Abstract
Seagrasses worldwide provide key habitats for fish assemblages. Biogeographical disparities in ocean climate conditions and seasonal regimes are well-known drivers of the spatial and temporal variation in seagrass structure, with potential effects on associated fish assemblages. Whether taxonomically disparate fish assemblages support a similar range of ecological functions remains poorly tested in seagrass ecosystems. In this study, we examined variation in the abundance, diversity (from a taxonomic and functional perspective), and assemblage structure of fish community inhabiting nine meadows of the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa across three regions in the Mediterranean (Mallorca and Alicante) and the adjacent Atlantic (Gran Canaria), and identified which attributes typifying the structure of meadows, and large-scale variability in ocean climate, contributed most to explaining such ecological variation. Despite a similar total number of species between Mallorca and Gran Canaria, the latter region had more taxonomically and functionally diverse fish assemblages relative to the western Mediterranean regions, which translated into differences in multivariate assemblage structure. While variation in the abundance of the most conspicuous fish species was largely explained by variation in seagrass structural descriptors, most variation in diversity was accounted for by a descriptor of ocean climate (mean seasonal SST), operating at regional scales. Variation in fish assemblage structure was, to a lesser extent, also explained by local variability in seagrass structure. Beyond climatic drivers, our results suggest that lower temporal variability in the canopy structure of C. nodosa meadows in Gran Canaria provides a more consistent source of food and protection for associated fish assemblages, which likely enhances the more abundant and diverse fish assemblages there.
1. Introduction
Understanding how biological diversity is distributed, and what the drivers of these patterns are, is a challenge in ecology [1,2,3,4,5], particularly in the current context of global change and biodiversity loss [6,7]. The “Environmental Stability Hypothesis” [8,9,10] postulates that the number of species in an environment is higher in areas with less environmental variability, because a more stable environment favors a higher degree of species specialization and more niche diversification, with a consequent increase in the species richness. Empirical evidence for this hypothesis is provided, for example, by the authors of [3], who found that areas with less climatic variation across China contained a larger number of species of terrestrial vertebrates, and they attributed this because of species coexistence being favored under environmental stability. Importantly, while environmental variability is most commonly considered in terms of abiotic factors (e.g., temperature, physical disturbance [11,12,13], variations in habitat structure may also be critical in driving diversity patterns, particularly in ecosystems underpinned by habitat-forming species or “ecological engineers” [11,14,15].
Taxonomic diversity metrics are still the most widely used indices to study ecological variation across a range of spatial and temporal scales, despite two decades of research on the importance of metrics that incorporate ecological (traits) differences between species mediating ecosystem functioning, stability, and resilience [16,17,18]. Functional Diversity (FD) indices consider the distribution and prevalence of species’ traits within and among assemblages [19], defining a trait as any morphological, physiological, phenological, or behavioral feature that can be measured for any individual, which is related to survival, growth, and foraging, and reproductive capabilities of organisms [20]. It has been increasingly recognized that to better understand the true complexity of ecosystems, it is necessary to study biodiversity from different points of view [16,21,22,23,24,25,26], while also considering the effects of environmental variability [27,28].
Seagrasses are key canopy-forming species in shallow coastal areas, as they create highly productive and diverse ecosystems worldwide [29,30]. In addition to contributing to coastal protection and carbon sinks [31,32,33], seagrass ecosystems are recognized as important in supporting fisheries [34,35], as they can be critical in providing refuge against predators and diverse food sources for fish assemblages [36,37,38,39]. It is widely recognized that seagrass habitats support more abundant and diverse fish faunas than adjacent unvegetated areas [40,41]. The abundance, diversity, and structure of fish assemblages associated with seagrass meadows are influenced by different environmental factors, such as the position of meadows (“oceanic” vs. “lagoon” meadows, [23] and their depth [39]. Additional factors associated with the type and quality of the seagrass habitat can also play a strong role in structuring associated fish assemblages, including seagrass species composition [42,43], plant morphology, and meadow architecture [44]. Much attention has been given to seagrass structural complexity as an important factor regulating fish assemblages [44,45,46,47]. For instance, some studies in meadows that undergo strong herbivory from macro-consumers, such as dugongs and turtles, suffer a decrease in seagrass abundance, supporting poorer fish assemblages (both in terms of lower species richness and abundances), when compared to “non-grazed” meadows [2]. Despite the identification of environmental and ecological processes driving the abundance, diversity, and structure of fish assemblage across local seagrass meadows [1,2,38,48,49], few studies have examined the contributions of local and large-scale drivers on the diversity and structure of fish assemblages associated with seagrass beds across broad macroecological (biogeographical) scales (but see [50]).
Cymodocea nodosa (Ucria) Ascherson 1870 is a dominant seagrass species in subtidal zones across the Mediterranean and the adjacent Atlantic Ocean, including southern Portugal, Mauritania, the Canary Islands, and Madeira [51]. Meadows created by this seagrass, therefore, encompass different ecoregions, with varying environmental conditions and seagrass bed configurations [52,53], providing an ideal case study to assess the contributions of local and regional drivers on fish abundance, diversity, and assemblage structure in seagrass beds. In this study, we aimed to examine the importance of varying environmental drivers, according to the scale at which they mainly operate, on influencing abundance, diversity (TD and FD), and structure of fish assemblages in seagrass beds. More specifically, we identified how attributes typifying seagrass structure, at small scales, within each of the three study regions, and large-scale environmental (ocean climate) variability among these three regions, contributed to explaining variation in such ecological patterns. By characterizing fish abundance and diversity patterns, and identifying their main drivers, this approach can help us identify areas of conservation interest, or vulnerability, particularly under the context of global change, predicting which environments may be more susceptible, not only considering the number of species they contain but also according to the traits (functional roles) of fish species and their functional redundancy [54].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
This study was conducted at three regions across the Temperate Northern Atlantic realm within the distribution range of the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa [55]: Southeast Iberia (Alicante), the Balearic Sea (Mallorca Island), both within the Western Mediterranean ecoregion, and the Canaries (Gran Canaria Island) within the Macaronesian ecoregion in the eastern Atlantic [55]. Both Gran Canaria and Mallorca islands are insular systems, while Alicante is a mainland region. Within each region, three shallow meadows, at least 4 km away from each other, were selected. These meadows were away from urbanized areas (ca. 500–800 m), and not under major evident local human disturbances such as pollution (e.g., sewage outlets, aquaculture facilities). Despite all the meadows being outside Marine Protected Areas (MPAs), fishing pressure by professional fleets is negligible, due to the shallow depths or meadows (Author’s personal observation), which also minored the potential effect of boat anchoring (Figure 1 and Table S1). Some degree of recreational fishing is, however, expected.
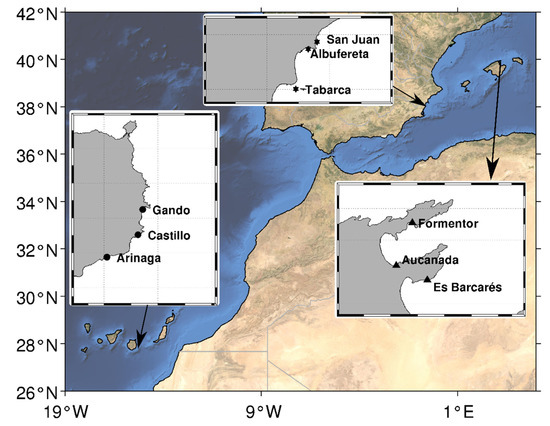
Figure 1.
Study area detailing the location of the three Cymodocea nodosa meadows sampled in each region, including the Atlantic region (black ellipses, Gran Canaria) and the Mediterranean regions (black stars, Alicante and black triangles, Mallorca).
As it has been assessed in previous studies, patterns in the functioning (structure and morphology) of C. nodosa differ among these three regions and nine localities. These patterns have been related to contributions from regional differences (“inter-regional”), including environmental seasonality and genetic variability of the meadows, as well as with local variability (“intra-regional”) factors, such as through the local genetic variability of the meadows. Most variability in the morphological attributes of these seagrass meadows has been related to regional seasonal variation [52,53], including their resilience to impacts [56]. In each meadow, seagrass structure and fish assemblages were sampled seasonally (i.e., four times a year; fall, winter, spring, and summer) from 2016 to 2018 (see details below).
2.2. Environmental (Ocean Climate) and Habitat Descriptors
To describe the intra- and inter-regional spatial and temporal variability in ocean climate, monthly data on Sea Surface Temperature (SST) and Photosynthetically Active Radiation (PAR) intensity were obtained throughout the entire study period (2016–2018). We initially monitored in situ seawater temperature, at each meadow, using HOBO Pendant probes. Unfortunately, some loggers were lost, so we used satellite-derived SST instead, for further statistical modeling. For shallow-water sites, SST derived from satellite data is a good surrogate for in situ temperatures on the sea bottom [57], including our study region [56]. In this sense, across study meadows, satellite-obtained SSTs were significantly correlated with in situ seawater temperatures acquired from the HOBO Pendant probes at small temporal scales (ca. 2 months, rs = 0.82, p < 0.0001). Therefore, we used satellite data to characterize temperature regimes at our study sites, as in [52]. Data were obtained from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer facility (MODIS-Aqua), using the Nasa Giovanni system (https://giovanni.gsfc.nassa.gov/giovanni/, accessed on 19 February 2019). The spatial resolution of all data collected was a 4 × 4 km2 grid that included each of the nine surveyed meadows. For each season (September, October, and November represent the fall season; December, January, and February for winter; March, April, and May for spring; and June, July, and August for summer) and meadow, we then calculated the mean seasonal (i.e., spring, summer, fall, winter) SST and PAR.
For each sampling time and meadow, plant biomass was measured by taking n = 10 cores (20 cm inner diameter, 50 cm depth) haphazardly located within each meadow. In the laboratory, sediment was removed from the cores, and aboveground biomass was separated and dried (60 °C at 48 h). Leaf biomass data were normalized to the core area and expressed as g DW cm−2. Shoot density was estimated by counting the number of shoots in a 20 × 20 cm2 quadrant (n = 10) haphazardly allocated at each meadow and time. In addition, 20 shoots were collected, and the number of leaves per shoot, the leaf width and leaf length (mm), and epiphytic loads were determined in the laboratory. For the latter, macroscopic epiphytes were removed using a razor blade and epiphytes and leaves were subsequently oven-dried to estimate epiphytic load (i.e., dry weight, DW, of epiphytes per DW of leaf biomass; data presented in [52]). Total leaf area (Seagrass Surface Area; SSA) was obtained as the sum of all the individual leaf areas of all leaves per shoot (cm2/shoot), and the Leaf Area Index (LAI) was estimated by multiplying the total leaf area per shoot by the mean shoot density. Epiphytic loads were expressed as g DW of epiphytes per g DW of leaf.
2.3. Fish Assemblages
The abundances of individual fish species were seasonally sampled by conducting randomly oriented, 25 m long × 4 m wide belt transects (n = 3; each 100m2 area), in which we visually identified and counted each fish [21,58] during daytime hours, between ca. 11.00 h and 15.00 h. For the species identified, we compiled functional traits from Fishbase (www.fishbase.org, accessed on 5 April 2019) and available published literature (adapted from [59,60]). The traits selected represent key attributes of species that are linked to species life history strategies, behavior, trophic ecology, and habitat utilization [61,62], and included: body size (maximum length), trophic breadth (1: specialist till 8: generalist), trophic group, water column position, preferred substrate, trophic level (1: primary producers, 2: herbivores, 3: carnivores, 4–5: predators), and body shape (Table S2).
2.4. Diversity Indices
For each region, the total number of species was estimated; a Venn diagram then illustrated similarities in fish assemblage composition (i.e., shared vs. unique species) among regions. The “EcoInd” R package [63] was used to calculate different types of biodiversity indices (taxonomic and functional), considering those fish species accounting for ca. 95% of the total study abundances (see Table S3), including species richness (Equation (1)), Margalef (Equation (2)) and Pielou (Equation (3)) indices, the D-star index (also known as the taxonomic distinctness; Equation (4)), and the Rao index of functional diversity (Rao’s quadratic entropy index; Equation (5)).
Equation (1). Richness (S; [64]):
where S represents the total number of species found at each locality in different seasons.
Equation (2). Margalef index (DMg [64]):
where N represents the total number of individuals in the sample.
Equation (3). Pielou index (J’ [65]):
We used the Shannon–Weaver (H’) equation to obtain Pielou’s index, as follows:
where pi represents the abundance’s proportion of species i. Once we got H′, we obtained Pielou’s index as follows:
Equation (4). Taxonomic distinctiveness (Dstar; [66]):
where w are the taxonomic distances among taxa and x are species abundances.
Equation (5). Rao’s quadratic entropy (Q; Rao [19]):
where pi is the abundance’s proportion of the species j and dij represents the difference between the i-th and j-th species and come from:
2.5. Statistical Analyses
Due to the large presence of zeros in the fish count data, we firstly averaged seasonal data through the different years of sampling, as a way to minimize data overdispersion and zero-inflated distributions. We then retained fish abundance data for each meadow in spring, summer, fall, and winter (n = 36). We initially visualized and tested for correlations (Spearman coefficients) between each pair of predictor variables typifying meadow structure and ocean climate conditions across meadows and times, using the “corrplot” R package [67]. An initial arbitrary cut-off at r > 0.6 was considered [68]. This was necessary to limit the inclusion of over-correlated predictor variables in further modeling and multivariate ordinations. When two predictor variables were correlated, we chose the one with a larger biological significance [69]. This analysis led to the selection of three uncorrelated predictors: shoot density and seagrass surface area, as descriptors of seagrass structure, and mean seasonal SST, as a descriptor of the ocean climate at each meadow (Figure S1). After modeling, Variance Inflation Factors (VIF) among predictors were always <5, indicating that multicollinearity was not a serious concern [70].
A distance-based redundancy analysis (db-RDA [71]), hereafter RDA) was implemented, as a constrained ordination technique, to visualize whether both ocean climate (i.e., mean seasonal SST) and meadow structure (i.e., shoot density and seagrass surface area) varied among regions, using the “vegan” R package [72]. Ellipsoids depicted confidence limits (0.95) areas encompassing meadows from each region. The PERMDISP routine, also implemented in the “vegan” R package [72] using the “betadisper” function, further tested whether multivariate dispersion of centroids varied among regions, via 999 permutations of the raw data.
Generalized Linear Models (GLMs) were carried out to test whether each diversity index varied among study regions, and also to partition the relative contribution of ocean climate and meadow structure descriptors on each index through a “model selection” approach [68], via the “MuMIn” R package [73]. Initially, all candidate models, that is, containing all combinations of 1, 2, or 3 predictors, were constructed, which were then ranked by their Akaike Information Criterion corrected for small sample size (AICc), and importance weights (wi) were provided for each individual predictor (being the sum of the importance scores (i.e., weights = 1). Model selection uncertainty was then approached by using a model averaging strategy; we obtained estimates of each model parameter by considering the weight of each candidate model [68] and importance scores were then provided for each individual predictor. The error structure family distribution and the link function were chosen, for each response variable, depending on their mathematical peculiarities (see results).
Another RDA was implemented, using the same criteria outlined before, to visualize whether both variation in ocean climate and meadow structure influenced multivariate variation in fish assemblage structure. Fish abundances were log-transformed to downweigh the relevance of the most abundant species. GLMs were then also fitted to the total abundance of the most abundant fish species (Atherina sp., Boops boops, Diplodus annularis, Diplodus vulgaris, Pagellus erythrinus, Sparisoma cretense, Spicara smaris, Sphoeroides marmoratus, Spondyliosoma cantharus, and Mullus surmuletus), and over the multivariate fish assemblage dataset, to test for differences among regions and to test the effects of meadow structure and ocean climate on such abundances. A “negative binomial” family structure and a “log” link function were selected to account for the overdispersion of fish count data, using the “mvabund” R package [74]. In all cases, the significance of differences was then tested by an Analysis of Deviance, which provided p-values calculated using 999 resampling iterations via a PIT-trap resampling procedure.
We further visualized whether changes in the taxonomic structure of the fish assemblage among regions translated into differences in their functional structure. A multidimensional functional space was built on a species-by-species Gower distance matrix [75], which can accommodate both continuous and categorical traits. Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) was then used to visualize changes in the functional structure, with the optimal number of dimensions chosen to minimize the deviation between the original trait-based distances and the Euclidean distances in the functional space [76]. We chose the first four PCoA axes as the optimal number of dimensions, as they minimized the mean absolute deviation (MAD) between trait and Euclidean distances, which captured 66% of the variation in the traits of the species considered. The correlation between individual traits and PCoA axes was calculated using a Kruskal–Wallis test for categorical traits and an r2 statistic from a simple linear regression for continuous traits (Figure S4). Variation in the functional identity of each meadow within each region, for the four seasons, was represented by calculating their abundance-weighted position in the multi-dimensional functional space. Analyses were carried out in the newly developed mFD R package [77].
3. Results
3.1. Environmental (Ocean Climate and Habitat) Descriptors
Gran Canaria underwent a low annual variation in ocean climate, with seasonal SST ranging between 19.6 °C in winter and 22.9 °C in autumn (Figure 2a). In contrast, the two Mediterranean regions (Alicante and Mallorca) exhibited marked seasonal patterns of SST, with maxima in summer (26.0 °C and 25.8 °C, respectively; Figure 2b,c) and minima in winter (15.5 °C and 15.2 °C respectively, Figure 2b,c).
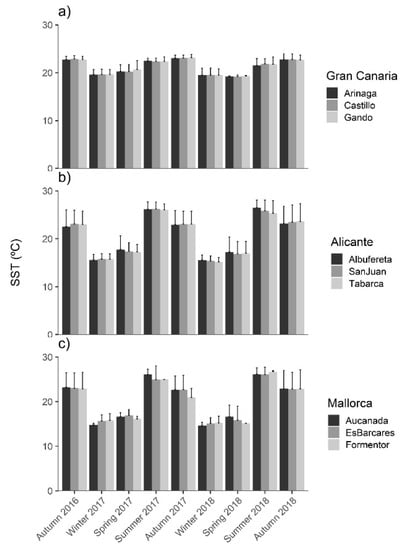
Figure 2.
Mean seasonal Sea Surface Temperature (SST; °C) at each meadow from (a) Gran Canaria, (b) Alicante and (c) Mallorca throughout the study period. Error bars are + SD of means (n = 9). Average of the three months per season between 2016–2018.
The RDA separated meadows across regions, in varying seasons, according to ocean climate (mean seasonal SST) and seagrass structure (shoot density and seagrass surface area) along the first two axes of the ordination space, which accounted for ca. 80% of the total variation (Figure 3), with the axes (components) 1 and 2 explaining 53.1% and 30.1% of the total variation, respectively. Mean seasonal SST was the variable with the greatest contribution to axis 1, followed by seagrass surface area, while shoot density contributed more than 90% in explaining variation along axis 2. The multivariate dispersion of the meadow from Gran Canaria was lower than that of the meadows from the Mediterranean (PERMDISP, p < 0.01 for all pairwise comparisons between Gran Canaria and Mediterranean regions), indicating that meadows from Gran Canaria have less environmental variation relative to Mediterranean meadows.
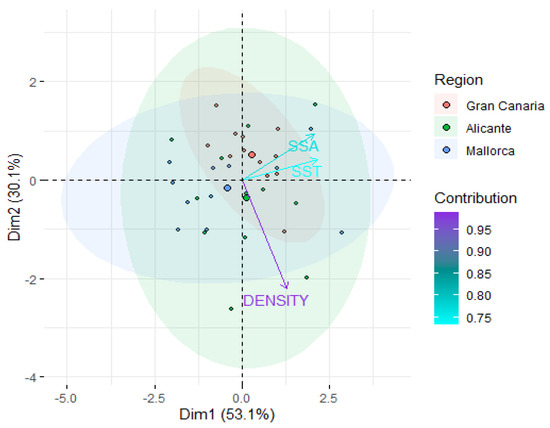
Figure 3.
Redundancy Analysis (RDA) examining differences in meadows according to ocean climate and seagrass habitat structure. SSA: seagrass surface area (cm2), SST: mean seasonal sea surface temperature (°C), and DENSITY: seagrass shoot density (shoots m−2). The colors of the arrows indicate their contribution relative to the variance explained by the axis, and the colors of the different circles represent meadows from each region. Centroids for each region are depicted by large-size dots. Ellipsoids show confidence limits (0.95) in areas encompassing meadows from each region.
3.2. Fish Assemblages: Differences among Regions
A total of 18,999 individuals, belonging to 48 species (Table S3), were counted during the study. A total of 30 species were observed in Gran Canaria and Mallorca, and 22 species in Alicante (Figure 4a).
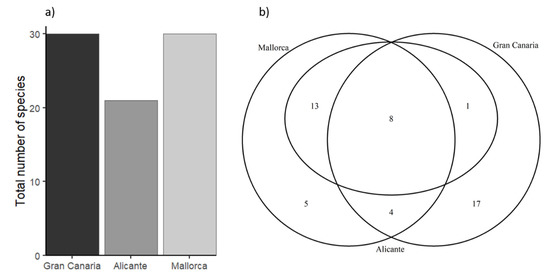
Figure 4.
(a) Total number of fish species at each region, and (b) Venn diagram denoting similarities in fish assemblage composition between regions (numbers within the circles denote number of shared species).
A large number of species [17] were only observed in Gran Canaria, while five fish species were only detected in Mallorca (Figure 4b). Mallorca and Alicante shared 13 species, while Mallorca and Gran Canaria only shared four species (Figure 4b). There were significant differences between Gran Canaria and the Mediterranean regions (Alicante and Mallorca) for all diversity indices, being higher in Gran Canaria (Figure 5; p < 0.05; Table S4). The only exception was the RAO index (Figure 5e; Table S4), for which differences were only detected between Gran Canari and Mallorca (p = 0.83; Table S4).
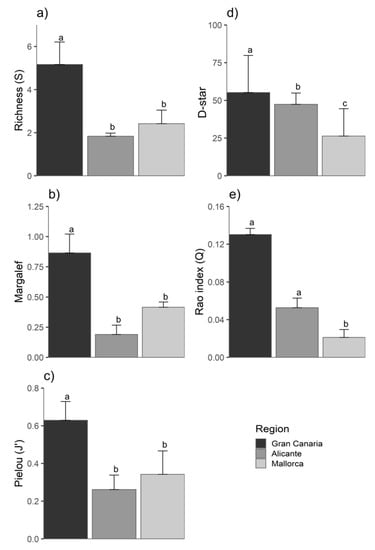
Figure 5.
Differences in biodiversity indices between regions: (a) Species Richness (S), (b) Margalef index, (c) Pielou index (J’), (d) D-star index and (e) RAO index. Different letters above denote statistically significant differences between regions. Errors are + SD of means per month. (n = 9).
In terms of fish assemblage structure (i.e., considering the abundances of all species), samples from Gran Canaria separated across the bidimensional ordination space relative to those from the Mediterranean (Figure 6), which was statistically corroborated by the multivariate GLM (p = 0.001, Table S5). Two sparid species, Diplodus vulgaris and Diplodus annularis, correlated with axis 1, which explained 22.9% of the total multivariate variation and separated fish assemblages between Mediterranean regions and Gran Canaria (Figure 6). These two species exhibited significantly larger abundances (two to three times) in Gran Canaria in comparison to Mallorca and Alicante (Table S5, Figure 7).
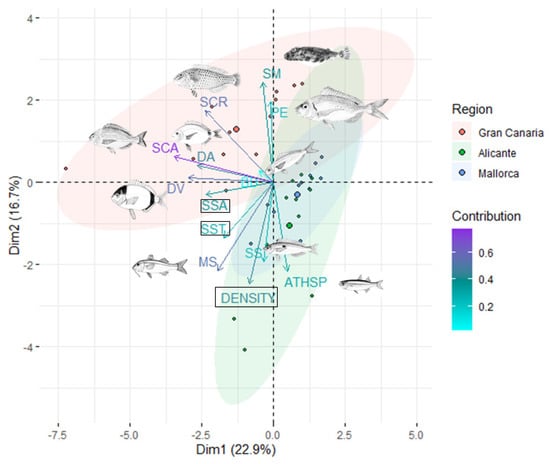
Figure 6.
Redundancy analysis (RDA) examining variation in fish assemblage structure according to ocean climate (SST; mean seasonal sea surface temperature) and seagrass structure descriptors (SSA: seagrass surface area, and DENSITY: seagrass shoot density). The 10 most abundant fish species are included; BB: Boops boops, ATHSP: Atherina sp., DA: Diplodus annularis, SS: Spicara smaris, SCA: Spondyliosoma cantharus, SCR: Sparisoma cretense, DV: Diplodus vulgaris, SM: Sphoeroides marmoratus, PE: Pagellus erythrinus and MS: Mullus surmuletus. The colors of the arrows indicate their contribution relative to the variance explained by the axis, and the colors of the different circles represent meadows from each region. Centroids for each region are depicted by large-size dots. Ellipsoids show confidence limits (0.95) in areas encompassing fish assemblages from each region. All fish images were downloaded from the FAO.org webpage, except Sphoeroides marmoratus, whose authorship belongs to Pedro M. Duarte.
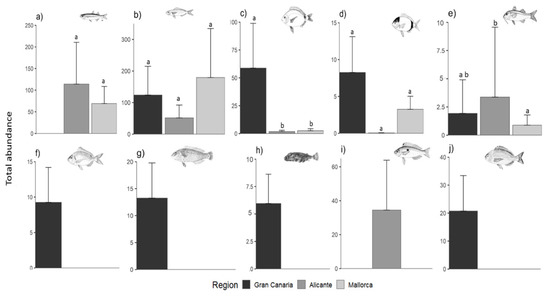
Figure 7.
Differences in fish total abundances (Ind m−2) between regions for: (a) Atherina sp., (b) Boops boops, (c) Diplodus annularis, (d) Diplodus vulgaris, (e) Mullus surmuletus, (f) Pagellus erythrinus, (g) Sparisoma cretense, (h) Sphoeroides marmoratus, (i) Spicara smaris and (j) Spondyliosoma cantharus. Different letters above bars denote statistically significant differences between regions. Error bars are + SE of means. n = 9 Data were pooled between meadows within regions and through seasons and years. All fish images were downloaded from the FAO.org webpage, except Sphoeroides marmoratus, whose authorship belongs to Pedro M. Duarte.
The rest of the species separated along axis 2, which explained an additional 16.7% of the total multivariate variation. The species Atherina sp., Spicara smaris, and Mullus surmuletus showed a negative correlation with this axis (Figure 6), indicative of a tendency of larger abundances in the Mediterranean regions (Table S5, Figure 7). On the other hand, the vectors depicting Pagellus erythrinus, Sparisoma cretense, and Sphoeroides marmoratus pointed toward fish assemblages from Gran Canaria (Figure 6), as these species were limited to this region (these species also showed significant differences among regions, p < 0.005; Table S5 and Figure 7).
Contrary to changes in the taxonomic structure, we found that the functional identity of fish assemblages did not vary substantially among regions; that is, there was high overlap in the centroids of the assemblages in the multidimensional functional space (Figure S4). Instead, there was high variability in the functional identity of fish assemblages within each region (Figure S4).
3.3. Fish Assemblages: “Model Selection” to Assess the Importance of Predictors
Most variation in the Pielou (p = 0.013), D-star (p = 0.017), and Rao Index (p = 0.021) was accounted for by variability in mean seasonal SST (Table S6); for these three indices, the importance scores of this predictor varied between 0.87 and 1 (Table S6). Despite a lack of statistical significance, mean seasonal SST was also selected as the most relevant predictor for Species Richness and the Margalef index, with importance scores between 0.59 and 0.63, respectively (Table S6). Overall, mean seasonal SST was selected as the most important predictor for all biodiversity indices.
In contrast to diversity indices, total fish abundances (of the 95% most abundant) appeared to be mostly driven by predictors typifying seagrass structure (Table S7). In this sense, the abundances of Diplodus annularis (p < 0.001), Sphoeroides marmoratus (p = 0.004), Spicara smaris (p = 0.004), and Spondyliosoma cantharus (p < 0.001) were positively correlated with seagrass surface area (Table S7). The abundances of Pagellus erythrinus and Sphoeroides marmoratus were negatively correlated with seagrass shoot density (p < 0.01 and p = 0.007; respectively; Table S7). Mullus surmuletus was the only species whose abundance was significantly accounted by mean seasonal SST (p < 0.001; Table S7). For the abundances of Atherina sp. and Boops boops, although not statistically significant, seagrass surface area was the most important predictor (Table S7).
4. Discussion
Our results indicated that fish assemblage diversity and taxonomic structure associated with meadows of the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa are influenced by climatic drivers, but also by the structure of available habitat across the Atlanto-Mediterranean province. The Atlantic region of Gran Canaria, located near the seagrass’ southernmost species distribution range, undergoes a narrower range of environmental variability (e.g., SST) relative to the Mediterranean regions (this study [52]), thus supporting the “Environmental Stability Hypothesis” [8], as lower variability in ocean climate in Gran Canaria would allow more species to coexist [78]. In fact, most variability in diversity indices was accounted for by environmental variability associated with SST, which majorly operates at large spatial scales across the study region [52]. Higher fish diversity estimates in Gran Canaria, as it often observed in more tropical areas [79,80], and even in Lanzarote Island [49] could be related to a higher niche specialization, due to enhanced coevolutionary processes, in warmer climates, whereas lower extinction rates are also predicted in less variable environments (see [81] and references therein). In addition, more stable and warmer temperatures would facilitate the existence of a higher number of warm-affinity fish species in seagrass meadows from the Canary Islands [49], whereas low winter temperatures in western Mediterranean waters likely constrain the distribution of more thermophilic species, such as Sphoeroides marmoratus or Sparisoma cretense [1]. Variation in fish assemblage diversity and taxonomic structure may also result from the higher temporal stability in the habitat provided by the seagrass [27,82]. Seasonal variability in the canopy structure of Cymodocea nodosa meadows is lower in Gran Canaria relative to Mediterranean meadows [52], and a more stable habitat would enable the provision of a more consistent source of food [82,83] and protection for associated fish assemblages [84,85,86]. In fact, we found that variations in fish assemblage structure, and the abundances of the most conspicuous species, were largely explained by variations in seagrass structural descriptors (seagrass surface area and shoot density). In this sense, seagrass canopy structure and complexity have been identified to play a crucial role in determining the composition and abundances of fish species in seagrass meadows [39,87,88,89], as well as in ensuring their key role as fish nurseries [2,84].
Even though our study detected a similar total number of species between Gran Canaria and Mallorca, the former region had more diverse fish assemblages, from both taxonomic and functional points of view, relative to the western Mediterranean regions. It is worth noting that these differences in functional diversity, despite no overall differences in the functional identity of the meadows, might be related to a different distribution of traits among dominant and rare species across regions, as the Rao Q is an entropy measure that reflects averaged pairwise functional dissimilarities, whilst accounting for species abundances. For instance, Mallorca had the lowest mean values of functional diversity, which could be explained by the fact that these meadows have relatively large abundances of functionally similar species. For instance, Mallorca meadows homed large abundances of Boop boops and Atherina spp., two species that form large schools in the water column and share similar traits, for example, both have a fusiform body and are planktivorous. Similarly, the Sparids Diplodus vulgaris and Diplodus annularis, which share similar functional attributes, were also very abundant in these meadows. The prevalence of marked seasonality (i.e., variability in SST and habitat structure) likely facilitates the persistence of similar species [90,91,92,93,94], as a result, for instance, of reducing competitive exclusion [14].
Typically, the greatest diversity of fish assemblages across latitudinal gradients, at least from a taxonomic perspective, is found in tropical and sub-tropical areas [5,79]. Our results provide evidence of the role of temperature in supporting more taxonomically diverse fish assemblages at low-latitude locations, whilst stressing the role of temperature in increasing the complementarity in the functional roles among co-occurring fishes [95,96,97]. Our results, however, contradict those obtained by Espino [1], when considering the total number of species per region, as they previously found a total number of species in the Canary Islands lower than in the Western Mediterranean. While our study was empirical, with the same number of sampled meadows per region and replication levels, results from [1] were derived from a literature review based on species lists. It is plausible, therefore, that the large number of studies in Mediterranean seagrass meadows, and thus the existence of a sampling bias, contribute to explaining such inconsistencies between ours and their work.
A complementary explanation for the lower fish diversity in Mediterranean waters, relative to meadows from the Canary Islands, may be the presence of extensive meadows created by the iconic endemic seagrass Posidonia oceanica in the Mediterranean, which may provide an alternative habitat for nearshore fish species [98,99,100]. This could help to explain the relatively “poor” fish assemblages associated with C. nodosa meadows in the two Mediterranean regions, although, to our knowledge, studies comparing fish diversity patterns between P. oceanica and C. nodosa meadows are lacking.
In contrast, the seagrass C. nodosa is the main habitat creator on shallow soft bottoms from the Canary Islands, providing consistent structural complexity to associated faunal assemblages [101], and so enabling a high abundance and diversity of fish assemblages and invertebrates [1,37,38,101,102]. Furthermore, C. nodosa meadows in the Canary Islands have been identified as playing a critical role in the recruitment of nearshore fishes [37,38], all of which suggests a strong dependence of fish assemblages on the presence and stability of their seagrass habitat in this region. Such diverse fish assemblages associated with stable environments may be especially vulnerable to increasing extreme events associated with climate change scenarios [103]. Furthermore, C. nodosa meadows in this region are less resistant and resilient to disturbances than Mediterranean meadows [56,104]. In brief, seagrass meadows created by C. nodosa in the Canary Islands and associated fish populations are likely to be more vulnerable under global change scenarios, with potentially critical consequences on fisheries stocks. Overall, our study has contributed to understanding variation in fish assemblages associated with seagrass meadows observed across large spatial (biogeographical) scales. This provides crucial information for the management and conservation programs aiming to protect seagrass habitats, included in the EU Nature 2000 network of protected areas.
In conclusion, this article shows how biodiversity is not only regulated by a global context but is also subject to variability on a local scale. In the current context of global change and considering the consequences that have been modeled in relation to how it will affect seagrass meadows, studies such as this one is highly relevant to understand the behavior that these consequences will have on the biodiversity associated with the habitats that generate.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d14100808/s1, Figure S1: Pearson correlations matrix between each pair of predictor variables, Figure S2: Biplot illustrating the quality of the multidimensional functional space, measure through the deviation (MAD) of original trait-based distances and Euclidean distances in the functional space, Figure S3: Boxplot illustrating the correlation between individual traits and PCoA axes, Figure S4: Variation in the functional structure of fish assemblages across seagrass meadows for each region, Table S1: Location and physical description of each seagrass meadow, Table S2: Summary of fish species traits, Table S3: Summary of fish species abundances for the overall study, Table S4: Results of the GLMs testing for differences in diversity indices between regions, Table S5: Results of the GLMs testing for differences in fish assemblage structure and species’ abundances (as a responses variables) between regions (as a predictor variables), Table S6: Results of the “model selection” approach to assess the relative importance of predictor variables on fish diversity indices, Table S7: Results of the “model selection” approach to assess the relative importance of predictor variables on fish abundances.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: J.M.-C., F.T., J.T. and F.T. (Fiona Tomas); Data curation, J.M.-C. and F.T. (Fernando Tuya); Formal analysis, J.M.-C.; Funding acquisition, F.T. (Fernando Tuya); Investigation, J.M.-C., F.T. (Fiona Tomas), Y.F.-T., L.R., F.E., L.A., N.E.B., I.C., G.H., C.M.-M., Á.M.-R., L.P.-B., Y.D.P.-R., J.T. and F.T. (Fernando Tuya); Project administration, F.T. (Fernando Tuya); Supervision, F.T. (Fiona Tomas) and F.T. (Fernando Tuya); Writing—original draft, J.M.-C.; Writing—review and editing, F.T. (Fiona Tomas) and F.T. (Fernando Tuya). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by a doctoral fellowship together with a fellowship to support the completion of the thesis from Universidad de Los Lagos (Chile) to Julia Máñez Crespo. The work was funded by a project (RESIGRASS, CGL2014-58829), supported by the Secretaría de Estado de Investigación, Desarrollo e Innovación (MINECO, Government of Spain) to F. Tomas and F. Tuya.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a doctoral fellowship together with a fellowship to support the completion of the thesis from Universidad de Los Lagos (Chile) to Julia Máñez Crespo. The work was funded by a project (RESIGRASS, CGL2014-58829), supported by the Secretaría de Estado de Investigación, Desarrollo e Innovación (MINECO, Government of Spain) to F. Tomas and F. Tuya. We acknowledge: Tony Sánchez, F. Otero-Ferrer, Luis M. Ferrero Vicente, Andrea García Hierro, Paula Anglada Vink, Rocío Jiménez, Gonzalo Egea, Donna Van der Lenn, Tiny Westra and José L. Sánchez-Lizaso for their help during fieldwork and different aspects of this study. We want to thank Alejandro H. Buschmann for providing feedback. We acknowledge Marina Alicante for providing nautical support for subtidal works at Alicante. We acknowledge Cástor Guisande for his help with the “EcoInd” R package and David Warton for his help with the “Mvabund” package. This study followed the national rules of Spain and permits were obtained when necessary to carry out subtidal experimentation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Espino, F.; Brito, A.; Haroun, R.; Tuya, F. Macroecological analysis of the fish fauna inhabiting Cymodocea nodosa seagrass meadows. J. Fish Biol. 2015, 87, 1000–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, H.; Mizutani, A.; Nanjo, K.; Tsutsumi, K.; Kohno, H. Fish assemblage structure response to seagrass bed degradation due to overgrazing by the green sea turtle Chelonia mydas at Iriomote Island, southern Japan. Ichthyol. Res. 2020, 68, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Tang, S.; Li, C.; Fang, H.; Hu, H.; Yang, J.; Ding, J.; Jiang, Z. Environmental effects on vertebrate species richness: Testing the energy, environmental stability and habitat heterogeneity hypotheses. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillebrand, H. On the generality of the latitudinal diversity gradient. Am. Nat. 2004, 163, 192–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, J.T.; Schluter, D. The latitudinal gradient in recent speciation and extinction rates of birds and mammals. Science 2007, 315, 1574–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecl, G.T.; Araújo, M.B.; Bell, J.D.; Blanchard, J.; Bonebrake, T.C.; Chen, I.-C.; Clark, T.D.; Colwell, R.K.; Danielsen, F.; Evengård, B.; et al. Biodiversity redistribution under climate change: Impacts on ecosystems and human well-being. Science 2017, 355, eaai9214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.G.; Calder, W.J.; Cumming, G.; Hughes, T.P.; Jentsch, A.; LaDeau, S.; Lenton, T.M.; Shuman, B.; Turetsky, M.R.; Ratajczak, Z.; et al. Climate change, ecosystems and abrupt change: Science priorities. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 375, 20190105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, H.L. Marine benthic diversity: A comparative study. Am. Nat. 1968, 102, 243–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopfer, P.H. Environmental determinants of faunal diversity. Am. Nat. 1959, 873, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopfer, P.H.; MacArthur, R.H. Niche size and faunal diversity. Am. Nat. 1960, 94, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavieres, L.; Arroyo, M.T.K.; Peñaloza, A.; Molina-Montenegro, M.; Torres, C. Nurse effect of Bolax gummifera cushion plants in the alpine vegetation of the Chilean Patagonian Andes. J. Veg. Sci. 2002, 13, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.B. The ‘Intermediate disturbance hypothesis’ of species coexistence is based on patch dynamics. N. Z. J. Ecol. 1994, 18, 176–181. [Google Scholar]
- Libralato, S.; Agnetta, D. From ecological trade-offs to resilience: Insights from exploited marine ecosystems. Curr. Opin. Syst. Biol. 2019, 13, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connell, J.H. Diversity in tropical rain forest and coral reefs: High diversity of trees and corals is maintained only in a nonequilibrium state. Science 1978, 199, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaffar, Z.; Pearman, J.K.; Curdia, J.; Ellis, J.; Calleja, M.L.; Ruiz-Compean, P.; Roth, F.; Villalobos, R.; Jones, B.H.; Moran, X.A.G.; et al. The role of seagrass vegetation and local environmental conditions in shaping benthic bacterial and macroinvertebrate communities in a tropical coastal lagoon. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petchey, O.L.; Gaston, K.J. Functional diversity (FD), species richness and community composition. Ecol. Lett. 2002, 5, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, B.J.; Enquist, B.J.; Weiher, E.; Westoby, M. Rebuilding community ecology from functional traits. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2006, 21, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadotte, M.; Albert, C.H.; Walker, S.C. The ecology of differences: Assessing community assembly with trait and evolutionary distances. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 1234–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R. Diversity and dissimilarity coefficients: A unified approach. Theor. Popul. Biol. 1982, 21, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violle, C.; Thuiller, W.; Mouquet, N.; Munoz, F.; Kraft, N.J.; Cadotte, M.W.; Livingstone, S.W.; Mouillot, D. Functional rarity: The ecology of outliers. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2017, 32, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, N.E.; Gonçalves, J.M.S.; Erzini, K.; Tuya, F. “How” and “what” matters: Sampling method affects biodiversity estimates of reef fishes. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadotte, M.W. The new diversity: Management gains through insights into the functional diversity of communities. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 48, 1067–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camara, E.M.; de Azevedo, M.C.C.; Franco, T.P.; Araújo, F.G. Hierarchical partitioning of fish diversity and scale-dependent environmental effects in tropical coastal ecosystems. Mar. Environ. Res. 2019, 148, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona, C.P.; de Bello, F.; Mason, N.W.H.; Lepš, J. Traits without borders: Integrating functional diversity across scales. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2016, 31, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamfeldt, L.; Lefcheck, J.S.; Byrnes, J.E.; Cardinale, B.J.; Duffy, J.E.; Griffin, J.N. Marine biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: What’s known and what’s next? Oikos 2015, 124, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuya, F.; Herrero-Barrencua, A.; Bosch, N.E.; Abreu, A.D.; Haroun, R. Reef fish at a remote tropical island (Principe Island, Gulf of Guinea): Disentangling taxonomic, functional and phylogenetic diversity patterns with depth. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2018, 69, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.P.; Jones, C.G.; Boeken, B.; Shachak, M. Predictability of ecosystem engineering effects on species richness across environmental variability and spatial scales. J. Ecol. 2006, 94, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dray, S.; Legendre, P. Testing the species traits-environment relationships: The fourth-corner problem revisited. Ecology 2008, 89, 3400–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilley, R.J.; Unsworth, R.K.F. Atlantic Cod (Gadus morhua) benefits from the availability of seagrass (Zostera marina) nursery habitat. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2014, 2, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwood, E.T.; Greening, H.S.; Johansson, J.O.R.; Kaufman, K.; Raulerson, G.E. Tampa Bay (Florida, USA): Documenting seagrass recovery since the 1980′s and reviewing the benefits. Southeast. Geogr. 2017, 57, 294–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourqurean, J.W.; Duarte, C.M.; Kennedy, H.; Marbà, N.; Holmer, M.; Mateo, M.A.; Apostolaki, E.T.; Kendrick, G.A.; Krause-Jensen, D.; McGlathery, K.J.; et al. Seagrass ecosystems as a globally significant carbon stock. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricart, A.M.; York, P.H.; Rasheed, M.A.; Pérez, M.; Romero, J.; Bryant, C.V.; Macreadie, P.I. Variability of sedimentary organic carbon in patchy seagrass landscapes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 100, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bañolas, G.; Fernández, S.; Espino, F.; Haroun, R.; Tuya, F. Evaluation of carbon sinks by the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa at an oceanic island: Spatial variation and economic valuation. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2020, 187, 105112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelli, C.M.; Unsworth, R.K.F. Protecting the hand that feeds us: Seagrass (Zostera marina) serves as commercial juvenile fish habitat. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 83, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Horinouchi, M.; Nakai, T.; Sano, M. Food habits of fishes in a seagrass bed on a fringing coral reef at Iriomote Island, southern Japan. Ichthyol. Res. 2003, 50, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, M.; Schmidt, A.; Romanuk, T.; Lotze, H.K. Food-web structure of seagrass communities across different spatial scales and human impacts. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espino, F.; Tuya, F.; Brito, A.; Haroun, R. Variabilidad espacial en la estructura de la ictiofauna asociada a praderas de Cymodocea nodosa en las Islas Canarias, Atlántico nororiental subtropical. Rev. Biol. Mar. Oceanogr. 2011, 46, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espino, F.; Tuya, F.; Brito, A.; Haroun, R. Ictiofauna asociada a las praderas de cymodocea nodosa en las islas canarias (Atlántico centro oriental): Estructura de la comunidad y función de “guardería”. Cienc. Mar. 2011, 37, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hayes, M.A.; McClure, E.C.; York, P.H.; Jinks, K.I.; Rasheed, M.A.; Sheaves, M.; Connolly, R.M. The differential importance of deep and shallow seagrass to nekton assemblages of the great barrier reef. Diversity 2020, 12, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, D.A. A review of ecological studies on seagrass-fish communities, with particular reference to recent studies in australia. Aquat. Bot. 1984, 18, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck Hay, K.; Hays, G.; Orth, R. Critical evaluation of the nursery role hypothesis for seagrass meadows. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 253, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaber, S.J.M.; Brewer, D.T.; Salini, J.P. Fish communities and the nursery role of the shallow inshore waters of a tropical bay in the gulf of Carpentaria, Australia. Estuarine, Coast. Shelf Sci. 1995, 40, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullström, M.; de la Torre Castro, M.; Bandeira, S.O.; Björk, M.; Dahlberg, M.; Kautsky, N.; Rönnbäck, P.; Öhman, M.C. Seagrass ecosystems in the western seagrass ecosystems in the western Indian ocean. AMBIO J. Hum. Environ. 2002, 31, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyndes, G.A.; Kendrick, A.J.; MacArthur, L.D.; Stewart, E. Differences in the species- and size-composition of fish assemblages in three distinct seagrass habitats with differing plant and meadow structure. Mar. Biol. 2003, 142, 1195–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.M. Feeding ecology of eelgrass fish communities. Trans. Am. Fish Soc. 1976, 105, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beu, J.D.; Westoby, M. Abundance of macrofauna in dense seagrass is due to habitat preference, not predation. Oecologia 1986, 68, 205–209. [Google Scholar]
- Connolly, R.M. Removal of seagrass canopy: Effects prey on small fish and their prey. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1994, 184, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.P.; Bellwood, D.R.; Connolly, S.R. Biodiversity hotspots, centres of endemicity, and the conservation of coral reefs. Ecol. Lett. 2002, 5, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuya, F.; Martín, J.A.; Luque, A. Seasonal cycle of a Cymodocea nodosa seagrass meadow and of the associated ichthyofauna at Playa Dorada (Lanzarote, Canary Islands, eastern Atlantic). Cienc. Mar. 2006, 32, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hemingson, C.R.; Bellwood, D.R. Biogeographic patterns in major marine realms: Function not taxonomy unites fish assemblages in reef, seagrass and mangrove systems. Ecography 2018, 41, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masucci, A.; Arnaud-Haond, S.; Eguíluz, V.M.; Hernández-García, E.; Serrão, E.A. Genetic flow directionality and geographical segregation in a cymodocea nodosa genetic diversity network. EPJ Data Sci. 2012, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuya, F.; Fernández-Torquemada, Y.; Zarcero, J.; Del Pilar-Ruso, Y.; Csenteri, I.; Espino, F.; Manent, P.; Curbelo, L.; Antich, A.; De La Ossa, J.A.; et al. Biogeographical scenarios modulate seagrass resistance to small-scale perturbations. J. Ecol. 2019, 107, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Máñez-Crespo, J.; Tuya, F.; Fernández-Torquemada, Y.; Royo, L.; del Pilar-Ruso, Y.; Espino, F.; Manent, P.; Antich, L.; Castejón-Silvo, I.; Curbelo, L.; et al. Seagrass Cymodocea nodosa across biogeographical regions and times: Differences in abundance, meadow structure and sexual reproduction. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 162, 105159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, C.R.; Yeager, L.A.; Bolser, D.G.; Bonsell, C.; Dichiera, A.M.; Hou, Z.; Keyser, S.R.; Khursigara, A.J.; Lu, K.; Muth, A.F.; et al. Does functional redundancy affect ecological stability and resilience? A review and meta-analysis. Ecosphere 2020, 11, e03184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalding, M.D.; Fox, H.E.; Allen, G.R.; Davidson, N.; Ferdaña, Z.A.; Finlayson, M.; Halpern, B.S.; Jorge, M.A.; Lombana, A.; Lourie, S.A.; et al. Marine ecoregions of the world: A bioregionalization of coastal and shelf areas. Bioscience 2007, 57, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuya, F.; Fernández-Torquemada, Y.; del Pilar-Ruso, Y.; Espino, F.; Manent, P.; Curbelo, L.; Otero-Ferrer, F.; de la Ossa, J.A.; Royo, L.; Antich, L.; et al. Partitioning resilience of a marine foundation species into resistance and recovery trajectories. Oecologia 2021, 196, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smale, D.A.; Wernberg, T. Satellite-derived SST data as a proxy for water temperature in nearshore benthic ecology. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 387, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuya, F.; Boyra, A.; Sanchez-Jerez, P.; Haroun, R.J. Multivariate analysis of the bentho-demersal ichthyofauna along soft bottoms of the Eastern Atlantic: Comparison between unvegetated substrates, seagrass meadows and sandy bottoms beneath sea-cage fish farms. Mar. Biol. 2005, 147, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, N.E.; Wernberg, T.; Langlois, T.J.; Smale, D.A.; Moore, P.J.; Franco, J.N.; Thiriet, P.; Feunteun, E.; Ribeiro, C.; Neves, P.; et al. Niche and neutral assembly mechanisms contribute to latitudinal diversity gradients in reef fishes. J. Biogeogr. 2021, 48, 2683–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart-Smith, R.D.; Bates, A.E.; Lefcheck, J.; Duffy, J.E.; Baker, S.C.; Thomson, R.J.; Stuart-Smith, J.F.; Hill, N.A.; Kininmonth, S.J.; Airoldi, L.; et al. Integrating abundance and functional traits reveals new global hotspots of fish diversity. Nature 2013, 501, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouillot, D.; Villéger, S.; Parravicini, V.; Kulbicki, M.; Arias-González, J.E.; Bender, M.; Chabanet, P.; Floeter, S.R.; Friedlander, A.; Vigliola, L.; et al. Functional over-redundancy and high functional vulnerability in global fish faunas on tropical reefs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13757–13762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villéger, S.; Brosse, S.; Mouchet, M.; Mouillot, D.; Vanni, M.J. Functional ecology of fish: Current approaches and future challenges. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 79, 783–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramer, E.J. Bird species diversity: Components of Shannon’s formula. Ecology 1969, 50, 927–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisande, C.; Heine, J.; García-Roselló, E.; González-Dacosta, J.; Vilas, L.G.; Perez-Schofield, B.J.G. An algorithm for comparing species diversity between assemblages. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 81, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margalef, R. Ecología, Biogeografía y Evolución. Rev. Univ. Madr. 1959, 8, 221–273. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10261/165713 (accessed on 27 September 2022).
- Pielou, E.C. Shannon’s formula as a measure of specific diversity: Its use and misuse. Am. Nat. 1966, 100, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. A taxonomic distinctness index and its statistical properties. J. Appl. Ecol. 1995, 35, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Simko, V. Visualization of a correlation matrix. Statistician 2017, 56, 316–324. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, X.A.; Donaldson, L.; Correa-Cano, M.E.; Evans, J.; Fisher, D.N.; Goodwin, C.E.D.; Robinson, B.S.; Hodgson, D.J.; Inger, R. A brief introduction to mixed effects modelling and multi-model inference in ecology. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolker, B.M. Ecological Models and Data in R; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Miles, J. Tolerance and variance inflation factor. In Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Legendre, P.; Anderson, M.J. Distance-based redundancy analysis: Testing multispecies responses in multifactorial ecological experiments. Ecol. Monogr. 1999, 69, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Ohara, B.; Henry, M.; Maintainer, H.S. The vegan package title community ecology package. Community Ecol. Package 2007, 10, 631–637. [Google Scholar]
- Bartoń, K. Multi-Model Inference; R package 1.43.15; 2019. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/MuMIn/MuMIn.pdf (accessed on 27 September 2022).
- Wang, Y.A.; Wright, S.T. mvabund-an R package for model-based analysis of multivariate abundance data. In Methods in Ecology and Evolution; British Ecological Society: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gower, J.C. A general coefficient of similarity and some of its properties. Biometrics 1971, 27, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maire, E.; Grenouillet, G.; Brosse, S.; Villéger, S. How many dimensions are needed to accurately assess functional diversity? A pragmatic approach for assessing the quality of functional spaces. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2015, 24, 728–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magneville, C.; Loiseau, N.; Albouy, C.; Casajus, N.; Claverie, T.; Escalas, A.; Leprieur, F.; Maire, E.; Mouillot, D.; Villéger, S. mFD: An R package to compute and illustrate the multiple facets of functional diversity. Ecography 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, S.F.; Hortal, J.; Cassemiro, F.A.S.; Rangel, T.F.; Diniz-Filho, J.A.F. Nonstationary effects of productivity, seasonality, and historical climate changes on global amphibian diversity. Ecography 2013, 36, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tittensor, D.P.; Mora, C.; Jetz, W.; Lotze, H.K.; Ricard, D.; Berghe, E.V.; Worm, B. Global patterns and predictors of marine biodiversity across taxa. Nature 2010, 466, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, G.J.; Alexander, T.J.; Lefcheck, J.S.; Bates, A.E.; Kininmonth, S.J.; Thomson, R.J.; Duffy, J.E.; Costello, M.J.; Stuart-Smith, R.D. Abundance and Local-Scale Processes Contribute to Multi-Phyla Gradients in Global Marine Diversity. Available online: http://advances.sciencemag.org/ (accessed on 27 September 2017).
- Mittelbach, G.G.; Schemske, D.W.; Cornell, H.V.; Allen, A.P.; Brown, J.M.; Bush, M.B.; Harrison, S.P.; Hurlbert, A.H.; Knowlton, N.; Lessios, H.A.; et al. Evolution and the latitudinal diversity gradient: Speciation, extinction and biogeography. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilby, B.; Olds, A.; Connolly, R.; Maxwell, P.; Henderson, C.; Schlacher, T. Seagrass meadows shape fish assemblages across estuarine seascapes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 588, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, R.; Hindell, J.; Gorman, D. Seagrass and epiphytic algae support nutrition of a fisheries species, Sillago schomburgkii, in adjacent intertidal habitats. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 286, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsworth, R.K.F.; Nordlund, L.M.; Cullen-Unsworth, L.C. Seagrass meadows support global fisheries production. Conserv. Lett. 2019, 12, e12566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordlund, L.M.; Jackson, E.L.; Nakaoka, M.; Samper-Villarreal, J.; Beca-Carretero, P.; Creed, J.C. Seagrass ecosystem services—What’s next? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 134, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verweij, M.C.; Nagelkerken, I.; Hans, I.; Ruseler, S.M.; Mason, P.R.D. Seagrass nurseries contribute to coral reef fish populations. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 1540–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacArthur, L.D.; Hyndes, G.A. Differential use of seagrass assemblages by a suite of odacid species. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2001, 52, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullström, M.; Bodin, M.; Nilsson, P.G.; Öhman, M.C. Seagrass structural complexity and landscape configuration as determinants of tropical fish assemblage composition. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 363, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, G.P.; Sutherland, C.R. The influence of habitat structure on nearshore fish assemblages in a southern Australian embayment: Colonisation and turnover rate of fishes associated with artificial macrophyte beds of varying physical structure. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1997, 218, 103–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barot, S.; Gignoux, J. Mechanisms promoting plant coexistence: Can all the proposed processes be reconciled? Oikos 2018, 106, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacala, S.W.; Tilman, D. Limiting similarity in mechanistic and spatial models of plant competition in heterogeneous environments. Am. Nat. 1994, 143, 222–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesson, P.; Pacala, S.; Neuhauser, C. Environmental niches and ecosystem functioning. In The Functional Consequences of Biodiversity; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 213–245. [Google Scholar]
- Tredennick, A.T.; Adler, P.B.; Adler, F.R. The relationship between species richness and ecosystem variability is shaped by the mechanism of coexistence. Ecol. Lett. 2017, 20, 958–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, N.E.; McLean, M.; Zarco-Perello, S.; Bennett, S.; Stuart-Smith, R.D.; Vergés, A.; Pessarrodona, A.; Tuya, F.; Langlois, T.; Spencer, C.; et al. Persistent thermally driven shift in the functional trait structure of herbivorous fishes: Evidence of top-down control on the rebound potential of temperate seaweed forests? Glob. Chang. Biol 2022, 28, 2296–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.H.; Piermarini, P.M.; Choe, K.P. The multifunctional fish gill: Dominant site of gas exchange, osmoregulation, acid-base regulation, and excretion of nitrogenous waste. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 97–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.H. Why are there so many species in the tropics? J. Biogeogr. 2014, 41, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marco-Méndez, C.; Ferrero-Vicente, L.M.; Prado, P.; Heck, K.L.; Cebrián, J.; Sánchez-Lizaso, J.L. Epiphyte presence and seagrass species identity influence rates of herbivory in Mediterranean seagrass meadows. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 154, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco-Méndez, C.; Ferrero-Vicente, L.M.; Prado, P.; Sánchez-Lizaso, J.L. Epiphytes and nutrient contents influence Sarpa salpa herbivory on Caulerpa spp vs. seagrass species in Mediterranean meadows. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 184, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogirou, S.; Corsini-Foka, M.; Sioulas, A.; Wennhage, H.; Pihl, L. Diversity, structure and function of fish assemblages associated with Posidonia oceanica beds in an area of the eastern Mediterranean Sea and the role of non-indigenous species. J. Fish Biol. 2010, 77, 2338–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuya, F.; Png-Gonzalez, L.; Riera, R.; Haroun, R.; Espino, F. Ecological structure and function differs between habitats dominated by seagrasses and green seaweeds. Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 98, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, M.C.; Martin, D.; Núñez, J. Polychaetes associated to a Cymodocea nodosa meadow in the Canary Islands: Assemblage structure, temporal variability and vertical distribution compared to other Mediterranean seagrass meadows. Mar. Biol. 2005, 146, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stott, P. How climate chanfe affects extreme weather events. Clim. Chang. 2016, 352, 2158–2164. [Google Scholar]
- Tuya, F.; Asensio, M.; Bosch, N.E.; García, A.; Navarro, A. Partitioning multiple diversity dimensions of nearshore fish assemblages within a coastal seascape. Hydrobiologia 2019, 834, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).