Abstract
This review evaluates the vulnerability of South African estuaries to Climate Change in a data-limited environment. The regional-scale assessment is based on physical characteristics and predicted/measured changes in the abiotic drivers and ecosystem responses. The major Climate Change stressors were identified in order of importance as change in climatic and hydrological processes, ocean circulation and temperature regimes, sea level rise, increase in frequency and intensity of sea storms, and ocean acidification. Flow-related ecosystem responses included changes in mouth state, salinity regimes, biochemical regimes (nutrient fluxes), and floods and related sediment deposition/erosion cycles. The regional vulnerability assessment provides a summary of the key shifts scaled as high, medium, and low in estuary state. Changes in oceanic processes and temperature regimes drive shifts in nearshore temperatures of the transitional zones, with related ecological responses (e.g., range expansion). However, most structural and functional changes are expected along cool temperate and subtropical biogeographical regions, leading to notable shifts in mouth closures and salinity regimes, which in turn will affect estuary function and estuary-associated species. Monitoring and management of resources (e.g., fresh water and fisheries allocations) need to consider this in long-term planning.
1. Introduction
Climate change is a measurable reality and South Africa is especially susceptible to its impacts [1,2,3,4,5,6]. South Africa has an economically divided society with wide-ranging socioeconomic disparities, and as a result, its population is characterised by a vulnerable majority with a high reliance on ecosystem services [1]. Along South Africa’s highly exposed linear coastline, estuaries play a major role in the provision of such services, given that they present sheltered, highly productive habitats [7]. Despite its vulnerability to Climate Change, South Africa currently does not have standard procedures or best practice guidelines to address this issue [2]. This, together with poor coverage of environmental data, makes the monitoring and understanding of vulnerability, and evaluation of adaptation, challenging at the national and local levels [8].
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) stressed the importance of providing socioeconomic perspectives (e.g., resource use implications) in the assessment of Climate Change scenarios, because adaptation to environmental change is central to building societal resilience [9]. The concept of vulnerability has become increasingly important in Climate Change research [6,10,11,12,13]. It defines a system’s susceptibility to adverse effects as a function of magnitude and rate of climatic variation, the character and sensitivity of a system, and its adaptive capacity [11]. However, defining and measuring geographical, spatial, temporal, environmental, and social dimensions of vulnerability are notably complex and have generated many methods [9]. Within coastal environments, estuaries are particularly vulnerable and have been the focus of several international and/or regional Climate Change vulnerability assessments (e.g., [14,15,16,17]). More recently, regional downscaling of the outputs from global climate models has allowed for improved assessments of estuarine responses to stressors, such as increased storminess and sea level rise, using site-specific dynamic models (e.g., [18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27]). All these models are resource and/or data hungry and would take considerable effort to apply in South Africa’s data-limited environment.
South Africa’s 3000 km coastline supports approximately 290 functional estuaries [28,29]. South Africa’s coast is generally characterised by low tidal ranges and high wave energy, making it a wave-dominated coast [30]. Estuaries are predominantly micro-tidal, highly dynamic, and shallow (water depth 2 to 3 m) [29,31]. Small tidal flows, together with relatively low freshwater inflow, high wave action, and high sediment availability, limit the ability of estuaries to maintain inlet stability (i.e., open mouth conditions). As a result, more than 90% of estuaries have restricted inlets, with more than 75% closing for varying periods of time when a sandbar forms across the mouth [30,31]. Thus, the estuaries of the region represent highly variable habitats in which conditions such as water depth, salinity, temperature, turbidity, and dissolved oxygen concentrations can fluctuate rapidly, both temporally and spatially [32].
The role of estuaries in the provision of key ecosystem services such as supporting blue carbon habitats, fish and prawn nursery grounds, and important feeding areas for migrant birds is of particular importance as they contain much of the only sheltered habitat along the high-energy, wave-dominated coastline [7,33]. Key to understanding the vulnerability of estuaries to Climate Change stressors are their physical features (e.g., size, shape, extent, marine/fluvial influence, and catchment characteristics), which are highly variable along South Africa’s coast as a result of the interplay between land and sea processes [29,32,34].
Aspects relating to the vulnerability of South Africa’s estuaries to Climate Change have been addressed in several studies (e.g., [35,36,37,38]). However, given progress in regional climate modelling and an ever-deepening understanding of associated responses, there was a need for a consolidated review and synthesis of the regional vulnerability of South African estuaries to Climate Change stressors, with a focus on the impacts of the near-future (2016–2035) and mid-future (2040–2060) Climate Change scenarios. The aim of this study, therefore, is to conduct a critical review of international literature and to distil key Climate Change stressors considered relevant to South African estuaries, including their associated effects on estuarine processes and biotic responses. This, together with expert knowledge, will then be used to rate the regional vulnerability of estuaries along the South African coastline to inform management and adaptation strategies in planning for Climate Change impacts.
2. Materials and Methods
The aim of this study is two-fold; to identify key Climate Change stressors and their associated potential impacts on South African estuarine systems. These insights are then used as a framework to assess and rate the vulnerability of South Africa’s estuaries to Climate Change at the regional scale.
A literature review was used to identify the Climate Change stressors globally considered most relevant to estuarine ecosystems. The review also focuses on identifying key estuarine abiotic processes and biological responses likely to be sensitive to identified key stressors. Together, the key stressors, processes, and responses considered most important within the South African context provide the basis for a framework against which the vulnerability of South African estuaries could be assessed.
To define the spatial resolution of the vulnerability assessment, available data and literature on South Africa’s climate zones, biogeographic regions, catchment characteristics, and coastal topography, as well as key features of estuaries (e.g., size and degree of connectivity with the sea) were interrogated. Coming from an estuarine perspective, relatively homogenous parts of the coast were demarcated, which could serve as the basis for regional-scale Climate Change vulnerability evaluation.
The expected Climate Change vulnerability of estuaries within each of the regions was based on available projected near-future and mid-future Climate Change projections for South Africa [37,39,40,41,42,43,44]. These projections were derived using regional climate models and the Coordinated Regional Downscaling Experiment (CORDEX) of the World Climate Research Programme, largely based on outputs from the global climate model analysed in Assessment Report Five (AR5), including projections for low-mitigation (RCP8.5) and high-mitigation (RCP4.5) futures and for near-future (2016–2035), mid-future (2036–2065), and far-future (2066–2099) time scales. This assessment considered projected precipitation and temperature shifts for the near-future to mid-future scenarios. A three-tier change rating system was applied (low = largely similar, medium= some change from present, high = substantial change is expected), where the degree of change from present represents the relative vulnerability to a specific Climate Change stressor. The rating is not directional in that it can reflect an increase or decrease in the functionality of the affected abiotic and biotic process and/or variables.
2.1. Key Climate Change Stressors and Associated Estuarine Responses
The following Climate Change stressors are relevant to estuarine ecosystems across the world, namely modification of land climatic conditions (e.g., precipitation and temperature), oceanic and coastal circulation processes, sea level rise, increased sea storminess, and ocean acidification [14,15,16,17,45]. This growing body of work is supported by ongoing detailed, controlled laboratory studies and in situ observations of estuarine organisms’ sensitivity to changes, e.g., ocean acidification and temperature (e.g., [46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54]).
From pre-industrial times (<1750) to 2019, the atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) has risen by 47% [5]. In response, the average global surface temperature has increased by 1.1°C compared to the average temperature in 1850–1900, which is the hottest level in 125,000 years [5]. However, recent climate trend analyses indicate that South Africa has been warming at more than twice the global rate of temperature increase over the past five decades [43,55,56,57,58]. The largest and smallest increases in maximum air temperature have been recorded during winter, autumn, and summer, respectively. This increase in temperature also affects rainfall patterns, potentially changing both the long-term average in rainfall and the frequency and occurrence of severe weather events (e.g., droughts and floods) [43,59]. Projected temperature increases in the average global surface atmosphere by 2100 range from 1 to 3 °C (low emission scenarios) to 6 °C (potential upper range).
Global warming is also expected to change oceanic circulation patterns (i.e., shifting currents and fronts) and lead to increased ocean temperatures [4], including that of the Benguela and Agulhas Currents bordering South Africa’s coast. The intensification and southward shift of Southern Hemisphere subtropical gyres have been attributed to global warming, and together with the hole in the ozone layer [60], this is likely to intensify the Benguela Current, which in turn, is expected to result in some intensification of large-scale upwelling along the west coast of South Africa [61,62]. However, the robustness of these projections remains unclear [63,64,65,66,67]. Numerous studies describe the Agulhas Current and its expected response to Climate Change [66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77]. Whilst earlier studies show that mesoscale variability in the source regions of the Agulhas Current system has intensified and strengthened the current along its northern parts (north of Coffee Bay), the southern part of the current appears to be slowing down, with greater meandering [78]. A more recent study based on both in situ and satellite-based observations [77] found that the Agulhas Current is not strengthening, but is becoming more turbulent at the mesoscale range. Changes in the path or strength of the Agulhas Current and an increasingly turbulent current will influence dynamically driven coastal and shelf-edge upwelling and cross-shelf exchange processes between the deep ocean and the coastal regions [66,72,77,78]. A more turbulent Agulhas Current may be associated with an increase in the occurrence of offshore cyclonic meanders (referred to as “Natal Pulses”) and the formation of Agulhas Rings, mechanisms driving heat exchange and dispersal of marine organisms between east coast waters and the Indian Ocean [66,75,76]. Similarly, changes in the Agulhas Leakage process, driving inter-ocean transfer between the Indian and Atlantic oceans [70,72] are also expected, although the “how” remains uncertain [79,80,81,82]. Leakage from the Agulhas Current sometimes drifts close inshore, raising the temperature of nearshore waters and occasionally interacting with upwelling plumes, both of which have important consequences for nearshore and estuarine fish recruitment [83].
Sea level rise has accelerated due to the combined increased ice loss from the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets. The total global mean sea level rise for 1902–2015 was 0.16 m, with the 3.6 mm yr−1 rise from 2006–2015 unprecedented over the last century, representing about 2.5 times the rate for 1901–1990 of 1.4 mm yr−1 [4]. A comparison between approximately 30 years of South African tide-gauge records and the longer-term records from elsewhere shows substantial agreement with observed global trends [84,85]. Recent global projections, based on a hotter climate, indicate that we may experience rates of sea level rise between 0.36 and 0.87 m by 2100 [4]. Antarctic ice loss alone is expected to contribute 9 cm to global sea levels by 2100 under a 2 °C warming scenario, though this increases dramatically to as much as 33 cm by 2100 under a 3 °C scenario [86]. Anthropogenic warming and sea level rise will continue for centuries due to the time scales associated with climate processes and feedback, even if greenhouse gas concentrations are stabilised [87,88]. Recent literature provides a range of sea level rise scenarios by 2100, including a best-case low scenario (+0.5 m), a mid-scenario (+1.0 m), and a worst-case scenario (+2 m) [88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96]. Model studies indicate multi-meter rise in sea level by 2300 (2.3–5.4 m for RCP8.5 and 0.6–1.07 m under RCP2.6), indicating the importance of reduced emissions for limiting sea level rise [4].
In addition, a warming climate is expected to affect wind patterns and storm characteristics, which in turn will impact wind and wave regimes and contribute to high coastal water level events [4]. The IPCC predicts an increase in frequency and intensity of extreme weather events into the 21st century associated with Climate Change [97]. Already, there is evidence of increases in general wave height and storm intensities in the Northern hemisphere [4,98,99,100], while similar observations have been recorded at locations in southern Africa, albeit at relatively short timescales [101,102]. Such changes in metocean climates are expected to have significant impacts on coastal ecosystems, resulting in more storm erosion and potentially more coastal sediment transport [95].
Fossil fuel burning and anthropogenic land-use changes have caused the atmospheric CO2 concentrations to rise from 280 ppm to about 400 ppm globally, of which the oceans have absorbed approximately 20–30% [4,13,103,104]. This resulted in a decrease in the pH of ocean surface water (0.1 unit over the past 250 years), referred to as ocean acidification [13,105]. Open ocean surface pH has declined by 0.017–0.027 pH units per decade since the late 1980s [4]. It is expected to decrease by a further 0.2–0.4 units towards the end of this century [13,106,107,108]. Globally the aragonite saturation state from preindustrial to the present has decreased below the envelope of natural variability [109].
Thus, the effect of Climate Change stressors on estuarine processes and variables and associated biotic responses is complex. Such interactions can both amplify or moderate shifts in biological responses, including processes such as primary production (e.g., structure/habitat-forming plants and eutrophication), contraction or expansion of species ranges, changes in recruitment patterns and nursery function, shifts in community composition, and general behavioural responses. An overview of the key relationships within this complex system is summarised in Table 1.

Table 1.
A summary of key Climate Change stressors, important estuarine processes, and variables affected, as well as associated biotic responses (large/small Circle = high/medium degree of change or vulnerability).
Specific characteristics of estuaries are likely to influence the severity or intensity of responses to various Climate Change stressors. For example, large estuaries are often buffered against flood scouring as they have greater storage capacity relative to flow, which translates into less loss of substrate, habitat, and biota, whilst smaller systems experience a complete reset of substrate and biotic composition during comparable flood events such as a 1 in 10-year flood. In addition, estuarine habitats are significantly degraded through freshwater reduction, habitat destruction, nutrient pollution, and overexploitation of living resources, which affect related ecosystem services (e.g., nursery function) [28,110]. These impacts reduce the capacity of estuaries to buffer the effects of change, albeit natural or anthropogenic. Thus, abiotic impacts and associated biotic responses predicted for the various Climate Change stressors need to be superimposed on existing anthropogenic pressures already experienced in, for example, highly urbanised areas (e.g., around Cape Town, Mossel Bay, East London, and Durban), as well as systems receiving large agricultural return flows (e.g., Great Berg, Olifants, Breede, Sundays, and uMfolozi estuaries) [111].
2.2. Delineation of Coastal Regions
The coast of South Africa comprises three broad biogeographical regions, namely the cool temperate west coast, warm temperate south and east coast, and subtropical east coast [29,111,112,113]. However, transition zones exist between the biogeographical regions that are shaped by the interplay between land and sea processes which are reflected in the distribution of estuarine and coastal biology along a continuum [29] (Figure 1). These are the warm-cool temperate, warm temperate-subtropical, but also the subtropical-tropical transition zone stretching into Mozambique.
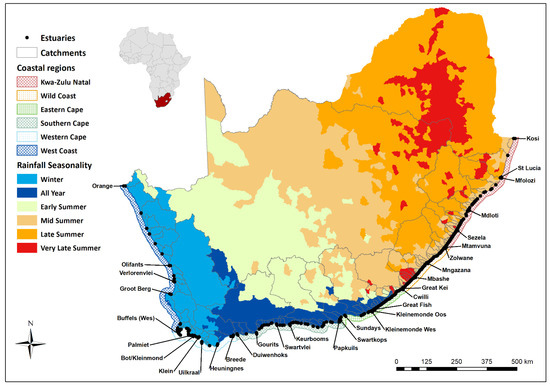
Figure 1.
Map showing the seven coastal regions, relative catchment size, and rainfall seasonality for South Africa.
Freshwater inflow to estuaries is determined by these climatic conditions, as well as the size and topography of their catchments. The latter controls the magnitude and flow distribution of runoff [114]. Catchment size also varies significantly, ranging from very small (less than 1 km2) to very large (greater than 10,000 km2) [114]. However, catchments in the cool temperate region tend to be larger than those in the warm temperate and subtropical regions [114,115]. As a result of the country’s highly variable climate, rainfall patterns across these regions vary greatly.
In the cool temperate region, the climate ranges from semiarid (extended periods of low to no rainfall interspersed with short flash rain events) along the west coast to Mediterranean (dominated by seasonal winter rainfall) along most of the south-western coast. In the warm temperate region along the south coast, rainfall is largely bi-modal, with peaks in spring and autumn, while the subtropical region along the east coast is dominated by seasonal summer rainfall [116,117].
Taking landscape and oceanic features into account, a total of seven relatively homogenous regions were delineated with respect to rainfall and catchment characteristics, coastal topography, beach slope, and estuarine features (e.g., dominant mouth position and size) (Table 2, refined from [29]). Five of the broad regional groupings were derived from the natural discontinuities in the biogeographical regions (i.e., transitions zones), while the warm temperate region was further subdivided based on rainfall seasonality and coastal topography. The overall zonation largely reflects the seasonality, and to a lesser extent, patterns in mean annual precipitation.

Table 2.
Summary of the climatic, oceanic, and estuarine characteristics typical of the seven coastal regions.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Land Climatic and Hydrological Processes and Responses
Land-based air temperatures have been rising significantly over Africa; with temperature increases over subtropical southern Africa (which have increased by 3.2 °C in the last 100 years) more than twice the global land-based air temperature increase. Annual air temperatures over the coastline of South Africa are predicted to be between 2.5 and 4 °C warmer in 2100 than they are today [43].
One of the ways global warming manifests on land is through changes in rainfall patterns [14,15,16,17,45,117,118,119]. For South Africa, there is strong evidence of statistically significant increases in rainfall over the southern interior regions [40,42], extending from the western interior of the Eastern Cape and eastern interior of the Western Cape northwards into the central interior region of the Northern Cape [57,120]. An increase in extreme rainfall events is projected to occur along the Southern Cape, Eastern Cape, and KwaZulu-Natal coasts during spring and summer, with a reduction in such events projected for winter and autumn (e.g., [40,42,121]). This is associated with an upsurge in the frequency of occurrence of cut-off lows and more frequent occurrence of tropical-temperate cloud bands over the region [40,122]. Tropical cyclone tracks are projected to shift northward, bringing more flood events to northern Mozambique and fewer to the Limpopo and KwaZulu-Natal provinces in South Africa [123]. Statistical models also show an increase in extreme precipitation events in the summer over the east coast of KwaZulu-Natal, along with an increase in rain days for much of the country, except possibly the extreme west/southwest [59].
3.1.1. Changes in Freshwater Inflows
Changes in rainfall patterns alter hydrological regimes, which, in turn, affect freshwater runoff to estuaries, in many instances exacerbating the existing human impacts, e.g., dam development [37,124,125,126,127]. Along the tropical (Delagoa), subtropical (KwaZulu-Natal), and warm temperate regions (Wild Coast and Eastern Cape), the combination of generally wetter conditions and heavy precipitation events will result in more runoff (indicated by a high and medium rating in Figure 2). However, a projected decrease in rainfall in the cool temperate regions (i.e., West Coast and Western Cape) and a related small increase in inter-annual variability will result in a decrease in freshwater runoff (indicated by a high and medium rating in Figure 2).

Figure 2.
Summary of vulnerability rating (high/medium/low) for estuaries in the seven coastal regions associated with change in land climatic and hydrological processes (colour zones on map depict (a) to (f) in the table moving outward from the coast with H = high, M = medium, L = low).
An intensification of the wet-dry cycles is also expected in these regions as changes in rainfall patterns are typically amplified in associated hydrological cycles [37,39,40,41,44]. The exception along this coast is the Orange Catchment, which drains more than half of the country, with most of the catchment falling in the summer rainfall area. The frequency and magnitude of large floods are expected to increase in this system, as are the intensity and duration of drought or zero-flow periods. The impacts of these changes on marine and estuarine habitats and biota are likely to be significant as this catchment provides more than 75% of the flow into the sea on the west coast.
South Africa’s relatively small estuarine systems are particularly vulnerable to changes in freshwater runoff as they depend on river inflow to offset the high wave energy that causes mouth closure along South Africa’s exposed coast [30]. Changes in freshwater inflows manifest through an array of important abiotic processes which include changes in the frequency and duration of mouth closure, salinity distribution patterns, sediment dynamics, and biogeochemical characteristics [37,128]. In freshwater-deprived estuaries, such as the Kariega Estuary which receives a proportionally limited amount of freshwater on a daily tidal cycle, primarily because of freshwater abstraction and prolonged drought conditions, extreme flood events can result in substantial increases in estuarine productivity, particularly the abundance of zooplankton and estuarine-associated fish [129,130,131]. Whereas increased flow, including flood events, have positive impacts on recruitment and survival, changes in the frequency and timing of events may have negative effects [132,133]. Negative effects range from the influence of aseasonal cues on recruitment and emigration to the unavailability of estuarine habitat at critical life-history stages. Predicted changes in river runoff for these abiotic processes across the various regions are elaborated on below.
3.1.2. Changes in Land-Sea and Alongshore Connectivity
In temporarily closed estuaries (TCEs), representing more than 75% of South Africa’s estuaries, changes in freshwater inflows affect the frequency and duration of mouth closures [29,134]. During low or no river flow periods, these systems become isolated from the sea by the formation of a sand berm across the mouth. These types of estuaries normally stay closed until their basins fill up and berms are breached, usually when river inflows increase again. In extreme circumstances, a marked reduction in freshwater inflow can cause systems to be permanently isolated from the sea. Alternatively, a significant increase in inflows can prevent the mouth from closing. Permanently open estuaries may also experience closure and switch to being TCEs. Figure 2 shows that mouth closure is sensitive to precipitation and run-off changes, with different responses predicted for different regions.
A significant decrease in runoff along the West Coast (high) and Western Cape (medium) is likely to cause a significant increase in closed conditions in TCEs along this coastline. Average flow conditions are predicted to remain largely similar along the Southern Cape (possible slight decrease) and Eastern Cape (possible slight increase) in most regional climate models and are indicated to be low in Figure 2. Although extreme events such as cut-off lows are predicted to increase, this is likely to lead to only a small change in closed mouth conditions depending on the size of the system and the inflow regime (indicated by a low rating in Figure 2). Wild Coast TCEs are likely to show slight reductions in closed mouth conditions as a result of increased river flow. However, these flow-driven increases in open mouth states could be offset by increased sedimentation from the highly erodible but severely degraded Wild Coast catchments [135]. KwaZulu-Natal TCEs have high vulnerability, as a predicted increase in precipitation will result in estuary mouths closing less often, thus reducing the periods of high productivity associated with closed-mouth conditions (indicated as high in Figure 2) [136,137]. The Delagoa region, which comprises estuarine lakes, will be sensitive to an increase in the frequency and intensity of droughts, with the Kosi estuarine lake system likely to close again (similar to 1970s) and average lake levels likely to become lower due to reduced groundwater inflow.
Changes in the mouth state and associated changes in water level and salinity regimes affect the distribution of estuary habitat types [138,139,140]. Changes in habitat availability can result in substantial decline in marine fish diversity and abundance in TCEs [141]. During closed states, the high water levels can reduce supratidal saltmarsh, reed, and sedge cover, which may result in bank destabilisation and erosion. A loss of submerged macrophytes due to water level fluctuations affects estuarine faunal composition and abundance, and thus the functioning of TCEs. The most vulnerable regions are the West Coast and KwaZulu-Natal (indicated by a high rating in Figure 2).
Estuarine faunal distribution is also affected by changes in mouth state in TCEs. For example, the mudprawn Upogebia africana has an obligatory marine phase of development during the larval stages. Thus, when mouth closure occurs for extended periods (e.g., >1 year), this life cycle is disrupted, resulting in local extirpation [142]. Some demersal zooplankton species exhibit tidally phased migratory behaviour [143], which is disrupted by alterations in mouth closure patterns. Prolonged mouth closure in TCEs results in low recruitment potential for juvenile marine fish and effectively prevents the emigration of adults back to sea [144]. Habitat unavailability due to droughts and estuary mouth closure may be the dominant driver, rather than temperature, of the movement of tropical and subtropical estuary-associated fish southwards on the east coast. Similarly, this may also explain the northwards movement and shift in abundance of cool-temperate fish on both the east and west coasts [145]. During extended closure, fish populations may also decrease due to predation by other fishes, birds, and mammals including humans [146,147]. In severe cases, when the mouth reopens, predation will result in little or no recruitment of the adult population in the sea. Some fishes may live out their lives in a closed estuary without ever having had the opportunity to breed. Under extreme conditions, extended periods of mouth closure will result in a significant loss of connectivity between estuaries and the sea, as well as alongshore connectivity among estuaries, resulting in increased population isolation and allopatric speciation [148].
Bird populations in estuaries are also adversely affected by extended periods of mouth closure, due to a loss of tidal habitats. For example, wading birds mainly forage on intertidal mudflats where they rely on the availability of intertidal benthic organisms [134]. Many of these are Palaearctic migrants, so local changes as a result of mouth closure can also potentially affect populations globally. High water levels are often experienced during mouth closure, resulting in a loss of shallow water habitats favoured by herons, flamingos, and other wading birds, and the loss of islands, which provide roosts and breeding sites safe from land predators [134].
Climate Change and sea level rise will intensify pressure on management agencies to implement assisted (and often premature) breaching, as increasingly low-lying properties will be at risk of flooding. The responses of humans to sea level rise are often damaging to estuaries and estuarine biota, e.g., armouring the coastline with berms/dykes that prevent biological systems from adjusting naturally (i.e., inland retreat of wetlands).
3.1.3. Changes in Salinity Regimes
Freshwater inflow is a key driver in determining the salinity distribution patterns in estuaries. Functionality in estuaries, especially permanently open systems, relies on well-developed salinity gradients, typically ranging from fresh upper reaches to brackish middle reaches (also referred to as the mixing zone) and saline lower reaches [149]. Reduced freshwater inflows may result in a reduction, or even complete elimination, of the estuarine mixing zone. If there is no freshwater input, a reverse salinity gradient may develop [37,150,151]. In TCEs, extended periods of mouth closure can result in hyper- or hypo-salinity, depending on freshwater flows. For example, under no or low freshwater inflow, when evaporation rates exceed inflow rates, hypersaline conditions are likely to develop. Paradoxically, if an estuary mouth is closed, provided that the river inflow still exceeds evaporation and seepage losses, a progressive freshening of the estuary occurs until rising water levels lead to breaching of the berm, closing the mouth [134,152]. In the latter case, almost a complete loss of marine species will occur, with only a few euryhaline estuarine and freshwater species remaining [152], in severe instances, leading to mass mortalities of marine fish species trapped in these systems [153]. Reproduction may be interrupted in species that breed in estuaries, e.g., Callichirus kraussi, or mass mortalities may result in species unable to escape intolerable conditions [154]. Therefore, the biotic impacts of salinity shifts are linked to salinity preferences in open systems and tolerances in closed systems [128].
Based on expected changes in freshwater inflows, the large permanently open estuaries in the West Coast and Western Cape regions will be especially vulnerable to increased salinity penetration, with a similar vulnerability rating rippling into the biotic responses as indicated by high and medium ratings in Figure 2, respectively. Some freshening (decline in average salinity) of small TCEs in the non-arid parts is likely to occur during periods of extended mouth closure, associated with persistent low river inflow and continuous seepage losses through the berm. Salinity regimes in Southern Cape estuaries are likely to remain similar to the present (low ranking in Figure 2), but there may still be some increase in salinity penetration in the larger permanently open estuaries in this region during low flow periods, albeit limited. Salinity patterns in Eastern Cape systems are also expected to remain similar to the present (low rating in Figure 2), although a slight decrease in salinity penetration can be expected for some of the larger permanently open estuaries associated with an increase in freshwater resetting events. It is expected that the smaller TCEs in the Eastern Cape region will show an increase in average salinity, depending on their size and shape, as a slight increase in freshwater inflows will increase open mouth conditions, subsequently increasing periods of tidal action. Permanently open systems along the Wild Coast are likely to experience some reduction in salinity penetration owing to increased freshwater flows (medium rating in Figure 2), whilst a slight increase in open mouth condition and an associated increase in tidal action is expected to increase average salinity. Higher freshwater inflows predicted from KwaZulu-Natal are likely to decrease average salinity in numerous small perched TCEs (<10 in this region), but in the deeper, non-perched TCEs, an increase in open mouth condition and an associated increase in tidal action will result in more saline conditions (10–20). In this region, the large permanently open estuaries are expected to become fresher under the predicted increase in freshwater inflows. Despite the potential overall increase in inflow predicted for the Kwa-Zulu Natal and Delagoa regions, the estuarine lakes in these regions are most sensitive to the predicted increase in the intensity of wet-dry cycles, owing to their large surface areas and associated high evaporation losses. Therefore, during extended drought periods, the salinities in these systems are expected to increase, e.g., St. Lucia > 150 and Kosi (upper lake) > 10. A significant change is thus expected for KwaZulu-Natal estuaries as indicated by the high rating in Figure 2.
3.1.4. Changes in Biogeochemical Regimes
Freshwater inflow has a marked influence on the biogeochemical characteristics of an estuary, including system variables (e.g., pH and turbidity), inorganic nutrients (e.g., nitrate and phosphate), and particulate organic matter (POM) [155,156,157,158,159,160]. Turbidity (or suspended solids) and pH levels in river inflow are primarily influenced by catchment characteristics such as vegetation, geology, and soil erodibility, as are nutrient characteristics [161]. For example, Western Cape rivers draining Table Mountain Sand, also referred to as black water systems, are naturally poor in nutrients and low in pH [162]. Rivers are a significant source of POM, especially during high flow events and floods. Changes in freshwater inflows also affect biogeochemistry through changes in hydrodynamic processes, e.g., altering mouth states [155]. When a system is open, tidal action introduces seawater into estuaries, while longer residence time during closed periods enhances the influence of in situ processes (e.g., primary production and remineralisation) on estuarine biogeochemistry. Overall, the vulnerability of estuaries to biogeochemical change associated with changes in freshwater inflows largely follows the rating of expected flow changes in the regions, using either average flow conditions (e.g., inorganic nutrients) or floods (e.g., POM) (Figure 2).
Anthropogenic activities, associated with urban, industrial, and agricultural development, have, however, altered the biogeochemical characteristics of river inflow to South Africa’s estuaries, to varying degrees, and may therefore influence how river inflow affects changes in the biogeochemical regimes of estuaries [110,163]. For example, in more pristine areas, reduced freshwater inflow can reduce nutrient inputs, affecting primary productivity of an estuary and thereby reducing the food availability to higher trophic levels, e.g., juvenile fish [130,164,165,166]. Systems, where changes in inflows result in higher anthropogenic nutrient inputs, can become more eutrophic, especially the TCEs during closed periods when nutrient assimilative capacity becomes limited [160,163,167]. In turn, excessive eutrophication increases oxygen stress. Predicted increases in temperature are likely to further stimulate these in situ processes, enhancing hypoxia, with potentially detrimental effects on estuarine biota [163,168,169,170]. Eutrophication can even override warming as a stressor, for example, in temperate African seagrass [53].
With increased industrial and agricultural development in catchments, but a decrease in freshwater runoff, waste streams (and associated toxin loads from metals and persistent organic pollutants) are going to make up a larger proportion of runoff entering estuaries, especially during the dry seasons. Moreover, toxins’ bioavailability can alter through changes in influencing variables, such as temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, and POM [171,172]. Chronic exposure to increased toxins will have a detrimental impact on biota, for example, affecting species richness and abundance of estuarine resident fish [173,174].
Along the West Coast and Western Cape regions, where a marked reduction in freshwater inflows is expected, estuaries will be vulnerable to biogeochemical change as indicated by a high and medium rating in Figure 2. For example, reduced runoff from the highly erodible catchments in these regions is likely to reduce average turbidity (or suspended solid) levels in the estuaries. A predicted reduction in floods is also expected to reduce catchment-derived POM to estuaries. This decrease in suspended matter will increase visibility, thus affecting predator-prey relationships [160,175]. With an expected increase in the duration of mouth closures in TCEs in these regions, an increase in water residence time is likely to stimulate in situ processes (e.g., primary production), especially in systems where anthropogenic nutrient enrichment already occurs [110,155,176]. During extended closed periods, other in situ processes (e.g., remineralisation) will also increase dissolved oxygen and pH stress, especially in smaller TCEs [169,170]. Reduced flow is also expected to elevate toxin loads (associated with the proportionally larger contribution of waste streams to river runoff), especially in areas where intensive agriculture and rapid urban growth are occurring. Considering the extent of change in freshwater inflows predicted for the West Coast and Western Cape regions, a relatively high degree of change can be expected in estuarine biogeochemistry, especially in terms of turbidity, nutrient dynamics, pH, dissolved oxygen, POM, and toxins.
As a result of the relatively smaller changes in freshwater inflows predicted for the Southern Cape and Eastern Cape regions, changes in the biogeochemical regimes of estuaries in these regions are not expected to be as severe, as in the West Coast region (medium rating in Figure 2). Most expected changes relate to increased droughts and floods. The predicted increase in intensity and frequency of droughts is very likely to intensify in situ processes (e.g., remineralisation), especially in the large number of TCEs estuaries and estuarine lake systems in these regions. While increased high flow and flood events (as a result of more cut-off lows) will potentially increase turbidity and provision of catchment-derived POM into estuaries, as well as assist with flushing pollutants from degraded systems.
Along the Kwazulu-Natal and Wild Coast regions, an expected increase in freshwater inflows is also expected to reflect the biogeochemical characteristics of estuaries in these regions. Systems are likely to become more turbid, and also to receive higher catchment-derived POM loads, especially during floods. In turn, higher suspended matter will decrease light attenuation (affecting water column primary production), as well as visibility (affecting predator-prey relationships) [160,175]. Moreover, higher inflows are expected to reduce periods of mouth closure in the TCEs of this region, thus reducing periods of high water retention. As a result, water column primary production is likely to drop, limiting food supply to higher trophic levels [164,165,166]. However, because of higher inflows, more frequent flushing is expected to reduce stress associated with hypoxia. Unlike the Wild Coast region which is still relatively undeveloped, the KwaZulu-Natal region has a high number of urban estuaries (e.g., uMdloti). These systems are likely to experience a significant increase in floods and thus more regular scouring of sediments, potentially reducing the persistence of high toxin levels. Therefore, it can be expected that the increase in freshwater flows predicted for the KwaZulu-Natal region will result in a relatively high degree of change in the biogeochemistry of its estuaries, especially in terms of turbidity, nutrient cycling, POM, and toxin accumulation (high rating in Figure 2). Although similar trends in biogeochemical responses are expected for the Wild Coast region, it will be less vulnerable to change compared with the KwaZulu-Natal region (medium rating in Figure 2).
Freshwater inflows to the two estuarine lakes in the Delagoa region are also expected to increase, therefore the average turbidity and catchment-derived POM loads can also be expected to increase. However, increased flows are not likely to flush these large, deep lake systems (e.g., KosiEstuarine Lake) as, for example, the shallow, small TCEs in the KwaZulu-Natal region. Rather, increased POM loads are more likely to accumulate in these systems over time. In extreme situations, especially during extended periods of drought, in situ remineralisation of accumulated POM can markedly affect the biogeochemical regimes by reducing oxygen levels and pH [170]. Therefore, estuaries in the Delagoa region will be highly vulnerable to biogeochemical changes associated with the predicted change in freshwater flow (indicated by a high rating in Figure 2).
3.1.5. Changes in Sediment Dynamics
Freshwater runoff, in particular floods, plays a critical role in scouring accumulated sediment from estuaries that were deposited during lower flow periods, either brought in from the catchment or from the sea during flood tides [133]. Accumulation of sediment as a result of soil erosion in the catchment, poses a major threat to estuaries, particularly those in the Wild Coast and KwaZulu-Natal regions characterised by highly erodible soils (Figure 1) [135,177]. Moreover, the denuding of vegetation in the more arid regions (i.e., West Coast and Western Cape) [178], coupled with an increase in the frequency of high-intensity rain events projected for these regions, will lead to a significant increase in the deposition of sediment in estuaries (high ranking in Figure 2).
Increased siltation, turbidity, and salinity changes associated with floods will influence the growth and distribution of mangroves, saltmarsh, and submerged macrophytes. For example, an increase in sediment delivery combined with increased rainfall promotes mangrove growth, productivity, and expansion [179,180]. However, extreme events can also scour estuary banks and lead to extended inundation, thereby removing mangroves and saltmarsh in intertidal habitats. Such habitats may be able to re-establish, but this can take decades. For example, mangroves that were removed by flooding in two warm temperate estuaries were only re-established after more than a decade [179]. Floods can also deposit sediments that cause the smothering and die-back of mangroves and saltmarsh. Sediment deposition may temporarily or permanently cover sandprawn, mudprawn, and other invertebrate burrows, resulting in a loss of habitat and refuge for benthic fishes, shrimps, and other burrow symbionts. Changes in discharge, sediment transport, and deposition may see a change in species composition, abundance, and size or age structure according to preference for sediment particle size. For example, 0+ dusky kob Argyrosomus japonicus recruit into turbid, muddy habitats for their first year of life, whereupon they disperse into less turbid, more sandy estuarine habitats or estuaries during the next 4–5 years of adolescence. The turbid muddy habitat is limited at <5%, whereas the less turbid, more sandy habitat is >50% of estuarine open-water area in South Africa [36].
Whilst the Western Cape is likely to experience only limited increases in flood events, the arid nature of the region and sparse land cover will make it highly vulnerable to erosion, especially in areas subjected to poor land-use. Estuaries in the Western Cape and Southern Cape regions are largely fed by runoff draining Table Mountain Sandstone with characteristically low turbidity levels [162], and, therefore, will be somewhat buffered from such effects. Systems in the Southern Cape and Eastern Cape regions will see some increase in the occurrence of flooding and substrate instability as indicated by medium and low ratings in Figure 2, respectively. Along the Wild Coast, the predicted increase in the frequency and magnitude of flood events, exacerbated by current land-use practices, will result in greater catchment erosion. This will lead to more infilling of estuaries and a change in habitat characteristics from sandy to more muddy habitats, resulting in a decline in substrate stability and changes in biotic community structure [133]. In KwaZulu-Natal’s small, incised estuaries, increased flooding will also negatively influence substrate stability, resulting in depauperate biotic communities as there is little intertidal habitat and lower floodplain habitat available for colonisation. Significant change is thus expected in Wild Coast and KwaZulu-Natal estuaries (high rating in Figure 2). The Delagoa region is somewhat buffered from increased erosion due to the sandy nature of the coastal plain around it; however, some additional scouring of estuary mouths and lake linking channels is expected (medium rating in Figure 2).
3.2. Ocean/Coastal Circulation and Temperature Regimes
There are diverse opinions on the Climate Change variables that may impact coastal temperatures [180]. However, overall, the major influencing stressors are land climatic conditions (with a focus on temperature) and ocean circulation [37,66,181,182]. This implies that estuaries, situated at the land-sea interface, are likely to be impacted by changes in land temperatures (land-sea temperature gradients), but also temperature changes as a result of changes in circulation pattern (alongshore temperature gradients) [183]. Overall, land temperatures are expected to increase significantly along all coastal regions of South Africa, with predicted increases between 1 and 6 °C (indicated by high ratings in Figure 3) [43,59].
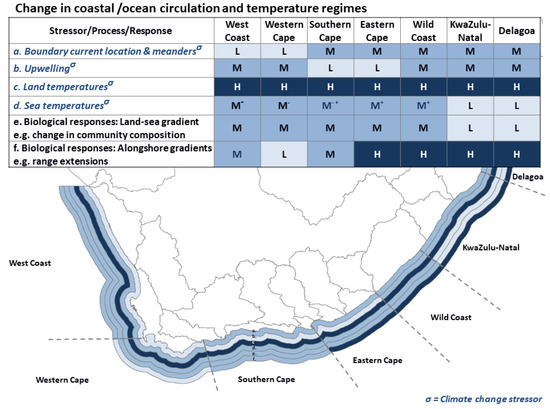
Figure 3.
Summary of vulnerability rating (high/medium/low) for estuaries in seven regions, associated with changing ocean circulation, focusing on temperature regimes (colour zones on map depict (a) to (f) in table moving outward from the coast with H = high, M = medium, L = low).
Concerning ocean circulation patterns, global warming is expected to impact both the Benguela and Agulhas currents along South Africa’s west and east coasts, respectively. The Benguela Current is the strongest wind-driven coastal upwelling system known. In the southern Benguela, seasonal shifts in the latitudinal location of the South Atlantic High along a north-west axis lead to strong seasonal variations in the wind intensity, with increased upwelling during the summer season [184]. On its offshore boundary, the dynamics of the Benguela Current circulation are modulated by the intermittent passing of warm Agulhas Rings and eddies [185]. Negative annual average temperature trends have been reported along the southern and western South African coastline over the last four decades [66,186,187]. The surface cooling of coastal waters along the western and southern South African coastline is thought to be driven by an intensification and poleward expansion of the South Atlantic High Pressure system and an associated increase in upwelling favourable winds [187,188]. Future projections based on regional simulations of the atmospheric circulation predict an intensification of the wind-driven upwelling circulation in the 21st century in the southern Benguela region [189]. The intensification of the Benguela Current is likely to increase coastal upwelling, especially along the West Coast and Western Cape regions [61,62]. These two regions are already subject to large-scale upwelling, so Climate Change is expected to incrementally increase the occurrence, therefore resulting in a decrease in coastal temperatures and an increase in temperature variability (indicated by medium rating in Figure 3).
While some modelling studies suggest that the Agulhas Current has intensified [80,190,191], observational data show that since the early 1990s, there has been an increase in turbulence rather than an intensification of the current [77,78]. Increased turbulence in the Agulhas Current will increase current meanders and affect the location of the current along the south and east coast of South Africa (e.g., South Coast, Eastern Cape, Wild Coast, Kwa-Zulu-Natal, and Delagoa regions) (medium rating in Figure 3).
Increased meandering in the Agulhas Current is also expected to increase the occurrence of existing upwelling cells along the east coast of South Africa—Wild coast, KwaZulu-Natal, and Delagoa regions—as indicated by the medium rating in Figure 3. The impact of an increasingly turbulent Agulhas Current on coastal temperature trends along the South African east and south coast remains uncertain, but increased meandering is expected to lead to more variability in coastal and shelf regions and increased cross-shelf exchange [192]. An increasing trend in Eddy Kinetic Energy at the Agulhas Current Retroflection was found to be associated with an increase in the number of Agulhas Rings propagating into the Atlantic [78]. The additional influx of warm Agulhas Current water into the southern Benguela would lead to an intensification of the cross-shelf gradients in the southern Benguela and might also impact the variability of the Benguela Jet and the transport of juvenile fish from the south to the west coast of South Africa. Earlier studies showed significant warming of the Agulhas Current sea surface temperature from late 1960 to early 2000s [191,192]. However, recent research shows that this warming trend has slowed significantly, at least at the surface as expressed by the SST [193].
Focusing on land-sea temperature gradients, shallow-water aquatic systems, particularly the small TCEs characteristic of the South African coast, will be more vulnerable to such increases compared with deeper water bodies [37,194] (Figure 3). In the larger, permanently open estuaries, the direct effect of atmospheric warming on surface waters will be mostly confined to the fresher upper reaches, strongest influenced by river inflows. However, water temperatures in the lower (more marine) reaches will most likely be more vulnerable to temperature shifts as a result of changes in ocean currents and upwelling conditions. When species are at the edge of their temperature tolerance ranges they can arrange themselves longitudinally according to the land-sea temperature gradient [183]. Thus, predicted temperature increases in the fresher, upper reaches of large permanently open estuaries are likely to support more tropical species due to increased temperature gradients between estuaries and the sea. However, the gradient is expected to be lower in subtropical regions (e.g., KwaZulu-Natal) where ambient seawater is typically warmer, compared with temperate regions with cooler ambient seawater. Such change is expected to be more noticeable in regions with relatively cooler coastal waters (i.e., West Coast, Western Cape, South Cape, Eastern Cape, and Wild Coast regions as indicated by medium rating in Figure 3, compared with relatively warmer coastal regions, such as Kwa-Zulu-Natal and Delgoa regions (indicated by low rating).
The higher coastal temperatures expected for the south coast, therefore, may result in an eastward extension of the subtropical climatic zone (Table 2), compacting the warm temperate climatic region against the cooling southern Benguela region, and expanding the cool temperate climatic region [195,196]. These marked geographical shifts in alongshore temperature gradients are expected to have marked effects on nearshore and estuarine biota, especially along the Eastern Cape, Wild Coast, and KwaZulu-Natal regions (indicated by the high rating in Figure 3).
Temperature influences community composition and species distribution as well as reproduction, growth, behaviour, mortality, predator-prey, and parasite-host relationships and competition for resources (see Table 1). Species are adapted to, and distributed within, specific temperature ranges [197,198,199] and tend to be more stressed near the edge of their distribution [200]. As temperature changes, the geographical distribution of species, depending on their tolerances or preferences, may contract or expand, leading to new and unpredictable species interactions [37,125,201,202,203,204]. While many species of fish and invertebrates in estuaries are tolerant of extreme temperatures (e.g., [54]), changes in the distribution and abundance of especially the marine species in estuaries are likely to be linked to coastal temperatures because of spawning and larval development taking place in the marine environment [205]. For example, the distribution and abundance of mugilids in African estuaries seem to be strongly linked to coastal temperatures rather than estuarine temperatures [205]. Thermal windows are narrow in the early life stages of fish (eggs and larvae) and widen in juveniles and young adults [206,207]. In recent years several estuarine-associated subtropical species as well as some tropical reef species have extended their ranges 200 to 1000 km south to the warm/cool temperate transition zone [208]. Furthermore, the increased occurrence of tropical fish species in estuaries along the Eastern Cape region (e.g., East Kleinemonde and Mngazana) has not displaced the numbers of temperate species, resulting in an increase in species (richness reviewed in [37]). Range expansion may also be accompanied by behavioural changes. Expansion of, for example, spotted grunter Pomadasy commersonnii into the warm-cool temperate bioregion transition zone (Table 2) has culminated in stock separation, loss of return migration, and the establishment of a spawning population in its new range [208]. Less mobile or sessile species that are less able to escape or compete with encroaching species for resources may face local or global extinction. The loss of species from an estuary that has become too warm may reduce species diversity in the short term, with recovery depending on the mobility of new colonisers, their ability to tolerate higher temperatures, and their tolerance of higher salinities in the marine environment.
Changes in temperature will also affect coastal vegetation, with more subtropical species moving further south, most notably the invasion of saltmarsh habitats by mangroves, the latter being tropical and subtropical in nature and ideal indicators of global warming [180,209,210,211,212]. Already, introduced mangrove communities are surviving in warm temperate estuaries along the Eastern Cape region as far south as East London, and will most likely expand under predicted increases in temperature [196,212]. The only inhibitor of mangrove expansion appears to be the absence of suitable habitat due to the dominance of temporarily open-closed estuaries to the west [213]. Frost may also play a role but in most cases, frost and plant cell damage are dampened in estuaries and the nearshore zone [196,214]. Several mangrove-associated invertebrates have already shifted further than mangroves and colonised “surrogate” saltmarsh and sedge habitat to the south. This includes the tropical fiddler crab Uca annulipes and mangrove snail Cerithidea decollate in the Knysna Estuary, a new southernmost limit for both genera [215,216].
3.3. Sea Level Rise
Previously, the rate of sea level rise along South Africa’s west, south, and east coasts was estimated at +1.9 mm yr−1, +1.5 mm yr−1, and +2.7 mm yr−1, respectively [84,85]. However, a recent reassessment of sea level rise for South Africa (SA), projected a sea level rise of 8 to 9 mm per year under RCP8.5 [217]. Sea level rise increases are 7% to 14% larger for South Africa than projections of global mean sea level, due to local amplification of increases in several components of sea level rise [217]. Taking these findings and projected sea level rise scenarios into account [4], this assessment assumes a sea level rise of between +0.5 and +2 m (Figure 4).
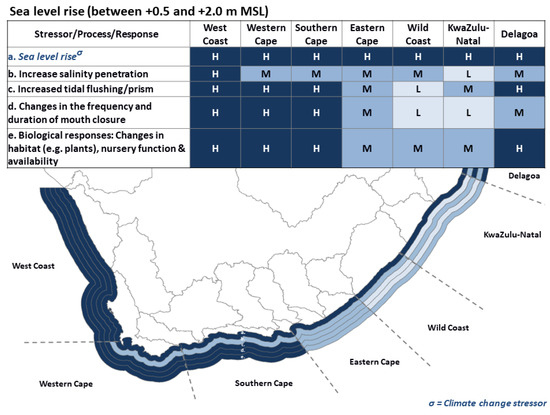
Figure 4.
Summary of vulnerability ranking (high/medium/low) for estuaries in seven regions associated with sea level rise (colour zones on map depict (a) to (e) in table moving outward from the coast with H = high, M = medium, L = low).
Effects of sea level rise on estuaries are complex and diverse and depend, for example, on the type of estuary, sediment availability, and wave energy characteristics along the coast (Table 2). For example, in some TCEs, sea level rise could assist in prolonging periods of open mouth conditions as it will increase the tidal prism, one of the forces maintaining such conditions in estuaries, especially along coasts sheltered from wave action and with limited sediment availability. Alternatively, along high-energy, sediment-rich coastlines, sea level rise could merely reset the level at which an estuary closes to the same relative height above mean sea level, without significantly affecting the frequency or duration of mouth closure. Coastal features, such as submerged rocky platforms, have the ability to dissipate wave action which drives estuary mouth closure—referred to as a barrier effect. Sea level rise, however, can dampen the barrier effect of such features, thus increasing the ability of wave action to close mouths, especially during low flow periods. In the case of permanently open estuaries, sea level rise may lead to an increase in saline penetration, especially into the middle reaches, reducing the size of these brackish, intermediate zones characteristic of estuaries, which are key to the functionality of their unique biota [218].
Changes in salinity penetration and mouth state have significant ripple effects on estuarine ecosystems (Table 1). For example, some mangrove and saltmarsh systems may not be able to keep pace with rapid sea level rise, and mangroves may outcompete saltmarshes in subtropical areas as a result of sea level rise [33,210,219]. Mangroves could rapidly colonise low lying areas, thus providing new habitat and nursery areas for fish and crustaceans [179]. Coastal squeeze along urban systems will, however, prevent landwards expansion of marshes and mangroves at many systems [218]. This loss in estuarine vegetation has ripple effects into higher trophic levels. For example, a loss in fringing vegetation (sediment-trapping mechanisms) may result in more turbid systems that benefit filter and feeders at the expense of “visual” selective feeders. Even more so, those opportunists are readily able to switch between feeding modes (e.g., southern mullet Chelon richardsonii and estuarine round herring Gilchristella aestuaria vs, Cape silverside Atherina breviceps [220,221]). Higher turbidity also reduces light penetration, thus affecting microalgal production and food supplies to higher trophic levels [163,222] Vulnerability ratings of estuarine biota to sea level rise therefore justify the high rankings given to salinity penetration or changes in mouth states.
As a result of the gentle topography of the West Coast and Western Cape regions, estuaries in these regions are likely to experience significant increases in tidal flows, and thus salinity penetration as a result of sea level rise, especially on the West Coast that supports a relatively large number of long, permanently open systems (e.g., 70 km long Great Berg Estuary) as indicated by high for West Coast and medium for Western Cape ratings in Figure 4. As a result of sea level rise, an increase in the tidal prisms is expected to increase the duration of open mouth conditions in the medium to larger TCEs characteristic of these regions (high rating in Figure 4). Although in some systems where coastal features are dissipating the effect of wave action on mouth states, sea level rise may reduce this barrier effect, and may counter the expected increases in open mouth periods. The higher tidal prisms and extended periods of open mouths may also increase salinity penetration in the TCEs of this region, thus, a net result is that the estuaries in these regions may become more saline in the long-term as a result of sea level rise.
Sea level rise will also increase tidal flows significantly in the estuaries of the Southern Cape Region, especially considering the gentle topography of the large estuarine lakes, bays, and permanently open systems in the region. This will result in stronger saline penetration and an increased duration in the period in which TCEs estuary mouths will stay open. As sediment availability is relatively low along this part of the coast, even the smaller systems will experience these effects (high rating in Figure 4). Therefore, sea level rise is likely to maintain open mouth conditions and longitudinal salinity gradients for longer in this region. Along the Eastern Cape region, the larger permanently open estuaries may experience a substantial increase (>1.0 m) in tidal flows, although the smaller systems, with generally steeper topography, will be relatively similar to the present day. Increased tidal prisms in medium to larger TCEs will assist with maintaining open mouth conditions and thus increase salinity intrusion as indicated by a medium rating in Figure 4.
Given the predominantly small nature of estuaries along the Wild Coast Region, as well as the area’s steep topography, tidal prisms and mouth states in these systems will remain fairly similar to the present (low rating in Figure 4). However, given the relatively low freshwater inflows, salinity is expected to increase significantly as a result of a relatively small increase in tidal flows and overall marine connectivity, with cascading impacts on the biota. In some cases, hypersalinity can even develop as a synergistic effect in systems with protected mouths where mouth closures are not likely to occur during the predicted increased drier periods as a result of increased tidal flows.
A large number of estuaries in the KwaZulu-Natal Region comprise small, perched TCEs with steep topography. Therefore, the tidal prism and associated mouth state and salinity penetration regimes in this type of system will only be altered marginally in response to sea level rise, as berm heights will likely reset themselves to a new elevated equilibrium within a relatively short period. However, this will not be the case for the region’s large estuarine lakes, e.g., St Lucia Lake, comprising more than half of South Africa’s estuarine area, with their extensive flood plains. Here sea level rise is likely to increase the tidal prism, thus contributing to a moderate increase in open mouth conditions and salinity penetration. However, this rating is in flux as it very much depends on St Lucia/iMfolozi Estuary management practices, with the ever-increasing buildup of sediments in the mouth region dampening the potential benefits of sea level rise. Given the disproportionally high contribution that estuarine lakes make to the estuarine area in this region, sea level rise can be expected to have a significant influence in this region as indicated by the high rating in Figure 4, despite the smaller systems largely remaining unaffected.
In general, the effect of sea level rise on estuarine lake systems in the Delagoa Region is expected to be similar to the estuarine lakes in the KwaZulu-Natal Region, given that these systems also have extensive flood plains. However, due to their restricted inlets, the effects of sea level rise and associated increased tidal amplitude on mouth conditions and salinity penetration will be dampened (medium rating in Figure 4). However, considering the low coastal and fluvial sediment input to the Delagoa estuaries, critical habitats such as mangroves and saltmarshes may not keep up with the rate of change, leading to overall habitat loss in these systems and cascading effects in trophic structure and species composition [223]. While a potential increase in salinity of the upper Kosi Lakes poses a significant risk to these unique, largely fresh tropical environments, the much smaller uMgobezeleni lake system may revert to a more natural state as marine connectivity increases.
3.4. Increased Intensity and Frequency of Coastal Storms
Large storms at sea generate wave conditions and sediment transport that can close estuary mouths, unless there is significant river flow to maintain the open mouth condition. The predicted changes in oceanic wind regimes off the coast of South Africa have not yet been sufficiently quantified to enable high-confidence projections of the future wave climate along the South African coast. The short time-series wave data that have been analysed show an increase in wave height of about 6% during storm events [224]. For this assessment, a relatively modest increase of 10% in wind velocity was therefore assumed, which translates into a 12% increase in wind stress, a 26% increase in deep sea wave height, and potentially as much as an 80% increase in wave power [225]. This is underpinned by the IPCC 5th Assessment Report [13], which states that Climate Change is indeed increasing the frequency and severity of storm surges, and that the mean significant wave height is likely (67–100% certain) to increase in the Southern Ocean. In fact, it is the combination of higher sea levels and increased sea storms that will have the most significant effect on the coastal processes. For example, under future wave climate and sea level rise predictions, the 1:50 year wave run-up elevation will be reduced to a 1:3 year return interval at a beach located on the South African South Coast [226]. Modelling the combined impact of sea level rise and a 10% increase in storm surge on the coast showed that the country is at risk of losing 600 km2 of coastal land [227]. An assessment of the change in the nearshore extreme wind and wave climate in Southeast Africa, based on long-term wind and wave data and wave modelling, found that future changes in wind and wave climate indicate that extreme events will be more intense in nearshore areas in almost all seasons [228].
A high number of estuaries in South Africa show great potential sensitivity to increased wave energy [29,229]. Especially vulnerable are small to medium-sized estuaries (associated with low tidal flows) along exposed, sediment-rich coastlines, which are more likely to close than estuaries that are located on sediment-starved coastlines. However, these generalisations are tempered by beach slope, protection against wave action, and changes in freshwater inflow. Storm events can also increase marine sediment transport into the mouth area of an estuary, causing gradual infilling. Overwash, which occurs when high waves overtop the berm and wash seawater into a closed estuary, is also likely to occur more frequently, especially in systems where availability of limited marine sediment slows or limits berm growth. Therefore, during extended periods of closure, e.g., during drought periods, an increase in storminess can increase salinity in estuaries with low berm heights through overwash.
Biological responses to the effects of increased sea storminess related to mouth state and overwash, both in terms of its effect on salinity and recruitment, are shown in Table 1. Interestingly, overwash acts as an alternative recruitment mechanism in estuaries during closed periods [230]. Waves can also deposit surplus sediments on seaward margins, causing mangrove smothering and mortality [132]. Deposited sediments can also close the mouths of estuaries to the sea, leading to inundation and dieback of mangroves [178].
Although increased sea storms will contribute to increased mouth closures in the West Coast and Western Cape regions, changes from the present may not be that high, as a number of the smaller arid systems in these regions are predominantly closed (due to a lack of inflow), while the large permanently open systems, Olifants and Great Berg estuaries, should remain open as a result of significant tidal flows as indicated by medium rating in Figure 5 [29]. While the steeper beach slopes along the West Coast region are likely to buffer against a significant increase in overwash and associated increases in salinity (medium ranking in Figure 5), such events are very likely to increase salinity in more sheltered systems with lower berms in the Western Cape Region (high ranking in Figure 5). The average berm height, which is estimated between 2.0 and 3.5 m mean sea level (MSL) in this region, with a gradient that runs from north to south, can increase by 0.5 to 1.0 m where sufficient sediment is available as a result of increased sediment transport potential.
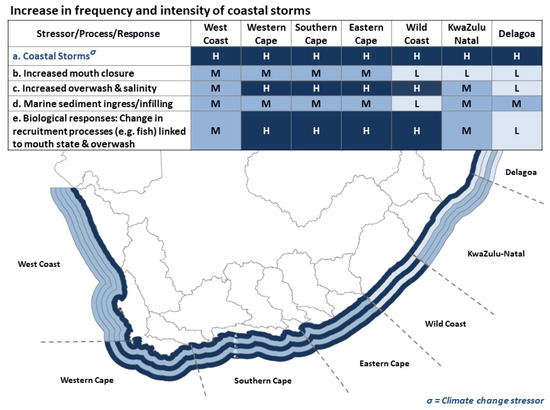
Figure 5.
Summary of vulnerability ranking (high/medium/low) for estuaries in seven regions associated with increased sea storminess (colour zones on map depict (a) to (e) in the table moving outward from the coast with H = high, M = medium, L = low).
Along the Southern Cape and Eastern Cape regions, marine sediment availability is usually not limited, and increased storminess is likely to translate into some increase in mouth closure and ingress of marine sediment into the lower reaches of estuaries along exposed areas of the coast (indicated by medium rating in Figure 5). Overwash events are also likely to occur more frequently, especially in systems where the limited availability of marine sediment slows down berm growth (high rating in Figure 5). The net result is that some estuaries in these regions may become more saline as a result of increases in sea storms, especially during drought years.
Estuaries along the Wild Coast Region are generally sheltered from sea storms, and sediment availability along this part of the coast is also limited. An increase in sea storms is, therefore, expected to have little impact on estuaries in this region (low rating in Figure 5). At present, average berm heights are estimated at 2.5 to 3.0 m MSL, but may rise by 0.5 = 1.0 m depending on overwash, increased sediment transport potential, and available sediment. These relatively low berm levels indicate sensitivity to increased overwash.
In the KwaZulu-Natal Region, estuaries are somewhat buffered against the effects of increased storminess as this coast is characteristically wave-dominated, resulting in most estuaries being “perched” high on the beach profile as indicated by a low ranking in Figure 5. Predicted increases in runoff are also likely to offset the potential small increases in mouth closure due to increased storminess. However, along this sediment-rich coast, increased storminess may contribute to some infilling of marine sediment in the lower reaches of estuaries (medium ranking in Figure 5). In this region, berm heights are relatively high at about 3 to 3.5 m MSL and could build up even more by 0.5 to 1.0 m by a combination of the predicted increases in wave runup and sediment transport potential. These high berm heights are also likely to limit the contribution of overwash to salinity and biotic recruitment processes. The estuarine lakes along the Delagoa Region are somewhat buffered against sea storms as a result of their restricted inlets and large tidal flows, in the case of Kosi, which reduce the risk of mouth closure due to increased storminess as indicated by low to medium rating in Figure 5.
The change in biological recruitment, such as fish, follows the same pattern as mouth state and overwash (see Figure 5). Overall predicted increases in overwash could offset some of the impacts of mouth closure on biotic processes along the Western and Southern Cape and increase connectivity along the Eastern Cape and Wild Coast (high in Figure 5). Some localised die back of mangroves is expected at systems with relative low berm levels. In addition to the direct effects of increased storminess on estuary mouth state are the indirect effects on human behaviour and pressure on estuary resources utilisation. For example, increased wind speeds have resulted in a significant decline in sea-days for the commercial marine linefishery on the southern Cape coast [231]. In an attempt to maintain fishing effort and catch levels, fishers are likely to build larger vessels (i.e., maintain fishing effort at sea) or find calmer waters elsewhere, resulting in a displacement of fishing effort into calmer estuarine waters. This has already happened in the Bot/Kleinmond Estuary with the resultant overexploitation, reduced nursery function, and user conflict.
3.5. Ocean Acidification
The pH of surface ocean waters is increasing under the influence of rising atmospheric CO2 levels [232]. Southern African upwelling systems have a naturally lower pH and a considerably lower carbonate saturation state [233]. For example, pH in the Southern Benguela current ranges between 7.60 and 8.25 depending on the season, averaging ~8.1 [234]. This system is predicted to have significantly lower pH (~7.8 to 7.5) by the year 2100 and even lower by 2300 (~7.3 to 6.7) [232].
In addition to transporting low pH oceanic water into coastal areas, which are likely to become even more acidic as a result of ocean acidification [235], upwelling naturally also introduces cool, nutrient-rich waters into coastal areas, driving important nearshore productivity [236,237].
While large-scale primary production associated with coastal upwelling is a natural phenomenon that drives nearshore productivity, subsequent die-off and remineralisation of algal blooms can have detrimental impacts on pH and dissolved oxygen levels. In extreme events, coastal waters can become anoxic and rich in hydrogen sulphide (so-called “black tides”), and are then advected into sheltered estuaries through tidal action, causing large-scale mortality of resident biota (e.g., Great Berg Estuary) [238]. Ocean acidification will ultimately result in a change in pH and oxygen in estuaries, with a related response in biotic processes such as community composition, nursery function, and behavioural responses.
Unlike the open ocean, estuarine pH levels are dependent on not just coastal upwelling, but also catchment geology and land-use, freshwater inflow, nutrient input, primary production, and decomposition [52,105,239]. Changes in land-use can result in changes in freshwater alkalinity and CO2 fluxes up to 0.5 units [46,52,239,240,241,242]. In South Africa, many rivers are acidic (e.g., pristine rivers of Western Cape Table Mountain Sandstone fynbos region have pH < 6), and have saturation states for aragonite (Ω) lower than receiving ocean waters [162]. However, as a result of anthropogenic interference (e.g., riparian clearing, agricultural return flow), many of these weakly buffered systems have lost their strong acidic character and pH levels can now exceed that of sea waters, e.g., Palmiet Estuary [160]. Dynamic gradients in pH and saturation states are driven by estuary mixing processes, but in situ metabolic processes can cause deviation from these gradients [46,52,240,242,243,244]. The pH in estuarine habitats (e.g., mangroves, saltmarshes, and macroalgal beds) reveals site-specific diel, semi-diurnal and stochastic patterns of varying amplitudes as high as 1.0 unit [170,245,246,247,248]. Nutrient enrichment stimulates primary production and eutrophication (e.g., phytoplankton blooms increase pH to 9.0); however once die-off occurs, organic matter is demineralised, leading to potential hypoxia and lower pH [52,105,163,170,222,239]. Increased residence times are likely to exacerbate remineralisation and the lowering of pH [169,170].
pH changes in estuaries, in addition to altering the acidity of water, may alter other abiotic processes (e.g., speciation and adsorption of chemical variables). In turn, these changes affect important biotic processes such as community composition, nursery function, and behavioural responses [245]. Lower pH will affect all calcifying organisms, such as coralline algae, echinoderms, crustaceans, and molluscs, as structures made of calcium carbonate dissolve, requiring more metabolic energy for an organism to maintain the integrity of its exoskeleton [37,125,239,249,250]. Calcifiers residing in cold water habitats such as upwelling systems are at a higher risk of ocean acidification and decreased seawater carbonate saturation, as their environment is only just supersaturated with respect to the carbonate phases they excrete [251]. Thus, natural variability in estuarine pH should be taken into account when the effects of ocean acidification are considered. Natural fluctuation in pH may play a large role in the development of resilience in estuarine populations. On the other hand, it may combine with the effects of ocean acidification to produce even more extreme events, resulting in an even greater impact on the biota [246].
Acidification will likely impact various life stages differently as CO2 tolerance varies between life stages of organisms [252]. For most fish species, egg and larval phases are more sensitive to elevated CO2 compared to the juvenile and adult stages [253]. Increases in CO2 levels may lead to hypercapnia (elevated CO2 partial pressure) and acidosis in the blood and tissues of fishes [252]. Ocean acidification will not only have a direct impact, but can also indirectly influence the ability of organisms to deal with local phenomena. Estuary-dependent species with a pelagic life-history stage will be particularly vulnerable. Slower growth and delayed metamorphosis of fish and invertebrate larvae may result in recruitment failure if these animals miss the brief recruitment window typical of most temporarily open-closed systems along the South African coastline. In some fish species, slow development and changes in the physical and chemical structure of otoliths (and other bone structures) may alter sensory perceptions and their ability to communicate, avoid danger, or detect prey [254]. Acid-induced otolith malformation leads to atypical behaviour such as reliance on visual rather than sound stimuli, as well as increased cortisol levels, stress levels, and suppressed immune systems in the Sciaenid Sciaenops ocellatus [255]. However, not all species will react in the same way to ocean acidification and an understanding of the process driving the different responses by fish is critical for future prediction [254]. Anomalous to the above in South African estuaries is the alkalinisation of acidic blackwater catchments (along the Western Cape and Southern Cape) brought about by riparian clearing, agricultural return flow, and other poor land-use practices, with some estuarine pH levels now exceeding that of marine inflow [162]. While, several species have enough physiological plasticity to cope with acidification, many may not be able to cope with the two extremes of acidity and alkalinity in the marine and estuarine environment. Abrupt changes and increases in pH and other environmental extremes raise the susceptibility of fish and invertebrates to disease [256]. The invasive potential of pathogens and their vectors may also increase [257]. Furthermore, the estuarine invasive potential of alien species e.g., Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas may increase in response to rising pH whilst they die-off in acidic conditions [258].
Regions adjacent to strong upwelling systems, such as the West Coast and Western Cape regions, will be most vulnerable to pH shifts and associated biological responses (Table 1) as a result of oceanic processes. In particular, the large permanently open systems adjacent to the Benguela upwelling system (e.g., Orange, Olifants, and Great Berg estuaries) will be at risk, as acidification in this current is expected to continuously increase towards 2100 and 2300 as indicated by medium rating in Figure 6. Less at risk are the small fluvially dominated black water systems of the region and the TCEs that are often closed off from the sea [29]. In general, estuaries along the Southern Cape and Eastern Cape coast are not subjected to regular regional-scale upwelling and are thus less vulnerable to ocean acidification (low rating in Figure 6). However, some localised upwelling may increase the vulnerability of systems with mouths located in localised upwelling cells. Similarly, systems along the Wild Coast and Kwa-Zulu Natal coasts may also be vulnerable to pH variability from localised coastal upwelling associated with changes in the Agulhas Current, although less vulnerable compared to those along the western boundary of South Africa (low rating in Figure 6). Again, permanently open systems that are freely connected to the sea are more likely to be affected. The Estuarine Lakes of the Delagoa region are relatively weakly connected to the sea and thus are not as vulnerable as upwelling regions (rated medium in Figure 6). Biological responses follow a similar pattern to abiotic processes.
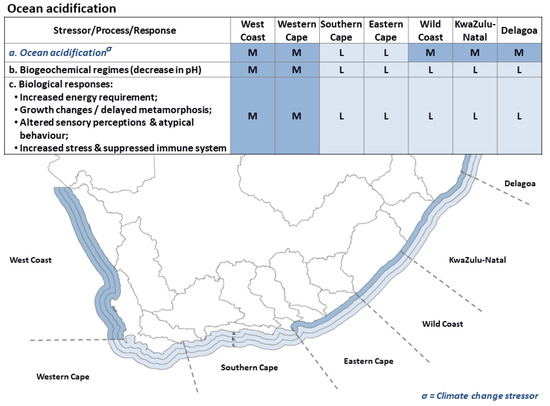
Figure 6.
Summary of vulnerability ranking (high/medium/low) for estuaries in seven regions associated with ocean acidification (colour zones on map depict (a) to (c) in table moving outward from the coast with H = high, M = medium, L = low).
Of note is that pH changes as a result of Climate Change are not the only pressure that induces acidification and pH variability in coastal ecosystems, situated at the land-sea interface [105]. Land-based nutrient enrichment, introduced by rapid urbanisation and intensive agriculture, has been found to contribute significantly to pH variability in these systems [52,105,169,170,239,248]. Such enrichment stimulates eutrophication with serious ripple effects on pH and dissolved oxygen dynamics, even acidification and anoxia [52,105,170,239], exacerbated by increased residence time [169,170]. This complex interaction of oceanic and land-based processes in coastal system areas is known as coastal acidification [46,259]. Any anticipated effects of ocean-driven acidification linked to Climate Change, therefore, will be superimposed on these existing, land-based impacts. Most at risk are the smaller TCEs in large urban and agricultural areas, which are usually too small to assimilate excessive nutrients, especially during high retention closed periods [110].
However, it may be possible to mitigate the continued development and impacts of corrosive conditions by addressing and reducing the land-derived anthropogenic pressures that contribute to their formation, such as increased nutrient and sediment inputs associated with land-use change and urbanisation [260].
4. Conclusions
The study conducted a critical review of international literature to identify key Climate Change stressors considered relevant to South African estuaries and their projected impacts on these vulnerable ecosystems. These insights, together with local understanding and expert knowledge of South African systems, were used to rank the regional vulnerability of estuaries along the country’s coast. The approach developed here is suitable for both data-rich and data-limited vulnerability assessments and thus lends itself to broader application across other regions of the developing world.
In summary, the critical impacts associated with key Climate Change stressors in order of importance comprise:
- Land climatic/hydrological processes forcing changes in freshwater inflow and associated inputs; shifts in land-sea and longshore connectivity; modifications in salinity regimes; changes in biochemical inputs; changes in sediment deposition/erosion cycles.
- Ocean circulation patterns resulting in shifts in temperature regimes and alongshore coastal connectivity;
- Sea level rise and related impact on salinity regime, mouth state, and inundation of estuarine flood plain;
- An increase in the frequency and intensity of coastal storms impacting salinity regimes and mouth state;
- Ocean acidification amplifying existing pH fluctuations and impacting oceanic phases of estuarine species.
Overall, this analysis showed that estuaries of the KwaZulu-Natal and West Coast regions will be the most influenced by Climate Change from a structural and functional perspective. In KwaZulu-Natal, the major driver of change is increased runoff into the numerous small, perched TCEs, resulting in more open mouth conditions, a decrease in retention time, and a related decrease in primary productivity and nursery function. An increased occurrence of large floods is also likely to cause more frequent resetting of abiotic and biotic processes, potentially disrupting productivity and impacting species with complex life cycles. While along the Delagoa Region, estuarine lakes will be sensitive to increased drought conditions and reduced groundwater inputs, leading to reduced connectivity in the form of mouth closure. West Coast estuaries will also experience a decline in primary production and loss of nursery function, but as a result of reduced freshwater input, while Wild Coast, Eastern Cape, and Southern Cape estuaries will show limited change in mouth state, nutrient supply, salinity regime, and ultimately production. The most obvious impacts of Climate Change along warm temperate coastal regions will be temperature regime changes (nearshore and land), associated species range expansions/contractions, and changes in community structure.
The effect of sea level rise and related increases in tidal prisms will be less apparent along the KwaZulu-Natal coastline, where except for estuarine lakes and bays, the majority of estuaries are perched. While it will be more apparent along the Southern and Western Cape regions with their extensive coastal floodplains. The effects of ocean acidification in the short-term will be negligible in comparison with the land signal—eutrophication resulting from urban runoff and agricultural return flow. Permanently open estuaries subjected to regular upwelling or increased upwelling along the West Coast are likely to display the effects of ocean acidification first, especially impacting those species with oceanic phases in their life cycles. South Africa is a wave-dominated coast, thus sensitive to increased sea storminess. However, highly protected estuaries (e.g., along the Wild Coast) or very exposed estuaries (along the KwaZulu-Natal) are less likely to change character, whereas smaller estuaries along the Western, Southern, and Eastern Cape may be very sensitive to the increase in frequency in this type of event.
Accelerated Climate Change is one of many pressures acting on estuaries and should be viewed as an additional form of anthropogenic stress impacting already stressed ecosystems. It is necessary to understand the potential amplification of variability that Climate Change may have on existing freshwater resources, the potential impact on estuarine and marine production, as well as the harvesting of resources in the marine and estuarine environments. It is thus necessary to integrate Climate Change and non-Climate Change threats. Climate Change should be seen as a catalyst to fast-track sustainable resource allocation processes, for example in the allocations of environmental flows, land-use planning processes, or the management of fisheries [126].
The ability to predict the response of estuaries to Climate Change and to plan mitigation and adaptation strategies is still hindered by a lack of good prediction tools and the lack of a fundamental understanding of many of the effects of climate variability on the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of these systems [119,261,262,263]. Assessments are limited by the availability of both data (e.g., long-term flow data, temperature data, mouth conditions, wave height, species data) and models (e.g., flow changes, linking hydrological regimes to ecosystem processes and large-scale ocean current changes). Significant research investment is urgently needed in measured and modelled data to develop a deeper understanding of site-specific Climate Change impacts on estuaries and how these ecosystems will respond in an uncertain future.
At the same time, uncertainty around forecasting change should not be seen as an impossible obstacle to understanding and developing adaptation mechanisms to reduce the effects of Climate Change on estuarine resources. Highly accurate forecasting is not obligatory to begin the process of adapting to Climate Change, as major trends are often evident enough for meaningful actions to be planned and implemented.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation: L.v.N.; methodology: L.v.N., S.J.L., N.C.J. and S.T.; investigation: L.v.N., S.J.L., N.C.J., S.T., J.B.A., A.K.T. and M.K.; resources: L.v.N.; writing—original draft preparation: L.v.N., S.J.L. and S.T.; writing—review and editing: L.v.N., S.J.L., N.C.J., S.T., J.B.A., A.K.T. and M.K.; visualisation: L.v.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We are grateful to the DSI CSIR Coastal Systems Parliamentary Grant (L.v.N., S.T.), DFFE (S.J.L., M.K.), SAIAB (N.C.J.), NMU (J.B.A.), and US (A.K.T.) for financial and logistical support. The DSI/NRF Research Chair in Shallow Water Ecosystems (UID: 84375) is thanked for supporting J.B.A. The South African National Biodiversity Institute is acknowledged for its support in dissemination of information relevant to the Estuaries Realm.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Alan Meyer and Bjorn Backeberg are thanked for their input in understanding potential responses of the marine environment to Climate Change. Ashton Maherry, Chantal Pietersen, John April, and Heidi van Deventer are thanked for their assistance with figures.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Department of Environmental Affairs (DEA). South Africa’s Second National Communication under the United Nations Framework Conversion on Climate Change; Department of Environmental Affairs: Pretoria, South Africa, 2010.
- Department of Environmental Affairs (DEA). Long-Term Adaptation Scenarios Flagship Research Programme (LTAS) for South Africa. Climate Change Implications for Marine Fisheries in South Africa; Department of Environmental Affairs: Pretoria, South Africa, 2013; 60p.
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Special Report: Global Warming of 1.5C; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- International Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). 2022: Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Beckley, L.E. The ichthyofauna of the Sundays River estuary with particular reference to the juvenile marine component. Estuaries 1984, 7, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Environmental Affairs (DEA). South Africa’s Third National Communication under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change; Draft Report; Department of Environmental Affairs (DEA): Pretoria, South Africa, 2017; 722p.
- Carter, T.R.; Jones, R.N.; Lu, X.; Bhadwal, S.; Conde, C.; Mearns, L.O.; O’Neill, B.C.; Rounsevell, M.D.A.; Zurek, M.B. New Assessment Methods and the Characterisation of Future Conditions. Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; pp. 133–171. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.N.; Preston, B.L. Adaptation and risk management. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Change 2011, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2001: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; McCarthy, J.J., Canziani, O.F., Leary, N.A., Dokken, D.J., White, K.S., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation. A Special Report D336 of Working Groups I and II of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2012; 582p. [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, L.A., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; 151p. [Google Scholar]
- Day, J.W.; Christian, R.R.; Boesch, D.M.; Yáñez-Arancibia, A.; Morris, J.; Twilley, R.R.; Naylor, L.; Schaffner, L.; Stevenson, C. Consequences of climate change on the ecogeomorphology of coastal wetlands. Estuaries Coasts 2008, 31, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.W.; Yáñez-Arancibia, A.; Rybczyk, J.M. Climate Change: Effects, Causes, Consequences: Physical, Hydromorphological, Ecophysiological, and Biogeographical Changes. Treatise on Estuarine and Coastal Science; Academic Press: London, UK, 2011; pp. 303–312. [Google Scholar]
- Gillanders, B.M.; Elsdon, T.S.; Halliday, I.A.; Jenkins, J.P.; Robins, J.B.; Valesini, F.J. Potential effects of climate change on Australian estuaries and fish utilising estuaries: A review. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 1115–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, P.E.; Skov, M.W.; Lewis, M.J.; Gimenez, L.; Davies, A.G.; Malham, S.K.; Neill, S.P.; McDonald, J.E.; Whitton, T.A.; Jackson, S.E.; et al. Impact of Climate Change on UK estuaries: A review of past trends and potential projections. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 169, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, A.C.; Newton, A.; Tett, P.; Fernandes, T.F. How will shallow coastal lagoons respond to climate change? A modelling investigation. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 112, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, R.; Duong, T.M.; Uhlenbrook, S.; Roelvink, D.; Stive, M. Climate-change impact assessment for inlet-interrupted coastlines. Nat. Clim. Change 2013, 3, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandle, D.; Lane, A. Sensitivity of estuaries to sea level rise: Vulnerability indices. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 160, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.; Ranasinghe, R.; Walstra, D.J.; Roelvink, D.J.A. Assessing Climate Change impacts on the stability of small tidal inlet systems: Why and how? Earth Sci. Rev. 2015, 154, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.; Ranasinghe, R.; Luijendijk, A.; Walstra, D.J.; Roelvink, D.J.A. Assessing Climate Change impacts on the stability of small tidal inlets: Part 1-Data poor environments. Mar. Geol. 2017, 390, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.; Nicholls, R.J.; Lowe, J.A.; Hinkel, J. Spatial variations of sea-level rise and impacts: An application of DIVA. Clim. Change 2016, 134, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.R.; Komoroske, L.M.; Wagner, R.W.; Morgan-King, T.; May, J.T.; Connon, R.E.; Fangue, N.A. Coupled Downscaled Climate Models and Ecophysiological Metrics Forecast Habitat Compression for an Endangered Estuarine Fish. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- House, A.R.; Thompson, J.R.; Roberts, C.; de Smeth, K.; Old, G.; Acreman, M.C. Projecting impacts of climate change on habitat availability in a macrophyte dominated chalk river. Ecohydrology 2017, 10, e1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, P.; Haigh, I.D.; Rohling, E.J.; Slangen, A. A new approach to projecting 21st century sea-level changes and extremes. Earths Future 2017, 5, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamunawala, J.; Dastgheib, A.; Ranasinghe, R.; van der Spek, A.; Maskey, S.; Murray, A.B.; Barnard, P.L.; Duong, T.M.; Sirisena, T.A.J.G. Probabilistic Application of an Integrated Catchment-Estuary-Coastal System Model to Assess the Evolution of Inlet-Interrupted Coasts Over the 21st Century. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 579203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Niekerk, L.; Adams, J.B.; Bate, G.C.; Forbes, A.T.; Forbes, N.T.; Huizinga, P.; Lamberth, S.J.; MacKay, C.F.; Petersen, C.; Taljaard, S.; et al. Country-wide assessment of estuary health: An approach for integrating pressures and ecosystem response in a data limited environment. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 130, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Niekerk, L.; Adams, J.B.; James, N.C.; Lamberth, S.J.; Mackay, C.F.; Rajkaran, A.; Turpie, J.K.; Weerts, S.P.; Whitfield, A.K. An Estuary Ecosystem Classification that encompasses biogeography and a high diversity of types in support of protection and management. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 45, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.A.G. Geomorphological variability among microtidal estuaries from the wave-dominated South African coast. Geomorphology 2001, 40, 99–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, A.K. A characterization of southern African estuarine systems. Southern Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 1992, 18, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.H. Estuarine Currents, Salinities and Temperatures. In Estuarine Ecology with Particular Reference to Southern Africa; Day, J.H., Ed.; A.A. Balkema: Cape Town, South Africa, 1981; pp. 27–44. [Google Scholar]
- Raw, J.L.; Adams, J.B.; Bornman, T.G.; Riddin, T.; Vanderklift, M.A. Vulnerability to sea-level rise and the potential for restoration to enhance blue carbon sequestration in salt marshes of an urban estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 260, 107495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddering, J.S.V. Coastal and catchment basin controls on estuary morphology of the south-eastern Cape coast, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Sci. 1988, 84, 153–157. [Google Scholar]
- James, N.C.; Hermes, J. (Eds.) Insights into Impacts of Climate Change on the South African Marine and Coastal Environment; South African Environmental Observation Network (SAEON): Pretoria, South Africa, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Van Niekerk, L.; Turpie, J.K. (Eds.) National Biodiversity Assessment 2011. Technical Report. Volume 3: Estuary Component; CSIR Report Number CSIR/NRE/ECOS/ER/2011/0045/B.; Council for Scientific and Industrial Research: Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- James, N.C.; van Niekerk, L.; Whitfield, A.K.; Potts, W.M.; Götz, A.; Paterson, A.W. Effects of climate change on South African estuaries and associated fish species. Clim. Res. 2013, 5, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driver, A.; Sink, K.J.; Nel, J.N.; Holness, S.; Van Niekerk, L.; Daniels, F.; Jonas, Z.; Majiedt, P.A.; Harris, L.; Maze, K. National Biodiversity Assessment 2011. An Assessment of South Africa’s Biodiversity and Ecosystems; Synthesis Report; Department of Environmental Affairs: Pretoria, South Africa, 2012; 180p.
- Hewitson, B.C.; Crane, R.G. Consensus between GCM Climate Change projections with empirical downscaling: Precipitation downscaling over South Africa. Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 26, 1315–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbrecht, F.A.; McGregor, J.L.; Engelbrecht, C. Dynamics of the conformal-cubic atmospheric model projected climate-change signal over southern Africa. Int. J. Climatol. 2009, 29, 1013–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbrecht, F.A.; Landman, W.A.; Engelbrecht, C.J.; Landman, S.; Bopape, M.M.; Roux, B.; McGregor, J.L.; Thatcher, M. Multi-scale climate modeling over Southern Africa using a variable-resolution global model. Water SA 2011, 37, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbrecht, C.J.; Engelbrecht, F.A.; Dyson, L. High-resolution model-projected changes in mid-tropospheric closed-lows and extreme rainfall events over southern Africa. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbrecht, F.; Adegoke, J.; Bopape, M.-J.; Naidoo, M.; Garland, R.; Thatcher, M.; McGregor, J.; Katzfey, J.; Werner, M.; Ichoku, C.; et al. Projections of rapidly rising surface temperatures over Africa under low mitigation. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumsden, T.G.; Schulze, R.E.; Hewitson, B.C. Evaluation of potential changes in hydrologically relevant statistics of rainfall in Southern Africa under conditions of Climate Change. Water SA 2009, 35, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, A.; Icely, J.; Cristina, S.; Brito, A.; Cardoso, A.C.; Colijn, F.; Riva, S.D.; Gertz, F.; Hansen, J.W.; Holmer, M.; et al. An overview of ecological status, vulnerability and future perspectives of European large shallow, semi-enclosed coastal systems, lagoons and transitional waters. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 140, 95–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Hendriks, I.E.; Moore, T.S.; Olsen, Y.S.; Steckbauer, A.; Ramajo, L.; Carstensen, J.; Trotter, J.A.; McCullochIs, M. Ocean Acidification an Open-Ocean Syndrome? Understanding Anthropogenic Impacts on Seawater pH. Estuaries Coasts 2013, 36, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizzini, S.; Di Leonardo, R.; Costa, V.; Tramati, C.D.; Luzzu, F.; Mazzola, A. Trace element bias in the use of CO2 vents as analogues for low pH environments: Implications for contamination levels in acidified oceans. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 134, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerfahi, D.; Hall-Spencer, J.M.; Tripathi, B.M.; Milazzo, M.; Lee, J.; Adams, J.M. Shallow water marine sediment bacterial community shifts along a natural CO2 gradient in the Mediterranean Sea off Vulcano, Italy. Microb. Ecol. 2014, 67, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milazzo, M.; Rodolfo-Metalpa, R.; San Chan, V.B.; Fine, M.; Alessi, C.; Thiyagarajan, V.; Hall-Spencer, J.M.; Chemello, R. Ocean acidification impairs vermetid reef recruitment. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, C.; Chai, Y.; Wang, H.; Kan, M. Ocean acidification: One potential driver of phosphorus eutrophication. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, A.P.; Turk-Kubo, K.A.; Al-Moosawi, L.; Alliouane, S.; Gazeau, F.; Hogan, M.E.; Zehr, J.P. Ocean acidification impacts on nitrogen fixation in the coastal western Mediterranean Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 186, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, A.; Fennel, K.; Cai, W.C.; Huang, W.H.; Barbero, L.; Wanninkhof, A.R. Eutrophication induced acidification of coastal waters in the northern Gulf of Mexico: Insights into origin and processes from a coupled physical-biogeochemical model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 946–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mvungi, E.F.; Pillay, D. Eutrophication overrides warming as a stressor for a temperate African seagrass (Zostera capensis). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, 0215129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Walt, K.A.; Porri, F.; Potts, W.M.; Duncan, M.I.; James, N.C. Thermal tolerance, safety margins and vulnerability of coastal species: Projected impact of climate change induced cold water variability in a temperate African region. Mar. Environ. Res. 2021, 169, 105346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.D.; Lister, D.H.; Osborne, T.J.; Harphan, C.; Salmon, M.; Morice, C.P. Hemispheric and large-scale land-surface air temperature variations: An extensive revision and an update to 2010. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D05127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, A.C.; Sekele, S. Trends in extreme temperature indices in South Africa: 1962–2009. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 33, 661–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKellar, N.; New, M.; Jack, C. Observed and modelled trends in rainfall and temperature for South Africa: 1960–2010. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2014, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, A.C.; Nxumalo, M. Surface Temperature Trends from Homogenised Time Series in South Africa: 1931–2015. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 2364–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitson, B.; Tadross, M.; Jack, C. Scenarios from the University of Cape Town. In Climate Change and Water Resources in Southern Africa: Studies on Scenarios, Impacts, Vulnerabilities and Adaptation; WRC Report, 1430/1/05; Schulze, R.E., Ed.; Water Research Commission: Pretoria, South Africa, 2005; pp. 39–56. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, W. Antarctic ozone depletion causes an intensification of the Southern Ocean super-gyre circulation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L03712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saenko, O.A.; Fyfe, J.C.; England, M.H. On the response of the oceanic wind-driven circulation to atmospheric CO2 increase. Clim. Dyn 2005, 25, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roemich, D. Physical Oceanography: Super spin in the southern seas. Nature 2007, 449, 34–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, B.; Feistel, R.; Agenbag, J.J.; Ohde, T. Seasonal and interannual changes in Intense Benguela Upwelling (1982–1999). Oceanol. Acta 2001, 24, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutjeharms, J.R.; Monteiro, P.M.S.; Tyson, P.D.; Obura, D. The oceans around southern Africa and regional effects of global change. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2001, 97, 119–130. [Google Scholar]
- Bakun, A.; Field, D.B.; Rodriguez, A.R.; Weeks, S.J. Greenhouse gas, upwelling-favorable winds, and the future of coastal ocean upwelling ecosystems. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 1213–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouault, M.; Pohl, B.; Penven, P. Coastal oceanic Climate Change and variability from 1982 to 2009 around South Africa. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2010, 32, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufois, F.; Rouault, M. Sea surface temperature in False Bay (South Africa): Towards a better understanding of its seasonal and inter-annual variability. Cont. Shelf Res. 2012, 43, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beal, L.M.; De Ruijter, W.P.M.; Biastoch, A.; Zahn, R. On the role of the Agulhas system in ocean circulation and climate. Nature 2011, 472, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gründlingh, M.L. On the Course of the Agulhas Current. S. Afr. Geogr. J. 1983, 65, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryden, H.L.; Beal, L.M.; Duncan, L.M. Structure and transport of the Agulhas Current and its temporal variability. J. Oceanogr. 2005, 61, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goschen, W.S.; Schumann, E.H. Agulhas current variability and inshore structures off the Cape Province, South Africa. J. Geophys. Res. 1990, 95, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouault, M.J.; Penven, P. New perspectives on Natal Pulses from satellite observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, C07013. [Google Scholar]
- Krug, M.; Tournadre, J.; Dufois, F. Interactions between the Agulhas Current and the eastern margin of the Agulhas Bank. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 81, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beal, L.M.; Elipot, S.; Houk, A.; Leber, G.M. Capturing the Transport Variability of a Western Boundary Jet: Results from the Agulhas Current Time-Series Experiment (ACT). J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2015, 45, 1302–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutjeharms, J.R.E.; van Ballegooyen, R.C. Anomalous Upstream Retroflection in the Agulhas Current. Science 1988, 240, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, P.J.; de Ruijter, W.P.M.; Lutjeharms, J.R.E. Natal pulses and the formation of Agulhas rings. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 6425–6436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beal, L.M.; Elipot, S. Broadening not strengthening of the Agulhas Current since the early 1990s. Nature 2016, 540, 570–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backeberg, B.C.; Penven, P.; Rouault, M. Impact of intensified Indian Ocean winds on mesoscale variability in the Agulhas system. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Cowan, T.; Dix, M.; Rotstayn, L.; Ribbe, J.; Shi, G.; Wijffels, S. Anthropogenic aerosol forcing and the structure of temperature trends in the southern Indian Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L14611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouault, M.; Penven, P.; Pohl, B. Warming in the Agulhas Current system since the 1980′s. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L12602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, A.L.; Lutjeharms, J.R.E.; Gründlingh, M.L. Stratification and circulation at the Agulhas Retroflection. Deep Sea Res. 1987, 34, 565–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matano, R.P.; Beier, E.J. A kinematic analysis of the Indian/Atlantic interocean exchange. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2003, 50, 229–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncombe Rae, C.M.; Boyd, A.J.; Crawford, R.J.M. “Predation” on anchovy by an Agulhas Ring: A possible contributory cause of the poor year-class of 1989. S. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 1992, 12, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, A.A.; Garland, G.G.; Stretch, D.D. Southern African sea levels: Corrections, influences and trends. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 31, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, A.A.; Stretch, D.D. A perspective on sea level rise and coastal storm surge from southern and eastern Africa: A case study near Durban, South Africa. Water 2012, 4, 237–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeConto, R.M.; Pollard, D.; Alley, R.B.; Velicogna, I.; Gasson, E.; Gomez, N.; Sadai, S.; Condron, A.; Gilford, D.M.; Ashe, E.L.; et al. The Paris Climate Agreement and future sea-level rise. Nature 2021, 593, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). AR5 SPM. Approved Summary for Policymakers. IPClimate Change WGI AR5 SPM 27 September 2013. Available online: http://www.climatechange2013.org/images/uploads/WGIAR5-SPM_Approved27Sep2013.pdf (accessed on 8 October 2013).
- Church, J.A.; Clark, P.U.; Cazenave, A.; Gregory, J.M.; Jevrejeva, S.; Levermann, A.; Merrifield, M.A.; Milne, G.A.; Nerem, R.S.; Nunn, P.D.; et al. Sea Level Change. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmstorf, S.; Cazenave, A.; Church, J.A.; Hansen, J.E.; Keeling, R.F.; Parker, D.E.; Somerville, R.C.J. Recent Climate Observations Compared to Projections. Science 2007, 316, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, W.T.; Harper, J.T.; O’Neel, S. Kinematic constraints on glacier contributions to 21st-century sea-level rise. Science 2008, 321, 1340–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milne, G.A.; Gehrels, R.W.; Hughes, C.W.; Tamisiea, M.E. Identifying the Causes of Sea-level Change-Sea Level Review Postscript. In Nature Geoscience Letters; Macmillan Publishers Limited: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rossouw, M.; Theron, A.K. Aspects of Potential Climate Change Impacts on Ports & Maritime Operations around the Southern African Coast. In Proceedings of the Proceedings-UNCTAD Intergovernmental Expert Meeting on “Maritime Transport and the Climate Change Challenge”, First Expert Meeting on Climate Change and Maritime Transport Issues, Geneve, Switzerland, 16–18 February 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Cazenave, A. Sea-Level Rise and Its Impact on Coastal Zones. Science 2010, 328, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SWIPA. Snow, Water, Ice and Permafrost in the Arctic (SWIPA). In Proceedings of the Assessment-Coordinated by AMAP and Produced in Collaboration with IASC, WMO/Clic and IASSA-Executive Summary, Nuuk, Greenland, 12 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Theron, A.K.; Barwell, L.B.; Rossouw, M.; Maherry, A. Coastal Planning and Adaptation to Mitigate Climate Change Impacts-Responding to Climate Change in Mozambique (Phase II, Theme 2); Report prepared for National Institute for Disaster Management (INGC) by CSIR; CSIR: Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2012; p. 266. [Google Scholar]
- Kopp, R.E.; DeConto, R.M.; Bader, D.A.; Hay, C.C.; Horton, R.M.; Kulp, S.; Oppenheimer, M.; Pollard, D.; Strauss, B.H. Evolving Understanding of Antarctic Ice-Sheet Physics and Ambiguity in Probabilistic Sea-Level Projections. Earths Future 2017, 5, 1217–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Solomon, S.D., Qin, M., Manning, Z., Chen, M., Marquis, K.B., Averyt, M., Miller, T., Miller, H.L., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.L.; Zwiers, F.W.; Swail, V.R. North Atlantic Ocean Wave Climate Change Scenarios for the Twenty-First Century. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 2368–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komar, P.D.; Allan, J.C. Increasing Hurricane-Generated Wave Heights along the U.S. East Coast and Their Climate Controls. J. Coast. Res. 2008, 24, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, P.; Komar, P.D.; Allan, J.C. Increasing Wave Heights and Extreme Value Projections: The Wave Climate of the U.S. Pacific Northwest. Coast. Eng. 2010, 57, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guastella, L.A.; Rossouw, M. What will be the impact of increasing frequency and intensity of coastal storms along the South African coast? Reef J. 2012, 2, 129–139. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, L.R. The Ecological Implications of Sea-Level Rise and Storms for Sandy Beaches in KwaZulu-Natal. Master’s Thesis, University of KwaZulu-Natal, Durban, South Africa, 2008. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10413/460 (accessed on 1 September 2019).
- Canadell, J.G.; Le Quere, C.; Raupach, M.R.; Field, C.B.; Buitenhuis, E.T.; Ciais, P.; Conway, T.J.; Gillett, N.P.; Houghton, R.A.; Marland, G. Contributions to accelerating atmospheric CO2 growth from economic activity, carbon intensity, and efficiency of natural sinks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18866–18870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Quéré, C.; Raupach, M.R.; Canadell, J.G.; Marland, G.; Bopp, L.; Ciais, P.; Conway, T.J.; Doney, S.C.; Feely, R.A.; Foster, P.; et al. Trends in the sources and sinks of carbon dioxide. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feely, R.A.; Alin, S.A.; Newton, J.; Sabine, C.L.; Warner, M.; Devol, M.; Krembs, C.; Maloy, C. The combined effects of ocean acidification, mixing, and respiration on pH and carbonate saturation in an urbanized estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 88, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feely, R.A.; Sabine, C.L.; Lee, K.; Berelson, W.; Kleypas, J.; Fabry, V.J.; Millero, F.J. Impact of anthropogenic CO2 on the CaCO3 system in the oceans. Science 2004, 305, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feely, R.A.; Doney, S.C.; Cooley, S.R. Ocean acidification: Present conditions and future changes in a high-CO2 world. Oceanography 2009, 22, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doney, S.C.; Fabry, V.J.; Feely, R.A.; Kleypas, J.A. Ocean acidification: The other CO2 problem. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2009, 1, 169–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauri, C.; Gruber, N.; Vogt, M.; Doney, S.C.; Feely, R.A.; Lachkar, Z.; Leinweber, A.; McDonnell, A.M.P.; Munnich, M.; Plattner, G.K. Spatiotemporal variability and long-term trends of ocean acidification in the California Current System. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 193–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Niekerk, L.; Taljaard, S.; Lamberth, S.J.; Adams, J.B.; Weerts, S.P.; MacKay, F. Disaggregation and assessment of estuarine pressures at the country-level to better inform management and resource protection-the South African experience. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2022, 47, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, B.P.; Bustamante, R.H.; Branch, G.M.; Eekhout, S.; Odendal, F.J. A zoogeographic and functional approach to the selection of marine reserves on the west coast of South Africa. South Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 1992, 12, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, T.D. Preliminary assessment of the biogeography of fishes in South African estuaries. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2002, 53, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turpie, J.K.; Beckley, L.E.; Kauta, S.M. Biogeography and the selection of priority areas for conservation of South African coastal fishes. Biol. Conserv. 2000, 92, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddering, J.S.V.; Rust, I.C. Historical changes and sedimentary characteristics of southern African estuaries. S. Afr. J. Sci. 1990, 86, 425–428. [Google Scholar]
- Jezewski, W.A.; Pyke, P.D.; Roberts, C.P.R. Estuarine and Lake Freshwater Requirements; Technical Report No TR123; Department of Water Affairs and Forestry: Pretoria, South Africa, 1984.
- Davies, B.; Day, J. Vanishing Waters; University of Cape Town Press: Cape Town, South Africa, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Schulze, R.E.; Lynch, S.D. Annual Precipitation. In South African Atlas of Climatology and Agrohydrology; WRC Report 1489/1/06, Section 6.2.; Schulze, R.E., Ed.; Water Research Commission: Pretoria, South Africa, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schulze, R.E.; Lumsden, T.G.; Horan, M.J.C.; Warburton, M.; Maharaj, M. An Assessment of Impacts of Climate Change on Agrohydrological Responses Over Southern Africa. In Climate Change and Water Resources in Southern Africa: Studies on Scenarios, Impacts, Vulnerabilities and Adaptation; WRC Report 1430/1/05; Schulze, R.E., Ed.; Water Research Commission: Pretoria, South Africa, 2005; pp. 141–189. [Google Scholar]
- Dieppois, B.; Rouault, M.; New, M. The impact of ENSO on Southern African rainfall in CMIP5 ocean atmosphere coupled climate models. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 45, 2425–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, A.C. Observed trends in daily precipitation indices in South Africa: 1910–2004. Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 26, 2275–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.H.; Hewitson, B.; Busuioc, A.; Chen, A.; Gao, X.; Held, I.; Jones, R.; Kolli, R.K.; Kwon, W.-T.; Laprise, R.; et al. Regional Climate Projections. In Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Engelbrecht, F.A. The Physical Basis for Climate Change over Southern Africa. In Climate Change and Trade: The Challenges for Southern Africa; Taylor & Francis: Oxfordshire, UK, 2010; ISBN 978-1-920196-28-8. [Google Scholar]
- Malherbe, J.; Landman, W.A.; Engelbrecht, F.A. The bi-decadal rainfall cycle, Southern Annular. Mode and tropical cyclones over the Limpopo River Basin, southern Africa. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 43, 3121–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alber, M. A conceptual model of estuarine freshwater inflow management. Estuaries 2002, 25, 1246–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Synthesis of Adaptation Options for Coastal Areas; Climate Ready Estuaries Program. EPA 430-F-08-024; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Bunn, S.E. Grand challenge for the future of freshwater ecosystems. Front. Environ. Sci. 2016, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- South African Weather Services (SAWS). A Climate Change Reference Atlas based on CMIP5–CORDEX Downscaling; Water Research Commission Report; SAWS: Pretoria, South Africa, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Van Niekerk, L.; Taljaard, S.; Adams, J.B.; Lamberth, S.J.; Huizinga, P.; Turpie, J.K.; Wooldridge, T.H. An environmental flow determination method for integrating multiple-scale ecohydrological and complex ecosystem processes in estuaries. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froneman, P.W.; Vorwerk, P.D. Response of the plankton to a freshwater pulse in a fresh water deprived, permanently open South African estuary. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2013, 5, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nodo, P.; James, N.C.; Childs, A.-R.; Naikin, M. Response of demersal fish assemblages to an extreme flood event in a freshwater deprived estuary, South Africa. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2018, 69, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorwerk, P.D.; Froneman, P.W.; Paterson, A.W.; Whitfield, A.K. Fish community response to increased river flow in the Kariega Estuary, a freshwater-deprived, permanently open southern African system. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 33, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, N.C.; Lamberth, S.J.; Midgley, C.; Whitfield, A.K. Resilience of fish assemblages in the Breede Estuary, South Africa, to environmental perturbations. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2018, 101, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, N.C.; Adams, J.B.; Connell, A.D.; Lamberth, S.J.; MacKay, C.F.; Snow, G.; Van Niekerk, L.; Whitfield, A.K. High flow variability and storm events shape the ecology of the Mbhashe Estuary, South Africa. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 45, 131–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, A.K.; Adams, J.B.; Bate, G.C.; Bezuidenhout, K.; Bornman, T.G.; Cowley, P.D.; Froneman, P.W.; Gama, P.T.; James, N.; Mackenzie, B.; et al. A multidisciplinary study of a small, temporarily open/closed South African estuary, with particular emphasis of the influence of mouth state on the ecology of the system. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 30, 453–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roux, J.J.; Morgenthal, T.L.; Malherbe, J.; Pretorius, D.J.; Sumner, P.D. Water erosion prediction at a national scale in South Africa. Water SA 2008, 34, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaisa, C.; Perissinottoa, R.; Titac, G. Seasonal dynamics of meiofauna in a South African temporarily open/closed estuary (Mdloti Estuary, Indian Ocean). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 62, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.M.; Perissinotto, R.; Kibirige, I. Phytoplankton biomass and size structure in two South African eutrophic, temporarily open/closed estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 65, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddin, T.; Adams, J.B. Influence of mouth status and water level on the macrophytes in a small temporarily open/closed estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 79, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddin, T.; Adams, J.B. The effect of a storm surge event on the macrophytes of a temporarily open/closed estuary, South Africa. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 89, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddin, T.; Adams, J.B. Predicting macrophyte states in a small temporarily open/closed estuary. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2012, 63, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, N.C.; Cowley, P.D.; Whitfield, A.K. The marine fish assemblage of the East Kleinemonde Estuary over 20 years: Declining abundance and nursery function? Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 214, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooldridge, T.H.; Loubser, H. Larval release rhythms and tidal exchange in the estuarine mudprawn, Upogebia africana. Hydrobiologia 1996, 337, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlacher, T.A.; Wooldridge, T.H. Small-scale distribution and variability of demersal zooplankton in a shallow, temperate estuary: Tidal and depth effects on species-specific heterogeneity. Cah. Biol. Mar. 1996, 36, 211–227. [Google Scholar]
- Vorwerk, P.D.; Whitfield, A.K.; Cowley, P.D.; Paterson, A.W. The influence of selected environmental variables on fish assemblage structure in a range of southeast African estuaries. Environ. Biol. Fishes. 2003, 66, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Environment, Forestry and Fisheries South (DEFF). Status of the South African Marine Fishery Resources; DEFF: Cape Town, South Africa, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Blaber, S.J.M. Population size and mortality of juveniles of the marine teleost Rhabdosargus holubi (Pisces: Sparidae) in a closed estuary. Mar. Biol. 1973, 21, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, P.D.; Whitfield, A.K. Biomass production estimates of a fish community in a small South African estuary. J. Fish Biol. 2002, 61, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von der Heyden, S.; Toms, J.; Teske, P.; Lamberth, S.; Holleman, W. Contrasting signals of genetic diversity and historical demography between two recently diverged marine and estuarine fish species. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 526, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bate, G.C.; Adams, J.B. The effects of a single freshwater release into the Kromme Estuary. 5. Overview and interpretation for the future. Water SA 2000, 26, 329–332. [Google Scholar]
- Bate, G.C.; Whitfield, A.K.; Adams, J.B.; Huizinga, P.; Wooldridge, T.H. The importance of the river-estuary interface zone in estuaries. Water SA 2002, 28, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, A.K. Distribution patterns of fishes in a freshwater deprived Eastern Cape estuary, with particular emphasis on the geographical headwater region. Water SA 2003, 29, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, A.K. Fishes and freshwater in South African estuaries–A review. Aquat. Living Resour. 2005, 18, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, B.A. A mass mortality of fish associated with low salinity conditions in the Bot River estuary. Trans. R. Soc. S. Afr. 1985, 45, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, A.K.; Taylor, R.H.; Fox, C.; Cyrus, D.P. Fishes and salinities in the St Lucia estuarine system—A Review. Rev. Fish. Biol. Fisheries 2006, 16, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taljaard, S.; Snow, G.; Gama, P.; Van Niekerk, L. Verification of a conceptual model of water quality for small temporarily open/closed estuaries: East Kleinemonde Estuary, South Africa. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2009, 60, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taljaard, S.; Van Niekerk, L.; Joubert, W. Extension of a qualitative model on nutrient cycling and transformation to include microtidal estuaries on wave-dominated coasts: Southern Hemisphere perspective. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 85, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallister, S.; Bauer, L.; Ducklow, J.E.; Canuel, E.A. Sources of estuarine dissolved and particulate organic matter: A multi-tracer approach. Org. Geochem. 2006, 37, 454–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Villiers, S.; Thiart, C. The nutrient status of South African rivers: Trends and fluxes from the 1970s to 2005. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2007, 103, 343–349. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.; Mead, R.N.; Belicka, L.; Pisani, O.; Jaffe, R. Assessing source contributions to particulate organic matter in a subtropical estuary: A biomarker approach. Org. Geochem. 2014, 75, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemley, D.A.; Adams, J.B.; Strydom, N.A. Testing the efficacy of an estuarine eutrophic condition index: Does it account for shifts in flow conditions? Ecol. Indic. 2017, 74, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omarjee, A.; Taljaard, S.; Ramjukadh, C.-L.; van Niekerk, L. pH variability in catchment flows to estuaries–A South African perspective. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 262, 107605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midgley, J.; Shafer, G. Correlates of water colour in streams rising in the southern Cape catchments vegetated by fynbos and/or forest. Water SA 1992, 18, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, J.B.; Taljaard, S.; Van Niekerk, L.; Lemley, D.A. Nutrient enrichment as a threat to the ecological resilience and health of microtidal estuaries. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 45, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strydom, N.A.; Whitfield, A.K. The effects of a single freshwater release into the Kromme Estuary. 4: Larval fish response. Water SA 2000, 26, 319–328. [Google Scholar]
- Snow, G.C.; Adams, J.B. Response of micro-algae in the Kromme Estuary to managed freshwater inputs. Water SA 2006, 32, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Strydom, N.A. Patterns in Larval Fish Diversity, Abundance, and Distribution in Temperate South African Estuaries. Estuaries Coasts 2015, 38, 268–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemley, D.A.; Adams, J.B.; Taljaard, S.; Strydom, N.A. Towards the classification of eutrophic condition in estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 164, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justic, D.; Bierman, V.J.; Scavia, D.; Hetland, R.D. Forecasting Gulf’s Hypoxia: The Next 50 Years? Estuaries Coasts 2007, 30, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Boyle, S.; McDermott, G.; Noklegaard, T.; Wilkes, R. A Simple Index of Trophic Status in Estuaries and Coastal Bays Based on Measurements of pH and Dissolved Oxygen. Estuaries Coasts 2013, 36, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, R.B.; Baumann, H.; Grear, J.S.; Aller, R.C.; Gobler, C.J. Coastal ocean acidification: The other eutrophication problem. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 148, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, V.S.; Twilley, R.R.; Kleypas, J.A.; Cowan, J.H., Jr.; Hare, S.R. Coastal and Marine Ecosystems and Global Climate Change: Potential Effects on U.S. Resources; Pew Center on Global Climate Change: Arlington, VA, USA, 2002; 52p. [Google Scholar]
- Schiedek, D.; Sundelin, B.; Readman, J.W.; Macdonald, R.W. Interactions between climate change and contaminants. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 1845–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, A.K. Mass mortalities of fish in South African estuaries. S. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 1995, 21, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, T.D.; Whitfield, A.K. A multi-metric fish index to assess the environmental condition of estuaries. J. Fish Biol. 2004, 65, 683–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, A.K. Biology and ecology of fishes in Southern African estuaries. Ichthyol. Monogr. J.L.B. Smith Inst. Ichthyol. 1998, 2, 1–223. [Google Scholar]
- Human, L.R.D.; Snow, G.C.; Adams, J.B.; Bate, G.C.; Yang, S.-C. The role of submerged macrophytes and macroalgae in nutrient cycling: A budget approach. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 154, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morant, P.; Quinn, N.W. Influence of man and management of South African estuaries. In Estuaries of South Africa; Allanson, B.R., Baird, D., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999; pp. 289–321. [Google Scholar]
- Skowno, A.L.; Poole, C.J.; Raimondo, D.C.; Sink, K.J.; Van Deventer, H.; Van Niekerk, L.; Harris, L.R.; Smith-Adao, L.B.; Tolley, K.A.; Zengeya, T.A.; et al. National Biodiversity Assessment 2018: The Status of South Africa’s Ecosystems and Biodiversity; Synthesis Report; South African National Biodiversity Institute, Department of Environment, Forestry and Fisheries: Pretoria, South Africa, 2019.
- Adams, J.B.; Rajkaran, A. Changes in mangroves at their southernmost African distribution limit. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 248, 107158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friess, D.A.; Adame, F.M.; Adams, J.B.; Lovelock, C.E. 2022. Mangrove forests under climate change in a 2 °C world. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Change 2022, 13, e792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, R.W.; Smit, A.J. Climate Change in Coastal Waters: Time Series Properties Affecting Trend Estimation. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 9113–9124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, F.; Wethey, D. Three decades of high-resolution coastal sea surface temperatures reveal more than warming. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooldridge, T.H.; Deyzel, S.H.P. Variability in estuarine water temperature gradients and influence on the distribution of zooplankton: A biogeographical perspective. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2012, 34, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veitch, J.; Penven, P.; Shillington, F. Modeling equilibrium dynamics of the Benguela Current System. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2010, 40, 1942–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veitch, J.; Hermes, J.; Lamont, T.; Penven, P.; Dufois, F. Shelf-edge jet currents in the southern Benguela: A modelling approach. J. Mar. Syst. 2018, 188, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont, T.; Garcia-Reyes, M.; Bograd, S.J.; van der Lingen, C.D.; Sydeman, W.J. Upwelling indices for comparative ecosystem studies: Variability in the Benguela Upwelling System. J. Mar. Syst. 2018, 118, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, M.I.; James, N.C.; Bates, A.E.; Goschen, W.S.; Potts, W.M. Localised intermittent upwelling intensity has increased along South Africa’s south coast due to el Niño-Southern Oscillation phase state. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2019, 41, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomety, F.S. Coastal Climate Change and Variability in the Benguela Current System. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, 2021. Available online: http://sillig.free.fr/Publis/Tomety_2022.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2022).
- Lima, D.C.A.; Soares, P.M.M.; Semedo, A.; Cardoso, R.M.; Cabos, W.; Sein, D.V. How will a warming climate affect the Benguela coastal low-level wind jet? J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 5010–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Cai, W.; Zhang, L.; Nakamura, H.; Timmermann, A.; Joyce, T.; McPhaden, M.J.; Alexander, M.; Qiu, B.; Visbeck, M.; et al. Enhanced warming over the global subtropical western boundary currents. Nat. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lohmann, G.; Wei, W.; Dima, M.; Ionita, M.; Liu, J. Intensification and poleward shift of subtropical western boundary currents in a warming climate. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans. 2016, 121, 4928–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malan, N.; Backeberg, B.; Biastoch, A.; Durgadoo, J.V.; Samuelsen, A.; Reason, C.; Hermes, J. Agulhas Current Meanders facilitate shelf-slope exchange on the Eastern Agulhas Bank. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2018, 123, 4762–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Leonelli, F.E.; Marullo, S.; Artale, V.; Beggs, H.; Bunogiorno Nardelli, B.; Chin, T.M.; De Toma, V.; Good, S.; Huang, B.; et al. Sea surface temperature intercomparison in the framework of the Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S). J. Clim. 2021, 34, 5257–5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijnsdorp, A.D.; Peck, M.A.; Engelhard, G.H.; Möllmann, C.; Pinnegar, J.K. Resolving the effect of Climate Change on fish populations. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 66, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blamey, L.K.; Shannon, L.J.; Bolton, J.J.; Crawford, R.J.M.; Dufois, F.; Evers-King, H.; Griffith, C.L.; Hutchings, L.; Jarre, A.; Rouault, M.; et al. Ecosystem change in the southern Benguela and the underlying processes. J. Mar. Syst. 2015, 144, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, A.K.; James, N.C.; Lamberth, S.J.; Adams, J.B.; Perissinotto, R.; Rajkaran, A.; Bornman, T.G. The role of pioneers as indicators of biogeographic range expansion caused by global change in southern African coastal waters. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 172, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maree, R.C.; Whitfield, A.K.; Booth, A.J. Effect of water temperature on the biogeography of South African estuarine fish species associated with the subtropical/warm temperate subtraction zone. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2002, 96, 184–188. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, M. An overview of the status, study and management of fishes in estuaries. In Fishes in estuaries; Elliott, M., Hemingway, K.L., Eds.; Blackwell Science Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2002; pp. 553–575. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, T.D.; Whitfield, A.K. Temperature and salinity as primary determinants influencing the biogeography of fishes in South African estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 66, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorte, C.J.B.; Hofmann, G.E. Changes in latitudes, changes in aptitudes: Nucella canaliculata (Mollusca: Gastropoda) is more stressed at its range edge. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 274, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murawski, S.A. Climate Change and marine fish distributions: Forecasting from historical analogy. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1993, 122, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, A.L.; Low, P.J.; Ellis, J.R.; Reynolds, J.D. Climate Change and distribution shifts in marine fishes. Science 2005, 308, 1912–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, B.M. Climate Change: A looming challenge for fisheries management in southern Africa. Mar. Policy 2006, 30, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, C.D.G.; Hughes, A.R.; Hultgren, K.M.; Miner, B.G.; Sorte, C.J.B.; Thornber, C.S.; Rodriguez, L.F.; Tomanek, L.; Williams, S.L. The impacts of Climate Change in coastal marine systems. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, N.C.; Whitfield, A.K.; Harrison, T.D. Grey mullet (Mugilidae) as possible indicators of global warming in South African estuaries and coastal waters. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 122, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pörtner, H.O.; Knust, R. Climate Change affects marine fishes through the oxygen limitation of thermal tolerance. Science 2007, 315, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pörtner, H.O.; Peck, M.A. Climate Change effects on fishes and fisheries: Towards a cause-and-effect understanding. J. Fish Biol. 2010, 77, 1745–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberth, S.J.; Da Silva, C.; Erasmus, C.; Kerwath, S.E.; McCord, M.E.; Wilke, C.G. Range Expansion and Behavioural Shifts in an Estuary Associated Fish Spotted Grunter Pomadasys Commersonnii, Hypothesis Testing with Acoustic Telemetry. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Fish Telemetry, Grahamstown, South Africa, 14–19 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Steinke, T.D. Mangroves in South African estuaries. In Estuaries of South Africa; Allanson, B.R., Baird, D., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999; pp. 119–140. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, P. Saltmarshes in a time of change. Environ. Conserv. 2002, 29, 39–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilman, E.L.; Ellison, J.; Duke, N.C.; Field, C. Threats to mangroves from Climate Change and adaptations options: A review. Aquat. Bot. 2008, 89, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe-Speer, S.C.L.; Adams, J.B.; Rajkaran, A. Mangrove expansion and population structure at a planted site, East London, South Africa. South. For. A J. For. Sci. 2015, 77, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raw, J.L.; Godbold, J.A.; van Niekerk, L.; Adams, J.B. Drivers of mangrove cover and species richness at a high-energy, wave-dominated, southern distribution limit. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 226, 106296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lange, W.P.; de Lange, P.J. An appraisal of factors controlling the latitudinal distribution of mangrove (Avicannia marina var. resinifera) in New Zealand. J. Coast. Res. 1994, 10, 539–548. [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson, A.N.; Dickens, J. Activity of the mangrove snail Cerithidea decollate (Gastropoda: Potamididae) in a warm temperate South African Estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 109, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peer, N.; Miranda, N.A.F.; Perissinotto, R. Fiddler crabs (genus Uca Leach 1814) in South Africa: A review and case study of the St Lucia Estuary community. Afr. Zool. 2015, 50, 187–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, L.C.; Palmer, M.D.; Haigh, I.D. Projections of 21st century sea level rise for the coast of South Africa. Environ. Res. Commun. 2022, 4, 025001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, B.M.; Turpie, J.K.; Cullis, J.D.S.; Dawson, J.; Dobinson, L.; Kunneke, M.M.; Horn, A. The impacts of long-term flow reductions and an extreme drought on a large, permanently open estuary, and implications for setting the ecological reserve. Water SA 2022, 48, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saintilan, N.; Kovalenko, K.E.; Guntenspergen, G.; Rogers, K.; Lynch, J.C.; Cahoon, D.; Lovelock, C.; Friess, D.A.; Ashe, E.; Krauss, K.; et al. Global patterns and drivers of tidal marsh response to accelerating sea-level rise. Science 2022. (in Literature). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, A.K.; Harrison, T.D. Gilchristella aestuaria (Pisces: Clupeidae) biomass and consumption of zooplankton in the Sundays Estuary. S. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 1996, 17, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashima, F.P.; Strydom, N.A.; Lamberth, S.J.; Connan, M.; Butler, M. Stable isotopes reveal trophic linkages among fish species utilising the Orange River Estuary Continuum. FoodWebs 2021, 24, e00145. [Google Scholar]
- Snow, G.C.; Adams, J.B.; Bate, G.C. Effect of river flow on estuarine microalgal biomass and distribution. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2000, 51, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.B. Salt marsh at the tip of Africa: Patterns, processes and changes in response to climate change. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 237, 06650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theron, A.K.; Rossouw, M.; Barwell, L.; Maherry, A.; Diedericks, G.; De Wet, P. Quantification of Risks to Coastal Areas and Development: Wave Run-Up and Erosion; In Proceedings of the CSIR 3rd Biennial Conference 2010. Science Real and Relevant, CSIR International Convention Centre, Pretoria, South Africa, 30 August–1 September 2010; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10204/4261 (accessed on 17 August 2022).
- Theron, A.K. Analysis of Potential Coastal Zone Climate Change Impacts and Possible Response Options in the Southern African Region. In Proceedings of the IPCC TGICA Conference: Integrating Analysis of Regional Climate Change and Response Options, Nadi, Fiji, 20–22 June 2007; pp. 205–216. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2018/08/tgica_reg-meet-fiji-2007.pdf (accessed on 17 August 2022).
- Nel, J.L.; Le Maitre, D.C.; Nel, D.C.; Reyers, B.; Archibald, S.; van Wilgen, B.W.; Forsyth, G.G.; Theron, A.K.; O’Farrell, P.J.; Kahinda, J.-M.M.; et al. Natural Hazards in a Changing World: A Case for Ecosystem-Based Management. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Laplante, B.; Murray, S.; Wheeler, D. Sea-level Rise and Storm Surges: A Comparative Analysis of Impacts in Developing Countries. World Bank Policy Res. Work. Pap. 2009, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamranzad, B.; Lavidas, G. Change of nearshore extreme wind and wave climate in Southeast Africa. Ital. J. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2020, 26, 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Booysen, Z.; Theron, A.K. Methods for predicting berm height at Temporarily Open / Closed Estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 245, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, P.D.; Whitfield, A.K.; Bell, K.N.I. The surf zone ichthyoplankton adjacent to an intermittently open estuary, with evidence of recruitment during marine overwash events. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2001, 52, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustyn, J.; Cockcroft, A.; Kerwath, S.; Lamberth, S.; Githaiga-Mwicigi, J.; Pitcher, G.; Roberts, M.; van der Lingen, C.; Auerswald, L. Chapter 15 South Africa. In The Impacts of Climate Change on Marine Fisheries and Aquaculture; Phillips, B., Perez-Ramirez, M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Oxford, UK, 2017; 1048p. [Google Scholar]
- Caldeira, K.; Wickett, M.E. Anthropogenic carbon and ocean pH. Nature 2003, 425, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, N.; Hauri, C.; Lachkar, Z.; Loher, D.; Frölicher, T.L.; Plattner, G.K. Rapid Progression of Ocean Acidification in the California Current System. Science 2012, 337, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregor, L. Seasonality of the Marine Carbonate System in the Southern Benguela: Nutrient Stoichiometry, Alkalinity Production, and CO2 Flux. Master’s Thesis, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chavez, F.P.; Sevadjian, J.; Wahl, C.; Friederich, J.; Friederich, G.E. Measurements of pCO2 and pH from an autonomous surface vehicle in a coastal upwelling system. Deep-Sea Res. Part II 2018, 151, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, R.F.; Granger, J.; Veitch, J.A.; Siedlecki, S.; Burger, J.M.; Pillay, K.; Fawcett, S.E. On-shelf nutrient trapping enhances the fertility of the southern Benguela upwelling system. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans. 2020, 125, e2019JC015948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rixen, T.; Lahajnar, N.; Lamont, T.; Koppelmann, R.; Martin, B.; van Beusekom, J.E.E.; Siddiqui, C.; Pillay, K.; Meiritz, L. Oxygen and nutrient trapping in the Southern Benguela Upwelling System. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 730591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberth, S.J.; Branch, G.M.; Clark, B.M. Estuarine refugia and fish responses to a large anoxic, hydrogen sulphide‚ black tide‘ event in the adjacent marine environment. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 86, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Chen, X.; Zhuang, J. The positive relationship between ocean acidification and pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 91, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howland, R.J.M.; Tappin, A.D.; Uncles, R.J.; Plummer, D.H.; Bloomer, N.J. Distributions and seasonal variability of pH and alkalinity in the Tweed Estuary, UK. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 251, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aufdenkampe, A.K.; Mayorga, E.; Raymond, P.A.; Melack, J.M.; Doney, S.C.; Alin, S.R.; Aalto, R.E.; Yoo, K. Riverine coupling of biogeochemical cycles between land, oceans, and atmosphere. Front Ecol Environ. 2011, 9, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.-J.; Hu, X.; Huang, W.-J.; Murrell, M.C.; Lehrter, J.C.; Lohrenz, S.E.; Chou, W.C.; Zhai, W.; Hollibaugh, J.T.; Wang, Y.; et al. Acidification of subsurface coastal waters enhanced by eutrophication. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salisbury, J.; Green, M.; Hunt, C.; Campbell, J. Coastal Acidification by Rivers: A Threat to Shellfish? Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2008, 89, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemley, D.A.; Lamberth, S.J.; Manuel, W.; Nunes, M.; Rishworth, G.M.; van Niekerk, L.; Adams, J.B. Effective management of closed hypereutrophic estuaries requires catchment-scale interventions. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 688933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spilling, K. Dense sub-ice bloom of dinoflagellates in the Baltic Sea, potentially limited by high pH. J. Plankton Res. 2007, 29, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, G.E.; Smith, J.E.; Johnson, K.S.; Send, U.; Levin, L.A.; Micheli, F.; Paytan, A.; Price, N.N.; Peterson, B.; Takeshita, Y.; et al. High-frequency dynamics of ocean pH: A multi-ecosystem comparison. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendriks, I.E.; Olsen, Y.S.; Ramajo, L.; Basso, L.; Steckbauer, A.; Moore, T.S.; Howard, J.; Duarte, C.M. Photosynthetic activity buffers ocean acidification in seagrass meadows. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, H.; Wallace, R.B.; Tagliaferri, T.; Gobler, C.J. Large Natural pH, CO2 and O2 fluctuations in a Temperate Tidal Salt Marsh on Diel, Seasonal, and Interannual Time Scales. Estuaries Coasts 2015, 38, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, L.B.; De Schryver, A.M.; Hendriks, A.J.; Huijbregts, M.A.J. Calcifying Species Sensitivity Distributions for Ocean Acidification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabry, V.J.; Seibel, B.A.; Feely, R.A.; Orr, J.C. Impacts of ocean acidification on marine fauna and ecosystem processes. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 414–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.; Karar, E.; Farolfi, S. Synthesis: IWRM lessons for implementation. Water S.A. 2008, 34, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pörtner, H.O.; Langenbuch, M.; Reipschläger, A. Biological impact of elevated ocean CO2 concentrations: Lessons from animal physiology and earth history. J. Oceanogr. 2004, 60, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimatsu, A.; Kikkawa, T.; Hayashi, M.; Lee, K.; Kita, J. Effects of CO2 on marine fish: Larvae and adults. J. Oceanogr. 2004, 60, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, W.M.; Gotz, A.; James, N.C. Review of the projected impacts of climate change on coastal fishes in southern Africa. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2015, 25, 603–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, Z.S.; Wilker, A.A.; Moore, E.J.; Lancon, T.W.; Clubb, F.J. The effect of otolith malformation on behavior and cortisol levels in juvenile red drum fish (Sciaenops ocellatus). Comp. Med. 2012, 62, 251–256. [Google Scholar]
- Huchzermeyer, K.D.A.; van der Waal, B.C.W. Epizootic ulcerative syndrome: Exotic fish disease threatens Africa’s aquatic ecosystems. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2012, 83, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conn, D.B. Aquatic invasive species and emerging infectious disease threats: A One Health perspective. Aquat. Invasions 2014, 9, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keightley, J.; von der Heyden, S.; Jackson, S. Introduced Pacific oysters Crassostrea gigas in South Africa: Demographic change, genetic diversity and body condition. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2015, 37, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, A.L.; Kroeker, K.J.; Teneva, L.T.; Mease, L.A.; Kelly, R.P. Ocean Acidification 2.0: Managing our Changing Coastal Ocean Chemistry. BioScience 2014, 64, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.P.; Foley, M.M.; Fisher, W.S.; Feely, R.A.; Halpern, B.S.; Waldbusser, G.G.; Caldwell, M.R. Mitigating Local Causes of Ocean Acidification with Existing Laws. Science 2011, 332, 1036–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.L.; Sale, M.J.; Mulholland, P.J.; Poff, N.L. Impacts of climate change on aquatic ecosystem functioning and health. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1999, 35, 1373–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.R.; Laizé, C.; Acreman, M.C. Climate Change uncertainty in environmental flows for the Mekong River. Hydrol Sci. J. 2014, 59, 935–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theron, A.K. Methods for Determination of Coastal Development Setback Lines in South Africa. Ph.D. Thesis, Stellenbosch University, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2016. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
