Genetic Diversity and Structure of Anax imperator Leach, 1815 Populations (Odonata: Aeshnidae) in Ponds at Regional and European Scales
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
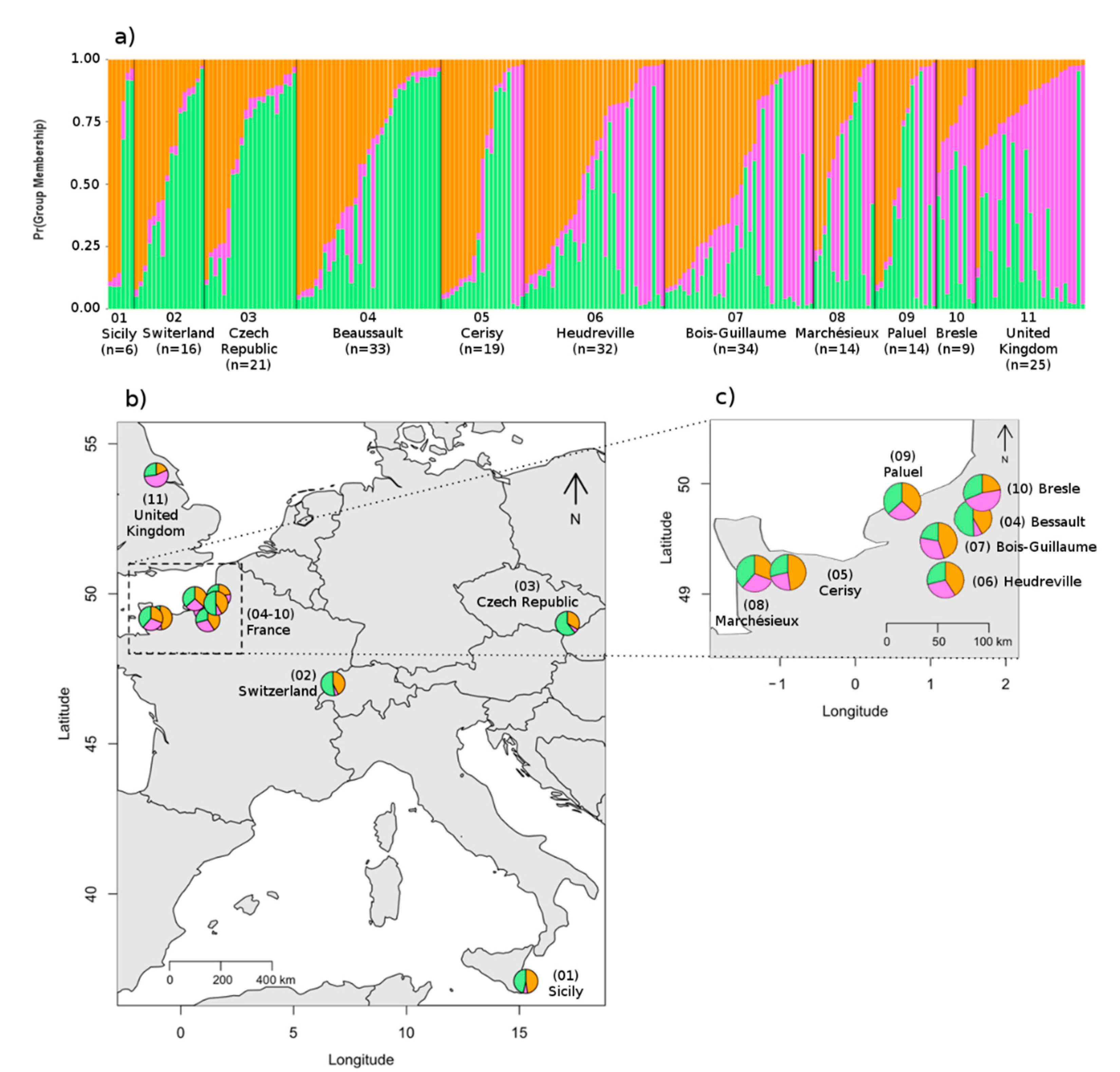
2.1. Study Populations and Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and Microsatellite Genotyping
2.3. Genetic Diversity
2.4. Population Genetic Analyses and Geographic Structure
2.5. Migration Rates between Studied Populations
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Diversity
3.2. Population Genetic Differentiation
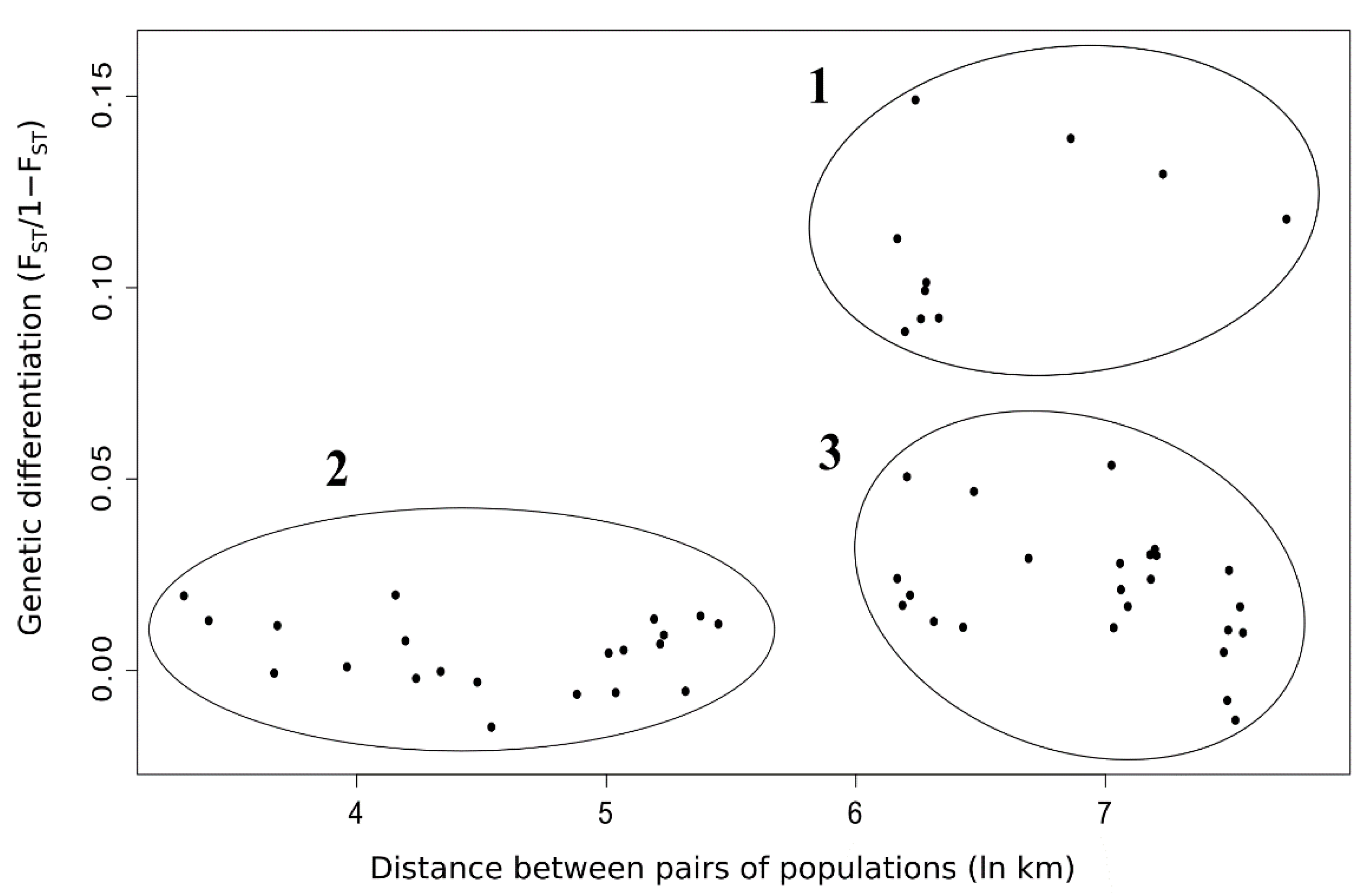
3.3. Spatial Genetic Structure
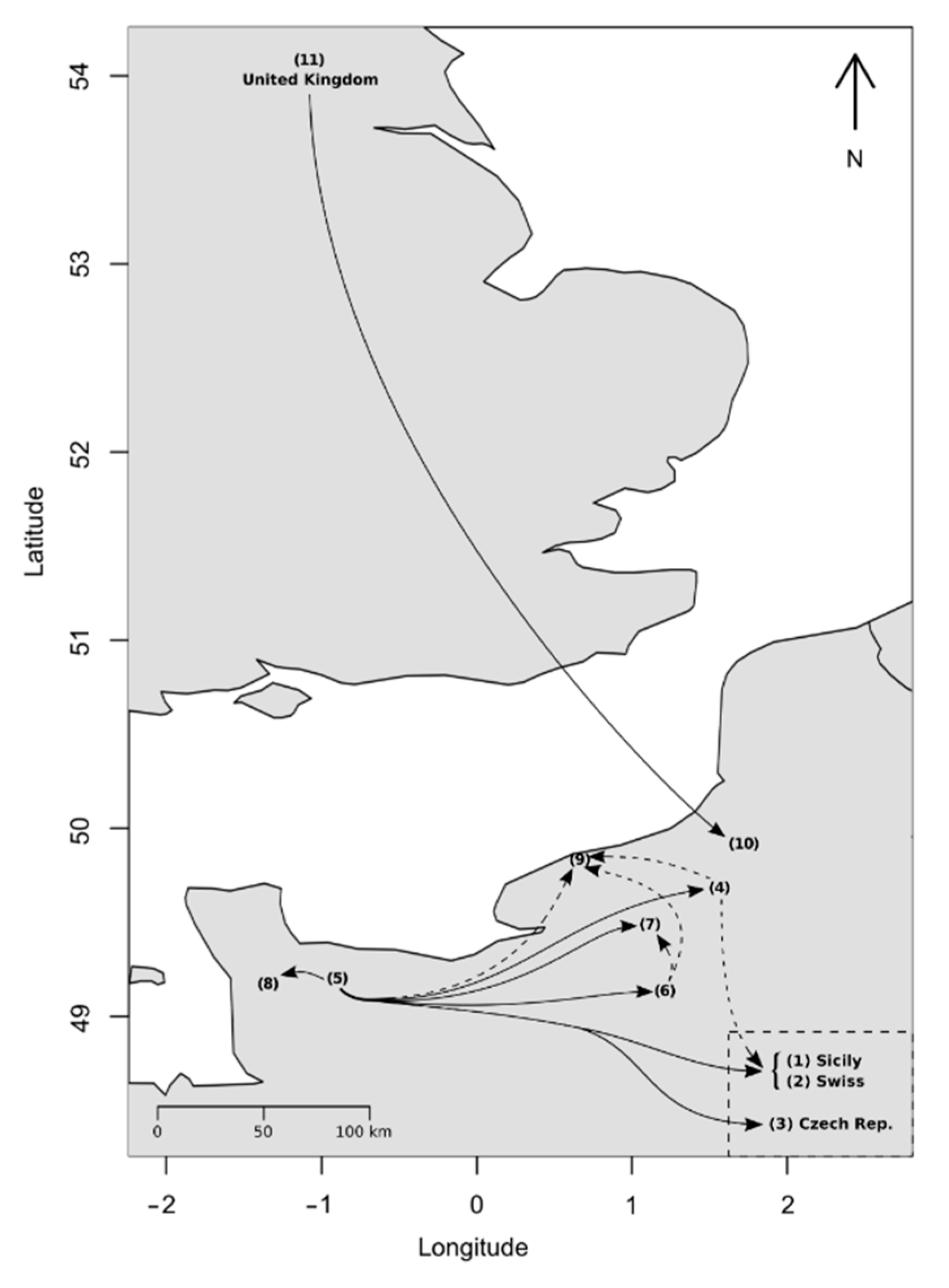
3.4. Recent Migration Rates among Populations
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, C.D.; Kunin, W.E. The Spatial Structure of Populations. J. Anim. Ecol. 1999, 68, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sexton, J.P.; Hangartner, S.B.; Hoffmann, A.A. Genetic Isolation by Environment or Distance: Which Pattern of Gene Flow Is Most Common? Evolution 2013, 68, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, A.J.; Stronen, A.V.; Fuglstad, G.-A.; Ruiz-Gonzalez, A.; Kindberg, J.; Street, N.R.; Spong, G. Landscape Relatedness: Detecting Contemporary Fine-Scale Spatial Structure in Wild Populations. Landsc. Ecoogyl. 2017, 32, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, S.L.; Fuller, R.A.; Brooks, T.M.; Watson, J.E. Biodiversity: The Ravages of Guns, Nets and Bulldozers. Nat. News 2016, 536, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankham, R.; Ballou, J.D.; Briscoe, D.A. Introduction to Conservation Genetics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dennis, R.L.H.; Dapporto, L.; Dover, J.W.; Shreeve, T.G. Corridors and Barriers in Biodiversity Conservation: A Novel Resource-Based Habitat Perspective for Butterflies. Biodivers. Conserv. 2013, 22, 2709–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allendorf, F.W.; Luikart, G.H.; Aitken, S.N. Conservation and the Genetics of Populations, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bergamaschi, A.C.B.; Lama, M.A.D.; Bergamaschi, A.C.B.; Lama, M.A.D. Gene Variation and Genetic Differentiation among Populations of the Solitary Mud Dauber Wasp Trypoxylon (Trypargilum) albitarse Fabricius 1804 (Hymenoptera, Crabronidae). Genet. Mol. Biol. 2015, 38, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- De Meester, L.; Gómez, A.; Okamura, B.; Schwenk, K. The Monopolization Hypothesis and the Dispersal–Gene Flow Paradox in Aquatic Organisms. Acta Oecologica 2002, 23, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habel, J.C.; Junker, M.; Schmitt, T. High Dispersal Ability and Low Genetic Differentiation in the Widespread Butterfly Species Melanargia galathea. J. Insect Conserv. 2010, 14, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinken, T.; Weber, E. Consequences of Habitat Fragmentation for Plant Species: Do We Know Enough? Perspectives in Plant Ecology. Evol. Syst. 2013, 15, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, M.K.; Sahlén, G.; Kuhn, W.R.; Ware, J.L. Extremely Low Genetic Diversity in a Circumpolar Dragonfly Species, Somatochlora sahlbergi (Insecta: Odonata: Anisoptera). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baguette, M.; Blanchet, S.; Legrand, D.; Stevens, V.M.; Turlure, C. Individual Dispersal, Landscape Connectivity and Ecological Networks. Biol. Rev. 2013, 88, 310–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordano, P. What Is Long-Distance Dispersal? And a Taxonomy of Dispersal Events. J. Ecol. 2017, 105, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Corre, V.; Kremer, A. Cumulative Effects of Founding Events during Colonisation on Genetic Diversity and Differentiation in an Island and Stepping-Stone Model. J. Evol. Biol. 1998, 11, 495–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlan, N.E.; Kelly, T.C.; Jansen, M.A.K. “Step by Step”: High Frequency Short-Distance Epizoochorous Dispersal of Aquatic Macrophytes. Biol. Invasions 2017, 19, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, R. Long-Distance Dispersal of Plants. Science 2006, 313, 786–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Fonte, L.F.M.; Mayer, M.; Lötters, S. Long-Distance Dispersal in Amphibians. Front. Biogeogr. 2019, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, I. The Migration Ecology of Birds; Elsevier/Acad. Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Brink, K.; Gough, P.; Royte, J.; Schollema, P.P.; Wanningen, H. From Sea to Source 2.0. Protection and Restoration of Fish Migration in Rivers Worldwide; World Fish Migration Foundation: Groningen, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bowen, B.W.; Karl, S.A. Population Genetics and Phylogeography of Sea Turtles. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 4886–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haest, B.; Hüppop, O.; van de Pol, M.; Bairlein, F. Autumn Bird Migration Phenology: A Potpourri of Wind, Precipitation and Temperature Effects. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 4064–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.J.; Figuerola, J. Recent Advances in the Study of Long-Distance Dispersal of Aquatic Invertebrates via Birds. Divers. Distrib. 2005, 11, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, C.A.; Hendry, A.P.; Kinnison, M.T. Contemporary Evolution Meets Conservation Biology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, E.; Phillips, B.L. Targeted gene flow for conservation. Conserv. Biol. 2016, 30, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, K.G. How to Measure Dispersal: The Genetic Approach. The Example of Fire Ants. In Dispersal; Oxford University Press: Oxford, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Leggett, H.C.; Jones, E.O.; Burke, T.; Hails, R.S.; Sait, S.M.; Boots, M. Population Genetic Structure of the Winter Moth, Operophtera brumata Linnaeus, in the Orkney Isles Suggests Long-Distance Dispersal. Ecol. Entomol. 2011, 36, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, J.; von Fumetti, S.; Kelly-Quinn, M. The Importance of Small Waterbodies for Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services: Implications for Policy Makers. Hydrobiologia 2017, 793, 3–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.J.; Biggs, J.; Thornhill, I.; Briers, R.A.; Gledhill, D.G.; White, J.C.; Wood, P.J.; Hassall, C. Urban Ponds as an Aquatic Biodiversity Resource in Modified Landscapes. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 986–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.; Weiss, G.H. The Stepping Stone Model of Population Structure and the Decrease of Genetic Correlation with Distance. Genetics 1964, 49, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, A.G.; Schlichting, P.; Billerman, S.; Jesmer, B.; Micheletti, S.; Fortin, M.-J.; Funk, C.; Hapeman, P.; Muths, E.L.; Murphy, M.A. How Spatio-Temporal Habitat Connectivity Affects Amphibian Genetic Structure. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youngquist, M.B.; Inoue, K.; Berg, D.J.; Boone, M.D. Effects of Land Use on Population Presence and Genetic Structure of an Amphibian in an Agricultural Landscape. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornhill, I.; Batty, L.; Hewitt, M.; Friberg, N.R.; Ledger, M.E. The Application of Graph Theory and Percolation Analysis for Assessing Change in the Spatial Configuration of Pond Networks. Urban Ecosyst. 2018, 21, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oertli, B.; Biggs, J.; Céréghino, R.; Grillas, P.; Joly, P.; Lachavanne, J.-B. Conservation and Monitoring of Pond Biodiversity: Introduction. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2005, 15, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.L.; Ousterhout, B.H.; Peterman, W.E.; Drake, D.L.; Semlitsch, R.D. Life History Differences Influence the Impacts of Drought on Two Pond-Breeding Salamanders. Ecol. Appl. 2015, 25, 1896–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhling, F.; Sahlén, G.; Gorb, S.; Kalkman, V.J.; Dijkstra, K.-D.B.; van Tol, J. Order Odonata. In Thorp and Covich’s Freshwater Invertebrates; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 893–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilton, D.T.; Freeland, J.R.; Okamura, B. Dispersal in Freshwater Invertebrates. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2001, 32, 159–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbet, P.S. Dragonflies: Behaviour and Ecology of Odonata; Harley Books: Colchester, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Suhling, F.; Martens, A.; Suhling, I. Long-Distance Dispersal in Odonata: Examples from Arid Namibia. Austral Ecol. 2017, 42, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, K.F.; Willson, K.H.; Harvey, I.F.; Thomas, C.J.; Sherratt, T.N. Dispersal Characteristics of Seven Odonate Species in an Agricultural Landscape. Ecography 1999, 22, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouquette, J.R.; Thompson, D.J. Patterns of Movement and Dispersal in an Endangered Damselfly and the Consequences for Its Management. J. Appl. Ecol. 2007, 44, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, M.; Chaput-Bardy, A.; Husté, A. Context-Dependent Local Movements of the Blue-Tailed Damselfly, Ischnura elegans: Effects of Pond Characteristics and the Landscape Matrix. J. Insect Conserv. 2017, 21, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troast, D.; Suhling, F.; Jinguji, H.; Sahlén, G.; Ware, J. A Global Population Genetic Study of Pantala flavescens. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo-Carballa, M.O.; Ferreira, S.; Sims, A.M.; Thompson, D.J.; Watts, P.C.; Cher, Y.; Damoy, V.; Evrard, A.; Gelez, W.; Vanappelghem, C. Impact of Landscape on Spatial Genetic Structure and Diversity of Coenagrion mercuriale (Zygoptera:Coenagrionidae) in Northern France. Freshw. Sci. 2015, 34, 1065–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellenreuther, M.; Sánchez-Guillén, R.A.; Cordero-Rivera, A.; Svensson, E.I.; Hansson, B. Environmental and Climatic Determinants of Molecular Diversity and Genetic Population Structure in a Coenagrionid Damselfly. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Carballa, M.O.; Hadrys, H.; Cordero-Rivera, A.; Andrés, J.A. Population Genetic Structure of Sexual and Parthenogenetic Damselflies Inferred from Mitochondrial and Nuclear Markers. Heredity 2012, 108, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purse, B.V.; Hopkins, G.W.; Day, K.J.; Thompson, D.J. Dispersal Characteristics and Management of a Rare Damselfly. J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 40, 716–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, P.C.; Saccheri, I.J.; Kemp, S.J.; Thompson, D.J. Population Structure and the Impact of Regional and Local Habitat Isolation upon Levels of Genetic Diversity of the Endangered Damselfly Coenagrion mercuriale (Odonata: Zygoptera). Freshw. Biol. 2006, 51, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudot, J.P.; Kalkman, V.J. Atlas of the European Dragonflies and Damselflies; KNNV Publishing: Zeist, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Flenner, I.; Sahlén, G. Dragonfly community re-organisation in boreal forest lakes: Rapid species turnover driven by climate change? Insect Conserv. Divers. 2008, 1, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, S.M.; Pitman, G.M.; Flockhart, D.T.T.; Norris, D.R. Radio-Tracking Reveals How Wind and Temperature Influence the Pace of Daytime Insect Migration. Biol. Lett. 2019, 15, 20190327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minot, M.; Le Gall, M.; Husté, A. Biometry of the Large Dragonfly Anax imperator (Odonata: Aeshnidae): A Study of Traits from Larval Development to Adults. Eur. J. Entomol. 2019, 116, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbet, P.S. The Life-History of the Emperor Dragonfly Anax imperator Leach (Odonata: Aeshnidae). J. Anim. Ecol. 1957, 26, 1–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minot, M.; Besnard, A.; Husté, A. Habitat Use and Movements of a Large Dragonfly (Odonata: Anax Imperator) in a Pond Network. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 66, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubertazzi, M.A.A.; Ginsberg, H.S. Persistence of Dragonfly Exuviae on Vegetation and Rock Substrates. Northeast. Nat. 2009, 16, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roland, H.-J. Haltbarkeit von Anax-Exuvien Am Ort Der Emergenz. Libellula 2010, 3, 231–240. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, D.; Brodbeck, S.; Holderegger, R. Characterization of Microsatellite Loci in Leucorrhinia caudalis, a Rare Dragonfly Endangered throughout Europe. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2009, 1, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadrys, H.; Timm, J.; Streit, B.; Giere, S. A Panel of Microsatellite Markers to Study Sperm Precedence Patterns in the Emperor Dragonfly Anax imperator (Odonata: Anisoptera). Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Adamack, A.T.; Gruber, B. Landgenreport: A new R function to simplify landscape genetic analysis using resistance surface layers. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 1172–1178. [Google Scholar]
- Paradis, E. Pegas: An R Package for Population Genetics with an Integrated–Modular Approach. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 419–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymond, M.; Rousset, F. An Exact Test for Population Differentiation. Evolution 1995, 49, 1280–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousset, F. Genepop’007: A Complete Re-Implementation of the Genepop Software for Windows and Linux. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2008, 8, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Yekutieli, D. The Control of the False Discovery Rate in Multiple Testing under Dependency. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, K.; McGinnity, P.; Cross, T.F.; Crozier, W.W.; Prodöhl, P.A. DiveRsity: An R Package for the Estimation of Population Genetics Parameters and Their Associated Errors. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2013, 4, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowski, S.T. Counting Alleles with Rarefaction: Private Alleles and Hierarchical Sampling Designs. Conserv. Genet. 2004, 5, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggiotti, O.E.; Lange, O.; Rassmann, K.; Gliddon, C. A Comparison of Two Indirect Methods for Estimating Average Levels of Gene Flow Using Microsatellite Data. Mol. Ecol. 1999, 8, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitlock, M.C.; Mccauley, D.E. Indirect Measures of Gene Flow and Migration: FST ≠ 1/(4Nm + 1). Heredity 1999, 82, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, B.S.; Cockerham, C.C. Estimating F-Statistics for the Analysis of Population Structure. Evolution 1984, 38, 1358–1370. [Google Scholar]
- Excoffier, L.; Smouse, P.E.; Quattro, J.M. Analysis of Molecular Variance Inferred from Metric Distances among DNA Haplotypes: Application to Human Mitochondrial DNA Restriction Data. Genetics 1992, 131, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousset, F. Genetic Differentiation and Estimation of Gene Flow from F-Statistics under Isolation by Distance. Genetics 1997, 145, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of Population Structure Using Multilocus Genotype Data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the Number of Clusters of Individuals Using the Software Structure: A Simulation Study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobsson, M.; Rosenberg, N.A. CLUMPP: A Cluster Matching and Permutation Program for Dealing with Label Switching and Multimodality in Analysis of Population Structure. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, F.I.; Adams, P.E.; Schneiders, B.B. Stratag: An r Package for Manipulating, Summarizing and Analysing Population Genetic Data. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jombart, T. Adegenet: A R Package for the Multivariate Analysis of Genetic Markers. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 1403–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillot, G.; Mortier, F.; Estoup, A. Geneland: A Computer Package for Landscape Genetics. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2005, 5, 712–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, C.; Weigel, D.E.; Balazik, M.; Keeley, A.T.; Walker, F.M.; Landguth, E.; Cushman, S.A.M.; Murphy, M.; Waits, L.; Balkenhol, N. A Simulation-Based Evaluation of Methods for Inferring Linear Barriers to Gene Flow. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2012, 12, 822–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G.A.; Rannala, B. Bayesian Inference of Recent Migration Rates Using Multilocus Genotypes. Genetics 2003, 163, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamerman, D. Markov Chain Monte Carlo: Stochastic Simulation for Bayesian Inference; Chapman & Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, D.; Brodbeck, S.; Flöss, I.; Vonwil, G.; Holderegger, R. Ecological and Genetic Measurements of Dispersal in a Threatened Dragonfly. Biol. Conserv. 2010, 143, 2658–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolný, A.; Šigutová, H.; Ožana, S.; Choleva, L. How Difficult Is It to Reintroduce a Dragonfly? Fifteen Years Monitoring Leucorrhinia dubia at the Receiving Site. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 218, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaegers, J.; Janssens, S.B.; Ferreira, S.; Watts, P.C.; Mergeay, J.; McPeek, M.A.; Stoks, R. Ecological and Evolutionary Drivers of Range Size in Coenagrion Damselflies. J. Evol. Biol. 2014, 27, 2386–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levett, S.; Walls, S. Tracking the Elusive Life of the Emperor Dragonfly Anax imperator Leach. J. Br. Dragonfly Soc. 2011, 27, 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hickling, R.; Roy, D.B.; Hill, J.K.; Fox, R.; Thomas, C.D. The Distributions of a Wide Range of Taxonomic Groups Are Expanding Polewards. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2006, 12, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickling, R.; Roy, D.B.; Hill, J.K.; Thomas, C.D. A Northward Shift of Range Margins in British Odonata. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S. Contemporary Human-Altered Landscapes and Oceanic Barriers Reduce Bumble Bee Gene Flow. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 993–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanden Broeck, A.; Maes, D.; Kelager, A.; Wynhoff, I.; WallisDeVries, M.F.; Nash, D.R.; Oostermeijer, J.G.B.; Van Dyck, H.; Mergeay, J. Gene Flow and Effective Population Sizes of the Butterfly Maculinea alcon in a Highly Fragmented, Anthropogenic Landscape. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 209, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PRAM Normandie. Available online: http://recensementmare.pramnormandie.com/API/ (accessed on 11 January 2022).
- Gilpin, E.M.; Hanski, I. Metapopulation Dynamics: Empirical and Theoretical Investigations. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1991, 42, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Pulliam, H.R. Sources, Sinks, and Population Regulation. Am. Nat. 1988, 132, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peery, M.Z.; Beissinger, S.R.; House, R.F.; Bérubé, M.; Hall, L.A.; Sellas, A.; Palsbøll, P.J. Characterizing Source–Sink Dynamics with Genetic Parentage Assignments. Ecology 2008, 89, 2746–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Thomaz, A.T.; He, Q. When Are Populations Not Connected like a Circuit? Identifying Biases in Gene Flow from Coalescent Times. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 19, 1381–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhling, F.; Martens, A.; Marais, E. How to Enter a Desert—Patterns of Odonata Colonisation of Arid Namibia. Int. J. Odonatol. 2009, 12, 287–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, S.; Bodin, Ö.; Fortin, M.-J. EDITOR’S CHOICE: Stepping Stones Are Crucial for Species’ Long-Distance Dispersal and Range Expansion through Habitat Networks. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 51, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atterby, H.; Aegerter, J.N.; Smith, G.C.; Conyers, C.M.; Allnutt, T.R.; Ruedi, M.; MacNicoll, A.D. Population Genetic Structure of the Daubenton’s Bat (Myotis daubentonii) in Western Europe and the Associated Occurrence of Rabies. Eur. J. Wildl. Resour. 2010, 56, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razgour, O.; Rebelo, H.; Puechmaille, S.J.; Juste, J.; Ibáñez, C.; Kiefer, A.; Burke, T.; Dawson, D.A.; Jones, G. Scale-Dependent Effects of Landscape Variables on Gene Flow and Population Structure in Bats. Divers. Distrib. 2014, 20, 1173–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minot, M.; Aubert, M.; Husté, A. Pond Creation and Restoration: Patterns of Odonate Colonization and Community Dynamics. Biodivers. Conserv. 2021, 30, 4379–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, M.L. A Critical Overview of Progress in Studies of Migration of Dragonflies (Odonata: Anisoptera), with Emphasis on North America. J. Insect Conserv. 2013, 17, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaput-Bardy, A.; Lemaire, C.; Picard, D.; Secondi, J. In-Stream and Overland Dispersal across a River Network Influences Gene Flow in a Freshwater Insect, Calopteryx splendens. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 3496–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monroe, E.M.; Lynch, C.; Soluk, D.A.; Britten, H.B. Nonlethal Tissue Sampling Techniques and Microsatellite Markers Used for First Report of Genetic Diversity in Two Populations of the Endangered Somatochlora hineana (Odonata: Corduliidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2010, 103, 1012–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero-Rivera, A.; Perez, F.E.; Andres, J.A. The Effect of Handling Damage, Mobility, Body Size, and Fluctuating Asymmetry on Lifetime Mating Success of Ischnura graellsii (Rambur) (Zygoptera: Coenagrionidae). Odonatologica 2002, 31, 117–128. [Google Scholar]
- Raebel, E.M.; Merckx, T.; Riordan, P.; Macdonald, D.W.; Thompson, D.J. The Dragonfly Delusion: Why It Is Essential to Sample Exuviae to Avoid Biased Surveys. J. Insect Conserv. 2010, 14, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, P.C.; Thompson, D.J.; Daguet, C.; Kemp, S.J. Exuviae as a Reliable Source of DNA for Population-Genetic Analysis of Odonates. Odonatologica 2005, 34, 183–187. [Google Scholar]
- Monroe, E.M.; Britten, H.B. Conservation in Hine’s Sight: The Conservation Genetics of the Federally Endangered Hine’s Emerald Dragonfly, Somatochlora hineana. J. Insect Conserv. 2014, 18, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incagnone, G.; Marrone, F.; Barone, R.; Robba, L.; Naselli-Flores, L. How Do Freshwater Organisms Cross the “Dry Ocean”? A Review on Passive Dispersal and Colonization Processes with a Special Focus on Temporary Ponds. Hydrobiologia 2015, 750, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epps, C.W.; Keyghobadi, N. Landscape Genetics in a Changing World: Disentangling Historical and Contemporary Influences and Inferring Change. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 6021–6040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Country | Pop | Site Name | Coordinates (WGS84) | Sex | Source of DNA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Adult Legs | Nymphal Legs | Fresh Exuviae | Old Exuviae | ||||
| Italy | 1 | Sicily | 37.086 N, 15.286 E | NA | NA | 6 | |||
| Switzerland | 2 | Neuchâtel | 47.002 N, 6.741 E | 12 | 4 | 16 | |||
| Czech Republic | 3 | Kyjov | 49.010 N, 17.128 E | 7 | 21 | 16 | 12 | ||
| France | 4 | Beaussault | 49.682 N, 1.555 E | NA | NA | 33 | |||
| France | 5 | Cerisy | 49.199 N, −0.912 E | NA | NA | 19 | |||
| France | 6 | Heudreville | 49.133 N, 1.198 E | 18 | 22 | 36 | 4 | ||
| France | 7 | Bois-Guillaume | 49.480 N, 1.102 E | 25 | 14 | 39 | |||
| France | 8 | Marchésieux | 49.178 N, −1.324 E | 9 | 5 | 14 | |||
| France | 9 | Paluel | 49.835 N, 0.624 E | 8 | 7 | 15 | |||
| France | 10 | Bresle | 49.914 N, 1.679 E | 7 | 3 | 10 | |||
| United Kingdom | 11 | York | 53.964 N, −1.086 E | 15 | 16 | 31 | |||
| Total (n = 251) | 22 | 82 | 90 | 57 | |||||
| Country/Site | Pop | n | Ho | He | Na | AR | FIS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Italy (Sicily) | 1 | 6 | 0.71 ± 0.07 | 0.62 ± 0.05 | 29 | 4.14 ± 0.46 | −0.17 |
| Switzerland | 2 | 16 | 0.65 ± 0.06 | 0.61 ± 0.06 | 42 | 4.02 ± 0.44 | −0.06 |
| Czech Republic | 3 | 21 | 0.61 ± 0.07 | 0.65 ± 0.06 | 47 | 4.26 ± 0.57 | 0.06 |
| France (Beau.) | 4 | 33 | 0.61 ± 0.07 | 0.65 ± 0.06 | 56 | 4.39 ± 0.52 | 0.06 |
| France (Cerisy) | 5 | 19 | 0.59 ± 0.08 | 0.68 ± 0.05 | 46 | 4.40 ± 0.54 | 0.15 |
| France (Heud.) | 6 | 32 | 0.47 ± 0.06 | 0.67 ± 0.06 | 60 | 4.75 ± 0.54 | 0.30 |
| France (Bois-G.) | 7 | 34 | 0.59 ± 0.06 | 0.69 ± 0.05 | 54 | 4.63 ± 0.45 | 0.16 |
| France (Marc.) | 8 | 14 | 0.75 ± 0.07 | 0.72 ± 0.04 | 46 | 4.76 ± 0.47 | −0.03 |
| France (Paluel) | 9 | 14 | 0.57 ± 0.06 | 0.66 ± 0.05 | 45 | 4.54 ± 0.38 | 0.15 |
| France (Bresle) | 10 | 9 | 0.43 ± 0.08 | 0.61 ±0.06 | 31 | 4.05 ± 0.53 | 0.25 |
| United Kingdom | 11 | 25 | 0.33 ± 0.11 | 0.63 ± 0.05 | 37 | 3.96 ± 0.35 | 0.51 |
| Italy (Sicily) | Switz | Cz. Rep. | France (Beaus.) | France (Cerisy) | France (Heud.) | France (Bois-G.) | France (March.) | France (Paluel) | France (Bresle) | U.K. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Italy (Sicily) | - | 0.0293 | 0.0307 | −0.0079 | 0.0163 | 0.0047 | 0.0104 | 0.0097 | −0.0132 | 0.0254 | 0.1055 |
| Switzerland | - | 0.0128 | 0.0167 | 0.0111 | 0.0234 | 0.0192 | 0.0446 | 0.0126 | 0.0481 | 0.1220 | |
| Czech Republic | - | 0.0110 | 0.0232 | 0.0272 | 0.0206 | 0.0291 | 0.0164 | 0.0509 | 0.1148 | ||
| France (Beau.) | - | 0.0037 | 0.0115 | 0.0143 | 0.0036 | −0.0021 | 0.0191 | 0.1297 | |||
| France (Cerisy) | - | −0.0059 | 0.0045 | 0.0049 | −0.0063 | −0.0055 | 0.0903 | ||||
| France (Heud.) | - | −0.0007 | 0.0019 | −0.0031 | −0.0151 | 0.0843 | |||||
| France (Bois-G.) | - | 0.0183 | 0.0009 | 0.0193 | 0.0841 | ||||||
| France (Marc.) | - | 0.0052 | 0.0119 | 0.0920 | |||||||
| France (Paluel) | - | 0.0043 | 0.1014 | ||||||||
| France (Bresle) | - | 0.0813 | |||||||||
| United Kingdom | - |
| Source of Variation | df | Sum of Squares | Variance Components | Percentage of Variance | Φ-Statistics | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Among countries | 4 | 138.79 | 0.78 | 6.37 | ΦCT = 0.06 | 0.02 |
| Among populations within countries | 6 | 82.21 | 0.11 | 0.90 | ΦSC = 0.01 | 0.09 |
| Within populations | 212 | 2405.45 | 11.35 | 92.73 | - | - |
| Total | 222 | 2626.45 | 12.24 | 100.00 | - | - |
| Target | Potential Donor Site | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Italy (Sicily) | Switz. | Cz. Rep. | France (Beaus.) | France (Cerisy) | France (Heud.) | France (Bois-G.) | France (March.) | France (Paluel) | France (Bresle) | U.K. | |
| Italy (Sicily) | 0.68 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Switzerland | 0.01 | 0.68 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Czech Republic | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.69 | 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| France (Beau.) | <0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.69 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| France (Cerisy) | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.78 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| France (Heud.) | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.72 | 0.04 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.02 |
| France (Bois-G.) | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.73 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 |
| France (Marc.) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.69 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 |
| France (Paluel) | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.68 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| France (Bresle) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.68 | 0.11 |
| United Kingdom | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.87 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Minot, M.; Husté, A. Genetic Diversity and Structure of Anax imperator Leach, 1815 Populations (Odonata: Aeshnidae) in Ponds at Regional and European Scales. Diversity 2022, 14, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14020068
Minot M, Husté A. Genetic Diversity and Structure of Anax imperator Leach, 1815 Populations (Odonata: Aeshnidae) in Ponds at Regional and European Scales. Diversity. 2022; 14(2):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14020068
Chicago/Turabian StyleMinot, Marceau, and Aurélie Husté. 2022. "Genetic Diversity and Structure of Anax imperator Leach, 1815 Populations (Odonata: Aeshnidae) in Ponds at Regional and European Scales" Diversity 14, no. 2: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14020068
APA StyleMinot, M., & Husté, A. (2022). Genetic Diversity and Structure of Anax imperator Leach, 1815 Populations (Odonata: Aeshnidae) in Ponds at Regional and European Scales. Diversity, 14(2), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14020068






