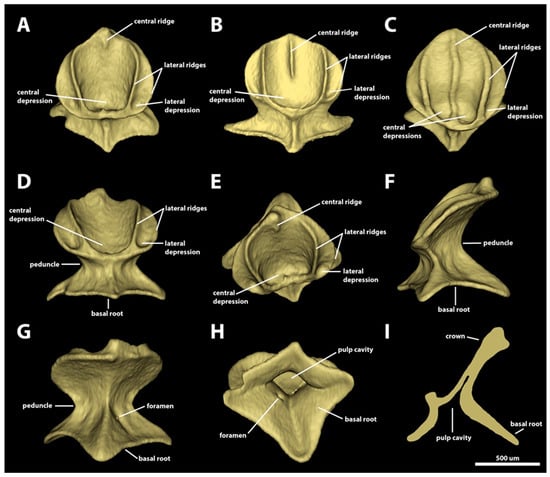
Figure 3.
Morphotype snout one denticles. The 3D models of examples of morphotype-snout-one denticles in the dorsal and ventral snout of Centroscymnus coelolepis and their morphotype characteristics. (A) Frontal crown view (dorsal snout, 650 mm TL specimen). (B) Frontal crown view (dorsal snout, 350 mm TL specimen). (C) Frontal crown view (ventral snout, 744 mm TL specimen). (D–I) are the same denticle as in panel (A). (D) Anterior view. (E) Dorsal view. (F) Side view. (G) Posterior view. (H) Ventral view. (I) Lateral cross section. Scale bar of 500 µm applies to all panels.
The denticle peduncle, where the crown above the epidermis joins the basal root embedded within the epidermis and dermis, is narrow; its width is one-half the width of the basal root (Figure 3D,F,G). The basal root is diamond-shaped, with four angular edges (one anterior, one posterior, and two lateral; Figure 3E). The aspect ratio of the basal root varies from 0.7 to 1. The anterior and lateral edges have similar lengths, but the posterior edge is 1.5 times longer than the anterior edge. Both anterior and posterior margins of the basal root are concave. The dorsal surface of the basal root is concave and has four ridges, with each ridge extending from each basal-root edge to the ventral surface of the crown. A pair of foramina is present on the posterodorsal surface of the basal root, with each foramen positioned on opposite sides of the posterior ridge of the basal root. The ventral surface of the basal root is smooth and convex, and it delineates the ventral region of the pulp cavity. The pulp cavity is wide and trapezoid-shaped (Figure 3H,I).
Morphotype snout two. The dermal denticles classified as morphotype snout two have surface areas ranging from 1.87 mm2 to 4.37 mm2 and volumes ranging from 0.07 to 0.21 mm3 (Figure 4). The crowns of morphotype snout two are drop-shaped and lack posterior cusps. The anterior margins are convex and continuous, with broad and rounded anterolateral edges. The lateral margins are convex and project posteromedially to form a broad, blunt posterior edge. The angle between the crown and the basal root varies greatly from 2.6 to 35.5 degrees. The dorsal surface of the crown is mostly concave, with an ample, rounded anteromedial central depression, anteriorly delimited by the inner pair of longitudinal ridges. A pair of additional lateral depressions is present in the anterolateral region of the crown, anteriorly surrounded by the origin of the outer pair of longitudinal ridges. Four to five longitudinal ridges are present on morphotype snout two. The inner pair of lateral longitudinal ridges surround anteriorly the central depression and project posteriorly, reaching the posterior edge of the crown. The outer pair of lateral longitudinal edges extends from the anterolateral region of the anterior margin and to the posterior region of the lateral margin of the crown (Figure 4A–F). The presence and extent of a central longitudinal ridge is variable. When present, this ridge can be restricted to the posterior region (Figure 4A), originating in the posterior region of the anterior central depression (Figure 4B), or it can cross the crown completely from the anterior to the posterior margin (Figure 4C). The ventral surface of the crown is smooth and concave.
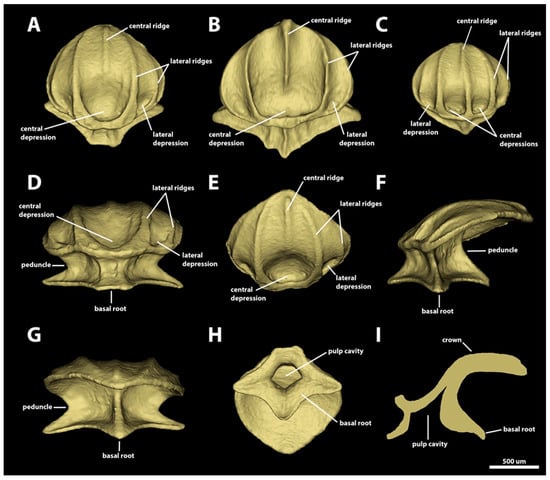
Figure 4.
Morphotype snout two denticles. The 3D models of examples of morphotype-snout-two denticles in the dorsal and ventral snout of Centroscymnus coelolepis and their morphotype characteristics. (A) Frontal crown view (ventral snout, 744 mm TL specimen). (B) Frontal crown view (dorsal snout, 650 mm TL specimen). (C) Frontal crown view (ventral snout, 744 mm TL specimen). (D–I) are the same denticle as in panel (A). (D) Anterior view. (E) Dorsal view. (F) Side view. (G) Posterior view. (H) Ventral view. (I) Lateral cross section. Scale bar of 500 µm applies to all panels.
The peduncle is broad. Its width is two-thirds the width of the basal root and wider than three-quarters of the crown’s width (Figure 4D,F,G). The basal root is diamond-shaped, with four angular edges, and its aspect ratio varies from 0.5 to 0.9 (Figure 4H). The lateral edges are angular, 1.5–2 times longer than their base width. The posterior edge is also angular, but broader, the width of its base similar to its length. The anterior edge is broad and short, and its length is half the length of its base width and twice as short as the length of the posterior edge. The antero-lateral margins of the basal root vary from straight to slightly concave, whereas the postero-lateral margins are deeply concave. The dorsal surface of the basal root is concave and has four ridges, each of which projects dorsally from the tip of each basal-root edge to the ventral margin of the crown. A pair of foramina is present on the posterodorsal surface of the basal root, with each foramen on opposing sides of the posterior ridge of the basal root. The ventral surface of the basal root is smooth and convex, delimiting the pulp cavity. The pulp cavity is wide and trapezoidal (Figure 4I).
Morphotype snout three. The dermal denticles defined as morphotype snout three have surface areas ranging from 2.49 mm2 to 8.79 mm2 and volumes from 0.11 to 0.59 mm3. The crowns of morphotype snout three are drop-shaped, without posterior cusps (Figure 5). The anterior margin is broad and convex, with broad and rounded anterolateral edges. The lateral margins are convex and project posteromedially to meet posteriorly, forming a blunt posterior edge. The crown angle in this morphotype varies from 1.3 to 15.7 degrees. The dorsal surface of the crown is mostly concave, with a large, rounded anteromedial central depression, which is anteriorly delimited by the inner pair of longitudinal ridges (Figure 5A–D). A pair of small lateral depressions is present on the anterolateral region of the crown, medially delimited by the inner pair of longitudinal ridges and laterally delineated by the first outer pair of longitudinal ridges. Six to ten ridges are present on the dorsal surface of the crown of morphotype snout three. The inner pair of longitudinal ridges extends from the anterior margin to the posterior edge of the crown. The first outer pair of longitudinal ridges is positioned on the lateral region of the crown, also originating on the anterior margin and projecting posteromedially to reach the posterior edge of the crown. The additional outer pairs of longitudinal ridges (e.g., the second and third) are relatively short and located adjacent to the lateral margin of the crown, projecting from the anterolateral region of the anterior margin and extending to the posterior region of the lateral margin of the crown. The presence of a central longitudinal ridge is variable, and it is absent in several denticles (present in Figure 5B; absent in Figure 5A,C). The extent of the central ridge, similar to that observed in other morphotypes, is also variable: it is restricted to the posterior edge of the crown, it extends from the central depression to the posterior edge, or it extends throughout the dorsal surface of the crown. The ventral surface of the crown is smooth and concave.
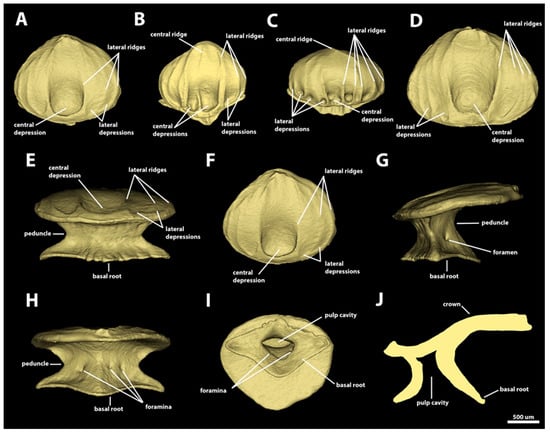
Figure 5.
Morphotype snout three denticles. The 3D models of examples of morphotype-snout-three denticles in the dorsal and ventral snout of Centroscymnus coelolepis and their morphotype characteristics. (A) Frontal crown view (dorsal snout, 895 mm TL specimen). (B) Frontal crown view (ventral snout, 744 mm TL specimen). (C) Frontal crown view (ventral snout, 895 mm TL specimen). (D) Frontal crown view (dorsal snout, 895 mm TL specimen). (E–J) are the same denticle as in panel (A). (E) Anterior view. (F) Dorsal view. (G) Side view. (H) Posterior view. (I) Ventral view. (J) Lateral cross section. Scale bar of 500 µm applies to all panels.
The denticle peduncle is broad, measuring more than three-quarters of both the basal root and the crown widths (Figure 5E). The basal root is rhomboid-shaped, with aspect ratio ranging from 0.6 to 0.9. The lateral edges are angular and long: the width of the edge-base is less than half of the length of the edge. The posterior edge is broad and blunt, and the base of the edge is wider than its length. The anterior edge is short, and its width two to three times the edge length. The shape of the margins of the anterior edge is highly variable. Some denticles have a basal cusp with a triangular anterior edge, whereas others have a rectangular anterior edge. In denticles with rectangular anterior edges, some denticles have straight and continuous edge margins, whereas others have indentations (Figure 5E,I). The dorsal surface of the basal root is concave and has four ridges, extending dorsally from the tip of each basal-root edge to the ventral surface of the crown. The basal roots of most morphotype-snout-three denticles have pairs of foramina on their posterodorsal surfaces, with one foramen adjacent to each side of the ridge extending from the posterior edge. In some denticles, an additional foramen is observable either on the left or the right side (Figure 5H). The ventral surface of the basal root is smooth and convex. The pulp cavity is ample and its shape varies from oval to elliptical, or triangular (Figure 5I,J).
3.1.2. Spiracular Region
Morphotype spiracular one. The dermal denticles defined as morphotype spiracular one have surface areas ranging from 0.96 mm2 to 2.46 mm2 and volumes from 0.02 to 0.10 mm3. The crowns of morphotype spiracular one have rounded anterior margins and posterior margins bearing one central and two lateral posterior cusps (Figure 6). The angle between the crown and the basal root varies from 36.5 to 59.7 degrees. The central cusp is 2.4–8.1 times longer and 1.9–5.6 times wider than the lateral cusps. The lateral margins of the lateral cusps are longitudinally aligned with the lateral edges of the anterior margin of the crown. The dorsal surface of the crown is concave, with a distinct central depression on its anterior region. Two lateral longitudinal ridges are present on the dorsal surface of the crown. The ridges surround the central depression anteriorly and project posteriorly adjacent to the lateral margins. The extent of the lateral longitudinal ridge is variable, reaching from the posterior half to the bases of the lateral cusps. The occurrence of a central ridge is variable; when present, the central ridge can be shallow and restricted to the longitudinal middle of the central cusp (Figure 6B), or it can extend through the entire dorsal midline of the crown (Figure 6C). The ventral surface of the cusp is smooth and convex.
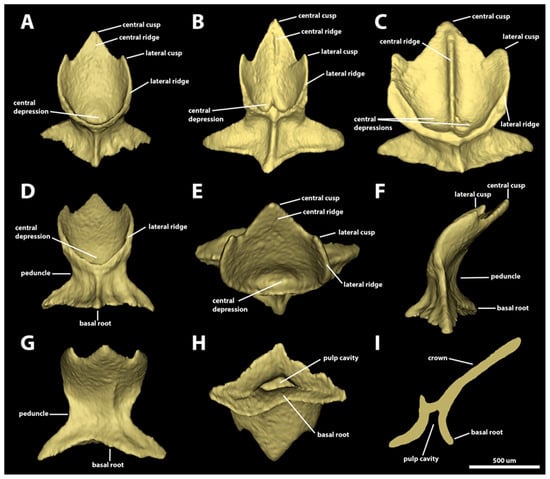
Figure 6.
Morphotype spiracular one denticles. The 3D models of examples of morphotype-spiracular-one denticles from the interspiracular region of Centroscymnus coelolepis and their morphotype characteristics. (A) Frontal crown view (650 mm TL specimen). (B) Frontal crown view (550 mm TL specimen). (C) Frontal crown view (744-millimeter-TL specimen). (D–I) are the same denticle as in panel (A). (D) Anterior view. (E) Dorsal view. (F) Side view. (G) Posterior view. (H) Ventral view. (I) Lateral cross section. Scale bar of 500 µm applies to all panels.
The peduncle is narrow: its width is approximately half of the width of the basal root (Figure 6D). The basal root has four angular edges (tetracuspid; one anterior, one posterior, and two lateral edges; Figure 6F,H), and it is rhomboidal-shaped, with an aspect ratio varying from 0.6 to 1.0. The anterior and lateral edges are similar in length, but the posterior is less developed, at approximately a third of the anterior edge’s length. The dorsal surface of the basal root is concave, with four ridges extending dorsally from the edge of each basal root cusp to the ventral surface of the crown (Figure 6A–G). A pair of foramina is present in the posterodorsal surface of the basal root, with each foramen positioned on each side of the ridge on the posterior cusp of the basal root. The ventral surface of the basal root is slightly convex, delineating ample pulp cavity (Figure 6H,I).
Morphotype spiracular two. The dermal denticles classified as morphotype spiracular two have surface areas ranging from 1.69 mm2 to 4.93 mm2 and volumes of 0.05–0.25 mm3. The angle between the crown and the basal root varies from 27.6 to 50.4 degrees (Figure 7). The crown of this morphotype has a convex anterior margin, extending laterally to a rounded edge. The lateral margins of the crown extend posteromedially. Three triangular posterior cusps are present: one large central cusp and two small lateral cusps (Figure 7A–C). The central cusp is 2.7–7.7 times longer and 1.8–5.5 times wider than the lateral cusps. The lateral margins of the posterior lateral cusp are located medially in relation to the anterior edge of the crown. The dorsal surface of the crown is mostly convex, with a central depression in the anterior region of the crown. A pair of lateral depressions is present on the anterolateral edge of the crown, between the inner and outer lateral ridges (Figure 7A–D). Four to five longitudinal ridges are present on the dorsal surface of the crown of spiracular morphotype trunk two. The inner pair of longitudinal ridges surrounds anteriorly the central depression and projects posterolaterally to the bases of the posterior lateral cusps. The outer pair of lateral ridges are small, located on the lateral margin of the crown, extending only through to the anterior edge and delineating the lateral depression. The central ridge is present in all the crowns of morphotype spiracular two. The prominence of the central ridge, however, is variable, with some denticles’ central ridges restricted to the extent of the posterior central cusp, whereas others have a central longitudinal ridge extending from the anterior central depression to the edge of the posterior central cusp (Figure 7A–C). The ventral surface of the crown is smooth and slightly convex.
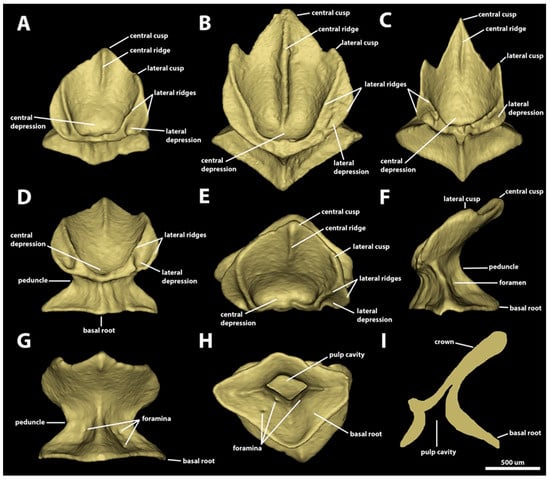
Figure 7.
Morphotype spiracular two denticles. The 3D models of examples of morphotype-spiracle-two denticles from the interspiracular region of Centroscymnus coelolepis and their morphotype characteristics. (A) Frontal crown view (650 mm TL specimen). (B) Frontal crown view (744 mm TL specimen). (C) Frontal crown view (550 mm TL specimen). (D–I) are the same denticle as in panel (A). (D) Anterior view. (E) Dorsal view. (F) Side view. (G) Posterior view. (H) Ventral view. (I) Lateral cross section. Scale bar of 500 µm applies to all panels.
The peduncle of morphotype spiracular two is robust, measuring approximately three-quarters of the crown width and two-thirds of basal root width (Figure 7D,F). The basal root of morphotype spiracular two is trapezoidal and diamond-shaped, and it has four edges (tetracuspid; one anterior, one posterior, and two lateral edges). Both anterior and posterior edges of the basal root are broad, with the anterior cusp relatively small, measuring approximately half the length of the posterior edge (Figure 7H). The lateral edges are narrower and usually longer than the posterior, and they are angular in shape. The aspect ratio of the basal root is variable, ranging from 0.7 to 1. The dorsal surface of the basal root is concave and has four ridges extending dorsally from the edge of each cusp to the base of the crown. The posterodorsal surface of the basal root has a pair of foramina, each positioned on each side of the ridge projecting from the posterior cusp (Figure 7G). The ventral surface of the basal root is convex and forms an ample, spool-shaped pulp cavity (Figure 7H,I).
Morphotype spiracular three. The dermal denticles classified as morphotype spiracular three have surface areas ranging from 2.21 mm2 to 8.42 mm2 and volumes of 0.07–0.63 mm3. The shape of the crown of this morphotype varies from oval to drop-shaped, without any posterior cusps (Figure 8). The anterior and lateral margins of the crown are rounded; the posterior margin varies from angular (Figure 8A,C) to rounded (Figure 8B). The angle between the crown and the basal root varies from 11.3 to 35.8 degrees. The dorsal surface of the crown is mostly concave, with a distinct central depression in its anterior region. Three to five longitudinal ridges are observed in the crowns of morphotype spiracular three: one central ridge and one to two pairs of longitudinal lateral ridges. The innermost pair of longitudinal lateral ridges surround the central depression anteriorly and extend posterolaterally (Figure 8A,C) or posteromedially (Figure 8B), reaching the posterior edge of the crown. The extent of the external pair of longitudinal ridges is highly variable, On MCZ 38297, the morphotype-spiracular-three denticles have an external pair of longitudinal ridges that is restricted on the anterolateral margin of the crown (Figure 8A). On MCZ 57703, the external pair of lateral ridges is also located on the margin of the crown, but these ridges extend posteriorly to the posterior half of the crown margin (Figure 8C). On adult MCZ 39621, the external pair of longitudinal ridges originates on the lateral portion of the anterior margin of the crown, projecting posteromedially over the lateral region of the crown (medial to the lateral margin), reaching the posterior margin of the crown (Figure 8B). The extent of the central longitudinal ridge is also variable: in some denticles, the central ridge is restricted to the posterior region of the crown (Figure 8A,B). In other denticles, the central ridge extends from the posterior edge to the anterior surface of the central depression of the crown (Figure 8C). The ventral surface of the crown is straight to slightly concave (Figure 8F,G,I).
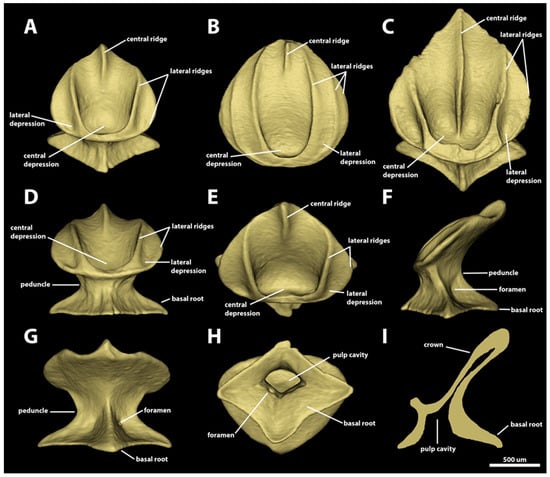
Figure 8.
Morphotype spiracular three denticles. The 3D models of examples of morphotype-spiracular-three denticles from the interspiracular region of Centroscymnus coelolepis and their morphotype characteristics. (A) Frontal crown view (650 mm TL specimen). (B) Frontal crown view (895 mm TL specimen). (C) Frontal crown view (744 mm TL specimen). (D–I) are the same denticle as in panel (A). (D) Anterior view. (E) Dorsal view. (F) Side view. (G) Posterior view. (H) Ventral view. (I) Lateral cross section. Scale bar of 500 µm applies to all panels.
The peduncle is relatively narrow, with a width approximately one-half of crown width (Figure 8D). The basal root is diamond-shaped, with an aspect ratio ranging from 0.6–0.9, and tetracuspid, with an anterior ridge, a posterior ridge, and two lateral edges (Figure 8H). All the edges are angular, with the lateral and anterior edges displaying similar dimensions. The posterior edge is slightly longer than and wider than the anterior. Both anterior and posterior margins of the basal root are slightly concave. The dorsal surface of the basal root is concave and has four ridges projecting dorsally from the edge of each cusp to the ventral surface of the crown (Figure 8A,C,D,F,G). On the posterodorsal surface of the basal root, a pair of foramina is present, with one on each side of the posterior ridge of the basal root. The ventral surface of the basal root is convex and forms an ample spool-shaped pulp cavity (Figure 8H,I).
Morphotype spiracular four. The dermal denticles classified as morphotype spiracular four have surface areas ranging from 5.91 mm2 to 7.82 mm2 and volumes of 0.39–0.55 mm3. The crown of morphotype spiracular four is round and pear-shaped, with a wider anterior region tapering posteriorly into a broad and convex posterior edge, without any posterior cusps (Figure 9). The anterior margin has a shallow indentation centrally. The anterolateral edges of the crown margin are broad and convex. The angle between the crown and the basal root varies from 7.3 to 8.5 degrees. The dorsal surface of the crown is slightly convex in its lateral portions, with a wide, deep central depression located anteromedially on the crown. The margins of the central depression are defined by the innermost pair of lateral ridges. Three pairs of longitudinal ridges are present on this morphotype. The innermost pair are anteriorly conjoined, delineating the anterior margin of the central depression. The anterolateral region of the innermost pair of longitudinal ridges projects posterolaterally, whereas the posterolateral portion of these ridges curves and projects posteromedially, reaching the margin of the posterior edge of the crown. Two additional pairs of lateral ridges are present, located on the lateral portion of the crown and extending from the anterior margin to the posterior region of the lateral margin of the crown. A short, central longitudinal ridge is present, restricted to the posterior edge of the crown. The ventral surface of the crown is smooth and mostly concave, except anteromedially, where the surface is convex (Figure 9F).
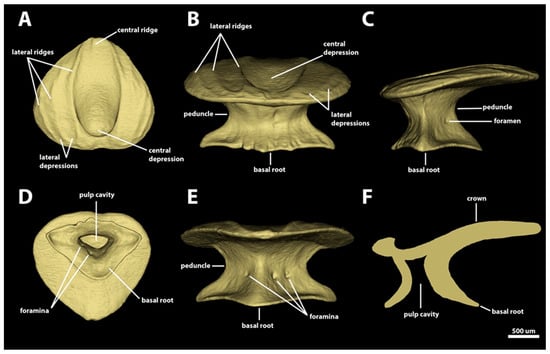
Figure 9.
Morphotype spiracular four denticles. The 3D models of an example morphotype spiracular four denticle from the interspiracular region of Centroscymnus coelolepis and its morphotype characteristics (895 mm TL specimen). (A) Dorsal crown view. (B) Anterior view. (C) Side view. (D) Ventral view. (E) Posterior view. (F) Lateral cross section. Scale bar of 500 µm applies to all panels.
The width of the peduncle of morphotype spiracular four is half of the crown width and two-thirds of the width of the basal root (Figure 9B). The basal root is triangular, with a convex anterior margin and concave posterolateral margins (Figure 9D). The length of the basal root is approximately two-thirds of its largest width (with aspect ratios ranging from 0.65 to 0.67). The anterolateral edges of the basal root have acute edges. The posterior edge, conversely, is broad and rounded (Figure 9D). The dorsal surface of the basal root is slightly concave and has three ridges, each extending from each edge of the basal root to the base of the crown (Figure 9B,C,F). Two, three, or four foramina are present on the posterolateral surfaces of the basal root, adjacent to the posterior ridge (Figure 9E). The ventral surface of the basal root is smooth and convex, forming an ample trapezoidal pulp cavity (Figure 9F).
3.1.3. Branchial, Trunk, and Tail Regions
Morphotype trunk one. The denticles classified as morphotype trunk one have surface areas ranging from 1.49 mm2 to 2.27 mm2 and volumes of 0.03–0.08 mm3. The crown of this morphotype has a rounded anterior margin and its posterior margin bears a central cusp and two lateral cusps (Figure 10). The angle between the crown and the basal root (crown angle) varies from 28.6 to 52.4 degrees. The central cusp is 1.7–4.1 times longer and 1.2–2.5 times wider than the lateral cusps. The lateral margins of the posterior lateral cusps are longitudinally aligned with the lateral edge of the anterior margin of the crown. The dorsal surface of the crown is concave, with a distinct central depression on its anterior region. Two lateral longitudinal ridges are present on the dorsal surface of the crown of morphotype trunk one, surrounding the anterior depression and extending posteriorly adjacent to the lateral margins of the crown (Figure 10A–C). The lateral ridges project posteriorly to the distal tip of the lateral cusps (Figure 10C). The presence of a central ridge is variable; when present, the central ridge is shallow and restricted within the longitudinal middle of the posterior central cusp. The ventral surface of the crown is smooth and slightly convex (Figure 10D,E).
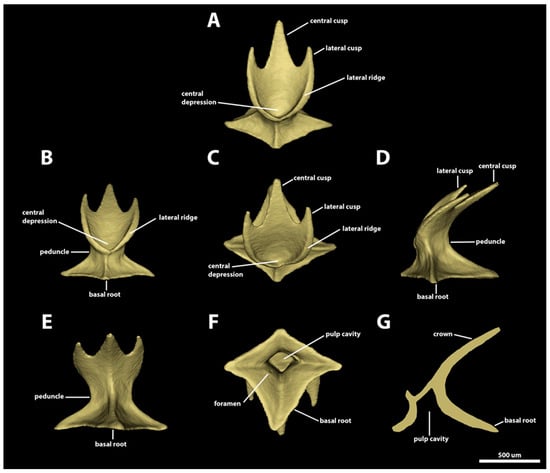
Figure 10.
Morphotype trunk one denticles. The 3D models of an example morphotype-trunk-one denticle in Centroscymnus coelolepis and its morphotype characteristics (trunk second dorsal spine, 350 mm TL specimen). (A) Frontal crown view. (B) Anterior view. (C) Dorsal view. (D) Side view. (E) Posterior view. (F) Ventral view. (G) Lateral cross section. Scale bar of 500 µm applies to all panels.
The peduncle is narrow: its width is approximately one-half of the width of the basal root (Figure 10B,D,E). The basal root is tetracuspid with an anterior cusp, a posterior cusp, and two lateral cusps. The basal root is rhomboid-shaped (Figure 10F), with an aspect ratio of 0.7–0.9. On morphotype trunk one, the posterior cusp is the longest, and the others have similar lengths. The anterior margins of the basal root are concave, whereas the posterior margins are straight. The dorsal surface of the basal root is concave and has four ridges, each of which extends from each tip of the basal root to the dorsal edge of the peduncle (Figure 10A–E). A pair of foramina is present in the posterodorsal surface of the basal root, with each foramen positioned on each side of the ridge on the posterior cusp of the basal root. The ventral surface of the basal root is slightly convex, and it forms an ample pulp cavity (Figure 10F). In the sagittal section, the outline of the pulp cavity is trapezoidal (Figure 10G).
Morphotype trunk two. The denticles classified as morphotype trunk two are characterized by surface areas ranging from 1.97 mm2 to 12.53 mm2, and volumes of 0.07–1.03 mm3. The angle between the crown and the basal root varies from 11.0 to 48.9 degrees. The crown of morphotype trunk two is rounded anteriorly, with its lateral margins projecting posteromedially, forming two anterolateral expansions. The posterior margin of the crown has one central and two lateral cusps (Figure 11 and Figure 12). The lengths of the cusps are highly variable, with the central cusp 1.5–8.6 times longer and 1.4–5.9 times wider than the lateral cusps (Figure 11). Centrally, the dorsal surface of the crown is concave, with a large central depression in the anterior region; the width of the central depression is more than half the width of the crown. The crowns of morphotype trunk two have four longitudinal lateral ridges. From the middle of the anterior region of the crown, the two inner lateral ridges surround the anterior depression and project posterolaterally, reaching either the base (Figure 11A–C,F) or the tip of the posterior lateral cusp (Figure 11D,E,G,H). The second pair of lateral longitudinal ridges are variable in length, extending from the anterolateral region of the anterior margin of the crown to either the anterior region (Figure 11A–D) or the middle of the lateral margin of the crown (Figure 11E–I). The lateral surface between the inner and outer lateral ridges forms the lateral depression on the anterolateral expansions. The length of the central ridge is variable, varying from restricted to the central posterior cusp (Figure 11C–E,G) to extending throughout the longitudinal middle of the crown (Figure 11H). The presence of the central ridge is also variable, and multiple crowns of morphotype trunk two might lack a central ridge entirely (Figure 11A,B,F,I). The ventral surface of the crown is smooth and slightly convex.
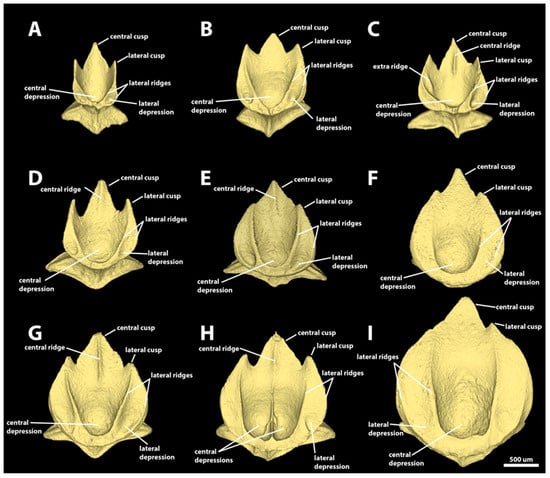
Figure 11.
Crown diversity of morphotype trunk two denticles. Frontal crown views of the observed crown shape diversity found in morphotype trunk two. Specimen lengths are arranged in horizontal rows: (A–C) are denticles from the 550 mm TL specimen. (D–F) are denticles from the 650 mm TL specimen. (G–I) are denticles from the 744 mm TL specimen. Sample locations are arranged in vertical columns: (A,D,G) are denticles from the trunk first gill region. (B,E,H) are denticles from the trunk first dorsal spine region. (C,F,I) are denticles from the trunk second dorsal spine region. Scale bar of 500 µm applies to all panels.
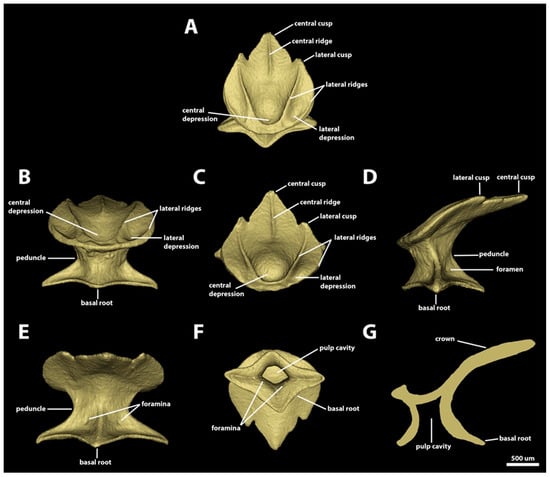
Figure 12.
Morphotype trunk two denticles. The 3D models of an example morphotype trunk two denticle in Centroscymnus coelolepis and its morphotype characteristics (trunk first gill, 744-millimer-TL specimen). (A) Frontal crown view. (B) Anterior view. (C) Dorsal view. (D) Side view. (E) Posterior view. (F) Ventral view. (G) Lateral cross section. Scale bar of 500 µm applies to all panels.
The peduncle is narrow. Its width is approximately one-half the width of basal root (Figure 12B,D,E). The basal root is rhomboidal, its aspect ratio varies from 0.6 to 1.6, and the lateral edges are longer and narrower than both anterior and posterior edges (Figure 12F). All the margins of the basal root are slightly concave. The dorsal surface of the basal root is smooth and slightly concave, with four ridges extending from each tip of the basal root to the dorsal edge of the peduncle. A pair of foramina is present on the posterodorsal surface of the basal root, with each foramen positioned on each side of the ridge on the posterior cusp of the basal root (Figure 12E). The ventral surface of the basal root is slightly convex. The pulp cavity is ample and it is trapezoid-shaped in the sagittal section (Figure 12F,G).
Morphotype trunk three. The denticles classified as morphotype trunk three have the largest absolute size observed in this series, with surface areas ranging from 6.89 mm2 to 18.37 mm2 and volumes from 0.42 mm3 to 1.98 mm3. The crown of morphotype trunk three is drop-shaped and lacks posterior cusps (Figure 13). In some denticles, the posterior margin of the crown may have a shallow indentation (Figure 13A,C), but cusps are absent. The angle between the crown and the basal root varies from 2.4 to 19 degrees. The dorsal surface of the crown is mostly smooth and slightly convex. The denticles have entirely smooth surfaces without ridges (Figure 13A–C,E). The anterior region of the dorsal surface of the crown has a shallow, circular depression. The ventral surface of the crown is smooth and slightly convex. In the smallest denticles of morphotype trunk three, the anterolateral wall of the central depression is sharper and vertically oriented (Figure 13C), but it is not surrounded by a lateral ridge (as observed in the other trunk denticles). In the smaller denticles of morphotype trunk three, some crowns might also have a shallow, sometimes inconspicuous, lateral depression.
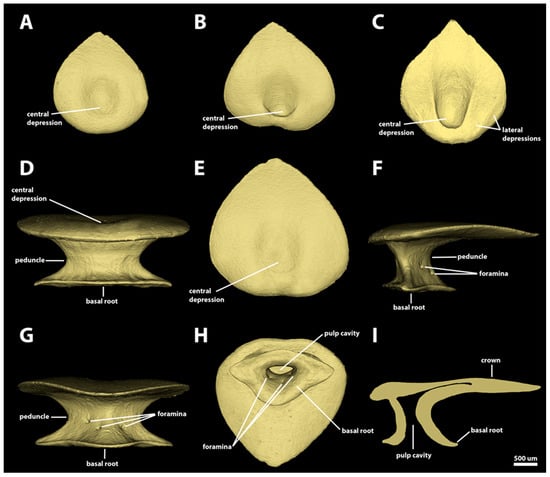
Figure 13.
Morphotype trunk three denticles. The 3D models of example morphotype trunk three denticles of Centroscymnus coelolepis and their morphotype characteristics. (A) Frontal crown view (trunk second dorsal spine, 895 mm TL specimen). (B) Frontal crown view (trunk first dorsal spine, 895 mm TL specimen). (C) Frontal crown view (trunk first dorsal, 744 mm TL specimen). (D–I) are the same denticle as in panel (A). (D) Anterior view. (E) Dorsal view. (F) Side view. (G) Posterior view. (H) Ventral view. (I) Lateral cross section. Scale bar of 500 µm applies to all panels.
The peduncle of morphotype trunk three is wide, approximately two thirds of the width of the basal root (Figure 13D,F,G). The basal root of morphotype trunk three is triangular, without an anterior edge as observed in the roots of the other trunk morphotypes (Figure 13H). The anterior margin of the base is convex, laterally extending into two sharp lateral edges. The posterior margins of the basal root are slightly concave, forming a broad posterior cusp with a rounded posterior edge. The dorsal surface of the basal root is smooth and slightly concave. In contrast to the base observed in other morphotypes, the dorsal surface of the basal root lacks ridges on both anterior and posterior regions (Figure 13D,G). The lateral edges have ridges projecting medially, extending dorsally to the middle of the peduncle (Figure 13F). The posterior surface of the basal root has at least one pair of foramina positioned centrally. Additional foramina (single or a pair) are observed in multiple denticles of morphotype trunk three (Figure 13G). The ventral surface of the basal root is convex and the pulp cavity is relatively smaller, flattened antero-posteriorly. In the sagittal section, the pulp cavity is spool-shaped (Figure 13H,I).
Morphotype trunk (branchial) four. This morphotype has a very narrow distribution, and it is observed only in the area dorsal to the gill openings in the smallest adult specimens of Centroscymnus coelolepis. The denticles of morphotype trunk (branchial) four have surface areas ranging from 3.20 mm2 to 7.80 mm2 and volumes of 0.12–0.47 mm3. The angle between the crown and the basal root varies from 13.8 to 26.8 degrees. Similar to morphotype trunk three, the crown of morphotype trunk four is drop-shaped, with straight posterior margins, without cusps. In contrast to morphotype trunk three, however, the crowns of morphotype trunk four have six to nine shallow longitudinal ridges in all their denticles (Figure 14). The inner pair of longitudinal ridges surrounds the anterior central cavity and extends posteriorly to the posterior region of the crown. The other lateral pairs of ridges extend from the anterior region to the middle of the lateral margin of the crown. The dorsal surface of the crown is mostly convex, except anteromedially, where the anterior depression of the crown with a concave surface is located. The ventral surface of the crown is mostly straight to slightly concave.
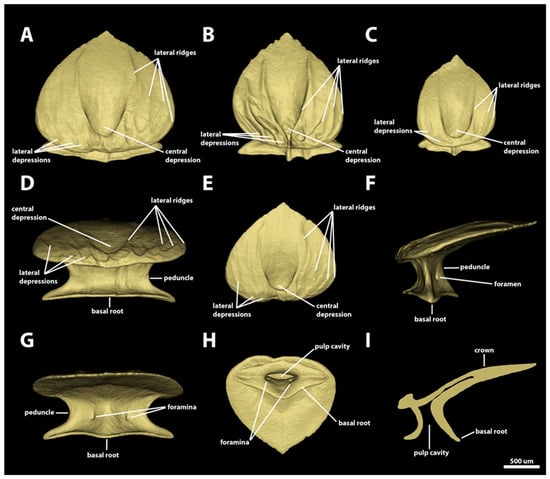
Figure 14.
Morphotype trunk four (branchial) denticles. The 3D models of an example morphotype trunk four (branchial) denticles of Centroscymnus coelolepis and their morphotype characteristics (first gill, 895 mm TL specimen). (A–C) Frontal crown view (D) Anterior view. (E) Dorsal view. (F) Side view. (G) Posterior view. (H) Ventral view. (I) Lateral cross section. Scale bar of 500 µm applies to all panels.
The peduncles of morphotype trunk four are wide, measuring approximately three-quarters of the crown width (Figure 14D,G). The basal root of this morphotype is trapezoidal, with a reduced anterior cusp, and a wide and rounded posterior cusp (Figure 14H). The lateral cusps of the basal root are large and angular. The dorsal surface of the basal root of morphotype trunk four is concave, with three ridges projecting dorsally from the tip of the posterior and lateral edges of the basal root and extending to the ventral surface of the crown (Figure 14D,F,G). On the posterior surface of the basal root, at the boundary with the peduncle, a pair of foramina are present, one on each side of the ridge projecting from the posterior cusp. The ventral surface of the basal root is convex, forming a semi-cylindrical and ample pulp cavity (Figure 14H,I).
3.2. Denticle Replacement
The replacement of denticles through the ontogeny among the different morphotypes in Centroscymnus coelolepis is not simultaneous, but gradual. The proportions of each denticle morphotype vary topologically and ontogenetically. Sexual dimorphism in the replacement was not observed in any of the regions.
3.2.1. Denticle Replacement in the Snout
In neonates, both the dorsal and the ventral anterior regions of the head, from the tip of the snout to the anterior edge of the eye aperture, are completely covered by morphotype snout one denticles (MCZ 38452, 269 mm TL). Across the snout, the replacement of different morphotypes consistently occurs earlier across ontogeny in the ventral region (Figure 15). In specimen MCZ132510 (350 mm TL), 97% of the denticles on the dorsal surface of the snout are from morphotype one, with only 3% being from morphotype snout two (Figure 15A); ventrally, 12% of the denticles are already morphotype snout two, with the remaining 88% from morphotype snout one (Figure 15F). In MCZ 38294 (550 mm TL), 71% of the denticles on the dorsal surface of the snout are from morphotype snout one and 29% are from morphotype snout two. No denticles from morphotype three are present (Figure 15B). On the ventral surface, however, morphotype snout three are already present and correspond to 19% of all denticles. Additionally, denticles from morphotype snout one are not the predominant morphotype ventrally as in the dorsal region; only 21% of denticles correspond to morphotype snout one. The predominant morphotype is snout two, with 62% of the denticles (Figure 15G). Similar proportions are observable in MCZ 38297 (650 mm TL; dorsal: SN1: 83%, SN2: 17%; ventral: SN1: 20%, SN2: 59%, SN3: 20%). The MCZ 57703 (744 mm TL) was the first specimen in which the dorsal surface of the snout was predominantly covered by morphotype snout two denticles (63%), whereas the remaining 37% were still from morphotype snout one (Figure 15C). The ventral surface of the snout is still predominantly covered by morphotype snout two (64%), with morphotype snout one representing only 10% of the denticles. Morphotype snout three accounts for 26% of denticles on the ventral surface of the snout (Figure 15H). The USNM 408586 (837 mm TL) was the first specimen observed in this series in which the dorsal surface of the snout was covered predominantly by morphotype snout three (59%), and it lacked morphotype snout one; the remaining denticles are all morphotype snout two (41%) (Figure 15D). No data are available for the ventral region of USNM 408586. In adults (e.g., MCZ 39621), both the dorsal and the ventral surface of the snout are completely covered by morphotype snout three (Figure 15E,I).
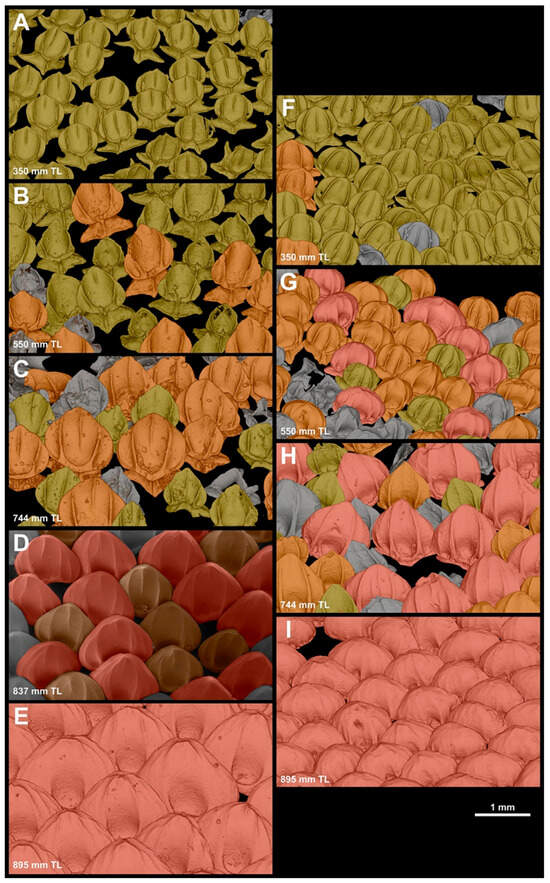
Figure 15.
Snout ontogeny and denticle-replacement patterns. The µCT-scan and scanning-electron microscopy (SEM) images of denticle samples from dorsal (A–E) and ventral (F–I) snout in Centroscymnus coelolepis. Individual denticles are colored according to morphotype. Yellow denticles are morphotype snout one, orange denticles are morphotype snout two, and coral-colored denticles are morphotype snout three. (A) Dorsal snout, MCZ 132510, 350 mm TL. (B) Dorsal snout, MCZ 38294, 550 mm TL. (C) Dorsal snout, MCZ 57704, 744 mm TL. (D) Dorsal snout, USNM 408586, 837 mm TL. (E) Dorsal snout, MCZ 39621, 895 mm TL. (F) Ventral snout, MCZ 132510, 350 mm TL. (G) Ventral snout, MCZ 38294, 550 mm TL. (H) Ventral snout, MCZ 57704, 744 mm TL. (I) Ventral snout, MCZ 39621, 895 mm TL. Scale bar of 1 mm applies to all panels.
We also observed that that the crown lengths of dorsal-snout morphotypes seemed larger than those of the same morphotypes in the ventral region. However, the results of the t-test comparing the crown lengths reported no significant differences in mean crown length between the dorsal and ventral snout denticles for morphotype snout one (t-value = 0.3, p-value = 0.7). In the morphotype snout two denticles, the mean crown length of dorsal denticles is significantly larger than those of the ventral denticles, with a t-value of 2.9 and a p-value of 0.02. The morphotype three denticles showed the strongest difference in mean-crown-length measurements between the dorsal and ventral denticles, with the dorsal denticles displaying significantly longer crowns (t-value = 5.9, p < 0.001).
3.2.2. Denticle Replacement in the Spiracular Region
From neonates to individuals measuring 396 mm TL (MNRJ 30244), the spiracular region is entirely covered by denticles of morphotype spiracular one (Figure 16A). The first occurrence of morphotype spiracular two was found in a specimen measuring 421 mm TL (MNRJ 30249). In specimen MCZ 38294 (550 mm TL; Figure 16B), the spiracular region is mostly covered by denticles from morphotype spiracular two (64%). The remaining denticles are morphotype spiracular one (36%). In MCZ 38297 (650 mm TL), most of the denticles covering the spiracular region are still of morphotype spiracular two (53%). In this specimen, the denticles of morphotype spiracular three are present and represent 36% of the denticles in this region. The remaining denticles (13%) are morphotype spiracular one. Specimen MCZ 57703 (744 mm TL; Figure 16D) has a similar morphotype distribution (SP1: 14%; SP2: 51%; SP3: 35%). Although it was slightly smaller (725 mm TL; Figure 16C), USNM 206061 was the first specimen to have a single denticle from morphotype spiracular four (2%). In this specimen, morphotype spiracular one was not present. However, in USNM 206061 (725 mm TL), morphotype spiracular two comprises only 18% of denticles in the spiracular region; the remaining denticles (80%) are morphotype spiracular three. In adults, denticles of morphotype spiracular two are not present. In USNM 408586 (837 mm TL; Figure 16E), 46% of the denticles covering the spiracular region are morphotype spiracular three, whereas 54% are morphotype spiracular four. In MCZ 39621 (895 mm TL; Figure 16F), morphotype spiracular three comprises only 36% of the denticles in this region. The remaining 66% is composed of morphotype spiracular four.
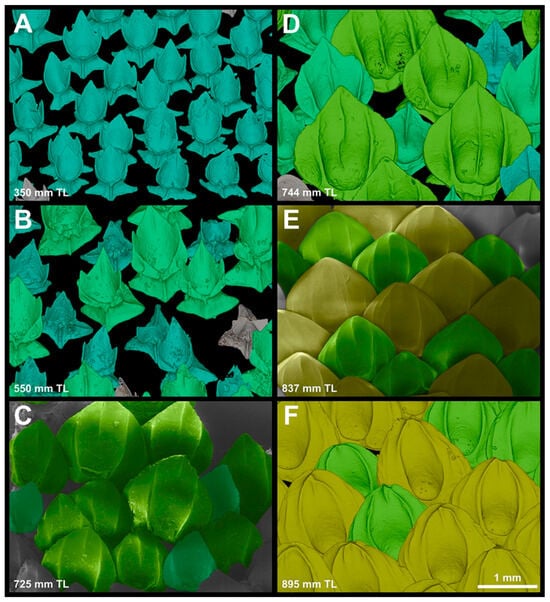
Figure 16.
Spiracular ontogeny and denticle-replacement Patterns. The µCT scans and SEM images of denticle samples from the spiracle region in Centroscymnus coelolepis. Individual denticles are colored according to morphotype. Blue denticles are morphotype spiracular one, blue/green denticles are morphotype spiracular two, light-green denticles are morphotype spiracular three, and yellow denticles are morphotype spiracular four. (A) MCZ 132510, 350 mm TL. (B) MCZ 38294, 550 mm TL. (C) USNM 206061, 725 mm TL. (D) MCZ 57704, 744 mm TL. (E) USNM 408586, 837 mm TL. (F) MCZ 39621, 895 mm TL. Scale bar of 1 mm applies to all panels.
3.2.3. Denticle-Replacement Patterns in the Branchial, Abdominal, and Caudal Regions
From neonates to individuals measuring 350 mm TL (MCZ 132510; Figure 17A,G,M), the branchial, abdominal, and caudal regions are covered by denticles from morphotype trunk one. The first appearance of morphotype trunk two occurs in the caudal region of MCZ 132510, as a single denticle. Replacement across different morphotypes in this region occurs in the tail first and progresses to the branchial region through ontogeny. In the branchial region of specimen MCZ 38294 (550 mm TL; Figure 17B), 47% of the denticles are from morphotype trunk one, whereas 54% of the denticles are from morphotype trunk two. In the abdominal region of MCZ 38294 (Figure 17H), morphotype trunk one comprises 17% of the denticles, with the remaining 83% composed by morphotype trunk two. In the caudal region of MCZ 38294 (550 mm TL; Figure 17N), fewer than one percent of the denticles are morphotype trunk one and 79% of the denticles covering this region are from morphotype trunk two. The remaining 21% of the denticles are composed of morphotype trunk three. In specimens MCZ 38297 (650 mm TL) and MCZ 57703 (744 mm TL), both the abdominal and the caudal region lack morphotype trunk one denticles. In the abdominal region of MCZ 38297 (650 mm TL), 55% of the denticles are of morphotype trunk two and 45% are of morphotype trunk three; in the caudal region, morphotype trunk two comprises 40% and, morphotype trunk three, 60%. The branchial region of MCZ 38297 is covered by morphotype trunk one (29%) and trunk two (71%) only. In the abdominal region of MCZ 57703 (744 mm TL; Figure 17I), 88% of the denticles are of morphotype trunk two and 13% are of morphotype trunk three; in the caudal region, morphotype trunk two comprises 41% and, in trunk three, 59% (Figure 17O). The branchial region of MCZ 57703 (Figure 17C) is covered by morphotype trunk one (11%) and trunk two (89%) at this size. In sub-adults and adults (>830 mm TL), both the abdominal and the caudal region are entirely covered by denticles of morphotype trunk three (Figure 17J–L,P,R). Variation occurs only in the branchial region. From 800 mm TL to 900 mm TL, the branchial region is mostly covered by morphotype trunk (branchial) four. In MCZ 39621 (895 mm TL; Figure 17E), all the denticles examined are from morphotype trunk (branchial) four. In USNM 408586 (837 mm TL; Figure 17D), however, 92% of the denticles are from morphotype trunk (branchial) four, and the remaining 8% are from morphotype trunk three. In specimens larger than 950 mm TL, the denticles covering the branchial region were entirely replaced by morphotype trunk three, similar to the abdominal and caudal regions (NSMT-P 32586, 949 mm TL; Figure 17F).
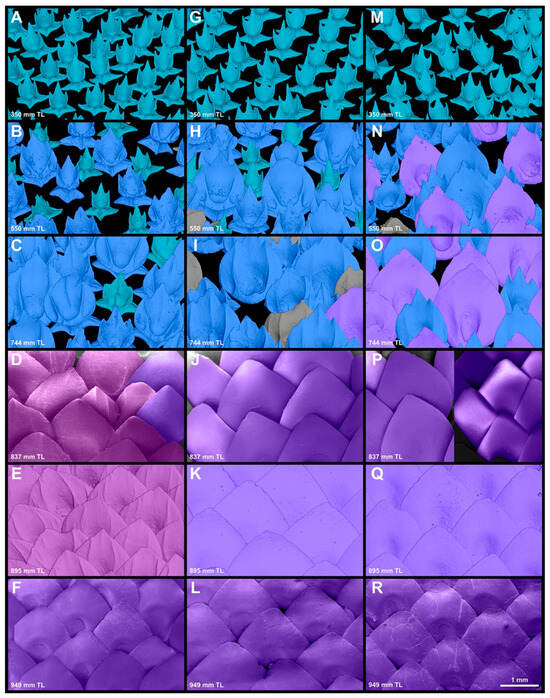
Figure 17.
Trunk-ontogeny and denticle-replacement patterns. The µCT scans and SEM images of denticle samples from the branchial, trunk, and tail region in Centroscymnus coelolepis. Individual denticles are colored according to morphotype. Light-blue denticles are morphotype trunk one, slate-blue denticles are morphotype trunk two, dark-purple denticles are morphotype trunk three, and fuchsia denticles are morphotype trunk four (branchial). Specimen sizes are organized by horizontal rows: (A,G,M) MCZ 132510, 350 mm TL. (B,H,N) MCZ 38294, 550 mm TL. (C,I,O) MCZ 57704, 744 mm TL. (D,J,P) USNM 408586, 837 mm TL. (E,K,Q) MCZ 39621, 895 mm TL. (F,L,R) NSMT-P 32586, 949 mm TL. Sample locations are organized by vertical columns: (A–F) dorsal to the first gill. (G–L) trunk, vertically aligned with the first dorsal spine. (M–R) trunk, vertically aligned with the second dorsal spine. Scale bar of 1 mm applies to all panels.
3.3. Size Variation within Each Dermal-Denticle Morphotype
The results from the linear regressions of the denticle-crown length versus the body length within each morphotype demonstrate that in the snout, both morphotype snout one and morphotype snout two have a significant positive correlation between crown length and body length, with p-values of 0.003 and 0.008, respectively, and R-correlation values of 0.58 and 0.63, respectively. Morphotype snout three does not have a significant correlation, displaying a p-value of 0.80 and an R-correlation value of 0.08. Morphotypes spiracular one, two, and three did not show significant correlations between their crown lengths and body lengths, with respective p-values of 0.2, 0.9, and 0.5, and R-correlation values of 0.30, 0.03, and 0.21. Denticles of morphotype spiracle four did not have sufficient data to fit a regression as they were only observed in one individual (895 mm TL). Morphotypes trunk one and three also did not show a correlation between crown length and body length, with p-values of 0.3 and 0.2, respectively; the R-correlation values for both morphotypes were 0.30. However, morphotype trunk two denticles showed a significant positive correlation between crown length and body length, with a p-value of <0.001 and an R-correlation value of 0.47. Since morphotype trunk four (branchial) denticles were only seen in one body length (895 mm TL), there were not sufficient data to run a regression.
3.4. Principal Component Analysis of Dermal-Denticle Morphotypes
Principal component analyses (PCA) facilitate comparisons of denticle-size and shape change across body location and ontogeny by collapsing the eleven denticle measurements (Figure 2) into a lower-dimension multivariate space. The PCA analysis also analytically reinforces the morphotype groupings described in Section 3.1. The first and second principal components captured the two axes with the highest percentage of variation. Therefore, they are presented in Figure 18, Figure 19 and Figure 20 (PCA plots for denticles on the snout, spiracle, and trunk regions, respectively).
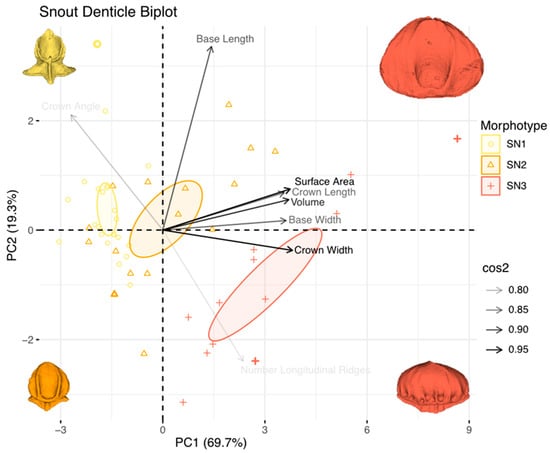
Figure 18.
Principal component analysis of snout denticles in Centroscymnus coelolepis. Point color and shape correspond to denticle morphotype: yellow circles are morphotype snout one, orange triangles are morphotype snout two, and coral-plus signs are morphotype snout three. Each point corresponds to a single denticle. The arrows show each measurement’s contribution to the PCA morphospace. The transparency of the arrows gives the assigned cos2 value with higher values, and darker colors showing a better representation of that variable by the first two principal components (PC1 and PC2). The denticle models in each corner of the graph are representative denticle shapes from each respective quadrant. The model corresponds to the enlarged marker in each quadrant. The 95% confidence ellipses are shown for each morphotype, and denticle-image color matches that shown in Figure 15.
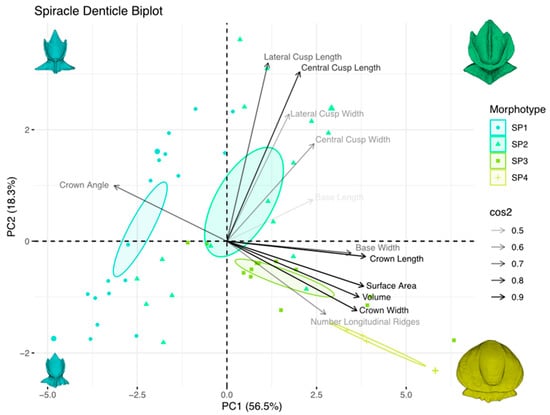
Figure 19.
Principal component analysis of spiracle denticles in Centroscymnus coelolepis. Point color and shape correspond to denticle morphotype: blue circles are morphotype spiracle one, blue-green triangles are morphotype spiracle two, light-green squares are morphotype spiracle three, and yellow-plus signs are morphotype spiracle four. Each point corresponds to a single denticle. The arrows show each measurement and its contribution to the PCA morphospace. The transparency of the arrows gives the assigned cos2 value with higher values, and darker colors showing a better representation of that variable by the first two principal components (PC1 and PC2). The denticle models in each corner of the graph are representative denticle shapes from each respective quadrant. The model corresponds to the enlarged marker in each quadrant. The 95% confidence ellipses are shown for each morphotype, and denticle-image color matches that shown in Figure 16.
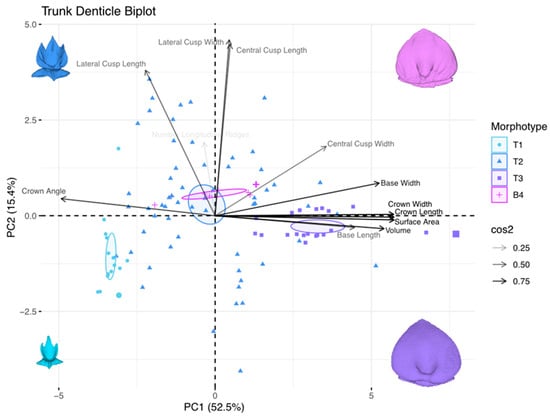
Figure 20.
Principal component analysis of trunk denticles in Centroscymnus coelolepis. The principal component analysis plot from denticle measurements collected from Centroscymnus coelolepis denticles from the trunk region. Point color and shape correspond to denticle morphotype: light-blue circles are morphotype trunk one, slate-blue triangles are morphotype trunk two, dark-purple squares are morphotype trunk three, and fuchsia-plus signs are morphotype trunk four (branchial). Each point corresponds to a single denticle. The arrows show each measurement and its contribution to the PCA morphospace. The transparency of the arrows gives the assigned cos2 value with higher values, and darker colors showing a better representation of that variable by the first two principal components (PC1 and PC2). The denticle models in each corner of the graph are representative denticle shapes from each respective quadrant. The model corresponds to the enlarged marker in each quadrant. The 95% confidence ellipses are shown for each morphotype, and denticle-image color matches that shown in Figure 17.
For the snout denticles (Figure 18), the first principal component accounts for 69.7% of the denticle-shape variation, while the second principal component accounts for 19.3% of the variation. Together, both axes account for 89% of the total shape variation. Lower PC1 values correspond to smaller denticles, and movement along PC1 reflects an increase in denticle size and crown growth. Along PC2, lower values represent rounder denticles with a lower crown angle, while denticles with higher PC2 values have larger crown angles and fewer longitudinal ridges. Variables including surface area, volume, and crown width, with crown length and base width, drive the change along PC1. Crown angle, base length, and the number of longitudinal ridges are variables that, while displaying low cos2 values, contribute to PC2. Morphotype snout one denticles have predominantly low PC2 values and zero-to-high PC1 values, which correspond to smaller denticles with high crown angles. Morphotype snout two denticles had higher PC1 values and a wide spread of values along PC2, ranging from smaller denticles with larger crown angles to medium- and larger-sized denticles with more longitudinal ridges. Morphotype snout three denticles showed a high PC1 value, mostly negative PC2 values, and a larger, rounder denticle shape with low crown-angle values and an increase in longitudinal ridges. The distribution of the points in the PCA shows substantial separation in morphospace among each of the three snout morphotypes (SN1, SN2, and SN3). Although there is some overlap, different morphotypes cluster separately in the snout-denticle morphospace, as shown by the 95% confidence ellipses, which occupy distinct locations in the multivariate space (Figure 18).
The PC1 of the denticles from the spiracular region (Figure 19) accounts for 56.5% of the measurement variation, while PC2 accounts for 18.3%. Together, the two axes explain 74.8% of total spiracular denticle variation. The shape change along PC1 is size-dependent, with smaller denticles having lower PC1 values and larger denticles displaying higher PC1 values. The crown length, crown width, volume, surface area, base width, and number of longitudinal ridges are positive on PC1, and in the negative PC2 quadrant. Crown angle is negative in PC1 and loads positively on PC2. The lateral cusp length, lateral cusp width, central cusp length, central cusp width, and basal-root length all load positively on PC1 and PC2 in the morphospace. Morphotypes spiracular one and two have low PC1 values and a wide spread of values along PC2, corresponding to smaller denticles with high crown angles and lateral and central cusps. Morphotypes spiracular three and four have high PC1 and a low PC2 values, reflecting a shape change in the crown, base, and overall growth, an increase in the longitudinal ridges, and the eventual loss of posterior cusps. Despite some overlap between individual denticles, different morphotypes cluster at different locations in the morphospace, as indicated by the 95% confidence ellipses (Figure 19).
The denticles from the branchial, trunk, and tail regions show size variation along PC1 similar to both the snout and spiracle regions, with smaller denticles positioned in the left quadrants of the morphospace and larger denticles in the right quadrants of the PC1 axis (Figure 20). The PC1 explains 52.5% of the total measurement variation, and PC2 explains 15.4%; combined, they explain 67.9% of the trunk-denticle-shape variation. The variables that contribute to the shape change along PC1 are the crown angle, central cusp width, base length and width, crown measurements, surface area, and volume. Along PC2, lateral and central cusp measurements drive the differences in shape, along with the number of longitudinal ridges. Small, tricusped denticles with large crown angles (morphotype trunk one) are positioned in the left (negative) quadrants of PC1. Morphotype trunk two denticles are spread around all quadrants of both PC1 and PC2, reflecting the wide range of crown shapes observed in this morphotype (Figure 11). The largest, oval-shaped, non-cusped denticles with small crown angles (morphotype trunk three) are found in the positive quadrants of PC1. Morphotype trunk four (branchial) denticles are clustered with low PC1 and low PC2 values. There is a high level of clustering in the morphospace of morphotypes trunk one, three, and four (branchial). Morphotype trunk two, however, is widespread throughout the morphospace.
3.5. Denticle Scaling
The results of the scaling regressions are presented in Table 4. The denticle surface area, volume, crown length, basal root length, and basal-root width all show negative allometry. The crown width, conversely, shows slight (although not statistically significant) positive allometry. The scaling plots for these measurements can be found in Figure 21. The regression fits for the log of the surface area and the log of the volume against the log of the body length show slopes of 1.38 and 2.23, respectively. The observed slopes are both less steep than is expected for isometric growth (Table 2: a slope of two for surface area, and a slope of three for volume); they therefore show strong negative allometry. The dermal denticle surface area and volume in the samples measured thus increase less than expected from the isometric growth over the ontogeny. If the denticles were to grow isometrically, variables like crown and base length and width would be expected to have a slope of 1.0 when plotted against the body length. The crown length is also negatively allometric, with a slope of 0.81. The denticle base length and width both show strong negative allometry, with slopes of 0.12 and 0.47, respectively (Table 4). The near-zero slope for the basal-root length shows that this denticle measurement is nearly constant as Centroscymnus coelolepis increases in total body length.

Table 4.
Scaling results from the linear regression of the common logarithm of the measurement against the common logarithm of total length.
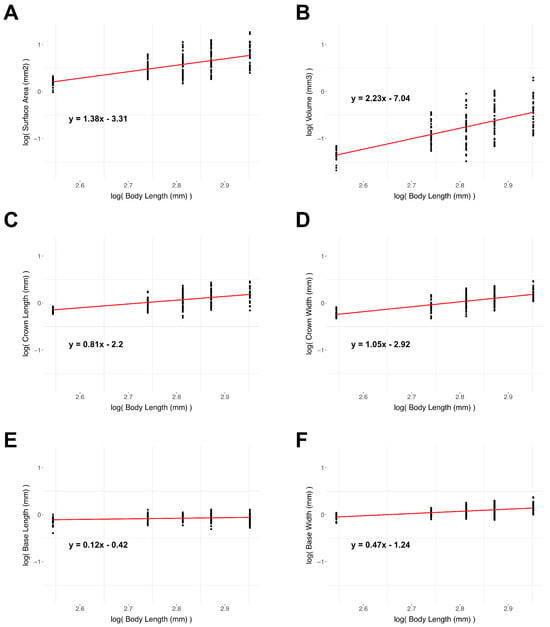
Figure 21.
Scaling plots of denticle dimensions. Scaling plots showing how six denticle measurements change with body length based on µCT-scanned denticles of Centroscymnus coelolepis. Linear regressions are shown in red with the corresponding equation above. Table 2 provides further data on these regressions. (A) Plot of the logarithm of surface area versus the logarithm of body length. (B) Plot of the logarithm of volume versus the logarithm of body length. (C) Plot of the logarithm of crown length versus the logarithm of body length. (D) Plot of the logarithm of crown width versus the logarithm of body length. (E) Plot of the logarithm of base length versus the logarithm of body length. (F) Plot of the logarithm of base width versus the logarithm of body length. Most denticle variables show negative allometry (see text for further discussion).
4. Discussion
Research on elasmobranch placoid scales or dermal denticles has grown considerably in recent years, following the pioneering studies by Reif [17,25,48], who first explored in depth the diversity of shark denticles. Since then, researchers have continued to document denticle diversity, emphasizing differences in morphology around the body [15,20,49,50,51,52], using differences between dermal denticles to make inferences in terms of taxonomy and systematics [7,28,53], constructing biomimetic models of denticles [54,55], and testing shark-skin-like surfaces for their propulsive and hydrodynamic functions [22,23,56,57]. In addition, shark denticles have served as a means of understanding shark-community structures [58,59]. Sibert and Rubin [16] used dermal denticles as vehicles for studying changing abundances of sharks through geological time. The use of solitary denticles, however, incurs the risk of overestimating the extent of interspecific variation due to the diversity of denticle morphotypes, which vary considerably during ontogeny and around the body, as suggested by other authors [60,61], as well in our study. Denticles can be present around the eye [62] and inside the mouth [20,63], and the homology of denticle and tooth developmental patterning is a recent focus of analyses of gene-expression patterns [64,65].
As research continues, the extent of known denticle diversity expands, and what we term the “denticle multiverse” grows as new axes of structural and functional variation are uncovered. However, one area that has not been actively studied is ontogenetic change in denticle morphology and patterning. How do skin denticles around the shark body change during growth? We know that denticles are shed and replaced in adult sharks [27,51], but few authors have considered that variation during ontogeny could be more extensive than interspecific variation, and that changes in denticle shape and size around the bodies of adult sharks could themselves be highly ontogenetically variable.
The overall goal of this paper is to document the dramatic ontogenetic changes we observed during growth in the somniosid Portuguese Dogfish shark (Centroscymnus coelolepis). Ontogenetic changes in denticle morphology at different locations around the body are so extensive in this species that they necessitated the development of nomenclature (morphotypes) and the use of statistical approaches, such as principal components analysis, to describe this variation. Furthermore this extensive ontogenetic denticle variation has considerable implications for taxonomy when considered within the context of other species within the family Somniosidae.
4.1. Denticle Morphology in Centroscymnus coelolepis
The variability of the dermal denticles of Centroscymnus coelolepis has intrigued ichthyologists through history. Bigelow et al. [43] examined three juvenile specimens of Centroscymnus coelolepis (MCZ 37420, MCZ 37424, MCZ 37452) and observed the presence of dermal denticles bearing crowns with three posterior cusps. At the time of Bigelow et al.’s study, dermal denticles with tricuspidated crowns were thought to be present exclusively in the genus Scymnodon [36,37], leading these authors to not only describe these individuals as a new species (i.e., Scymnodon melas), but also to allocate this putative new taxon to the genus Scymnodon. A year later, however, Bigelow and Schroeder [29] had access to a gravid female of Centroscymnus coelolepis with late embryos, and they were able to compare late embryos of this species with an adult specimen. Bigelow and Schroeder [29] were not only able to observe the occurrence of distinct dermal denticles among embryos, juveniles, and adults (confirming a brief observation made by Tortonese, [66]), but they were also able to determine that their recently described new species, Scymnodon melas, was actually a junior synonym of Centroscymnus coelolepis. Bigelow and Schroeder [29] also provided a brief description and illustration of the ontogenetic variation of dermal denticles on the trunk of C. coelolepis. These accounts, however, were limited because of the low size range of their sample, which was focused on a single topological location (the vertical middle of the trunk, aligned with the first dorsal fin). A complete description of the ontogenetic variation in the dermal denticles of Centroscymnus coelolepis eluded researchers for years, given the difficulty in obtaining a complete ontogenetic series. C. coelolepis is a deep-water species, and it is not commonly caught in either commercial or research fleets. Therefore, the scarcity of specimens in museums (in comparison to coastal species) led previous studies to focus mostly on the dermal denticles of adults e.g., [9,67]. Now, after a decade-long endeavor that included visits to multiple museums around the globe, in conjunction with the incorporation of CT-scanning and SEM techniques, we can now describe the considerable extent of the ontogenetic morphological variation in dermal denticles in C. coelolepis. This new dataset not only reveals morphological variability, but also allows new taxonomic and systematic inferences similar to those as described by White et al. [33,34,35].
4.2. Denticles and the Taxonomy of Centroscymnus coelolepis and C. owstonii
The close phylogenetic relationship between Centroscymnus coelolepis and C. owstonii and the recognition of these taxa as two distinct species is widely accepted in the literature [4,5,6,9,11,32,36,37,38,67,68,69,70,71,72]. One of the previous characteristics based on dermal denticle morphology used to distinguish these two species was relative size, since the placoid scales of Centroscymnus coelolepis are larger than those from C. owstonii [6,38,67,68]. The present study, continuing from the studies from Vaz [8] and Weigmann et al. [6], confirmed that not only adults, but also juveniles of Centroscymnus coelolepis larger than 550 mm TL have denticles on the trunk and tail that are 1.5–2.0 times larger than those from C. owstonii (Figure 22).
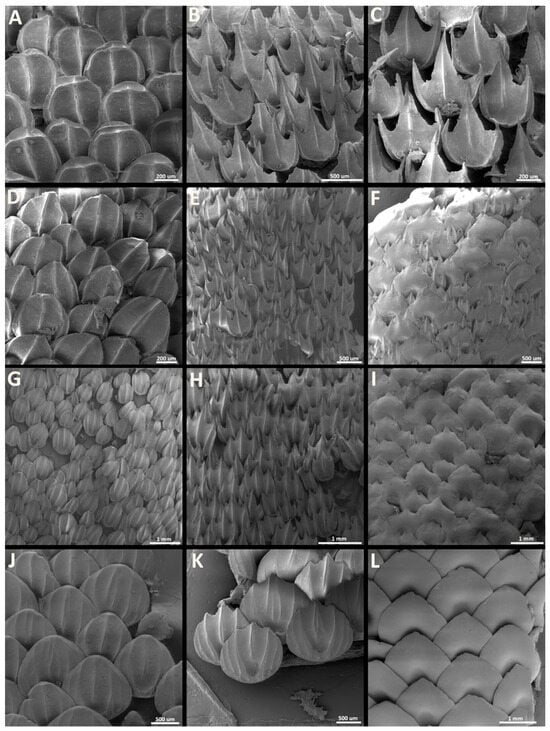
Figure 22.
Morphological diversity and ontogenetic variation of dermal denticles in Centroscymnus owstonii. Columns depict different locations on the body. (A,D,G,J) dorsal snout; (B,E,H,K) dorsal to the first gill; (C,F,I,L) middle of the tail, aligned with the base of the second dorsal fin. Lines represent specimens. (A–C) MCZ 35038 (280.2 mm TL). (D–F) MNHN 1989 0654 (525 mm TL). (G–I). TMFE 577 (659 mm TL). (J–L) BMNH 1973.7.9.9 (1071 mm TL).
Cadenat and Blache [32], Yano and Tanaka [9], Last and Stevens [71], and Weigmann et al. [6] proposed that denticles dorsal to the gill-arch apertures and in the trunks of C. coelolepis lack posterior cusps in the posterior edge of the crown, whereas C. owstonii has cuspidated denticles in this region (Figure 22). Our series of examined materials also revealed this feature to be distinctive between these species. Cadenat and Blache [32], Compagno [70], and Last and Stevens [71], however, considered that all denticles of adults of C. coelolepis are smooth, without ridges. We, conversely, demonstrated that, not only in adults, but throughout growth, most of the head of C. coelolepis is covered by denticles, with three or more (up to nine) ridges in their crowns (Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 15 and Figure 16).
Yano and Tanaka [9] proposed that adults of Centroscymnus coelolepis have dermal denticles with rounded crowns on the head, similar to those on the trunk, whereas the head of C. owstonii supports denticles with tridentate margins and three to five longitudinal ridges. Yano and Tanaka [9], however, generalized their observations from the region dorsal to the first branchial aperture to the entire head ([9], Figure 6). We demonstrate here that adults from both species of Centroscymnus have rounded crowns bearing three to nine longitudinal ridges around the snout, mouth, and spiracular region (Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 15, Figure 16 and Figure 22), similar to those described for Centroscymnus owstonii by Rincon et al. ([47], Figure 7A,B). The variation between C. coelolepis and C. owstonii occurs only in the region dorsal to the branchial apertures. Indeed, adults of Centroscymnus owstonii have denticles bearing crowns with three posterior cusps in the region dorsal to the branchial apertures, with three to five longitudinal ridges (Figure 22K), whereas adults of Centroscymnus coelolepis have the region dorsal to the branchial apertures supporting denticles with rounded crowns, similar to described by Yano and Tanaka [9] (Figure 17D–F). The surfaces of the crowns of the denticles in the region dorsal to the branchial apertures, however, is variable in adults of C. coelolepis. In smaller adults (up to 950 mm TL), crowns of denticles might have six to nine longitudinal ridges, which are distinct from the trunk and tail denticles, which have smooth surfaces. Denticles with triangular crowns and smooth surfaces in the region dorsal to the branchial apertures, similar to those on the trunk, are present only in larger adults of C. coelolepis (larger than 950 mm TL; Figure 17D–F).
Weigmann et al. [6] described denticles dorsal to the branchial region of C. coelolepis with one pair of lateral ridges. This statement, however, was based on the use of scanning-electron microscopy, which often does not allow the visualization of parts of denticles that overlap with adjacent denticles. The use of computed tomography scanning allowed the examination of individual denticles of C. coelolepis, including the regions that overlap with nearby denticles. This technique demonstrated that the branchial denticles of adult Centroscymnus coelopis can have up to four pairs of longitudinal ridges, rather than only one pair, as suggested by Weigmann et al. [6]. We also demonstrated that the crowns of denticles with longitudinal ridges dorsal to the branchial region are present only in the smallest adults. Specimens larger than 950 mm TL have branchial denticles with smooth crowns, similar to those observed in the trunk and tail (NSMT-P 32586; Figure 17F). Rincon et al. [47] describe the trunk of adults of C. owstonii, at the level of the first dorsal fin, with denticle crowns bearing up to 12 posterior cusps. This feature was not observed in any of our samples (which included UERJ 1634). Such high number of cusplets seems to be an anomaly. Similar to C. coelolepis, C. owstonii oval trunk denticles with three to five posterior cusps (morphotype trunk two; Figure 22F,I) are replaced by denticles without cusps, with their posterior margins, when present, bearing only small indentations (Figure 22L; similar to the description, by Rincon et al. [47], of denticles on the lateral line).
A potential new characteristic that allows the distinction between juveniles up to 525 mm TL of Centroscymnus coelolepis and C. owstonii is the crown ratio of the denticles in the dorsal region of the snout. In most examined denticles from C. coelolepis, the crown ratio ranges from 0.8 to 1.0, with a single denticle displaying a ratio of 1.1. Most of the examined denticles from the dorsal region of the snout in C. owstonii have a ratio higher than one, varying from 1.0–1.2 (Figure 22A,D). The effectiveness of this characteristic, however, needs to be assessed with three-dimensional data, as the crown-ratio measurements of the C. owstonii were taken from two dimensional images.
4.3. Monophyly of Centroscymnus: Additional Support from Dermal Denticles
The composition of the genus Centroscymnus has varied through time [18,31,36,38] and, currently, only two species are included in this genus: Centroscymnus coelolepis and C. owstonii [4,7,8,11,72,73]. One of the features previously used to support the argument for the close relationship among these two species was the morphology of the dermal denticles from the trunk and tail of adults, which have large oval crowns with smooth dorsal surfaces, and an anterior circular cavity and lacking longitudinal ridges [5,7,38,47]. The phylogenetic hypotheses of Naylor et al. [1], Straube et al. [2], and Silva and Vaz [74], however, consistently recover the genus Centroscymnus as a polyphyletic assemblage.
The data presented here, conversely, present additional morphological features shared by Centroscymnus coelolepis and C. owstonii that further suggest their monophyly. At 550 mm TL, the tail of Centroscymnus coelolepis presents denticles with large, oval crowns, classified here as morphotype trunk three (Figure 17). In specimens of Centroscymnus owstonii of a similar size (MNHN 1989 0654, 525 mm TL; Figure 22F), a large denticle, with wide, rounded crowns, lacking longitudinal ridges and bearing an anterior, circular cavity is present in similar proportions to morphotype trunk three in C. coelolepis. The change in replacement observed in larger specimens is also similar across these two species. On specimens of C. owstonii HUMZ 101723 (627 mm TL) and TMFE 577 (659 mm TL; Figure 22I), the proportions of denticles similar to those from morphotype trunk three are close to those observed in MCZ 38297 (650 mm TL). Therefore, both species not only share this morphologically unique dermal denticle (morphotype trunk three) on the trunks and tails of adults, but they also share similar rates of denticle replacement across ontogeny.
4.4. Ontogenetic Variation and Phylogenetic Inference within the Family Somniosidae
The family Somniosidae currently comprises six genera: Somniosus, Centroscymnus, Scymnodon, Centroselachus, Scymnodalatias, and Zameus [4,5]. Their interrelationships are not entirely clear, and the monophyly of this family was previously questioned [1,2,74]. Dermal-denticle morphology was used in the past for inferring phylogenetic relationships between sleeper sharks [18,31]. As previously mentioned by Bigelow and Schroeder [29], a large series of specimens is needed to properly assess the phylogenetic signal, not only for dermal-denticle morphology, but for any character in general [75]. The examination of complete ontogenetic series allows the recognition of new morphological characters that are potentially phylogenetically informative.
Somniosus is unique among genera of Somniosidae in having conical denticle crowns, without a pair of lateral posterior cusps, and for having a broad crown peduncle, continuous with the tip of the crown. In Centroscymnus, Scymnodon, Centroselachus, Scymnodalatias, and Zameus, denticles have peduncles that are narrower than the crown width throughout the ontogeny (Figure 23). The determination of the apomorphic state, however, is highly dependent on the phylogeny, as similar variations occur intragenerically across the diversity of Squaliformes. The phylogenetic hypothesis by Silva and Vaz [74] recovered a polyphyletic Somniosidae, with species of Somniosus established as the sister group of a clade formed by species of Squaliolus and Euprotomicrus. The remaining species of Somniosidae and Oxynotus form a monophyletic group, which is a sister of the clade comprising species of Etmopteridae. Assuming the hypothesis proposed by Silva and Vaz [74], the conical crowns shared by species of Somniosus could be a putative synapomorphy supporting the monophyly of this genus. Euprotomicrus and Squaliolus have rectangular crowns (with independent occurrences in other Dalatiinae and some species of Etmopteridae [32,76]). Denticles with crown widths 1.5–2.0× wider than the width of the peduncle are shared by Centroscymnus, Scymnodon, Centroselachus, Zameus, and Scymnodolatias, and this feature could be a putative synapomorphy, suggesting the close relationship among genera, with a reversion in Oxynotus. Although a combined analysis is needed to properly assess the optimization of these characters, denticle morphology shows potential for supporting the non-monophyly of Somniosidae, as suggested by Naylor et al. [1], Straube et al. [2], and Silva and Vaz [74].
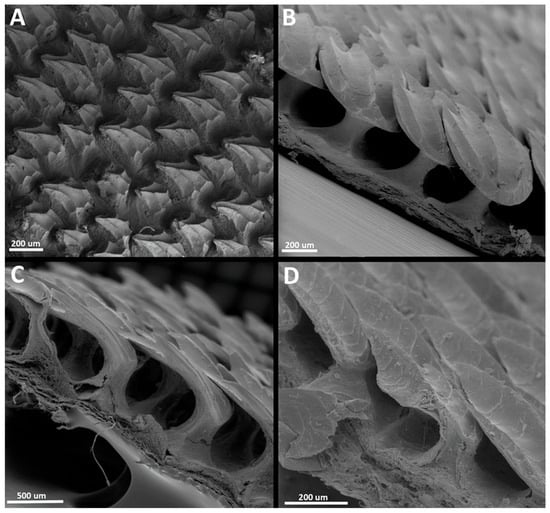
Figure 23.
Denticle-peduncle morphology across Somniosidae. (A,C) Posterolateral view of dermal denticles on the region dorsal to the first branchial aperture. (B,D) Posterolateral view of dermal denticles on the middle of the trunk, vertical to the base of the first dorsal fin. A. Somniosus cf. rostratus MZUSP uncatalogued (1090 mm TL). Note the broad peduncle. (B) Centroselachus crepidater MNHN 1998 1299A (768 mm TL). (C) Scymnodon ringens BMNH 1987.1.21.86 (674 mm TL). (D) Zameus squamulosus USNM 220489 (532 mm TL).
Within Somniosidae, denticle ontogeny along distinct denticle developmental trajectories (morphotypes) is a feature shared by species of Centroscymnus, Scymnodon, and Centroselachus. In addition to Centroscymnus coelolepis, the first denticle morphotype to appear on the trunk of small juveniles (usually smaller than 400 mm TL) of Centroscymnus owstonii, Scymnodon macracanthus, Scymnodon ringens, Scymnodon ichiharai (see [10]), and Centroselachus crepidater is morphologically similar to the morphotype trunk one described here for Centroscymnus coelolepis (Figure 10 and Figure 17A,G,M). The crowns of the denticles in these juveniles have three elongated posterior cusps (Figure 24), with the central cusp extending anteriorly to approximately half or more of the crown length (in C. coelolepis, 0.4–0.5 of the crown length; two-thirds in S. ringens; Figure 10 and Figure 17A,G,M). The crowns of the denticles of the adults in the Scymnodon species are leaf-shaped (Figure 23 and Figure 24; see also [7,10]); in Centroscymnus, crowns are oval-shaped without longitudinal ridges (Figure 13, Figure 17 and Figure 22); and in Centroselachus, the crown is also oval, but bears five longitudinal ridges (Figure 24G). In Zameus, Scymnodalatias, and Somniosus, the crowns of the denticles are morphologically similar throughout the ontogeny (Figure 25; see also Taniuchi and Garrick [18]) and have short central cusps (Zameus: 0.22 times the crown length; Scymnodalatias: 0.34 times the crown length; Somniosus lacks posterior cusps).
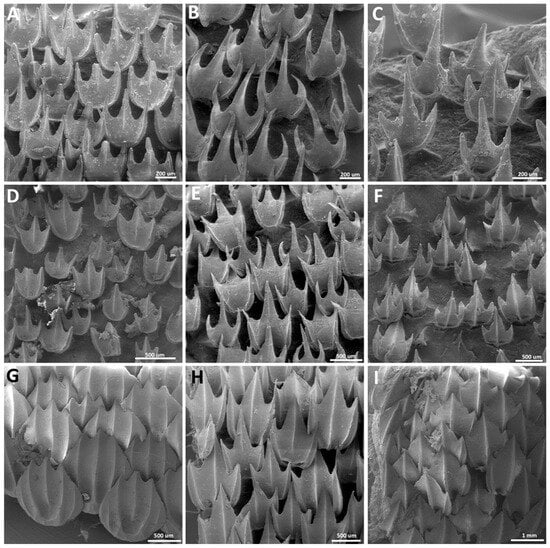
Figure 24.
Ontogeny of dermal denticles on the trunks of species of Centroselachus and Scymnodon. (A,D,G) Centroselachus crepidater AMNH 58099 (297 mm TL; (A)), USNM 408581 (525 mm TL; (D)), and MNHN 1998 1299 (768 mm TL; (G)). (B,E,H) Scymnodon ringens BMNH 1991.7.9.690 (317 mm TL; (B)) BMNH 1991.7.9.688 (518 mm TL; (E)), BMNH 1987.1.21.86 (674 mm TL; (H)). (C,F,I) Scymnodon macracanthus MNHN 2008 1916 (582 mm TL; (C)), MNHN 2003 1708 (691 mm TL; (F)), NSMT-P 32079 (1179 mm TL; (I)). Note in (A–C) (small juveniles) that samples consist only of denticles from morphotype one, which are replaced by morphologically distinct denticles in larger juveniles and adults (D–I).
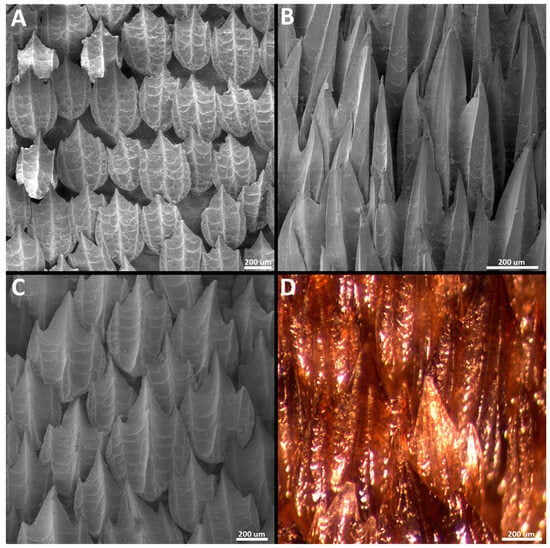
Figure 25.
Dermal-denticle morphology in the tail region with growth in specimens of Zameus squamulosus (A,C) and Scymnodalatias spp. (B,D). Note the lack of morphological differences among denticles except for relative size. A. Zameus squamulosus USNM 220496 (juvenile, 341 mm TL). (B) Scymnodalatias cf albicauda HUMZ 129360 (embryo, aprox. 160 mm TL). (C) Zameus squamulosus USNM 220489 (adult, 532 mm TL). (D) Scymnodalatias cf. garrick 122774 (juvenile, 417 mm TL).
The available accounts of dermal-denticle morphology in other Squaliformes species suggest that most of the genera from this order present little ontogenetic variation in denticle morphology [32,37,38,43]. The main exception is the genus Centrophorus. In this genus, juveniles of Centrophorus longipinnis and C. leslei have dermal denticles with distinct peduncles and elongated, elliptically shaped crowns, whereas the denticles of adults have short peduncles and broad, tear-drop-shaped crowns [32,34]. In Centrophorus uyato, juveniles have pyramidal crowns, with short and broad peduncles, which are gradually replaced by denticles with wider and flatter crowns, resulting in a tear-drop shape [35]. The dermal denticles of adults of Centrophorus granulosus are similar to those from the other species of Centrophorus, but the juvenile denticles have distinct, broad pedicels and tricuspidate crowns, similar to morphotype trunk one, described herein, in Centroscymnus coelolepis [33]. Assuming the phylogenetic hypothesis presented by Silva and Vaz [74], juveniles bearing dermal denticles with tricuspidate crowns (i.e., morphotype trunk one) that are replaced with distinct denticles in the later stages of ontogeny could be considered a putative synapomorphy for the clade, including Centroselachus, Zameus, Centroscymnus spp., Scymnodon spp., and Oxynotus, with reversions in Zameus, Oxynotus, and an independent occurrence in Centrophorus granulosus. A similar optimization was recovered when mapping this character in the phylogenetic hypothesis by Naylor et al. [1].
Additionally, Zameus and Scymnodalatias both present microreliefs (i.e., transverse ridges) among the longitudinal ridges of their crowns (Figure 25; see also [18]). No other species of Somniosidae and none of the other squaliform sharks examined have microreliefs among the longitudinal ridges of the crowns of the dermal denticles that can be interpreted as a potential synapomorphy, suggesting the monophyly of Zameus and Scymnodalatias, as previously proposed by Taniuchi and Garrick [18].
4.5. Denticle Replacement and Function
Shark-skin denticles are extremely diverse in size and shape, and our results on denticle ontogeny in Centroscymnus coelolepis expand the boundaries of the denticle multiverse by showing that considerable changes in spacing, size, crown-ridge number and morphology, and base shape can all occur within a single individual during growth. These changes most likely occur through denticle replacement and the eruption of new denticles in the gaps between existing denticles as sharks grow through ontogeny. Dillon et al. [27,59] have shown that shark denticles are shed through time and can be collected from both sediments on the ocean floor and the bottoms of laboratory tanks holding captive sharks. Sibert and Rubin [16] recovered shark denticles from deep-sea sediment cores, used them to reconstruct shark abundances through time, and identified a Miocene shark-extinction event. Thus, denticles must be shed from the skin, and Popp et al. [51] were able to observe the process of denticle replacement in skin samples from adult thresher sharks. Replacement denticles can be seen emerging from below the epidermis into the gap formed by a shed denticle, and examination of the skin surface reveals numerous gaps between denticles that have been previously shed [51].
What are the functions of this diversity of shark-skin denticles in general and of the different denticle morphotypes identified here specifically? Most researchers have suggested that shark-skin denticles function by reducing drag forces and, hence, they reduce the effort of swimming through the water [77,78,79,80]. Furthermore, experimental evidence strongly suggests that longitudinally arranged denticle ridges can function in a similar manner to engineered riblets, which are known to reduce drag [81,82,83]. In addition, the close packing of denticles in many adult pelagic sharks (e.g., [49]) may create a smooth hydrodynamic surface with exposed riblets, which can further reduce drag. One additional aspect of denticle function has been demonstrated by testing shark-skin surfaces and biomimetic models in a robotic propulsive device [22,54,55,56,57]: shark denticles can act not only to reduce drag, but also to increase thrust and, thus, enhance propulsion by altering the attachment of leading-edge vortices on the posterior body and tail.
While these hypothesized functions of shark denticles could be reasonable for the adult denticles observed here in Centroscymnus coelolepis, where the skin surface is covered with closely-spaced denticles with few gaps (e.g., Figure 15E,I; Figure 16E,F; Figure 17K,L,Q,R), hydrodynamic explanations would seem unlikely for skin denticle patterns early in ontogeny. At that time, denticles are spaced more widely, there are noticeable gaps in the denticle field (e.g., Figure 17E,G), and denticle crown angles are large relative to adults and the posterior cusp points project away from the skin surface and into the water flowing over the body. Such denticle configurations would be better suited to another function such as deterring predation by cephalopods by limiting attachment of arm suckers. Smaller and slower moving C. coelolepis may be more vulnerable to attack by predators that attempt to attach to or grab the body, and denticles with sharply pointed cusps and projecting crowns may limit the extent to which individual suckers can attach.
One noteworthy result of our analysis of denticle ontogeny is the negative scaling that we observed between surface area, volume, and linear measurements with the sole exception of denticle crown width which scales nearly isometrically. At present, no other studies of denticle scaling are available for comparison to these data, but previous studies of shark body scaling reveal that many aspects of shark body shape scale isometrically, with negative allometry observed only for some aspects of tail shape [84]. Irschick et al. [85] concluded that for eight shark species, large sharks are in general geometrically similar to smaller individuals based on 12 linear measurements that captured overall body and tail shape characteristics.
Gayford et al. [86] studied body scaling in the brown smoothhound shark Mustelus henlei and observed a mixture of positive and negatively allometric linear variables, with five linear body measurements scaling isometrically, and tail measurements displaying negative allometry. Regions showing positive allometry include body width (span) at the pectoral fin location, and the circumference of the caudal peduncle.
The scaling relationships of denticles observed here may reflect the necessity of packing denticles onto the skin surface as sharks grow and the relative increase in crown surface area which results in a nearly complete covering of the skin by denticle crowns in large individuals. Denticle bases may be constrained in how much they can grow given the relative expansion of crown surfaces in adults which overlap with adjacent denticles. Denticle bases remain separate from nearby denticle bases despite the overlap of the crowns of these same denticles.
5. Conclusions
We discovered considerable variation in denticle shape through ontogeny in the squaliform shark Centroscymnus coelolepis, which has eleven distinct morphotypes that are expressed during development and in different regions on the body. The extent of this variation is larger than most of the currently described interspecific differences in denticle shape and size. Three distinct regions of the body of C. coelolepis have denticle replacement in a distinct series of morphotypes across ontogeny: the snout, spiracular, and trunk regions (the latter ranging from the gill openings to the tail). Within the trunk region, replacement to the end point of larger denticles of the same morphotype or to distinct morphotypes occurs in a tail-to-head direction, with juvenile specimens possessing larger denticles and with morphotypes trunk two and three being the most common in the tail, whereas the branchial region of the same specimen presents large percentages of morphotype trunk one.
Smaller adults (830–950 mm TL) of Centroscymnus coelolepis have a transitory denticle morphotype on the surface dorsal to the branchial apertures (morphotype trunk four). In adults larger than 950 mm TL, the branchial region is replaced by denticles from morphotype trunk three, which is similar to the remaining regions of the trunk and tail. The growth in the dermal denticles of Centroscymnus coelolepis is negatively allometric with the denticle-surface area, volume, crown length, basal-root length, and basal-root width, with lower-than-isometric scaling exponents. The scaling equation for the basal-root length shows that the basal-root length is nearly constant as the body length increases. The crown width, conversely, shows slight positive allometry.
Centroscymnus coelolepis shares with Centroscymnus owstonii the presence of denticles from morphotype three in the trunk and tail regions. These species also share similar rates of denticle replacement across morphotypes through ontogeny. Centroscymnus coelolepis shares with Centroscymnus owstonii, Centroselachus crepidater, Scymnodon ringens, Scymnodon macracanthus, and Scymnodon ichiharai the presence of denticle morphotype trunk one in the branchial, trunk, and tail regions of its juveniles.
While the functional significance of the dramatic changes in denticle size and shape during ontogeny in C. coelolepis is unknown, we hypothesize that the denticles of smaller individuals have a primarily anti-predator function, while adult denticles may function to reduce drag and the cost of swimming. Future analyses are needed to demonstrate the extent to which this high level of ontogenetic variation among denticles is common among Squaliformes and other shark orders.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d15111105/s1. S1, Table of Raw Individual Denticle Dataset. S2, R script of statistical analysis. S3, Figure with global PCA of all denticle morphotypes.
Author Contributions
D.F.B.V. conceived and outlined the study, collected samples from museums, prepared and examined materials for S.E.M. D.F.B.V., T.M.A. and M.K.G.-S. prepared, examined, and analyzed the data obtained with µCT scanning. D.F.B.V., T.M.A., M.K.G.-S. and G.V.L. wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
D.F.B.V. was funded by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq Processo 155593/2012-9), Fundação de Amparo e Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP 2012/07712-3, 2013/13137-4), and the E. O. Wilson Biodiversity Postdoctoral Fellowship at the Museum of Comparative Zoology, Harvard University. D.F.B.V. is currently funded by NSF Guam EPSCoR (OIA-1946352). M.K.G. was supported by NSF PRFB1907211, and M.K.G. and T.M.A. are supported by NSF IOS-2128033 N00014-23-1-2684 to G.V.L.
Institutional Review Board Statement
No animal experiments were performed, and no specimens were collected for this study. All examined specimens and samples were obtained from material previously deposited in natural history museum collections.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the results of this manuscript are available through direct (and reasonable) request to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Enio Mattos and Phillip Lenktaitis are thanked for SEM support. The following museum curators and staff are greatly thanked for access to specimens: N. Menezes, H. Britski, J. Figueiredo, M. Pinna, A. Datovo, O. Oyakawa, and M. Gianetti (MZUSP); U. Gomes and H. Santos (UERJ); M Britto, P. Buckup, and C. Moreira (MNRJ); R. Vari (in memory), C. Baldwin, J. Williams, S. Raredon, K. Murphy, D. Pitiassy, and J. Clayton (USNM); L. Page, G. Burgess, R. Robins, and Z. Randall (FLMNH); K. Hartel, A. Williston, and M. Sorce (MCZ); J. Sparks, M. Stiassny, B. Brown, R. Arrindel, and R. Schelly (AMNH); D. Catania and John Fong (CAS); O. Crimmen and J. Maclaine (BMNH); R. Thiel, I. Eidus, and S. Weigmann (ZMH); B. Serét, P. Pruvost, Z. Gabsi, and C. Ferrara (MNHN); W. White and A. Graham (CSIRO); M. Nakae, G. Shinohara, and K. Matsuura (NSMT); M. Yabe and Toshio Kauai (HUMZ); and Sho Tanaka (TMFE). Lastly, the first author is immensely thankful to the Polynesian civilizations who invented surfing hundreds of years ago: this is the only thing that keeps him sane. And for his rescue dog, Sting, the reason he wakes up every morning.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Appendix A. Complete List of Examined Specimens
Family Somniosidae (526 specimens)
Centroscymnus coelolepis. AMNH 78261, adult female, 1104 mm TL, North Atlantic Ocean, Mid-Atlantic Ridge, Westward of Rift Valley, 46°50.6′ N, 27°35.5′ W; AMNH 259393, adult female, 892 mm TL, North Atlantic, MARE 86, N° data; AMNH 78251, adult male, 901 mm TL, depth 880 m, Canary Islands, Eastern North Atlantic, 28°19.2′ N, 16°16.0′ W; AMNH 59843, juvenile male, 626 mm TL, Namibia, Eastern South Atlantic, 23°02′ S, 12°45′ E; AMNH 78197, adult female, 1039 mm TL, Canary Islands, Eastern North Atlantic, 28°16.5′ N, 15°32.2′ W; AMNH 78182, adult female, 1019 mm TL, Canary Islands, Eastern North Atlantic, 28°22.3′ N, 16°12.95′ W; AMNH 78189, adult female, 1025 mm TL, Canary Islands, Eastern North Atlantic, 28°16.5′ N, 15°32.2′ W; AMNH 78254, adult female, 986 mm TL Canary Islands, Eastern North Atlantic, 28°16.5′ N, 15°32.2′ W; AMNH 78194, adult male, 883 mm TL, Canary Islands, Eastern North Atlantic, 28°16.5′ N, 15°32.2′ W; AMNH 78253, juvenile male, 684 mm TL, Canary Islands, Eastern North Atlantic, 28°16.5′ N, 15°32.2′ W; AMNH 78195, adult male, 831 mm TL, Canary Islands, Eastern North Atlantic, 28°16.5′ N, 15°32.2′ W; AMNH 78190, adult female, 974 mm TL, Canary Islands, Eastern North Atlantic, 28°16.5′ N, 15°32.2′ W; BMNH 1880.9.14:71, adult female 1059 mm TL, 42°40′ N, 53°50′ W, 100 m depth; BMNH 1982.12.10:3, juvenile female 802 mm TL, off West Coast of France, 48°21′ N, 10°24′ W; BMNH 1998.2.12:45, juvenile male 734 mm TL, Eastern Central Atlantic, 29°20.24.000 N, 12°35.6.000 W; BMNH 2013.9.20.1, adult male 905 mm TL, Northeastern Atlantic; BMNH 2013.9.20.2, adult male 965 mm TL, Northeastern Atlantic; BMNH 2013.9.20.3, adult male 837 mm TL, Northeastern Atlantic; BMNH 2013.9.20.5, adult male 898 mm TL, Northeastern Atlantic; BMNH 2013.9.20.6, juvenile male 650 mm TL, Northeastern Atlantic; BMNH 2013.9.20.7, adult male 881 mm TL, Northeastern Atlantic; BMNH 2013.9.20.8, juvenile male 842 mm TL, Northeastern Atlantic; BMNH 2013.9.20.9, adult male 942 mm TL, Northeastern Atlantic; BMNH uncataloged, adult female 996 mm TL, no locality data; CAS 218702, embryo male, 249,89 mm TL, depth 813–1000 m, 34°34.81′ N, 168°57.79′ E; HUMZ 148699, juvenile female, 496 mm TL, off Namibia; MCZ 38297, juvenile male, 674 mm TL, Atlantic Ocean, 39.15 S,–72.35 W; MCZ 38294, juvenile male, 550 mm TL, Atlantic Ocean, 38.71667 S, −72.9333 W; MCZ 35237, adult female, 1103 mm TL, S.W. peak Banquero, Atlantic Ocean; MCZ 38295, adult female, 1024 mm TL, Atlantic Ocean, depth 570–610 fathoms, 38°41′ N, 73°1′ W; MCZ 39621, adult male, 895 mm TL, depth 223 fathoms, United States, Atlantic Ocean, 41°29′ N, 65°35′ W; MCZ 61979, adult female, 986 mm TL, depth 160–170 m, Atlantic Ocean, 42°19′ N, 67°24′ W; MCZ 57703, subadult female, 744 mm TL, depth 1280 m, Atlantic Ocean, 39°9′ N, 72°11′ W; MCZ 37452, juvenile female, 447 mm TL, depth 350–500 fathoms, United States, south of Georges Bank, Atlantic Ocean, 40°0′ N, 68°52′ W; MCZ 125402, juvenile male, 397 mm TL, depth 439–915 m, southern slope of Georges Bank, United States, Atlantic Ocean, 39°55′ N, 70°35′ W; MCZ 37420, juvenile male, 326 mm TL, depth 440–495 fathoms, Slope water, So. New England, United States, Atlantic Ocean, 39°51′ N, 70°48′ W; MCZ 37424, juvenile male, 306,38 mm TL, depth 759–804 fathoms, Slope Water, So. New England, United States, Atlantic Ocean, 39°52′ N, 70°43′ W; MCZ 38452, juvenile female, 270.6 mm TL, depth 460–520 fathoms, Slope Water, Atlantic Ocean, 39°9′ N, 72°21′ W; MCZ 132510, two juvenile specimens, 350 mm TL, depth 920–948 m, South slope of Georges Bank, United States, Atlantic Ocean, 39°48′ N, 71°19′ W; MCZ 38296, 12 embryos, 264,3 mm TL, depth 570–610 fathoms, Atlantic Ocean, 38°41′ N, 73°1′ W; MNHN 1986 262, juvenile female 857 mm TL, no locality data; MNHN 1986 264, adult male 941 mm TL, no locality data; MNHN 1986 265, adult female 975 mm TL, no locality data; MNHN 1986 266, adult female 958 mm TL, no locality data; MNHN 1986 267, adult female 943 mm TL, no locality data; MNHN 1986 268, juvenile female 857 mm TL, no locality data; MNHN 1986 269, juvenile female 852 mm TL, no locality data; MNHN 1987 1583, juvenile male 328 mm TL, Congo-Gabon, 3°25′ S, 9°33′ E, depth 900–1030 m; MNHN 1997 388, adult female 1054 mm TL, no locality data; MNHN 1997 389, adult male 888 mm TL, no locality data; MNHN 1999 1163, embryo male 293,06 mm TL, Hebrides Sea, North Atlantic, 55°13′ 1″ N, 10°10′ 1″ W, depth 1194 m; MNHN 2001 2577, four embryos (one male, 238, 39 mm TL; three females, 254,30 mm TL, 249 mm TL, 242,96 mm TL), Scotland, 57°46′ 1″ N, 9°43′ 59″ W; MNHN 2001 3226, juvenile male 670 mm TL, 46°25′ 59″ S, 66°34′ 1″ E, depth 1325–1885 m; MNHN 2002 2967, adult female 1042 mm TL, West Scotland, Northeastern Atlantic Ocean, 57°46′ 1″ N, 9°43′ 59″ W; MNHN 2003 0376, adult male 873 mm TL, Bologne-sur-Mer, Pas-de-Calais, France, Atlantic Ocean; MNHN 2003 1772, four embryos (two males, 262 mm TL, 249 mm TL; two females, 249 mm TL, 245 mm TL), Norfolk ridge, Tasman Sea, Pacific Ocean, depth 813–1000 m; MNHN 2004 0961, adult female 997 mm TL, Eastern Africa; MNHN 2011 0882, juvenile female 742 mm TL, Lorient, Morbihan, France; MNHN A-4800, adult (head only), Setubal, Portugal; MNRJ 30243, juvenile female, 350 mm TL, 14°36′ 36″ S, 38°49′ 21″ W; MNRJ 30249, juvenile female, 421 mm TL, 19°58′ 56″ S, 39°38′ 39″ W; MNRJ 30246, juvenile male, 352 mm TL 19°58′ 56″ S, 39°38′ 39″ W; MNRJ 30248, juvenile male, 355 mm TL, 19°58′ 56″ S, 39°38′ 39″ W; MNRJ D-506.1, juvenile male, 363 mm TL, 19 42.711 S, 038 36.487 W; MNRJ D-506.3, juvenile female, 361 mm TL, 19 42.711 S, 038 36.487 W; MNRJ D-506.4, juvenile female, 300 mm TL,19 42.711 S, 038 36.487 W; MNRJ D-506.2, juvenile male, 351 mm TL, 19 42.711 S, 038 36.487 W; MNRJ E-547.2, juvenile female, 358 mm TL, 21 46.569 S, 039 53.364 W; MNRJ E-547.1, juvenile female, 395 mm TL, 21 46.569 S, 039 53.364 W; MNRJ E-506.1, juvenile male, 367 mm TL, no locality data; MNRJ E- 506.2, juvenile male, 309 mm TL; MNRJ 30244, juvenile male, 396 mm TL, 19°42′ 33″ S, 38°32′ 2″ W; MNRJ 30221, juvenile female, 635 mm TL, 14°13′ 59″ S, 38°40′ 17″ W; MNRJ 30220, juvenile male, 517 mm TL 14°13′ 59″ S, 38°40′ 17″ W; MNRJ 30223, juvenile male, 592 mm TL, 19°48′ 29″ S, 39°2′ 21″ W; MNRJ 30224, juvenile female, 587 mm TL, 20°26′ 51″ S, 39°41′ 38″ W; MNRJ 30245, juvenile female, 339 mm TL, 19°58′ 56″ S, 39°38′ 39″ W; MNRJ 30242, juvenile male, 318 mm TL, 19°42′ 43″ S, 38°36′ 30″ W; MNRJ 30247, juvenile female, 359 mm TL, 19°58′ 56″ S, 39°38′ 39″ W; MZUSP 118097, juvenile female, 371 mm TL, continental slope of South America, between 11° and 22° S (REVIZEE); MZUSP 118098, juvenile female, 328 mm TL, continental slope of South America, between 11° and 22° S (REVIZEE); NSMT-P 21826, sub-adult female, 794 mm TL, Suruga Bay, off Yui, Japan, depth 840 m; NSMT-P 21827, sub-adult female, 854 mm TL, Suruga Bay, Senoumi, Japan, depth 900 m; NSMT-P 21828, adult male, 812 mm TL, Suruga Bay, off Okij, depth 810 m; NSMTP 21829, juvenile female, 742 mm TL, Suruga Bay, off Fujigawa River, depth 690 m; NSMT-P 32284, adult male, 923 mm TL, Lord Howe Rise, 36°21.49′ S, 164°53.32′ E, depth 960–980 m; NSMT-P 32422, adult male, 882 mm TL, Lord Howe Rise, 36°21.49′ S, 164°53.32′ E, depth 960–980 m; NSMT-P 32423, adult male, 906 mm TL, the same locality as NSMT-P 32422; NSMT-P 32475, adult male, 954 mm TL, Lord Howe Rise, 36°21.49′ S, 164°53.32′ E, depth 960–980 m; NSMT-P 32477, adult male, 891 mm TL, Lord Howe Rise, 36°21.49′ S, 164°53.32′ E, depth 960–980 m; NSMT-P 32586, adult male, 949 mm TL, Challenger Plateau, 38°15.40′ S, 167°25.67′ E, depth 770–965 m; TMFE 562, juvenile male, 671 mm TL, Suruga Bay, Japan; TMFE 603, sub-adult male, 821 mm TL, Suruga Bay, Japan; TMFE 929, adult female, 1008 mm TL, Suruga Bay, Japan; TMFE 1660, adult female, 1053 mm TL, Suruga Bay, Japan; TMFE 1661, adult female, 1006 mm TL, Suruga Bay, Japan; TMFE 1662, adult female, 1013 mm TL, Suruga Bay, Japan; UF 44334, adult female, 948 mm TL, Japan, Pacific Ocean, 35°2′ N, 138°36′ E; UF 229687, juvenile male, 510 mm TL, depth 670–700 m, USA, Atlantic Ocean, 39°9′ N, 72°12′ W; UF 101352, juvenile male, 392 mm TL, depth 1372 m, Bahamas Island, Andros Island, Atlantic Ocean, 23°44′ 15″ N, 77°13′ 6″ W; UF 44563, juvenile female, 660 mm TL, Namibia, Atlantic Ocean, 23°20′ S, 12°48′ E; UF 44978, juvenile male, 740 mm TL, Iceland, Atlantic Ocean, 59°7′ N, 18°14′ W; USNM 220993, four juvenile specimens, 39°09′ N, 072°12′ W; USNM 408573, subadult female, 781 mm TL, −35.17 S, 53.67 E; USNM 408579, subadult female, 774 mm TL, USNM 408586, subadult male, 837 mm TL, −39 S, 47.17 E; −37 S, 52 E; USNM 206064, seven juvenile specimens, 585 mm TL, 39°09′ N, 72°12′ W; USNM 206603, two juvenile specimens, 620 mm TL, 39°10′ N, 72°16′ W; USNM 206062, five juvenile specimens, 653 mm TL, depth 535–630 fathoms, 37°54′ N, 73°54′ W; USNM 206061, four juvenile specimens, 725 mm TL, depth 668 fathoms, 39°49′ N, 70°55′ W; USNM 206038, adult female, 1115 mm TL, Western Atlantic Ocean, USA, off New York, Hydrographer Canyon, depth 128–165 m; USNM 206050, adult female, 993 mm TL, 24.35 N, −83.60 W, Off Florida, depth 0–732 m; USNM 220271, juvenile female, 565 mm TL, depth 1189 m, Delaware, USA, 38.65 N, −73.18 W; ZMH 26037, juvenile female, 397 mm TL, off South Mozambique, 25°28′3″ S, 35°28′7″ E to 25°31′5″ S, 35°25′9″ E, depth 1230–1260 m; ZMH 100227, adult female 1105 mm TL, Northeastern Atlantic, 63°10′ N, 12°2′ W; ZMH 100815, adult male 891 mm TL,63°09′ N, 13°8′ W, depth 730–760 m; ZMH 101577, adult male 895 mm TL, Northeastern Atlantic, 62°58′ N, 23°40′ W; ZMH 102358, adult male 837 mm TL, 63°13′ N, 25°50′ W, depth 810 m; ZMH 102538, juvenile male 730 mm TL, 63°13′ N, 25°50′ W; ZMH 102817, juvenile female 820 mm TL, 63°6′ N, 21°33′ W; ZMH 111346, subadult male 800 mm TL, 64°53′ N, 28°3′ W; ZMH 111765, juvenile male 738 mm TL, 63°14′ N, 25°40′ W; ZMH 119939, two juvenile females (341 mm TL, 301 mm TL), 39°46′ N, 71°28′ W, depth 1000–1016 m; ZMH 119669, four juvenile males (420 mm TL, 401 mm TL, 384 mm TL and 356 mm TL), off New York, USA, 39°11.5′ N, 72°13′ W, depth 1000–1080 m; ZMH 119681, two juveniles (male 300 mm TL; female 319 mm TL), 36°22′ N, 74°42′ W, depth 1000 m; ZMH 119684, two juvenile males (401 mm TL, 351 mm TL), 39°50′ N, 70°55′ W, depth 1004–1008 m; ZMH119701, three juveniles (two males, 398 mm TL and 377 mm TL; one female, 404 mm TL), 36°22′ N, 74°42′ W, depth 1000 m; ZMH 119702, three juveniles (two males, 467 mm TL and 417 mm TL; one female, 478 mm TL), off New York, USA, 39°11.5′ N, 72°13′ W, depth 1000–1050 m; ZMH 119748, two juvenile males (527 mm TL and 472 mm TL), 39°50′ N, 70°55′ W, depth 1004–1008 m; ZMH 119896, juvenile female 325 mm TL, 39°46.3′ N, 71°33′ W, depth 824–844 m; ZMH 120249, four embryos (two males, 273 mm TL, 270 mm TL; two females, 272 mm TL, 271 mm TL), 49°28.6′ N, 12°11.8′ W; ZMH 120581, juvenile male 305 mm TL, off Mauritania, 17°22.2′ N, 16°55′ N, 1175– depth 1205 m; ZMH ISH 331, adult male 885 mm TL, Western Indian Ocean; ZMH ISH 332, adult female 911 mm TL, Western Indian Ocean.
Centroscymnus owstonii. BMNH 1865.5.20:14, holotype of Centroscymnus cryptacanthus, adult male 771 mm TL, Madeira Islands, Portugal, Eastern Central Atlantic; AMNH 78181, adult female, 950 mm TL, Canary Islands, Eastern North Atlantic, 28°12.0′ N, 15°36.5′ W; AMNH 78177, adult female, 1052 mm TL, Canary Islands, Eastern North Atlantic, 28°19.2′ N, 16°16.7′ W; AMNH 78178, adult male, 811 mm TL Canary Islands, Eastern North Atlantic, 28°19.2′ N, 16°16.0′ W; AMNH 55525, juvenile female, 316 mm TL, Western North Atlantic, Off North Carolina, USA; AMNH 78249, adult female, 1075 mm Canary Islands, Eastern North Atlantic, 28°19.0′ N, 16°19.4′ W; BMNH 1937.7.11:1, juvenile female 280.06 mm 360 TL, South Pacific Coast of Japan, Northwestern Pacific; BMNH 1939.7.20:4, subadult male 656 mm TL, Japan; BMNH 1973.7.9.8, adult female 1054 mm TL, Assumption Island, Seychelles, Western Indian Ocean, 9° S, 46° E, depth 100–1000 m; BMNH 1973.7.9.9, adult female 1071 mm TL, Farquhar and Cerf Islands, Seychelles, Western Indian Ocean, 9° S 50° E, depth 0–900 m; BMNH 2013.9.20.13, adult female 997 mm TL, Northeastern Atlantic; CAS SU 23510, two juvenile specimens, 294 mm TL, Misaki, Japan, Sagami Sea, Pacific Ocean; CAS SU 35475, juvenile female, 244.82 mm TL, Tenoshima, Japan; SU 35476, juvenile female, 272,19 mm TL, same data as SU 35475; CAS SU 63950, juvenile female, 269.85 mm TL, Enoshima, Sagami Sea, Japan; CAS 90678, embryo female, 238.75 mm TL, South Pacific, New Caledonia, 24°16′ S, 161°45′ W; HUMZ 71894, adult female, 825 mm TL, no locality data; HUMZ 72025, adult female, 1091 mm TL, 31°02′ N, 175°50′ E; HUMZ 96723, juvenile female, 487 mm TL, Kumano Noda, marginal border of continental shelf of Japan; HUMZ 101539, adult female, 907 mm TL, off Okinawa, 25°08.2′ N, 128°14.5′ E; HUMZ 101722, adult male, 792 mm TL, off Okinawa, Japan, 25°08.2′ N, 125°18.1′ E; HUMZ 101723, juvenile male, 627 mm TL, off Okinawa, Japan; HUMZ 124745, adult male, 801 mm TL, Kii Strait, off Wakayama, Japan; HUMZ 149406, juvenile female, 295,66 mm TL, off Okinawa, Japan; HUMZ 177930, adult female, 1079 mm TL, no locality data; KAUM I. 51402, juvenile male, 321 mm TL, Japan; MCZ S-1126, adult male, 807 mm TL, Pacific Ocean, Suruga Gulf, Japan; MCZ S-1105, newborn male, 250,12 mm TL, Pacific Ocean, Sagami Sea, Misaki, Japan; MCZ S-1119, embryo male, 213 mm TL, Pacific Ocean, Sagami Sea, Misaki, Japan; MCZ 35308, two juveniles (280.2 mm TL, 252.7 mm TL) Pacific Ocean, Sagami Sea, Japan; MNHN 1989 0654, juvenile female 525 mm TL, Reunion Islands, Western Indian Ocean; MNHN 1997 3428, adult female 966 mm TL, Mont Aramis, Coral Sea, Loyauté Islands, New Caledonia, 25°22′ 59″ S, 168°55′ 59″ E, depth 640–740 m; MNHN 1997 3429, juvenile female 681 mm TL, Lord Howe ridge, Coral Sea, New Caledonia, 24°31′ 59″ S, 161°52′ 59″ E, depth 1060–1130 m; MNHN 1998 1018, juvenile male 398 mm TL, Lord Howe ridge, Coral Sea, Pacific Ocean, 23°55′ 59″ S, 161°52′ 59″ E, depth 1034–1056 m; MNHN 1998 1030, five embryos (two males, 253 mm TL, 245 mm TL; three females, 265 mm TL, 256 mm TL, 255 mm TL), Loyauté ridge, Coral Sea, New Caledonia, Pacific Ocean, 660–756 mm TL; MNHN 2003 1682, juvenile female 698 mm TL, Lord Howe ridge, Tasman Sea, Pacific Ocean, 32°25′ 8″ S, 161°47′ 6″ E, depth 1132–1197 m, MNHN 2003 1691, juvenile male 359 mm TL, Norfolk ridge, Tasman Sea, Pacific Ocean, 32°42′ 50″ S, 162°33′ 7″ E, depth 850–872 m; MNHN 2003 1692, juvenile male 335 mm TL, Norfolk ridge, Tasman Sea, Pacific Ocean, 32°42′ 50″ S, 162°33′ 7″ E, depth 850–872 m; MNHN 2003 1693, adult male 730 mm TL, Norfolk ridge, Tasman Sea, Pacific Ocean, 32°42′ 50′ S, 162°33′ 7″, depth 850–872 m; MNHN 2003 1711, juvenile male 622 mm TL, Norfolk ridge, Tasman Sea, Pacific Ocean, 33°49′ 23″ S, 167°3′32″ E, depth 805–936 m; MNHN 2003 1768, juvenile female 634 mm TL, Norfolk ridge, Tasman Sea, Pacific Ocean, 34°14′ 35″ S; 168°21′ 18″ E, depth 1195–1202 m; MNRJ 30222, adult female, 870 mm TL, 13°30′ 28″ S, 38°38′ 59″ W; MNRJ 30229, adult female, 1041 mm TL, 13°30′ 28″ S, 38°38′ 59″ W; NSMT-P 21830, sub-adult female, 762 mm TL; Suruga Bay, Japan; NSMT-P 21831, adult female, 800 mm TL, Suruga Bay, Japan; NSMT-P 21832, sub-adult male, 745 mm TL, Suruga Bay, Japan; NSMT-P 21833, sub-adult male, 745 mm TL, Suruga Bay, Japan; NSMT-P 32271, sub-adult male, 763 mm TL, Tasman Sea, Three Kings Ridge, 28°10.52′ S, 175°25.78′ E, depth 445–840 m; NSMT-P 32340, juvenile female, 321 mm TL, Tasman Sea, Three Kings Ridge, 30°16′ S, 172°54′ E, depth 730–840 m; NSMT-P 32341, juvenile male, 324,5 mm TL, same locality as NSMTP 32340; NSMT-P 32342, juvenile female, 353 mm TL, same locality as NSMT-P 32340; NSMT-P 32343, juvenile male, 323 mm TL, same locality as NSMT-P 32340; NSMT-P 32344, juvenile male, 374 mm TL, same locality as NSMT-P 32340; NSMT-P 32345, juvenile male, 332 mm TL, same locality as NSMT-P 32340; NSMT-P 32346, juvenile male, 387 mm TL; NSMT-P 32229, adult female, 1031 mm TL, 40° S, 167°42′ E, depth 1100 m; NSMT-P 32407, adult female, 1004 mm TL, Three Kings Ridge, 28°43′ S, 172°57′ E, depth 320–1100 m; NSMT-P 32890, juvenile male, 314 mm TL, Three Kings Ridge, 30°16.0′ S, 172°54′ E 730–840 m; NSMT-P 32891, juvenile male, 331 mm TL, same locality as NSMT-P 32890; NSMT-P 32892, juvenile male, 400 mm TL, same locality as NSMT-P 32890; NSMT-P 32893, juvenile male, 352 mm TL, same locality as NSMT-P 32890; NSMT-P 32894, juvenile female, 333 mm TL, same locality as NSMT-P 32890; NSMT-P 42783, adult female, 1023 mm TL, no locality data; NSMT-P 92247, head only, New Zealand, 43°56.6′ S, 176°05.2′ E, 499–507 m; TMFE 156, adult female, 1170 mm TL, Suruga Bay, Japan; TMFE 464, sub-adult male, 752 mm TL, Suruga Bay, Japan; TMFE 465, sub-adult male, 727 mm TL; TMFE 548, adult female, 1062 mm TL; TMFE 557, juvenile female, 659 mm TL, Suruga Bay, Japan; TMFE 589, sub-adult male, 738 mm TL, Suruga Bay, Japan; TMFE 1745, sub-adult male, 774 mm TL; TMFE 4221, sub-adult male, 789 mm TL, Suruga Bay, Japan; TMFE 4222, sub-adult male, 726 mm TL, Suruga Bay, Japan; UF 45229, juvenile female, 333 mm TL, Gulf of Mexico, Atlantic Ocean, 27°47′ N, 85°30′ W; UF 45229, juvenile female, 333 mm TL, Gulf of Mexico, Atlantic Ocean, 27°47′ N, 85°30′ W; UF 44333, adult female, 753 mm TL, Japan, Pacific Ocean; UF 27956, juvenile male, 303.68 mm TL, Gulf of Mexico, USA, Atlantic Ocean, 29°12′ N, 87°45′ W; UF 233413, juvenile male, 286.23 mm TL, Straits of Florida, USA, Atlantic Ocean, 24°10′ 30″ N, 80°58′ W; UF 233440, two juvenile specimens, 320 mm TL, Straits of Florida, USA, Atlantic Ocean, 24°8′ N, 81°13′ W; UF 27957, juvenile male, 312 mm TL, Gulf of Mexico, USA, Atlantic Ocean, 29°11′ N, 87°17′ W; UF 28001, adult female, 960 mm TL, French Guiana, Atlantic Ocean, 7°37′ N, 53°24′ W; UERJ 1633, adult male, 775 mm TL, São Paulo state, Brazil; UERJ 1634, adult male, 808 mm TL, São Paulo state, Brazil; USNM 206039, adult male, 810 mm TL, 0–735 m, 07°41′ N, 53°37′ W; USNM 206052, adult male, 805 mm TL, depth 0–680 m 07°37′ N, 53°24′ W; USNM 206060, adult male, 783 mm, depth 604–631 m, 07°26′ N, 53°16′ W; USNM 206051, adult male, 781 mm TL, depth 0–680 m, 07°37′ N, 53°24′ W; USNM 220254, two juvenile specimens, 365 mm TL Gulf of Mexico, off Alabama, Atlantic Ocean, 29°09′ N, 87°58′ W; ZMH 26038, juvenile male, 342 mm TL, off Southwest Madagascar, 22°27′4″ S, 43°00′5″ E to 22°29′2″ S, 43°01′2″ E, depth 940–960 m; ZMH 104894, adult male 732 mm TL, 33°43′ S, 51°2′ W, depth 800 m; ZMH 119929, adult female 993 mm TL, 31°3′ N, 77°49′ W, depth 1007–1016 m.
Centroselachus crepidater. AMNH 59842, adult female, 705 mm TL, Eastern South Atlantic, Namibia, 25°08′ S, 13°39′E; AMNH 49506, juvenile female, 297.83 mm TL, depth 798–800 m, 61°03.2′ N, 11°14.9′ W; AMNH 49505, juvenile male, 305.87 mm TL; depth 803–805 m, 60°44′ N, 12°46′ W; AMNH 55521, newborn female, 260.21 mm TL, Eastern North Atlantic, Iceland, 63°03′ N, 20°30′ W; AMNH 58099, four juvenile specimens, 284 mm TL Eastern North Atlantic, 60°02.1′ N, 13°08.0′ W; BMNH 1925.7.2.3.2, adult male 618 mm TL, Westman Islands, Iceland; BMNH 1978.11.15:4, adult male 570 mm TL, Flannan Islands, Scotland, 58°16.6′ N, 9°40.8′ W to 58°14′ N, 9°40.6′ W, depth 1110 m; BMNH 1981.3.16.21, adult male 589 mm TL, West of St. Kilda, Scotland, 57°45′ N, 9°47′ W to 57°39′ N, 9°49′ W, depth 1090–1020 m; BMNH 1981.3.16:22–23, two male specimens (one adult, 590 mm TL; and one juvenile, 343 mm TL), West of Sulisker, Scotland, 59°26′ N, 7°40′ W to 59°30′ N, 7°51′ W, depth 1140–1170 m; BMNH 1982.7.28:1, adult male 618 mm TL, SE edge of Farm Bank, Off Southwestern Ireland, 50°50′ N 14°06′ W to 50°45.6′ N t°14°13.7′ W, depth 920–960 m; BMNH 1987.1.21:88–89, two juvenile females (304.3 mm TL and 286.2 mm TL), Northeastern Atlantic, 50°22.6′ N, 11°12.5′ W to 50°19′ N 11°14.5′ W, depth 920–960 m; BMNH 1987.1.21:90–92, three adult females (90: 744 mm TL; 91: 698 mm TL; 92: 785 mm TL), United Kingdom, Northwestern Atlantic, 59°26.0.000 N, 7°40.0.000 W; BMNH 2000.2. 24:4, adult female 735 mm TL, Ireland, Northeastern Atlantic; BMNH 2013.9.20.12, adult female 786 mm TL, Northeastern Atlantic; HUMZ 55639, adult male, 681 mm TL, no locality data; HUMZ 73508, juvenile female, 407 mm TL, 33°14.7′ S, 44°14,2′ E; HUMZ 73193, juvenile female, 430 mm TL, no locality data; HUMZ 73909, juvenile female, 686 mm TL, Saya de Malha Bank, 48°09′ S, 71°06′ E; HUMZ 148749, adult female, 767 mm TL, off Namibia, 18°28′ S,11°22′ E; MCZ 39570, adult female, 821 mm TL, Pacific Ocean, New Zealand; MCZ 39577, adult female, 786 mm TL, Azores-Britain, Southwest of the Faroes, Atlantic Ocean; MNHN 1987 0974, juvenile male, newborn 228 mm TL, Senegal; MNHN 1998 1298, adult male 602 mm TL, Finistere, France, 47° N, 4° W; MNHN 1998 1299, three adult specimens (one female, 771 mm TL; two males, 602 mm TL, 578 mm TL), Finistere, France, 47° N, 4° W; MNHN 2003 1600, adult female 687 mm TL; Golf of Gascoyne, Northeastern Atlantic, 46° N 10° W; MNHN 2003 1601, 4 embryos (three males, 251 mm TL, 251 mm TL, 247 mm TL; one female, 252.4 mm TL), same locality data as MNHN 2003 1600; MNHN 2003 1608, embryo female 256 mm TL, same locality as MNHN 2003 1600; MNHN 2003 1710, adult male 650 mm TL, Norfolk ridge, Tasman Sea, Pacific Ocean, 33°49′ 23″ S, 167°3′ 32″ E, depth 805–936 m; MNHN 2003 1743, juvenile male 520 mm TL, Norfolk ridge, Tasman Sea, Pacific Ocean, 32°35′ 6″ S, 167°47′ 2″ E, depth 957–977 m; MNHN 2003 1744, juvenile male 346 mm TL, Norfolk ridge, Tasman Sea, Pacific Ocean, 32°35′ 6″ S; 167°47′ 2″ E, depth 957–977 m; MNHN 2003 1745, juvenile female 507 mm TL, Norfolk ridge, Tasman Sea, Pacific Ocean, 32°35′ 6″ S, 167°47′ 2″ E, depth 957–977 m; MNHN 2003 1756, juvenile female 443 mm TL, Norfolk ridge, Tasman Sea, Pacific Ocean, 32°36′ 22″ S, 167°47′ 10″ E, depth 926–969 m; MNHN 2003 1757, juvenile male 407 mm TL, Norfolk ridge, 32°36′ 22″ S, 167°47′ 10″ E, depth 926–969 m; NSMT-P 32588, adult female, 859 mm TL, Challenger Plateau, 38°15.40′ S, 167°25.67′ E, depth 770–965 m; NSMT-P 43463, adult male, 646 mm TL, 37°27′ S, 167°56′ E, depth 944–970 m; NSMT-P 43505, juvenile female, 347 mm TL, 42°53′ S, 177°52′ E, depth 427–432 m; NSMT-P 42959, juvenile male, 319 mm TL, 42°45′ S, 176°46′ E; NSMT-P 42960, juvenile male, 369 mm TL, same locality as NSMT-P 42959; NSMT-P 42961, juvenile male, 339 mm TL, same locality as NSMT-P 42959; NSMT-P42962, juvenile male, 363 mm TL, same locality as NSMT-P 42959; NSMT-P 42963, juvenile female, 278 mm TL, same locality as NSMT-P 42959; NSMT-P 42964, juvenile female, 372 mm TL, same locality as NSMT-P 42959; NSMT-P 42965, juvenile female, 344 mm TL, same locality as NSMT-P 42959; NSMT-P 42966, juvenile female, 380 mm TL, same locality as NSMT-P 42959; UF 44733, juvenile female, 569 mm TL, Chile, Pacific Ocean, 40 29′ S, 74°18′ W; UF 44734, juvenile male, 326 mm TL, depth 482 m, Chile, Pacific Ocean, 40 29′ S, 74°17′ W; UF 44736, juvenile female, 417 mm TL, same data as UF 44734; UF 44737, adult male, 615 mm TL, same data as UF 44734; UF 42480, juvenile male, 479 mm TL, East of South Island, New Zealand, Pacific Ocean, 44°48′ 18″ S, 173°53′ 30″ E; UF 44972, two juvenile specimens, 293.39 mm TL, United Kingdon, Scotland, Atlantic Ocean, 60°1′ 54″ N, 12°54′ W; UF 44590, adult male, 586 mm TL, Namibia, Atlantic Ocean, 23°6′ S, 13°5′ E; UF 44979, two adults female, United Kingdon, Atlantic Ocean, 57°57′ N, 9°40′ W; USNM 408580, adult female, 859 mm TL, depth 1000–1300 m, Indian Ocean, South Africa, −34.50 S, 44.08 E; USNM 408575, adult male, 639 mm TL, depth 800–1000 m, Indian Ocean, South Africa, −39.00 S, 46.50 E; USNM 408581, juvenile female, 525 mm TL, depth 900–1000 m, Indian Ocean, South Africa, 38.67 S, 47.17 E; USNM 408576, adult female, 716 mm TL, depth 800–1000 m, Indian Ocean, South Africa, 34.17 S, 45.08 E; USNM 408578, adult male, 720 mm TL, depth 800–1200 m, Indian Ocean, South Africa, 39.00 S, 46.50 E; USNM 94522, adult female, 731 mm TL, Madeira Islands, Eastern Atlantic; USNM 408582, juvenile female, 426 mm TL, depth 900–1000 m, Indian Ocean, South Africa, −38.67 S, 47.17 E; ZMH 100073, adult female 752 mm TL, no locality data; ZMH 101566, five specimens (two adult males, 625 mm TL, 554 mm TL; one juvenile male, 527 mm TL; two juvenile females, 577 mm TL, 573 mm TL), 63°45′ N; 26°40′ W, depth 760–810 m; ZMH 101588, adult male (head and pectoral fins only), Iceland, 62°58′ N, 23°40′ W; ZMH 101567, adult male 643 mm TL, 63°45′ N, 26°40′ W; ZMH 101806, adult female 755 mm TL, 60°49′ N, 9°56′ W; ZMH 101820, two females (one adult, 810 mm TL; one juvenile, 301 mm TL), 60°21′ N, 11°54′ W, depth 710–740 m; ZMH 102400, two adult males (616 mm TL, 607 mm TL), 63°13′ N, 25°50′ W, depth 810 m; ZMH 102592, one juvenile and three female embryos (juvenile, 363 mm TL; embryos, 283 mm TL, 282 mm TL, 275 mm TL), 63°6′ N; 21°33′ W, depth 750–800 m; ZMH 102594, two adult males (646 mm TL, 586 mm TL), 63°6′ N; 21°33′ W, depth 750–800 m; ZMH 102598, adult female 772 mm TL, 65°13′ N, 27°38′ W; ZMH 103185, two specimens (one embryo, 257.8 mm TL; one newborn, 286.3 mm TL); ZMH 123515, juvenile male 523 mm TL, 51°35′ N, 13°5′ W; ZMH 123540, adult female 759 mm TL, 56°48′ N,13°24′ W; ZMH 123541, adult female 788 mm TL, 58°37′ N, 8°59′ W, depth 1285–1300 m; ZMH 123547, adult female 798 mm TL, 58°37′ N, 8°59′ W; ZMH 123548, adult female 831 mm TL, 59°1′ N, 7°55′ W, depth 1320 m.
Scymnodon ringens. AMNH 98163, juvenile female, 529 mm TL, South Ireland, 50°43.3′ N, 11°25.5′ W; AMNH 98164, juvenile male, 646 mm TL depth 794 m, South Ireland, 50°43.3′ N, 11°24.5′ W; BMNH 1907.6.20:1, juvenile female 720 mm TL, 51°30′ N, 11°50′ W, depth 225–275 m; BMNH 1973.10.29:27, juvenile female 610 mm TL, 52°06′ N, 12°10′ W to 52°06′ N, 12°20.5′ W, depth 160–190 m; BMNH 1987.1.21:85, juvenile female 540 mm TL, 51°44′ N, 11°46.5′ W to 51°41.5′ N, 11°53.8′ W, depth 600–740 m; BMNH 1987.1.21:86–87, two adult males (86: 660 mm TL, 87; 665 mm TL), Ireland, Northeastern Atlantic; BMNH 1990.8.16:1, adult male 689 mm TL, 51°19.5′ N, 14°20.7′ W to 51°19.5′ N, 14°20.3′ W, depth 460–495 m; BMNH 1990.8.21:423, juvenile female 585 mm TL, 49°24.0′ N, 11°45.4′ W to 49°26.1′ N, 11°45.1′ W, depth 2215–2235 m; BMNH 1991.7.9:686–690, five juvenile specimens (686: male 625 mm TL, 687: male 559 mm TL, 688: female 507 mm TL, 689: female 519 mm TL, 690: female 314 mm TL), 49°33.9′ N, 11°36.1′ W, depth 736–790 m; BMNH 2002.3.1:791–792, two embryos females (791: 210.7 mm TL, 792: 208.3 mm TL); MNHN 1969 90, juvenile male 314 mm TL, 47°45′ N, 7°55′ W, depth 800–920; MNHN 1988 625, juvenile male 402 mm TL, Iberomorrocan Golf, 34°22′ 1″ N, 7°22′ 59″ W, depth 948 m; MNHN 1988 403, juvenile female 305 mm TL, Mauritania, 16°12′ N, 16°49′ 59″ W, depth 400 m; MNHN 2003 1605, juvenile male 447 mm TL, Gascoigne Golf, 46° N, 10° W; MNHN 2003 0534, juvenile male 535 mm TL, Ireland, Hebrides Sea, North Atlantic Ocean, 53°50′ 31″ N, 13°57′ 0″ W, depth 1030–1080 m; MNHN 2003 0367, juvenile female 592 mm TL, no locality data; MNHN 2003 0372, subadult male 654 mm TL, Strait of Dover, between English channel and North Sea, Bologne-sur-Mer, North Atlantic Ocean; ZMH 112266, three juveniles male (536 mm TL, 448 mm TL, 432 mm TL), 52°44′ N, 14°46′ W, depth 642–655 m; ZMH 113292, two male specimens (one adult, 666 mm TL; one juvenile, 559 mm TL), 49°31′ N, 11°50′ W, depth 978–985 m; ZMH 112331, juvenile male 441 mm TL, 53°45′ N, 14°03′ W, depth 818–854 m; ZMH 113882, two male specimens (one adult, 689 mm TL; one juvenile, one juvenile), 55°40′ N, 9°28′ W, depth 550–650 m; ZMH 113264, juvenile female 667 mm TL, 53°41′ N, 14°21′ W, depth 997–1005 m; ZMH 119565, juvenile female 381 mm TL, 50°49.3′ N, 11°24.5′ W, depth 794 m; ZMH 119581, two adult females (1062 mm TL, 1014 mm TL), 51°27.6′ N, 14°51.8′ W, depth 814 m.
Scymnodon macracanthus. MNHN 1991 408, juvenile male 643 mm TL, no locality data; MNHN 2003 1708, juvenile male 695 mm TL, Norfolk ridge, Tasman Sea, Pacific Ocean, 33°49′ 23″ S 167°3′ 32″ E, depth 805–936 m; MNHN 2008 1916, juvenile male 582 mm TL, Amsterdam Island, Kerguelen Archipelago, Indian Ocean, 37°59′ 38″ S, 77°46′ 5″ E, depth 719–1260 m; NSMT-P 32079, adult male, 1166 mm TL, depth 560–930 m, Wanganella bank, 32°41.5′ S, 167°42.01′E; NSMT-P 42501, adult male, 1166 mm TL, depth 585–632 m; NSMT-P 42790, subadult male, 1019 mm TL, depth 657–644 m TL, 47°23′ S, 169°43′ E; NSMT-P 42791, adult male, 1163 mm TL, same data as NSMT-P 42790; NSMT-P 42800, juvenile male, 947 mm TL, depth 244–264 m, 43°17.5 S, 176°55′ W; UF 89183, juvenile male, 958 mm TL, Tasman Sea, New Zealand; USNM 408587, adult male, 1166 mm TL, depth 800–1000 m, Indian Ocean, South Africa, −37 S, 52 E; USNM 408585, juvenile female, 859 mm TL, depth 800–1200 m, Indian Ocean, South Africa, −39.00 S, 46.50 E; USNM 408584, adult female, 1215 mm TL, depth 800–1000 m, Indian Ocean, South Africa, −37 S, 52 E; USNM 408583, adult male, 1162 mm TL, depth 700–1100 m, Indian Ocean, South Africa, 39.33 S, 46 E.
Scymnodalatias albicauda. HUMZ 129360, 20 embryos, 157–192 mm TL, Taiwa
Maru, 43°54′ S, 07°45′ E; ZMH 122774, juvenile female 416 mm TL, 52°56.3′ N,
16°18.4′ W, depth 2200–2300 m.
Somniosus microcephalus/pacificus complex. AMNH 78351, juvenile female, 1138 mm TL, Canary Islands, Eastern North Atlantic; CAS 38917, juvenile male, 800 mm TL, depth 600 fathoms, USA, California, Lopez Bank, off Morro Bay, NE Pacific, 35°25′ N, 121°40′ W; CAS 27084, juvenile female, 1001 mm TL, depth 145 fathoms, USA, California, Humboldt, West of Trinindad, NE Pacific, 41°2′ 60′ N, 124°22′ 60′’ W; HUMZ 122816, juvenile (sex and size not available), Western Greenland, 69°53′ N, 60°20′ W; HUMZ 124830, juvenile male, 1338 mm TL, Port Irifune, Bay of Hakoda, Japan; MCZ 37826, juvenile male, 1425 mm TL depth 180 fathoms, Iceland, Eastern North Atlantic, 66°48′ S, 25°10′ W; MCZ 39609, juvenile male, 1274 mm TL, depth 32 fathoms, off Boston Light, Atlantic Ocean; MNHN 2003 0531, juvenile male 1115 mm TL, Ireland, Northeastern Atlantic, 55° S, 15° W; MNHN 2003 1063, juvenile male 1322 mm TL, Ireland, Northeastern Atlantic, 51′ S, 11°40′ 59″ W, depth 1100–1400 m; MNRJ 30230, juvenile female, 1474 mm TL, 19°45.258 S, 039 03.003 W; UF 162500, juvenile male, 1505 mm TL, USA, Pacific Ocean; ZMH 107754, juvenile male 1145 mm TL, Arctic Ocean, 70°47′ N, 17°8′ E; ZMH 123507, juvenile female 1190 mm TL, off Greenland, Northern Atlantic, 65°12′ N, 33°54′ W.
Somniosus cf. rostratus. MNHN 1976 0012, holotype of Somniosus bauchotae, adult female 1318 mm TL, Yeu Island, 46°50′ N, 5°10′–15′ W, depth 220 m; BMNH 1906.11.12:1, juvenile female 815 mm TL, Mediterranean Sea; BMNH 1906.11.12:7, juvenile, skeleton only, Mediterranean Sea; MNHN A-7827, juvenile female 950 mm TL, Iceland, 62° N, 20° W; MNHN 1883 0883, juvenile female 534 mm TL, Mediterranean Sea, 43°42′ N, 7°16′ 1″ E; MNHN 1898 1240, juvenile female 467 mm TL, Nice, France, Mediterranean Sea, 43°42′ N 7°16′ 1″ E; MNHN 1898 1242, juvenile male 537 mm TL, Nice, France, Mediterranean Sea, 43°
42′ N, 7°16′ 1″ E; MNHN 2000 1158, juvenile female 1027 mm TL, Ireland, Northeastern Atlantic Ocean, 57° N, 9°30′ W.
Zameus squamulosus. MNHN 1884 388, holotype of Centroscymnus obscurus, juvenile female 588 mm TL, Coast of Sudan; AMNH 33435, seven juvenile specimens, 324 mm TL, depth 402 fathoms, French Guiana, 07°41′ N, 53°37′ W; BMNH 1986.5.15:1, juvenile male 406 mm TL, off Senegal, 13°25′ N, 18°22′ W, depth 0–900 m; HUMZ 75689, adult female, 32°51 S, 175°30′ W; CAS 214591, juvenile female, 256,06 mm TL, Taiwan, Pacific Ocean; CAS 235537, juvenile male, 288.8 mm TL, Angola, Atlantic Ocean, 8°4′ S, 12°36′ E, depth 726–732 m; CAS (SU) 26784, adult male, 470 mm TL, Off Inoshima, Sagami Sea, Japan, Pacific Ocean; HUMZ 95209, juvenile female, 321 mm TL, East Sea China, 28°16.5′ N, 127°0.6′E; HUMZ 101532, adult female, 670 mm TL, off Okinawa, 26°08.5 N, 128°05′E; HUMZ 148995, juvenile female, 554 mm TL, off Okinawa; HUMZ 181652, juvenile female, 474 mm TL, 36°52.10′ N, 141°48.87′ E; KAUM I. 51392, juvenile female, 471 mm TL, Yoron Island, Japan, 27°07.02′ N, 128°28.08′ E; MNHN 1997 3427, adult female 705 mm TL, Lord Howe ridge, Coral Sea, New Caledonia, Pacific Ocean, 25°28′ 59″ S, 163°13′ 1″ E, depth 1315–1357 m; MNHN 2002 1408, adult female 770 mm TL, Coral Sea, New Caledonia, Pacific Ocean, 23°16′ 59″ S, 166°55′ 1″ E, depth 992 m; MNHN 2002 1412, adult female 755 mm TL, same locality as MNHN 1408; MNHN 2002 1414, juvenile female 659 mm TL, same locality as MNHN 1408; MNHN 2002 1415, adult female 753 mm TL, same locality as MNHN 1408; MNHN 2012 188, juvenile female 664 mm TL, Reunion Island, Western Indian Ocean, 23°16′ 59″ S 54°54′ E, depth 290–300 m; MNRJ 30225, adult female, 650 mm TL, 13°17′ 35″ S, 38°17′ 36″ W; MNRJ 30226, adult female, 742 mm TL, 21°7′ 30″ S, 39°46′ 25″ W; NSMT-P 57351, juvenile male, 233 mm TL, 33°11.36′ N, 133°53.79′ E, depth 786–744 m; NSMT-P 92169, Northwestern Pacific, 34°27.387′ N, 154°56. 927′ E; UF 35687, nine juvenile specimens (males and females ranging from 297 to 432 mm TL), 7°1′ N, 53°37′ W, depth 402 m; UF 35688, juvenile male, 452 mm TL, South of Mobile Bay, Gulf of Mexico, Alabama, USA, 29°9′ N 87°58′ W, depth 460 fathoms; UF 159701, juvenile female, 245,77 mm TL, Taiwan, Pacific Ocean; USNM 94520, juvenile female, 351 mm TL; USNM 382537, adult female, 662 mm TL, depth 750 m, off Florida, Gulf of Mexico, 27°15′ N, 85°00′ W; USNM 400734, adult male, 509 mm TL, depth 915–990 m, Panamá, Caribbean Sea, 9.69800 N, −78.6096 W; USNM 400764, juvenile female, 455 mm TL, depth 724–755 m, Panamá, Caribbean Sea, 9.3818 N, −77.91955 W; USNM 220358, juvenile female, 270 mm TL, Surinam, Atlantic Ocean, 7°44′ N, 54°19′ W, depth 0–350 fathoms; USNM 220361, juvenile male, 398 mm TL, 7°46′ N, 54°0′ W, depth 0–400 fathoms; USNM 220364, juvenile male, 316 mm TL, French Guiana, Atlantic Ocean, 7°46′ N, 54°17′ W; USNM 220489, adult male, 532 mm TL, depth 786 m, Atlantic Caribbean Sea, Lesser Antilles, 17.70 N, −63.72 W; USNM 220490, juvenile male, 302 mm TL, French Guiana, Atlantic Ocean, 7°18′ N, 52°59′ W, depth 350 fathoms; USNM 220493, subadult male, 491 mm TL, depth 777 m, Atlantic Ocean, Surinam, 7.85 N, −54.38 W; USNM 220494, two newborns, size not recorded, French Guiana, Atlantic Ocean; USNM 220495, juvenile female, 314 mm TL, French Guiana, Atlantic Ocean, 7°37′, 53°24′ W, depth 365 fathoms; USNM 220496, juvenile male, 341 mm TL, Surinam, Atlantic Ocean, 7°46′ N, 54°17′ W, depth 350 fathoms; USNM 220497, juvenile male, 324 mm TL, 9°10′ N 15°39′ W, depth 600–610 m; USNM 220498, three juvenile female specimens (A: 365 mm TL; B: 331 mm TL; C: 291 mm TL), Atlantic Ocean, French Guiana, 7°41′ N, 53°35′ W, depth 482 fathoms; USNM 220499, two juvenile specimens (female, 311 mm TL; male, 305 mm TL), French Guiana, Atlantic Ocean, 7°25′ N, 53°06′ W, depth 338 fathoms; USNM 220500, juvenile male, 244 mm TL, Atlantic Ocean, French Guiana; USNM 220503, juvenile female, 316 mm TL, 7°30′ N, 55°29′ W, depth 440 fathoms; USNM 220505, juvenile male, 297 mm TL, French Guiana, Atlatntic Ocean, 7°41′ N, 53°37′ W, depth 402 fathoms; USNM 220506, nine specimens (juvenile males and females ranging from 299 to 495 mm TL), Surinam, Atlantic Ocean, 7°42′ N, 53°51′ W, depth 348 fathoms; USNM 220508, seven specimens (four females: A, 362 mm TL; B, 326 mm TL; C, 280 mm TL; D, 269 mm TL; three males: E, 390 mm TL; F, 351 mm TL; G, 325 mm TL), Surinam, Atlantic Ocean, 7°51′ N, 54°23′ W; USNM 220509, five specimens (three females: A, 395 mm TL; B, 370 mm TL; C, 265 mm TL; two males: D, 382 mm TL; E, 360 mm TL), 7°37′ N, 53°23′ W, depth 395 fathoms; USNM 220510, juvenile female, 485 mm TL, depth 777 m, Atlantic 373 Ocean, Surinam, 7.85 N, −54.38 W; USNM 220865, juvenile male, 333 mm TL, French Guiana, Atlantic Ocean, 7°41′ N, 53°37′ W, depth 0–735 m; USNM 201761, adult male, 470 mm TL, depth 823 m, Atlantic, Caribbean Sea, Venezuela, 12.03 N, −69.35 W; USNM 201909, juvenile male, 301 mm TL, off Surinam, depth 350 fathoms; USNM 318617, juvenile female, 318 mm TL, depth 2000 m, Sulu Sea, off Southern Negros Island, Philippines, Pacific Ocean; USNM 400745, juvenile female, 347 mm TL, depth 723–761 m, Panamá, Caribbean Sea, 9.0347 N, −81.06095 W; USNM 220865, juvenile male, 334 mm TL, depth 0–735 m, French Guiana, 7.68 N, −53.62 W; USNM 220509, juvenile female, 397 mm TL, depth 722 m, French Guiana, 7.62 N, −53.38 W; ZMH 105520, adult male 502 mm TL, off Senegal, 16°8′ N, 22°22′ W, depth 580 m; ZMH 106147, juvenile male 454 mm TL, Southwestern Atlantic, 32°11′ S, 45°08′ W, depth 560–580 m; ZMH 108574, juvenile female 315 mm TL, 39°55′ S, 26°2′ W, depth 2000 m; ZMH 120262, two juveniles (female 328 mm TL, male 290 mm TL), 7°44′ N, 53°58′ W, depth 660 m; ZMH 120485, juvenile male 468 mm TL, off Senegal, 14°21′ N, 17°40′ 1″ W, depth 1000 m.
Other Squaliformes.
Centroscyllium fabricii. USNM 35579, juvenile female, 530 mm TL; FLMNH
159844, juvenile female, 420 mm TL.
Centrophorus granulosus. USNM 220221, juvenile female, 395 mm TL.
Dalatias licha. USNM 157844, juvenile female, 361 mm TL.
Deania calcea. MZUSP 123066., adult female, 1035 mm TL.
Deania quadrispinosum. SAIAB 188437, juvenile female, 540 mm TL.
Etmopterus cf. princeps. MNHN 1998 1294, adult male 572 mm TL; MNHN 1998 1296, three adult females (695 mm TL, 680 mm TL, 668 mm TL; MNHN 1998 1299, four specimens (two adult males, 679 mm TL, 603 mm TL; two females, one adult 689 mm TL, one juvenile 633 mm TL.
Etmopterus pusillus. USNM 221042, juvenile female, 530 mm TL.
Oxynotus bruniensis. USNM 320641, juvenile female, 465 mm TL; HUMZ 91383, juvenile male, 545 mm TL.
Oxynotus centrina. MCZ 39629, adult female, 640 mm TL.
References
- Naylor, G.J.; Caira, J.N.; Jensen, K.; Rosana, K.A.; Straube, N.; Lakner, C. Elasmobranch phylogeny: A mitochondrial estimate based on 595 species. In The Biology of Sharks and Their Relatives; Carrier, J.C., Musick, J.A., Heithaus, M.R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 31–56. [Google Scholar]
- Straube, N.; Li, C.; Claes, J.M.; Corrigan, S.; Naylor, G.J.P. Molecular phylogeny of Squaliformes and first occurrence of bioluminescence in sharks. BMC Evol. Biol. 2015, 15, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, D. Deep-sea cartilaginous fishes of the Indian Ocean. Volume 1. Sharks. FAO Species Cat. Fish. Purp. 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ebert, D.A.; Dando, M.; Fowler, S. Sharks of the World: A Complete Guide; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- White, W.T.; Vaz, D.F.B.; Ho, H.; Ebert, D.A.; de Carvalho, M.R.; Corrigan, S.; Rochel, E.; de Carvalho, M.; Tanaka, S.; Naylor, G.J.P. Redescription of Scymnodon ichiharai Yano and Tanaka 1984 (Squaliformes: Somniosidae) from the western North Pacific, with comments on the definition of somniosid genera. Ichthyol. Res. 2015, 62, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigmann, S.; Vaz, D.F.B.; White, W.T.; de Carvalho, M.R.; Thiel, R. Distribution and comments on the morphology of Centroscymnus owstonii Garman, 1906 (Squaliformes: Somniosidae), with focus on its occurrence in the Indian Ocean. Mar. Biodivers. 2016, 46, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, D.F.B. Scymnodon plunketi (Waite, 1910): A junior synonym of Scymnodon macracanthus (Regan, 1906) (Somniosidae: Elasmobranchii). J. Fish Biol. 2021, 99, 472–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz, D.F.B. Revisão Taxonômica e Morfológica do Gênero Centroscymnus Barboza du Bocage & Britto-Capello, 1864, com Comentários no Arranjo Genérico da Família Somniosidae (Chondrichthyes: Squaliformes); Universidade de São Paulo: São Paulo, Brazil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yano, K.; Tanaka, S. Portuguese shark, Centroscymnus coelolepis from Japan, with notes on C. owstoni. Jpn. J. Ichthyol. 1983, 30, 208–216. [Google Scholar]
- Yano, K.; Tanaka, S. Review of the deep sea squaloid shark genus Scymnodon of Japan, with a description of a new species. Jpn. J. Ichthyol. 1984, 30, 341–360. [Google Scholar]
- Compagno, L.J.V.; Dando, M.; Fowler, S.A. Field Guide to the Sharks of the World; Harper Collins Publishers Ltd.: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Didier, D.; Kemper, J.M.; Ebert, D.A. Phylogeny, Biology, and Classification of Extant Holocephalans. In Biology of Sharks and Their Relatives, 2nd ed.; Carrier, J.C., Musick, J.A., Heithaus, M.R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 97–122. [Google Scholar]
- Last, P.R.; White, W.T.; de Carvalho, M.R.; Séret, B.; Stehmann, M.F.W.; Naylor, G.J.P. Rays of the World; CSIRO Publishing: Clayton South, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue, P.C.; Rücklin, M. The ins and outs of the evolutionary origin of teeth. Evol. Dev. 2016, 18, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ankhelyi, M.; Wainwright, D.K.; Lauder, G.V. Diversity of dermal denticle structure in sharks: Skin surface roughness and three-dimensional morphology. J. Morphol. 2018, 279, 1132–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibert, E.C.; Rubin, L.D. An early Miocene extinction in pelagic sharks. Science 2021, 372, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reif, W.-E. Squamation and Ecology of Sharks. Cour. Forsch.-Inst. Senckenberg 1985, 78, 1–255. [Google Scholar]
- Taniuchi, T.; Garrick, J.A.F. A new species of Scymnodalatias from southern oceans, and comments on other Squaliform sharks. Jpn. J. Ichthyol. 1986, 33, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deynat, P.P.; Séret, B. Le revêtement cutané des raies (Chondrichthyes, Elasmobranchii, Batoidea). Morphologie et arrangement des denticules cutanés. Ann. Des Sci. Nat. Zool. 1996, 17, 65–83. [Google Scholar]
- Poscai, A.N.; Silva, J.P.C.B.; Casas, A.L.; Lenktaitis, P.; Gadig, O.B.F. Morphological study of the oral denticles of the porbeagle shark Lamna nasus. J. Fish Biol. 2022, 101, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, W.-E. Morphology and hydrodynamic effects of the scales of fast swimming sharks. Fortschr. Zool. 1985, 30, 483–485. [Google Scholar]
- Oeffner, J.; Lauder, G.V. The hydrodynamic function of shark skin and two biomimetic applications. J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 215, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauder, G.V.; Wainwright, D.K.; Domel, A.G.; Weaver, J.; Wen, L.; Bertoldi, K. Structure, biomimetics, and fluid dynamics of fish skin surfaces. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2016, 1, 060502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschi, W.; Tabit, C. Functional aspects of placoid scales: A review and update. Aust. J. Mar. Fresh. Res. 1992, 43, 123–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, W. Protective and hydrodynamic function of the dermal skeleton of elasmobranchs. Neues Jahrb. Für Geol. Und Paläontologie Abh. 1978, 157, 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Reif, W.-E. Wound healing in sharks. Zoomorphologie 1978, 90, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, E.M.; Bagla, A.; Plioplys, K.D.; McCauley, D.J.; Lafferty, K.D.; O’Dea, A. Dermal denticle shedding rates vary between two captive shark species. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2022, 682, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, D.F.; De Carvalho, M.R. Morphological and taxonomic revision of species of Squatina from the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean (Chondrichthyes: Squatiniformes: Squatinidae). Zootaxa 2013, 3695, 1–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigelow, H.B.; Schroeder, W.C. Deep water elasmobranchs and chimaeroids from north-western Atlantic slope. Bull. Mus. Comp. Zool. 1954, 112, 37–87. [Google Scholar]
- Garrick, J.A.F. The systematic position of Centroscymnus waitei (Thompson, 1930), Selachii. Trans. R. Soc. New Zealand 1955, 83, 227–239. [Google Scholar]
- Garrick, J.A.F. Scymnodon plunketi (Waite, 1910), an abundant deep-water shark of New Zealand waters. Trans. R. Soc. New Zealand 1959, 87, 271–282. [Google Scholar]
- Cadenat, J.; Blache, J. Requins de Mediterranée et d’ Atlantique. Faune Tropicale. ORSTOM 1981, 21, 1–330. [Google Scholar]
- White, W.T.; Ebert, D.A.; Naylor, G.J.P.; Ho, H.C.; Clerkin, P.; Verissimo, A.; Cotton, C.F. Revision of the genus Centrophorus (Squaliformes: Centrophoridae): Part 1-Redescription of Centrophorus granulosus (Bloch & Schneider), a senior synonym of C. acus Garman and C. niaukang Teng. Zootaxa 2013, 3752, 35–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- White, W.T.; Ebert, D.A.; Naylor, G.J.P. Revision of the genus Centrophorus (Squaliformes: Centrophoridae): Part 2—Description of two new species of Centrophorus and clarification of the status of Centrophorus lusitanicus Barbosa du Bocage & de Brito Capello, 1864. Zootaxa 2019, 4344, 86–114. [Google Scholar]
- White, W.T.; Guallart, J.; Ebert, D.A.; Naylor, G.J.P.; Verissimo, A.; Cotton, C.F.; Harris, M.; Serena, F.; Iglesias, S.P. Revision of the genus Centrophorus (Squaliformes: Centrophoridae): Part 3—Redescription of Centrophorus uyato (Rafinesque) with a discussion of its complicated nomenclatural history. Zootaxa 2022, 5155, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garman, S. The Plagiostomia (sharks, skates, and rays). Mem. Mus. Comp. Zool. 1913, 36, 1–515. [Google Scholar]
- Bigelow, H.B.; Schroeder, W.C. Sharks. In Fishes of the Western North Atlantic; Tee-Van, J., Breder, C.M., Hildebrand, S.F., Parr, A.E., Schroeder, W.C., Eds.; Sears Foundation for Marine Research, Yale University: New Haven, CT, USA, 1948; pp. 59–546. [Google Scholar]
- Bigelow, H.B.; Schroeder, W.C. A study of the sharks of the suborder Squaloidea. Bull. Mus. Comp. Zool. 1957, 117, 1–150. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, J.I. The Sharks of North America; Oxford Univ. Press: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Garrick, J.A.F. Studies on New Zealand Elasmobranchii. Part V. Scymnodalatias n. g. Based on Scymnodon sherwoodi Archey, 1921 (Selachii). Trans. R. Soc. N. Z. 1956, 83, 555–571. [Google Scholar]
- Garrick, J.A.F. Two northern hemisphere species of Centroscymnus in New Zealand Waters. Trans. R. Soc. N. Z. 1959, 87, 75–89. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa du Bocage, J.V.; de Brito Capello, F. Sur quelque espèces inédites de Squalidae de la tribu Acanthiana, Gray, qui fréquentent les côtes du Portugal. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. B 1864, 1864, 260–263. [Google Scholar]
- Bigelow, H.B.; Schroeder, W.C.; Springer, S. New and little known sharks from the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico. Bull. Mus. Comp. Zool. 1953, 109, 211–276. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, C.J.L.; Collin, S.P. Structure and topographic distribution of oral denticles in elasmobranch fishes. Biol. Bull. 2012, 222, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, C.J.L.; Martin, K.J.; Fraser, G.J.; Collin, S.P. Morphology and distribution of taste papillae and oral denticles in the developing oropharyngeal cavity of the bamboo shark, Chiloscyllium punctatum. Biol. Open 2017, 5, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabaj, M.H. Standard Symbolic Codes for Institutional Resource Collections in Herpetology and Ichthyology: An Online Reference. Version 7.1 (21 March 2019). Am. Soc. Ichthyol. Herpetol. 2019. Available online: http://www.asih.org/ (accessed on 8 October 2023).
- Rincon, G.; Mota, R.; Mazzoleni, R.; Lessa, R.; de Moura, M.F.; Charvet, P. Dermal denticle variations on a newborn Roughskin Dogfish Centroscymnus owstonii (Chondrichthyes: Somniosidae) captured off northeastern Brazil with notes on ontogenetic differentiation. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 44, 101761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, W. Morphogenesis and function of the squamation in sharks. Neues Jahrb. Für Geol. Und Paläontologie Abh. 1982, 164, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, P.; Habegger, M.L.; Lang, A.; Hueter, R.; Davis, J. Scale morphology and flexibility in the shortfin mako Isurus oxyrinchus and the blacktip shark Carcharhinus limbatus. J. Morphol. 2012, 273, 1096–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabler-Smith, M.K.; Wainwright, D.K.; Wong, G.A.; Lauder, G.V. Dermal denticle diversity in sharks: Novel patterns on the interbranchial skin. Integr. Org. Biol. 2021, 3, obab034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popp, M.; White, C.F.; Bernal, L.P.; Wainwright, S.A.; Lauder George, V. The denticle surface of thresher shark tails: Three-dimensional structure and comparison to other pelagic species. J. Morphol. 2020, 281, 938–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macías-Cuyare, M.; Oddone, M.C. Morphological pattern of the dermal denticles of the Southern sawtail catshark Galeus mincaronei Soto, 2001. J. Morphol. 2022, 283, 1120–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz, D.F.; de Carvalho, M.R. New Species of Squatina (Squatiniformes: Squatinidae) from Brazil, with comments on the taxonomy of angel sharks from the Central and Northwestern Atlantic. Copeia 2018, 106, 144–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Weaver, J.C.; Lauder, G.V. Biomimetic shark skin: Design, fabrication, and hydrodynamic function. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 217, 1656–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Weaver, J.C.; Thornycroft, P.J.M.; Lauder, G.V. Hydrodynamic function of biomimetic shark skin: Effect of denticle pattern and spacing. Bioinsp. Biomimet. 2015, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domel, A.G.; Saadat, M.; Weaver, J.; Haj-Hariri, H.; Bertoldi, K.; Lauder, G.V. Shark denticle-inspired designs for improved aerodynamics. J. Roy. Soc. Inter. 2018, 15, 20170828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domel, A.G.; Domel, G.; Weaver, J.; Saadat, M.; Bertoldi, K.; Lauder, G.V. Hydrodynamic properties of biomimetic shark skin: Effect of denticle size and swimming speed. Bioinsp. Biomimet. 2018, 13, 056014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, E.M.; Norris, R.D.; O’Dea, A. Dermal denticles as a tool to reconstruct shark communities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 566, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, E.M.; McCauley, D.J.; Morales-Saldaña, J.M.; Leonard, N.D.; Zhao, J.-X.; O’Dea, A. Fossil dermal denticles reveal the preexploitation baseline of a Caribbean coral reef shark community. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2017735118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feichtinger, I.; Adnet, S.; Cuny, G.; Guinot, G.; Kriwet, J.; Neubauer, T.; Pollerspöck, J.; Shimada, K.; Straube, N.; Underwood, C. Comment on “An early Miocene extinction in pelagic sharks”. Science 2021, 374, eabk0632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, G.J.P.; de Lima, A.; Castro, J.I.; Hubbell, G.; de Pinna, M.C.C. Comment on “An early Miocene extinction in pelagic sharks”. Science 2021, 374, eabj8723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, T.; Murakumo, K.; Komoto, S.; Dove, A.; Kino, M.; Miyamoto, K.; Toda, M. Armored eyes of the whale shark. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, G.J. Pharyngeal denticles (placoid scales) of sharks, with notes on the dermal skeleton of vertebrates. Amer. Mus. Nov. 1970, 2415, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, K.J.; Rasch, L.J.; Cooper, R.L.; Metscher, B.D.; Johanson, Z.; Fraser, G.J. Sox2+ progenitors in sharks link taste development with the evolution of regenerative teeth from denticles. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 14769–14774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, R.L.; Nicklin, E.F.; Rasch, L.J.; Fraser, G.J. Teeth outside the mouth: The evolution and development of shark denticles. Evol. Dev. 2022, 25, 54–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortonese, E. Studi sui Plagiostimi. Arch. Zool. Ital. 1952, 37, 383–398. [Google Scholar]
- Nakabo, T. Fishes of Japan with Pictorial Keys to the Species; Tokai University Press: Tokyo, Japan, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Garman, S. New Plagiostomia. Bull. Mus. Comp. Zool. 1906, 11, 202–208. [Google Scholar]
- Compagno, L.J.V. Sharks of the world. An annotated and illustrated catalogue of sharks species known to date. FAO Fish. Synop. 1984, 125, 1–655. [Google Scholar]
- Compagno, L.J.V. Sharks. In The Living Marine Resources of the Western Central Atlantic. Vol. 1: Introduction, Molluscs, Crustaceans, Hagfishes, Sharks, Batoid Fishes and Chimaeras; Carpenter, K.E., Ed.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2002; pp. 357–505. [Google Scholar]
- Last, P.R.; Stevens, J.D. Sharks and Rays of Australia, 2nd ed.; Fisheries Research & Development Corporation: Canberra, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ebert, D.A.; Fowler, S.L.; Compagno, L.J. Sharks of the World: A Fully Illustrated Guide; Wild Nature Press: Plymouth, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Weigmann, S. Annotated checklist of the living sharks, batoids and chimaeras (Chondrichthyes) of the world, with a focus on biogeographical diversity. J. Fish Biol. 2016, 88, 837–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.P.C.B.; Vaz, D.F.B. Morphology and phylogenetic significance of the pelvic articular region in elasmobranchs (Chondrichthyes). Cladistics 2023, 39, 155–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, D.F.B.; Hilton, E.J. The caudal skeleton of Batrachoidiformes (Teleostei: Percomorphacea): A study of morphological diversity, intraspecific variation, and phylogenetic inferences. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2020, 189, 228–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petean, F.d.; de Carvalho, M.R. Comparative morphology and systematics of the cookiecutter sharks, genus Isistius Gill (1864) (Chondrichthyes: Squaliformes: Dalatiidae). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201913. [Google Scholar]
- Bechert, D.W.; Bartenwerfer, M.; Hoppe, G.; Reif, W.E. Drag reduction mechanisms derived from shark skin. AIAA 1986, 2, 1044–1068. [Google Scholar]
- Bixler, G.D.; Bhushan, B. Fluid Drag Reduction with Shark-Skin Riblet Inspired Microstructured Surfaces. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 4507–4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Alkahtani, M.; Hemmer, P.R.; Liang, H. Drag-reduction of 3D printed shark-skin-like surfaces. Friction 2019, 7, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, D.; Song, W. Recent developments in fabricating drag reduction surfaces covering biological sharkskin morphology. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 93–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabler-Smith, M.K.; Lauder, G.V. Ridges and riblets: Shark skin surfaces versus biomimetic models. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 975062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raayai-Ardakani, S.; McKinley, G.H. Drag reduction using wrinkled surfaces in high Reynolds number laminar boundary layer flows. Phys. Fluids 2017, 29, 093605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raayai-Ardakani, S.; McKinley, G.H. Geometric optimization of riblet-textured surfaces for drag reduction in laminar boundary layer flows. Phys. Fluids 2019, 31, 053601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irschick, D.J.; Hammerschlag, N. Morphological scaling of body form in four shark species differing in ecology and life history. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2014, 114, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irschick, D.J.; Fu, A.; Lauder, G.; Wilga, C.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Hammerschlag, N. A comparative morphological analysis of body and fin shape for eight shark species. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2017, 122, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayford, J.H.; Godfrey, H.; Whitehead, D.A. Ontogenetic morphometry of the brown smoothhound shark Mustelus henlei with implications for ecology and evolution. J. Morphol. 2023, 284, e21608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).