Parasites, Bacteria and Viruses of the Edible Dormouse Glis glis (Rodentia: Gliridae) in the Western Palaearctic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Parasites, Bacteria and Viruses of Glis glis in the Western Palaearctic
2.1. Viruses of Glis glis
2.2. Protozoa of Glis glis
2.3. Helminths of Glis glis
2.4. Ectoparasites of Glis glis
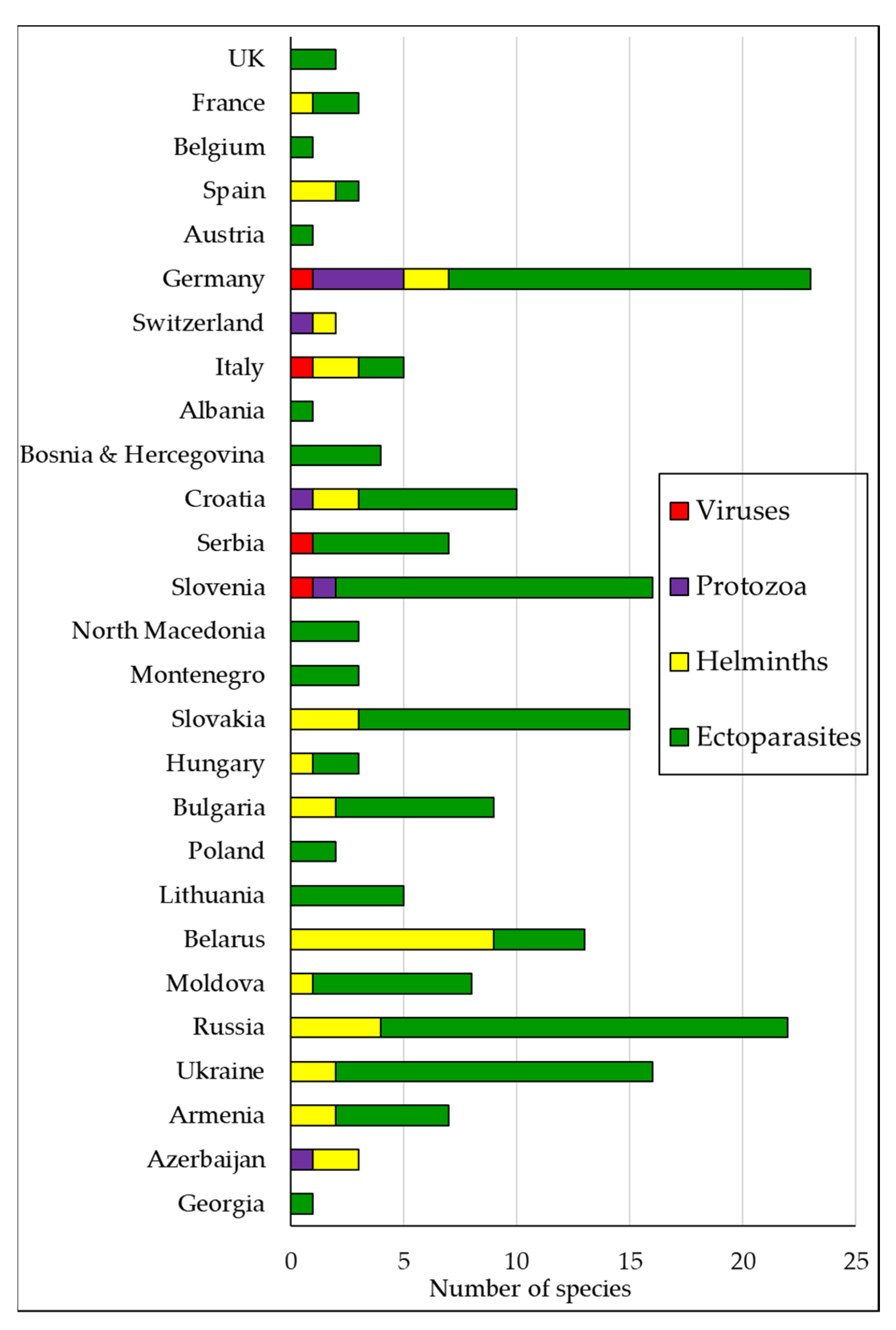
2.5. Distribution of the Research Effort on Parasites, Bacteria and Viruses of Glis glis among European Countries
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gremyachikh, V.A.; Kvasov, D.A.; Ivanova, E.S. Patterns of mercury accumulation in the organs of bank vole Myodes glareolus (Rodentia, Cricetidae). Biosyst. Divers. 2019, 27, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutovskaya, M.V.; Aleksandrov, A.N.; Podshivalina, V.N.; Soboleva, A.S.; Glushenkov, O.V. Habitat conditions of Desmana moschata (Talpidae, Eulipotyphla, Mammalia) in the buffer zone of the Prisurskiy state nature reserve (Russia). Nat. Conserv. Res. 2020, 5, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermakov, O.A.; Mishta, A.V.; Sheftel, B.I.; Obolenskaya, E.V.; Lada, G.A.; Bystrakova, N.V.; Ruchin, A.; Lissovsky, A. Does the Mediterranean water shrew Neomys anomalus (Soricidae, Eulipotyphla) expand the eastern part of the distribution range? Rus. J. Ther. 2020, 19, 112–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahissa, L.; Akpatou, B.K.; Bohoussou, H.K.; Kadjo, B.; Kone, I. Species composition and community structure of terrestrial small mammals in Tanoe-Ehy Swamp Forest (South-East Ivory Coast): Implication for conservation. Nat. Conserv. Res. 2020, 5, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakimova, A.E.; Gaidysh, I.S. The species composition and abundance of terrestrial small mammals in the Finnish-Russian friendship nature reserve. Nat. Conserv. Res. 2021, 6 (Suppl. 1), 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrovskiy, V.Y.; Tumasian, P.A. Populations of small mammals (Rodentia, Insectivora) in small river valleys before and after a flood. Biol. Bull. 2021, 48, 166–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashinskiy, I.V. Beaver impact on water coverage of forest-steppe territories (Penza region, European Russia). Nat. Conserv. Res. 2021, 6, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airapetyants, A.E. Dormice; Leningrad University Press: Leningrad, Russia, 1983; pp. 3–192. [Google Scholar]
- Holden, M.E. Family Gliridae. In Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference, 3rd ed.; Wilson, D.E., Reeder, D.M., Eds.; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, USA, 2005; pp. 3–841. [Google Scholar]
- Amori, G.; Hutterer, R.; Kryštufek, B.; Yigit, N.; Mitsainas, G.; Muñoz, L.; Meinig, H.; Juškaitis, R. Glis glis. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2021: E.T39316A197292692. 2021. Available online: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-1.RLTS.T39316A197292692.en.1 (accessed on 11 March 2022).
- Vekhnik, V.A. Comparative analysis of biology and ecology of Glis glis (Gliridae, Rodentia) in the Zhiguli state nature reserve (Russia) and adjacent territories. Nat. Conserv. Res. 2020, 5, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashkina, V.A. Abundance and activity of the edible dormouse (Glis glis L. 1766) in the Zhiguli Mountains (Russia, Middle Volga Region). Pol. J. Ecol. 2006, 54, 337–344. [Google Scholar]
- Ioff, I.G.; Tiflov, V.E. Keys to Aphaniptera (Suctoria-Aphaniptera) of the South-East of the USSR; Stavropol Book Publisher: Stavropol, Russia, 1954; pp. 3–201. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillova, N.Y.; Kirillov, A.A. Estimation of the epizootic role of small mammals in the Samara region. Bull. Sam. Luk. 2005, 16, 196–202. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillova, N.Y.; Kirillov, A.A. Ectoparasites of rodents (Rodentia) from the Samarskaya Luka. Proceed. Sam. Sci. Cent. RAS 2008, 10, 479–487. [Google Scholar]
- Meerburg, B.G.; Singleton, G.R.; Kijlstra, A. Rodent-borne diseases and their risks for public health. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 35, 221–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirillov, A.A.; Kirillova, N.Y.; Chikhlyaev, I.V. Trematodes of Land Vertebrates from the Middle Volga Region; Cassandra: Togliatti, Russia, 2012; pp. 3–329. [Google Scholar]
- Bordes, F.; Blasdell, K.; Morand, S. Transmission ecology of rodent-borne diseases: New frontiers. Integr. Zool. 2015, 10, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krucken, J.; Blumke, J.; Maaz, D.; Demeler, J.; Ramunke, S.; Antolova, D.; Schaper, R.; von Samson-Himmelstjerna, G. Small rodents as paratenic or intermediate hosts of carnivore parasites in Berlin, Germany. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levykh, A.Y.; Panin, V.V. Species composition and community structure of small mammals in Parapolsky Dol (Koryak State Nature Reserve, Kamchatka). Nat. Conserv. Res. 2019, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillova, N.; Ruchin, A.; Kirillov, A. Helminths in myomorph rodents (Rodentia, Myomorpha) from the National park “Smolny” and its surroundings (European Russia). Forests 2021, 12, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossolimo, O.L.; Potapova, E.G.; Pavlinov, I.Y.; Kruskop, S.V.; Voltzit, O.V. Dormice (Myoxidae) of the world. Arch. Zool. Mus. Mos. St. Univ. 2001, 42, 3–229. [Google Scholar]
- Kryštufek, B. Glis glis (Rodentia: Gliridae). Mammal. Spec. 2010, 42, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kryštufek, B. Edible dormouse—Characteristics and life. In Polh in Človek: Ekološki Forum LDS; Kryštufek, B., Flajsman, B., Eds.; Liberalna Akademija: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2007; pp. 43–89. [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantzev, B.I. Ixodid ticks (Ixodidae). Fauna of USSR. Volume 4. Arachnida; Academy of Sciences of the USSR Publisher: Moscow-Leningrad, Russia, 1950; pp. 3–224. [Google Scholar]
- Ioff, I.G.; Mikulin, M.A.; Skalon, O.I. Keys to Fleas of Central Asia and Kazakhstan; Medicine: Moscow, Russia, 1965; pp. 3–370. [Google Scholar]
- Bregetova, N.G.; Bulanova-Zahvatkina, E.M.; Volgin, V.I.; Dubinin, V.B.; Zahvatkin, A.A.; Zemskaya, A.A.; Lange, A.B.; Pavlovsky, E.N.; Serdyukova, G.V.; Schluger, E.G. Mites of Rodents of Fauna of the SSSR; Academy of Sciences of the USSR Publisher: Moscow-Leningrad, Russia, 1955; pp. 3–459. [Google Scholar]
- Filippova, N.A. Ixodid Ticks of the Subfamily Ixodinae. Fauna of the USSR. Arachnida; Nauka: Leningrad, Russia, 1977; Volume 4, pp. 3–393. [Google Scholar]
- Filippova, N.A. Ixodid Ticks of the Subfamily Amblyomminae. Fauna of Russia and Adjacent Countries. Arachnida; Nauka: St. Petersburg, Russia, 1997; Volume 4, pp. 3–436. [Google Scholar]
- Ryzhikov, K.M.; Gvozdev, E.V.; Tokobaev, M.M.; Shaldybin, L.C.; Matsaberidze, G.V.; Merkusheva, I.V.; Nadtochy, E.V.; Khokhlova, I.G.; Sharpilo, L.D. Keys to the Helminths of Rodents in the USSR Fauna. Cestodes and Trematodes; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1978; pp. 3–232. [Google Scholar]
- Ryzhikov, K.M.; Gvozdev, E.V.; Tokobaev, M.M.; Shaldybin, L.C.; Matsaberidze, G.V.; Merkusheva, I.V.; Nadtochy, E.V.; Khokhlova, I.G.; Sharpilo, L.D. Keys to the Helminths of Rodents in the USSR Fauna. Nematodes and Acanthocephalans; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1979; pp. 3–272. [Google Scholar]
- Kolonin, G.V. World Distribution of Ixodid Ticks (Genus Ixodes); Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1981; pp. 3–116. [Google Scholar]
- Kudryashova, N.I. Chigger mites (Acariformes, Trombiculidae) of Eastern Palearctic. Proceed. Zool. Mus. Mos. St. Univ. 1998, 39, 3–342. [Google Scholar]
- Andreyko, O.F. Parasites of Mammals in Moldova; Stiinta: Kishinev, Moldova, 1973; pp. 3–185. [Google Scholar]
- Genov, T. Helminths of Insectivores and Rodents in Bulgaria; Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Publishing: Sofia, Bulgaria, 1984; pp. 3–348. [Google Scholar]
- Bychkova, E.I.; Akimova, L.Y.; Degtyarik, S.M.; Yakovich, M.M. Helminths of Vertebrates and Humans on the Territory of Belarus; Belaruskaya Navuka: Minsk, Belarus, 2017; pp. 3–317. [Google Scholar]
- Traub, R.; Wisseman, C.I. The ecology of murine typhus—A critical review. Trop. Dis. Bull. 1978, 75, 237–317. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.W.; Baek, L.J.; Johnson, K.M. Isolation of Hantaan virus, the etiologic agent of Korean hemorrhagic fever, from wild urban rats. J. Infect. Dis. 1982, 146, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azad, A.F.; Traub, R. Experimental transmission of murine typhus by Xenopsylla cheopis flea bites. Med. Vet. Entomol. 1989, 3, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, G.F.; Wang, D.Q.; Gu, Y.M.; Meng, Y.C. Economic Insect Fauna of China. Fasc 40, Acari, Dermanyssoidea; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1993; pp. 26–50. [Google Scholar]
- Tarasov, V.V. Medical Entomology; Moscow University: Moscow, Russia, 1996; pp. 3–324. [Google Scholar]
- Bugert, J.J.; Welzel, T.M.; Zeier, M.; Darai, G. Hantavirus infection—haemorrhagic fever in the Balkans—Potential nephrological hazards in the Kosovo war. Nephr. Dial. Transpl. 1999, 14, 1843–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wall, R.; Shearer, D. Veterinary Entomology: Biology, Pathology and Control; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2001; pp. 3–262. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, S.; Yeruham, I.; Braverman, Y. Dermatitis in humans associated with the mites Pyemotes tritici, Dermanyssus gallinae, Ornithonyssus bacoti and Androlaelaps casalis in Israel. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2002, 16, 442–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, D.; Klug, B.; Spielman, A.; Matuschka, F.-R. Adaptation of diverse Lyme disease spirochetes in a natural rodent reservoir host. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 2442–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valiente Moro, C.; Chauve, C.; Zenner, L. Vectorial role of some dermanyssoid mites (Acari, Mesostigmata, Dermanyssoidea). Parasite 2005, 12, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, W.K.; Dowling, A.P.G.; Dasch, A.D. Rickettsial agents from parasitic Dermanyssoidea (Acari: Mesostigmata). Exper. Appl. Acarol. 2006, 38, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.A.; Coop, R.L.; Wall, R.L. Veterinary Parasitology, 3rd ed.; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 3–2080. [Google Scholar]
- Carocci, M.; Bakkali-Kassimi, L. The encephalomyocarditis virus. Virulence 2012, 3, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Litusov, N.V. The Causative Agent of the Plague; Ural State Medical Academy Publishing: Ekaterinburg, Rusia, 2012; pp. 3–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kotti, B.K. A Checklist of the Fleas (Siphonaptera) of the Fauna of Russia and Adjacent Countries; Al’fa Print: Stavropol, Russia, 2013; pp. 3–156. [Google Scholar]
- Stekolnikov, A.A.; Santibáñez, P.; Palomar, A.M.; Oteo, J.A. Neotrombicula inopinata (Acari: Trombiculidae)—A possible causative agent of trombiculiasis in Europe. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaevskaya, A.V. The World of Human Parasites. 3. Cestodes and Foodborne Cestodoses; Institute of Biology of the Southern Seas RAS: Sevastopol, Russia, 2017; pp. 3–357. [Google Scholar]
- Hurst, C.J. Opportunistic bacteria associated with mammalian livestock disease. In Advances in Environmental Microbiology. 5. The Connections between Ecology and Infectious Disease; Hurst, C.J., Ed.; Universidad del Valle: Santiago de Cali, Colombia, 2018; pp. 185–238. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillova, N.Y.; Kirillov, A.A. Mouse-like rodents as facultative hosts of Dicrocoelium dendriticum (Rudolphi, 1819). In Theory and Practice of Parasitic Disease Control: Proceedings of the International Scientific Conference (Moscow, Russia, 15–17 May 2019); Indyuhova, E.N., Ed.; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 2019; Volume 20, pp. 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, J.; Lythe, G.; Lopez-Garcıa, M.; Gillard, J.; Laws, T.R.; Lukaszewski, R.; Molina-Parıs, C. Stochastic dynamics of Francisella tularensis infection and replication. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1007752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauna Europaea. Available online: https://fauna-eu.org/ (accessed on 18 February 2022).
- Global Cestode Database. Available online: http://tapewormdb.uconn.edu (accessed on 12 February 2022).
- Makarikov, A.A. A taxonomic review of hymenolepidids (Eucestoda, Hymenolepididae) from dormice (Rodentia, Gliridae), with descriptions of two new species. Acta Parasitol. 2017, 62, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarikov, A.A.; Stakheev, V.V.; Tkach, V.V. Phylogenetic relationships of the genus Armadolepis Spassky, 1954 (Eucestoda, Hymenolepididae), with descriptions of two new species from Palaearctic dormice (Rodentia, Gliridae). Syst. Parasitol. 2018, 95, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarikov, A.A.; Georgiev, B.B. Review of records of hymenolepidids (Eucestoda: Hymenolepididae) from dormice (Rodentia: Gliridae) in Europe, with a redescription of Armadolepis spasskyi Tenora & Barus, 1958 and the description of A. genovi n. sp. Syst. Parasitol. 2020, 97, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaddeo, D.; Cardeti, G.; Autorino, G.L. Isolamento del virus dell’encefalomiocardite (EMCV) dal ghiro (Myoxus glis L., 1766). Atti Soc. Ital. Sci. Vet. 1991, 45, 1197–1201. [Google Scholar]
- Amaddeo, D.; Cardeti, G.; Autorino, G.L. Isolation of Encephalomyocarditis virus from dormice (Myoxus glis) in Italy. J. Wildl. Dis. 1995, 31, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ehlers, B.; Anoh, A.E.; Ben Salem, N.; Broll, S.; Couacy-Hymann, E.; Fischer, D.; Gedvilaite, A.; Ingenhütt, N.; Liebmann, S.; Martin, M.; et al. Novel Polyomaviruses in mammals from multiple orders and reassessment of Polyomavirus evolution and taxonomy. Viruses 2019, 11, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prosenc, K.; Avsic-Zupanc, T.; Trilar, T.; Petrovec, M.; Poljak, M. The fat dormouse Myoxus glis as a natural host of medically important microorganisms. Nat. Croat. 1997, 6, 252–262. [Google Scholar]
- Stanojevic, M.; Nikolic, V.; Stajkovic, N.; Stamenkovic, G.; Bozovic, B.; Cekanac, R.; Marusic, P.; Gligic, A. Genetic detection of Dobrava-Belgrade hantavirus in the edible dormouse (Glis glis) in Central Serbia. Epidemiol. Infect. 2015, 143, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moens, U.; Krumbholz, A.; Ehlers, B.; Zell, R.; Johne, R.; Calvignac-Spencer, S.; Lauber, C. Biology, evolution, and medical importance of polyomaviruses: An update. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 54, 18–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moens, U.; Calvignac-Spencer, S.; Lauber, C.; Ramqvist, T.; Feltkamp, M.C.; Daugherty, M.D.; Verschoor, E.J.; Ehlers, B. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Polyomaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1159–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klempa, B.; Avsic-Zupanc, T.; Clement, J.; Dzagurova, T.K.; Henttonen, H.; Heyman, P.; Jakab, F.; Kruger, D.H.; Maes, P.; Papa, A.; et al. Complex evolution and epidemiology of Dobrava-Belgrade hantavirus: Definition of genotypes and their characteristics. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turk, N.; Milas, Z.; Margaletic, J.; Turk, R.; Barbic, L.; Konjevic, D.; Peric, S.; Stritof, Z.; Staresina, V. The role of fat dormouse (Glis glis L.) as reservoir host for spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in the region of Gorski Kotar, Croatia. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2008, 54, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, D.; Matuschka, F.-R. Differential contribution of various dormice to the natural transmission cycle of Lyme disease spirochetes in Central Europe. Peckiana 2012, 8, 235–244. [Google Scholar]
- Fietz, J.; Tomiuk, J.; Matuschka, F.-R.; Richter, D. Seasonal prevalence of Lyme disease spirochetes in a heterothermic mammal, the edible dormouse (Glis glis). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 3615–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fietz, J.; Langer, F.; Havenstein, N.; Matuschka, F.R.; Richter, D. The vector tick Ixodes ricinus feeding on an arboreal rodent—The edible dormouse Glis glis. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, D.; Matuschka, F.-R.; Tomiuk, J.; Fietz, J. Seasonal prevalence of Lyme disease spirochetes in the edible dormouse (Glis glis). In 9th International Dormouse Conference (Svendborg, Denmark, 18–23 September 2014). Book of Abstracts; Aarhus University Publisher: Aarhus, Denmark, 2014; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Trilar, T.; Radulovic, S.; Walker, D.H. Identification of a natural cycle involving Rickettsia typhi infection of Monopsyllus sciurorum sciurorum fleas from the nests of the fat dormouse (Glis glis). Eur. J. Epidemiol. 1994, 10, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musaev, M.A.; Veysov, A.M. New species of Coccidia from Edible dormouse Glis glis (Linnaeus, 1766). Proceed. Acad. Sci. Azerbaijan. SSR 1961, 17, 1085–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Friedl, A.; Heinzer, I.; Fankhauser, H. Tularemia after a dormouse bite in Switzerland. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2005, 24, 352–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margos, G.; Wilske, B.; Sing, A.; Hizo-Teufel, C.; Cao, W.-C.; Chu, C.; Scholz, H.; Straubinger, R.K.; Fingerle, V. Borrelia bavariensis sp. nov. is widely distributed in Europe and Asia. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 4284–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanincova, K.; Taragelova, V.; Koci, J.; Schäfer, S.M.; Hails, R.; Ullmann, A.J.; Piesman, J.; Labuda, M.; Kurtenbach, K. Association of Borrelia garinii and B. valaisiana with songbirds in Slovakia. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLeod, M.P.; Qin, X.; Karpathy, S.E.; Gioia, J.; Highlander, S.K.; Fox, G.E.; McNeill, T.Z.; Jiang, H.; Muzny, D.; Jacob, L.S.; et al. Complete genome sequence of Rickettsia typhi and comparison with sequences of other Rickettsiae. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 5842–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shimalov, V.T.; Shimalov, V.V. Helminth fauna of dormice (Rodentia: Gliridae) in Belarus. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. Bel. Agr. Ser. 2000, 2, 123–125. [Google Scholar]
- Stcherbakova, E.Y. To the study of helminth fauna of rodents in Armenia. Proc. Arm. Bran. Acad. Sci. USSR 1942, 1–2, 159–173. [Google Scholar]
- Morozov, Y.F. Materials on helminth fauna of rodents and insectivores of the Belovezhskaya Pushcha. Proc. Nat. Res. Hunt. Farm “Belovezhskaya Pushcha” 1958, 1, 151–175. [Google Scholar]
- Sosnina, E.F. Parasites of Glis glis caspicus Sat. in the Caucasus National Park. Proc. Leningrad. Univ. (Biol.). 1949, 101, 128–144. [Google Scholar]
- Merkusheva, I.V. About helminths of dormice (Myoxidae) and jumping mice (Zapodidae) on the territory of Belarus. Proc. Acad. Sci. Belorus. SSR 1974, 18, 278–281. [Google Scholar]
- Merkusheva, I.V. Helminths of rodents. In Fauna and Ecology of Rodent Parasites; Chebotarev, R.S., Ed.; Nauka i Tekhnika: Minsk, Belarus, 1963; pp. 53–137. [Google Scholar]
- Faivre, J.P.; Vaucher, C. Redescription de Hymenolepis sulcata (von Linstow, 1879), parasite du loir Glis glis (L.). Bull. Soc. Neuchat. Sci. Nat. 1978, 101, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Barus, V.; Tenora, F. A contribution to the knowledge of the helminth fauna of dormice (Myoxidae) in Czechoslovakia. Biologia 1956, 11, 651–661. [Google Scholar]
- Barus, V.; Tenora, F. To the study of helminth fauna of dormice (Myoxidae) in South Slovakia. Ceskoslov. Parasitol. 1957, 4, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Tenora, F. Supplementary notes on hymenolepidid tapeworms parasitizing glirid dormice in South Slovakian Limestone Area (Czechoslovakia). Ceskoslov. Parazitol. 1965, 12, 299–303. [Google Scholar]
- Tenora, F.; Barus, V.; Koubkova, B. Remarks on tapeworms of the family Hymenolepididae (Cyclophyllidea) parasitizing dormice (Gliridae: Rodentia) in Europe. Acta Univ. Agric. Silv. Mendel. Brun. 1999, 47, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Salamatin, R.; Cielcka, D.; Kabowiak, G.; Stanko, M. Hymenolepis sulcata (von Linstow, 1879): Occurrence in dormice, Glis glis (Rodentia) in Slovak Republic. Helminthologia 2005, 42, 171–186. [Google Scholar]
- Konjevic, D.; Spaculova, M.; Beck, R.; Godlova, M.; Severin, K.; Margaletic, J.; Pintur, K.; Keros, T.; Peric, S. First evidence of Paraheligmonina gracilis and Hymenolepis sulcata among fat dormice (Glis glis L.) from Croatia. Helminthologia 2007, 44, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Busch, I. Parazitofauna Probavnog Sustava Sivoga Puha (Glis glis). Master’s Thesis, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Murai, E.; Tenora, F. Hymenolepis sulcata (von Linstow, 1879): Occurrence in Glis glis (Rodentia) in Hungary. Parasitol. Hung. 1977, 10, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Mas-Coma, S.; Feliu, C.; Rey, J.M. Contribucion al Conocimiento de la Helmintofauna de Micromamiferos Ibericos. VI. Parasitos de Glis glis Linnaeus, 1766 (Rodentia: Gliridae). Rev. Iber. Parasitol. 1978, 38, 579–584. [Google Scholar]
- Feliu, C. Efecto de la dispersion geografica de una especie hospedadora sobre su parasitofauna: El caso de los helmintos de las poblaciones ibericas de Glis glis (Linnaeus, 1766) (Rodentia: Gliridae) y Clethrionomys glareolus (Schreber, 1780) (Rodentia: Arvicolidae). Rev. Iber. Parasitol. Extraord. 1987, 16, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Von Linstow, O. Helminthologische Untersuchungen. Würt. Nat. Jahresh. 1879, 35, 313–342. [Google Scholar]
- Janicki, C. Studien an Säugetiercestoden. Zeitschrift für wissenschaftliche. Zoologie 1906, 81, 505–597. [Google Scholar]
- Makarikov, A.A.; Stakheev, V.V.; Orlov, V.N. On helminth fauna of rodents from the Northwest Caucasus. Parazitologiia 2017, 51, 317–328. [Google Scholar]
- Makarikov, A.A.; Kornienko, S.A.; Makarikova, T.A.; Stakheev, V.V. Helminths of small mammals of the Northwest Caucasus. In Proceeding of 6th Interregional Scientific Conference “Parasitological studies in Siberia and Far East”, Novosibirsk, Russia, 4–6 September 2019; Ishigenova, L.A., Konyaev, S.V., Kornienko, S.A., Eds.; Garamond: Novosibirsk, Russia, 2019; pp. 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- Andreyko, O.F. Parasite fauna in dormice from Moldova. Parasit. Anim. Plant. 1965, 1, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Fataliev, G.G. The helminth fauna of rodents (Rodentia) in Azerbaijan and the ways of its formation. South Rus. Ecol. Develop. 2009, 4, 118–122. [Google Scholar]
- Sharpilo, L.D. General characteristic of rodent helminths of Ukraine and its ecological analysis. In Parasites and Parasitoses of Animals and Humans; Mazurmovich, B.N., Ed.; Naukova Dumka: Kiev, Ukraine, 1975; pp. 62–70. [Google Scholar]
- Schiro, G.; Pieri, D.; Lo Valvo, M.; Gradoni, L.; Caccio, S.M.; Severini, F.; Marucci, G.; Galuppo, L.; Cumbo, V.; Puleio, R.; et al. Monitoring campaign over an edible dormouse population (Glis glis; Rodentia: Gliridae) in Sicily: First report of mesocestodiasis. Animals 2021, 11, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stammer, H.J. Die Parasiten deutscher Kleinsauger. Verhandlungen. der Deutschen Zoologischen Gesselschaft in Erlangen. Zool. Anz. 1956, 19, 362–390. [Google Scholar]
- Durette-Desset, M.-C. Redescription de l’Heligmosome du Loir (Glis glis L.). Ann. Parasitol. 1969, 44, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpilo, L.D. New helminth species in rodents and insectivores of Ukrainian fauna. Probl. parasitol. 1964, 3, 206–215. [Google Scholar]
- Vysotskaya, S.O. Helminths of small mammals from Transcarpathian region (The East Carpathians, Ukraine). Parazitologiia 1997, 3, 346–355. [Google Scholar]
- Schakhnazarova, S.S. New species of nematodes in rodents of Azerbaijan. Proc. Helminthol. Lab. Acad. Sci. USSR 1949, 2, 69–86. [Google Scholar]
- Alojan, M.T. Nematodes of rodents in Armenia. Zool. Digest Stud. Faun. Armen. SSR 1956, 9, 125–170. [Google Scholar]
- Movsesyan, S.O.; Nikoghosian, M.A.; Petrosian, R.A.; Vlasov, E.A.; Kuznetsov, D.N. Nematodes of rodents of Armenia. Ann. Parasitol. 2018, 64, 173–180. [Google Scholar]
- Rudolphi, K.A. Entzoorum Synopsis cui Accedunt Mantissa Duplex el Incides Locopletissim; Sumtibus, A., Ed.; Rücker: Berolini, Germany, 1819; pp. 3–831. [Google Scholar]
- Diesing, K.M. Systema Helminthum; Braumüller, W., Ed.; Vindobonae: Vienna, Austria, 1851; Volume 2, pp. 3–591. [Google Scholar]
- Quentin, J.-C. Essai de classification des nematodes Rictulaires. Mem. Mus Nat. d’Hist. Nat. Ser. A Zool. 1969, 54, 55–115. [Google Scholar]
- Sharpilo, V.P.; Iskova, N.P. Fauna of Ukraine. Trematodes. Plagiorchiata; Naukova Dumka: Kiev, Ukraine, 1989; Volume 34, pp. 3–280. [Google Scholar]
- Matsaberidze, G.V.; Khotenovskiy, I.A. Lecithodendrium dryomi n. sp. (Lecithodendriidae Odhner 1911) from the intestine of Dryomys nitedula. Coll. Art. Akad. Sci. Georg. SSR 1966, 1, 290–293. [Google Scholar]
- Sharpilo, L.D. Parasitisation in rodents of helminths peculiar to other animals. In Parasites and Parasitoses of Animals and Humans; Mazurmovich, B.N., Ed.; Naukova Dumka: Kiev, Ukraine, 1975; pp. 211–216. [Google Scholar]
- Merkusheva, I.V.; Bobkova, A.F. Helminths of Domesticated and Wild Animals in Belarus; Nauka i Tehnika: Minsk, Belarus, 1981; pp. 3–120. [Google Scholar]
- Moravec, F. Review of capillariid and trichosomoidid nematodes from mammals in the Czech Republic and the Slovak Republic. Acta Soc. Zool. Bohem. 2000, 64, 271–304. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, R.C. Nematode Parasites of Vertebrates. Their Development and Transmission, 2nd ed.; CABI Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 3–578. [Google Scholar]
- Bychovskaya-Pavlovskaya, I.E.; Vysotskaya, S.O.; Kulakova, A.P. Trematodes of small mammals from Transkarpathian region. Parazitologiia 1970, 4, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Melnichenko, E.D.; Panasenko, N.A. To the Helminth Fauna of Dormice from the Middle Dnieper Region. In Proceedings of the 9th Conference of Ukrainian Parasitological Society, Lviv, Ukraine, 14–16 September 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Ershova, M.M. To the helminth fauna of rodents in Caucasus Nature Reserve. Proc. Gorky St. Pedagog. Inst. 1960, 27, 108–110. [Google Scholar]
- Shaldybin, L.S. Helminth fauna in mammals from the Mordovia state nature reserve. Proc. Mord. St. Nat. Res. 1964, 2, 135–180. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillova, N.Y. Helminths of Small Mammals from the Samarskaya Luka; Lambert Academic Publishing: Saarbrucken, Germany, 2011; pp. 3–251. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillova, N.Y.; Kirillov, A.A. Overview of helminths in small mammals in the Zhiguli State Reserve. Nat. Conserv. Res. 2017, 2, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blagoveshtchenskiy, D.L. New species of sucking lice (Siphunculidae) that are parasites of rodents. Communication I. Entomol. Rev. 1965, 44, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Durden, L.A.; Musser, G.G. The sucking lice (Insecta, Anoplura) of the world: A taxonomic checklist with records of mammalian hosts and geographical distribution. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 1994, 218, 1–90. [Google Scholar]
- Vas, Z.; Rekasi, J.; Rozsa, L. A checklist of lice of Hungary (Insecta: Phthiraptera). Ann. Hist.-Nat. Mus Nat. Hung. 2012, 104, 1–105. [Google Scholar]
- Trilar, T.; Gogala, A.; Gogala, M. Distribution of the swallow bug (Oeciacus hirundinis) in Slovenia, with an unusual finding in a fat dormouse (Myoxus glis) nest. Acta Entomol. Sloven. 1997, 5, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Orszagh, I.; Krumpal, M.; Cyprich, D. Contribution to the knowlidge of the Martin bug Oeciacus hirundinis (Heteroptera, Cimicidae) in Czechoslovakia. Zbor. Slov. Nar. Muz. Prir. Vedy 1990, 36, 43–60. [Google Scholar]
- Trilar, T. Dormice ectoparasites from Western and Central Balkans. In 4th International Conference on Dormice (Rodentia, Gliridae) (Edirne, Turkey, 13–16 September 1999). Book of Abstracts; Trakya University: Edirne, Turkey, 1999; p. 31. [Google Scholar]
- Brelih, S.; Trilar, T. Siphonaptera of squirrels and dormice (Rodentia: Sciuridae, Gliridae) from the Western and Central Balkans. Acta Entomol. Sloven. 2000, 8, 147–189. [Google Scholar]
- Vysotskaya, S.O. Fleas of small mammals from Transcarpathian region. Parasitol. Coll. Pap. Zool. Inst. 1964, 22, 153–172. [Google Scholar]
- Saakyan, M.S. Fauna of rodents in northern-eastern Armenia. Proc. Armen. Anti-Plag. Stat. 1964, 3, 329–346. [Google Scholar]
- Kotti, B.K.; Stakheev, V.V.; Zhiltsova, M.V. Fleas (Siphonaptera) of small mammals in the forest altitudinal belt of Western Caucasus. Med. Parasitol. Par. Dis. 2019, 2, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarinov, K.A. Animals of the Western Regions of Ukraine; Academy of Sciences of the Ukrainian SSR Publisher: Kiev, Ukraine, 1956; pp. 3–188. [Google Scholar]
- Nazarova, I.V. Fleas of the Volga-Kama Region; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1981; pp. 3–168. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillova, N.Y.; Kirillov, A.A.; Ivashkina, V.A. Ectoparasites of the edible dormouse Glis glis L. of Samarskaya Luka Peninsula (Russia). Pol. J. Ecol. 2006, 54, 387–390. [Google Scholar]
- Kotti, B.K. Fleas (Siphonaptera) of mammals and birds in the Great Caucasus. Parazitologiia 2015, 49, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotti, B.K.; Kotova, E.G. Fleas (Siphonaptera) of mammals from the mountain area between the Kuban and Great Laba Rivers. Parazitologiia 2014, 48, 393–403. [Google Scholar]
- Krampitz, H.E. Present-day Sicily from a hygienic-zoological point of view. Z. Trop. Parasitol. 1958, 9, 111–128. [Google Scholar]
- Peus, F. Flöhe aus dem Mittelmeergebiet (Insecta, Siphonaptera) III. Sizilien. Mitt. Mus. Nat. Berl. Zool. Mus. Inst. Spez. Zool. 1959, 35, 79–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, E. Die freilebenden Nagetiere Deutschlands und der Nachbarlander, Dritte Auflage; Gustav Fischer Verlag: Jena, Germany, 1954; pp. 3–212. [Google Scholar]
- Von Vietinghoff-Riesch, A.; Frhr, V. Der Siebenschläfer (Glis glis L.). Monographien der Wildsäugetiere; Bd. XIV; VEB Gustav Fischer Verlag: Jena, Germany, 1960; pp. 3–196. [Google Scholar]
- Lipatova, I.; Stanko, M.; Paulauskas, A.; Spakovaite, S.; Gedminas, V. Fleas (Siphonaptera) in the nests of dormice (Gliridae: Rodentia) in Lithuania. J. Med. Entomol. 2015, 52, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scuratovicz, W.A.; Bartkowska, K. Pchly (Siphonaptera) zebrane w Jugoslawii. Fragm. Faunist. 1977, 23, 51–65. [Google Scholar]
- Nikitchenko, N.T.; Samarskiy, S.L. Ectoparasites of the Edible dormouse Glis glis in the Middle Dniester region. In Problems of Parasitology: Proceedings of 6th Scientific Conference of Parasitologists of the Ukrainian SSR; Markevich, A.P., Ed.; Naukova Dumka: Kiev, Ukraine, 1969; Volume 2, p. 145. [Google Scholar]
- Avetisyan, G.A. Overview of the flea fauna of the Armenian SSR. Fauna Ecol. Harm. Invert. Arm. SSR. 1970, 15, 21–49. [Google Scholar]
- Arzamasov, I.T. Ectoparasites of rodents. In Fauna and Ecology of Rodent Parasites; Chebotarev, R.S., Ed.; Minsk: Nauka i Tekhnika, Belarus, 1963; pp. 138–235. [Google Scholar]
- Szabo, I. A magyarorszagi emlosallatok bolhai. Állat. Közlem. 1967, 54, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Scuratovicz, W.A. Katalog fauny Polski, cz 31. Pchly (Aphaniptera); Muzeum i Instytut Zoologii Polskiej Akademii Nauk: Warszawa, Poland, 1964; pp. 3–59. [Google Scholar]
- Khristov, L. Aphaniptera of insectivores and rodents in the Valley of Roses. Proceed. Zool. Inst. Mus. Bulg. Acad. Sci. 1974, 39, 195–205. [Google Scholar]
- Dittmar de la Crus, K.; Worschech, K. Siphonapterafauna aus siebenschlafernestern Myoxus glis (Linnaeus, 1766) der region Altenburg. Saugetier. Mitt. 2002, 5, 197–200. [Google Scholar]
- Brelih, S.; Trilar, T. Ceratophyllus (Monopsyllus) carniolicus, new flea species from the family Ceratophyllidae (Siphonaptera). Acta. Entomol. Sloven. 2001, 9, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Alaniya, I.I.; Dzneladze, M.T.; Rostigayev, B.A.; Shiranovich, P.I. A landscape-ecological analysis of the fauna of small mammals and their fleas in the Adjarian ASSR. Zool. Zhurn. 1971, 50, 561–571. [Google Scholar]
- Beaucournu, J.-C.; Launay, H. Les Puces (Siphonaptera) de FRANCE et du Basin Méditerranéen Occidental. Faune de France; Fédération Française des Sociétés de Sciences Naturelles: Paris, France, 1990; Volume 76, pp. 3–548. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, H.V. The Edible dormouse (Glis glis L.) in England, 1902–1951. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1953, 12, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brelih, S. Ectoparasitical entomofauna of Yugoslav mammals. II. Siphonaptera from Dinaromys bogdanovi and Chionomys nivalis (Rodentia: Cricetidae). Scopolia 1986, 11, 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Brelih, S.; Trilar, T. New data on Siphonaptera from Dinaromys bogdanovi (Rodentia: Muridae). Scopolia 2000, 43, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, J. Beitrage zur kenntnis der Aphanipterenfauna Jugoslaviens. Bull. Soc. Sci. Skoplje 1939, 20, 155–163. [Google Scholar]
- Lipatova, I. Data on the distribution of Hystrichopsylla orientalis fleas (Siphonaptera) in Lithuania. Biologija 2020, 66, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masan, P.; Fenda, P. A Review of the Laelapid Mites Associated with Terrestrial Mammals in Slovakia, with a Key to the European Species (Acari: Mesostigmata: Dermanyssoidea); Institute of Zoology, Slovak Academy of Sciences Publishing: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2010; pp. 3–187. [Google Scholar]
- Matuschka, F.R.; Eiffert, H.; Ohlenbusch, A.; Spielman, A. Amplifying role of edible dormice in Lyme disease transmission in Central Europe. J. Infect. Dis. 1994, 170, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erhardt, S.; Langer, F.; Matuschka, F.-R.; Richter, D.; Fietz, J. Collecting ticks: Infestation rates in edible and garden dormice (Glis glis and Eliomys quercinus). In Proceedings of the 10th International Dormouse Conference, Liege, Belgium, 11–16 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vesenjak-Hirjan, J.; Calisher, C.H.; Brudnjak, Z.; Tovornik, D.; Galinovic-Veissglass, M. Brac-Focus of Arboviruses. In Proceedings of the 6th FEMS Symposium “Arboviruses in the Mediterranean Countries”, Supetar-Brac, Yugoslavia, 8–10 September 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Sosnina, E.F.; Vysotskaya, S.O.; Markov, G.N.; Atanasov, L.K. Predatory mites of the family Bdellidae (Acarina, Prostigmata) from the rodent nests in Bulgaria. Proceed. Zool. Inst. 1965, 35, 272–287. [Google Scholar]
- Canestrini, G. Family Sarcoptidae. In Demodicidae und Sarcoptidae. Das Tierreich; Canestrini, G., Kramer, P., Eds.; R. Friedländer und sohn: Berlin, Germany, 1899; pp. 4–132. [Google Scholar]
- Canestrini, G. Uber einen neuen Parasiten der Saugethiere. Zool. Anz. 1895, 18, 114–115. [Google Scholar]
- Sklyar, B.E.; Bochkov, A.V. Mites Myocoptidae (Acariformes: Listrophoroidea: Myocoptidae) of small mammals in Ukraine. In Proceedings of the 4th Congress of the Russian Society of Parasitologists “Parasitology in XXI Century—Problems, Methods, Solutions”, St. Petersburg, Russia, 20–25 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Fain, A.; Munting, A.J.; Lukoschus, F.S. Les Myocoptidae parasites des rongeurs en Hollande et en Belgique. Acta Zool. Pathol. Antverp. 1970, 50, 67–172. [Google Scholar]
- Dubinin, W.B. Superfamily Listrophoroidea (Megn. et Trt.). Fur mites (Sarcoptes pilicoles Megn. et Trt. 1884). In Acari of Rodents of the Fauna USSR; Pavlovsky, E.N., Ed.; Academy of Science of USSR: Moscow-Leningrad, Russia, 1955; pp. 124–141. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkov, A.V. Myocoptid mites (Acariformes: Myocoptidae) of the fauna of the former USSR. Zootaxa 2016, 4193, 451–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesmanis, I.E.; Lukoschus, F.S. Radfordia (Graphiurobia) gliricola sp. n. from Glis glis (Acari: Prostigmata: Myobiidae). Int. J. Acar. 1978, 4, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkov, A.V. Mites of the subgenus Graphiurobia of the genus Radfordia (Myobiidae) of the fauna of Russia and surrounding states. Parazitologiia 1994, 28, 421–428. [Google Scholar]
- Kepka, O. Die Trombiculinae (Acari, Trombiculidae) in Osteireich. Zeitsch. Parasitenk. 1964, 23, 548–642. [Google Scholar]
- Schluger, E.G.; Vysotskaya, S.O. On the fauna of chigger-mites (Acariformes, Trombiculidae) from Transcarpathian region. Parazitologiia 1970, 4, 153–164. [Google Scholar]
- Bobrovsky, V.N.; Kudryashova, N.I. Fauna and ecology of red velvet mites (Acariformes: Trombiculidae) in Moldova. Parasit. Anim. Plant. 1966, 2, 162–167. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillova, N.Y. Exchange of ectoparasites between small mammals in the Samarskaya Luka. In Ecological Papers: Proceedings of the Young Scientists of the Volga Region; Saxonov, S.V., Ed.; Institute of the Ecology of the Volga River Basin Publisher: Togliatti, Russia, 2007; pp. 102–106. [Google Scholar]
- Medvedev, S.G.; Tretyakov, K.A. Fleas of small mammals in St. Petersburg. Parazitologiia 2014, 48, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Species | Distribution | Host Range | Medical & Veterinary Significance | Country | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family Picornoviridae Encephalocarditis virus (EMCV) | E | small rodents | cause myocarditis, diabetes mellitus, reproductive disorders and nervous system damage | Italy | [62,63] |
| family Polyomaviridae Polyomavirus | E | Glis glis | — | Germany | [64] |
| Family Bunyaviridae Hantaan orthohantavirus (HTNV) | E | small rodents | main causative agent of Korean hemorrhagic fever in humans | Slovenia | [65] |
| Dobrava-Belgrade orthohantavirus (DOBV) | E | Apodemus mice | cause hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome | Serbia | [66] |
| Species | Distribution | Host Range | Medical & Veterinary Significance | Country | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family Borreliaceae Borrelia afzelii Canica et al. 1994 | E | rodents, | causative agent of Lime disease (LD) | Croatia | [70] |
| dormice | Germany | [71,72,73,74] | |||
| Borrelia garinii Baranton et al., 1992 | E | birds | causative agent of LD | Germany | [72] |
| Borrelia bavariensis Margos et al., 2009 | E | rodents, dormice | causative agent of LD | Germany | [72] |
| Borrelia miyamotoi Fukunaga et al., 1995 | E | dormice | — | Germany | [72] |
| Family Rickettsiaceae Rickettsia typhi (Wolbach and Todd, 1920) | C | rodents | causative agent of murine typhus, an endemic human typhus | Slovenia | [75] |
| Family Yersiniaceae Yersinia pestis (Lehmann and Neumann, 1896) | C | wild and domestic animals (mainly rodents) | plague pathogen | Europe | [54] |
| Family Eimeriidae Eimeria gliris Musaev and Veysov, 1961 | E | Glis glis | — | Azerbaijan | [76] |
| Family Francisellaceae Francisella tularensis (McCoy and Chapin 1912) | H | rodents, humans | pathogen of gram-negative coccobacillus, causative agent of tularemia | Switzerland | [77] |
| Species | Distribution | Host Range | Medical & Veterinary Significance | Country | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family Dicrocoeliidae Dicrocoelium dendriticum (Rudolphi, 1819) | C | mammals (mainly ungulates) | causative agent of dicroceliosis of livestock | Belarus | [81] |
| Lyperosomum armenicum (Stcherbakova, 1942) | E | Glis glis | — | Armenia | [82] |
| Belarus | [36,81,83] | ||||
| Family Brachylaimidae Brachylaima recurva (Dujardin, 1845) | P | small rodents | — | Russia | [84] |
| Family Plagiorchiidae Plagiorchis elegans (Rudolphi, 1802) | H | birds, small mammals, reptiles | — | Belarus | [36,81] |
| Family Lecithodendriidae Lecithodendrium semen (Kirschenblatt, 1941) | E | Glis glis | — | Belarus | [36,81,85] |
| Family Diplostomidae Alaria alata (Goeze, 1782), msc. | C | amphibians, reptiles, small mammals | causative agent of alariasis of farmed fur animals | Belarus | [86] |
| Family Hymenolepididae Armadolepis myoxi (sensu stricto) (Rudolphi, 1819) (syn.: Hymenolepis sulcata (von Linstow, 1879)) | E | Glis glis | — | Switzerland | [87] reported as H. sulcata |
| Slovakia | [88,89,90,91,92] reported as H. sulcata | ||||
| Croatia | [93] reported as H. sulcata, [94] | ||||
| Hungary | [95] reported as H. sulcata | ||||
| Spain | [96,97] reported as H. sulcata | ||||
| Germany | [98,99] reported as H. sulcata | ||||
| Armadolepis longisoma Makarikov, Stakheev and Tkach, 2018 | E | Glis glis | — | Russia | [100] reported as Armadolepis sp. 1, [60,101] |
| Armadolepis genovi Makarikov and Georgiev, 2020 | E | Glis glis | — | Bulgaria | [35] reported as H. myoxi, [61] |
| Armadolepis sp. | E | Glis glis | — | Russia | [84] reported as H. myoxi |
| Hymenolepididae sp. | E | — | — | Moldova | [34,102] reported as Hymenolepis horrida (Linstow, 1901) |
| Belarus | [36] reported as H. horrida and Rodentolepis straminea (Goeze, 1782) | ||||
| Azerbaijan | [103] reported as Hymenolepis diminuta (Rudolphi, 1819) | ||||
| Ukraine | [104] reported as R. straminea | ||||
| Slovakia | [91] reported as Rodentolepis sp. | ||||
| Family Mesocestoididae Mesocestoides lineatus (Goeze, 1782), tetrathyridia | P | reptiles, small mammals | cause mesocestidosis in humans, carnivores | Italy | [105] |
| Family Capillariidae Pterothominx sadovskoi (Morozov, 1956) (syn.: Thominx sadovskoi Morozov, 1956; Armocapillaria sadovskoi (Morozov, 1956)) | P | small rodents | — | Belarus | [36,81,83] |
| Family Heligmonellidae Paraheligmonina gracilis (Leuckart, 1842) (syn.: Heligmosomum gracile (Leuckart, 1842); Longistriata schulzi Schachnasarova, 1949; Longistriata elpatievskii Schachnasarova, 1949) | WP | Glis glis | — | Russia | [84,100,101] |
| Belarus | [36,81,83,86] | ||||
| Germany | [106,107] | ||||
| Bulgaria | [35] | ||||
| Ukraine | [104,108,109] | ||||
| Azerbaijan | [103,110] | ||||
| Armenia | [111,112] | ||||
| Croatia | [93,94] | ||||
| Spain | [96] | ||||
| Italy, France | [107] | ||||
| Slovakia | [88,89] | ||||
| Family Rictulariidae Rictularia cristata (Frölich, 1802) | E | small rodents | — | Central Europe | [113,114,115] |
| Rictularia amurensis Schulz, 1927 | P | small rodents | — | Belarus | [36,81] |
| Species | Distribution | Host Range | Medical & Veterinary Significance | Country | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family Hoplopleuridae Schizophthirus gliris Blagoveshtchensky, 1965 | E | Glis glis | — | Poland, Bulgaria, North Makedonia | [128,129] |
| Schizophthirus pleurophaeus (Burmeister 1839) | WP | dormice | — | West Europe, Belarus | [128,129] |
| Hungary | [130] | ||||
| Family Cimicidae Oeciacus hirundinis (Lamarck, 1816) | P | birds (mainly swallows) | — | Slovenia | [131] |
| Slovakia | [132] | ||||
| Family Pulicidae Pulex irritans Linnaeus, 1758 | C | mammals (including humans), birds | vector of plague bacteria Yersinia pestis; intermediate host of the cucumber tapeworm Dipylidium caninum (Linnaeus, 1758), which cause helminthiasis in dogs and cats | Slovenia | [133,134] |
| Family Ceratophyllidae Amalareus penicilliger (Grube, 1851) | P | forest rodents | — | Ukraine | [135] |
| Leptopsylla taschenbergi (Wagner, 1898) | P | forest rodents, insectivores | — | Armenia | [136] |
| Russia | [137] | ||||
| Leptopsylla segnis (Schönherr, 1811) | C | house mice, rats | vector of plague and tularemia | Croatia | [133,134] |
| Leptopsylla sciurobia (Wagner, 1934) | P | squirrels, dormice, Apodemus mice | — | Serbia | [133,134] |
| Peromyscopsylla bidentata (Kolenati, 1863) | P | forest rodents | — | Ukraine | [135,138] |
| Ceratophyllus sciurorum (Schrank, 1803) | P | squirrels, dormice | vector of tularemia | Russia | [13,15,51,84,137,139,140,141,142] |
| Italy | [105,143,144] | ||||
| Germany | [106,145,146] | ||||
| Lithuania | [147] | ||||
| Serbia, Croatia, Montenegro, Slovenia, North Macedonia | [75,133,134] | ||||
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | [75,133,134,148] | ||||
| Ukraine | [135,149] | ||||
| Armenia | [136,150] | ||||
| Belarus | [127,151] | ||||
| Moldova | [34,102] | ||||
| Hungary | [152] | ||||
| Poland | [153] | ||||
| Bulgaria | [154] | ||||
| Ceratophyllus sciurorum sciurorum (Schrank, 1803) | P | squirrels, dormice | — | Slovenia | [75] |
| Germany | [155] | ||||
| Ceratophyllus rusticus Wagner, 1903 | E | birds | — | Slovenia | [133,134] |
| Ceratophyllus carniolicus Brelih and Trilar, 2001 | E | Glis glis | — | Slovenia | [156] |
| Ceratophyllus hirundinis (Curtis, 1826) | P | birds | — | Slovenia | [133,134] |
| Ceratophyllus gallinae (Schrank, 1803) | C | birds | — | Slovenia | [134] |
| Germany | [155] | ||||
| Lithuania | [147] | ||||
| Ceratophyllus borealis Rothschild, 1907 | P, G | birds | — | Russia | [84] |
| Ceratophyllus (Monopsyllus) sp. | E | — | — | Slovenia | [134] |
| Dasypsyllus gallinulae gallinulae (Dale, 1878) | C | birds | — | Slovenia | [134] |
| Megabothris turbidus (Rothschild, 1909) | P | forest rodents | vector of viral hemorrhagic fever and tularemia | Ukraine | [135,138,149] |
| Germany | [155] | ||||
| Russia | [13,140] | ||||
| Lithuania | [147] | ||||
| Megabothris walkeri (Rothschild, 1902) | P | forest rodents | vector of tularemia | Russia | [13,140] |
| Myoxopsylla jordani Ioff and Argyropoulo, 1934 | E, I | dormice | — | Armenia | [150] |
| Russia | [51,84,141,142] | ||||
| Georgia | [157] | ||||
| Myoxopsylla laverani (Rothschild, 1911) | WP | dormice | — | Germany | [145,146,155] |
| France | [158] | ||||
| Nosopsyllus consimilis (Wagner, 1898) | P | forest rodents | vector of plague and tularemia | Armenia | [136] |
| Russia | [13,140] | ||||
| Nosopsyllus fasciatus (Bosc d’Antic, 1800) | C | house mice, rats | vector of the rat tapeworm H. diminuta | Serbia | [148] |
| Orchopeas howardi (Baker, 1895) (syn.: Orchopeas wickhami (Baker, 1895)) | N | Sciurus carolinensis Gmelin, 1788 | — | UK | [159] |
| Family Ctenophthalmidae Ctenophthalmus wagneri Tiflov, 1927 | P | voles | vector of tularemia | Russia | [13,140] |
| Ctenophthalmus monticola (Kohaut, 1904) | E | insectivores | — | Serbia | [133,134] |
| Ctenophthalmus agyrtes (Heller, 1896) | E | Apodemus mice | vector of tularemia | Ukraine | [135,138] |
| Germany | [155] | ||||
| Ctenophthalmus agyrtes ohridanus Wagner, 1939 | E | small mammals | — | Croatia | [133,134] |
| Ctenophthalmus agyrtes wagnerianus Peus, 1950 | E | small mammals | — | Slovenia | [133,134] |
| Ctenophthalmus proximus (Wagner, 1903) | E | small mammals | — | Russia | [137] |
| Ctenophthalmus assimilis (Taschenberg, 1880) | P | voles | — | Ukraine | [135] |
| Ctenophthalmus congener Rothschild, 1907 | WP | small mammals | — | Slovenia | [133,134] |
| Ctenophthalmus nifetodes Wagner, 1933 | E | Dinaromys bogdanovi (V. and E. Martino, 1922) | — | Bosnia & Herzegovina, Montenegro | [133,134,160] |
| Ctenophthalmus nifetodes brelihi Rosicky and Carnelutti, 1959 | E | Dinaromys bogdanovi | — | Slovenia | [133,134,160,161] |
| Ctenophthalmus nifetodes tvrtkovici Brelih, 1986 | E | Dinaromys bogdanovi | — | Croatia | [133,134,160] |
| Palaeopsylla soricis (Dale, 1878) | P | insectivores | vector and reservoir of tularemia | Germany Russia | [155] [13,140] |
| Doratopsylla dasycnema dasycnema (Rothschild, 1897) | P | insectivores | — | former Yugoslavia | [162] |
| Germany | [155] | ||||
| Family Hystrichopsyllidae Hystrichopsylla talpae (Curtis 1826) | P | Talpa europaea | vector and reservoir of tick-borne encephalitis | Lithuania | [147] |
| Russia | [13,140] | ||||
| Hystrichopsylla orientalis Smit, 1956 | E | small rodents, insectivores | — | Lithuania | [163] |
| Hystrichopsylla orientalis orientalis Smit, 1956 | E | small rodents, insectivores | — | Bosnia & Herzegovina | [133,134] |
| Family Ischnopsyllidae Ischnopsyllus intermedius (Rothschild, 1898) | E | bats | — | Germany | [155] |
| Family Laelapidae Androlaelaps casalis (Berlese, 1887) (syn.: Haemolaelaps casalis (Berlese, 1887) | C | birds | cause human dermatitis | Moldova | [34,102] |
| Ukraine | [138] | ||||
| Belarus | [151] | ||||
| Laelaps agilis C.L. Koch, 1836 | P | forest mice, insectivores, carnivores | vector of plague, tularemia, hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS), tick-borne encephalitis, leptospirosis, brucellosis | Slovakia | [164] |
| Eulaelaps stabularis (C.L. Koch, 1836) | C | small mammals, birds | vector of tularemia, Q fever, tick-borne encephalitis, brucellosis, leptospirosis | Slovakia | [164] |
| Myonyssus gigas (Oudemans, 1912) | P | rodents, insectivores, carnivores | — | Slovakia | [164] |
| Haemogamasus horridus Michael, 1892 | WP | rodents, insectivores, carnivores | — | Slovakia | [164] |
| Haemogamasus nidi Michael, 1892 | H | rodents, insectivores, carnivores | vector of tularemia | Slovakia | [164] |
| Haemogamasus pontiger (Berlese, 1904) | C | rodents, insectivores, carnivores | — | Slovakia | [164] |
| Family Hirstionyssidae Hirstionyssus sciurinus (Hirst, 1921) | P | Sciurus vulgaris, Glis glis | vector of tularemia, tick-borne encephalitis, brucellosis, leptospirosis | Russia | [13,140] |
| Slovakia | [164] | ||||
| Hirstionyssus gliricolus Masan and Ambros, 2010 | E | Glis glis | — | Slovakia | [164] |
| Hirstionyssus paulisimilis Masan and Fenda, 2010 | E | Glis glis | — | Slovakia | [164] |
| Hirstionyssus sunci Wang, 1962 | P | small rodents, insectivores | cause human dermatitis | Slovakia | [164] |
| Family Glycyphagidae Labidophorus talpae Kramer, 1877 | E | moles | — | Europe | [27] |
| Family Ixodidae Ixodes (Ixodes) ricinus (Linnaeus, 1758) | P | mammals, birds | vector of louping-ill virus of sheep, Lyme disease, ehrlichiosis (tick-borne fever) of cattle; transmits Babesia spp., which causes Redwater fever in cattle and sheep | Russia | [84] |
| Moldova | [34] | ||||
| Ukraine | [138,149] | ||||
| Germany | [71,73,165,166] | ||||
| Belarus | [151] | ||||
| Ixodes (Ixodes) acuminatus Neumann, 1901 (syn. I. redikorzevi Olenev, 1927) | P | rodents, insectivores, carnivores | vector of LD, tularemia, Q fever | Europe | [29] |
| Ixodes (Ixodes) laguri Olenev, 1929 (syn.: I. laguri colchicus Pomerantzev, 1948) | P | small rodents, hedgehogs, small carnivores | vector of plague and tularemia | Russia | [25,28,84] |
| Ixodes (Exopalpiger) trianguliceps Birula, 1895 | P | rodents, insectivores, carnivores | vector of LD | Ukraine | [138,149] |
| Germany | [166] | ||||
| Family Amblyommidae Dermacentor marginatus (Sulzer, 1776) | P | mammals, insectivores, small carnivores | vector of tick-borne Russian spring–summer encephalitis (TBRSSE), North Asian tick typhus | Croatia | [167] |
| Family Bdellidae Bdella muscorum Ewing, 1909 | H | small mammals | — | Bulgaria | [168] |
| Cyta latirostris (Hermann, 1804) | C | small mammals | — | Bulgaria | [168] |
| Cyta coerulipes (Duges, 1834) | C | small mammals | — | Bulgaria | [168] |
| Family Myocoptidae Gliricoptes glirinus (Canestrini, 1895) (syn.: Myocoptes glirinus Can. 1895) | WP | Glis glis | — | Germany | [146,169] |
| Italy | [170,171] | ||||
| France | [170,171] | ||||
| Belgium | [172] | ||||
| Armenia | [171,173] | ||||
| Russia | [174] | ||||
| UK | [169] | ||||
| Family Myobiidae Radfordia (Graphiurobia) gliricola Vesmanis and Lukoschus, 1978 | WP | Glis glis | — | Germany | [175] |
| Russia | [176] | ||||
| Family Trombiculidae Ascoschoengastia latyshevi (Schluger, 1955) | P | rodents, insectivores, birds | — | Europe | [33] |
| Leptotrombidium europaeum (Daniel and Brelih, 1959) (syn.: Leptotrombidium intermedia europaea Daniel and Brelih, 1959 | P | rodents, insectivores | vector of rickettsiosis tsutsugamushi | former Czechoslovakia, former Yugoslavia, Bulgaria, Albania, Spain | [177] |
| Leptotrombidium sylvaticum Hushcha and Schluger, 1967 | P | rodents, insectivores | vector of rickettsiosis tsutsugamushi | Ukraine | [149,178] |
| Miyatrombicula muris (Oudemans, 1910) | E | rodents, insectivores | — | Central and South Europe, Russia | [33] |
| Neotrombicula vernalis (Willmann, 1942) | WP | rodents, insectivores | vector of rickettsiosis tsutsugamushi | Austria | [177] |
| Neotrombicula austriaca Kepka, 1964 | E | rodents, insectivores | vector of rickettsiosis tsutsugamushi | Bulgaria, Moldova | [33] |
| Neotrombicula inopinata (Oudemans, 1909) (syn.: N. germanica Willmann, 1952; N. autumnalis germanica (Willmann, 1952) | WP | rodents, insectivores, birds | vector of rickettsiosis tsutsugamushi, cause human trombiculiasis | Germany | [33,146] |
| Ukraine | [33,178] | ||||
| Neotrombicula japonica (Tanaka, Kaiwa, Teramura & Kagaya, 1930) (syn.: Trombicula dubinini Schluger, 1955) | P | rodents, insectivores | vector of rickettsiosis tsutsugamushi | Ukraine | [33,149] |
| Neotrombicula nagayoi Sasa, Hayashi, Sato, Miura and Asahima, 1950 | P | rodents | vector of rickettsiosis tsutsugamushi | Moldova | [34,179] |
| Neotrombicula vulgaris (Schluger, 1955) | E | rodents | vector of rickettsiosis tsutsugamushi | Ukraine | [149] |
| Hirsutiella zachvatkini (Schluger, 1948) (syn.: Trombicula zachvatkini Schluger, 1948; Neotrombicula zachvatkini) | P | rodents | vector of diseases causes by Rickettsia spp. | Moldova | [34,102] |
| Ukraine | [33,149,178] | ||||
| Russia | [13,140] | ||||
| Schoutedenichia sp. | P | — | — | Moldova | [34] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kirillov, A.A.; Kirillova, N.Y.; Ruchin, A.B. Parasites, Bacteria and Viruses of the Edible Dormouse Glis glis (Rodentia: Gliridae) in the Western Palaearctic. Diversity 2022, 14, 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14070562
Kirillov AA, Kirillova NY, Ruchin AB. Parasites, Bacteria and Viruses of the Edible Dormouse Glis glis (Rodentia: Gliridae) in the Western Palaearctic. Diversity. 2022; 14(7):562. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14070562
Chicago/Turabian StyleKirillov, Alexander A., Nadezhda Yu. Kirillova, and Alexander B. Ruchin. 2022. "Parasites, Bacteria and Viruses of the Edible Dormouse Glis glis (Rodentia: Gliridae) in the Western Palaearctic" Diversity 14, no. 7: 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14070562
APA StyleKirillov, A. A., Kirillova, N. Y., & Ruchin, A. B. (2022). Parasites, Bacteria and Viruses of the Edible Dormouse Glis glis (Rodentia: Gliridae) in the Western Palaearctic. Diversity, 14(7), 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14070562








