Abstract
The gut microbiome is important for host health and can be influenced by environmental and hormonal changes. We studied the interactions between anthropogenic land use, glucocorticoid hormones, and gut bacterial communities in common toads (Bufo bufo). We sampled tadpoles from ponds of three habitat types (natural, agricultural, and urban ponds), examined gut microbiome composition using amplicon sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene, and measured the associated stress physiology using water-borne hormones. Tadpoles from different habitat types significantly differed in bacterial composition. However, bacterial richness, Shannon diversity, and Firmicutes to Bacteroidota ratio did not vary with habitat type. In contrast with other studies, we found a positive correlation between baseline corticosterone release rate and bacterial diversity. Stress response and negative feedback were not significantly correlated with bacterial diversity. These results suggest that, despite alterations in the composition of intestinal bacterial communities due to land-use change, common toad tadpoles in anthropogenic habitats may maintain their physiological health in terms of the “gut-brain axis”.
1. Introduction
Human-induced environmental change is occurring at an alarming rate and threatens wildlife health. Populations unable to adapt to these changes may not persist in altered environments. Commensal microbiota contributes to host health by maintaining immune homeostasis, aiding in nutrient uptake and metabolic processes [1,2,3,4]. Habitat shifts can change environmental microbial communities which in turn shape the host’s microbial community [5,6,7,8,9]. On the one hand, environmental stressors alter the environmental microbiome [10,11,12,13,14], but the gut microbiome can also mediate adaptation to environmental stressors [15,16,17]. These two components shape the gut microbial community and affect organismal health [18,19,20].
Agricultural and urban land use alter environments via an increase in chemical pollutants and multiple other factors associated with anthropogenic areas including urban heat island effects [21] and altered environmental and host microbiomes [9,22] Much of this knowledge on wildlife microbiome comes from terrestrial animals [23] while aquatic organisms are relatively under-studied in this regard. Anthropogenic influences on urban aquatic habitats include introduction of sewage water, fecal matter from terrestrial mammals, and pollutants from urban storm water run-off which lead to eutrophication [24,25,26]. In habitats altered for crop production, organisms living in adjacent water bodies are exposed to agrochemicals, nutrients, wastewater and even manure wastes associated with agricultural run-off [27,28,29]. These changes in land use alter the environmental microbial communities in soil and water [24,25,26]. In turn, anthropogenically altered environmental bacterial communities create a potential health risk to aquatic organisms, likely associated with the greater decline in biodiversity observed in freshwater environments than in terrestrial environments [30].
In vertebrates, glucocorticoid stress hormones are released in response to environmental stressors via activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA or interrenal HPI in amphibians) axis [31]. Glucocorticoids are metabolic hormones that aid in energy regulation [31]. Elevated glucocorticoids are associated with altered host microbial biodiversity (reviewed in [32]). In turn, host gut microbiome can also modulate stress response of the HPA/HPI axis and this bi-directional interaction is known as the ‘gut-brain axis’ [33,34,35]. The bi-directional interaction aids in host health and homeostasis [36]. In fish, the gut microbiome affects the “gut-brain axis” such that when the main fish glucocorticoid stress hormone, cortisol, is elevated, gut microbiome diversity is reduced [10]. Similar results have been found for other species (red squirrel [32], fish [37]) whereas other studies have found no relationship in unmanipulated populations [38,39,40]. Anthropogenic environments can alter glucocorticoid physiology in wildlife including aquatic vertebrates [41,42], but little is known about the relationship between land use change, associated shifts in host and environmental microbial communities, and stress physiology in the host. Understanding these interactions would provide additional insight into the mechanism associated with tolerance to environmental change.
Amphibians are an especially sensitive group of aquatic organisms and human-induced environmental change is among the most likely causes of their global population declines [43,44]. Amphibians inhabiting different environments have different skin and gut microbiomes [45,46,47] and these changes can be due to environmental pollutants [39,48] and pathogens [49] which can have negative health effects on amphibians (reviewed by [48,50,51]). To better understand these interactions, here we aimed to investigate the consequences of anthropogenic environmental change on amphibian gut bacterial communities and explore the relationship of host gut bacterial communities with glucocorticoid profile. We examined whether tadpole gut bacterial communities differ between natural, agricultural and urban habitats. We also examined if there was a relationship between gut bacterial communities and major components of the host glucocorticoid profile, specifically the baseline levels of corticosterone (the main glucocorticoid hormone of amphibians), the stress-induced change in corticosterone, and the rate of post-stress recovery in corticosterone. These aspects of glucocorticoid regulation are related to fitness in vertebrates [42,52,53] and differ between natural and anthropogenic habitats in our study species, the common toad Bufo bufo [41]. This species is widespread in Europe, where it breeds in standing water bodies. Breeding adults typically return to the pond in which they developed as larvae, and they rarely migrate farther than 500 m from the pond [54,55]. Adults are predators of invertebrates whereas tadpoles graze on algae and detritus; the re-organization of the digestive tract at metamorphosis likely comes with significant re-structuring in gut microbiomes, as in other amphibians [56]. For these reasons, tadpole gut bacterial communities are likely to be strongly influenced by local environmental factors.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tadpole Collection and Processing
We collected tadpoles in developmental stages 27–31 [57] from 9 ponds (3 rural, 3 urban, and 3 agricultural) in Hungary from 9–17 May 2019 as part of a previously published study [41]. These stages are the early stages before tadpoles show limb toe development. Distances between our ponds vary between 650 m and 49 km; the ponds that are closest to each other are separated by roads and built areas (for coordinates, see [41]). After collection, we placed the tadpoles in 100 mL of spring water for 1h, 3 times sequentially to measure water-borne corticosterone release rates [41]. The first hour of sampling quantifies “baseline” corticosterone release rates, the second hour is a “stressed” phase where a stress response is elicited by agitation, and the third hour is a “recovery” phase for estimating negative feedback [41]. Water-borne method for measuring corticosterone provides an integrated measure from a longer time period than plasma measurements [58] making this measure more appropriate to explore the relationship between corticosterone and bacterial communities. Following water-borne hormone sampling we weighed each tadpole after which they were euthanized and placed into 70% ethanol. Subsequently we aseptically dissected the whole gut from a subsample of 41 tadpoles (14 natural, 14 agricultural, and 13 urban; n = 4−5/population) and placed them in 95% ethanol before storing them at −20 °C for gut bacteria processing.
We performed all procedures in this study in accordance with animal ethics guidelines and they were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Plant Protection Institute, Centre for Agricultural Research. The Environment Protection and Nature Conservation Department of the Pest County Bureau of the Hungarian Government issued the permit for this study (PE-06/KTF/8060-3/2018, PE-06/KTF/8060-1/2018, PE/EA/295-7/2018).
2.2. Corticosterone Analysis
To measure corticosterone, we extracted hormones from the water samples using single phase extraction columns (SPE, SepPak Vac3 cc/500 mg; Waters, Inc., Milford, MA, USA), then used methanol to release the bound hormone into a test tube. We dried the methanol with nitrogen gas and resuspended the residue in assay buffer (Cayman Chemical Inc., Ann Arbor, MI, USA) and used 96 well ELISA plates to analyze corticosterone levels (Cayman Chemical Inc.; (see [41] for details)).
We quantified corticosterone release rates as the amount of water-borne corticosterone measured over one hour, divided by tadpole body mass (pg/g/h). To quantify the magnitude of stress response, we calculated the relative change of corticosterone release rate in response to stress (stress-induced change) as: 100 × (stressed − baseline)/baseline. Similarly, we quantified negative feedback as the relative change from stressed to recovery levels as: 100 × (stressed − recovery)/stressed [59].
2.3. Bacterial Communities Analysis
We used a 16S rRNA gene (V4 region) amplicon sequencing approach. The V4 region is one of the most commonly used in host microbiome studies and provides greater depth and taxa coverage than other 16S rRNA hypervariable regions (compatible with Nextera XT Library Prep, Illumina) across different sample types [60]. DNA was extracted from the guts using Pure Link™ Microbiome DNA Purification Kit. Amplicon libraries were constructed according to [61]. Briefly, we used tagged MiSeq primers targeting the V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene (primers: forward—GTGCCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA; reverse—GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT) [62,63] in polymerase chain reactions (PCR), using KAPA HiFi HotStart ReadyMix (2X) (KAPA Biosystems, Boston, MA, USA). We ran all samples in triplicate under the following conditions: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 3 min, 25 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s, 55 °C for 30 s, 72 °C for 30 s, and a final elongation step at 72 °C for 5 min. We included a non-template control reaction and submitted this for sequencing. We sequenced pooled amplicon libraries with the paired-end Illumina MiSeq platform in the Department of Biology at Texas State University.
We filtered sequencing reads, trimmed, clustered into amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) and taxonomically classified using the DADA 2 pipeline [64] in R and the SILVA 138.1 database [65]. We did not rarefy our data for the analyses presented in the main text [66,67]; however, we repeated the analyses of microbial diversity after rarefaction, which did not alter our conclusions (see Supplementary Material). The sequencing datasets used in this study can be found in the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) repository of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) under the accession number PRJNA883763.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
We used the ‘microbiome’ package in R [68] to calculate relative abundance of each phylum to characterize each tadpole’s microbiome per habitat type. To test if tadpole gut microbiome composition differed between the three habitat types, we applied permutational multivariate analysis of variance (permANOVA) on Bray–Curtis dissimilarity matrices with 10,000 permutations (function ‘adonis’ in R package ‘vegan’). We used Kruskal–Wallis tests to identify ASVs with relative abundances significantly different across habitats, correcting the significance levels for the number of comparisons by the false discovery rate (FDR) method [69]. To visualize the among-habitat differences in bacterial composition, we characterized the bacterial community of each tadpole along three nMDS (non-metric multidimensional scaling) axes using the default settings in the R function ‘metaMDS’ (package ‘vegan’). We used 3 nMDS axes because that fitted the data better than nMDS with 2 axes (based on the stress value which reflects how well the ordination summarizes the observed distances). To test if similarities in tadpole gut microbial community composition are explained by spatial proximity between ponds, we used a partial Mantel test (function ‘mantel.partial’ in ‘vegan’) to quantify the correlation between the Bray–Curtis dissimilarity matrix of ASVs and the spatial distance matrix, conditioned on a third matrix that encoded sameness of habitat type.
To test if tadpoles in different habitats differ in microbial diversity, we calculated the following variables for each tadpole: (i) number of bacterial ASVs, reflecting “bacterial richness”; (ii) Shannon diversity, characterized at the ASV level; and (iii) ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidota (synonym to Bacteroidetes). In humans, the latter ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidota (F/B ratio) influences intestinal homeostasis and changes in that ratio can lead to pathologies [70]. To compare these three variables between habitats, we used each microbial metric as dependent variable in a generalized estimation equations (GEE) model (function ‘geeglm’ in the R package ‘geepack’), with habitat type as fixed factor and pond identity as random factor. In these models, we allowed for the non-independence among tadpoles captured from the same pond using the “exchangeable correlation” (or “compound symmetry”) association structure [71]. For pairwise comparisons among the three habitat types, we extracted linear contrasts (function ‘emmeans’ in the R package ‘emmeans’) from the GEE models and corrected the significance levels with the FDR method.
Lastly, we tested the relationships of microbial diversity measures with the three aspects of the corticosterone profile. Because these relationships are expected to be bi-directional, first we used simple correlation tests (Spearman’s rank correlation) for each pair of variables. Then, to control these relationships for the potential effects of habitat type, we used two sets of GEE models. In the first set of these analyses, the dependent variable was either baseline corticosterone release rate or the stress response or the negative feedback. The predictor variable was either one of the above 3 metrics of microbiome species richness, Shannon diversity, and F/B ratio. Additionally, we included habitat type as a fixed factor and pond identity as random factor as described above. In the second set of GEE analyses, the dependent (hormonal) and predictor (microbial) variables were swapped.
3. Results
We generated a microbial 16SrRNA data set consisting of a total of 209,741 filtered high-quality reads for 41 tadpole intestinal samples. We found 436 unique ASVs, of which 431 could be classified representing 16 phyla, 28 classes, 67 orders, and 79 families of bacteria (Table S1). The top three phyla with highest relative abundance were Bacteroidota, Proteobacteria, and Firmicutes (Figure 1).
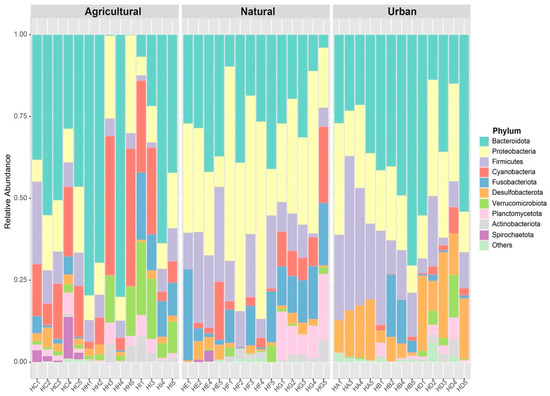
Figure 1.
Relative abundance of bacterial phyla found in the guts of tadpoles collected from 9 ponds across three different habitat types. Sample names on the X-axis are individual tadpole identifiers.
ASV richness and Shannon diversity of the gut bacterial communities, and the F/B ratio did not differ significantly between the 3 habitat types (p ≥ 0.124 for all pairwise comparisons, Table S2). However, the bacterial composition did differ significantly between the 3 habitat types (nested permANOVA: F2,32 = 5.38, p = 0.001), with all 3 pairwise comparisons among natural, agricultural and urban habitat significant (FDR-corrected p < 0.001; Figure 1 and Figure 2). Spatial distance did not correlate with dissimilarity in gut bacterial composition (partial Mantel test: r = 0.03, p = 0.223).
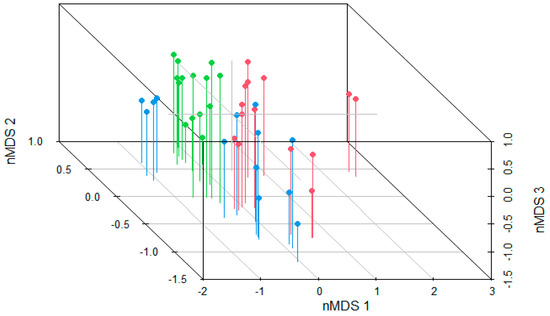
Figure 2.
Clustering of tadpoles from natural (green), agricultural (red), and urban (blue) ponds along 3 non-metric multidimensional scaling (nMDS) axes representing the composition of the gut bacterial communities. The two tadpoles in red on the far right stand out because they do not have Bacteroidota, which was the most abundant phylum in the rest of the tadpoles.
Out of the 436 ASVs, 20 had significantly different relative abundances across the 3 habitat types (Table S1). However, most of these differences were driven by a few non-zero data points, as only two out of the 20 ASVs had a greater than zero median (Table S1). The latter ASVs showed that tadpoles from natural habitats had the highest relative abundance of a group from the Sutterellaceae family, whereas, urban tadpoles had the highest relative abundance a Desulfovibrio genus (Figure 3). Additionally, there was a difference just above the significance level (p = 0.059) showing that agricultural tadpoles had the highest relative abundance of an Rs-E47 termite group (Figure 3).
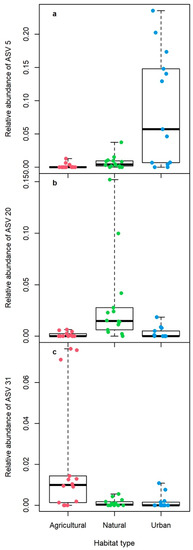
Figure 3.
Relative abundance of the three most common ASVs that differed the most across habitat type: (a) ASV 5 from the genus Desulfovibrio (phylum Desulfobacterota, class Desulfovibrionia, order Desulfovibrionales, family Desulfovibrionaceae), (b) ASV 20 from family Sutterellaceae (phylum Proteobacteria, class Gammaproteobacteria, order Burkholderiales), and (c) ASV 31 from Rs-E47 termite group (phylum Bacteroidota, class Bacteroidia, order Bacteroidales). Colored dots represent individual tadpoles from each habitat type (natural: green, agricultural: red, urban: blue); boxplots show the median (thick line), interquartile range (box), and data range (whiskers).
Using bi-directional correlations, we found significant positive relationship for baseline corticosterone release rate with both the ASV richness (rs = 0.386, p = 0.020) and the Shannon diversity (rs = 0.327, p = 0.040) of the gut bacterial communities (Figure 4), whereas stress response and negative feedback were not significantly correlated with these diversity metrics (p > 0.6), nor with the F/B ratio (p > 0.5). Most of these relationships remained qualitatively unchanged when habitat type was controlled for in GEE models (Table S3).
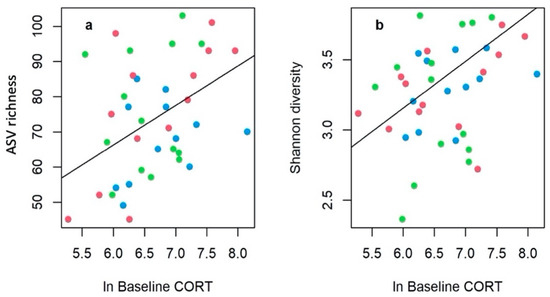
Figure 4.
The significantly positive relationships between natural log transformed baseline corticosterone release rates (pg/g/h) and (a) bacterial (ASV) richness and (b) Shannon diversity of the tadpole gut bacterial communities. Regression lines were fitted from GEE models (Table S3) controlling for habitat type (natural: green, agricultural: red, urban: blue).
4. Discussion
Anthropogenic habitat modification alters the associated terrestrial and aquatic microbial communities and in turn the host microbiome [45,46,72,73]. Our results support these findings as the gut bacterial composition differed for Bufo bufo tadpoles across the three habitat types, with unique microbial profiles characterizing natural, agricultural and urban populations (Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure S3). Similarly to many species of vertebrates including amphibians, we found that the most abundant phyla of intestinal bacteria were Firmicutes, Proteobacteria and Bacteroidota (amphibians: [39,45,74,75], review of vertebrates: [37]. Bacteroidota and Firmicutes are considered more pathogenic bacteria and are associated with the breakdown of organic matter; an earlier study found that these taxa are more abundant in urban lakes [24]. Similar differences may account for the distinct gut bacterial communities we found here, although we have no data on the aquatic microbial communities inhabiting our study sites. Compared to natural ponds in our study, the ponds in anthropogenic habitats tended to have higher pH, temperature, salinity, conductivity and total dissolved solids, and also had higher concentrations of several chemical pollutants [41,76]. These environmental differences might select for different microbes colonizing the water and thereby the tadpoles’ guts, although the environmental changes may also affect the animals’ physiology and thereby exert selective pressures on the gut microbiome as has been found in fish [9]. Separating the effects mediated by the environmental microbiome versus the host is a worthwhile next step for understanding how differences between habitats emerge.
The habitat differences in gut bacterial composition were driven by several ASVs, belonging to different phyla. Urban tadpoles had the highest abundance of Desulfovibrionaceae (genus Desulfovibrio); similarly, this taxon is found in high numbers in the gut of adult Bufo raddei collected from areas with environmental heavy-metal pollution [77]. We also found that one group of bacteria of the order Burkholderiales (family Sutterellaceae) was most common in tadpole guts in natural environments. Methylmercury exposure decreased the relative abundance of Sutterellaceae in rat gut microbiome [78]. So, pollution might explain why we found more Sutterellaceae in tadpoles from natural habitats. In another paper, community structure variability was negatively correlated with bacterial order Burkholderiales on the skin of frogs. This order inhibits growth of the disease causing fungus, Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis (Bd) in the lab, but the exact role this bacterial group plays in nature is not clear [79]. Our results could indicate tadpoles could have a better ability to fight Bd infection when they are found in natural ponds where this bacterial group is more abundant. We also found that a group of bacteria from the order Bacteroidales (belonging to Rs-E47 termite group) was slightly more abundant in the gut of tadpoles found in agricultural ponds, in contrast to a study on Fejervarya limnocharis [45] which found Bacteroidales to be more abundant in the gut of frogs in natural habitats over farmland frogs. Bacteroidales may provide essential digestive activity as indicated from other species such as fish [80]. However, we do not know much more about the specific roles these specific bacteria play in tadpoles across these environments.
Despite the above differences in microbial composition, the Shannon diversity and ASV richness of gut bacteria did not differ among the three habitat types. The lack of relationship between bacterial diversity and land use is unexpected as it contrasts earlier studies on other species of frogs. For example, a study on adult F. limnocharis [45] found that gut bacterial diversity was higher in agricultural environments than forest environments. Another study [81] replicated this finding and further found that the gut microbiota of Babina adenopleura frogs from farmlands consisted of more functional bacterial diversity. In contrast, a study on ornate chorus frogs (Pseudacris ornata) [82] found that tadpole skin bacterial richness was positively associated with ponds surrounded by forest while Shannon diversity was higher in ponds with more developed land and with less canopy cover. These studies suggest that higher microbial diversity may help cope with anthropogenic environmental change in several species. However, in other vertebrate species, the composition of the gut microbiome is more important for fitness than its diversity, as individuals hosting increased abundances of opportunistic pathogens are more likely to die [83]. The latter might also explain the altered composition but similar diversity of toad bacterial communities in anthropogenic habitats.
In humans, the F/B ratio plays an important role in regular intestinal homeostasis and increased or decreased ratios indicate dysbiosis [70]. Another study of gut microbiome across habitats [45] found that Firmicutes was more dominant in farmland frogs than in those from natural environments, where Bacteroidota was more numerous. Similarly, tadpoles of B. raddei had a lower F/B ratio in heavy metal polluted areas than in unpolluted areas [39]. In contrast, we found no difference in the F/B ratio across natural, agricultural, and urban tadpoles of the common toad in the present study. This fits with our finding that toad tadpoles in anthropogenic habitats had similar bacterial diversity as tadpoles in natural habitats. These results correspond with our earlier findings that common toad populations in anthropogenic habitats may maintain their health in terms of reproduction [76] and pathogenic infections [41] and may even upregulate certain aspects of immunity [84], suggesting high tolerance by this species to human-induced environmental stressors.
The bi-directional gut-brain axis likely works together adaptively and helps cope with environmental change [32,33]. We found a positive correlation between baseline corticosterone release rate and two measures of diversity in host gut bacterial communities (ASV richness and Shannon diversity). These results are in contrast with studies on other species that either found a negative relationship between glucocorticoids and oral microbiome diversity in squirrels and fish [10,32,85] or no relationship in squirrels and gorillas [38,86]. While some studies consider elevated glucocorticoid levels to be costly, these hormones can also enhance fitness as they are important in metamorphosis in amphibians [87] and aid in maintaining homeostasis in response to changing environmental conditions [88]. Toad tadpoles in our urban sites have elevated baseline corticosterone release rates [41], which might be an adaptation to cope with the metabolic demands and stressors associated with urbanization. Combining this with our present finding that elevated baseline corticosterone release rates correlated with increased microbial diversity, one would expect higher microbial diversity in urban habitats, yet we did not detect the latter difference. This suggests that the correlation between corticosterone and bacterial diversity might not be due to a direct effect of one on the other but, instead, may arise because both are influenced by other factor(s) that are not associated with anthropogenic land use in common toad tadpoles.
Earlier we showed that toad tadpoles differ in several aspects of their glucocorticoid stress physiology across different habitats [41]. Tadpoles from both urban and agricultural habitats had stronger stress response as well as more efficient negative feedback than those in natural habitats. These facets of glucocorticoid regulation are related to fitness in birds and fish [42,52,53], and so is the microbiome in some mammals [83,89]. Yet, here we found no correlation between the corticosterone stress response and negative feedback on the one hand, and bacterial diversity and F/B ratio on the other hand. As a potential explanation, it is possible that the more efficient negative feedback of tadpoles in anthropogenic habitats [41], combined with a higher incidence of stressors in such habitats may result in an overall similar level of physiological stress (allostatic load) compared to natural habitats, and this might lead to similar “healthiness” of their gut microbiome across habitats.
When interpreting our results, it must be kept in mind that our sample sizes were not large. Thus, we urge further research on the relationship between host bacterial composition and endocrine flexibility (especially the glucocorticoid stress response and negative feedback), given the great importance of both for wildlife fitness and conservation. Further study is also required to fully understand the bidirectional role of the gut-brain-axis in organismal health in response to anthropogenic changes.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d15010023/s1; Figure S1. Rarefaction curves of the 41 samples, Figure S2. Relationship between Shannon diversity indices calculated with and without rarefaction of microbial data., Figure S3. Venn diagram showing the overlap of ASVs with minimum relative abundance of 0.01% and prevalence of at least 60% of samples in each habitat type, Table S1: Taxonomic classification of the amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) found in Bufo bufo tadpole gut in Hungary, Table S2. Pairwise comparisons (linear contrast estimates with standard error, SE) of tadpole gut microbiome diversity metrics between 3 habitat types from GEE models. Ref. [90] is cited in Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
C.R.G. and V.B. conceptualized the project; C.R.G., N.U., M.V.-C. and V.B. performed the research, C.R.G., M.V.-C., C.C.-S. and V.B. analyzed the data; C.R.G., N.U., M.V.-C. and V.B. wrote and edited the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The study was supported by a Fulbright Research Grant to C.R.G., Texas State university start-up funds to C.C.-S., and by the NRDI Fund of the National Research, Development and Innovation Office of Hungary (grants to V.B.: “OTKA”-K 115402 & 135016, ÚNKP-21-5, and 2019-2.1.11-TÉT-2019-00026). V.B. was supported by the János Bolyai Research Scholarship of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All protocols and housing were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Texas State University (IACUC #5636, 22 March 2019).
Data Availability Statement
The data from the study can be obtained upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank Judit Vörös for extracting the tadpole guts. The graphic abstract was created with Biorender.com.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jandhyala, S.M.; Talukdar, R.; Subramanyam, C.; Vuyyuru, H.; Sasikala, M.; Nageshwar Reddy, D. Role of the normal gut microbiota. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8787–8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFall-Ngai, M.; Hadfield, M.G.; Bosch, T.C.; Carey, H.V.; Domazet-Lošo, T.; Douglas, A.E.; Dubilier, N.; Eberl, G.; Fukami, T.; Gilbert, S.F.; et al. Animals in a bacterial world, a new imperative for the life sciences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3229–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, L.V.; Littman, D.R.; Macpherson, A.J. Interactions between the microbiota and the immune system. Science 2012, 336, 1268–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rea, K.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The microbiome: A key regulator of stress and neuroinflammation. Neurobiol. Stress 2016, 4, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ujszegi, J.; Vajna, B.; Móricz, Á.M.; Krüzselyi, D.; Korponai, K.; Krett, G.; Hettyey, A. Relationships Between Chemical Defenses of Common Toad (Bufo bufo) Tadpoles and Bacterial Community Structure of their Natural Aquatic Habitat. J. Chem. Ecol. 2020, 46, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teyssier, A.; Matthysen, E.; Hudin, N.S.; de Neve, L.; White, J.; Lens, L. Diet contributes to urban-induced alterations in gut microbiota: Experimental evidence from a wild passerine. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2020, 287, 20192182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, E.M.; Kutos, S.; Naghshineh, N.; Mesko, M.; You, Q.; Lewis, J.D. Assembly of the amphibian microbiome is influenced by the effects of land-use change on environmental reservoirs. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 4595–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stražar, M.; Temba, G.S.; Vlamakis, H.; Kullaya, V.I.; Lyamuya, F.; Mmbaga, B.T.; Joosten, L.A.B.; van der Ven, A.J.A.M.; Netea, M.G.; de Mast, Q.; et al. Gut microbiome-mediated metabolism effects on immunity in rural and urban African populations. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.; Rawls, J.F. Intestinal microbiota composition in fishes is influenced by host ecology and environment. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 3100–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uren Webster, T.M.; Rodriguez-Barreto, D.; Consuegra, S.; Garcia De Leaniz, C. Cortisol-Related Signatures of Stress in the Fish Microbiome. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 01621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galley, J.D.; Nelson, M.C.; Yu, Z.; Dowd, S.E.; Walter, J.; Kumar, P.S.; Lyte, M.; Bailey, M.T. Exposure to a social stressor disrupts the community structure of the colonic mucosa-associated microbiota. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohl, K.D.; Yahn, J. Effects of environmental temperature on the gut microbial communities of tadpoles. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1561–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krotman, Y.; Yergaliyev, T.M.; Shani, R.A.; Avrahami, Y.; Szitenberg, A. Dissecting the factors shaping fish skin microbiomes in a heterogeneous inland water system. Microbiome 2020, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaneveld, J.R.; McMinds, R.; Vega Thurber, R. Stress and stability: Applying the Anna Karenina principle to animal microbiomes. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberdi, A.; Aizpurua, O.; Bohmann, K.; Zepeda-Mendoza, M.L.; Gilbert, M.T.P. Do Vertebrate Gut Metagenomes Confer Rapid Ecological Adaptation? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2016, 31, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennison, D.J.; Rudman, S.M.; Schluter, D. Parallel changes in gut microbiome composition and function during colonization, local adaptation and ecological speciation. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 286, 20191911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houwenhuyse, S.; Stoks, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Decaestecker, E. Locally adapted gut microbiomes mediate host stress tolerance. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2401–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorriehzahra, M.J.; Delshad, S.T.; Adel, M.; Tiwari, R.; Karthik, K.; Dhama, K.; Lazado, C.C. Probiotics as beneficial microbes in aquaculture: An update on their multiple modes of action: A review. Vet. Q. 2016, 36, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetel, M.J.; de Vries, G.J.; Melcangi, R.C.; Panzica, G.; O’Mahony, S.M. Steroids, stress and the gut microbiome-brain axis. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2018, 30, e12548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.A.; Rinaman, L.; Cryan, J.F. Stress & the gut-brain axis: Regulation by the microbiome. Neurobiol. Stress 2017, 7, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brans, K.I.; Engelen, J.M.T.; Souffreau, C.; De Meester, L. Urban hot-tubs: Local urbanization has profound effects on average and extreme temperatures in ponds. Landsc. Urban Plann. 2018, 176, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Marshall, C.W.; Cheng, M.; Xu, H.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; Zheng, T. Changes in land use driven by urbanization impact nitrogen cycling and the microbial community composition in soils. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colston, T.J.; Jackson, C.R. Microbiome evolution along divergent branches of the vertebrate tree of life: What is known and unknown. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 3776–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numberger, D.; Zoccarato, L.; Woodhouse, J.; Ganzert, L.; Sauer, S.; Grossart, H.-P.; Greenwood, A. Urbanization promotes specific bacteria in freshwater microbiomes including potential pathogens. bioRxiv 2020, 845, 157321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLellan, S.L.; Fisher, J.C.; Newton, R.J. The microbiome of urban waters. Int. Microbiol. 2015, 18, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, R.J.; McLellan, S.L.; Dila, D.K.; Vineis, J.H.; Morrison, H.G.; Eren, A.M.; Sogin, M.L. Sewage reflects the microbiomes of human populations. mBio 2015, 6, e02574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vonesh, J.; De la Cruz Cabrera, O. Complex life cycles and density dependence: Assessing the contribution of egg mortality to amphibian declines. Oecologia 2002, 133, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givens, C.E.; Kolpin, D.W.; Borchardt, M.A.; Duris, J.W.; Moorman, T.B.; Spencer, S.K. Detection of hepatitis E virus and other livestock-related pathogens in Iowa streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, E.; Graml, M.; Behle, C.; Müller, E.; Horn, H. Influence of Particle Association and Suspended Solids on UV Inactivation of Fecal Indicator Bacteria in an Urban River. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 225, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.-I.; Knowler, D.J.; Lévêque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.-H.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L.J.; et al. Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol. Rev. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapolsky, R.M.; Romero, L.M.; Munck, A.U. How do glucocorticoids influence stress responses? Integrating permissive, suppressive, stimulatory, and preparative actions. Endocr. Rev. 2000, 21, 55–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrullo, L.; Ren, T.; Wu, M.; Boonstra, R.; Palme, R.; Boutin, S.; McAdam, A.G.; Dantzer, B. Glucocorticoids coordinate changes in gut microbiome composition in wild North American red squirrels. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, J.A.; Neufeld, K.-A.M. Gut–brain axis: How the microbiome influences anxiety and depression. Trends Neurosci. 2013, 36, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekirov, I.; Russell, S.L.; Antunes, L.C.M.; Finlay, B.B. Gut microbiota in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 859–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenham, S.; Clarke, G.; Cryan, J.; Dinan, T. Brain-gut-microbe communication in health and disease. Front. Physiol. 2011, 2, 94, External Resources Crossref (DOI)2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, R.L.; Volkoff, H. Gut Microbiota and Energy Homeostasis in Fish. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.S.; Shin, N.-R.; Lee, J.-B.; Kim, M.-S.; Whon, T.W.; Hyun, D.-W.; Yun, J.-H.; Jung, M.-J.; Kim, J.Y.; Bae, J.-W. Host habitat is the major determinant of the gut microbiome of fish. Microbiome 2021, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stothart, M.R.; Palme, R.; Newman, A.E.M. It’s what’s on the inside that counts: Stress physiology and the bacterial microbiome of a wild urban mammal. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 286, 20192111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sparks, J.B.; Karyala, S.V.; Settlage, R.; Luo, X.M. Host adaptive immunity alters gut microbiota. ISME J. 2015, 9, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, R.J.; Vennard, C.T.; Buckling, A.; Charnley, A.K. Diversity of locust gut bacteria protects against pathogen invasion. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bókony, V.; Ujhegyi, N.; Hamow, K.A.; Bosch, J.; Thumsova, B.; Voros, J.; Aspbury, A.S.; Gabor, C.R. Stressed tadpoles mount more efficient glucocorticoid negative feedback in anthropogenic habitats due to phenotypic plasticity. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 141896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolonin, A.M.; Bókony, V.; Bonner, T.H.; Zúñiga-Vega, J.J.; Aspbury, A.S.; Guzman, A.; Molina, R.; Calvillo, P.; Gabor, C.R. Coping with urban habitats via glucocorticoid regulation: Physiology, behavior, and life history in stream fishes. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2022, 62, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaustein, A.R.; Kiesecker, J.M. Complexity in conservation: Lessons from the global decline of amphibian populations. Ecol. Lett. 2002, 5, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, R.M.; Hyne, R.V.; Choung, C.B.; Wilson, S.P. Amphibians and agricultural chemicals: Review of the risks in a complex environment. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 2903–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-W.; Huang, B.-H.; Lin, S.-M.; Huang, C.-L.; Liao, P.-C. Changes of diet and dominant intestinal microbes in farmland frogs. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krynak, K.L.; Burke, D.J.; Benard, M.F. Landscape and water characteristics correlate with immune defense traits across Blanchard’s cricket frog (Acris blanchardi) populations. Biol. Conserv. 2016, 193, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walke, J.B.; Becker, M.H.; Loftus, S.C.; House, L.L.; Cormier, G.; Jensen, R.V.; Belden, L.K. Amphibian skin may select for rare environmental microbes. ISME J. 2014, 8, 2207–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, K.D.; Cary, T.L.; Karasov, W.H.; Dearing, M.D. Larval exposure to polychlorinated biphenyl 126 (PCB-126) causes persistent alteration of the amphibian gut microbiota. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujszegi, J.; Ludányi, K.; Móricz, Á.M.; Krüzselyi, D.; Drahos, L.; Drexler, T.; Németh, M.Z.; Vörös, J.; Garner, T.W.J.; Hettyey, A. Exposure to Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis affects chemical defences in two anuran amphibians, Rana dalmatina and Bufo bufo. BMC Ecol. Evol. 2021, 21, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, R.R.; Sommer, S. The amphibian microbiome: Natural range of variation, pathogenic dysbiosis, and role in conservation. Biodivers. Conserv. 2017, 26, 763–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Q.; Liu, X.-N.; Hu, Z.-F.; Ding, J.-F.; Bie, J.; Wang, H.-B.; Zhang, J.-T. Effects of Captivity and Season on the Gut Microbiota of the Brown Frog (Rana dybowskii). Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 01912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taff, C.C.; Vitousek, M.N. Endocrine Flexibility: Optimizing Phenotypes in a Dynamic World? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2016, 31, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taff, C.C.; Zimmer, C.; Vitousek, M.N. Efficacy of negative feedback in the HPA axis predicts recovery from acute challenges. Biol. Lett. 2018, 14, 20180131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reading, C.J.; Loman, J.; Madsen, T. Breeding pond fidelity in the common toad, Bufo bufo. J. Zool. 1991, 225, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsch, U. Seasonal changes in the migratory behaviour of the toad Bufo bufo: Direction and magnitude of movements. Oecologia 1988, 76, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohl, K.D.; Cary, T.L.; Karasov, W.H.; Dearing, M.D. Restructuring of the amphibian gut microbiota through metamorphosis. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosner, K. A simplified table for staging anuran embryos and larvae with notes on identification. Herpetologica 1960, 16, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Narayan, E.J.; Forsburg, Z.R.; Davis, D.R.; Gabor, C.R. Non-invasive Methods for Measuring and Monitoring Stress Physiology in Imperiled Amphibians. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 00431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattin, C.R.; Kelly, T.R. Glucocorticoid negative feedback as a potential mediator of trade-offs between reproduction and survival. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2020, 286, 113301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasimuddin; Schlaeppi, K.; Ronchi, F.; Leib, S.L.; Erb, M.; Ramette, A. Evaluation of primer pairs for microbiome profiling from soils to humans within the One Health framework. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 1558–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arango, R.A.; Schoville, S.D.; Currie, C.R.; Carlos-Shanley, C. Experimental Warming Reduces Survival, Cold Tolerance, and Gut Prokaryotic Diversity of the Eastern Subterranean Termite, Reticulitermes flavipes (Kollar). Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 632715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadrosh, D.W.; Ma, B.; Gajer, P.; Sengamalay, N.; Ott, S.; Brotman, R.M.; Ravel, J. An improved dual-indexing approach for multiplexed 16S rRNA gene sequencing on the Illumina MiSeq platform. Microbiome 2014, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.T.; Highlander, S.K.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a Dual-Index Sequencing Strategy and Curation Pipeline for Analyzing Amplicon Sequence Data on the MiSeq Illumina Sequencing Platform. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Waste not, want not: Why rarefying microbiome data is inadmissible. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014, 10, e1003531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, S.; Xu, Z.Z.; Peddada, S.; Amir, A.; Bittinger, K.; Gonzalez, A.; Lozupone, C.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Birmingham, A.; et al. Normalization and microbial differential abundance strategies depend upon data characteristics. Microbiome 2017, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahti, L.; Shetty, S. Microbiome R package. Bioconductor 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, N. Using false discovery rates for multiple comparisons in ecology and evolution. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2011, 2, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanov, S.; Berlec, A.; Štrukelj, B. The Influence of Probiotics on the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio in the Treatment of Obesity and Inflammatory Bowel disease. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuur, A.; Ieno, E.N.; Walker, N.; Saveliev, A.A.; Smith, G.M. Mixed Effects Models and Extensions in Ecology with R.; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick, B.M.; Allison, A.L. Similarity and differentiation between bacteria associated with skin of salamanders (Plethodon jordani) and free-living assemblages. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 88, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughey, M.C.; Walke, J.B.; Becker, M.H.; Umile, T.P.; Burzynski, E.A.; Minbiole, K.P.C.; Iannetta, A.A.; Santiago, C.N.; Hopkins, W.A.; Belden, L.K. Short-Term Exposure to Coal Combustion Waste Has Little Impact on the Skin Microbiome of Adult Spring Peepers (Pseudacris crucifer). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 3493–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, L.; Dong, Z.; Chen, A.; Wang, H. Changes in intestinal microbiota of Bufo gargarizans and its association with body weight during metamorphosis. Arch. Microbiol. 2018, 200, 1087–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalvenzi, T.; Clavereau, I.; Bourge, M.; Pollet, N. Gut microbial ecology of Xenopus tadpoles across life stages. Peer Community J. 2021, 1, e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bókony, V.; Üveges, B.; Ujhegyi, N.; Verebélyi, V.; Nemesházi, E.; Csíkvári, O.; Hettyey, A. Endocrine disruptors in breeding ponds and reproductive health of toads in agricultural, urban and natural landscapes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 1335–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, R.; Yang, Y.; Ding, J.; Zhang, Y. Long-term effect of heavy-metal pollution on diversity of gastrointestinal microbial community of Bufo raddei. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 258, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.; He, L.; Wang, L.; Chang, D.; Cui, L.; Gao, Y.; Li, B.; Chen, C.; et al. Acute oral methylmercury exposure perturbs the gut microbiome and alters gut-brain axis related metabolites in rats. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, S.; Knapp, R.; Vredenburg, V. Longitudinal patterns in the skin microbiome of wild, individually marked frogs from the Sierra Nevada, California. ISME Commun. 2021, 1, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullam, K.E.; Essinger, S.D.; Lozupone, C.A.; O’Connor, M.P.; Rosen, G.L.; Knight, R.; Kilham, S.S.; Russell, J.A. Environmental and ecological factors that shape the gut bacterial communities of fish: A meta-analysis. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 3363–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.-H.; Chang, C.-W.; Huang, C.-W.; Gao, J.; Liao, P.-C. Composition and Functional Specialists of the Gut Microbiota of Frogs Reflect Habitat Differences and Agricultural Activity. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 02670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goff, C.B.; Walls, S.C.; Rodriguez, D.; Gabor, C.R. Changes in physiology and microbial diversity in larval ornate chorus frogs are associated with habitat quality. Conserv. Physiol. 2020, 8, coaa047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worsley, S.F.; Davies, C.S.; Mannarelli, M.-E.; Hutchings, M.I.; Komdeur, J.; Burke, T.; Dugdale, H.L.; Richardson, D.S. Gut microbiome composition, not alpha diversity, is associated with survival in a natural vertebrate population. Anim. Microbiome 2021, 3, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bókony, V.; Üveges, B.; Verebélyi, V.; Ujhegyi, N.; Móricz, Á.M. Toads phenotypically adjust their chemical defences to anthropogenic habitat change. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stothart, M.R.; Bobbie, C.B.; Schulte-Hostedde, A.I.; Boonstra, R.; Palme, R.; Mykytczuk, N.C.; Newman, A.E. Stress and the microbiome: Linking glucocorticoids to bacterial community dynamics in wild red squirrels. Biol. Lett. 2016, 12, 20150875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlčková, K.; Shutt-Phillips, K.; Heistermann, M.; Pafčo, B.; Petrželková, K.J.; Todd, A.; Modrý, D.; Nelson, K.E.; Wilson, B.A.; Stumpf, R.M. Impact of stress on the gut microbiome of free-ranging western lowland gorillas. Microbiology 2018, 164, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glennemeier, K.A.; Denver, R.J. Small changes in whole-body corticosterone content affect larval Rana pipiens fitness components. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2002, 127, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, L.M.; Wikelski, M. Corticosterone levels predict survival probabilities of Galapagos marine iguanas during El Nino events. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 7366–7370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.A. Links between Natural Variation in the Microbiome and Host Fitness in Wild Mammals. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2017, 57, 756–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong , J.; Liu, P.; Zhou, G.; Xia, J. Using MicrobiomeAnalyst for comprehensive statistical, functional, and meta-analysis of microbiome data. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 799–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).