Abstract
Resource utilization strategies of avian migrants are a major concern for conservation and management. Understanding seasonal habitat selection by migratory birds helps us explain the ongoing continental declines of migratory bird populations. Our objective was to compare the second-order and third-order habitat selection by the American White Pelican (Pelecanus erythrorhynchos; hereafter pelican) between the breeding and non-breeding grounds. We tested the Lack hypothesis that habitat selection by migratory birds is stronger on the breeding grounds than on the non-breeding grounds. We used random-effect Dirichlet-multinomial models to estimate the second-order habitat selection between the seasons with the GPS locations of 32 tracked pelicans. We used Gaussian Markov random field models to estimate the third-order habitat selection by pelicans at the breeding and non-breeding grounds, accounting for spatial autocorrelation. Pelicans strongly selected waterbodies and wetlands at both non-breeding and breeding grounds, tracking their foraging habitats between the seasons at the home range level. However, pelicans exhibited seasonal differences in the strength of the third-order selection of wetlands and waterbodies with foraging habitat selection being stronger at the breeding grounds than at the non-breeding grounds, supporting the Lack hypothesis.
1. Introduction
Habitat and resource selection by animals is a central topic of animal ecology [1,2,3]. Habitats provide animals with food, shelter (e.g., from predators and inclement climate), and reproductive sites in a hierarchical manner [3,4]. Johnson [5] defines habitat selection as a 4-level hierarchical behavioral process. The first-order habitat selection is for species’ geographic range. The second-order selection determines the placement of home ranges on the landscape. The third-order selection is the nonproportional use of habitat patches to their availability within home ranges. The fourth-order selection is for the locations of resource procurement [5]. Different ecological processes may govern habitat selection by animals on the different levels. For instance, birds and mammals may select habitats for the locations of home ranges to maximize food and resource availability and acquisition, whereas landscape heterogeneity and predation avoidance may be the primary factors influencing the third- or fourth-order habitat selection [6,7,8]. However, predator avoidance may affect habitat or resource selection consistently across the hierarchical levels [9,10]. Few studies have investigated multiscale habitat selection by waterbirds [11,12].
Animals may exhibit seasonal shifts in habitat and resource selection in response to seasonal variation in resource availability [13,14]. Migratory birds make seasonal movements between their breeding and non-breeding grounds each year [15]. Differences in resource availability and habitat conditions between spatially disjoint seasonal habitats may result in seasonal variation in habitat selection by migratory birds. Lack [16] proposed that migratory birds would move to high-latitude habitats for greater reproductive success with higher resource productivity and longer daylight time than on the non-breeding grounds in low latitudes during the summer [17]. Lack’s hypothesis predicts that migratory birds would exhibit a stronger selection of foraging habitats on the breeding grounds than on the non-breeding grounds [16].
Anthropogenic disturbances result in habitat fragmentation and loss, thereby reducing the amount of available habitats [18]. The habitat amount hypothesis posits that reductions in habitats would cause population declines [18,19]. One third of North American avian populations, many of which are migratory birds, have declined during the past half century [20]. Habitat loss on the breeding and non-breeding grounds can result in the population declines of wetland-dwelling species. Studies of seasonal differences in the habitat selection and requirements of migratory waterbirds can help us understand the causes of waterbird population declines and develop plans to conserve and manage migratory waterbird populations. However, there are fewer studies of the ecology of migratory birds at the non-breeding (or wintering) grounds than at the breeding grounds and habitat selection by migration birds during the annual cycle [21,22,23].
The American White Pelican (Pelecanus erythrorhynchos) is one of the largest flying birds of North America (King et al. 2017). Pelican populations had declined from the 1970s to the 1990s but have recovered since the 1990s (King 2005). Pelicans have recently become an economically important species due to increases in abundance and their impacts on the channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) aquacultural operation (King 2005). Pelicans wintering in the Gulf of Mexico (GOM) migrate to the Northern Great Plains each year [24,25,26]. Furthermore, although pelicans are piscivorous, primarily feeding on fish, they also eat salamanders and crawfish in wetlands and shallow waterbodies [27,28,29]. Waterbodies not only provide food, but also shelter against mammalian predators. Inland freshwater wetlands are an important part of the foraging habitat of pelicans. We hypothesized that pelicans would select wetlands and waterbodies at the home-range level for food resources at both breeding and non-breeding grounds. About 50% of wetlands were lost due to changes in land use and warming in the lower 48 states of the US in the 1970s and 1980s [30]. Understanding the seasonal habitat selection and requirements of pelicans can help avian ecologists assess the effects of habitat losses and changes in land use and land cover (LULC) on pelican population dynamics. However, no studies have investigated the second- and third-order habitat selection by pelicans simultaneously.
Our objectives were to compare pelican habitat selection between the breeding and non-breeding seasons and test the following two predictions. First, pelicans would select wetlands and waterbodies at both the second and third order for food acquisition on both breeding and non-breeding grounds. Second, pelicans would exhibit stronger third-order selection of wetlands and waterbodies for foraging habitats on the breeding than the non-breeding grounds.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Areas and GPS Tracking of American White Pelicans
Pelicans have two metapopulations, which are divided by the Continental Divide [24]. The American white pelicans east of the Continental Divide migrate between the Northern Great Plains (the breeding grounds) and the GOM (the non-breeding grounds) [25,31]. Pelicans remain on the breeding ground from May through September and spend winter on the non-breeding grounds from October to May [25]. In this study, the boundary of the breeding range was delineated to encompass the geographic locations of known pelican colonies [24] and the survey transects of non-zero pelican relative abundance in the North America Breeding Bird Survey [25]. The 35° N latitudinal line was used as the southern boundary of pelican’s non-breeding range [25].
We captured pelicans at sites near aquaculture-intensive areas in Alabama, Arkansas, Louisiana, and Mississippi, USA using rocket nets and modified foot-hold traps during March and April from 2002 to 2009 [32]. We aged captured pelicans (≥3 yr old = adult; <3 yr old = immature) by plumage and eye and skin color characteristics, and sexed captured pelicans by culmen length [33]. We attached 70-g solar-powered GPS transmitters (PTT-100, Microwave Telemetry, Columbia, MD, USA) to captured pelicans using a backpack harness [34].
The GPS transmitters were programmed to collect location data with two different daily tracking schedules: (1) location recording from 500 h to 1900 h from 2002 to 2005 and (2) for consecutive 24 h from 2006 to 2010. The GPS tracking duration of the 32 pelicans ranged from one to a maximum of three years [35]. The 32 GPS tracked pelicans consisted of 25 immature males, 10 adult males, six immature females, and six mature females. Mature pelicans have a greater propensity of spring migration than immature pelicans, and male pelicans depart from the nonbreeding ground earlier than female birds [36]. Pelicans were rarely active during the GPS-off hours of Schedule 1 [37]. We divided the GPS locations of each pelican into the breeding grounds (i.e., locations between the first arrival at and departure from the breeding grounds) and non-breeding grounds (i.e., locations between the first arrival at and departure from the non-breeding grounds). We excluded pelican GPS locations during the seasonal migration from our analysis. All GPS transmitters stopped working at the end of the tracking of each pelican.
2.2. Land Use and Land Cover Data
We used the LULC data from North American Land Change Monitoring System (https://www.mrlc.gov/data/north-american-land-change-monitoring-system; accessed on 1 June 2020) based on MODIS satellite imagery to obtain land cover data [38]. We reclassified the original LULC classes needleleaf forest, broadleaf forest, temperate deciduous forest, mixed forest, and shrubland as woody cover and barren land as developed using the R package raster [39]. Reclassifications resulted in six LULC classes cropland, developed, grassland, waterbody (or water in short), wetland, and woody. We aggregated 250-m LULC raster by a factor 4 and calculated the proportion of each LULC class over 16 250-m grid cells to produce a 1 km resolution raster file for each of six LULC classes using the function aggregate of the package raster. For each individual pelican and for each GPS location, we extracted the selected land cover variables using the function extract of the package raster.
2.3. Habitat Selection
Grassland constituted much less than 1% of the total LULC at the non-breeding ground. Both crop plants and grasses create an open environment without woody stems and may be associated with similar thermal and wind conditions. Furthermore, in the rural areas on the breeding and non-breeding grounds, barren lands and developed areas were often close to cropland and constituted much less than 1% at the breeding ground. Therefore, we combined cropland, grassland, and developed into one LULC class of open, non-woody covers (hereafter, non-woody) for the second-order and third-order habitat selection. Pelicans are soaring birds using thermals and air uplifts for flying. Given that vegetative density is a good predictor of uplift intensity [40], woody and non-woody vegetation classifications are appropriate to distinguish them for thermal and uplift conditions for the purpose of habitat selection by soaring birds.
2.3.1. Random-effect Dirichlet-multinomial Models for the Second-order Habitat Selection
We used random-effect Dirichlet-multinomial distribution models (hereafter, D-M models) to estimate the second-order habitat selection by pelican. Random-effect D-M models were modified from the D-M model of fixed-effect only [41,42]. The distribution of GPS location counts (n1, n2, …, n4) over four different LULC classes was assumed to follow the multinomial distribution, denoted as Mult(). The probabilities (p1, p2, …, p4) of selecting a LULC class were assumed to have a Dirichlet distribution, denoted as Dir() [41]. The D-M models used in this study assume that habitat selection is proportional to resource availability times a type-specific linear preference coefficient or index h (h > 0 and Σh = 1). Resource availability (a) was measured by the proportion of LULC classes within a non-convex polygon which encompassed all GPS locations at the non-breeding or breeding grounds. The greater the coefficient h for an LULC class, the stronger the selection for the LULC class. The D-M model for the second-order habitat selection is of the form:
where N is the total GPS location counts over the four LULC classes per pelican; τ is a parameter to account for the overdispersion of multivariate compositional counts n1, n2, …, and n4; and ai measures LULC availability. The D-M models account for correlations between LULC classes with the Dirichlet distribution. To account for temporal autocorrelation of the same pelican between seasons or years, we developed a new random-effect D-M model for habitat selection with pelican ID as a random effect following a normal distribution; thus,
where μi is a normal variate for pelican individual i (= 1, 2, …, M), and is the variance of the random effect. The exponential function of makes random-effect variates to be non-negative. Our random-effect D-M model is similar to that of Martin, et al. [43] using a univariate random effect.
Unknown parameter h for each LULC class was estimated in the Bayesian framework with the following prior distributions ; ; ; and . The 95% credible intervals (CIs) of selection index h were generated with three Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) chains using software rstan [39]. Each MCMC chain had a total of 2000 iterations with the first 1000 being discarded as a burn-in or warmup period. The convergence of MCMC chains were assessed with the Gelmen-Rubin split index R-hat and rstan’s check_hmc_diagnostics function [44].
2.3.2. Gaussian Markov Random Field Models for Third-order Habitat Selection
We first created a non-convex hull polygon to encompass all pelican GPS locations at the breeding and non-breeding grounds, respectively. Then, we overlaid a 5 km 5 km grid over the polygon and determined the number of pelican GPS locations within each 5-km grid cell within the polygon. In a preliminary analysis, we found that the average hourly movement distance of pelicans during the active hours (900–1700 h) on both the breeding and non-breeding grounds was about 5 km. We used the GPS location count per cell as response variable and the geographic coordinates of grid-cell centroids to build geospatial models to account for spatial autocorrelation. We used this aggregation mainly for the consideration of computational speed and burden. Kang, et al. [45] also demonstrated grid-level spatial models produced a good fit to spatial point data.
We used pelican GPS location count y per cell to measure spatial use intensity. We assumed that pelican GPS location counts (y) followed Poisson distributions with a spatial use intensity λ, that is, the Poisson parameter. The spatial use intensity of pelican was represented as:
where λi is mean pelican occurrence count at a geographic location i; β0 is intercept; βp (p = 1, 2, and 3) is the coefficient of LULC proportions; covariates water (i.e, waterbody), wetland, and woody are the proportions of waterbodies, wetland, and woody cover in the grid cell i; and ui is a spatially correlated random variate evaluated at location i for spatial autocorrelation. To avoid multicollinearity in the third-order habitat selection analysis, we used a backwards stepwise process with the variance inflation factor (VIF) function of the R package uSDM, starting from the initial pool of four LULC predictor variables [46]. At each step, a covariate of the largest VIF value (>4.0) was removed until all remaining covariates have VIF < 4 [47]. We calculated a matrix of pairwise Pearson’s correlation r of the remaining variables and discarded one with greater VIF between two correlated predictors if r > 0.7. Average proportions of non-woody cover had variation inflation factor >4.0 and were excluded from the third-order habitat selection models.
We used Gaussian Markov random field (GMRF) to represent spatially structured random variable u [48]. Spatially autocorrelated error u is assumed to be generated by a continuously indexed Gaussian random field (GF) on a 2-dimension plane [48]. Stochastic partial differential equation (SPDE) is used to approximate the continuous GF with the discretely indexed GMRF. The SPDE uses the vertices of a mesh built with the Voronoi triangulation as the discrete indices (Figure A1) [49]. Therefore, the solution to the SPDE can be assumed to be a stationary GF with the Matern spatial covariance function [48]. In SPDE, the continuous GF is approximated by the finite element method with linear piecewise functions, producing a sparse covariance matrix [48]. The sparseness of GMRF covariance matrices allows the SPDE model to approximate continuous spatial stochastic processes reliably with a fast runtime [49,50]. The Matern spatial covariance function predicts that spatial correlation decreases curvilinearly to 0.1 with distance between two locations increasing to a value ρ, that is, the spatial range parameter.
We implemented the GMRF models in R Template Model Builder (TMB), a C++ template-based statistical software [51], by modifying the codes publicly available from https://kaskr.github.io/adcomp/spde_8cpp-example.html (accessed on 1 June 2020). We built eight models of all possible combinations of three covariates water, wetland, and woody. The R function optim was used to maximize the likelihood function of each model to estimate unknown parameters. We checked if the optimization algorithm converged for each fitting. The maximized likelihood value was used to compute Akaike Information Criterion corrected for small sample size (AICc) and ΔAICc for each of the eight models [52]. The best approximating model has the lowest AICc and a model with ΔAICc < 2.0 is a competing model.
3. Results
A total 46,821 GPS locations of 32 GPS-tracked pelicans were used in this study, including 31,522 locations at the non-breeding ground and 15,299 locations at the breeding grounds. A set of GPS location counts over four LULC classes from a tracked bird comprised a multinomial sample during a season. The number of repeated-measures multinomial samples of a tracked pelican ranged from one to five. The random-effect D-M model used a total of 47 multinomial samples in this study.
Resource availability changed slightly on the non-breeding ground from 2005 to 2010 with more waterbodies in 2010 than in 2005, whereas resource availability was similar at the breeding ground between 2005 and 2010 (Figure 1). The second-order habitat selection index was greatest for waterbodies with its 95% CI exceeding those of wetland, non-woody, and woody covers (Figure 2a). Pelicans exhibited the least selection for woody cover for their home range placement with the 95% CIs being below those of the other three LULC classes (Figure 2a). Despite the greater variability (i.e., wider 95% CIs) of selection index estimates for the breeding than non-breeding seasons, pelicans exhibited similar second-order habitat selection between the breeding and non-breeding seasons, primarily selecting waterbodies and wetlands (Figure 2a).
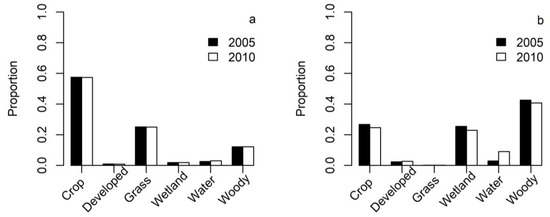
Figure 1.
Proportions of six land-use and land cover classes at the breeding (a) and non-breeding (b) grounds of American white pelicans in the United States.
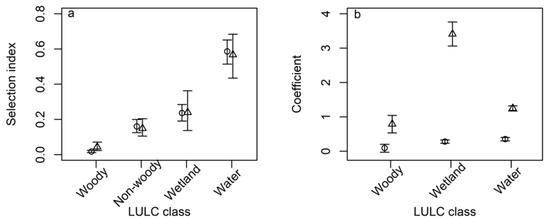
Figure 2.
Selection coefficients of the (a) second-order and (b) third-order habitat selection by American white pelicans.at the breeding (open triangle) and non-breeding (open circle) ground of American white pelicans. Vertical lines are 95% confidence (panel a) and credible (panel b) intervals.
There were 1500 5-km grid cells having GPS locations at the non-breeding ground. The count per cell ranged from 1 to 950 GPS locations. The best GMRF model for the third order habitat selection at the non-breeding ground included the proportions of waterbodies, wetland, and woody cover as covariates (Table 1). In general, pelicans selected waterbodies and wetlands in the third-order habitat selection, consistent with the second-order habitat selection (Figure 2b).

Table 1.
Model selection of Gaussian Markov Random Field (GMRF) models for fine-scale habitat selection by American white pelicans at the non-breeding ground in the Northern Gulf of Mexico. Symbols AICc and ΔAICc stands for Akaike information criterion corrected for small sample size and different in AICc between a model and the best model, respectively. Letter K denotes the number of unknown parameters.
There were 1275 5-km cells having one or more GPS locations at the breeding ground. The count per cell ranged from 1 to 1448 GPS locations. Likewise, the best GMRF model for the third-order habitat selection at the non-breeding ground included the proportions of waterbody, wetland, and woody cover as covariates (Table 2). Pelicans also selected waterbody and wetland more than woody cover within the home ranges at the breeding ground. However, the selection coefficient for wetland was almost three times greater than that for waterbodies (Figure 2b). The 95% credible intervals of the selection coefficients of all three land covers on the breeding grounds exceeded those on the non-breeding grounds, suggesting stronger forage habitat selection by pelicans on the breeding grounds than on the non-breeding grounds.

Table 2.
Model selection of Gaussian Markov Random Field (GMRF) models for fine-scale habitat selection by American white pelicans at the breeding ground in the Northern Great Plains. Symbols AICc and ΔAICc stands for Akaike information criterion corrected for small sample size and different in AICc between a model and the best model, respectively. Letter K denotes the number of unknown parameters.
4. Discussion
This study is among the few studies which have used multivariate mixed-effect models to estimate the second-order habitat selection by wildlife accounting for the repeated-measure samples of the same individuals at both breeding and non-breeding grounds. The second-order and third-order habitat selection by pelicans were restricted to waterbodies and wetlands at both breeding and non-breeding grounds. Pelicans are soaring birds and fly with thermals [31,53]. Scacco, Flack, Duriez, Wikelski and Safi [40] found that thermal uplift intensity was low above waterbodies and wetlands. Therefore, selection for waterbodies and wetlands by pelicans was probably related to foraging activities. The strength of the second-order habitat selection by pelicans was consistent between the breeding and non-breeding grounds with resource availability being measured at the landscape scales. Furthermore, our findings support the hypothesis that the fine-scale habitat selection of migratory pelicans is stronger on the breeding grounds than on the non-breeding grounds with resource availability being quantified at the local (e.g., 25 km2) scale [16]. Spatiotemporal scales of resource availability may determine variability in habitat selection by animals.
Spatial scales or extents, at which resource availability is measured, are important for revealing hierarchical habitat selection processes [5]. Spatial and temporal scales of resource availability are closely related [54]. We assessed resource availability across the landscapes within the spatial extent pelicans can reach. Similarly, Dupke, Bonenfant, Reineking, Hable, Zeppenfeld, Ewald and Heurich [7] used LULC proportions within a polygon, which encompassed all relocations of all tracked roe deer (Capreolus capreolus) to quantify resource availability. Furthermore, the D-M model used the GPS locations of a bird for the home-range level habitat selection during the entire summer or winter season in this study, reflecting season-level and home-range-level habitat selection by pelicans. On the other hand, in the GMRF model for the third-order habitat selection, resource availability was measured with LULC proportions within a 5-km grid cell, which is equivalent to average hourly movement distance of pelicans, more or less, reflecting habitat selection on an hourly temporal scale during a season. A possible consequence of such differences in the spatial (between- vs. within- home range) and temporal (seasonal vs. daily or hourly) scales is that the second-order habitat selection is more consistent between regions or seasons than the third-order selection due to the scale-up emergent property [54].
Zurell, et al. [55] found that habitat selection by white storks (Ciconia ciconia) was more conservative between regions than at the within-home range level. Home-range level habitat selection by white storks is relatively consistent between difference regions [55], similar to home-range level habitat selection by pelicans. Likewise, lesser prairie-chickens (Tympanuchus pallidicinctus) do not exhibit seasonal or regional variation in the second-order habitat selection [8]. Fine-scale habitat selection by white storks is more variable among different regions and more variable among individuals than home-range level habitat selection. Pelicans rely on food resources in the freshwater wetlands [27,29]. Dietary specialization may cause pelicans to select waterbodies and wetlands at the home-range (i.e., second-order) levels consistently to maximize food acquisition. The Dalmatian pelican (Pelecanus crispus) also exhibit the consistent selection of wetlands on the breeding grounds [56]. It is also plausible that lack of variation in seasonal home-range level habitat selection by pelicans, prairie-chickens, and white storks is an emergent property from local to large spatial scales, with local resource availability being more variable within a region than that at the landscape scales between regions [54].
Satellite or GPS tracking provides data on the habitat use of the same individuals or populations between the breeding and non-breeding grounds, allowing for comparisons of the fine-scale habitat selection of migratory birds between the nesting and wintering grounds. Seasonal variation in habitat selection is surprisingly under-represented in the literature of waterbirds [12]. Our findings are consistent with the prediction of the Lack hypothesis that fine-scale habitat selection by pelicans is stronger on the breeding grounds than on the non-breeding grounds. The seasonal difference in fine-scale habitat selection by pelicans between the breeding and non-breeding season may result from increased requirements for food during the nesting season as Lack hypothesized [16]. Zurell, Von Wehrden, Rotics, Kaatz, Groß, Schlag, Schäfer, Sapir, Turjeman and Wikelski [55] also demonstrated differences in the within-home-range habitat selection between the breeding and non-breeding storks. Alternatively, the seasonal differences in the fine-scale habitat selection between the nesting and wintering grounds may be a form of functional responses in habitat selection, which predicts that the strength of habitat selection is a function of resource availability [57]. For instance, given 20 times more wetlands available on the non-breeding grounds than on the breeding grounds (Figure 1), pelicans might increase the strength of their selection of wetlands after arriving at the breeding grounds. Therefore, fine-scale habitat selection by pelicans may be contextually dependent, varying with differences in resource availability and physiological conditions between animal individuals [12,58].
Individual variation in habitat selection has been found in many mammals and birds [58]. For instance, breeding and non-breeding white storks differ in both the second-order and third-order habitat selection [55]. Individual differences in habitat selection, a form of Grinnellian niche specialization, makes animals more adaptive to varying environments [59]. Realized niches of individual animals may become narrow and diverge (i.e., individual niche specialization) to reduce intraspecific competition [60]. Intraspecific niche specialization may enhance the plasticity of resource use and adaptability of whole populations to varying environments with the portfolio and insurance effects [61]. Consequently, population-level responses of habitat or resource selection by animals to resource availability may differ from individual-level responses [58]. Future studies of habitat selection need to consider habitat selection at the individual levels [58,62].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.L.C., G.W. and D.T.K.; methodology, G.W. and D.T.K.; formal analysis, G.W.; investigation, D.T.K. and G.W.; writing—original draft preparation, F.L.C. and G.W.; writing—review and editing, F.L.C., G.W. and D.T.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the USDA APHIS (Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service) Wildlife Services, National Wildlife Research Center, agreement No. 15-7428-1060-CA. G.W. also was funded by Mississippi State University.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All experimental protocols of animal capture and handling were approved by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), National Wildlife Research Center, Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC Protocol QA-1018).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are openly available in a public repository after the manuscript is accepted for publication.
Acknowledgments
This publication is a contribution of the Forest and Wildlife Research Center, Mississippi State University. We also thank students, colleagues and technicians at the Department of Wildlife, Fisheries & Aquaculture, MSU and APHIS for critical help in the field. The findings and conclusions in this publication are those of the author(s) and should not be construed to represent any official USDA or U.S. Government determination or policy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
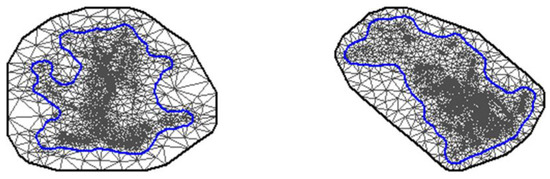
Figure A1.
The meshes created by the Voronoi triangulation for the stochastic partial differentiation equation (SPDE) model for the GPS location density at the non-breeding (left panel) and breeding (right panel) grounds of American white pelicans. The mesh for the SPDE consisted of triangles and two outer polygons. The inner non-convex polygon (the blue line) encompassed all GPS locations at the non-breeding or breeding grounds defining the domain of the spatial effects. The area between the inner and outer polygons was used to account for the edge effect. The meshes were created for demonstrative purpose with the maximum edge length of 100 km and 200 km. The SPDE analysis used the maximum edge length of 40 km and 60 km.
References
- Boyce, M.S.; McDonald, L.L. Relating populations to habitats using resource selection functions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1999, 14, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manly, B.F.J.; McDonald, L.L.; Thomas, D.L.; McDonald, T.L.; Erickson, W.P. Resource Selection by Animals: Statistical Design and Analysis for Field Studies, 2nd ed.; Kluwer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fuller, R.J. Birds and Habitat: Relationships in Changing Landscapes; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzweig, M.L. A theory of habitat selection. Ecology 1981, 62, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.H. The comparison of usage and availability measurements for evaluating resource preference. Ecology 1980, 61, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLoughlin, P.; Gaillard, J.-M.; Boyce, M.; Bonenfant, C.; Messier, F.; Duncan, P.; Delorme, D.; Moorter, B.V.; Said, S.; Klein, F. Lifetime reproductive success and composition of the home range in a large herbivore. Ecology 2007, 88, 3192–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupke, C.; Bonenfant, C.; Reineking, B.; Hable, R.; Zeppenfeld, T.; Ewald, M.; Heurich, M. Habitat selection by a large herbivore at multiple spatial and temporal scales is primarily governed by food resources. Ecography 2017, 40, 1014–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumb, R.T.; Lautenbach, J.M.; Robinson, S.G.; Haukos, D.A.; Winder, V.L.; Hagen, C.A.; Sullins, D.S.; Pitman, J.C.; Dahlgren, D.K. Lesser prairie-chicken space use in relation to anthropogenic structures. J. Wildl. Manag. 2019, 83, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rettie, W.J.; Messier, F. Hierarchical habitat selection by woodland caribou: Its relationship to limiting factors. Ecography 2000, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebblewhite, M.; Merrill, E.H. Trade-offs between predation risk and forage differ between migrant strategies in a migratory ungulate. Ecology 2009, 90, 3445–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickens, B.A.; King, S.L.; Vasseur, P.L.; Zimorski, S.E.; Selman, W. Seasonal movements and multiscale habitat selection of whooping crane (Grus americana) in natural and agricultural wetlands. Waterbirds 2017, 40, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northrup, J.M.; Vander Wal, E.; Bonar, M.; Fieberg, J.; Laforge, M.P.; Leclerc, M.; Prokopenko, C.M.; Gerber, B.D. Conceptual and methodological advances in habitat-selection modeling: Guidelines for ecology and evolution. Ecol Appl 2022, 32, e02470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, J.S.; Satgé, Y.G.; Jodice, P.G. Seasonal variation in environmental and behavioural drivers of annual-cycle habitat selection in a nearshore seabird. Divers. Distrib. 2020, 26, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barras, A.G.; Marti, S.; Ettlin, S.; Vignali, S.; Resano-Mayor, J.; Braunisch, V.; Arlettaz, R. The importance of seasonal environmental factors in the foraging habitat selection of Alpine Ring Ouzels Turdus torquatus alpestris. Ibis 2020, 162, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, I. The Migration Ecology of Birds; Academic Press: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lack, D. Bird migration and natural selection. Oikos 1968, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salewski, V.; Bruderer, B. The evolution of bird migration—A synthesis. Naturwissenschaften 2007, 94, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrig, L. Effects of habitat fragmentation on biodiversity. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2003, 487–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.; Wang, G.; Martin, J.; Belant, J.; Butler, A.; Rush, S.; Godwin, D. Landscape-abundance relationships of male Eastern Wild Turkeys Meleagris gallopavo silvestris in Mississippi, USA. Acta Ornithol. 2017, 52, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, K.V.; Dokter, A.M.; Blancher, P.J.; Sauer, J.R.; Smith, A.C.; Smith, P.A.; Stanton, J.C.; Panjabi, A.; Helft, L.; Parr, M. Decline of the North American avifauna. Science 2019, 366, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Tris, J.; Tellería, J.L. Migratory and sedentary blackcaps in sympatric non-breeding grounds: Implications for the evolution of avian migration. J. Anim. Ecol. 2002, 71, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, P.P.; Cohen, E.B.; Loss, S.R.; Rutter, J.E.; Tonra, C.M. A call for full annual cycle research in animal ecology. Biol. Lett. 2015, 11, 20150552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, C.Q.; Dudash, M.R.; Ryder, T.B.; Shriver, W.G.; Serno, K.; Adalsteinsson, S.; Marra, P.P. Seasonal variation in habitat selection for a Neotropical migratory songbird using high-resolution GPS tracking. Ecosphere 2021, 12, e03421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.T.; Anderson, D.W. Recent population status of the American White Pelican: A Continental perspective. Waterbirds 2005, 28, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.T.; Wang, G.M.; Yang, Z.; Fischer, J.W. Advances and environmental conditions of spring migration phenology of American White Pelicans. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strait, L.E.; Sloan, N.F. Movements and mortality of juvenile white pelicans from North Dakota. Wilson Bull. 1975, 87, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- King, D.T.; Michot, T.C. Distribution, abundance and habitat use of American White Pelicans in the Delta Region of Mississippi and along the Western Gulf of Mexico Coast. Waterbirds 2002, 25, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibley, D. The Sibley Guide to Bird Life and Behavior; Alfred A. Knopf: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- King, D.T.; Belant, J.; Harrel, B.; Glahn, J. Superabundant food at catfish aquaculture facilities improves body condition in American White Pelicans. Waterbirds 2010, 33, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Van Asselen, S.; Verburg, P.H.; Vermaat, J.E.; Janse, J.H. Drivers of wetland conversion: A global meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, H.D.; Young, G.S.; Yates, M.A.; Fuller, M.R.; Seegar, W.S. American white pelican soaring flight times and altitudes relative to changes in thermal depth and intensity. Condor 2002, 104, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.T.; Paulson, J.D.; Leblanc, D.J.; Bruce, K. Two capture techniques for American White Pelicans and Great Blue Herons. Waterbirds 1998, 21, 258–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorr, B.S.; King, D.T.; Harrel, J.B.; Gerard, P.; Spalding, M.G. The use of culmen length to determine sex of American White Pelicans (Pelecanus erythrorhynchos). Waterbirds 2005, 28, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunstan, T.C. A harness for radio-tagging raptorial birds. Inland Bird Band. News 1972, 44, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- King, D.T.; Fischer, J.; Strickland, B.; Walter, W.D.; Cunningham, F.L.; Wang, G. Winter and summer home ranges of American White Pelicans (Pelecanus erythrorhynchos) captured at loafing sites in the Southeastern United States. Waterbirds 2016, 39, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- King, D.T.; Wang, G.; Cunningham, F.L. Large-and Small-Scale Climate Influences Spring Migration Departure Probability of American White Pelicans. Diversity 2022, 14, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.T.; Werner, S.J. Daily activity budgets and population size of American White Pelicans wintering in South Louisiana and the Delta Region of Mississippi. Waterbirds 2001, 24, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifovic, R.; Homer, C.; Ressl, R.; Pouliot, D.; Hossain, S.; Colditz Colditz, R.; Olthof, I.; Giri, C.; Victoria, A. North American land change monitoring system (NALCMS). In Remote Sensing of Land use and Land Cover: Principles and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hijmans, R.J. "Raster": Geographic Data Analysis and Modeling. R package ver. 2.5-8. 2016. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=raster (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Scacco, M.; Flack, A.; Duriez, O.; Wikelski, M.; Safi, K. Static landscape features predict uplift locations for soaring birds across Europe. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 181440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Valpine, P.; Harmon-Threatt, A.N. General models for resource use or other compositional count data using the Dirichlet-multinomial distribution. Ecology 2013, 94, 2678–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G. Bayesian and frequentist approaches to multinomial count models in ecology. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 61, 101209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, I.; Uh, H.W.; Supali, T.; Mitreva, M.; Houwing-Duistermaat, J.J. The mixed model for the analysis of a repeated-measurement multivariate count data. Stat. Med. 2019, 38, 2248–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, B.; Gelman, A.; Hoffman, M.D.; Lee, D.; Goodrich, B.; Betancourt, M.; Brubaker, M.; Guo, J.; Li, P.; Riddell, A. Stan: A probabilistic programming language. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 76, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.Y.; McGree, J.; Mengersen, K. Bayesian hierarchical models for analysing spatial point-based data at a grid level: A comparison of approaches. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 2015, 22, 297–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimi, B.; Araújo, M.B. sdm: A reproducible and extensible R platform for species distribution modelling. Ecography 2016, 39, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, M.H. Confronting multicollinearity in ecological multiple regression. Ecology 2003, 84, 2809–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, F.; Rue, H.; Lindström, J. An explicit link between Gaussian fields and Gaussian Markov random fields: The stochastic partial differential equation approach. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 2011, 73, 423–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, F.; Rue, H. Bayesian spatial modelling with R-INLA. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 63, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rue, H.; Riebler, A.; Sørbye, S.H.; Illian, J.B.; Simpson, D.P.; Lindgren, F.K. Bayesian computing with INLA: A review. Annu. Rev. Stat. Its Appl. 2017, 4, 395–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, K.; Nielsen, A.; Berg, C.W.; Skaug, H.J.; Bell, B. TMB: Automatic differentiation and laplace approximation. J. Stat. Softw. 2016, 70, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Model Selection and Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Illan, J.G.; Wang, G.; Cunningham, F.L.; King, D.T. Seasonal effects of wind conditions on migration patterns of soaring American white pelican. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186948. [Google Scholar]
- Van Moorter, B.; Rolandsen, C.M.; Basille, M.; Gaillard, J.M. Movement is the glue connecting home ranges and habitat selection. J. Anim. Ecol. 2016, 85, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurell, D.; Von Wehrden, H.; Rotics, S.; Kaatz, M.; Groß, H.; Schlag, L.; Schäfer, M.; Sapir, N.; Turjeman, S.; Wikelski, M. Home range size and resource use of breeding and non-breeding white storks along a land use gradient. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 6, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounas, A.; Catsadorakis, G.; Naziridis, T.; Bino, T.; Hatzilacou, D.; Malakou, M.; Onmus, O.; Siki, M.; Simeonov, P.; Crivelli, A.J. Site fidelity and determinants of wintering decisions in the Dalmatian pelican (Pelecanus crispus). Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysterud, A.; Ims, R.A. Functional responses in habitat use: Availability influences relative use in trade-off situations. Ecology 1998, 79, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newediuk, L.; Prokopenko, C.M.; Vander Wal, E. Individual differences in habitat selection mediate landscape level predictions of a functional response. Oecologia 2022, 198, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, B.S.; Rotics, S.; Nathan, R.; Wikelski, M.; Jetz, W. Individual environmental niches in mobile organisms. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolnick, D.I.; Svanbäck, R.; Fordyce, J.A.; Yang, L.H.; Davis, J.M.; Hulsey, C.D.; Forister, M.L. The ecology of individuals: Incidence and implications of individual specialization. Am. Nat. 2003, 161, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, M.; Weissing, F.J. Animal personalities: Consequences for ecology and evolution. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.S.; Hooten, M.B.; Kuhn, C.E. Estimating animal resource selection from telemetry data using point process models. J. Anim. Ecol. 2013, 82, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).