Abstract
Steindachneridion melanodermatum is the largest catfish of the Lower Iguaçu River and is endangered due to the habitat fragmentation caused by dams. Currently, the wild population’s last refuge is restricted to an area of 190 km. This study presents the first analysis of its genetic diversity and population structure, using microsatellite loci and mtDNA. The population has an adequate level of genetic diversity, but signs of a recent bottleneck were observed. The Baixo Iguaçu Hydroelectric Power Plant has recently fragmented the population and threatened it with extinction in a reduced area of nearly 30 km. Based on our results, we strongly advise against the stocking of breeding specimens below the Salto Caxias HPP to not compromise the integrity of the native gene pools at the receptor sites. In addition, we recommend manual fish transposition, trap-and-haul, to maintain the genetic connectivity of individuals upstream and downstream of the dam as a conservation strategy. Furthermore, studies on behavior and swimming capacities, and suitable fishways for this species must be developed. We strongly recommend that the Lower Iguaçu River and its tributaries be protected and preserved as free from additional barriers to prevent future habitat disruption for the benefit of S. melanodermatum and several other endemic and endangered species.
1. Introduction
The world’s aquatic environments have faced intense deterioration due to habitat loss or degradation, water pollution, and over-exploitation [1,2]. Among the main drivers of river deterioration is the construction of dams to produce hydroelectricity, with 63 percent of rivers over 1000 km long impacted globally [3]. The resulting hydroelectric plants cause habitat fragmentation, affecting the migration or dispersion of fish species [4] and, consequently, causing loss of genetic diversity [5]. Despite this, there are no diversion channels for fish movement downstream in the HPP in Brazil, and only a few hydroelectric dams have fish passages (mainly fish ladders) [6,7].
The Iguaçu River is one of the largest southern tributaries of the Paraná River, integrating the most heavily fragmented watershed in South America [8]. This river is the second most polluted urban river in Brazil [9], and the pollution is mainly from industrial and domestic sewage from urban areas in the Higher Iguaçu region [10]. Water pollution, especially from contamination by pesticides used in agriculture, has negatively affected fish species in streams in the middle and lower portions of the basin [11,12,13]. In addition, the Iguaçu river basin is significant, being considered an ecoregion [14] with many endemic fishes [14,15]. Of the 127 known fish species in the basin [16,17], 76 were identified only in the Lower Iguaçu river basin, of which 42% are endemic, and three are endangered and sampled in low abundance (<1%) (Gymnogeophagus taroba, Psalidodon gymnogenys, and S. melanodermatum) [18]. Those species are partially protected by the Iguaçu National Park (INP), a world heritage site and one of the few remaining areas of Atlantic Forest protected by law. Due to the favorable topographical relief of the Lower Iguaçu River, six hydroelectric dams (Figure 1) have been built since 1975, transforming the original rapids and waterfalls into a sequence of flooded areas [17,19]. These constructions changed the landscape and the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics [17], generating a decline in habitat quality and occupation area for rheophilic fishes [20]. The Baixo Iguaçu HPP operation was authorized in 2019 [19] by the Brazilian Federal Government [21,22,23], despite being very controversial, due to the possible impacts on the INP, located only about 500 m downstream of the HPP [19].
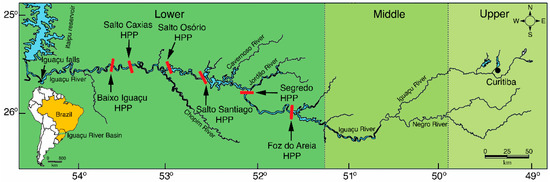
Figure 1.
Map showing the location of six hydroelectric power plants (HPP) (red bars) built in the main channel of the Lower Iguaçu River.
Steindachneridion melanodermatum Garavello, 2005, popularly known as ‘Surubim’ (suru’wi in Tupi language), is a common designation for some Pimelodidae catfish. This species is the largest fish in the Iguaçu River [24]. It is rheophilic and possibly migratory [20,25], inhabiting deep pools with rocky bottoms [19,24]. The species is rare and restricted to the lower Iguaçu River. However, the wild population of S. melanodermatum likely no longer exists in most areas of the Lower Iguaçu River. The lack of proper sampling along the basin means that the precise limit of its distribution upstream of Salto Caxias has not been established [20]. Nevertheless, there are records of the species downstream of the Segredo reservoir [20], below the Salto Osório dam [26], and in lotic environments in Salto Caxias [27]. However, since 2003, monitoring the ichthyofauna between the Salto Osório HPP and Salto Caxias HPP led to the capture of only a single specimen in 2006 [26]. This realization led the Ministry of Environment of Brazil to decree the status of an endangered species (EN) for S. melanodermatum [28] in 2014. On the other hand, downstream of the Salto Caxias HPP, 500 specimens were collected in 1998 [25], and 180 between 2012 and 2016 [29], demonstrating that the region is essential for the maintenance of S. melanodermatum; mainly in the domains of the INP, where this species seems to be more abundant [19]. Therefore, the S. melanodermatum population was possibly restricted along the 190 km downstream from Salto Caxias HPP to upstream of the Iguaçu Falls until 2019 but then suffered a new fragmentation following the construction of the Baixo Iguaçu HPP [19]. Currently, the last uninterrupted stretch of the Lower Iguaçu River is approximately 160 km long and extends downstream of the Baixo Iguaçu HPP dam to the Iguaçu Falls.
Only Gymnogeophagus taroba has been genetically evaluated in the region [30], although the peculiarity of the Lower Iguaçu River and the negative impact of dams in the distribution of fish genetic diversity have been recognized. The inspection of endangered species’ genetic diversity and structure is fundamental for their conservation [31]. Long-term persistence depends on sufficient genetic diversity to adapt and survive in changing environments [32]. When populations evolve in response to environmental changes, a small and isolated population is more likely to lose genetic diversity, and consequently, present population decline, than a large population with high genetic diversity [33,34]. If local populations are small, gene flow is the key factor in preventing stochastic loss of genetic diversity [35].
Molecular markers are powerful tools for quantifying genetic variation in individuals and populations, contributing to the management and conservation of species [36,37]. Therefore, evaluating genetic diversity and characterizing population structure are of fundamental importance as management strategies that minimize the probability of population extinction [38]. Furthermore, since mtDNA includes haploid uniparental inheritance, an absence of genetic recombination, and mutation rates lower than in microsatellite loci (nuclear DNA), approaches combining these markers are advantageous, allowing investigating past (mtDNA) and contemporary (nuclear loci) interferences of the distribution of genetic diversity [34]. Thus, this study was developed to estimate the genetic diversity and population structure of S. melanodermatum in its last refuge [21,29] in the Lower Iguaçu river basin downstream of the Salto Caxias HPP.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
The specimens of S. melanodermatum used in this study were the same in two recently published studies dealing with reproductive biology [29] and the species’ spatial distribution and abundance [19]. For more details on collection techniques, see the cited articles. Samples of adipose fin and muscle of the S. melanodermatum were stored in microtubes containing 100% ethanol and maintained at −20 °C. Samples used in the present study came from the Lower Iguaçu River from three different sampling points, S1, S2, and S3 (Figure 2), located between downstream of the Salto Caxias HPP (25°32′52.61″ S, 53°31′29.96″ W) and upstream of the Iguaçu Falls (25°35′51.85″ S, 54°23′29.89″ W), comprising a 190-km stretch of river. It is important to note that the samples were collected before the construction of the Baixo Iguaçu HPP. Of the 180 specimens used in previous studies [19,27], 95 were analyzed in this study (S1 − N = 5; S2 − N = 45 and S3 − N = 45). Despite the same sampling effort in the three study sites (57 samplings between 2012 and 2016), only six individuals were captured at the S1 site [19], and, of these, it was only possible to extract the DNA from five individuals. S2 (also known as Poço Preto) and S3 are in the Conservation Unit of the Iguaçu National Park (INP), a protected area of dense forest. All sampling sites are characterized by deep pools and rapids with rocky basaltic-rock bottoms [19]. Of the 95 specimens of S. melanodermatum used in our study, 63 specimens were returned alive to the sampling site after removing a small part of the adipose fin.
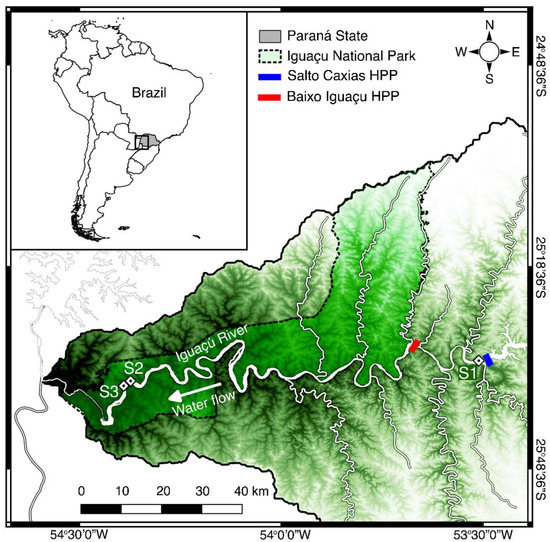
Figure 2.
Map of southern South America showing sampling sites of Steindachneridion melanodermatum in the Lower Iguaçu River. The red bar represents the Baixo Iguaçu HPP, the blue bar indicates the Salto Caxias HPP, and the dashed lines indicate the Iguaçu National Park area in Brazil (Parque Nacional do Iguaçu) and Argentina (Parque Nacional Iguazú).
2.2. DNA Extraction and Quantification
Total genomic DNA was obtained using a Chelex protocol [39]. NanoDropTM 1000 was used to determine DNA concentrations, and samples were diluted to the concentration of 5 ng/μL.
2.3. Microsatellite Markers (SSR)
For SSR analysis, cross-amplification tests were conducted from 12 pairs of primers available for other species of the family Pimelodidae: eight of S. parahybae (Spa) [40] and four of Pimelodus maculatus (Pma) [41]. Reagent concentrations and PCR conditions were performed according to a previous report [5]. The annealing temperatures of successful cross-amplification loci were 48 °C (Pma4 and Pma6), 50 °C (Spa11), 52 °C (Pma9), 54 °C (Spa2, Spa4, Spa8, Spa12, Spa17, and Spa18), and 56 °C (Spa14, Pma2). Individual genotyping was performed in an ABI 3500-XL automated sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA), with the GeneScan 600 Liz (Applied Biosystems) molecular weight marker. Genotypes were determined using GeneMarker 1.85 software (Soft Genetics, State College, PA, USA). The Micro-Checker v. 2.2.1 program [42] was employed to evaluate null alleles or genotyping errors, such as allelic dropout and stutter peaks.
2.4. mtDNA (D-Loop) Haplotypes
A portion of the D-loop region of the mitochondrial DNA of S. melanodermatum was amplified with primers L2910—5′CTA ACT CCC AAA GCT AGT ATT C 3′ and H3010—(5′ C TTC AGT GTT ATG CTT TAT TTA AGC TAC 3′) [43]. PCR reactions were performed in a 15 μL final volume, containing 1X GoTaq Master Mix (Promega), 1 μM of each primer, 15 ng DNA, and ultrapure water to the volume. The thermal profiling included an initial denaturation at 94 °C for 3 min, followed by 41 cycles at 94 °C for 1 min, annealing at 52 °C for 45 s, and extension at 72 °C for 2 min, with a final extension at 72 °C for 10 min. The PCR products were checked for amplification using gel electrophoresis, with 1% agarose gels purified using ExoSAP IT (Life Technologies Corporation, Carlsbad, CA, EUA). Sequencing reactions were performed using BigDye TM Terminator v. 3.1 (Applied Biosystems), and an ABI-PRISM 3500 XL automated sequencer (Applied Biosystems) was used for sequence analysis. Each individual’s DNA sequences were edited using the ClustalW application [44] in BioEdit 7.1.3.0 [45]. NCBI’s BLAST search (Basic Local Alignment SearchTool) [46] was used to confirm the origin of the fragment. An online version of the tRNAscan-SE [47] was used to search for possible tRNA, available at http://lowelab.ucsc.edu/tRNAscan-SE (accessed on 18 March 2021). Sequences of the 27 different haplotypes were deposited in GenBank (MZ672137 to MZ672163).
2.5. Genetic Diversity Analyses
For microsatellite analysis, the Cervus 3.0 program [48] was employed to test the potential of loci showing positive cross-amplification in the population analysis assessing the polymorphic information content (PIC). The total allele number per population (A), average alleles per locus (NA), the average number of effective alleles (NE), observed heterozygosity (HO), expected heterozygosity (HE), and the number of private alleles were estimated using the Popgen v. 1.31 program [49]. The Fstat v. 2.9.3 program [50] was used to estimate the rate of inbreeding (FIS). Testing for deviations from the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) and linkage disequilibrium was performed using the Genepop v. 1.2 program [51], and alpha values were adjusted using sequential Bonferroni corrections [52]. In mtDNA data, the overall genetic diversity was estimated using DnaSP software [53] parameters: haplotype number (Nh), haplotype diversity (h), and nucleotide diversity (π). Median-joining networks were obtained using NETWORK 4.6.1.1 (www.fluxus-engineering.com) (accessed on 26 March 2021) to study the relationships between haplotypes and their geographic distribution [54]. Sequences from S. parahybae (accession MG12754–MG012789) [36] and S. scriptum (accession MF045370–MF045412) [55], available in GenBank, were added to help identify recent and older haplotypes present in S. melanodermatum.
2.6. Population Structure Analyses
We initially tested the hypothesis that there would be a single population of S. melanodermatum in the restricted area since it is considered a migratory species. Two Bayesian clustering approaches were used: STRUCTURE [56] and Bayesian analysis of population structure (BAPS) [57].
The assumed subpopulations (K) were set between 1 and 10 [58]. Twenty independent runs of 100,000 Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) iterations were discarded as burn-in, followed by 1,000,000 MCMC iterations for each value of K. The accurate estimate of K was obtained from convergent values of K summary statistics. The lnPr (X/K) values [56] and ΔK ad hoc statistics [59] were used to choose the most likely number of clusters (K) using Structure Harvester v. 0.6.7 [60]. The results of independent Structure runs were summarized for the best K using the ‘greedy’ algorithm in Clumpp 1.1.2 [61]. BAPS software [57] was used to access the number of populations without prior information of the sampling location for the mitochondrial dataset, with one replicate for each level of K (1–6). Genetic differentiation estimates on microsatellite data were assessed from pairwise FST values among sampling sites using Arlequin v. 3.5.1.3 [62], with estimates based on 10,000 permutations. Subsequently, p-values, corresponding to alpha = 0.05, were adjusted after Holm–Bonferroni correction for multiple tests [63]. The Arlequin program was also used on mtDNA data to estimate the genetic differentiation (pairwise ΦST) among the samples, using a mutation model provided by likelihood-ratio tests implemented on JModeltest [64].
2.7. Demographic Analyses
Signs of recent population bottlenecks were evaluated on microsatellite data using the Bottleneck v. 1.2.02 program [65] and considering deviations from the mutation–drift equilibrium: ‘Wilcoxon sign-rank test’, which indicates bottlenecks in the presence of significant excess heterozygosity, based on the infinite alleles model (IAM), stepwise mutation model (SMM) and two-phase model (TPM—with 90% SMM and 10% IAM), with a p-value < 0.05, and the ‘model shift test’, which indicates bottlenecks resulting from alterations in allele frequency distributions [66]. From mtDNA variation, DnaSP 5 was used to test any demographic expansion, to calculate the neutrality test indexes Tajima’s D [67] and Fu’s Fs [68], as well as the mismatch distribution analysis, using the sudden expansion model [69]. In addition, to analyze population size dynamics over time, we used the Bayesian skyline plot method (BSP) [70], implemented in BEAST 1.6.1 [71]. Two independent runs were performed, each with 50 million steps for the Markov chains Monte Carlo (MCMC), using an initial UPGMA tree and HKY + G substitution model, as indicated by the jModelTest software [64], and based on the Akaike information criterion correction for reduced sample size (AICc). Trees and parameters were sampled every 10,000 steps, with a burn-in of 10%. The dating of variations in effective population size was based on a strict molecular clock with log-normal distribution and a replacement rate of 1.8% (dp 0.05%) per million years (Ma), indicated for mtDNA in fish [72]. The convergence of parameters along the MCMC chains and the BSP performance (ESS values > 200) was observed using the Tracer v1.6 (BEAST package). The runs were combined using LogCombiner software (BEAST package) to analyze the convergence of strings, with 25% burn-in. The effective population size (Ne) from microsatellite data was calculated based on the linkage disequilibrium (LD) method [73], using the program NeEstimator v. 2.0 [74], and considering a random mating model and PCrit of 0.02 to allele frequencies.
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Diversity
In the cross-amplification test with the 12 primers, nine microsatellite loci were successfully amplified, but only six were polymorphic (Pma2, Spa2, Spa4, Spa8, Spa12, and Spa17) and used in the present study. The mean polymorphic information content (PIC) for the six loci was 0.574. Following a scale proposed by [75], four loci (Spa2, Spa8, Spa12, and Spa17) were highly informative, with PIC > 0.5, and two loci (Spa4 and Pma2) were moderately informative (PIC > 0.25). Thirty-eight microsatellite alleles, an average of 6.3 alleles per locus (NA), were obtained in the analysis. S1 showed the lowest number of alleles (19 alleles), while S2 showed the highest number (36 alleles). Per sample, the observed heterozygosity (HO) ranged from 0.644 (S3) to 0.693 (S2), and the expected heterozygosity (HE) from 0.567 (S1) to 0.626 (S2). S1 did not have any private alleles, while S2 and S3 had respectively five and two. The highest mean number of alleles per locus (NA = 6.000) and the mean number of effective alleles (NE = 3.754) were found in the S2 sample, while S1 had the lowest average for alleles per locus (NA = 13.167) and the smallest mean number of effective alleles (NE = 2.797). The inbreeding coefficient (FIS) was not significant for any of the samples (p-value > 0.05) (Table 1). The loci Spa4 and Spa17 presented significant deviation from the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) (p < 0.05), and evidence of linkage disequilibrium (LD) between three pairs of loci were observed (Spa4 × Spa17; Spa8 × Spa17; Spa12 × Spa17). The Micro-Checker program found no null alleles among the samples.

Table 1.
Genetic diversity and effective population size of Steindachneridion melanodermatum in three locations of the Lower Iguaçu River, based on microsatellite markers and mitochondrial haplotypes (D-Loop). N—number of individuals examined; A—total number of alleles; NA—mean number of alleles; NE—mean number of effective alleles; HO—observed heterozygosity; HE—expected heterozygosity; FIS—inbreeding coefficient; Ne—effective population size; Nh—number of haplotypes; h—haplotype diversity; π—nucleotide diversity; D—Tajima’s neutrality test, Fs—Fu’s neutrality test.
A fragment of 869 bp of the D-loop region was sequenced for each of the 95 captured S. melanodermatum specimens. The mtDNA analyzes showed high values of haplotype diversity (h > 0.5), ranging from 0.759 (S3) to 1.000 (S1), and low values of nucleotide diversity (π < 0.5%), ranging from 0.0029 (S3) to 0.0048 (S1) (Table 1). Twenty-seven different haplotypes were revealed, resulting from 22 polymorphic sites (16 transition and six transversion mutations), and two indel sites were found. The haplotype network showed no genetic structure, with few mutational steps among the haplotypes. H1 was the most common internal haplotype (n = 27) in all samples. The sample with the highest number of singletons was S2, with 11 haplotypes, followed by S1, with four haplotypes. Seventeen different haplotypes were observed in S. scriptum and 27 in S. parahybae. At least 14 and 109 mutational steps separate S. scriptum and S. parahybae from S. melanodermatum, respectively (Figure 3).
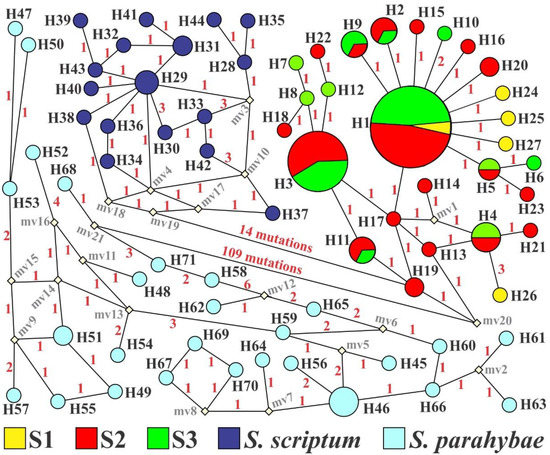
Figure 3.
Median-joining network among 27 haplotypes of 95 individuals of Steindachneridion melanodermatum samples, 27 haplotypes of S. parahybae, and 17 haplotypes of S. scriptum, based on partial sequencing of the D-loop region (mtDNA). The colors indicate locality; circle sizes are proportional to haplotype frequency, and small black circles are hypothetical ancestors or unsampled haplotypes. Numbers between haplotypes denote mutational steps between sequences.
3.2. Population Structure
The results indicated the existence of a single population in the study area. The Bayesian clustering analysis (STRUCTURE) used on the microsatellite data showed no clustering pattern (Figure 4a–c). The graphic representation (Figure 4c) and the results generated by the BAPS revealed only one cluster, without differentiation between individuals (Figure 4d). Additionally, the ΦST values were not significant for both molecular markers (nuclear DNA and mtDNA), indicating the absence of genetic structuring among the samples (Table 2).
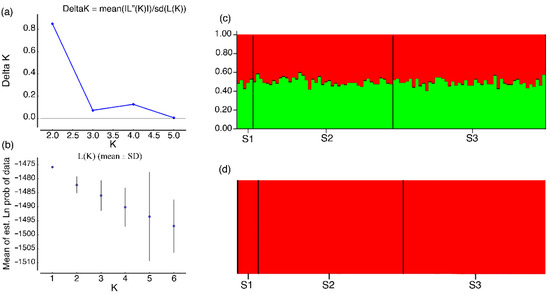
Figure 4.
Estimate of the probable groups of populations produced by the STRUCTURE (a–c) and BAPS (d), between 95 samples of Steindachneridion melanodermatum from the Lower Iguaçu River. (a) Values of K obtained based on ΔK. (b) K obtained based on mean likelihood Ln (K). (c) Graphic representation of K = 2. (d) Graphic representation of K = 1.

Table 2.
Pairwise genetic differentiation between samples of Steindachneridion melanodermatum collected in the three sites of the Lower Iguaçu River. p ≤ 0.05 (significance test using 1010 permutations). ΦST—parameter based on Wright’s F statistics.
3.3. Demographic Analysis
Microsatellite data analysis revealed signs of a recent bottleneck in the IAM and TPM models of the Wilcoxon signed-rank test, with significant values for excess heterozygosity, allowing accepting the genetic bottleneck hypothesis from the analyzed data. However, it showed a typical L-shaped distribution (absence of genetic bottleneck) in the frequency of the alleles in the mode-shift test (Table 3). In the neutrality tests, all Tajima (D) and Fu (Fs) tests values were negative and not significant.

Table 3.
Bottleneck tests on 95 samples of Steindachneridion melanodermatum collected from the Lower Iguaçu River. Wilcoxon signed-rank test for excess heterozygosity and mode-shift test for allelic frequency distribution patterns. N—number of individuals; He—number of loci exhibiting excess heterozygosity; Hd—number of loci exhibiting low heterozygosity. *e Significant values for excess heterozygosity (p ≤ 0.05). Normal L-shaped distribution = non-bottlenecked population. a Infinite allele model, b Two-phase model (90% SSM), and c Stepwise mutation model.
The mitochondrial mismatch distribution graph (Figure 5a) demonstrates the unimodal distribution for all haplotype frequencies, indicating demographic expansion. The BSP analysis revealed an initial demographic expansion between 50 to 40 kya, with a considerable change in effective population size between 40 to 30 kya, accompanied by stabilization (Figure 5b). According to the linkage disequilibrium (LD) method, the Ne was 148.4 (confidence interval—CI 95%: 70.2–977.6) (Table 2).
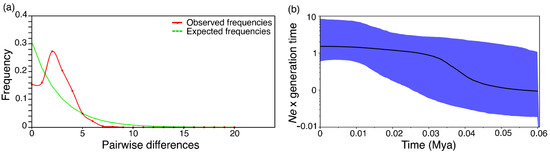
Figure 5.
Estimated population demographic changes of mitochondrial haplotypes obtained from 95 individuals of Steindachneridion melanodermatum in the Lower Iguaçu River. (a) Demographic history depicted by Pairwise mismatch distributions. Pairwise differences (X-axis) are shown against frequency (Y-axis). (b) Bayesian skyline plot (BSP) shows the fluctuations over time in the effective population size. The black line represents the median, and the blue area indicates 95% of the estimates’ HPDs (highest posterior densities). The X-axis represents time in millions of years (mya), and the Y-axis is the inference of changes in effective population size per generation over time.
4. Discussion
In S. melanodermatum, the genetic diversity levels from the microsatellite markers (HE = 0.567 to 0.626) and D-loop region (h = 0.759 to 1.000) followed the pattern observed for natural populations of migratory fish of the Pimelodidae family [5,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83], including other Steindacheneridion species [38,55]. Although the number of microsatellite loci used in this study (six) was not ideal [84], most S. melanodermatum genetic diversity was satisfactorily accessed. On the other hand, the HE and the number of alleles per locus were low in S. parahybae, even with the more significant number of 20 loci selected.
From the haplotype network, the closest relationship of S. melanodermatum was to S. scriptum, as only 14 mutational steps are separating them, while S. parahybae has 109. Whereas H19, present in S2, is the closest haplotype to the other two species, we can consider it the oldest haplotype in S. melanodermatum, followed by H11 present in S2 and S3. The H26 haplotype, exclusive to S1, originated from H4 by three mutational steps, while haplotypes H24, H25, and H27 of the same locality originated from H1 by one mutational step (Figure 3). Considering that S2 is the location with the highest number of old and recent haplotypes, we can consider it a priority for the conservation of S. melanodermatum.
The current variations in nuclear and mitochondrial DNA are evenly distributed across the population, indicating the absence of significant genetic structure among samples and suggesting the existence of a single population distributed in a stretch of approximately 190 km. The Bayesian clusters and the significant FIS also corroborate the single population, which may be due to the restricted size of its current area of occurrence [19]. However, it is noteworthy that the small number of individuals in S1 (five) may have contributed some biases to the analysis, as estimates of alleles per locus in small sample sizes can be quite biased, especially when compared to populations with larger samples sizes [85]. Therefore, the results should be analyzed with caution, despite S. melanodermatum being a vagile species [20,25] and sharing haplotypes and alleles among individuals from the three sampling points (S1, S2, and S3). The low number of individuals collected in S1 over five consecutive years [19] is probably due to habitat changes and degradations caused by the hydroelectric plant and high anthropogenic pressure (e.g., poaching and agriculture [22]). Furthermore, this region is outside the domains of the INP.
A previous study using molecular markers of randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) in S. melanodermatum demonstrated low genetic diversity [86] when compared to our results and with the values obtained for congener S. scriptum [55,87]. Although the genetic marker and the number of specimens (n = 27) used by that study [86] were different from our study, those results are worrying, as the specimens tested are used in the restocking program. Furthermore, there are no data on the genetics of the founders kept as breeding stock, the number of individuals used in reproduction, and the released number of fish for the restocking program [86]. Therefore, restocking has been made in several reservoirs above Salto Caxias, but without monitoring the effectiveness of this management strategy to restore both population sizes and connectivity among them. The lack of genetic monitoring of the farmed broodstocks can lead to inbreeding and fixation of harmful alleles [88]. In addition, individuals born in captivity and released into the wild may have substantially lower fitness than those born in the wild, and this decrease in fitness can occur after only a few generations in captivity [89,90]. Genetic diversity is an essential attribute for species and can provide the basis for adaptation to environmental changes [91], especially in endangered species such as S. melanodermatum [26].
As demonstrated by the plot in the BSP based on mtDNA data, the demographic expansion probably started around 50 kya, with a significant change in effective population size between 40 to 30 kya, accompanied by stabilization to the present, possibly associated with climate change during the Late Pleistocene. The dated demographic expansion event predates the end of the last glacial maximum (LGM) [92], as observed in another neotropical fish (Poecilia vivipara), which began its demographic expansion at around 75 kya and peaked at approximately 25 kya [93]. Negative D and Fs values, although not significant, could indicate population expansion events [94]. In addition, patterns containing high h (>0.5) values combined with low π (<0.5%) values often demonstrate the occurrence of rapid population growth and an accumulation of mutations [95]. Therefore, the current levels of S. melanodermatum mitochondrial diversity might be related to the demographic expansion that occurred in the past. According to the BSP data, it is possible to suggest that a Ne of approximately 147 (from microsatellite data) for the S. melanodermatum population studied here has been present since before the LGM. Therefore, the population can maintain its genetic diversity under current environmental conditions because a Ne = 50 is the minimum recommended value to prevent inbreeding problems [96]. On the other hand, a Ne = 500 would be ideal to avoid significant genetic drift and for genetic variability to present the adaptive flexibility necessary for the population to adapt to environmental changes [96,97]. Thus, to keep species under protection and management, the main objective of conservation must be to maintain their greatest possible genetic variability [98].
Although data from our study, especially those on levels of genetic diversity, might suggest that the sampled population could maintain a sufficient population size in a limited stretch of the river, analysis of the microsatellite data revealed recent bottleneck signs from significant excess heterozygosity values (p-value < 0.05) in two mutations models, IAM and TPM. Most loci will exhibit an excess of heterozygosity in populations that have experienced a recent reduction in effective population size [66]. In addition, the recent construction of the Baixo Iguaçu HPP [19] has fragmented this population and further stressed the isolation of upstream individuals. Thus, individuals currently populating the approximately 30 km between the two HPPs may suffer a drastic reduction or become extinct, especially in the reservoir area. The same has already happened with other populations of S. melanodermatum upstream of the Salto Caxias HPP due to hydroelectric projects which destroyed part of the area where this species can or could be found [20].
Migratory species generally require free stretches to reach their spawning grounds, located in the main river and tributaries [99,100]. However, dams block these species’ natural dispersion, including the upstream migration and downstream dispersal of eggs and juveniles, interfering with breeding and eliminating important migratory routes [101,102]. Thus, dams subdivide populations and may lead to disturbances in the genetic distribution patterns of species [101], representing a significant threat to gene flow and genetic diversity within and among natural populations [103,104]. Mitigation measures, such as implementing fishways, elevators, locks, nature-like channels, and fish ladders [105,106], have been used to minimize the impacts caused by HPPs on fish populations [7,107,108], reestablishing the connectivity between upstream and downstream areas [105,107]. Despite this, contrasting with other Paraná River tributaries, in the Iguaçu River, there are no fishways [7]. The recent building of the Baixo Iguaçu HPP could be an opportunity to start such practices in the Iguaçu River because compensatory measures for the wildlife are likely still open. However, some Brazilian states, including Paraná state, do not have specific legislation requiring fishway construction when HPPs are built [7]. The lack of legislation on this issue has hindered knowledge generation and decision-making, warranting changes in the legislation.
Natural-like long and gentle by-pass channels with sufficient discharge could be a solution for S. melanodermatum. However, this large catfish could not move efficiently through the fishway, and it could be an investment for only one species. Studies conducted for goliath catfish (Brachyplatystoma spp.) in a large dam in the Amazon Basin provided evidence of the inefficiency of the semi-natural fishway [109]. For the surubim-do-Iguaçu that inhabits deep pools, the entry of a fishway would have to be connected to the bottom, reaching to talweg. Moreover, before risking a construction that may be beneficial, it would be necessary to perform studies to assess if the species could use a fishway and which type would be most suitable. Regardless of the fishway adopted, it is important to allow fish movement in both directions, upstream and downstream [107,110,111], favoring access to suitable areas for reproduction [108,112]. Furthermore, monitoring the fish passage efficiency with genetic analysis of the S. melanodermatum population over time is extremely important.
A recent contribution [19] showed 24 deep pools (ranging from 5 to 25 m depth) in the S. melanodermatum distribution range, where 180 specimens were captured between 2010 to 2016, mainly in the main channel of the river under the influence or in protected areas of the INP [19]. This distribution suggests that S. melanodermatum, similarly to its congeners [113], prefers deep pools and that protected areas are important for the conservation of this species. Furthermore, deep pools are habitats of great ecological importance for conserving fish species [114,115], and these sites, in recent years, have been extensively studied, mapped, and turned into conservation zones or sanctuaries, where fishing is not permitted [116,117], directly affecting the increased abundance of various sedentary and migratory species [118].
Given the threats to the conservation of the wild population of the giant catfish, S. melanodermatum, an iconic species of the Lower Iguaçu River basin, based on our results, we strongly advise against the stocking of breeding specimens released below the Salto Caxias HPP to prevent compromising the integrity of the native gene pools at the receptor sites. In addition, we recommend the manual transposition of fish (trap-and haul); meanwhile, fishways and studies of swimming behavior and capacity should be developed for this species. This method has been used to allow gene flow from reservoirs to downstream areas (dam-free stretch) and vice versa, avoiding loss of genetic diversity from dams without a fish passage system and could be a conservation strategy for maintaining or restoring fish populations [119,120] in the area influenced by the Baixo Iguaçu HPP. Furthermore, it is critical to keep the tributaries of the Lower Iguaçu River free from additional dams, especially the Santo Antônio, Gonçalves Dias, Capanema, and Floriano rivers, where S. melanodermatum was collected [19,29]. At the same time, the deep pools must be transformed into conservation areas and no-fishing zones under intense supervision [13]. The establishment of habitat protection areas, such as sanctuaries, protected areas for fish, and the prohibition of fishing in certain regions, has been efficient for conserving endemic fish species [121].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: L.S.-S., M.C.M., S.M., S.H.S. and O.A.S.; methodology: L.S.-S., D.G.F., L.d.A., S.F.R.P. and P.S.d.S.; formal Analysis: L.S.-S. and D.G.F.; data Curation: L.S.-S., M.C.M. and O.A.S.; writing: L.S.-S., D.G.F., L.d.A., S.F.R.P. and P.S.d.S.; writing—review, and editing: L.S.-S., D.G.F., S.H.S., O.A.S., M.C.M. and S.M.; supervision: L.S.-S., M.C.M. and S.M.; project administration: M.C.M. and S.M.; funding acquisition: M.C.M. and S.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Macuco Safari and Consórcio Empreendedor Baixo Iguaçu (CEBI) funded this research.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All fieldwork for fish sampling complied with the legal regulations of Brazil. The collection licenses were granted through the Authorizations of the Environmental Institute of Paraná-IAP (License No. 37788 and No. 43394), by the Chico Mendes Institute for Biodiversity Conservation—ICMBio (No. 003/2014 and Official SEI No. 63/2016-DIBIO/ICMBio), and by the Biodiversity Authorization and Information System (SISBIO) (No. 25648-3 and 25648-4). The Ethics Committee on the Use of Animals—CEUA of the Universidade Estadual do Oeste do Paraná (Protocol code 62/09; 1 November 2009) approved the procedures.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank ICMBio/Iguaçu National Park and Água Viva Institute for logistics; Consórcio Empreendedor Baixo Iguaçu—CEBI; Group of Research in Technology in Ecohydraulics and Conservation of Fishing, Water Resources/GETECH, for the technical team that assisted the field sampling. We thank Henrique Batalha-Filho for his immense help with BSP analysis and Jhony Ferry Mendonça da Silva for helping with the map.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Collen, B.; Whitton, F.; Dyer, E.E.; Baillie, J.E.; Cumberlidge, N.; Darwall, W.R.; Pollock, C.; Richman, N.I.; Soulsby, A.M.; Bohm, M. Global patterns of freshwater species diversity, threat and endemism. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2014, 23, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grill, G.; Lehner, B.; Lumsdon, A.E.; MacDonald, G.K.; Zarfl, C.; Liermann, C.R. An index-based framework for assessing patterns and trends in river fragmentation and flow regulation by global dams at multiple scales. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill, G.; Lehner, B.; Thieme, M.; Geenen, B.; Tickner, D.; Antonelli, F.; Babu, S.; Borrelli, P.; Cheng, L.; Crochetiere, H.; et al. Mapping the world’s free-flowing rivers. Nature 2019, 569, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarossa, V.; Schmitt, R.J.P.; Huijbregts, M.A.J.; Zarfl, C.; King, H.; Schipper, A.M. Impacts of current and future large dams on the geographic range connectivity of freshwater fish worldwide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3648–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, D.G.; Souza-Shibatta, L.; Shibatta, O.A.; Sofia, S.H.; Carlsson, J.; Dias, J.H.P.; Makrakis, S.; Makrakis, M.C. Genetic structure and diversity of migratory freshwater fish in a fragmented Neotropical river system. Rev. Fish Biol. Fisher. 2017, 27, 209–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lira, N.A.; Pompeu, P.S.; Agostinho, C.S.; Agostinho, A.A.; Arcifa, M.S.; Pelicice, F.M. Fish passages in South America: An overview of studied facilities and research effort. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2017, 15, e160139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makrakis, S.; Bertão, A.P.S.; Silva, J.F.M.; Makrakis, M.C.; Sanz-Ronda, L.F.; Celestino, L.F. Hydropower development and fishways: A need for connectivity in rivers of the Upper Paraná Basin. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilson, C.; Reidy, C.A.; Dynesius, M.; Revenga, C. Fragmentation and flow regulation of the world’s large river system. Science 2005, 308, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. Indicadores de Desenvolvimento Sustentável, 1st ed.; IBGE/Coordenação de Recursos Naturais e Estudos Ambientais e Coordenação de Geografia: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2015.
- Bueno-Krawczyk, A.C.D.; Guiloski, I.C.; Piancini, L.D.S.; Azevedo, J.C.; Ramsdorf, W.A.; Ide, A.H.; Guimarães, A.T.B.; Cestari, M.M.; Assis, H.C.S. Multibiomarker in fish to evaluate a river used to water public supply. Chemosphere 2015, 135, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisi, N.C.; Larentis, C.; Oliveira, E.C.; Neves, M.P.; Zavaski, A.G.; Roque, A.A.; Wachtel, C.C.; Silva, A.P.; Lima, E.B.S.; Costa, G.O.N.; et al. Environmental assessment of Neotropical streams using fish as bioindicators: A multibiomarker and integrated approach. Hydrobiologia 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimet, J.; Guimarães, A.T.B.; Delariva, R.L. Use of Muscular Cholinesterase of Astyanax bifasciatus (Teleostei, Characidae) as a Biomarker in Biomonitoring of Rural Streams. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 99, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimet, J.; Neves, M.P.; Viana, N.P.; Amorim, J.P.A.; Delariva, R.L. Histopathological alterations in gills of a fish (Astyanax bifasciatus) in neotropical streams: Negative effects of riparian forest reduction and presence of pesticides. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abell, R.; Thieme, M.L.; Revenga, C.; Bryer, M.; Kottelat, M.; Bogutskaya, N.; Coad, B.; Mandrak, N.; Balderas, S.C.; Bussing, W.; et al. Freshwater Ecoregions of the World: A New Map of Biogeographic Units for Freshwater Biodiversity Conservation. BioScience 2008, 58, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garavello, J.C.; Pavanelli, C.S.; Suzuki, H.I. Caracterização da ictiofauna do rio Iguaçu. In Reservatório de Segredo: Bases Ecológicas Para o Manejo; Agostinho, A.A., Gomes, L.C., Eds.; Eduem: Maringá, Brazil, 1997; pp. 61–84. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, R.B.; Frota, A.; Depra, G.D.C.; Ota, R.R.; Graca, W.J. Freshwater fishes from Paraná State, Brazil: An annotated list, with comments on biogeographic patterns, threats, and future perspectives. Zootaxa 2020, 4868, 451–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, G.; Pavanelli, C.S.; Baumgartner, D.; Bifi, A.G.; Debona, T.; Frana, V.A. Peixes do Baixo Rio Iguaçu; Eduem: Maringá, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pini, S.F.R.; Makrakis, M.C.; Neves, M.P.; Makrakis, S.; Shibatta, O.A.; Kashiwaqui, E.A.L. Ichthyofauna in the last free-flowing river of the Lower Iguaçu basin: The importance of tributaries for conservation of endemic species. ZooKeys 2021, 1041, 183–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assumpção, L.D.; Makrakis, M.C.; Silva, J.F.M.; Moraes, K.A.S.; Pini, S.F.R.; Silva, P.S.; Kashiwaqui, E.A.L.; Gentil, E.; Souza-Shibatta, L.; Shibatta, O.A.; et al. Deep Pools: Ecological Sanctuaries for Steindachneridion melanodermatum, a Large Endemic and Endangered Pimelodid of the Iguaçu River. Water 2021, 13, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehm, M.; Filippin, R.F.; Moura, R.R. O impacto ambiental causado à ictiofauna do rio Iguaçu pela exploração do potencial hidrelétrico: O caso do surubim do iguaçu (Steindachneridion melanodermatum). Rev. Bras. Ener. 2016, 22, 30–47. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO [United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization]; World Heritage Committee. Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage. Report: 36th Session. WHC-12/36. COM/7B. Add. Saint-Petersburg. 2012. Available online: http://whc.unesco.org/archive/2012/whc12-36com-7BAdd-en.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2021).
- Assumpção, L.; Makrakis, S.; Silva, P.S.; Makrakis, M.C. Espécies de peixes ameaçadas de extinção no Parque Nacional do Iguaçu. Biodivers. Bras.-BioBrasil 2017, 7, 4–17. [Google Scholar]
- Delariva, R.L.; Neves, M.P.; Larentis, C.; Kliemann, B.C.K.; Baldasso, M.C.; Wolff, L.L. Fish fauna in forested and rural streams from an ecoregion of high endemism, lower Iguaçu river basin, Brazil. Biota Neotrop. 2018, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garavello, J.C. Revision of genus Steindachneridion (Siluriformes: Pimelodidae). Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2005, 3, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, L.A.M.; Gomes, E.; Artoni, R.F. Um método de reprodução induzida para o surubim Steindachneridion melanodermatum (Siluriformes: Pimelodidae) do Rio Iguaçu. Ciênc Biol. Saúde 2005, 11, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Akama, A.; Netto-Ferreira, A.L.; Zanata, A.M.; Calegari, B.B.; de Figueiredo, C.A.A.; Alves, C.B.M.; Cramer, C.A.; Zawadzki, C.H.; Röpke, C.P.; Moreira, C.R.; et al. Steindachneridion melanodermatum Garavello, 2005. In Livro Vermelho da Fauna Brasileira Ameaçada de Extinção: Volume 6 (Peixes); Instituto Chico Mendes de Conservação da Biodiversidade (Org.), ICMBio: Brasília, DF, Brazil, 2018; pp. 214–217. [Google Scholar]
- Agostinho, A.A.; Pavanelli, C.S.; Suzuki, H.I.; Latini, J.D.; Gomes, L.C.; Hahn, N.S.; Fugi, R.; Domingues, W.M. Reservatório de Salto Caxias-Bases Ecológicas Para o Manejo; Copel: Maringá, Brazil, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Chico Mendes de Conservação da Biodiversidade. Lista de Espécies Ameaçadas [ICMBio 2014]. Available online: https://www.icmbio.gov.br/portal/especies-ameacadas-destaque (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- Assumpção, L.; Fávaro, L.F.; Makrakis, S.; Silva, P.S.; Pini, S.F.R.; Kashiwaqui, E.A.L.; Makrakis, M.C. Population structure and reproduction of Steindachneridion melanodermatum (Siluriformes: Pimelodidae), a large catfish endemic to Neotropical ecoregion. Mar. Fresh. Res. 2021, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza-Shibatta, L.; Kotelok-Diniz, T.; Ferreira, D.G.; Shibatta, O.A.; Sofia, S.H.; Assumpção, L.; Pini, S.F.R.; Makrakis, S.; Makrakis, M.C. Genetic Diversity of the Endangered Neotropical Cichlid Fish (Gymnogeophagus setequedas) in Brazil. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.Q.; Shen, S.K.; Zhang, X.J.; Wang, Y.H.; Sun, W.B. Genetic diversity and population structure of an extremely endangered species: The world’s largest Rhododendron. AoB Plants 2015, 7, plu082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.R.; Inouye, B.D.; Johnson, M.T.J.; Underwood, N.; Vellend, M. Ecological consequences of genetic diversity. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankham, R.; Ballou, J.J.D.; Briscoe, D.D.A. Introduction to Conservation Genetics; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Allendorf, F.W.; Luikart, G.H.; Aitken, S.N. Conservation and the Genetics of Populations; Wiley Blackwell Press: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Palstra, F.P.; Ruzzante, D.E. Genetic estimates of contemporary effective population size: What can they tell us about the importance of genetic stochasticity for wild population persistence? Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 3428–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allendorf, F.W.; Hohenlohe, P.A.; Luikart, G. Genomics and the future of conservation genetics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, T.; Rajiv, K. Molecular markers and their applications in fisheries and aquaculture. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2010, 1, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, F.S.; Domingues, R.R.; Hallerman, E.M.; Hilsdorf, A.W.S. Genetic Diversity of an Imperiled Neotropical Catfish and Recommendations for Its Restoration. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantine-Silva, W.; Sofia, S.H.; Orsi, M.L.; Almeida, F.S. DNA barcoding of freshwater ichthyoplankton in the Neotropics as a tool for ecological monitoring. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 1226–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, A.P.; Hilsdorf, A.W.S.; Leite, A.C.; Yang, A.; Izuno, A.; He, C.; Zhou, C.; Kyogoku, D.; Caneppele, D.; Zhu, D.; et al. Microsatellite records for Volume 8, Issue 4. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2016, 8, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.L.B.; Kalapothakis, E. Isolation and characterization of microsatellite loci in Pimelodus maculatus (Siluriformes: Pimelodidae). Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2008, 8, 1078–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oosterhout, C.; Hutchinson, W.F.; Wills, D.P.M.; Shipley, P. MICRO-CHECKER: Software for identifying and correcting genotyping errors in microsatellite data. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2004, 5, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iervolino, F.; Resende, E.K.; Hilsdorf, A.W.S. The lack of genetic differentiation of pacu (Piaractus mesopotamicus) populations in the Upper-Paraguay Basin revealed by the mitochondrial DNA D-loop region: Implications for fishery management. Fish. Res. 2010, 101, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, T.M.; Eddy, S.R. tRNAscan-SE: A program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, T.C.; Slate, J.; Kruuk, L.E.; Pemberton, J.M. Statistical confidence for likelihood-based paternity inference in natural populations. Mol. Ecol. 1998, 7, 639–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, F.C.; Yang, R.; Boyle, T.J.; Xiyan, J.M. Pop Gene 32: Microsoft Window-Based Freeware for Population Genetic Analysis; University of Alberta: Edmonton, AB, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Goudet, J. FSTAT, a Program to Estimate and Test Gene Diversities and Fixation Indices (Version 2.9.3). 2001. Available online: http://www.unil.ch/izea/softwares/fstat.html (accessed on 13 November 2020).
- Raymond, M.; Rousset, F. GENEPOP (Version 1.2): Population Genetics Software for Exact Tests and Ecumenicism. J. Hered. 1995, 86, 248–249. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, W.R. Analyzing tables of statistical tests. Evolution 1989, 43, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandelt, H.J.; Forster, P.; Rohl, A. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paixão, R.V.; Ribolli, J.; Zaniboni-Filho, E. Genetic Variation of the Endangered Neotropical Catfish Steindachneridion scriptum (Siluriformes: Pimelodidae). Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corander, J.; Marttinen, P.; Sirén, J.; Tang, J. BAPS: Bayesian Analysis of Population Structure; University of Helsinki: Helsinki, Finland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont, M.A.; Rannala, B. The Bayesian revolution in genetics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, D.J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software structure: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 10, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earl, D.A.; von Holdt, B.M. STRUCTURE HARVESTER: A website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Cons. Gen. Res. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, M.; Rosenberg, N.A. CLUMPP: A cluster matching and permutation program for dealing with label switching and multimodality in analysis of population structure. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, S. A simple sequentially rejective multiple test procedure. Scand. J. Stat. 1979, 6, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Posada, D. jModelTest: Phylogenetic model averaging. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piry, S.; Luikart, G.; Cornuet, J.M. BOTTLENECK: A computer program for detecting recent reductions in the effective population size using allele frequency data. J. Hered. 1999, 90, 502–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luikart, G.; Allendorf, F.W.; Cornuet, J.M.; Sherwin, W.B. Distortion of allele frequency distributions provides a test for recent population bottlenecks. J. Hered. 1998, 89, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, F. Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 1989, 123, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.X. Statistical test of neutrality of mutations against population growth, hitchhiking and background selection. Genetics 1997, 147, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, A.R.; Harpending, H. Population growth makes waves in the distribution of pairwise genetic differences. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1992, 9, 552–569. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A.; Shapiro, B.; Pybus, O.G. Bayesian coalescent inference of past population dynamics from molecular sequences. Mol. Biol Evol. 2005, 22, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, K.A.; Wilson, R.R., Jr. Amphi-panamic geminates of snook (Percoidei: Centropomidae) provide a calibration of the divergence rate in the mitochondrial DNA control region of fishes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1999, 13, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waples, R.S.; Do, C. LdNe: A program for estimating effective population size from data on linkage disequilibrium. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2008, 8, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, C.; Waples, R.S.; Peel, D.; Macbeth, G.M.; Tillett, B.J.; Ovenden, J.R. NeEstimator v2: Re-implementation of software for the estimation of contemporary effective population size (Ne) from genetic data. Mol. Ecol. Resour 2014, 14, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botstein, D.; White, R.L.; Skolnick, M.; Davis, R.W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1980, 3, 314–331. [Google Scholar]
- Revaldaves, E.; Pereira, L.H.G.; Foresti, F.; Oliveira, C. Isolation and characterization of microsatellite locos in Pseudoplatystoma corruscans (Siluriformes: Pimelodidae) and cross-species amplification. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2005, 5, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignotto, T.S.; Prioli, A.J.; Prioli, S.M.A.P.; Maniglia, T.C.; Boni, T.A.; Lucio, L.C.; Gomes, V.N.; Prioli, R.A.; Oliveira, A.V.; Júlio-Junior, H.F.; et al. Genetic divergence between Pseudoplatystoma corruscans and Pseudoplatystoma reticulatum (Siluriformes: Pimelodidae) in the Paraná River Basin. Braz. J. Biol. 2009, 69, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Batista, J.S.; Alves-Gomes, J.A. Phylogeography of Brachyplatystoma rousseauxii (Siluriformes–Pimelodidae) in the Amazon Basin offers preliminary evidence for the first case of “homing” for an Amazonian migratory catfish. Genet. Mol. Res. 2006, 5, 723–740. [Google Scholar]
- Huergo, G.M.; Filgueiras-Souza, R.J.; Batista, J.D.S.; Formiga-Aquino, K.; Alves-Gomes, J.A. Molecular genetics as a tool for fisheries management in the Brazilian Amazon: Piraíba (Brachyplatystoma filamentosum and Brachyplatystoma capapretum) (Siluriformes: Pimelodidae) in white-water rivers. Pan-Am. J. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 6, 280–289. [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa, L.E.; Pereira, L.H.G.; Costa-Silva, G.J.; Roxo, F.F.; Batista, J.S.; Formiga, K.; Foresti, F.; Oliveira, C. Genetic structure and historical diversification of catfish Brachyplatystoma platynemum (Siluriformes: Pimelodidae) in the Amazon basin with implications for its conservation. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 5, 2005–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, N.; Maes, G.E.; Volckaert, F.A.M. High genetic diversity in cryptic populations of the migratory sutchi catfish Pangasianodon hypophthalmus in the Mekong River. Heredity 2006, 96, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, J.S.; Farias, I.P.; Formiga-Aquino, K.; Sousa, A.C.B.; Alves-Gomes, J.A. DNA microsatellite markers for "dourada" (Brachyplatystoma rousseauxii, Siluriformes: Pimelodidae), a migratory catfish of utmost importance for fisheries in the Amazon: Development, characterization and inter-specific amplification. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2010, 2, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telles, M.P.C.; Collevatti, R.G.; Braga, R.S.; Guedes, L.B.S.; Castro, T.G.; Costa, M.C.; Silva Júnior, N.J.; Barthem, R.B.; Diniz Filho, J.A.F. Geographical genetics of Pseudoplatystoma punctifer (Castelnau, 1855) (Siluriformes, Pimelodidae) in the Amazon basin. Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 3656–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koskinen, M.T.; Hirvonen, H.; Landry, P.A.; Primmer, C.R. The benefits of increasing the number of microsatellites utilized in genetic population studies: An empirical perspective. Hereditas 2004, 141, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit, R.; El Mousadik, A.; Pons, O. Identifying populations for conservation on the basis of genetic markers. Conserv. Biol. 1998, 12, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoso, D.A.; Silva, M.; Cortinhas, M.C.S.; Cestari, M.M.; Almeida, M.C.; Vicari, M.R.; Artoni, R.F. Two genetic stocks of Steindachneridion melanodermatum living in sympatry in nature and genetic variability of wild parents and F1 generation. Genet. Mol. Res. 2011, 10, 2606–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramella, M.S.; Kroth, M.A.; Meurer, S.; Nuñer, A.P.O.; Zaniboni-Filho, E.; Arisi, A.C.M. Genetic variability in four fish species (Pimelodus maculatus, Prochilodus lineatus, Salminus brasiliensis and Steindachneridion scripta) from Uruguay river basin. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2006, 49, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwersen, L.H.L.; Melo, C.M.R.; Lazoski, C.; Zaniboni-Filho, E.; Ribolli, J. Genetic implications of restocking programs on wild populations of streaked prochilod Prochilodus lineatus. Bol. Inst. Pesca 2019, 45, e497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, K.S.; Murdoch, A.R.; Pearsons, T.N.; Ward, E.J.; Ford, M.J. Factors influencing the relative fitness of hatchery and wild spring Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) in the Wenatchee River, Washington, USA. Can. J. Fish. Aquat Sci. 2010, 67, 1840–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, M.R.; Marine, M.L.; French, R.A.; Blouin, M.S. Genetic adaptation to captivity can occur in a single generation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piorski, N.M.; Sanches, A.; Carvalho-Costa, L.F.; Hatanaka, T.; Carrillo-Avila, M.; Freitas, P.D.; Galetti, P.M., Jr. Contribution of conservation genetics in assessing neotropical freshwater fish biodiversity. Braz. J. Biol. 2008, 68, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Clark, P.U.; Dyke, A.S.; Shakun, J.D.; Carlson, A.E.; Clark, J.; Wohlfarth, B.; McCabe, A.M. The Last Glacial Maximum. Science 2009, 325, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.L.N.; Ivan Perez, S.; Louvise, J.; Tonhatti, C.H.; Clemente-Carvalho, R.B.G.; Petry, A.C.; dos Reis, S.F. Demographic Expansion and Contraction in a Neotropical Fish during the Late Pleistocene-Holocene. Open J. Stat. 2019, 9, 470–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Laval, G.; Schneider, S. ARLEQUIN v. 3.0: An integrated software/package for population genetics data analysis. Evol. Bioinform. Online 2005, 281, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, W.S.; Bowen, B.W. Shallow population histories in deep evolutionary lineages of marine fishes: Insights from sardines and anchovies and lessons for conservation. J. Hered. 1998, 89, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, I.R. Evolutionary change in small populations. In Conservation Biology: An Evolutionary Ecological Perspective; Soulé, M.E., Wilcox, B.A., Eds.; Sinauer: Sunderland, MA, USA, 1980; pp. 135–149. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, D.; Fernandez, F.A.S. Dealing with extinction is forever: Understanding the risks faced by small populations. Ciênc. Cul. 2000, 52, 161–170. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, G.M.; O’dvlyer, C. Genetic variability and population structure of the endangered golden sun moth, Synemon plana. Biol. Conserv. 2000, 92, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carolsfeld, J.; Harvey, B.; Ross, C.; Baer, A. Migratory Fishes of South America; World Fisheries Trust: Victoria, BC, Canada, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Makrakis, M.C.; Miranda, L.E.; Makrakis, S.; Fontes, H.M., Jr.; Morlis, W.G.; Dias, J.H.P.; Garcia, J.O. diversity in migratory patterns among Neotropical fishes in a highly regulated river basin. J. Fish. Biol. 2012, 81, 866–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrere-Jr, M. Fisheries in large tropical reservoirs in South America. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 1996, 2, 111–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilsdorf, A.W.S.; Petrere-Jr, M. Conservação de peixes da Bacia do rio Paraíba do Sul. Ciência Hoje 2002, 30, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Vrijenhoek, R.C. Conservation genetics of freshwater fish. J. Fish. Biol. 1998, 53, 394–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esguícero, A.L.H.; Arcifa, M.S. Fragmentation of a Neotropical migratory fish population by a century-old dam. Hydrobiologia 2010, 638, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clay, C.H. Design of Fishways and Other Fish. Facilities, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Larinier, M. Environmental Issues, Dams and Fish Migration. In Dams, Fish and Fisheries: Opportunities, Challenges and Conflict Resolution; Marmulla, G., Ed.; Fisheries Technical Paper; FAO Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2001; pp. 45–90. ISBN 92-5-104694-8. [Google Scholar]
- Celestino, L.F.; Sanz-Ronda, F.J.; Miranda, L.E.; Makrakis, M.C.; Dias, J.H.P.; Makrakis, S. Bidirectional connectivity via fish ladders in a large Neotropical river. River Res. Appl. 2019, 35, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makrakis, S.; Miranda, L.E.; Gomes, L.C.; Makrakis, M.C.; Junior, H.M.F. Ascent of neotropical fish in the Itaipu reservoir fish pass. River Res. Appl. 2011, 27, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, L.; Martins, E.G.; Nunes, L.D.; Machado, L.S.; Lopes, T.M.; Câmara, L.F. Semi-natural fishway efficiency for goliath catfish (Brachyplatystoma spp.) in a large dam in the Amazon Basin. Hydrobiologia 2020, 849, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makrakis, S.; Makrakis, M.C.; Wagner, R.L.; Dias, J.H.P.; Gomes, L.C. Utilization of the fish ladder at the Engenheiro Sergio Motta Dam, Brazil, by long distance migrating potamodromous species. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2007, 5, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, A.L.; Kynard, B. Migratory fishes of Brazil: Life history and fish passage needs. River Res. Appl. 2008, 25, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, P.S.; Makrakis, M.C.; Miranda, L.E.; Makrakis, S.; Assumpção, L.; Paula, S.; Dias, J.H.P.; Marques, H. Importance of reservoir tributaries to spawning of migratory fish in the upper Paraná River. River Res. Appl. 2015, 31, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaniboni-Filho, E.; Schulz, U.H. Migratory fishes of the Uruguay River. In Migratory Fishes of the South América: Biology, Fisheries and Conservation Status; Carosfeld, J., Harvey, B., Ross, C., Baer, A., Eds.; World Fisheries Trust: Victoria, BC, Canada, 2003; pp. 161–192. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, S.; Putrea, S.; Hortle, H.G. Using local knowledge to inventory deep pools, important fish habitats in Cambodia. In Proceedings of the 6th Technical Symposium on Mekong Fisheries, Pakse, Laos, 26–28 November 2003; Burnhill, T.J., Hewitt, M.M., Eds.; Mekong River Commission: Vientiane, Laos, 2003; pp. 57–76. [Google Scholar]
- Rakowitz, G.; Berger, B.; Schludermann, E.; Tritthart, M.; Habersack, H.; Keckeis, H. Deep pools of the Danube River: Ecological function or turbulent sink? Hydrobiologia 2014, 729, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, I.G.; Kisouvannalath, P.; Inthaphaisy, V.; Phylavanh, B. The Potential for Ecological Classification as a Tool for Establishing and Monitoring Fish Conservation Zones in the Mekong River. In Technical Report. Environmental Protection and Community Development in Siphandone Wetland Project; CESVI Cooperation and Development: Pakse, Laos, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, I.G.; Flaherty, M.S. Mekong river fish conservation zones in Southern Laos: Assessing effectiveness using local ecological knowledge. Environ. Manag. 2005, 36, 439–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, A.F.; Poeu, O.; Virvong, S.; Suntornratana, U.; Tung, N.T. Deep Pools as Dry Season Fish Habitats in the Mekong Basin. In MRC Technical Paper No. 4; Mekong River Commission: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sard, N.M.; Johnson, M.A.; Jacobson, D.P.; Hogansen, M.J.; O’Malley, K.G.; Banks, M.A. Genetic monitoring guides adaptive management of a migratory fish reintroduction program. Anim. Conserv. 2016, 19, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusardi, R.A.; Moyle, P.B. Two-way trap-and-haul as a conservation strategy for anadromous salmonids. Fisheries 2017, 42, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajan, S.; Mercy, A.T.V.; Malika, V. Age, growth and population dynamics of an endangered fish Sahyadria denisonii (Day 1865) from the western ghats hotspot of India. Asian Fish. Sci. 2015, 28, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).