Two New Amanita Species in Section Amanita from Thailand
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Morphological Study
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing
2.3. Phylogenetic Analyses
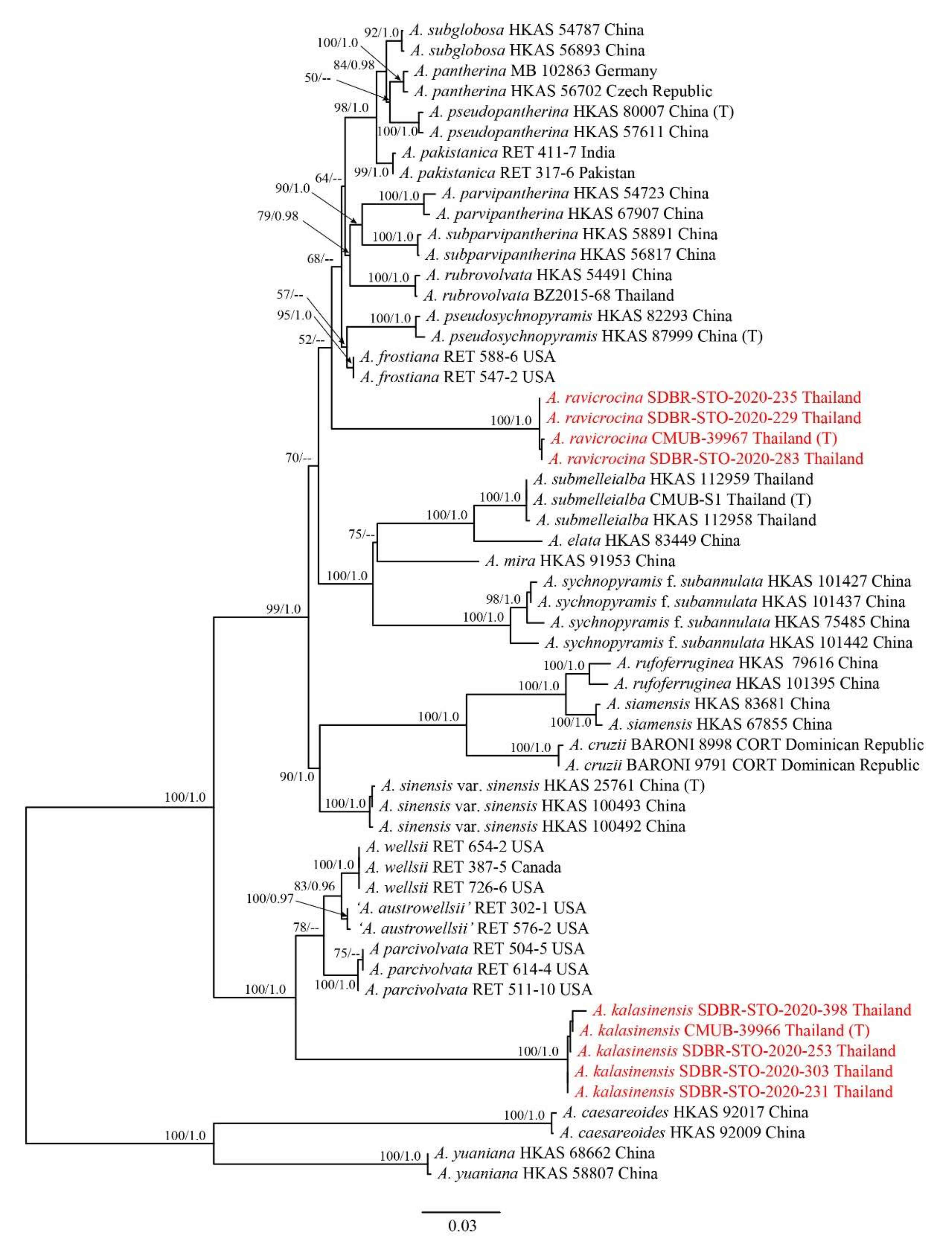
3. Results
3.1. Phylogenetic Analyses
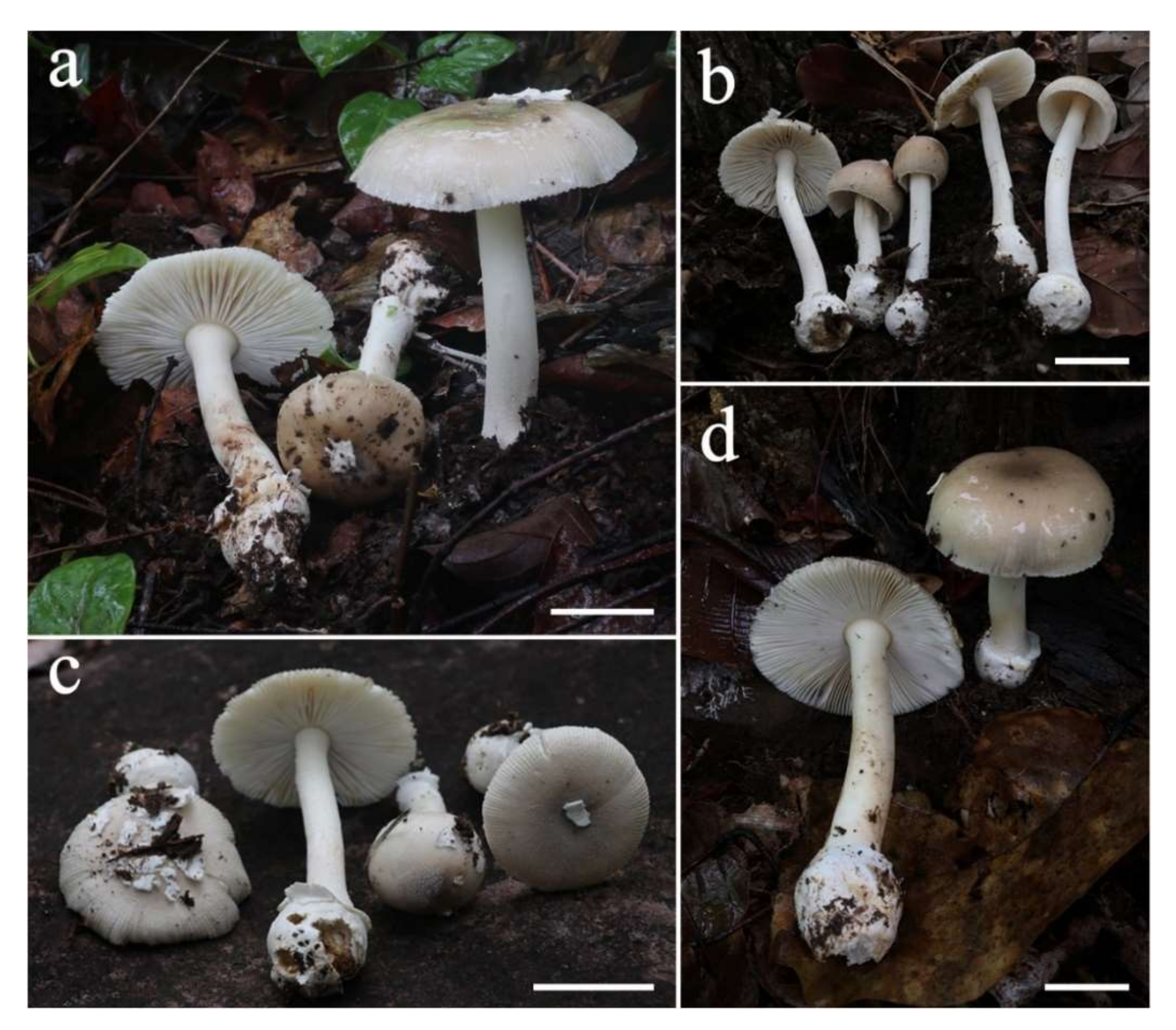
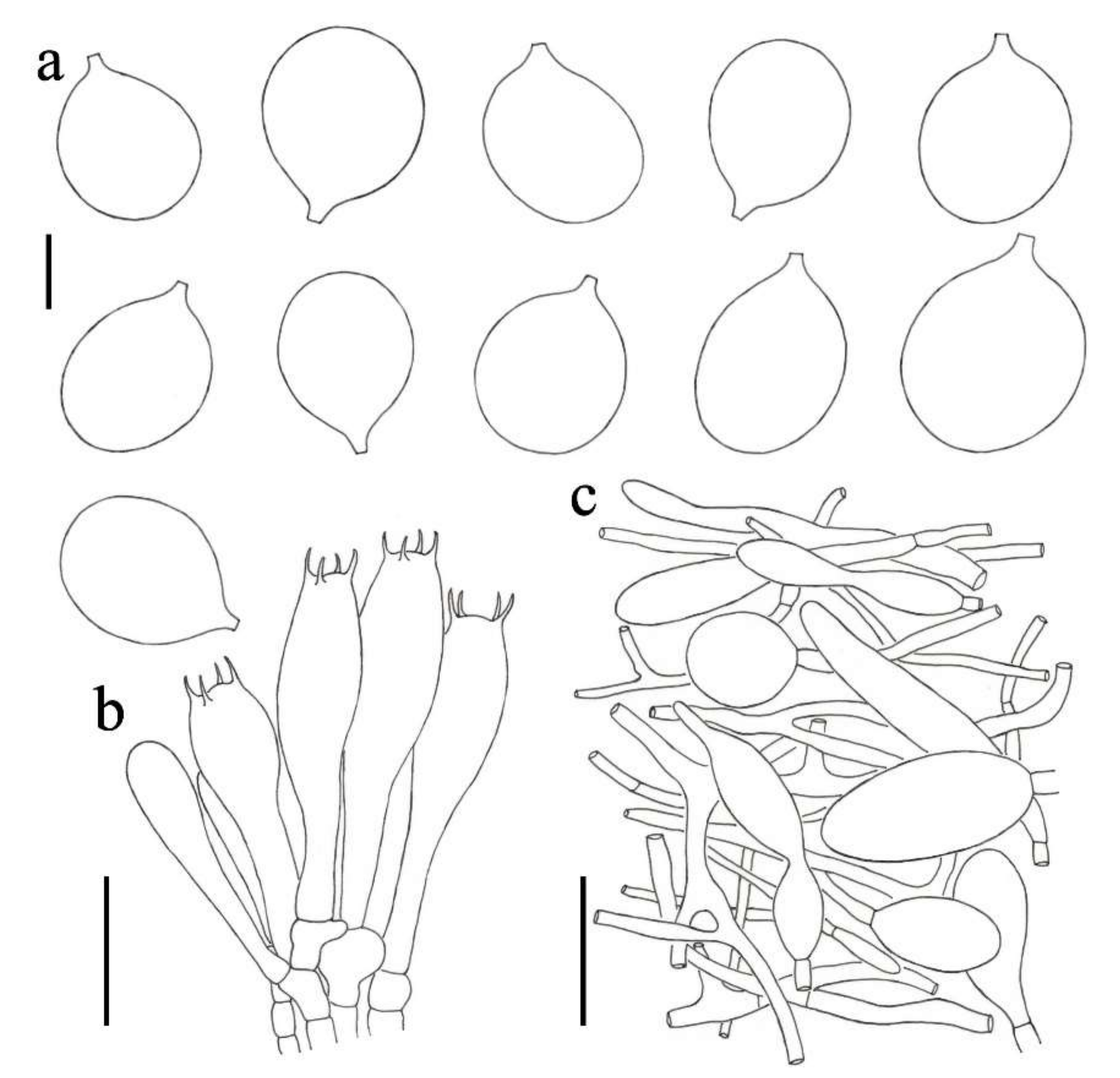
3.2. Taxonomy
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Z.L. Die Amanita-Arten von Südwestchina. Bibl. Mycol. 1997, 170, 1–240. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.L. Amanitaceae. Flora Fungorum Sinicorum 27; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 1–258. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.L. Atlas of the Chinese Species of Amanitaceae; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 1–213. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.Y.; Cai, Q.; Tang, L.P.; Liu, J.W.; Yang, Z.L. The family Amanitaceae: Molecular phylogeny, higher-rank taxonomy and the species in China. Fungal Divers. 2018, 91, 5–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanitaceae org. Available online: http://www.amanitaceae.org/?Genus%20Amanita (accessed on 5 December 2021).
- Sanmee, R.; Tulloss, R.E.; Lumyong, P.; Dell, B.; Lumyong, S. Studies on Amanita (Basidiomycetes: Amanitaceae) in Northern Thailand. Fungal Divers. 2008, 3, 97–123. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.J.; Hyde, K.D.; Zhao, R.L.; Hongsanan, S.; Abdel-Aziz, F.A.; AbdelWahab, M.A.; Alvarado, P.; Alves-Silva, G.; Ammirati, S.F.; Ariyawansa, H.A.; et al. Fungal diversity notes 253–366: Taxonomic and phylogenetic contributions to fungal taxa. Fungal Divers. 2016, 78, 1–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongbai, B.; Tulloss, R.E.; Miller, S.L.; Hyde, K.D.; Chen, J.; Zhao, R.L.; Raspé, O. A new species and four new records of Amanita (Amanitaceae; Basidiomycota) from Northern Thailand. Phytotaxa 2016, 286, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thongbai, B.; Miller, S.L.; Stadler, M.; Stadler, M.; Wittstein, K.; Hyde, K.D.; Lumyong, S.; Raspé, O. Study of three interesting Amanita species from Thailand: Morphology, multiple-gene phylogeny and toxin analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thongbai, B.; Hyde, K.D.; Lumyong, S.; Raspé, O. High undescribed diversity of Amanita section Vaginatae in northern Thailand. Mycosphere 2018, 9, 462–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phookamsak, R.; Hyde, K.D.; Jeewon, R.; Bhat, D.J.; Jones, E.B.G.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Raspe, O.; Karunarathna, S.C.; Wanasinghe, D.N.; Hongsanan, S.; et al. Fungal diversity notes 929–1035: Taxonomic and phylogenetic contributions on genera and species of fungi. Fungal Divers. 2019, 95, 1–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.S.; Liu, J.K.; Mortimer, P.E.; Lumyong, S.L. Amanita submelleialba sp. nov. in section Amanita from northern Thailand. Phytotaxa 2021, 513, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.F.; Yang, Z.L. Recommendation of several methods for preserving the materials of macro fungi for molecular biological research. J. Fungal Res. 2004, 2, 60–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kornerup, A.; Wanscher, J.H. Methuen Handbook of Colour, 3rd ed.; Eyre Methuen: London, UK, 1978; pp. 1–243. [Google Scholar]
- Bas, C. Morphology and subdivision of Amanita and a monograph of its section Lepidella. Persoonia 1969, 5, 285–579. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Q.; Cui, Y.Y.; Yang, Z.L. Lethal Amanita species in China. Mycologia 2016, 108, 993–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J.W. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; Volume 38, pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Gardes, M.; Bruns, T.D. ITS primers with enhanced specificity for basidiomycetes application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Mol. Ecol. 1993, 2, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilgalys, R.; Hester, M. Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 4238–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rehner, S.A.; Buckley, E. A Beauveria phylogeny inferred from nuclear ITS and EF1-α sequences: Evidence for cryptic diversification and links to Cordyceps teleomorphs. Mycologia 2005, 97, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.; Tulloss, R.E.; Tang, L.P.; Tolgor, B.; Zhang, P.; Chen, Z.H.; Yang, Z.L. Multi-locus phylogeny of lethal amanitas: Implications for species diversity and historical biogeography. BMC Evol. Biol. 2014, 14, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Castresana, J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dissanayake, A.J.; Bhunjun, C.S.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Liu, J.K. Applied aspects of methods to infer phylogenetic relationships amongst fungi. Mycosphere 2020, 11, 2652–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nylander, J.A.A. MrModeltest v2. Program Distributed by the Author; Evolutionary Biology Centre, Uppsala University: Uppsala, Sweden, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for Inference of Large Phylogenetic Trees. In Proceedings of the Gateway Computing Environments Workshop, New Orleans, LA, USA, 14 November 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML Version 8: A tool for Phylogenetic Analysis and Post-Analysis of Large Phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rannala, B.; Yang, Z. Probability distribution of molecular evolutionary trees: A new method of phylogenetic inference. J. Mol. Evol. 1996, 43, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larget, B.; Simon, D.L. Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithms for the Bayesian analysis of phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FigTree v1.4.4. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 25 November 2021).
- Yang, Z.L.; Weiß, M.; Oberwinkler, F. New species of Amanita from the Eastern Himalaya and adjacent regions. Mycologia 2004, 96, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, R.P.; Mehmood, T.; Uniyal, P.; Singh, U. Six new records of genus Amanita (Amanitaceae) from Uttarakhand, India. Curr. Res. Environ. Appl. Mycol. 2017, 7, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongo, T. Notulae Mycologicae (10). Mem. Shiga Univ. 1971, 21, 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Corner, E.J.H.; Bas, C. The genus Amanita in Singapore and Malaya. Persoonia 1962, 2, 241–304. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.S. A Field Guide to the Larger Fungi of FRIM; Forest Research Institute Malaysia: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2017; pp. 1–174. [Google Scholar]
- Oda, T.; Yamazaki, T.; Tanaka, C.; Terashita, T.; Taniguchi, N.; Tsuda, M. Amanita ibotengutake sp. nov., a poisonous fungus from Japan. Mycol. Prog. 2002, 1, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Species Name | Voucher | Country | GenBank Accession Number | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITS | nrLSU | RPB2 | TEF1-α | TUB | |||
| ‘Amanita austrowellsii’ | RET 302-1 | USA | MN963578 | MN963578 | — | — | — |
| ‘A. austrowellsii’ | RET 576-2 | USA | MN963579 | MN963579 | — | — | — |
| A. cruziiT | BARONI 8998 (CORT) | Dominican Republic | KC855222 | KC855222 | — | MH508750 | MH485478 |
| A. cruzii | BARONI 9791 (CORT) | Dominican Republic | KC855223 | KC855223 | — | MH508751 | — |
| A. elata | HKAS 83449 | China | MH508334 | MH486486 | MH485965 | MH508763 | MH485488 |
| A. frostiana | RET 547-2 | USA | KP313581 | — | — | — | — |
| A. frostiana | RET 588-6 | USA | KP313583 | — | — | — | — |
| A. kalasinensis | SDBR-STO-2020-231 | Thailand | OM040561 | OM040552 | — | — | — |
| A. kalasinensisT | CMUB-39966 | Thailand | OM040562 | OM040553 | OM066913 | OM066919 | OM066925 |
| A. kalasinensis | SDBR-STO-2020-253 | Thailand | OM040563 | OM040554 | OM066914 | OM066920 | |
| A. kalasinensis | SDBR-STO-2020-303 | Thailand | OM040564 | OM040555 | — | — | — |
| A. kalasinensis | SDBR-STO-2020-398 | Thailand | OM040565 | OM040556 | — | — | — |
| A. mira | HKAS 91953 | China | MH508437 | MH486646 | MH486097 | — | — |
| A. pakistanica | RET 317-6 | Pakistan | KX365198 | KX365199 | — | — | — |
| A. pakistanica | RET 411-7 | India | MG991745 | MG991814 | — | — | — |
| A. pantherina | HKAS 56702 | Czech Republic | MH508487 | KR824782 | KR824789 | KR824825 | MH485670 |
| A. pantherina | MB-102863 | Germany | MH508488 | MH486743 | MH486167 | MH508976 | MH485671 |
| A. parcivolvata | RET 504-5 | USA | KP313586 | — | — | — | — |
| A. parcivolvata | RET 511-10 | USA | KP313584 | — | — | — | — |
| A. parcivolvata | RET 614-4 | USA | MN963585 | MN963584 | — | — | — |
| A. parvipantherina | HKAS 54723 | China | MH508495 | KR824780 | KR824802 | KR824807 | MH485676 |
| A. parvipantherinaa | HKAS 67907 | China | MH508498 | KR824781 | KR824803 | KR824808 | MH485679 |
| A. pseudopantherina T | HKAS 80007 | China | MH508514 | MH486777 | MH486191 | MH509004 | MH485698 |
| A. pseudopantherina | HKAS 57611 | China | MH508511 | MH486774 | MH486188 | — | MH485695 |
| A. pseudosychnopyramis | HKAS 82293 | China | MH508529 | MH486790 | MH486204 | — | MH485712 |
| A. pseudosychnopyramis T | HKAS 87999 | China | MH508530 | KR824778 | KR824790 | KR824824 | MH485713 |
| A. rubrovolvata | BZ2015-68 | Thailand | KY747465 | KY747477 | KY656882 | — | KY656863 |
| A. rubrovolvata | HKAS 54491 | China | JN943178 | JN941153 | JQ031116 | KR824823 | — |
| A. rufoferruginea | HKAS 101395 | China | MH508578 | MH486839 | MH486249 | — | MH485753 |
| A. rufoferruginea | HKAS 79616 | China | MH508579 | MH486842 | MH486252 | — | MH485756 |
| A. siamensis | HKAS 67855 | China | MH508592 | MH486864 | MH486271 | — | MH485773 |
| A. siamensis | HKAS 83681 | China | MH508593 | MH486866 | MH486273 | — | MH485774 |
| A. sinensis var. sinensis T | HKAS 25761 | China | AB096059 | AF024474 | — | — | AB095864 |
| A. sinensis var. sinensis | HKAS 100492 | China | MH508594 | MH486867 | MH486274 | — | MH485775 |
| A. sinensis var. sinensis | HKAS 100493 | China | MH508595 | MH486868 | MH486275 | — | MH485776 |
| A. subglobosa | HKAS 54787 | China | MH508618 | MH486900 | MH486301 | MH509121 | MH485801 |
| A. subglobosa | HKAS 56893 | China | JN943176 | JN941157 | JQ031120 | KR824826 | MH485802 |
| A. submelleialba T | CMUB-S1 | Thailand | MZ045688 | MZ045693 | MZ048619 | MZ048624 | MZ048629 |
| A. submelleialba | HKAS 112958 | Thailand | MZ045685 | MZ045690 | MZ048616 | MZ048621 | MZ048626 |
| A. submelleialba | HKAS 112959 | Thailand | MZ045686 | MZ045691 | MZ048617 | MZ048622 | MZ048627 |
| A. subparvipantherina | HKAS 56817 | China | JN943171 | JN941160 | JQ031114 | KR824815 | MH485818 |
| A. subparvipantherina | HKAS 58891 | China | MH508628 | MH486918 | MH486316 | MH509136 | MH485819 |
| A. sychnopyramis f. subannulata | HKAS 101427 | China | MH508631 | MH486922 | — | MH509139 | MH485824 |
| A. sychnopyramis f. subannulata | HKAS 101437 | China | MH508632 | MH486923 | MH486319 | MH509140 | MH485825 |
| A. sychnopyramis f. subannulata | HKAS 101442 | China | MH508633 | MH486925 | MH486321 | MH509142 | MH485826 |
| A. sychnopyramis f. subannulata | HKAS 75485 | China | MH508634 | MH486926 | — | MH509143 | MH485827 |
| A. wellsii | RET 387-5 | Canada | KU248115 | OK285332 | — | — | — |
| A. wellsii | RET 654-2 | USA | OK299151 | OK299151 | — | — | — |
| A. wellsii | RET 726-6 | USA | OK299169 | OK299169 | — | — | — |
| A. ravicrocina | SDBR-STO-2020-229 | Thailand | OM040566 | OM040557 | OM066915 | OM066921 | OM066926 |
| A. ravicrocina | SDBR-STO-2020-235 | Thailand | OM040567 | OM040558 | OM066916 | OM066922 | OM066927 |
| A. ravicrocinaT | CMUB-39967 | Thailand | OM040568 | OM040559 | OM066917 | OM066923 | — |
| A. ravicrocina | SDBR-STO-2020-283 | Thailand | OM040569 | OM040560 | OM066918 | OM066924 | — |
| Outgroup | |||||||
| A. caesareoides | HKAS 92009 | China | MH508285 | MH486421 | MH485901 | MH508708 | — |
| A. caesareoides | HKAS 92017 | China | MH508286 | MH486422 | MH485902 | MH508709 | — |
| A. yuaniana | HKAS 58807 | China | MH508653 | MH486954 | MH486347 | MH509174 | MH485852 |
| A. yuaniana | HKAS 68662 | China | MH508654 | MH486957 | MH486350 | MH509177 | MH485854 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.S.; Liu, J.; Kumla, J.; Lumyong, S. Two New Amanita Species in Section Amanita from Thailand. Diversity 2022, 14, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14020101
Liu YS, Liu J, Kumla J, Lumyong S. Two New Amanita Species in Section Amanita from Thailand. Diversity. 2022; 14(2):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14020101
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yuan S., Jiankui Liu, Jaturong Kumla, and Saisamorn Lumyong. 2022. "Two New Amanita Species in Section Amanita from Thailand" Diversity 14, no. 2: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14020101
APA StyleLiu, Y. S., Liu, J., Kumla, J., & Lumyong, S. (2022). Two New Amanita Species in Section Amanita from Thailand. Diversity, 14(2), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14020101








