Aquatic Insects in Habitat-Forming Sponges: The Case of the Lower Mekong and Conservation Perspectives in a Global Context
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
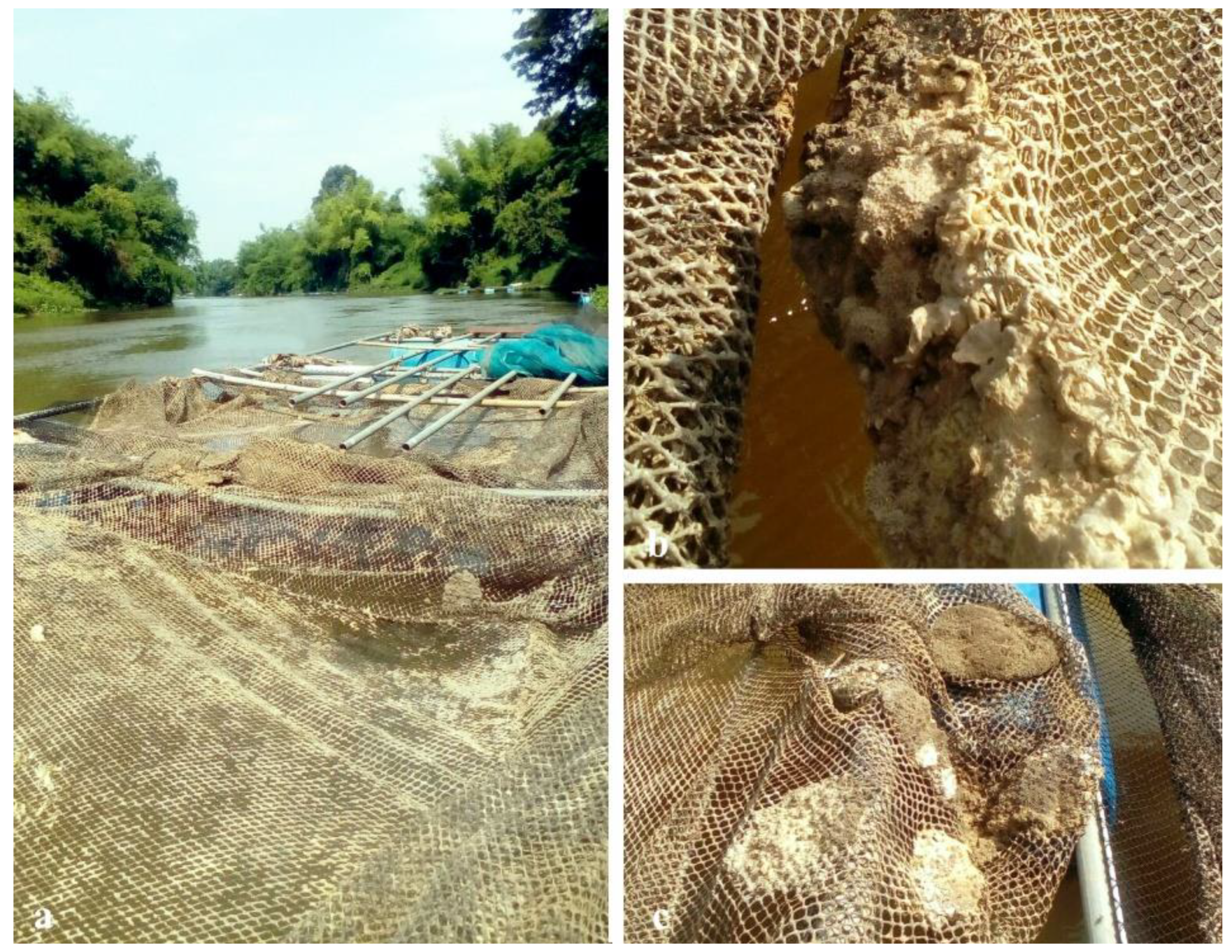
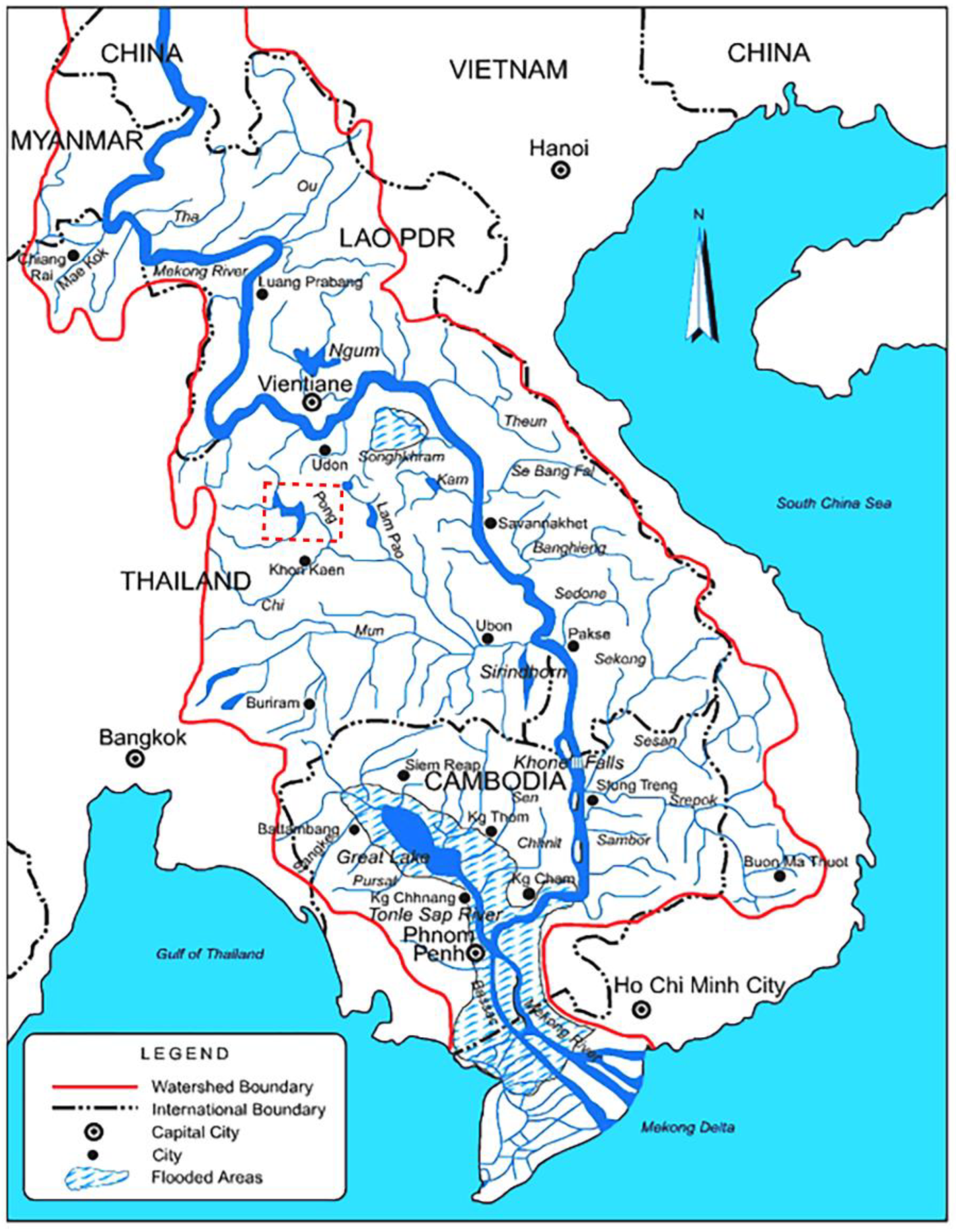
2.1. Study Area
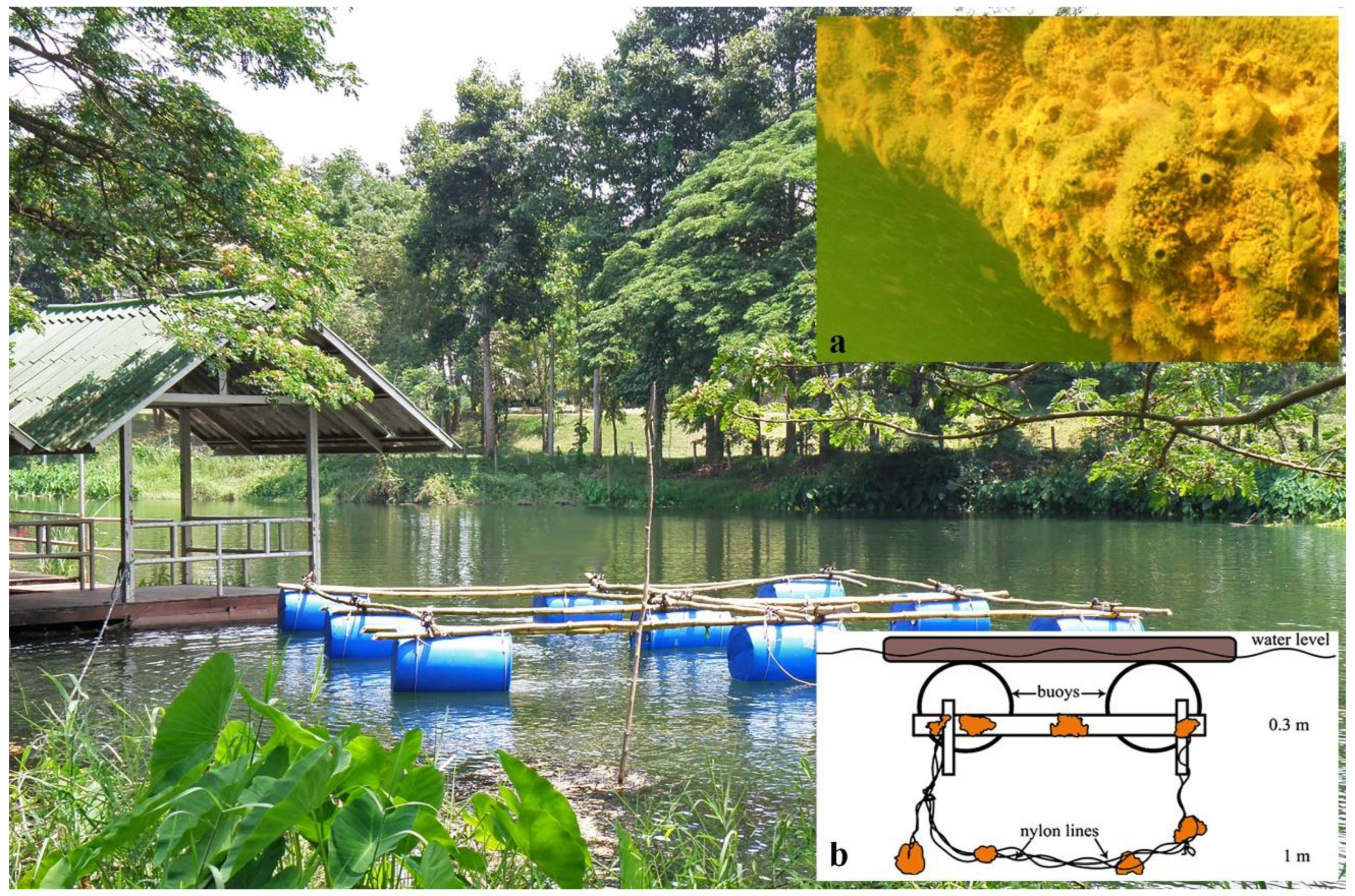
2.2. Sampling Methods
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Parameters
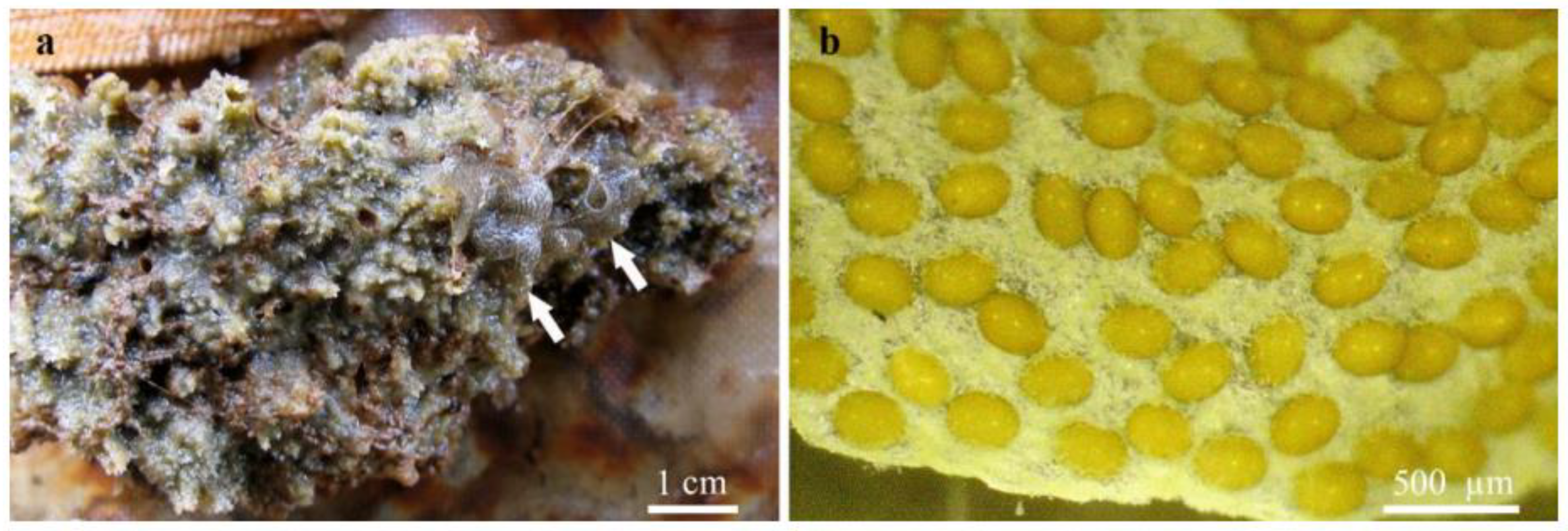
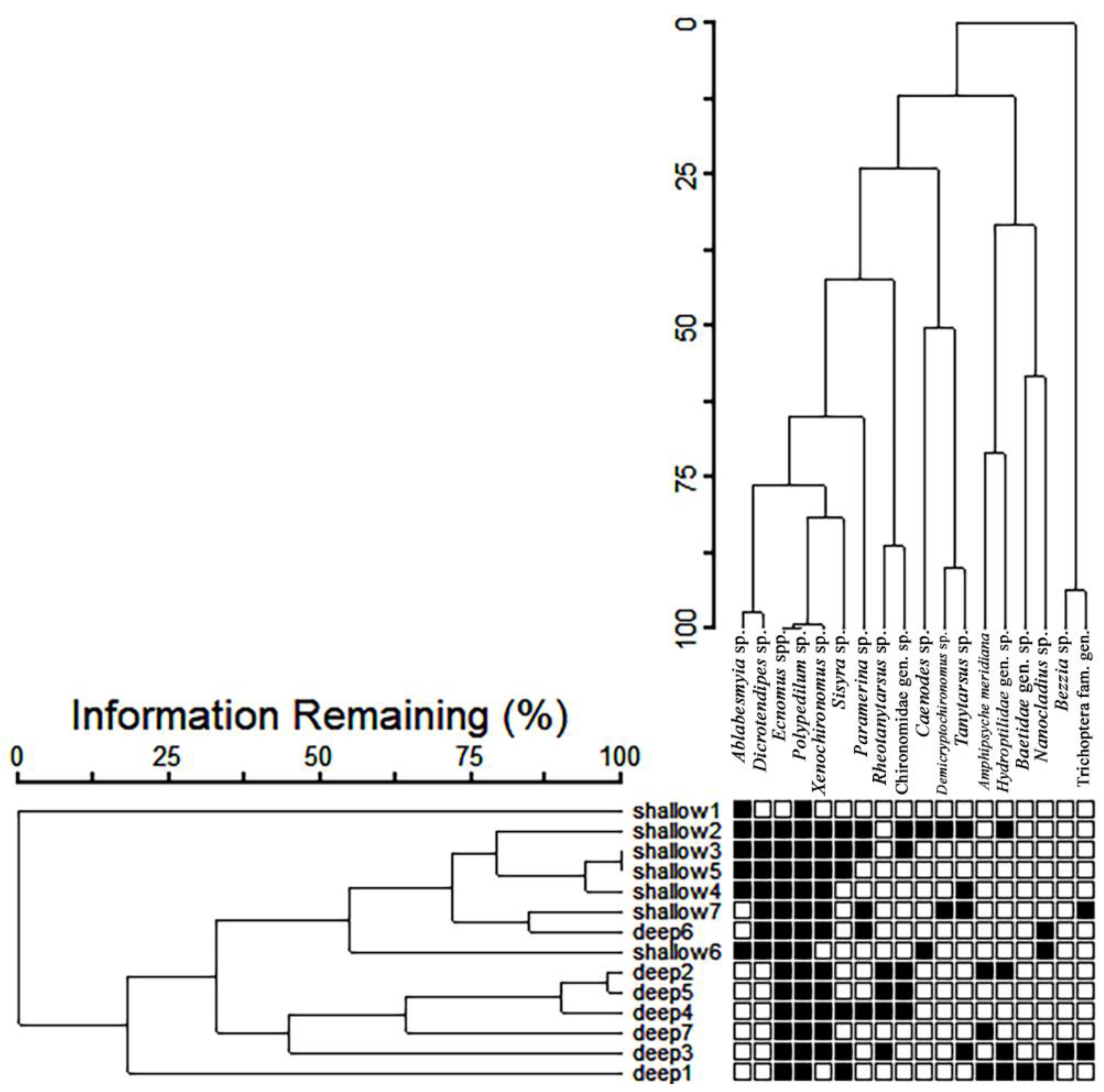
3.2. Composition and Abundance of Associated Aquatic Insects
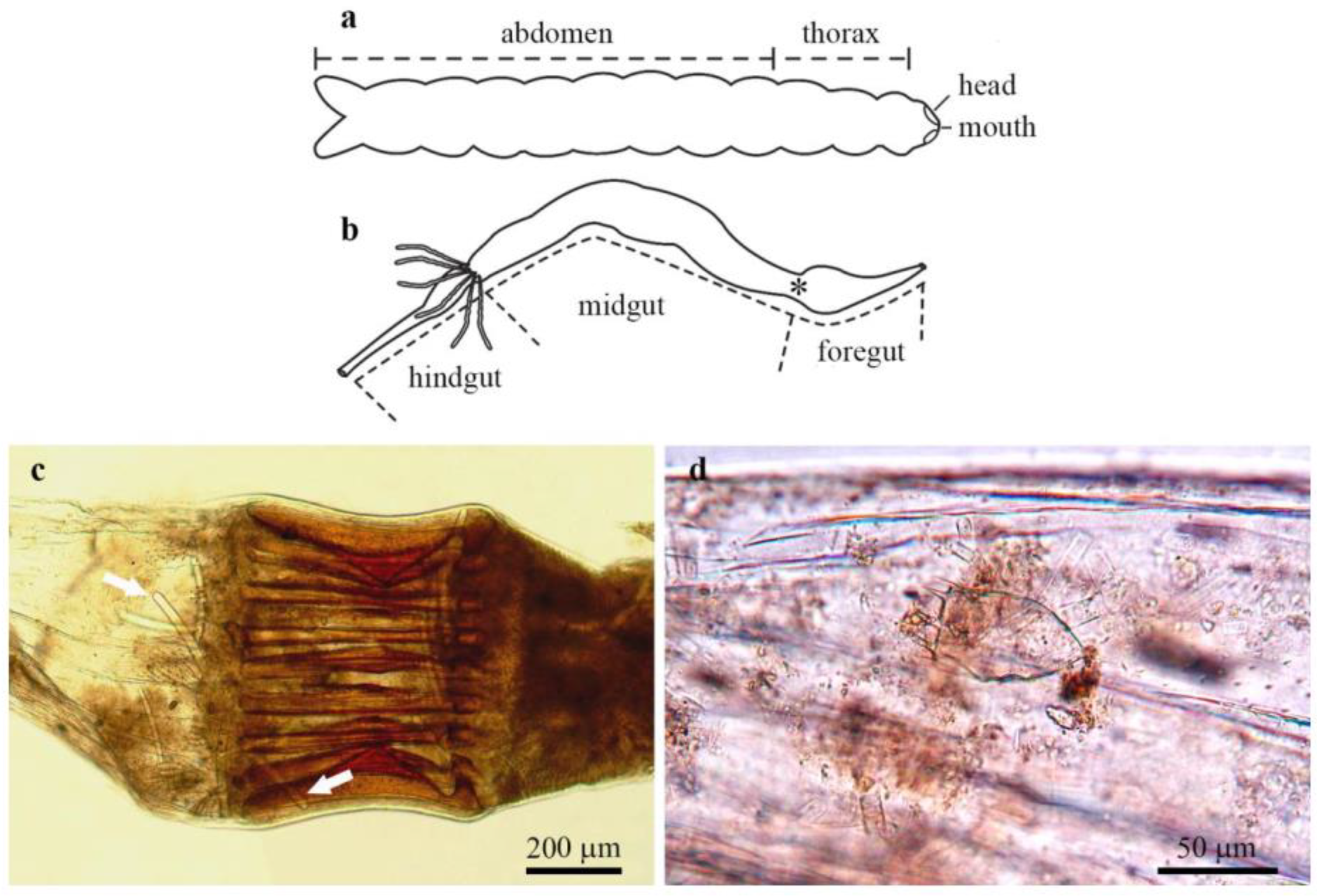
3.3. Gut Content Analysis
4. Discussion
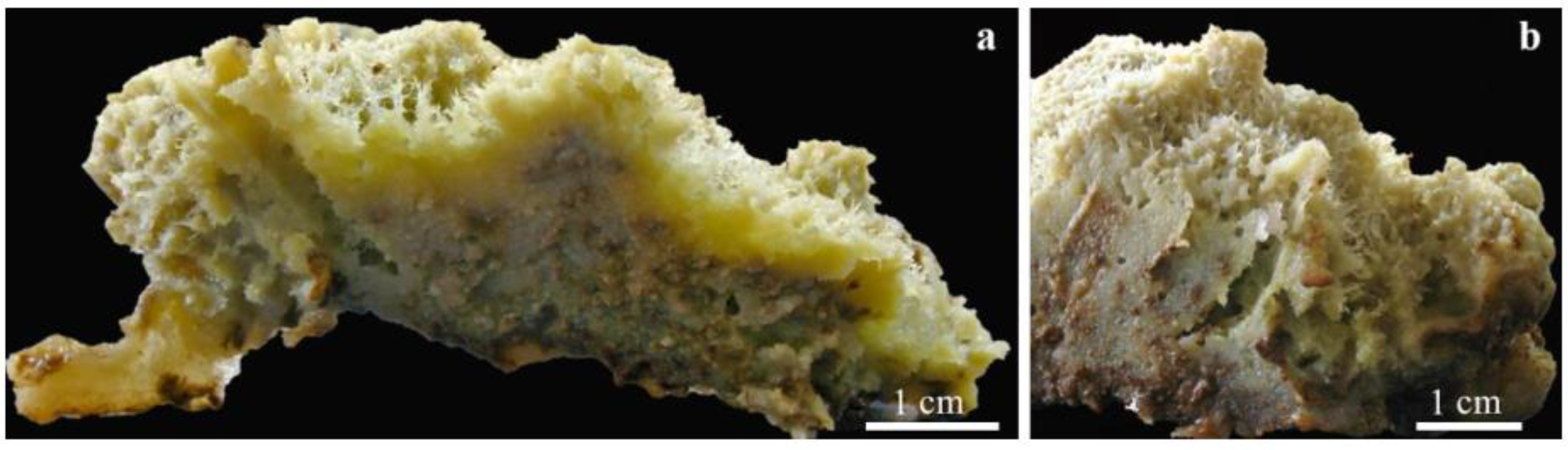
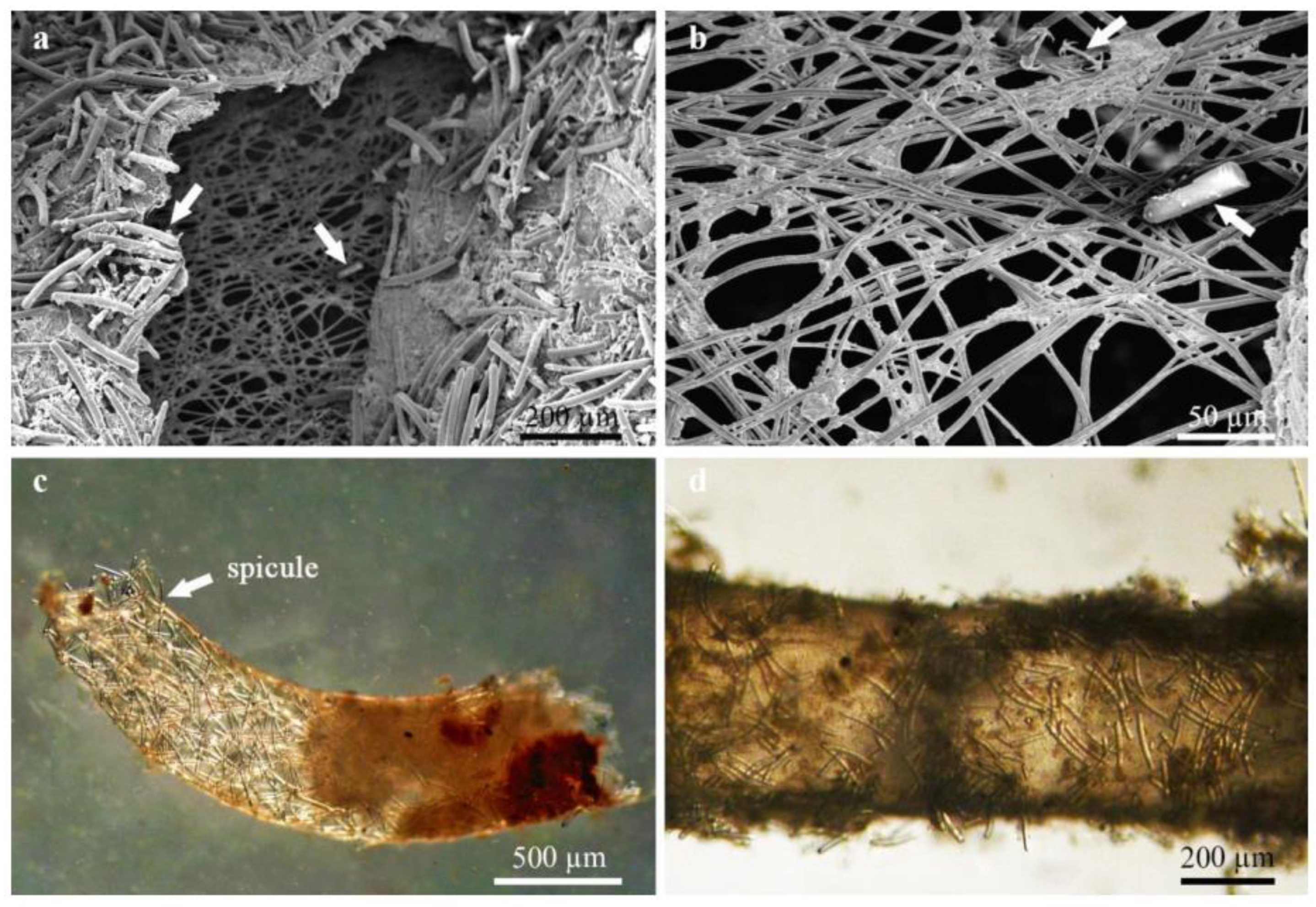
4.1. Freshwater Sponges as Microhabitat for Associated Insects
4.2. Associated Insects and Environmental Conditions
4.3. Aquatic Insect Abundance, Sponge Size and Body Architecture
4.4. Interspecific Relationships between Aquatic Insects and Sponges
4.5. Sponges and Gut Content of Their Associated Aquatic Insects
4.6. Biodiversity and Conservation Perspectives
Synthesis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manconi, R.; Pronzato, R. Global Diversity of Sponges (Porifera: Spongillina) in Freshwater. Hydrobiologia 2008, 595, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manconi, R.; Pronzato, R. Chapter 8—Phylum Porifera. In Thorp and Covich’s Freshwater Invertebrates, 4th ed.; Thorp, J.H., Rogers, D.C., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 133–157. ISBN 978-0-12-385026-3. [Google Scholar]
- Manconi, R.; Pronzato, R. Chapter 3—Phylum Porifera. In Thorp and Covich’s Freshwater Invertebrates, 4th ed.; Thorp, J.H., Rogers, D.C., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 39–83. ISBN 978-0-12-385028-7. [Google Scholar]
- Skelton, J.; Strand, M. Trophic Ecology of a Freshwater Sponge (Spongilla Lacustris) Revealed by Stable Isotope Analysis. Hydrobiologia 2013, 709, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisz, J.B.; Lindquist, N.; Martens, C.S. Do Associated Microbial Abundances Impact Marine Demosponge Pumping Rates and Tissue Densities? Oecologia 2008, 155, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiswig, H.M. Particle Feeding in Natural Populations of Three Marine Demosponges. Biol. Bull. 1971, 141, 568–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morganti, T.M.; Ribes, M.; Yahel, G.; Coma, R. Size Is the Major Determinant of Pumping Rates in Marine Sponges. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morganti, T.M.; Ribes, M.; Moskovich, R.; Weisz, J.B.; Yahel, G.; Coma, R. In Situ Pumping Rate of 20 Marine Demosponges Is a Function of Osculum Area. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 583188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledda, F.D.; Pronzato, R.; Manconi, R. Mariculture for Bacterial and Organic Waste Removal: A Field Study of Sponge Filtering Activity in Experimental Farming. Aquac. Res. 2014, 45, 1389–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manconi, R.; Pronzato, R. How to Survive and Persist in Temporary Freshwater? Adaptive Traits of Sponges (Porifera: Spongillida): A Review. Hydrobiologia 2016, 782, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, T.M.; Reiswig, H.M.; Ricciardi, A. Porifera. In Ecology and Classification of North American Freshwater Invertebrates; Thorp, J.H., Covich, A.P., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 97–133. [Google Scholar]
- Pronzato, R.; Manconi, R. Atlas of European Freshwater Sponges. Ann. Mus. Civ. Storia Nat. Ferrara 2001, 4, 3–64. [Google Scholar]
- Reiswig, H.M.; Frost, T.M.; Ricciardi, A. Porifera. In Ecology and Classification of North American Freshwater Invertebrates, 3rd ed.; Thorp, J.H., Covich, A.P., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2010; pp. 91–123. [Google Scholar]
- Manconi, R.; Ruengsawang, N.; Vannachak, V.; Hanjavanit, C.; Sangpradub, N.; Pronzato, R. Biodiversity in South East Asia: An Overview of Freshwater Sponges (Porifera: Demospongiae: Spongillina). J. Limnol. 2013, 72, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, T.; Mori, S. Preliminary Hydrobiological Survey of Some Southeast Asian Inland Waters. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1970, 2, 77–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangsurasak, C.; Hsieh, H.-N.; Wongphathanakul, W.; Wirojanagud, W. Water Quality Modeling in the Nam Pong River, Northeast Thailand. ScienceAsia 2006, 32, 071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollution Control Department. Thailand State of Pollution Report 2007; Pollution Control Department: Bangkok, Thailand, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Van Zalinge, N.; Degen, P.; Pongsri, C.; Nuov, S.; Jensen, J.G.; Nguyen, V.H.; Choulamany, X. The MekongRiverSystem; RAP publication 16; FAO Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ruengsawang, N. The Distribution, Growth, Reproduction, and Ecology of Freshwater Sponges in the Pong River. Ph.D. Dissertation, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, Thailand, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ruengsawang, N.; Sangpradub, N.; Hanjavanit, C.; Manconi, R. Biodiversity Assessment of the Lower Mekong Basin: A New Species of Corvospongilla (Porifera: Spongillina: Spongillidae) from Thailand. Zootaxa 2012, 3320, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manconi, R.; Erpenbeck, D.; Fromont, J.; Wörheide, G.; Pronzato, R. Discovery of the Freshwater Sponge Genus Corvospongilla Annandale (Porifera: Spongillida) in Australia with the Description of a New Species and Phylogeographic Implications. Limnology 2022, 23, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manconi, R.; Pronzato, R. The Genus Corvospongilla Annandale, 1911 (Porifera: Demospongiae: Spongillida) from Madagascar Freshwater with Description of a New Species: Biogeographic and Evolutionary Aspects. Zootaxa 2019, 4612, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morse, J.C.; Yang, L.; Tian, L. Aquatic Insects of China Useful for Monitoring Water Quality, 1st ed.; Hohai University Press: Nanjing, China, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Epler, J.H. Identification Manual for the Larval Chironomidae (Diptera) of North and South Carolina; North Carolina Department of Environment and Natural Resources: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sangpradub, N.; Boonsoong, B. Identification of Freshwater Invertebrates of the Mekong River and Its Tributaries; Mekong River Commission: Vientiane, Laos, 2006; ISBN 978-92-95061-00-2. [Google Scholar]
- Cranston, P.S. The Chironomidae Larvae Associated with the Tsunami-impacted Waterbodies of the Coastal Plain of Southwestern Thailand. Raffles Bull. Zoo. 2007, 55, 231–244. [Google Scholar]
- Sangpradub, N.; Giller, P.S. Gut Morphology, Feeding Rate and Gut Clearance in Five Species of Caddis Larvae. Hydrobiologia 1994, 287, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manconi, R.; Ruengsawang, N.; Ledda, F.D.; Hanjavanit, C.; Sangpradub, N. Biodiversity Assessment in the Lower Mekong Basin: First Record of the Genus Oncosclera (Porifera: Spongillina: Potamolepidae) from the Oriental Region. Zootaxa 2012, 3544, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annandale, N. Notes on the freshwater fauna of India. No. 5. Some animals found with Spongilla carteri in Calcutta. J. Asiat. Soc. Bengal 1906, 2, 187–196. [Google Scholar]
- Schröder, K. Spongillidenstudien VII, Susswasserschwamme von Neuseeland, Borneo und Madagaskar. Zool. Anz. 1935, 109, 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Mansell, M.W. Neuropterology in Southern Africa. In Recent Research in Neuropterology: Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Neuropterology (Insecta, Megaloptera, Raphidioptera, Planipennia), Hamburg, Germany, 20–26 August 1984; Gepp, J., Aspock, H., Hölzel, H., Eds.; Gedruckt von Druckhaus Thalerhof: Österreich, Austria, 1986; pp. 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, A. New Caledonian Hydroptilidae (Trichoptera), with New Records, Descriptions of Larvae and a New Species. Aquat. Insects 1995, 17, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, A.; Johanson, K. Review of the New Caledonian Species of Acritoptila Wells, 1982 (Trichoptera, Insecta), with Descriptions of 3 New Species. ZooKeys 2014, 397, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forteath, G.N.R.; Osborn, A.W. Biology, Ecology and Voltinism of the Australian Spongillafly Sisyra Pedderensis Smithers (Neuroptera: Sisyridae). Pap. Proc. R. Soc. Tasman. 2012, 146, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forteath, G.N.R.; Purser, J.; Osborn, A.W. A New Species of Sisyra Burmeister 1839 (Neuroptera: Sisyridae) from Four Springs Lake and Wadley’s Dam, Northern Tasmania. Austral Entomol. 2015, 54, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavesi, P. Di una spugna d’acqua dolce nuova per l’Italia. Rendiconti del Reale Istituto Lombardo di Scienze e Lettere Ser. II 1881, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Arndt, W. Porifera, Schwämme, Spongien. In Die Tierwelt Deutschlands und der Angrenzenden Meeresteile nach ihren Merkmalen und ihrer Lebensweise 4 (Porifera-Hydrozoa-Coelenterata-Echinodermata); Dahl, F., Ed.; Gustav Fischer Verlag: Leipzig, Germany, 1928; pp. 1–94. [Google Scholar]
- Rezvoi, P.D. Presnovodnye gubki. [Freshwater sponges]. In Fauna SSSR [The Fauna of the USSR]; Rezvoi, P.D., Ed.; Akad Nauk SSSR: Moscow, Russia, 1936; Volume 2. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Berg, K. Biological studies on the river Susaa. Faunistic and biological investigations. Porifera. Folia Limnol. Scand. 1948, 4, 10–23. [Google Scholar]
- Gaumont, J. L’appareil digestif de la larve d’un Planipenne associé aux éponges d’eau douce: Sisyra fuscata. Ann. Soc. Entomol. Fr. (NS) 1965, 1, 335–357. [Google Scholar]
- Moretti, G.; Corallini-Sorcetti, C. Al Lago Trasimeno è arrivata Ceraclea fulva Ramb. (Trichoptera–Leptoceratidae). Riv. Idrobiol. 1980, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Konopacka, A.; Siciński, J. Macrofauna Inhabiting the Colonies of the Sponge Spongilla lacustris (L.) in the River Gać. SIL Proc. 1922–2010 1985, 22, 2968–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaltynov, R.M.; Chernykh, V.I.; Slugina, Z.V.; Karabanov, E.B. The Consortium of the Sponge Lubomirskia Baicalensis in Lake Baikal, East Siberia. Hydrobiologia 1993, 271, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissmair, V.W.; Mildner, P. Zur Kenntnis der Schwammfliegen (Neuroptera: Sisyridae), ihrer Wirte und Wohngewässer in Kärnten. Carinthia II 1995, 105(2), 535–552. [Google Scholar]
- Gugel, J. Life Cycles and Ecological Interactions of Freshwater Sponges (Porifera, Spongillidae) in the River Rhine in Germany. Limnologica 2001, 31, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corallini, C.; Gaino, E. Peculiar Digestion Patterns of Sponge-Associated Zoochlorellae in the Caddisfly Ceraclea Fulva. Tissue Cell 2001, 33, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corallini, C.; Gaino, E. The Caddisfly Ceraclea fulva and the Freshwater Sponge Ephydatia Fluviatilis: A Successful Relationship. Tissue Cell 2003, 35, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaino, E.; Lancioni, T.; La Porta, G.; Todini, B. The Consortium of the Sponge Ephydatia fluviatilis (L.) Living on the Common Reed Phragmites Australis in Lake Piediluco (Central Italy). Hydrobiologia 2004, 520, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, I.D.; Wallace, B.; Philipson, G.N. Keys to the Case-Bearing Caddis Larvae of Britain and Ireland; Freshwater Biological Association—Scientific Publication: Ambleside, UK, 2003; Volume 61, p. 259. [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg, I.; Glyzina, O.; Weinberg, E.; Kravtsova, L.; Rozhkova, N.; Sheveleva, N.; Natyaganova, A.; Bonse, D.; Janussen, D. Types of interactions in consortia of Baikalian sponges. Boll. Mus. Ist. Biol. Univ. Genova 2004, 68, 655–663. [Google Scholar]
- Loru, L.; Pantaleoni, R.A.; Sassu, A. Overwintering Stages of Sisyra iridipennis A. Costa, 1884 (Neuroptera Sisyridae). Ann. Mus. Cívico Stor. Nat. Ferrara 2007, 8, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Schiffels, S. Commensal and parasitic Chironomidae. Lauterbornia 2009, 68, 9–33. [Google Scholar]
- Sokolova, A.M.; Palatov, D.M. Macroinvertebrate Associations of Sponges (Demospongiae: Spongillidae) from some Fresh Waters in the Palaearctic (in Russian). Povolzhskiy J. Ecol. 2014, 4, 618–627. [Google Scholar]
- Palatov, D.M.; Sokolova, A.M. Freshwater Sponges and Their Associated Invertebrates in the Great Lakes Basin (Mongolia). Ukr. J. Ecol. 2017, 7, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zvereva, Y.; Medvezhonkova, O.; Naumova, T.; Sheveleva, N.; Lukhnev, A.; Sorokovikova, E.; Evstigneeva, T.; Timoshkin, O. Variation of Sponge-Inhabiting Infauna with the State of Health of the Sponge Lubomirskia Baikalensis (Pallas, 1776) in Lake Baikal. Limnology 2019, 20, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrovsky, A.M. New Finds and Species of Caddisflies (Trichoptera) in Southeastern Belarus. Inland Water Biol. 2021, 14, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melão, M.G.G.; Rocha, O. Macrofauna Associada a Metania spinata (Cárter, 1881), Porifera, Metaniidae. Acta Limnol. Bras. 1996, 8, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- De Roque, F.O.; Trivinho-Strixino, S.; Couceiro, S.R.M.; Hamada, N.; Volkmer-Ribeiro, C.; Messias, M.C. Species of Oukuriella Epler (Diptera, Chironomidae) inside Freshwater Sponges in Brazil. Rev. Bras. Entomol. 2004, 48, 291–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusari, L.M.; Roque, F.O.; Hamada, N. Sponge-Dwelling Chironomids in the Upper Paraná River (Brazil): Little Known but Potentially Threatened Species. Neotrop. Entomol. 2008, 37, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusari, L.M.; Roque, F.O.; Hamada, N. Oukuriella Pesae, a New Species of Sponge-Dwelling Chironomid (Insecta: Diptera) from Amazonia, Brazil. Zootaxa 2009, 2146, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusari, L.M.; Oliveira, C.S.N.; Hamada, N.; Roque, F.O. New Species of Ablabesmyia Johannsen from the Neotropical Region: First Report of a Sponge-Dwelling Tanypodinae. Zootaxa 2012, 3239, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusari, L.M.; Bellodi, C.F.; Lamas, C.J.E. A New Species of Sponge-Dwelling Oukuriella (Chironomidae) from Brazil. Zootaxa 2014, 3764, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavier, S.; Guillemet, L.; Rhone, M.; Thomas, A. First Report of the Aquatic Genus Climacia McLachlan, 1869 in French Guiana (Neuroptera, Sisyridae). Ephemera 2011, 12, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Hamada, N.; Pes, A.M.O.; Fusari, L.M. First Record of Sisyridae (Neuroptera) in Rio De Janeiro State, Brazil, with Bionomic Notes on Sisyra Panama. Fla. Entomol. 2014, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, D. New Distributional Records for Neotropical Spongillaflies (Neuroptera: Sisyridae). Insecta Mundi 2015, 0400, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ardila-Camacho, A.; Martins, C.C. First Record of Spongillaflies (Neuroptera: Sisyridae) from Colombia. Zootaxa 2017, 4276, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assmar, A.C.; Salles, F.F. Taxonomic and Distributional Notes on Spongilla-Flies (Neuroptera: Sisyridae) from Southeastern Brazil with First Interactive Key to the Species of the Country. Zootaxa 2017, 4273, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.L.; Mower, R.C.; Nelson, C.R. Climacia Californica Chandler, 1953 (Neuroptera: Sisyridae) in Utah: Taxonomic Identity, Host Association and Seasonal Occurrence. Aquat. Insects 2019, 40, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Fernandes, I.S.; Nicacio, G.; Rodrigues, G.G.; Silva, F.L. da Freshwater Sponge-Dwelling Chironomidae (Insecta, Diptera) in Northeastern Brazil. Biotemas 2019, 32, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, H.P. The Life History of Climacia areolaris (Hagen), a Neuropterous “Parasite” of Fresh Water Sponges. Am. Midl. Nat. 1952, 47, 130–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfin, S.I.; Gurney, A.B. The Spongilla-Flies, with Special Reference to Those of the Western Hemisphere (Sisyridae, Neuroptera). Proc. U. S. Natl. Mus. 1956, 105, 421–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Roback, S.S. Insects Associated with the Sponge Spongilla fragilis in the Savannah River. Not. Nat. 1968, 412, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Heiman, D.R.; Knight, A.W. A North American Trichopteran Larva Which Feeds on Freshwater Sponges (Trichoptera: Leptoceridae; Porifera: Spongillidae). Am. Midl. Nat. 1970, 84, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirrier, M.A. Some Fresh-Water Sponge Hosts of Louisiana and Texas Spongilla-Flies, with New Locality Records. Am. Midl. Nat. 1969, 81, 573–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirrier, M.A.; Arceneaux, Y.M. Studies on Southern Sisyridae (Spongilla-Flies) with a Key to the Third-Instar Larvae and Additional Sponge-Host Records. Am. Midl. Nat. 1972, 88, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resh, V.H. Life Cycles of Invertebrate Predators of Freshwater Sponge. In Aspects of Sponge Biology; Harrison, F.W., Cowden, R.R., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1976; pp. 299–314. ISBN 978-0-12-327950-7. [Google Scholar]
- Pennak, R.W. Fresh-Water Invertebrates of the United States, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA; Ronald Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Matteson, J.D.; JacobiI, G.Z. Benthic Macroinvertebrates Found on The Freshwater Sponge Spongilla lacustris. Gt. Lakes Entomol. 1980, 3, 162–172. [Google Scholar]
- Stoaks, R.D.; Neel, J.K.; Post, R.L. Observations on North Dakota Sponges (Haplosclerina: Spongillidae) and Sisyrids (Neuroptera: Sisyridae). Gt. Lakes Entomol. 1983, 16, 171–176. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, W.H. First Record of Climacia Californica (Neuroptera: Sisyridae) and Its Host Sponge, Ephydatia mulleri (Porifera: Spongillidae), from Idaho with Water Quality Relationships. Gt. Basin Nat. 1985, 45, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Pupedis, R.J. Foraging Behavior and Food of Adult Spongila-Flies (Neuroptera: Sisyridae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1987, 80, 758–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitlock, H.N.; Morse, J.C. Ceraclea Enodis, a New Species of Sponge-Feeding Caddisfly (Trichoptera: Leptoceridae) Previously Misidentified. J. North Am. Benthol. Soc. 1994, 13, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, D.E. Spongillaflies (Neuroptera: Sisyridae) of North America with a Key to the Larvae and Adults. Zootaxa 2006, 1357, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Cover, M.R.; Resh, V.H. Global Diversity of Dobsonflies, Fishflies, and Alderflies (Megaloptera; Insecta) and Spongillaflies, Nevrorthids, and Osmylids (Neuroptera; Insecta) in Freshwater. In Freshwater Animal Diversity Assessment; Developments in Hydrobiology; Balian, E.V., Lévêque, C., Segers, H., Martens, K., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 409–417. ISBN 978-1-4020-8259-7. [Google Scholar]
- Rothfuss, A.H.; Heilveil, J.S. Distribution of Sisyridae and Freshwater Sponges in the Upper-Susquehanna Watershed, Otsego County, New York with a New Locality for Climacia areolaris (Hagen). Am. Midl. Nat. 2018, 180, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, D.E.; Courtney, G.W. The Aquatic Neuropterida of Iowa. Proc. Entomol. Soc. Wash. 2020, 122, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, S. Current-Induced Flow through Living Sponges in Nature. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 2069–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, T.M. Clearance Rate Determinations for the Fresh Water Sponge Spongilla Lacustris Effects of Temperature Particle Type and Concentration and Sponge Size. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1980, 90, 330–356. [Google Scholar]
- Hanjavanit, C.; Tangpirotewong, N. Comparison of Benthic Macroinvertebrate Community Structure in Relation to Different Types of Human Disturbance along the Pong River, Khon Kaen Province (Thai). Asia-Pac. J. Sci. Technol. 2007, 12, 402–419. [Google Scholar]
- Annandale, N. Freshwater Sponges, Hydroids and Polyzoa. In The Fauna of British India, including Ceylon and Burma; Shipley, A.E., Ed.; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 1911; pp. 49–94. [Google Scholar]
- Koukouras, A.; Russo, A.; Voultsiadou-Koukoura, E.; Arvanitidis, C.; Stefanidou, D. Macrofauna Associated with Sponge Species of Different Morphology. Mar. Ecol. 1996, 17, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, G.; Omena, E. Influence of Sponge Morphology on the Composition of the Polychaete Associated Fauna from Rocas Atoll, Northeast Brazil. Coral Reefs 2003, 22, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, P.J. Adaptive Strategies of Amphipsyche Larvae (Trichoptera: Hydropsychidae) Downstream of a Tropical Impoundment. In The Ecology of Regulated Streams; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1979; pp. 237–255. [Google Scholar]
- De Oliveira Roque, F.; Trivinho-Strixino, S. Xenochironomus ceciliae (Diptera: Chironomidae), a New Chironomid Species Inhabiting Freshwater Sponges in Brazil. Hydrobiologia 2005, 534, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sata, N.U.; Kaneniwa, M.; Masuda, Y.; Ando, Y.; Iida, H. Fatty Acid Composition of Two Species of Japanese Freshwater Sponges Heterorotula multidentata and Sponilla alba. Fish. Sci. 2002, 68, 236–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffan, A.W. Ectosymbiosis in aquatic insects. In Symbiosis; Henry, M.S., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, USA, 1967; pp. 207–289. [Google Scholar]
- Sangpradub, N.; Inmuong, Y.; Hanjavanit, C.; Inmuong, U. Biotic Indices for Biological Classification of Water Quality in the Pong Catchment Using Benthic Macroinvertebrates. KKU Sci. J. 1998, 6, 289–304. [Google Scholar]
- Sriariyanuwath, E.; Sangpradub, N.; Hanjavanit, C. Diversity of Chironomid Larvae in Relation to Water Quality in the Phong River, Thailand. Aquac. Aquar. Conserv. Legis. 2015, 8, 933–945. [Google Scholar]
- Weissmair, W.; Waringer, J. Identification of the Larvae and Pupae of Sisyra Fuscata (Fabricius, 1793) and Sisyra Terminalis Curtis, 1854 (Insecta: Planipennia: Sisyridae), Based on Austrian Material. Aquat. Insects 1994, 16, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navás, L. Névroptères et Insectes Voisins. Chine et Pays Environnants. 4e Série. Notes d'Entomologie Chinoise 1933, 1, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Lin, A.; Wang, D.; Liu, X. The First Mitochondrial Genome of Spongillafly from Asia (Neuroptera: Sisyridae: Sisyra aurorae Navás, 1933) and Phylogenetic Implications of Osmyloidea. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2021, 6, 2369–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monserrat, V.J. Sobre los Sisiridos de la Región Oriental (Neuroptera, Planipennia, Sisyridae). Rev. Esp. Entomol. 1982, 57, 165–186. [Google Scholar]
- New, T.R. The Neuroptera of Malesia; Brill: Leiden, Netherlands, 2003; 204p. [Google Scholar]
- Boon, P.J. Gastric Mill Structure and Its Phylogenetic Significance in Larval Hydropsychidae (Trichoptera). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 1985, 84, 301–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; Da Fonseca, G.A.; Kent, J. Biodiversity Hotspots for Conservation Priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- New Species Discoveries in The Greater Mekong. 2020. Available online: https://www.wwf.org.la/publications/new_species_discoveries_in_the_greater_mekong_2020/ (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Ruengsawang, N.; Sangpradub, N.; Artchawakom, T.; Pronzato, R.; Manconi, R. Rare Freshwater Sponges of Australasia: New Record of Umborotula Bogorensis (Porifera: Spongillida: Spongillidae) from the Sakaerat Biosphere Reserve in Northeast Thailand. Eur. J. Taxon. 2017, 260, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Calcinai, B.; Cerrano, C.; Núñez-Pons, L.; Pansini, M.; Thung, D.C.; Bertolino, M. A New Species of Spongilla (Porifera, Demospongiae) from a Karst Lake in Ha Long Bay (Vietnam). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.J.; McGrath, E.; Biggerstaff, A.; Bates, T.; Cárdenas, C.A.; Bennett, H. Global Conservation Status of Sponges. Conserv. Biol. 2015, 29, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.-L.; Chen, J.-E.; Yiew, T.-H.; Habibullah, M.S. Habitat Change and Biodiversity Loss in South and Southeast Asian Countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 63260–63276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soest, R.W.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Vacelet, J.; Dohrmann, M.; Erpenbeck, D.; de Voogd, N.J.; Santodomingo, N.; Vanhoorne, B.; Kelly, M.; Hooper, J.N. Global Diversity of Sponges (Porifera). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.G.; Lawton, J.H.; Shachak, M. Organisms as Ecosystem Engineers. In Ecosystem Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; pp. 130–147. [Google Scholar]
- Ormerod, S.J. A Golden Age of River Restoration Science? Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2004, 14, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Taxa | Number of Individuals | Total | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depth 0.3 m | Depth 1.0 m | ||||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | ||
| Ephemeroptera | |||||||||||||||
| Baetidae gen. sp. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| Caenidae | |||||||||||||||
| Caenodes sp. | - | 2 | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3 |
| Polymitarcyidae | |||||||||||||||
| Povilla heardi | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | * | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Neuroptera | |||||||||||||||
| Sisyridae | |||||||||||||||
| Sisyra sp. | - | 3 | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | 2 | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | 9 |
| Trichoptera | |||||||||||||||
| Ecnomidae | |||||||||||||||
| Ecnomus spp. | - | 8 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 21 | 27 | 12 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 92 |
| Hydropsychidae | |||||||||||||||
| Amphipsyche meridiana | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 62 | 20 | - | - | - | - | 2 | 84 |
| Hydroptilidae gen. sp. | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 4 | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | 7 |
| Trichoptera fam. gen. | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | 2 |
| Diptera | |||||||||||||||
| Chironomidae | |||||||||||||||
| Ablabesmyia sp. | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 10 |
| Demicryptochironomus sp. | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3 |
| Dicrotendipes sp. | - | 2 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 14 |
| Nanocladius sp. | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 3 |
| Paramerina sp. | - | 3 | 2 | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | 8 |
| Polypedilum sp. | 2 | 12 | 9 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 7 | 3 | 4 | 8 | 6 | 8 | 3 | 3 | 76 |
| Rheotanytarsus sp. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | - | 9 |
| Tanytarsus sp. | - | 1 | - | 2 | - | - | 2 | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | 6 |
| Xenochironomus sp. | - | 9 | 10 | 1 | 3 | - | 2 | - | 7 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 43 |
| Chironomidae gen. sp. | - | 1 | 4 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | 8 |
| Ceratopogonidae | |||||||||||||||
| Bezzia sp. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| Total | 3 | 47 | 38 | 11 | 16 | 6 | 19 | 94 | 65 | 29 | 21 | 13 | 9 | 8 | 379 |
| Insect Taxa | Sponge Taxa | References | Biogeographic Region/Country |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ephemeroptera (Baetidae, Caenidae, Polymitarcyidae) Neuroptera (Sisyridae) Trichoptera (Ecnomidae, Hydroptilidae, Hydropsychidae) Diptera (Ceratopogonidae, Chironomidae) | Corvospongilla siamensis | Present paper, Annandale [29], Schröder [30] | Oriental-Himalayan Thailand; Borneo; India; Java; Philippines |
| Eunapius carteri | |||
| Radiospongilla crateriformis | |||
| Spongilla alba Spongillida fam. gen. sp. | |||
| --- | Spongilla alba | Schröder [30], Mansell [31] | Afrotropical Madagascar; South Africa |
| Spongillida fam. gen. sp. | |||
| Trichoptera (Hydroptilidae) | Spongillida fam. gen. sp. | Wells [32], Wells & Johanson [33], Forteath & Osborne [34], Forteath et al. [35] | Australasian Australia; New Zealand; New Caledonia; Tasmania |
| Diptera (Chironomidae) Ephemeroptera (Baetidae, Caenidae) Neuroptera (Sisyridae) Megaloptera (Sialidae) Trichoptera (Apataniidae, Brachycentridae, Ecnomidae, Hydropsychidae, Hydroptilidae, Leptoceridae, Limnephilidae, Polycentropodidae, Psychomyiidae) | Ephydatia fluviatilis | Pavesi [36], Arndt [37], Rezvoi [38], Berg [39], Gaumont [40], Moretti & Corallini-Sorcetti [41], Konopacka & Socinski [42], Kamaltynov et al. [43], Weissmair & Mildner [44], Gugel [45], Corallini & Gaino [46,47], Gaino et al. [48], Wallace et al. [49], Weinberg et al. [50], Loru et al. [51], Schiffels [52], Sokolova & Palatov [53], Palatov & Sokolova [54], Zvereva et al. [55], Ostrovsky [56] | Palaearctic Algeria; Austria; China; East Siberia; Denmark; England; France; Germany; Italy; Japan; Mongolia; Poland; Russia; Scandinavia; Serbia; Spain |
| Ephydatia muelleri | |||
| Eunapius fragilis | |||
| Heteromeyenia sp. | |||
| Lubomirskia baikalensis | |||
| Spongilla lacustris Spongillida fam. gen. sp. | |||
| Diptera (Chironomidae, Simuliidae) Coleoptera (Dytiscidae) Ephemeroptera (Polymitarcyidae, Tricorythidae) Hemiptera (Belostomatidae) Lepidoptera (Pyralidae) Neuroptera (Sisyridae) Odonata (Coenagrionidae, Libellulidae) Trichoptera (Hydropsychidae, Polycentropodidae) | Acalle recurvata | Melão & Rocha [57], Roque et al. [58], Fusari et al. [59,60,61,62], Clavier et al. [63], Hamada et al. [64], Bowles [65], Ardila-Camacho & Martins [66], Assmar & Salles [67], Fisher et al. [68], da Silva Fernandes [69] | Neotropical Argentina; Belize; Bolivia; Brazil; Chile; Cuba; French Guiana; Guatemala; Guyana; Honduras; Mexico; Panama; Paraguay; Peru; Suriname; Uruguay; Venezuela |
| Drulia uruguayensis | |||
| Corvoheteromeyenia australis | |||
| Corvospongilla seckti | |||
| Heteromeyenia cristalina | |||
| Metania spinata | |||
| Metania reticulata | |||
| Oncosclera navicella | |||
| Oncosclera spinifera | |||
| Radiospongilla inesi | |||
| Trochospongilla paulula | |||
| Neuroptera (Sisyridae) Megaloptera Trichoptera (Leptoceridae) | Eunapius fragilis | Brown [70], Parfin & Gurney [71], Roback [72], Heiman & Knight [73], Poirrier [74], Poirrier & Arceneaux [75], Resh [76], Pennak [77], Matteson & Jacobi [78], Stoakes et al. [79], Clark [80], Pupedis [81], Whitlock & Morse [82], Bowles [65,83], Cover & Resh [84], Rothfuss & Heilveil [85], Fisher et al. [68], Bowles & Courtney [86] | Nearctic United States of America Canada |
| Ephydatia muelleri | |||
| Ephydatia fluviatilis | |||
| Eunapius igloviformis | |||
| Dosilia radiospiculata | |||
| Heteromeyenia argirosperma | |||
| Heteromeyenia baileyi | |||
| Heteromeyenia repens | |||
| (as H. baileyi) | |||
| Racekiela ryderi | |||
| (as Heteromeyenia ryderi) | |||
| Radiospongilla crateriformis | |||
| Spongilla lacustris | |||
| Ephydatia robusta | |||
| (as Meyenia subdivisa) | |||
| Trochospongilla horrida | |||
| Trochospongilla leidii | |||
| (as T. leidyi) | |||
| Trochospongilla muelleri | |||
| Trochospongilla pennsylvanica | |||
| (as Tubella pennsylvanica) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruengsawang, N.; Sangpradub, N.; Manconi, R. Aquatic Insects in Habitat-Forming Sponges: The Case of the Lower Mekong and Conservation Perspectives in a Global Context. Diversity 2022, 14, 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14110911
Ruengsawang N, Sangpradub N, Manconi R. Aquatic Insects in Habitat-Forming Sponges: The Case of the Lower Mekong and Conservation Perspectives in a Global Context. Diversity. 2022; 14(11):911. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14110911
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuengsawang, Nisit, Narumon Sangpradub, and Renata Manconi. 2022. "Aquatic Insects in Habitat-Forming Sponges: The Case of the Lower Mekong and Conservation Perspectives in a Global Context" Diversity 14, no. 11: 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14110911
APA StyleRuengsawang, N., Sangpradub, N., & Manconi, R. (2022). Aquatic Insects in Habitat-Forming Sponges: The Case of the Lower Mekong and Conservation Perspectives in a Global Context. Diversity, 14(11), 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14110911










