Abstract
Although spiders constitute a highly diversified group of animals, the knowledge regarding their geographic distribution (i.e., the so-called Wallacean shortfall) and diversity patterns is incipient on a global scale; while attempts to explore such patterns have been made for the highly diversified Neotropical fauna, several Old World regions are historically neglected. Aiming to close this gap, the present study provides the most comprehensive review of spatial variation in the diversity patterns of the spider fauna of Iran. We also examined the effects of sampling biases on the results. We gathered a database with 4434 non-duplicate records of 935 species of spiders from Iran, 215 of which are currently considered endemic to the country. We showed that, despite a significant improvement in state-of-the-art taxonomic research regarding this fauna in the past 20 years, the Iranian spider fauna suffers from a highly uneven distribution of records throughout the country and its ecoregions. Additionally, highly sampled areas are typically near large cities. We also found a high correlation between the number of records and species of spiders and the number of records of plants and other animals in Iran, suggesting that the biodiversity shortfalls herein described for spiders are corroborated by other taxa. The biases reported herein are likely to be observed for other countries, as the area alone explained only 33.24% of the spider species richness among 171 compared countries. We hope that the present study stimulates further sampling and research aiming to explore this fauna and the underlying biological processes related to its patterns of diversity and distribution.
1. Introduction
Spiders (Araneae), with over 50,000 known species in 132 families [1], form the largest order within the class Arachnida and rank as the sixth most speciose order in the animal kingdom. Considering their rich evolutionary history dating back to the Late Carboniferous [2], spiders are considered one of the most successful groups of organisms. Thanks to the astonishing dispersal abilities of many species, spiders occur in almost all terrestrial habitats, and may reach peak densities of up to 700,000 individuals in a hectare of a tropical rainforest [3]. A few groups inhabit relatively unusual habitats, including fresh water and littoral ecosystems, and altitudes as high as 6700 m on Mount Everest [4,5]. Despite this vast diversity, our knowledge of the systematics, distribution, and natural history of spiders remain relatively incipient on a global scale; it is estimated that at least around 80,000 species of spiders are awaiting discovery, and it would not be surprising if their global diversity exceeds 200,000 species [6]. The uncertainty regarding the true species richness of spiders represents the Linnean shortfall, i.e., lack of taxonomic knowledge [7], which is usually evaluated based on species description accumulation curves (see [6,8]) or the opinions of taxonomic experts (see [6]).
Spatially, the species richness is defined as the number of species inhabiting a specific region or ecosystem. The distribution of records of spider species at a large geographic scale is usually heterogeneous [8,9,10,11], due to a biased sampling closer to main access routes, large cities, and historically important research institutions—the so-called ‘museum effect’ [12]. As a result, huge areas have very few or no records of their spider fauna, which hinders an evaluation of their true species richness [8].
Recently, a significant effort has been made to provide detailed information on the diversity and distribution patterns of the spider fauna in the Neotropical region e.g., [8,11,12]. However, although the spider fauna of some regions have been long studied by scientists [13,14,15,16], detailed information (as available for the Neotropics) is absent for other regions. Therefore, in the present contribution, we aim to explore the diversity and distribution patterns of spiders of Iran, a Middle Eastern country.
Iran is a large country, covering an area of 1,648,195 km2 in western Asia and forming the greater part of the Iranian plateau, a NW–SE-oriented geographical unit of mountainous highlands uplifted during the Miocene as a result of the collision of the Eurasian and the Arabian plates [17]. There are several mountainous regions in Iran, such as the Alborz range in the north and the Zagros range extending from south-eastern Turkey and northern Iraq to southern Iran, both of which have been considered to be biodiversity hotspots [18]. From a zoogeographical point of view, Iran is a ‘bridge’ between three biogeographic realms: although primarily located within the Palaearctic, its southern regions comprise the north-western and north-eastern peripheries of the Oriental and Afrotropical realms, respectively, and the country as a whole houses a diverse array of elements from all three realms [19]. Climatologically, Iran is an arid to semi-arid country: 18 terrestrial ecoregions can be recognized within the borders of Iran, with more than 55% of the country’s area corresponding to three desert ecoregions [20]. The Lut desert in the southeast is particularly noteworthy, as it displays the highest recorded land surface temperature (80.83 °C in 2018) and thus has been dubbed as the ‘thermal pole of the Earth’ [21]. Iran also comprises six main watersheds and more than twenty larger lakes, including the Urmia lake which at its greatest extent was considered the world’s sixth largest saltwater lake. The northern slopes of the Alborz mountains are the most humid regions of Iran and receive 800–2000 mm of annual rainfall [19].
Over the past two decades, the spiders of Iran have been the subject of many extensive taxonomic and faunistic surveys [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42]. Currently, there are 921 species of 324 genera and 55 families of spiders known from this country [39]. However, we hypothesize that the country remains poorly investigated regarding spiders, with vast regions inadequately studied or completely unsampled. Here, we evaluate the effect of sampling bias on the current understanding of the distribution of Iranian spiders and provide detailed information on their known diversity patterns.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Spider Database
We constructed a database of points of occurrences of all spider species from Iran. It is based on the most recent version of the checklist of Iranian spiders [39] but also comprises published articles (until 20 December 2022) with data points not yet included in the checklist, as well as some unpublished records of described species and those of 14 undescribed species of Dysdera Latreille, 1804 (Dysderidae).
More than 300 publications were examined, most of which are available from the World Spider Catalog [1]. The coordinates were taken from the original publications or georeferenced a posteriori using online sources (e.g., Google Earth) if no coordinates were provided. The coordinates were checked and clipped based on the Iranian shapefile using ArcMap 10.8 (ESRI, Redlands, CA, USA). Records with coordinates outside of the Iranian borders were removed. A map with occurrence points was produced with a background raster layer with natural cover [43]. All raster files are shown with a stretched symbology with 2.5 standard deviations.
A literature review was conducted to compare the spider species richness of Iran with those of other countries. This search aimed to find sources that provide spider species counts and/or checklists for each country. Alternatively, the World Spider Catalog [1] database was filtered, counting the number of valid spider species with a distribution explicitly cited for each country. This approach underestimates the species richness per country, as it does not consider the species whose distribution are cited in the World Spider Catalog [1] as continents only. However, it allows the information taken from the literature to be updated. As some published checklists are not recent, if the species richness data extracted from the World Spider Catalog was higher, this number was preferred. For example, the most recent Brazilian spider checklist published [11] includes 3103 species, while the World Spider Catalog [1] provides a list of 3960 species, the number used herein. Combined, these procedures yielded data for 203 countries, of which 171 were used in the analyses, based on an arbitrary lower minimum of 20 recorded spider species per country (see details and references in Table S2). To test if the country’s area (in square kilometres) explains the spider species richness, a generalized linear model with quasi-Poisson distribution and log as link function was used. This approach was preferred over a Poisson distribution owing to overdispersion, and also over a Gaussian distribution based on a log-transformed country area, as changing only the link function affects the model but not the variance of the variables [44]. Model prediction was accessed by calculating the percentage of the test model deviance compared to a null model deviance. These analyses and a corresponding graph were performed using base R functions.
2.2. Biogeographic Analyses
An endemism index was calculated as the inverse number of 0.5 side-by-side degree hexagons occupied by each species. This index has a higher value of 1, for a species known (in Iran) only by localities within the same hexagon, therefore representing a narrowly distributed species in the Iranian territory. This index was calculated as parameter to evaluate the Linnean and the Wallacean shortfalls throughout time.
We estimated the area without records of spiders in Iran by calculating the percentage of the Iranian area occupied by two buffers with different radii surrounding the points of occurrences of spiders: 5 km (a more realistic estimate) and 10 km (a more conservative estimate). We used two distinct ranges aiming to consider the imprecision of the coordinates used. The spatial variation in the density of records and species was, respectively, accessed using the functions ‘Sampling Effort’ (search radius = 50,000 m) and ‘Species Richness’ (hexagon size = 0.5; minimum number of samples = 10; Lambda smoothing factor of spline = 40) in the package BioDinamica, developed for the DinamicaEGO 7 software [45]. To compare the observed patterns for spiders, we downloaded (in July 2022) all specimen-based records of plants and animals from Iran from the Global Biodiversity Information Facility—GBIF, excluding those records flagged as suspicious. Duplicate records (i.e., records of the same species with the same coordinates) were deleted. The density of records of arthropods-only (n = 2523), all animals (n = 7954), and all taxa (i.e., plants and animals) (n = 17,762) were calculated using the same methods and parameters as for spiders. A Spearman correlation index was further calculated using the raw numbers of species (for spiders-only) and records (for all compared groups) from each 0.5 side-by-side degree hexagon. Although the GBIF database includes records of spiders, these records were not excluded to allow the comparison of the GBIF data with the literature and museum databases gathered for the present contribution. The GBIF database is biased towards its contributors; therefore, the spider records share similar biases as other taxa, making them useful for the purpose of the present study. Lastly, a pairwise Jaccard dissimilarity index was calculated between the spider fauna of Iranian ecoregions with at least 50 records using the function ‘beta.pair’ of the package ‘betapart’ for R [46].
3. Results
The present study is based on a total of 4434 non-duplicate records (Figure 1) of 935 species of spiders from Iran, 14 currently undescribed. The database analysed here includes 215 spider species endemic to (or currently only known from) Iran, 38 species known only from the Middle East, 36 species known only from the Middle East and Caucasus, 60 species known only from the Middle East and Central Asia, 23 species known only from the Caucasus, Middle East, and Central Asia, 455 species known only from the Old World, and 108 species known from both the Old and New World (see Table S1).
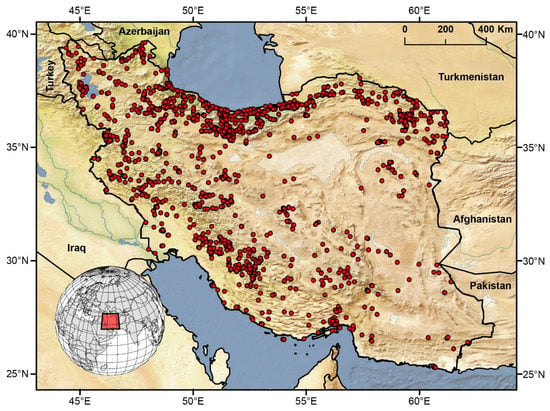
Figure 1.
Distribution records of spiders in Iran. Each point represents a unique record of at least a single spider species in a given location.
Four families exceeded four hundred records (Figure 2a): Lycosidae (n = 699), Linyphiidae (n = 688), Salticidae (n = 459), and Gnaphosidae (n = 428), while six families (Caponiidae, Cyrtaucheniidae, Mysmenidae, Nesticidae, Synaphridae, and Zoropsidae) are known from a single record. The most recorded families are also the most diverse in Iran: Gnaphosidae (134 spp.), Salticidae (115 spp.), Linyphiidae (85 spp.), and Lycosidae (84 spp.). Twelve families are represented by a single species. Only nine species exhibited more than forty records (Figure 2b), the lycosids Arctosa tbilisiensis Mcheidze, 1946 (n = 65), Aulonia kratochvili Dunin, Buchar & Absolon, 1986 (n = 43), and Pardosa pontica (Thorell, 1875) (n = 40); and the linyphiids Erigone dentipalpis (Wider, 1834) (n = 60), Archaraeoncus prospiciens (Thorell, 1875) (n = 50), Gnathonarium dentatum (Wider, 1834) (n = 49), Prinerigone vagans (Audouin, 1826) (n = 46), Agyneta fuscipalpa (C. L. Koch, 1836) (n = 44), and Tenuiphantes tenuis (Blackwall, 1852) (n = 40). Additionally, 380 species (i.e., 40.64%) recorded from Iran are represented by a single record, and 142 species (i.e., 15.2%) are represented by only two records. The proportion of species known from one or two records increases significantly if only the Iranian endemic spider species are considered: 176 out of 215 species (i.e., 81.86%).
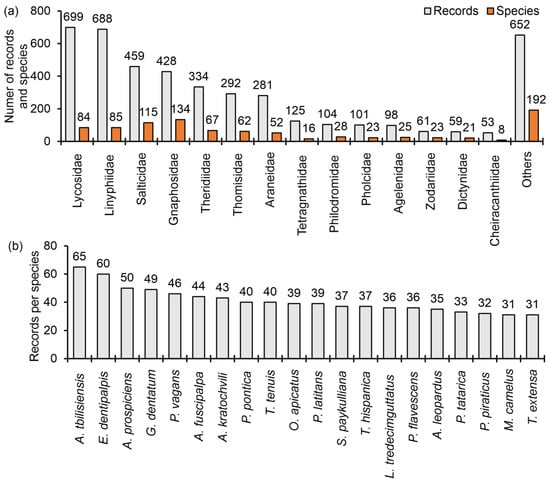
Figure 2.
(a) Number of records (grey bars) and species (orange bars) per family, with more than 50 records. (b) Number of records per species with more than 30 records. Other species sum 3611 records. Full species names in alphabetical order: Agyneta fuscipalpa (C. L. Koch, 1836), Archaraeoncus prospiciens (Thorell, 1875), Arctosa leopardus (Sundevall, 1833); Arctosa tbilisiensis Mcheidze, 1946; Aulonia kratochvili Dunin, Buchar & Absolon, 1986; Erigone dentipalpis (Wider, 1834); Gnathonarium dentatum (Wider, 1834); Latrodectus tredecimguttatus (Rossi, 1790); Megalepthyphantes camelus (Tanasevitch, 1990); Oedothorax apicatus (Blackwall, 1850); Pardosa pontica (Thorell, 1875); Pardosa tatarica (Thorell, 1875); Pirata piraticus (Clerck, 1757); Piratula latitans (Blackwall, 1841); Plexippoides flavescens (O. Pickard-Cambridge, 1872); Prinerigone vagans (Audouin, 1826); Steatoda paykulliana (Walckenaer, 1806); Tenuiphantes tenuis (Blackwall, 1852); Tetragnatha extensa (Linnaeus, 1785); and Trochosa hispanica Simon, 1870.
The oldest record of a spider species from Iran is from the late 19th century [47]. However, subsequent studies revealed records of 30 species described by Clerck [47] in 1757, several of them known from a wide geographic area in Europe, Asia, and the Middle East and/or introduced to the New World [1] but reported from Iran many decades later. The rate at which spider species recorded from Iran were described follows a somewhat continuous and homogeneous curve, with an abnormal increase in the mid-19th century and in the past twenty years (Figure 3a). Most impressive, however, is that the curve that shows the cumulative number of recorded species from Iran greatly ascends in the past 20 years (Figure 3a). Recently described species and Iranian endemics also exhibit a higher endemism level, suggesting that species with narrower distributions in Iran have been described throughout time (Figure 3b).
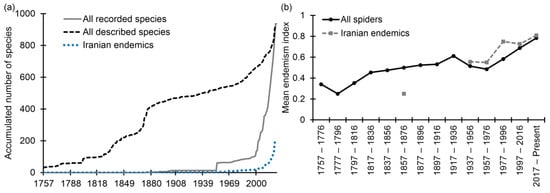
Figure 3.
(a) Accumulated number of recorded (grey line) and described (black and blue dotted lines) spider species in Iran. Iranian endemics are separately shown by the blue dotted line. (b) Mean endemism index of spider species (black line) recorded from Iran, per decade, from 1757 until 2022. The index ranges from 0 (i.e., a species known from many sites) to 1 (i.e., a species known from a single site). Iranian endemics are also separately shown by the grey dotted line. No Iranian endemics were described from 1875 to 1954, yielding an interrupted line.
The sampling coverage of the Iranian territory by spider records encompasses from 5.14% (based on the 5 km buffers) to 14.70% (based on the 10 km buffers). Therefore, ca. 85% of the country remains without a single record of its spider fauna. This vast proportion of area without records is reflected in the number of species per area. At least 29 other countries worldwide, among the 171 countries compared (see Table S2 for details), are known by a higher spider species richness than reported from Iran. The area of each country significantly encompasses about 33.24% of the variation in the number of recorded spider species (p < 0.000, F = 82.499, d.f. = 169). Larger countries harbour a higher number of spider species (Figure 4), as expected. Considering the area of the country, Iran has approximately 0.00058 species/km2, ranking in the 132nd position out of the 171 countries compared. Within the Middle East, the Iranian spider species richness per area is larger than nine other countries (e.g., Yemen: 0.00053 spp./km2; Oman: 0.00046 spp./km2; and Egypt: 0.00041 spp./km2), but smaller than those reported for Israel (0.03037 spp./km2), Lebanon (0.00596 spp./km2), Tunisia (0.00253 spp./km2), Turkey (0.00160 spp./km2), Morocco (0.00121 spp./km2), and United Arab Emirates (0.00119 spp./km2) (see Table S2 for details).
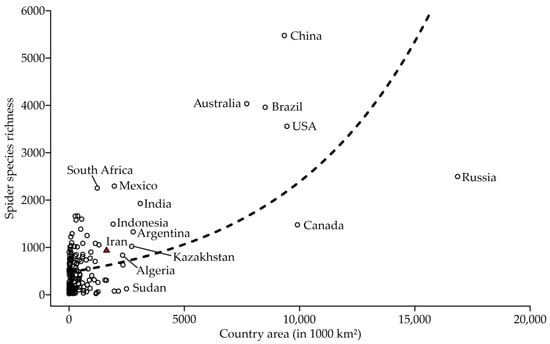
Figure 4.
Correlation between area (in 1000 km2) and spider species richness recorded for 171 countries. Raw data is available in Table S2. Iran is highlighted with a red triangle. Some countries with a larger area, highest spider species richness, or highest mean number of species per km2 are labelled in the figure. The dotted line is the regression curve (p < 0.000, F = 82.499, d.f. = 169).
The low number of species per area unit in Iran also reflects the uneven distribution of records. In the northern regions, a large area with a high density of records is observed in the Alborz mountains, near the large cities of Tehran, Rasht, Karaj, Sari, and Gorgan (Figure 1 and Figure 5d). In the western and central regions, there are several areas with a high density of records along the Zagros mountains, some of them near major cities such as Hamadan, Kermanshah, Kashan, Isfahan, Ahvaz, Yasuj, and Shiraz (Figure 1, Figure 5d and Figure S2). In the northern-most and eastern-most parts of Iran, there are high density areas near the cities of Khoy and Mashhad, respectively (Figure 1, Figure 5d and Figure S2). Most of eastern and south-eastern Iran is poorly sampled, dominated by areas without records or with a low density of records of spiders (Figure 1 and Figure 5d). The aforementioned pattern is relatively highly correlated with those observed for a different (and independent) source of data, based on available online databases for plants and animals (Figure 5a–c; Table 1). The distribution of spider records is also highly correlated with the spatial variation in species richness (Figure 5d,e; Table 1).

Figure 5.
Density of records of plants and animals (a), all animals (b), arthropods (c), and spiders (d), and the spatial variation of spider species richness (e) in Iran. Most populated Iranian cities are labelled in (d).

Table 1.
Spearman correlation index between the number of spider records and species and the number of records of plants and animals from Iran. Correlation calculated using count numbers per 0.5 side-by-side degree hexagon. This index ranges from 0 (no correlation between the compared variables) to 1 (very high correlation between the compared variables).
This clumped distribution of spider records in Iran reflects an uneven distribution of records between ecoregions (Table 2). The three largest Iranian ecoregions (Central Persian desert basins, South Iran Nubo-Sindian desert and semi-desert, and Zagros mountains forest steppe) encompass about 73% of the country’s area, but the number of spider records in these ecoregions is disproportionately low, i.e., 52.1% (n = 2309) of the records. Three ecoregions present more than twice the expected number of records proportional to their areas (Table 2): Caspian Hyrcanian mixed forests (n = 1007 observed records), Alborz range forest steppe (n = 458), and Azerbaijan shrub desert and steppe (n = 80). The biodiversity shortfalls regarding Iranian ecoregions are emphasized by the high mean dissimilarity between them, ranging from 56 to 76% (Table 3).

Table 2.
Observed and expected number of records of spiders, recorded number of spider species, and the percentage of species known from Iran recorded from each Iranian ecoregion [20]. The expected number of records was calculated based on the total number of spider records in Iran proportionally to the area of each ecoregion. Lake Urmia, although not an ecoregion, is also included.

Table 3.
Pairwise Jaccard dissimilarity index for the spider communities at each ecoregion in Iran and their mean values. Only ecoregions with at least 50 records of spiders are included. Ecoregions: Alborz: Alborz range forest steppe; Azerbaijan: Azerbaijan shrub desert and steppe; Caspian: Caspian Hyrcanian mixed forests; Central Persian: Central Persian desert basins; Eastern Anatolian: Eastern Anatolian montane steppe; Kopet Dag: Kopet Dag woodlands and forest steppe; Kuh Rud: Kuh Rud and Eastern Iran montane woodlands; South Iran: South Iran Nubo-Sindian desert and semi-desert; and Zagros: Zagros mountains forest steppe. Shown index ranges from 0 (high similarity between the species at each pairwise ecoregions) to 1 (high dissimilarity).
4. Discussion
The diversity and distribution of spiders from Iran are detailed here for the first time. The Iranian spider fauna, although quite diverse, clearly suffers from huge Linnean and Wallacean shortfalls. Compared to nearby countries in the Middle East and north Africa, the number of spider species known from Iran (935 spp.; mean 0.00058 spp./km2) is disproportionately lower than those reported for smaller countries such as Israel (631 spp.; 0.03037 spp./km2), Turkey (1251 spp.; 0.00160 spp./km2), and Morocco (487 spp.; 0.00121 spp./km2). Contrarily, north African and Middle Eastern countries larger than Iran, such as Algeria (836 spp.; 0.00036 spp./km2) and Saudi Arabia (77 spp.; 0.00004 spp./km2), present a lower number of species per area. Based on the environmental similarities among these countries, a similar species richness should be observed per area unit in them. Worldwide, the estimated species–area relationship is weak (ca. 33.24%), suggesting that the observed differences are explained by other factors, e.g., the environmental differences between these countries, level of investment in scientific research, and historical social factors (i.e., existence of larger research centres, numbers of researchers, etc.). In this sense, the negligence undergone by the Iranian spider fauna before the 21st century is likely to explain the different observed pattern regarding the other two aforementioned Middle Eastern countries (i.e., Israel and Turkey). As shown herein, the knowledge regarding the Iranian spider fauna has significantly increased in the past 20 years, which might have decreased these regional discrepancies. Furthermore, the results shown herein suggest that the biodiversity shortfalls undergone by the spider faunas of countries such as Algeria and Saudi Arabia in north Africa and the Middle East, or in other parts of the world, e.g., Australia, Argentina, Brazil (see [12]), and the United States, might be much stronger.
The rate at which the Iranian spider fauna has been described followed the general trend observed for spider species until the early 20th century (see ‘Statistics’ in World Spider Catalog [1]). However, a higher rate can be seen for Iranian spiders from the mid-20th century to the current year (Figure 3a). Such a high rate is comparable to the significantly high rates of species descriptions owing to the extraordinary taxonomic revisions of Herbert W. Levi [48,49,50,51,52,53] and the results of ‘The Goblin Spider PBI’ project [8]. Additionally, the mean endemism index for Iranian endemic spider species is higher than for non-endemic spider species recorded in Iran, both increasing in the past fifty years (Figure 3b). Such a pattern shall be treated as evidence that the current taxonomic studies regarding the Iranian spider fauna have focused on narrowly distributed taxa known from a single or only a few localities, corroborating the raw data that 81.86% of the Iranian endemic spider species are singletons or doubletons (i.e., known from one or two localities, respectively).
Alternatively, the higher mean endemism index might reflect a tremendous Wallacean shortfall, or a true general pattern of high endemism of the Iranian spider fauna. Although the Linnean shortfall has decreased in the past twenty years (e.g., Figure 3a), the same cannot be affirmed regarding the Wallacean shortfall. The increase in the number of recorded species from Iran yielded a large number of species known from a small number of localities owing to biased sampling. Although the first collection of spiders in Iran dates back to 1859 [54], most of the taxonomic and faunistic data from Iranian spiders are based on material collected in the 1960s and 1970s [35,40] in expeditions conducted by American, Austrian, German, Italian, and Swiss researchers. The Swiss arachnologist Antoine Senglet conducted extensive collecting primarily in northern, western, and north-eastern Iran in 1973 and 1974 [25]. This material, which is now almost completely studied, remains the most diverse and extensive collection of Iranian spiders in the world [55]. Sampling by the few Iranian spider researchers is rather small and mostly limited to agricultural fields, city parks, and areas close to the residencies of the researchers (A. Zamani, pers. obs.), resulting in vast areas of the country (particularly in central, eastern, and south-eastern areas) remaining mostly unsampled (Figure 1).
The distribution of areas with a higher density of records is highly correlated with the most populated cities in the country (Figure 5d and Figure S1). Considering the location of roads in Iran (see Figure S2), it is likely that the density of records is more closely associated with large cities than the availability of access routes. For example, even areas with a high number of roads in Yazd, Kerman, Sistan and Baluchistan, and South Khorasan are poorly sampled. This may be linked to the overall arid and semi-arid environments of these parts of the country, which has probably been a discouraging factor for both local and foreign researchers who conducted more research in the humid and lush lowlands and montane forests of northern Iran [19]. This is further evident when considering the number of records reported per ecoregion: Caspian Hyrcanian mixed forests encompass 22.71% of all records and 40.4% of known reported species despite comprising only 3.47% of the country’s area (Table 2).
It is also noteworthy that the relatively high number of species currently considered endemic to Iran is likely to be heavily biased by more severe Linnean and Wallacean shortfalls in the fauna of the neighbouring countries (e.g., Iraq, Turkmenistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan). It is very probable that with further taxonomic studies on the fauna of these countries, many of these species will be found outside of the Iranian borders. Some cases have already been documented: Phrurolithus azarkinae Zamani & Marusik, 2020 (Phrurolithidae), recently described from Azerbaijan and Iran, was shortly afterwards reported from Armenia, Turkey, and Cyprus [37,56]. Another example is Artema doriae (Thorell, 1881), a large and common pholcid and one of the first species described from Iran. Until very recently, this species was considered endemic, a scenario that changed after the taxonomic revision by Aharon et al. [57], thus being currently known from Turkey, Israel, United Arab Emirates, Iraq, Iran, and Afghanistan, with an introduced population reported from Japan.
Taxonomic knowledge and information on species distribution form the backbone of any additional biodiversity studies. Furthermore, an evaluation of the conservation status of Iranian spiders based on the criteria approved by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) would be possible only after a satisfactory amount of data on their diversity and distribution is available. As predators of mainly insects and other arthropods, spiders occupy a high trophic level which makes them particularly vulnerable to the effects of biodiversity loss; such effects have not yet been evaluated for any spider species from Iran.
A large number of spider species are still waiting to be found and described from Iran, and every new record improves our understanding of the biodiversity of the area. It is possible only through new distribution records for described species to test whether the endemism level suggested here reflects the true pattern or merely the Wallacean shortfall. Since most of the existing records are concentrated near the largest cities, it is important to actively steer collecting efforts towards poorly sampled areas in the eastern and southern parts of the country and less sampled environments or ecoregions, ideally through extensive systematic surveys and not opportunistic sampling. We hope that this contribution motivates more local students to become interested in arachnology and continue the important taxonomic work of collecting, studying, and describing spiders. As we have shown here, species with narrower distributions are being described more recently, and it appears that most of the common, widespread species have already been described; the discovery of uncommon species typically requires more effort and ideally should be supported by well-funded biodiversity projects. Therefore, we also hope that the funding agencies will support basic taxonomic research by financing such projects and the institutions maintaining and expanding the valuable natural history collections, as they house an irreplaceable source of data waiting to be explored and documented.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d15010022/s1, Figure S1. Raw count numbers of records of plants and animals, all animals, arthropods and spiders, and spider species richness in Iran; Figure S2. Density of records of spiders and roads in Iran; Table S1. Spider species from Iran, with their respective general distribution and the number of records analysed in the present study; Table S2. Spider species richness per country, with their respective area (in km2) and mean number of species per area.
Author Contributions
A.Z., V.V., I.E.S. and L.S.C.: conception and design of the research; A.Z.: acquisition of data; L.S.C. and A.Z.: analysis and interpretation of data; A.Z., V.V., I.E.S. and L.S.C.: drafting the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Academy of Finland (grant No. 319913).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ubirajara de Oliveira (Belo Horizonte, Brazil) for providing a new version of the BioDinamica package and for data analyses suggestions, Robert Bosmans (Ghent, Belgium) for providing information regarding the distribution of Phrurolithus azarkinae, and the three anonymous reviewers for their comments on the manuscript. Sarah C. Crews (San Francisco, CA, USA) kindly checked the English of an earlier draft. Philip Russo da Silva shared ideas on the use of the World Spider Catalog database.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- WSC. World Spider Catalog Version 22.5. Available online: http://www.wsc.nmbe.ch/ (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- Selden, P.A.; Shcherbakov, D.E.; Dunlop, J.A.; Eskov, K.Y. Arachnids from the Carboniferous of Russia and Ukraine, and the Permian of Kazakhstan. Paläont. Z. 2014, 88, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coddington, J.A.; Agnarsson, I.; Miller, J.A.; Kuntner, M.; Hormiga, G. Undersampling bias: The null hypothesis for singleton species in tropical arthropod surveys. J. Anim. Ecol. 2009, 78, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanless, F.R. Spiders of the family Salticidae from the upper slopes of Everest and Makalu. Bull. Br. Arachnol. Soc. 1975, 3, 132–136. [Google Scholar]
- Crews, S.C.; Garcia, E.L.; Spagna, J.C.; Van Dam, M.H.; Esposito, L.A. The life aquatic with spiders (Araneae): Repeated evolution of aquatic habitat association in Dictynidae and allied taxa. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2020, 189, 862–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnarsson, I.; Coddington, J.A.; Kuntner, M. Systematics: Progress in the study of spider diversity and evolution. In Spider Research in the 21st Century: Trends and Perspectives; Penney, D., Ed.; Siri Scientific Press: Manchester, UK, 2013; pp. 58–111. [Google Scholar]
- Hortal, J.; de Bello, F.; Diniz-Filho, J.A.F.; Lewinsohn, T.M.; Lobo, J.M.; Ladle, R.J. Seven shortfalls that beset large-scale knowledge of biodiversity. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2015, 46, 523–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.J.; Brescovit, A.D.; de Oliveira-Tomasi, M.; Russo, P.; Oliveira, U. Curves, maps and hotspots: The diversity and distribution of araneomorph spiders in the Neotropics. In Behaviour and Ecology of Spiders; Vieira, C., Gonzaga, M.O., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Nentwig, W. Spiders of Panama: Biogeography, Investigation, Phenology, Check List, Key, and Bibliography of a Tropical Spider Fauna, 1st ed.; Nentwig, W., Ed.; Sandhill Crane Press, Inc.: Gainesville, FL, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, K.; Li, S.; Murphy, R.W. Biogeographical patterns of Chinese spiders (Arachnida: Araneae) based on a parsimony analysis of endemicity. J. Biogeogr. 2008, 35, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, U.; Brescovit, A.D.; Santos, A.J. Sampling effort and species richness assessment: A case study on Brazilian spiders. Biodivers. Conserv. 2017, 26, 1481–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, U.; Paglia, A.P.; Brescovit, A.D.; de Carvalho, C.J.B.; Silva, D.P.; Rezende, D.T.; Leite, F.S.F.; Batista, J.A.N.; Barbosa, J.P.P.P.; Stehmann, J.R.; et al. The strong influence of collection bias on biodiversity knowledge shortfalls of Brazilian terrestrial biodiversity. Divers. Distrib. 2016, 22, 1232–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubick, D.; Paquin, P.; Cushing, P.E.; Roth, V. Spiders of North America: An Identification Manual, 2nd ed.; Ubick, D., Paquin, P., Cushing, P.E., Roth, V., Eds.; American Arachnological Society: Denver, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dippenaar-Schoeman, A.S.; Jocqué, R. African Spiders. An Identification Manual. Plant Prot. Res. Inst. Handb. 1997, 9, 1–392. [Google Scholar]
- Sebastian, P.; Peter, K. Spiders of India, 1st ed.; Sebastian, P., Peter, K., Eds.; Universities Press: Hyderabad, India, 2014; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Jocqué, R.; Alderweireldt, M.; Dippenaar-Schoeman, A. Biodiversity—An African perspective. In Spider Research in the 21st Century: Trends and Perspectives; Penney, D., Ed.; Siri Scientific Press: Manchester, UK, 2013; pp. 18–57. [Google Scholar]
- Ballato, P.; Cifelli, F.; Heidarzadeh, G.; Ghassemi, M.R.; Wickert, A.D.; Hassanzadeh, J.; Dupont-Nivet, G.; Balling, P.; Sudo, M.; Zeilinger, G.; et al. Tectono-sedimentary evolution of the northern Iranian Plateau: Insights from middle–late Miocene foreland-basin deposits. Basin Res. 2017, 29, 417–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noroozi, J.; Talebi, A.; Doostmohammadi, M.; Rumpf, S.B.; Linder, H.P.; Schneeweiss, G.M. Hotspots within a global biodiversity hotspot—Areas of endemism are associated with high mountain ranges. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehzad, B.; Kiabi, B.H.; Madjnoonian, H. The natural areas and landscape of Iran: An overview. Zool. Middle East 2002, 26, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, D.M.; Dinerstein, E.; Wikramanayake, E.D.; Burgess, N.D.; Powell, G.V.N.; Underwood, E.C.; D’amico, J.a.; Itoua, I.; Strand, H.E.; Morrison, J.C.; et al. Terrestrial Ecoregions of the World: A New Map of Life on Earth: A new global map of terrestrial ecoregions provides an innovative tool for conserving biodiversity. Bioscience 2001, 51, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarderakhsh, M.; Prakash, S.; Zhao, Y.; AghaKouchak, A. Satellite-based analysis of extreme land surface temperatures and diurnal variability across the hottest place on Earth. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 2025–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logunov, D.V.; Marusik, Y.M.; Mozaffarian, F. Faunistic review of the jumping spiders of Iran (Aranei: Salticidae). Arthropoda Sel. 2002, 10, 155–167. [Google Scholar]
- Ono, H.; Martens, J. Crab Spiders of the families Thomisidae and Philodromidae (Arachnida: Araneae) from Iran. Acta Arachnol. 2004, 53, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senglet, A. New species of Pholcus and Spermophora (Pholcidae, Araneae) from Iran and Afghanistan, with notes on mating mechanisms. Rev. Suisse Zool. 2008, 115, 355–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanasevitch, A.V. On linyphiid spiders (Araneae) collected by A. Senglet in Iran in 1973-1975. Rev. Suisse Zool. 2008, 115, 471–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanasevitch, A.V. The linyphiid spiders of Iran (Arachnida, Araneae, Linyphiidae). Rev. Suisse Zool. 2009, 116, 379–420. [Google Scholar]
- Logunov, D.V. Taxonomic notes on a collection of jumping spiders from Iran (Araneae, Salticidae). Arachnology 2010, 15, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradmand, M.; Jäger, P. A review on the huntsman spider genus Spariolenus Simon, 1880 (Araneae: Sparassidae: Heteropodinae) in Iran with description of four new species. Zootaxa 2011, 2910, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirshamsi, O.; Zamani, A.; Marusik, Y.M. A survey of Hersiliidae (Arachnida: Araneae) of Iran with description of one new genus and two new species. J. Nat. Hist. 2016, 50, 1447–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirshamsi, O.; Marusik, Y.M.; Zamani, A.; Moradmand, M.; Kashefi, R. Fauna Iranica: I. Annotated checklist of the spiders of Iran (Arachnida: Araneae). Iran. J. Anim. Biosyst. 2015, 1, 1–108. [Google Scholar]
- Marusik, Y.M.; Nadimi, A.; Omelko, M.M.; Koponen, S. First data about cave spiders (Arachnida: Araneae) from Iran. Zool. Middle East 2014, 60, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marusik, Y.M.; Zamani, A. The spider family Filistatidae (Araneae) in Iran. ZooKeys 2015, 2015, 123–135. [Google Scholar]
- Zamani, A.; Altın, Ç.; Szűts, T. A black sheep in Eresus (Araneae: Eresidae): Taxonomic notes on the ladybird spiders of Iran and Turkey, with a new species. Zootaxa 2020, 4851, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, A.; Chatzaki, M.; Esyunin, S.L.; Marusik, Y.M. One new genus and nineteen new species of ground spiders (Araneae: Gnaphosidae) from Iran, with other taxonomic considerations. Eur. J. Taxon. 2021, 751, 68–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, A.; Marusik, Y.M. The spider genera Azerithonica and Tegenaria (Aranei: Agelenidae: Tegenariini) in Iran. Arthropoda Sel. 2019, 28, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, A.; Marusik, Y.M. A review of Agelenini (Araneae: Agelenidae: Ageleninae) of Iran and Tajikistan, with descriptions of four new genera. Arachnology 2020, 18, 368–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, A.; Marusik, Y.M. A survey of Phrurolithidae (Arachnida: Araneae) in southern Caucasus, Iran and Central Asia. Zootaxa 2020, 4758, 311–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, A.; Marusik, Y.M. Revision of the spider family Zodariidae (Arachnida, Araneae) in Iran and Turkmenistan, with seventeen new species. ZooKeys 2021, 1035, 145–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, A.; Mirshamsi, O.; Marusik, Y.M.; Moradmand, M. The Checklist of the Spiders of Iran. Available online: http://www.spiders.ir/ (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- Zamani, A.; Nadolny, A.A.; Dolejš, P. New data on the spider fauna of Iran (Arachnida: Araneae), Part X. Arachnology 2022, 19, 551–573. [Google Scholar]
- Zamani, A.; Seiedy, M.; Saboori, A.; Marusik, Y.M. The spider genus Pterotricha in Iran, with the description of a new genus (Araneae, Gnaphosidae). ZooKeys 2018, 777, 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, B.A. Revisions of Holocnemus and Crossopriza: The spotted-leg clade of Smeringopinae (Araneae, Pholcidae). Eur. J. Taxon. 2022, 795, 1–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earth, N. 1:10 m Natural Earth II, Version 2.1. Available online: http://www.naturalearthdata.com/downloads/10m-raster-data/10m-natural-earth-2/%3E (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- Lindsey, J.K.; Jones, B. Choosing among generalized linear models applied to medical data. Stat. Med. 1998, 17, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, U.; Soares-Filho, B.; Leitão, R.F.M.H.; Rodrigues, H.O. BioDinamica: A toolkit for analyses of biodiversity and biogeography on the Dinamica-EGO modelling platform. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, A.; Orme, D.; Villeger, S.; De Bortoli, J.; Leprieur, F.; Logez, M. Package ´Betapart´: Partitioning Beta Diversity into Turnover and Nestedness Components. R Package Version 1.5.6. 2022. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/betapart/index.html (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Clerck, C. Aranei Svecici. Svenska Spindlar, Uti Sina Hufvud-Slågter Indelte Samt under Några Och Sextio Särskildte Arter Beskrefne Och Med Illuminerade Figurer Uplyste; Laurentius Salvius: Stockholm, Sweeden, 1757. [Google Scholar]
- Levi, H.W. The spider genera Enoplognatha, Theridion, and Paidisca in America north of Mexico (Araneae, Theridiidae). Bull. Am. Museum Nat. Hist. 1957, 112, 5–123. [Google Scholar]
- Levi, H.W. The Neotropical and Mexican species of the orb-weaver genera Araneua, Dubiepeira, and Aculepeira (Araneae: Araneidae). Bull. Museum Comp. Zool. 1991, 152, 167–315. [Google Scholar]
- Levi, H.W. The orb-weaver genus Mecynogea, the subfamily Metinae and the genera Pachygnatha, Glenognatha and Azilia of the subfamily Tetragnathinae north of Mexico (Araneae: Araneidae). Bull. Museum Comp. Zool. 1980, 149, 1–75. [Google Scholar]
- Levi, H.W. The Neotropical orb-weaver genera Chrysometa and Homalometa (Araneae: Tetragnathidae). Bull. Museum Comp. Zool. 1986, 151, 91–215. [Google Scholar]
- Levi, H.W. The orb-weaver genera Argiope, Gea, and Neogea from the Western Pacific Region (Araneae: Araneidae, Argiopinae). Bull. Museum Comp. Zool. 1983, 150, 336–338. [Google Scholar]
- Levi, H.W. The spiny orb-weaver genera Micrathena and Chaetacis (Araneae: Araneidae). Bull. Museum Comp. Zool. 1985, 150, 429–618. [Google Scholar]
- Mozaffarian, F.; Marusik, Y. A checklist of Iranian spiders (Aranei). Arthropoda Sel. 2001, 10, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Schwendinger, P.J.; Monnerat, C. Antoine Senglet (10.IX.1927—29.III.2015), a little-known Swiss entomologist and arachnologist. Rev. Suisse Zool. 2022, 129, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecigne, S. A new species of Sintula (Linyphiidae), redescription of Brigittea innocens (Dictynidae) and eight spider species newly recorded for Turkey (Araneae). Arachnol. Mitteilungen 2021, 62, 11–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharon, S.; Huber, B.A.; Gavish-Regev, E. Daddy-long-leg giants: Revision of the spider genus Artema Walckenaer, 1837 (Araneae, Pholcidae). Eur. J. Taxon. 2017, 376, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).