Ancient Faunal History Revealed by Interdisciplinary Biomolecular Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Evolution and Extinction during the Pleistocene
2.1. Cave Bears
2.2. Woolly Mammoth
2.3. Woolly Rhinoceros
2.4. Bison
3. Faunal Transformations during and after the Late Pleistocene/Holocene Transition
3.1. Dogs
3.2. Sheep
3.3. Cattle
3.4. Pigs
3.5. Horses
3.6. Cats
4. Final Remarks and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pruvost, M.; Bellone, R.; Benecke, N.; Sandoval-Castellanos, E.; Cieslak, M.; Kuznetsova, T.; Morales-Muñiz, A.; O’Connor, T.; Reissmann, M.; Hofreiter, M.; et al. Genotypes of Predomestic Horses Match Phenotypes Painted in Paleolithic Works of Cave Art. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, C.; Rajora, O.P. Paleogenomics: Genome-Scale Analysis of Ancient DNA; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 9783030047535. [Google Scholar]
- Birks, H.J.B. Paleoecology. In Encyclopedia of Ecology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 494–504. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, O.E.; Steele, V.J.; Fischer, A.; Hartz, S.; Andersen, S.H.; Donohoe, P.; Glykou, A.; Saul, H.; Jones, D.M.; Koch, E.; et al. Ancient Lipids Reveal Continuity in Culinary Practices across the Transition to Agriculture in Northern Europe. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17910–17915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, E.J.; Speller, C.F. Novel Substrates as Sources of Ancient DNA: Prospects and Hurdles. Genes 2017, 8, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slon, V.; Hopfe, C.; Weiß, C.L.; Mafessoni, F.; de la Rasilla, M.; Lalueza-Fox, C.; Rosas, A.; Soressi, M.; Knul, M.V.; Miller, R.; et al. Neandertal and Denisovan DNA from Pleistocene Sediments. Science 2017, 356, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocherens, H.; Fizet, M.; Mariotti, A. Diet, Physiology and Ecology of Fossil Mammals as Inferred from Stable Carbon and Nitrogen Isotope Biogeochemistry: Implications for Pleistocene Bears. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1994, 107, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, Y.I.; Honch, N.V.; Chikaraishi, Y.; Ohkouchi, N.; Yoneda, M. Quantitative Evaluation of Marine Protein Contribution in Ancient Diets Based on Nitrogen Isotope Ratios of Individual Amino Acids in Bone Collagen: An Investigation at the Kitakogane Jomon Site. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2010, 143, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, R.; Bowman, B.; Freiberger, M.; Ryder, O.A.; Wilson, A.C. DNA Sequences from the Quagga, an Extinct Member of the Horse Family. Nature 1984, 312, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palkopoulou, E.; Mallick, S.; Skoglund, P.; Enk, J.; Rohland, N.; Li, H.; Omrak, A.; Vartanyan, S.; Poinar, H.; Götherström, A.; et al. Complete Genomes Reveal Signatures of Demographic and Genetic Declines in the Woolly Mammoth. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 1395–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breker, M.; Schuldiner, M. The Emergence of Proteome-Wide Technologies: Systematic Analysis of Proteins Comes of Age. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guil-Guerrero, J.L.; Tikhonov, A.; Rodríguez-García, I.; Protopopov, A.; Grigoriev, S.; Ramos-Bueno, R.P. The Fat from Frozen Mammals Reveals Sources of Essential Fatty Acids Suitable for Palaeolithic and Neolithic Humans. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guil-Guerrero, J.L.; Rodríguez-García, I.; Kirillova, I.; Shidlovskiy, F.; Ramos-Bueno, R.P.; Savvinov, G.; Tikhonov, A. The PUFA-Enriched Fatty Acid Profiles of Some Frozen Bison from the Early Holocene Found in the Siberian Permafrost. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucquin, A.; Gibbs, K.; Uchiyama, J.; Saul, H.; Ajimoto, M.; Eley, Y.; Radini, A.; Heron, C.P.; Shoda, S.; Nishida, Y.; et al. Ancient Lipids Document Continuity in the Use of Early Hunter-Gatherer Pottery through 9,000 Years of Japanese Prehistory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3991–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courel, B.; Robson, H.K.; Lucquin, A.; Dolbunova, E.; Oras, E.; Adamczak, K.; Andersen, S.H.; Astrup, P.M.; Charniauski, M.; Czekaj-Zastawny, A.; et al. Organic Residue Analysis Shows Sub-Regional Patterns in the Use of Pottery by Northern European Hunter-Gatherers. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 192016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokhman, D.; Malul, A.; Carmel, L. Inferring Past Environments from Ancient Epigenomes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 2429–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanghøj, K.; Seguin-Orlando, A.; Schubert, M.; Madsen, T.; Pedersen, J.S.; Willerslev, E.; Orlando, L. Fast, Accurate and Automatic Ancient Nucleosome and Methylation Maps with epiPALEOMIX. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 3284–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanghøj, K.; Orlando, L. Ancient Epigenomics. In Paleogenomics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 75–111. [Google Scholar]
- Fromm, B.; Tarbier, M.; Smith, O.; Marmol-Sanchez, E.; Dalen, L.; Gilbert, T.P.; Friedlander, M.R. Ancient microRNA Profiles of a 14,300-Year-Old Canid Samples Confirm Taxonomic Origin and Give Glimpses into Tissue-Specific Gene Regulation from the Pleistocene. RNA 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerman, M.; Malik, H.S. Paleovirology--Modern Consequences of Ancient Viruses. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warke, S.; Tembhurne, P.; Bobade, S.; Ingle, V.C. Paleovirology: Blessing or Curse of Ancient Viruses—A Review. Agric. Rev. 2019, 40, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, B.; Hofreiter, M. A Paleogenomic Perspective on Evolution and Gene Function: New Insights from Ancient DNA. Science 2014, 343, 1236573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlando, L.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; Willerslev, E. Reconstructing Ancient Genomes and Epigenomes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonardi, M.; Librado, P.; Der Sarkissian, C.; Schubert, M.; Alfarhan, A.H.; Alquraishi, S.A.; Al-Rasheid, K.A.S.; Gamba, C.; Willerslev, E.; Orlando, L. Evolutionary Patterns and Processes: Lessons from Ancient DNA. Syst. Biol. 2017, 66, e1–e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappellini, E.; Prohaska, A.; Racimo, F.; Welker, F.; Pedersen, M.W.; Allentoft, M.E.; de Barros Damgaard, P.; Gutenbrunner, P.; Dunne, J.; Hammann, S.; et al. Ancient Biomolecules and Evolutionary Inference. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2018, 87, 1029–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheu, A. Neolithic Animal Domestication as Seen from Ancient DNA. Quat. Int. 2018, 496, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunson, K.; Reich, D. The Promise of Paleogenomics beyond Our Own Species. Trends Genet. 2019, 35, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, K.J.; Rawlence, N.J. Examining Natural History through the Lens of Palaeogenomics. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2021, 36, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drucker, D.G.; Stevens, R.E.; Germonpré, M.; Sablin, M.V.; Péan, S.; Bocherens, H. Collagen Stable Isotopes Provide Insights into the End of the Mammoth Steppe in the Central East European Plains during the Epigravettian. Quat. Res. 2018, 90, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Seth, J.; Niemann, J.; Dalén, L. Genomics of Extinction. In Paleogenomics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 393–418. [Google Scholar]
- Kathleen Lyons, S.; Amatangelo, K.L.; Behrensmeyer, A.K.; Bercovici, A.; Blois, J.L.; Davis, M.; DiMichele, W.A.; Du, A.; Eronen, J.T.; Tyler Faith, J.; et al. Holocene Shifts in the Assembly of Plant and Animal Communities Implicate Human Impacts. Nature 2015, 529, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitt, G. The Genetic Legacy of the Quaternary Ice Ages. Nature 2000, 405, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provan, J.; Bennett, K.D. Phylogeographic Insights into Cryptic Glacial Refugia. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2008, 23, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, J.R.; Lister, A.M.; Barnes, I.; Dalén, L. Refugia Revisited: Individualistic Responses of Species in Space and Time. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnosky, A.D.; Koch, P.L.; Feranec, R.S.; Wing, S.L.; Shabel, A.B. Assessing the Causes of Late Pleistocene Extinctions on the Continents. Science 2004, 306, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, M.; Christopher Carleton, W.; Groucutt, H.S. Climate Change, Not Human Population Growth, Correlates with Late Quaternary Megafauna Declines in North America. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fordham, D.A.; Brown, S.C.; Reşit Akçakaya, H.; Brook, B.W.; Haythorne, S.; Manica, A.; Shoemaker, K.T.; Austin, J.J.; Blonder, B.; Pilowsky, J.; et al. Humans Hastened the Range Collapse and Extinction of Woolly Mammoth. bioRxiv 2021, 2021.02.17.431706. [Google Scholar]
- Isotopic Tracking of Large Carnivore Palaeoecology in the Mammoth Steppe. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2015, 117, 42–71. [CrossRef]
- Gretzinger, J.; Molak, M.; Reiter, E.; Pfrengle, S.; Urban, C.; Neukamm, J.; Blant, M.; Conard, N.J.; Cupillard, C.; Dimitrijević, V.; et al. Large-Scale Mitogenomic Analysis of the Phylogeography of the Late Pleistocene Cave Bear. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, A.; Paijmans, J.L.A.; Alberti, F.; Gasparyan, B.; Bar-Oz, G.; Pinhasi, R.; Foronova, I.; Puzachenko, A.Y.; Pacher, M.; Dalén, L.; et al. Middle Pleistocene Genome Calibrates a Revised Evolutionary History of Extinct Cave Bears. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacher, M.; Stuart, A.J. Extinction Chronology and Palaeobiology of the Cave Bear (Ursus Spelaeus). Boreas 2009, 38, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajcarz, M.; Pacher, M.; Krajcarz, M.T.; Laughlan, L.; Rabeder, G.; Sabol, M.; Wojtal, P.; Bocherens, H. Isotopic Variability of Cave Bears (δ15N, δ13C) across Europe during MIS 3. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 131, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocherens, H. Isotopic Insights on Cave Bear Palaeodiet. Hist. Biol. 2019, 31, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ramos, A.; Romero, A.; Rodriguez, E.; Figueirido, B. Three-Dimensional Dental Topography and Feeding Ecology in the Extinct Cave Bear. Biol. Lett. 2020, 16, 20200792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naito, Y.I.; Meleg, I.N.; Robu, M.; Vlaicu, M.; Drucker, D.G.; Wißing, C.; Hofreiter, M.; Barlow, A.; Bocherens, H. Heavy Reliance on Plants for Romanian Cave Bears Evidenced by Amino Acid Nitrogen Isotope Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiller, M.; Baryshnikov, G.; Bocherens, H.; Grandal d’Anglade, A.; Hilpert, B.; Münzel, S.C.; Pinhasi, R.; Rabeder, G.; Rosendahl, W.; Trinkaus, E.; et al. Withering Away--25,000 Years of Genetic Decline Preceded Cave Bear Extinction. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 975–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortes, G.G.; Grandal-d’Anglade, A.; Kolbe, B.; Fernandes, D.; Meleg, I.N.; García-Vázquez, A.; Pinto-Llona, A.C.; Constantin, S.; de Torres, T.J.; Ortiz, J.E.; et al. Ancient DNA Reveals Differences in Behaviour and Sociality between Brown Bears and Extinct Cave Bears. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 4907–4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, M.; Rohland, N.; Weinstock, J.; Baryshnikov, G.; Sher, A.; Nagel, D.; Rabeder, G.; Pinhasi, R.; Schmidt, H.A.; Hofreiter, M. First DNA Sequences from Asian Cave Bear Fossils Reveal Deep Divergences and Complex Phylogeographic Patterns. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 1225–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bon, C.; Berthonaud, V.; Fosse, P.; Gély, B.; Maksud, F.; Vitalis, R.; Philippe, M.; van der Plicht, J.; Elalouf, J.-M. Low Regional Diversity of Late Cave Bears Mitochondrial DNA at the Time of Chauvet Aurignacian Paintings. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2011, 38, 1886–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiller, M.; Molak, M.; Prost, S.; Rabeder, G.; Baryshnikov, G.; Rosendahl, W.; Münzel, S.; Bocherens, H.; Grandal-d’Anglade, A.; Hilpert, B.; et al. Mitochondrial DNA Diversity and Evolution of the Pleistocene Cave Bear Complex. Quat. Int. 2014, 339–340, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, K.K.; Svensson, A.; Johnsen, S.J.; Rasmussen, S.O.; Bigler, M.; Röthlisberger, R.; Ruth, U.; Siggaard-Andersen, M.-L.; Steffensen, J.P.; Dahl-Jensen, D. The Greenland Ice Core Chronology 2005, 15–42ka. Part 1: Constructing the Time Scale. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2006, 25, 3246–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veres, D.; Lane, C.S.; Timar-Gabor, A.; Hambach, U.; Constantin, D.; Szakács, A.; Fülling, A.; Onac, B.P. The Campanian Ignimbrite/Y5 Tephra Layer—A Regional Stratigraphic Marker for Isotope Stage 3 Deposits in the Lower Danube Region, Romania. Quat. Int. 2013, 293, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzsimmons, K.E.; Hambach, U.; Veres, D.; Iovita, R. The Campanian Ignimbrite Eruption: New Data on Volcanic Ash Dispersal and Its Potential Impact on Human Evolution. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staubwasser, M.; Drăgușin, V.; Onac, B.P.; Assonov, S.; Ersek, V.; Hoffmann, D.L.; Veres, D. Impact of Climate Change on the Transition of Neanderthals to Modern Humans in Europe. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 9116–9121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obreht, I.; Zeeden, C.; Hambach, U.; Veres, D.; Marković, S.B.; Bösken, J.; Svirčev, Z.; Bačević, N.; Gavrilov, M.B.; Lehmkuhl, F. Tracing the Influence of Mediterranean Climate on Southeastern Europe during the Past 350,000 Years. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirocko, F.; Knapp, H.; Dreher, F.; Förster, M.W.; Albert, J.; Brunck, H.; Veres, D.; Dietrich, S.; Zech, M.; Hambach, U.; et al. The ELSA-Vegetation-Stack: Reconstruction of Landscape Evolution Zones (LEZ) from Laminated Eifel Maar Sediments of the Last 60,000 Years. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2016, 142, 108–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, W.J.; Goñi, M.F.S.; Allen, J.R.M.; Cheddadi, R.; Combourieu-Nebout, N.; Huntley, B.; Lawson, I.; Londeix, L.; Magri, D.; Margari, V.; et al. Millennial-Scale Variability during the Last Glacial in Vegetation Records from Europe. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2010, 29, 2839–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, L.; Bonjean, D.; Bocherens, H.; Thenot, A.; Argant, A.; Otte, M.; Hänni, C. Ancient DNA and the Population Genetics of Cave Bears (Ursus Spelaeus) through Space and Time. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 1920–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loreille, O.; Orlando, L.; Patou-Mathis, M.; Philippe, M.; Taberlet, P.; Hänni, C. Ancient DNA Analysis Reveals Divergence of the Cave Bear, Ursus Spelaeus, and Brown Bear, Ursus Arctos, Lineages. Curr. Biol. 2001, 11, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocherens, H.; Stiller, M.; Hobson, K.A.; Pacher, M.; Rabeder, G.; Burns, J.A.; Tütken, T.; Hofreiter, M. Niche Partitioning between Two Sympatric Genetically Distinct Cave Bears (Ursus Spelaeus and Ursus Ingressus) and Brown Bear (Ursus Arctos) from Austria: Isotopic Evidence from Fossil Bones. Quat. Int. 2011, 245, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münzel, S.C.; Stiller, M.; Hofreiter, M.; Mittnik, A.; Conard, N.J.; Bocherens, H. Pleistocene Bears in the Swabian Jura (Germany): Genetic Replacement, Ecological Displacement, Extinctions and Survival. Quat. Int. 2011, 245, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, A.J.; Sulerzhitsky, L.D.; Orlova, L.A.; Kuzmin, Y.V.; Lister, A.M. The Latest Woolly Mammoths (Mammuthus Primigenius Blumenbach) in Europe and Asia: A Review of the Current Evidence. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2002, 21, 1559–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, A.M.; Stuart, A.J. The Impact of Climate Change on Large Mammal Distribution and Extinction: Evidence from the Last Glacial/interglacial Transition. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2008, 340, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartanyan, S.L.; Arslanov, K.A.; Tertychnaya, T.V.; Chernov, S.B. Radiocarbon Dating Evidence for Mammoths on Wrangel Island, Arctic Ocean, Until 2000 BC. Radiocarbon 1995, 37, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthrie, R.D.; Dale Guthrie, R. Radiocarbon Evidence of Mid-Holocene Mammoths Stranded on an Alaskan Bering Sea Island. Nature 2004, 429, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, A.D.; Lee, F.; Capelli, C.; DeSalle, R.; Tikhonov, A.; Marx, P.A.; MacPhee, R.D. Evolution of Endogenous Retrovirus-like Elements of the Woolly Mammoth (Mammuthus Primigenius) and Its Relatives. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001, 18, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, J.; Dear, P.H.; Pollack, J.L.; Slatkin, M.; Spriggs, H.; Barnes, I.; Lister, A.M.; Ebersberger, I.; Pääbo, S.; Hofreiter, M. Multiplex Amplification of the Mammoth Mitochondrial Genome and the Evolution of Elephantidae. Nature 2006, 439, 724–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enk, J.; Devault, A.; Debruyne, R.; King, C.E.; Treangen, T.; O’Rourke, D.; Salzberg, S.L.; Fisher, D.; MacPhee, R.; Poinar, H. Complete Columbian Mammoth Mitogenome Suggests Interbreeding with Woolly Mammoths. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohland, N.; Malaspinas, A.-S.; Pollack, J.L.; Slatkin, M.; Matheus, P.; Hofreiter, M. Proboscidean Mitogenomics: Chronology and Mode of Elephant Evolution Using Mastodon as Outgroup. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohland, N.; Reich, D.; Mallick, S.; Meyer, M.; Green, R.E.; Georgiadis, N.J.; Roca, A.L.; Hofreiter, M. Genomic DNA Sequences from Mastodon and Woolly Mammoth Reveal Deep Speciation of Forest and Savanna Elephants. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, I.; Shapiro, B.; Lister, A.; Kuznetsova, T.; Sher, A.; Guthrie, D.; Thomas, M.G. Genetic Structure and Extinction of the Woolly Mammoth, Mammuthus Primigenius. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyström, V.; Dalén, L.; Vartanyan, S.; Lidén, K.; Ryman, N.; Angerbjörn, A. Temporal Genetic Change in the Last Remaining Population of Woolly Mammoth. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 2331–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyström, V.; Humphrey, J.; Skoglund, P.; McKeown, N.J.; Vartanyan, S.; Shaw, P.W.; Lidén, K.; Jakobsson, M.; Barnes, I.; Angerbjörn, A.; et al. Microsatellite Genotyping Reveals End-Pleistocene Decline in Mammoth Autosomal Genetic Variation. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 3391–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debruyne, R.; Chu, G.; King, C.E.; Bos, K.; Kuch, M.; Schwarz, C.; Szpak, P.; Gröcke, D.R.; Matheus, P.; Zazula, G.; et al. Out of America: Ancient DNA Evidence for a New World Origin of Late Quaternary Woolly Mammoths. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 1320–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palkopoulou, E.; Dalén, L.; Lister, A.M.; Vartanyan, S.; Sablin, M.; Sher, A.; Edmark, V.N.; Brandström, M.D.; Germonpré, M.; Barnes, I.; et al. Holarctic Genetic Structure and Range Dynamics in the Woolly Mammoth. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2013, 280, 20131910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pečnerová, P.; Palkopoulou, E.; Wheat, C.W.; Skoglund, P.; Vartanyan, S.; Tikhonov, A.; Nikolskiy, P.; van der Plicht, J.; Díez-Del-Molino, D.; Dalén, L. Mitogenome Evolution in the Last Surviving Woolly Mammoth Population Reveals Neutral and Functional Consequences of Small Population Size. Evol. Lett. 2017, 1, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Knapp, M.; Enk, J.; Lippold, S.; Kircher, M.; Lister, A.; MacPhee, R.D.E.; Widga, C.; Czechowski, P.; Sommer, R.; et al. The Evolutionary and Phylogeographic History of Woolly Mammoths: A Comprehensive Mitogenomic Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enk, J.; Devault, A.; Widga, C.; Saunders, J.; Szpak, P.; Southon, J.; Rouillard, J.-M.; Shapiro, B.; Brian Golding, G.; Zazula, G.; et al. Mammuthus Population Dynamics in Late Pleistocene North America: Divergence, Phylogeography, and Introgression. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 4, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellows Yates, J.A.; Drucker, D.G.; Reiter, E.; Heumos, S.; Welker, F.; Münzel, S.C.; Wojtal, P.; Lázničková-Galetová, M.; Conard, N.J.; Herbig, A.; et al. Central European Woolly Mammoth Population Dynamics: Insights from Late Pleistocene Mitochondrial Genomes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehasque, M.; Pečnerová, P.; Muller, H.; Tikhonov, A.; Nikolskiy, P.; Tsigankova, V.I.; Danilov, G.K.; Díez-del-Molino, D.; Vartanyan, S.; Dalén, L.; et al. Combining Bayesian Age Models and Genetics to Investigate Population Dynamics and Extinction of the Last Mammoths in Northern Siberia. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2021, 259, 106913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, M.T.P.; Drautz, D.I.; Lesk, A.M.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Qi, J.; Ratan, A.; Hsu, C.-H.; Sher, A.; Dalén, L.; Götherström, A.; et al. Intraspecific Phylogenetic Analysis of Siberian Woolly Mammoths Using Complete Mitochondrial Genomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 8327–8332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Valk, T.; Pečnerová, P.; Díez-Del-Molino, D.; Bergström, A.; Oppenheimer, J.; Hartmann, S.; Xenikoudakis, G.; Thomas, J.A.; Dehasque, M.; Sağlıcan, E.; et al. Million-Year-Old DNA Sheds Light on the Genomic History of Mammoths. Nature 2021, 591, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roca, A.L. Million-Year-Old DNA Provides a Glimpse of Mammoth Evolution. Nature 2021, 591, 208–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Members, N.G.I.C.P. North Greenland Ice Core Project members High-Resolution Record of Northern Hemisphere Climate Extending into the Last Interglacial Period. Nature 2004, 431, 147–151. [Google Scholar]
- Barker, S.; Knorr, G.; Edwards, R.L.; Parrenin, F.; Putnam, A.E.; Skinner, L.C.; Wolff, E.; Ziegler, M. 800,000 Years of Abrupt Climate Variability. Science 2011, 334, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elderfield, H.; Ferretti, P.; Greaves, M.; Crowhurst, S.; McCave, I.N.; Hodell, D.; Piotrowski, A.M. Evolution of Ocean Temperature and Ice Volume through the Mid-Pleistocene Climate Transition. Science 2012, 337, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisiecki, L.E.; Raymo, M.E. A Pliocene-Pleistocene Stack of 57 Globally Distributed Benthic δ18O Records. Paleoceanography 2005, 20, PA1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waelbroeck, C.; Labeyrie, L.; Michel, E.; Duplessy, J.C.; McManus, J.F.; Lambeck, K.; Balbon, E.; Labracherie, M. Sea-Level and Deep Water Temperature Changes Derived from Benthic Foraminifera Isotopic Records. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2002, 21, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, G.; Heinrich, H.; Broecker, W.S.; Others, A. 11 Evidence for massive discharges of icebergs into the North Atlantic ocean during the last glacial period. Nature 1992, 360, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, M.R.; Shackleton, N.J. Global Ice-Volume Fluctuations, North Atlantic Ice-Rafting Events, and Deep-Ocean Circulation Changes between 130 and 70 Ka. Geology 1999, 27, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blockley, S.P.E.; Bourne, A.J.; Brauer, A.; Davies, S.M.; Hardiman, M.; Harding, P.R.; Lane, C.S.; MacLeod, A.; Matthews, I.P.; Pyne-O’Donnell, S.D.F.; et al. Tephrochronology and the Extended Intimate (integration of Ice-Core, Marine and Terrestrial Records) Event Stratigraphy 8–128 Ka b2k. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2014, 106, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pečnerová, P.; Díez-Del-Molino, D.; Dussex, N.; Feuerborn, T.; von Seth, J.; van der Plicht, J.; Nikolskiy, P.; Tikhonov, A.; Vartanyan, S.; Dalén, L. Genome-Based Sexing Provides Clues about Behavior and Social Structure in the Woolly Mammoth. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 3505–3510.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandt, A.L.; Ishida, Y.; Georgiadis, N.J.; Roca, A.L. Forest Elephant Mitochondrial Genomes Reveal That Elephantid Diversification in Africa Tracked Climate Transitions. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1175–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koren, L.; Matas, D.; Pečnerová, P.; Dalén, L.; Tikhonov, A.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; Wynne-Edwards, K.E.; Geffen, E. Testosterone in Ancient Hair from an Extinct Species. Palaeontology 2018, 61, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocherens, H.; Pacaud, G.; Lazarev, P.A.; Mariotti, A. Stable Isotope Abundances (13C, 15N) in Collagen and Soft Tissues from Pleistocene Mammals from Yakutia: Implications for the Palaeobiology of the Mammoth Steppe. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1996, 126, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz-Narbonne, R.; Longstaffe, F.J.; Kardynal, K.J.; Druckenmiller, P.; Hobson, K.A.; Jass, C.N.; Metcalfe, J.Z.; Zazula, G. Reframing the Mammoth Steppe: Insights from Analysis of Isotopic Niches. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2019, 215, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clementz, M.T.; Fox-Dobbs, K.; Wheatley, P.V.; Koch, P.L.; Doak, D.F. Revisiting Old Bones: Coupled Carbon Isotope Analysis of Bioapatite and Collagen as an Ecological and Palaeoecological Tool. Geol. J. 2009, 44, 605–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocherens, H.; Fizet, M.; Mariotti, A.; Gangloff, R.A.; Burns, J.A. Contribution of Isotopic Biogeochemistry (13C,15N,18O) to the Paleoecology of Mammoths (mammuthus Primigenius). Hist. Biol. 1994, 7, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, J.Z.; Longstaffe, F.J.; Hodgins, G. Proboscideans and Paleoenvironments of the Pleistocene Great Lakes: Landscape, Vegetation, and Stable Isotopes. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2013, 76, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz-Narbonne, R.; Longstaffe, F.J.; Metcalfe, J.Z.; Zazula, G. Solving the Woolly Mammoth Conundrum: Amino Acid 15N-Enrichment Suggests a Distinct Forage or Habitat. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacumin, P.; Nikolaev, V.; Ramigni, M. C and N Stable Isotope Measurements on Eurasian Fossil Mammals, 40 000 to 10 000 Years BP: Herbivore Physiologies and Palaeoenvironmental Reconstruction. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2000, 163, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpak, P.; Gröcke, D.R.; Debruyne, R.; MacPhee, R.D.E.; Dale Guthrie, R.; Froese, D.; Zazula, G.D.; Patterson, W.P.; Poinar, H.N. Regional Differences in Bone Collagen δ13C and δ15N of Pleistocene Mammoths: Implications for Paleoecology of the Mammoth Steppe. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2010, 286, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.G. The Flickering Genes of the Last Mammoths. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 3379–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzen, E.D.; Nogués-Bravo, D.; Orlando, L.; Weinstock, J.; Binladen, J.; Marske, K.A.; Ugan, A.; Borregaard, M.K.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; Nielsen, R.; et al. Species-Specific Responses of Late Quaternary Megafauna to Climate and Humans. Nature 2011, 479, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogués-Bravo, D.; Rodríguez, J.; Hortal, J.; Batra, P.; Araújo, M.B. Climate Change, Humans, and the Extinction of the Woolly Mammoth. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, A.; Turney, C.; Hughen, K.A.; Brook, B.W.; McDonald, H.G.; Bradshaw, C.J.A. PALEOECOLOGY. Abrupt Warming Events Drove Late Pleistocene Holarctic Megafaunal Turnover. Science 2015, 349, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drucker, D.G.; Bocherens, H.; Péan, S. Isotopes Stables (13C, 15N) Du Collagène Des Mammouths de Mezhyrich (Epigravettien, Ukraine): Implications Paléoécologiques. L’Anthropologie 2014, 118, 504–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuitems, M.; van Kolfschoten, T.; Tikhonov, A.N.; van der Plicht, J. Woolly Mammoth δ13C and δ15N Values Remained Amazingly Stable throughout the Last ∼50,000 Years in North-Eastern Siberia. Quat. Int. 2019, 500, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, R.W.; Belmecheri, S.; Choy, K.; Culleton, B.J.; Davies, L.J.; Froese, D.; Heintzman, P.D.; Hritz, C.; Kapp, J.D.; Newsom, L.A.; et al. Timing and Causes of Mid-Holocene Mammoth Extinction on St. Paul Island, Alaska. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9310–9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pečnerová, P.; Díez-del-Molino, D.; Vartanyan, S.; Dalén, L. Changes in Variation at the MHC Class II DQA Locus during the Final Demise of the Woolly Mammoth. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arppe, L.; Karhu, J.A.; Vartanyan, S.; Drucker, D.G.; Etu-Sihvola, H.; Bocherens, H. Thriving or Surviving? The Isotopic Record of the Wrangel Island Woolly Mammoth Population. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2019, 222, 105884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, A.J.; Lister, A.M. Extinction Chronology of the Woolly Rhinoceros Coelodonta Antiquitatis in the Context of Late Quaternary Megafaunal Extinctions in Northern Eurasia. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2012, 51, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiunov, A.V.; Kirillova, I.V. Stable Isotope (13 C/12 C and 15 N/14 N) Composition of the Woolly Rhinoceros Coelodonta Antiquitatis Horn Suggests Seasonal Changes in the Diet. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 24, 3146–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolmachev, A. (Ed.) The Arctic Ocean and Its Coast in the Cenozoic Era; Amerind Publ. Co.: New Delhi, India, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, D.M.; Macneil, F.S.; Merklin, R.L.; Petrov, O.M. Quaternary Correlations across Bering Strait: Recent Soviet and American Studies Cast New Light on the History of the Bering Land Bridge. Science 1965, 147, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, L.; Leonard, J.A.; Thenot, A.; Laudet, V.; Guerin, C.; Hänni, C. Ancient DNA Analysis Reveals Woolly Rhino Evolutionary Relationships. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 28, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willerslev, E.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; Binladen, J.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Campos, P.F.; Ratan, A.; Tomsho, L.P.; da Fonseca, R.R.; Sher, A.; Kuznetsova, T.V.; et al. Analysis of Complete Mitochondrial Genomes from Extinct and Extant Rhinoceroses Reveals Lack of Phylogenetic Resolution. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, E.; Dussex, N.; Kierczak, M.; Díez-Del-Molino, D.; Ryder, O.A.; Stanton, D.W.G.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; Sánchez-Barreiro, F.; Zhang, G.; Sinding, M.-H.S.; et al. Pre-Extinction Demographic Stability and Genomic Signatures of Adaptation in the Woolly Rhinoceros. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 3871–3879.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Iglesia, A.; Lister, A.M.; Stuart, A.J.; Bocherens, H.; Szpak, P.; Willerslev, E.; Lorenzen, E.D. Late Pleistocene Paleoecology and Phylogeography of Woolly Rhinoceroses. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2021, 263, 106993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grange, T.; Brugal, J.-P.; Flori, L.; Gautier, M.; Uzunidis, A.; Geigl, E.-M. The Evolution and Population Diversity of Bison in Pleistocene and Holocene Eurasia: Sex Matters. Diversity 2018, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, E.W.; Redford, K.H.; Weber, B.; Aune, K.; Baldes, D.; Berger, J.; Carter, D.; Curtin, C.; Derr, J.; Dobrott, S.; et al. The Ecological Future of the North American Bison: Conceiving Long-Term, Large-Scale Conservation of Wildlife. Conserv. Biol. 2008, 22, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucek, Z.; IUCN/SSC Bison Specialist Group. European Bison: Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan; World Conservation Union: Gland, Switzerland; Cambridge, UK, 2004; ISBN 9782831707624. [Google Scholar]
- Wójcik, J.M.; Kawałko, A.; Tokarska, M.; Jaarola, M.; Vallenback, P.; Pertoldi, C. Post-Bottleneck mtDNA Diversity in a Free-Living Population of European Bison: Implications for Conservation. J. Zool. 2009, 277, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertoldi, C.; Tokarska, M.; Wójcik, J.M.; Demontis, D.; Loeschcke, V.; Gregersen, V.R.; Coltman, D.; Wilson, G.A.; Randi, E.; Hansen, M.M.; et al. Depauperate Genetic Variability Detected in the American and European Bison Using Genomic Techniques. Biol. Direct 2009, 4, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderung, C.; Baubliene, J.; Daugnora, L.; Götherström, A. Medieval Remains from Lithuania Indicate Loss of a Mitochondrial Haplotype in Bison Bonasus. Mol. Ecol. 2006, 15, 3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, K.C. Comparing the Genetic Diversity of Late Pleistocene Bison with Modern Bison Bison Using Ancient DNA Techniques and the Mitochondrial DNA Control Region. Master’s Thesis, Baylor University, Waco, TX, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wecek, K.; Hartmann, S.; Paijmans, J.L.A.; Taron, U.; Xenikoudakis, G.; Cahill, J.A.; Heintzman, P.D.; Shapiro, B.; Baryshnikov, G.; Bunevich, A.N.; et al. Complex Admixture Preceded and Followed the Extinction of Wisent in the Wild. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 598–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazula, G.D.; Hall, E.; Gregory Hare, P.; Thomas, C.; Mathewes, R.; La Farge, C.; Martel, A.L.; Heintzman, P.D.; Shapiro, B. A Middle Holocene Steppe Bison and Paleoenvironments from the Versleuce Meadows, Whitehorse, Yukon, Canada. Can. J. Earth Sci. 2017, 54, 1138–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stronen, A.V.; Iacolina, L.; Pertoldi, C.; Tokarska, M.; Sørensen, B.S.; Bahrndorff, S.; Oleński, K.; Kamiński, S.; Nikolskiy, P. Genomic Variability in the Extinct Steppe Bison (Bison Priscus) Compared to the European Bison (Bison Bonasus). Mammal Res. 2019, 64, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, M.-A.; Bocherens, H.; Burke, A.; Drucker, D.G.; Patou-Mathis, M.; Krotova, O.; Péan, S. Were European Steppe Bison Migratory? 18O, 13C and Sr Intra-Tooth Isotopic Variations Applied to a Palaeoethological Reconstruction. Quat. Int. 2012, 271, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.; Parboosingh, J.S.; Bridge, P.J.; Ceri, H. Identification of Archaeological Animal Bone by PCR/DNA Analysis. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2002, 29, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen-Marsh, C.M.; Ostrom, P.H.; Gandhi, H.; Shapiro, B.; Cooper, A.; Hauschka, P.V.; Collins, M.J. Sequence Preservation of Osteocalcin Protein and Mitochondrial DNA in Bison Bones Older than 55 Ka. Geology 2002, 30, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, B.; Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A.; Wilson, M.C.; Matheus, P.E.; Sher, A.V.; Pybus, O.G.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; Barnes, I.; Binladen, J.; et al. Rise and Fall of the Beringian Steppe Bison. Science 2004, 306, 1561–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirillova, I.V.; Zanina, O.G.; Chernova, O.F.; Lapteva, E.G.; Trofimova, S.S.; Lebedev, V.S.; Tiunov, A.V.; Soares, A.E.R.; Shidlovskiy, F.K.; Shapiro, B. An Ancient Bison from the Mouth of the Rauchua River (Chukotka, Russia). Quat. Res. 2015, 84, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsolier-Kergoat, M.-C.; Palacio, P.; Berthonaud, V.; Maksud, F.; Stafford, T.; Bégouën, R.; Elalouf, J.-M. Hunting the Extinct Steppe Bison (Bison Priscus) Mitochondrial Genome in the Trois-Frères Paleolithic Painted Cave. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massilani, D.; Guimaraes, S.; Brugal, J.-P.; Bennett, E.A.; Tokarska, M.; Arbogast, R.-M.; Baryshnikov, G.; Boeskorov, G.; Castel, J.-C.; Davydov, S.; et al. Past Climate Changes, Population Dynamics and the Origin of Bison in Europe. BMC Biol. 2016, 14, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintzman, P.D.; Froese, D.; Ives, J.W.; Soares, A.E.R.; Zazula, G.D.; Letts, B.; Andrews, T.D.; Driver, J.C.; Hall, E.; Hare, P.G.; et al. Bison Phylogeography Constrains Dispersal and Viability of the Ice Free Corridor in Western Canada. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 8057–8063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soubrier, J.; Gower, G.; Chen, K.; Richards, S.M.; Llamas, B.; Mitchell, K.J.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Kosintsev, P.; Lee, M.S.Y.; Baryshnikov, G.; et al. Early Cave Art and Ancient DNA Record the Origin of European Bison. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13158. [Google Scholar]
- Palacio, P.; Berthonaud, V.; Guérin, C.; Lambourdière, J.; Maksud, F.; Philippe, M.; Plaire, D.; Stafford, T.; Marsolier-Kergoat, M.-C.; Elalouf, J.-M. Genome Data on the Extinct Bison Schoetensacki Establish It as a Sister Species of the Extant European Bison (Bison Bonasus). BMC Evol. Biol. 2017, 17, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onar, V.; Soubrier, J.; Toker, N.Y.; van Loenen, A.; Llamas, B.; Siddiq, A.B.; Pasicka, E.; Tokarska, M. Did the Historical Range of the European Bison (Bison Bonasus, L.) Extend Further South?—A New Finding from the Yenikapı Metro and Marmaray Excavation, Turkey. Mammal Res. 2017, 62, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, D.; Stiller, M.; Heintzman, P.D.; Reyes, A.V.; Zazula, G.D.; Soares, A.E.R.; Meyer, M.; Hall, E.; Jensen, B.J.L.; Arnold, L.J.; et al. Fossil and Genomic Evidence Constrains the Timing of Bison Arrival in North America. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 3457–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vershinina, A.O.; Kapp, J.D.; Soares, A.E.R.; Heintzman, P.D.; Lowson, C.; Cassatt-Johnstone, M.; Shidlovskiy, F.K.; Kirillova, I.V.; Shapiro, B. Ancient DNA Analysis of a Holocene Bison from the Rauchua River, Northwestern Chukotka, and the Existence of a Deeply Divergent Mitochondrial Clade. Зooлoгический журнал 2019, 98, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neov, B.; Spassov, N.; Hristova, L.; Hristov, P.; Radoslavov, G. New Data on the Evolutionary History of the European Bison (Bison Bonasus) Based on Subfossil Remains from Southeastern Europe. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 2842–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkaar, E.L.C.; Nijman, I.J.; Beeke, M.; Hanekamp, E.; Lenstra, J.A. Maternal and Paternal Lineages in Cross-Breeding Bovine Species. Has Wisent a Hybrid Origin? Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 21, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, J.E.; Pires, J.C.; Conant, G.C.; McKay, S.D.; Heaton, M.P.; Chen, K.; Cooper, A.; Vilkki, J.; Seabury, C.M.; Caetano, A.R.; et al. Resolving the Evolution of Extant and Extinct Ruminants with High-Throughput Phylogenomics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 18644–18649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funck, J.; Heintzman, P.D.; Murray, G.G.R.; Shapiro, B.; McKinney, H.; Huchet, J.-B.; Bigelow, N.; Druckenmiller, P.; Wooller, M.J. A Detailed Life History of a Pleistocene Steppe Bison (Bison Priscus) Skeleton Unearthed in Arctic Alaska. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2020, 249, 106578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocherens, H.; Drucker, D.G.; Bonjean, D.; Bridault, A.; Conard, N.J.; Cupillard, C.; Germonpré, M.; Höneisen, M.; Münzel, S.C.; Napierala, H.; et al. Isotopic Evidence for Dietary Ecology of Cave Lion (Panthera Spelaea) in North-Western Europe: Prey Choice, Competition and Implications for Extinction. Quat. Int. 2011, 245, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocherens, H.; Hofman-Kamińska, E.; Drucker, D.G.; Schmölcke, U.; Kowalczyk, R. European Bison as a Refugee Species? Evidence from Isotopic Data on Early Holocene Bison and Other Large Herbivores in Northern Europe. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0115090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojar, A.-V.; Guja, O.; Pelc, A.; Piotrowska, N.; Vasile, Ş. Bison Bonasus Skull from the Bihor Mountains, Romania: Isotopic and Morphological Investigations. Holocene 2015, 25, 1134–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofman-Kamińska, E.; Bocherens, H.; Drucker, D.G.; Fyfe, R.M.; Gumiński, W.; Makowiecki, D.; Pacher, M.; Piličiauskienė, G.; Samojlik, T.; Woodbridge, J.; et al. Adapt or die—Response of Large Herbivores to Environmental Changes in Europe during the Holocene. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 2915–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeder, M.A.; Emshwiller, E.; Smith, B.D.; Bradley, D.G. Documenting Domestication: The Intersection of Genetics and Archaeology. Trends Genet. 2006, 22, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, J.F.; Richards, M.B.; Macaulay, V.A.; Colson, I.B.; James, I.T.; Bradley, D.G.; Hedges, R.E.; Sykes, B.C. Ancient DNA Suggests a Recent Expansion of European Cattle from a Diverse Wild Progenitor Species. Proc. Biol. Sci. 1996, 263, 1467–1473. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, S.D.E.; Magee, D.A.; McGettigan, P.A.; Teasdale, M.D.; Edwards, C.J.; Lohan, A.J.; Murphy, A.; Braud, M.; Donoghue, M.T.; Liu, Y.; et al. Genome Sequencing of the Extinct Eurasian Wild Aurochs, Bos Primigenius, Illuminates the Phylogeography and Evolution of Cattle. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermes, T.R.; Frachetti, M.D.; Voyakin, D.; Yerlomaeva, A.S.; Beisenov, A.Z.; Doumani Dupuy, P.N.; Papin, D.V.; Motuzaite Matuzeviciute, G.; Bayarsaikhan, J.; Houle, J.-L.; et al. High Mitochondrial Diversity of Domesticated Goats Persisted among Bronze and Iron Age Pastoralists in the Inner Asian Mountain Corridor. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, A.; Frantz, L.; Schmidt, R.; Ersmark, E.; Lebrasseur, O.; Girdland-Flink, L.; Lin, A.T.; Storå, J.; Sjögren, K.-G.; Anthony, D.; et al. Origins and Genetic Legacy of Prehistoric Dogs. Science 2020, 370, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugo, G.P.; Dover, M.J.; MacHugh, D.E. Unlocking the Origins and Biology of Domestic Animals Using Ancient DNA and Paleogenomics. BMC Biol. 2019, 17, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, G.; Piperno, D.R.; Allaby, R.G.; Purugganan, M.D.; Andersson, L.; Arroyo-Kalin, M.; Barton, L.; Climer Vigueira, C.; Denham, T.; Dobney, K.; et al. Current Perspectives and the Future of Domestication Studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6139–6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeder, M.A. Why Evolutionary Biology Needs Anthropology: Evaluating Core Assumptions of the Extended Evolutionary Synthesis. Evol. Anthropol. 2018, 27, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, C.; Pfrengle, S.; Münzel, S.C.; Molak, M.; Feuerborn, T.R.; Breidenstein, A.; Reiter, E.; Albrecht, G.; Kind, C.-J.; Verjux, C.; et al. A Refined Proposal for the Origin of Dogs: The Case Study of Gnirshöhle, a Magdalenian Cave Site. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germonpré, M.; Sablin, M.V.; Stevens, R.E.; Hedges, R.E.M.; Hofreiter, M.; Stiller, M.; Després, V.R. Fossil Dogs and Wolves from Palaeolithic Sites in Belgium, the Ukraine and Russia: Osteometry, Ancient DNA and Stable Isotopes. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2009, 36, 473–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoglund, P.; Ersmark, E.; Palkopoulou, E.; Dalén, L. Ancient Wolf Genome Reveals an Early Divergence of Domestic Dog Ancestors and Admixture into High-Latitude Breeds. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 1515–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botigué, L.R.; Song, S.; Scheu, A.; Gopalan, S.; Pendleton, A.L.; Oetjens, M.; Taravella, A.M.; Seregély, T.; Zeeb-Lanz, A.; Arbogast, R.-M.; et al. Ancient European Dog Genomes Reveal Continuity since the Early Neolithic. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 16082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalmann, O.; Shapiro, B.; Cui, P.; Schuenemann, V.J.; Sawyer, S.K.; Greenfield, D.L.; Germonpré, M.B.; Sablin, M.V.; López-Giráldez, F.; Domingo-Roura, X.; et al. Complete Mitochondrial Genomes of Ancient Canids Suggest a European Origin of Domestic Dogs. Science 2013, 342, 871–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, A.H.; Gronau, I.; Schweizer, R.M.; Ortega-Del Vecchyo, D.; Han, E.; Silva, P.M.; Galaverni, M.; Fan, Z.; Marx, P.; Lorente-Galdos, B.; et al. Genome Sequencing Highlights the Dynamic Early History of Dogs. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Merriwether, D.A.; Kasparov, A.K.; Nikolskiy, P.A.; Sotnikova, M.V.; Pavlova, E.Y.; Pitulko, V.V. Ancient DNA Analysis of the Oldest Canid Species from the Siberian Arctic and Genetic Contribution to the Domestic Dog. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, L.M.; Boyko, R.H.; Castelhano, M.; Corey, E.; Hayward, J.J.; McLean, C.; White, M.E.; Abi Said, M.; Anita, B.A.; Bondjengo, N.I.; et al. Genetic Structure in Village Dogs Reveals a Central Asian Domestication Origin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 13639–13644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-D.; Zhai, W.; Yang, H.-C.; Fan, R.-X.; Cao, X.; Zhong, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, F.; Wu, H.; Cheng, L.-G.; et al. The Genomics of Selection in Dogs and the Parallel Evolution between Dogs and Humans. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-D.; Zhai, W.; Yang, H.-C.; Wang, L.; Zhong, L.; Liu, Y.-H.; Fan, R.-X.; Yin, T.-T.; Zhu, C.-L.; Poyarkov, A.D.; et al. Out of Southern East Asia: The Natural History of Domestic Dogs across the World. Cell Res. 2016, 26, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vonholdt, B.M.; Pollinger, J.P.; Lohmueller, K.E.; Han, E.; Parker, H.G.; Quignon, P.; Degenhardt, J.D.; Boyko, A.R.; Earl, D.A.; Auton, A.; et al. Genome-Wide SNP and Haplotype Analyses Reveal a Rich History Underlying Dog Domestication. Nature 2010, 464, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, L.A.F.; Mullin, V.E.; Pionnier-Capitan, M.; Lebrasseur, O.; Ollivier, M.; Perri, A.; Linderholm, A.; Mattiangeli, V.; Teasdale, M.D.; Dimopoulos, E.A.; et al. Genomic and Archaeological Evidence Suggest a Dual Origin of Domestic Dogs. Science 2016, 352, 1228–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deguilloux, M.F.; Moquel, J.; Pemonge, M.H.; Colombeau, G. Ancient DNA Supports Lineage Replacement in European Dog Gene Pool: Insight into Neolithic Southeast France. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2009, 36, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollivier, M.; Tresset, A.; Frantz, L.A.F.; Bréhard, S.; Bălăşescu, A.; Mashkour, M.; Boroneanţ, A.; Pionnier-Capitan, M.; Lebrasseur, O.; Arbogast, R.-M.; et al. Dogs Accompanied Humans during the Neolithic Expansion into Europe. Biol. Lett. 2018, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelsson, E.; Ratnakumar, A.; Arendt, M.-L.; Maqbool, K.; Webster, M.T.; Perloski, M.; Liberg, O.; Arnemo, J.M.; Hedhammar, A.; Lindblad-Toh, K. The Genomic Signature of Dog Domestication Reveals Adaptation to a Starch-Rich Diet. Nature 2013, 495, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-D.; Shao, X.-J.; Bai, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Cao, X.; Liu, Y.-H.; Wang, X.; Yin, T.-T.; Zhang, S.-J.; et al. Structural Variation during Dog Domestication: Insights from Gray Wolf and Dhole Genomes. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2019, 6, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendleton, A.L.; Shen, F.; Taravella, A.M.; Emery, S.; Veeramah, K.R.; Boyko, A.R.; Kidd, J.M. Comparison of Village Dog and Wolf Genomes Highlights the Role of the Neural Crest in Dog Domestication. BMC Biol. 2018, 16, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocherens, H.; Drucker, D.G.; Germonpré, M.; Lázničková-Galetová, M.; Naito, Y.I.; Wissing, C.; Brůžek, J.; Oliva, M. Reconstruction of the Gravettian Food-Web at Předmostí I Using Multi-Isotopic Tracking (13C, 15N, 34S) of Bone Collagen. Quat. Int. 2015, 359–360, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.; Olsen, J.; Richards, M.; Heinemeier, J.; Sveinbjörnsdóttir, Á.E.; Bennike, P. Coast–inland Mobility and Diet in the Danish Mesolithic and Neolithic: Evidence from Stable Isotope Values of Humans and Dogs. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2007, 34, 2125–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monagle, V.; Conrad, C.; Jones, E.L. What Makes a Dog? Stable Isotope Analysis and Human-Canid Relationships at Arroyo Hondo Pueblo. Open Quat. 2018, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rick, T.C.; Culleton, B.J.; Smith, C.B.; Johnson, J.R.; Kennett, D.J. Stable Isotope Analysis of Dog, Fox, and Human Diets at a Late Holocene Chumash Village (CA-SRI-2) on Santa Rosa Island, California. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2011, 38, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus-Fry, E.; Knecht, R.; Dobney, K.; Richards, M.P.; Britton, K. Dog-Human Dietary Relationships in Yup’ik Western Alaska: The Stable Isotope and Zooarchaeological Evidence from Pre-Contact Nunalleq. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2018, 17, 964–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, O.; Dunshea, G.; Sinding, M.-H.S.; Fedorov, S.; Germonpre, M.; Bocherens, H.; Gilbert, M.T.P. Ancient RNA from Late Pleistocene Permafrost and Historical Canids Shows Tissue-Specific Transcriptome Survival. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chessa, B.; Pereira, F.; Arnaud, F.; Amorim, A.; Goyache, F.; Mainland, I.; Kao, R.R.; Pemberton, J.M.; Beraldi, D.; Stear, M.J.; et al. Revealing the History of Sheep Domestication Using Retrovirus Integrations. Science 2009, 324, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzun, M.; Gutiérrez-Gil, B.; Arranz, J.-J.; San Primitivo, F.; Saatci, M.; Kaya, M.; Bayón, Y. Genetic Relationships among Turkish Sheep. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2006, 38, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Handley, L.-J.L.; Byrne, K.; Santucci, F.; Townsend, S.; Taylor, M.; Bruford, M.W.; Hewitt, G.M. Genetic Structure of European Sheep Breeds. Heredity 2007, 99, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaise, E.; Balasse, M. Seasonality and Season of Birth of Modern and Late Neolithic Sheep from South-Eastern France Using Tooth Enamel δ18O Analysis. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2011, 38, 3085–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornero, C.; Bălăşescu, A.; Ughetto-Monfrin, J.; Voinea, V.; Balasse, M. Seasonality and Season of Birth in Early Eneolithic Sheep from Cheia (Romania): Methodological Advances and Implications for Animal Economy. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 4039–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasse, M.; Boury, L.; Ughetto-Monfrin, J.; Tresset, A. Stable Isotope Insights (δ18O,δ13C) into Cattle and Sheep Husbandry at Bercy (Paris, France, 4th Millennium BC): Birth Seasonality and Winter Leaf Foddering. Environ. Archaeol. 2012, 17, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjögren, K.-G.; Douglas Price, T. A Complex Neolithic Economy: Isotope Evidence for the Circulation of Cattle and Sheep in the TRB of Western Sweden. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 690–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henton, E. The Combined Use of Oxygen Isotopes and Microwear in Sheep Teeth to Elucidate Seasonal Management of Domestic Herds: The Case Study of Çatalhöyük, Central Anatolia. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2012, 39, 3264–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganbold, O.; Lee, S.-H.; Seo, D.; Paek, W.K.; Manjula, P.; Munkhbayar, M.; Lee, J.H. Genetic Diversity and the Origin of Mongolian Native Sheep. Livest. Sci. 2019, 220, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemi, M.; Bläuer, A.; Iso-Touru, T.; Nyström, V.; Harjula, J.; Taavitsainen, J.-P.; Storå, J.; Lidén, K.; Kantanen, J. Mitochondrial DNA and Y-Chromosomal Diversity in Ancient Populations of Domestic Sheep (Ovis Aries) in Finland: Comparison with Contemporary Sheep Breeds. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2013, 45, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rannamäe, E.; Lõugas, L.; Speller, C.F.; Valk, H.; Maldre, L.; Wilczyński, J.; Mikhailov, A.; Saarma, U. Three Thousand Years of Continuity in the Maternal Lineages of Ancient Sheep (Ovis Aries) in Estonia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dymova, M.A.; Zadorozhny, A.V.; Mishukova, O.V.; Khrapov, E.A.; Druzhkova, A.S.; Trifonov, V.A.; Kichigin, I.G.; Tishkin, A.A.; Grushin, S.P.; Filipenko, M.L. Mitochondrial DNA Analysis of Ancient Sheep from Altai. Anim. Genet. 2017, 48, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, S.; Baştanlar, E.K.; Dağtaş, N.D.; Pişkin, E.; Engin, A.; Özer, F.; Yüncü, E.; Doğan, Ş.A.; Togan, İ. Mitochondrial DNA Diversity of Modern, Ancient and Wild Sheep (Ovis Gmelinii Anatolica) from Turkey: New Insights on the Evolutionary History of Sheep. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunson, K.; Lele, R.; Xin, Z.; Xiaoling, D.; Hui, W.; Jing, Z.; Flad, R. Zooarchaeology, Ancient mtDNA, and Radiocarbon Dating Provide New Evidence for the Emergence of Domestic Cattle and Caprines in the Tao River Valley of Gansu Province, Northwest China. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2020, 31, 102262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yang, P.; Li, M.; Fang, W.; Yue, X.; Nanaei, H.A.; Gan, S.; Du, D.; Cai, Y.; Dai, X.; et al. A Hu Sheep Genome with the First Ovine Y Chromosome Reveal Introgression History after Sheep Domestication. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, F.-H.; Peng, W.-F.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Y.-X.; Li, W.-R.; Liu, M.-J.; Ma, Y.-H.; Zhao, Q.-J.; Yang, G.-L.; Wang, F.; et al. Mitogenomic Meta-Analysis Identifies Two Phases of Migration in the History of Eastern Eurasian Sheep. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 2515–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kijas, J.W.; Lenstra, J.A.; Hayes, B.; Boitard, S.; Porto Neto, L.R.; Cristobal, M.S.; Servin, B.; McCulloch, R.; Whan, V.; Gietzen, K.; et al. Genome-Wide Analysis of the World’s Sheep Breeds Reveals High Levels of Historic Mixture and Strong Recent Selection. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-X.; Yang, J.; Lv, F.-H.; Hu, X.-J.; Xie, X.-L.; Zhang, M.; Li, W.-R.; Liu, M.-J.; Wang, Y.-T.; Li, J.-Q.; et al. Genomic Reconstruction of the History of Native Sheep Reveals the Peopling Patterns of Nomads and the Expansion of Early Pastoralism in East Asia. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 2380–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciani, E.; Econogene Consortium; Mastrangelo, S.; Da Silva, A.; Marroni, F.; Ferenčaković, M.; Ajmone-Marsan, P.; Baird, H.; Barbato, M.; Colli, L.; et al. On the Origin of European Sheep as Revealed by the Diversity of the Balkan Breeds and by Optimizing Population-Genetic Analysis Tools. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2020, 52, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, M.; Kansa, S.W.; Howard, S.; Campbell, S.; Thomas-Oates, J.; Collins, M. Distinguishing between Archaeological Sheep and Goat Bones Using a Single Collagen Peptide. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2010, 37, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendergast, M.E.; Janzen, A.; Buckley, M.; Grillo, K.M. Sorting the Sheep from the Goats in the Pastoral Neolithic: Morphological and Biomolecular Approaches at Luxmanda, Tanzania. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2019, 11, 3047–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, W.T.T.; Pruvost, M.; Posth, C.; Rendu, W.; Krajcarz, M.T.; Abdykanova, A.; Brancaleoni, G.; Spengler, R.; Hermes, T.; Schiavinato, S.; et al. Evidence for Early Dispersal of Domestic Sheep into Central Asia. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeder, M.A. Domestication and Early Agriculture in the Mediterranean Basin: Origins, Diffusion, and Impact. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11597–11604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meadows, J.R.S.; Cemal, I.; Karaca, O.; Gootwine, E.; Kijas, J.W. Five Ovine Mitochondrial Lineages Identified from Sheep Breeds of the near East. Genetics 2007, 175, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiendleder, S.; Kaupe, B.; Wassmuth, R.; Janke, A. Molecular Analysis of Wild and Domestic Sheep Questions Current Nomenclature and Provides Evidence for Domestication from Two Different Subspecies. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2002, 269, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiendleder, S.; Lewalski, H.; Wassmuth, R.; Janke, A. The Complete Mitochondrial DNA Sequence of the Domestic Sheep (Ovis Aries) and Comparison with the Other Major Ovine Haplotype. J. Mol. Evol. 1998, 47, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapio, M.; Marzanov, N.; Ozerov, M.; Cinkulov, M.; Gonzarenko, G.; Kiselyova, T.; Murawski, M.; Viinalass, H.; Kantanen, J. Sheep Mitochondrial DNA Variation in European, Caucasian, and Central Asian Areas. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 1776–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, S., Jr.; Kolte, A.P.; Kumar, S. Extensive Variation and Sub-Structuring in Lineage a mtDNA in Indian Sheep: Genetic Evidence for Domestication of Sheep in India. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivieri, C.; Ermini, L.; Rizzi, E.; Corti, G.; Luciani, S.; Marota, I.; De Bellis, G.; Rollo, F. Phylogenetic Position of a Copper Age Sheep (Ovis Aries) Mitochondrial DNA. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.-W.; Han, L.; Zhang, X.-L.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, H. DNA Analysis of Archaeological Sheep Remains from China. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2007, 34, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Tang, Z.; Yu, H.; Han, L.; Ren, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, H. Early History of Chinese Domestic Sheep Indicated by Ancient DNA Analysis of Bronze Age Individuals. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2011, 38, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meadows, J.R.S.; Li, K.; Kantanen, J.; Tapio, M.; Sipos, W.; Pardeshi, V.; Gupta, V.; Calvo, J.H.; Whan, V.; Norris, B.; et al. Mitochondrial Sequence Reveals High Levels of Gene Flow between Breeds of Domestic Sheep from Asia and Europe. J. Hered. 2005, 96, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, S.-Y.; Duan, Z.-Y.; Sha, T.; Xiangyu, J.; Wu, S.-F.; Zhang, Y.-P. Origin, Genetic Diversity, and Population Structure of Chinese Domestic Sheep. Gene 2006, 376, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Du, L.-X.; Ma, Y.-H.; Guan, W.-J.; Li, H.-B.; Zhao, Q.-J.; Li, X.; Rao, S.-Q. A Novel Maternal Lineage Revealed in Sheep (Ovis Aries). Anim. Genet. 2005, 36, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, F.; Davis, S.J.M.; Pereira, L.; McEvoy, B.; Bradley, D.G.; Amorim, A. Genetic Signatures of a Mediterranean Influence in Iberian Peninsula Sheep Husbandry. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 1420–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbianelli, F.; Gargani, M.; Pariset, L.; Mariotti, M.; Alhaique, F.; De Minicis, E.; Barelli, L.; Ciammetti, E.; Redi, F.; Valentini, A. Mitochondrial DNA Analysis of Medieval Sheep (Ovis Aries) in Central Italy Reveals the Predominance of Haplogroup B Already in the Middle Ages. Anim. Genet. 2015, 46, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kechin, A.A.; Dymova, M.A.; Tishkin, A.A.; Grushin, S.P.; Dashkovskiy, P.K.; Filipenko, M.L. Targeted Sequencing for Studying Economically Useful Traits and Phylogenetic Diversity of Ancient Sheep. Russ. J. Genet. 2019, 55, 1499–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemi, M.; Sajantila, A.; Ahola, V.; Vilkki, J. Sheep and Cattle Population Dynamics Based on Ancient and Modern DNA Reflects Key Events in the Human History of the North-East Baltic Sea Region. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2018, 18, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela-Lamas, S.; Orengo, H.A.; Bosch, D.; Pellegrini, M.; Halstead, P.; Nieto-Espinet, A.; Trentacoste, A.; Jiménez-Manchón, S.; López-Reyes, D.; Jornet-Niella, R. Shipping Amphorae and Shipping Sheep? Livestock Mobility in the North-East Iberian Peninsula during the Iron Age Based on Strontium Isotopic Analyses of Sheep and Goat Tooth Enamel. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermes, T.R.; Frachetti, M.D.; Doumani Dupuy, P.N.; Mar’yashev, A.; Nebel, A.; Makarewicz, C.A. Early Integration of Pastoralism and Millet Cultivation in Bronze Age Eurasia. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2019, 286, 20191273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, S.E.P.; Pilaar Birch, S.E.; Scheu, A.; Buckley, M.; Çakırlar, C. Combined Osteomorphological, Isotopic, aDNA, and ZooMS Analyses of Sheep and Goat Remains from Neolithic Ulucak, Turkey. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2019, 11, 1669–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troy, C.S.; MacHugh, D.E.; Bailey, J.F.; Magee, D.A.; Loftus, R.T.; Cunningham, P.; Chamberlain, A.T.; Sykes, B.C.; Bradley, D.G. Genetic Evidence for Near-Eastern Origins of European Cattle. Nature 2001, 410, 1088–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, C.J.; MacHugh, D.E.; Dobney, K.M.; Martin, L.; Russell, N.; Horwitz, L.K.; McIntosh, S.K.; MacDonald, K.C.; Helmer, D.; Tresset, A.; et al. Ancient DNA Analysis of 101 Cattle Remains: Limits and Prospects. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2004, 31, 695–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollongino, R.; Burger, J.; Powell, A.; Mashkour, M.; Vigne, J.-D.; Thomas, M.G. Modern Taurine Cattle Descended from Small Number of near-Eastern Founders. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 2101–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colominas, L.; Schlumbaum, A.; Saña, M. The Impact of the Roman Empire on Animal Husbandry Practices: Study of the Changes in Cattle Morphology in the North-East of the Iberian Peninsula through Osteometric and Ancient DNA Analyses. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2014, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemi, M.; Bläuer, A.; Iso-Touru, T.; Harjula, J.; Nyström Edmark, V.; Rannamäe, E.; Lõugas, L.; Sajantila, A.; Lidén, K.; Taavitsainen, J.-P. Temporal Fluctuation in North East Baltic Sea Region Cattle Population Revealed by Mitochondrial and Y-Chromosomal DNA Analyses. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123821. [Google Scholar]
- Meiri, M.; Stockhammer, P.W.; Marom, N.; Bar-Oz, G.; Sapir-Hen, L.; Morgenstern, P.; Macheridis, S.; Rosen, B.; Huchon, D.; Maran, J.; et al. Eastern Mediterranean Mobility in the Bronze and Early Iron Ages: Inferences from Ancient DNA of Pigs and Cattle. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Cai, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, R.; Wang, K.; Huang, Y.; Hu, S.; Huang, S.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Whole-Genome Resequencing Reveals World-Wide Ancestry and Adaptive Introgression Events of Domesticated Cattle in East Asia. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasse, M.; Gillis, R.; Živaljević, I.; Berthon, R.; Kovačiková, L.; Fiorillo, D.; Arbogast, R.-M.; Bălăşescu, A.; Bréhard, S.; Nyerges, É.Á.; et al. Seasonal Calving in European Prehistoric Cattle and Its Impacts on Milk Availability and Cheese-Making. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, D.; Sevane, N.; Nicolazzi, E.L.; MacHugh, D.E.; Park, S.D.E.; Colli, L.; Martinez, R.; Bruford, M.W.; Orozco-terWengel, P. Domestication of Cattle: Two or Three Events? Evol. Appl. 2019, 12, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caramelli, D. The Origins of Domesticated Cattle. Hum. Evol. 2006, 21, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vuure, C.; van Vuure, T. Retracing the Aurochs: History, Morphology and Ecology of an Extinct Wild Ox; Pensoft Pub: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Paijmans, J.L.A.; Chang, F.; Wu, X.; Chen, G.; Lei, C.; Yang, X.; Wei, Z.; Bradley, D.G.; Orlando, L.; et al. Morphological and Genetic Evidence for Early Holocene Cattle Management in Northeastern China. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Sun, Y.; Tang, Z.; Hu, S.; Li, W.; Zhao, X.; Xiang, H.; Zhou, H. The Origins of Chinese Domestic Cattle as Revealed by Ancient DNA Analysis. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2014, 41, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lin, B.-Z.; Baig, M.; Mitra, B.; Lopes, R.J.; Santos, A.M.; Magee, D.A.; Azevedo, M.; Tarroso, P.; Sasazaki, S.; et al. Zebu Cattle Are an Exclusive Legacy of the South Asia Neolithic. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.Z.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.C.; Cai, X.; Liu, R.Y.; Luo, L.Y.; Wang, C.F.; Zhang, W.; Ge, Q.L.; Zhang, R.F.; et al. Origin and Phylogeographical Structure of Chinese Cattle. Anim. Genet. 2006, 37, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, P.; Spassov, N.; Iliev, N.; Radoslavov, G. An Independent Event of Neolithic Cattle Domestication on the South-Eastern Balkans: Evidence from Prehistoric Aurochs and Cattle Populations. Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2017, 28, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdugo, M.P.; Mullin, V.E.; Scheu, A.; Mattiangeli, V.; Daly, K.G.; Maisano Delser, P.; Hare, A.J.; Burger, J.; Collins, M.J.; Kehati, R.; et al. Ancient Cattle Genomics, Origins, and Rapid Turnover in the Fertile Crescent. Science 2019, 365, 173–176. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; Balasse, M.; Yuan, J.; Zhao, C.; Hu, Y.; Vigne, J.-D. Cattle and Sheep Raising and Millet Growing in the Longshan Age in Central China: Stable Isotope Investigation at the Xinzhai Site. Quat. Int. 2016, 426, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthon, R.; Kovačiková, L.; Tresset, A.; Balasse, M. Integration of Linearbandkeramik Cattle Husbandry in the Forested Landscape of the Mid-Holocene Climate Optimum: Seasonal-Scale Investigations in Bohemia. J. Anthropol. Archaeol. 2018, 51, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towers, J.; Gledhill, A.; Bond, J.; Montgomery, J. An Investigation of Cattle Birth Seasonality Using δ 13 C and δ 18 O Profiles within First Molar Enamel. Archaeometry 2014, 56, 208–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gron, K.J.; Montgomery, J.; Rowley-Conwy, P. Cattle Management for Dairying in Scandinavia’s Earliest Neolithic. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, S.; Elsner, J.; Derek Hamilton, W.; Sayle, K.L.; Schlumbaum, A.; Bartosiewicz, L. Matrilines in Neolithic Cattle from Orkney, Scotland Reveals Complex Husbandry Patterns of Ancestry. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2017, 14, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Frantz, L.; Meijaard, E.; Gongora, J.; Haile, J.; Groenen, M.A.M.; Larson, G. The Evolution of Suidae. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2016, 4, 61–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, G.; Dobney, K.; Albarella, U.; Fang, M.; Matisoo-Smith, E.; Robins, J.; Lowden, S.; Finlayson, H.; Brand, T.; Willerslev, E.; et al. Worldwide Phylogeography of Wild Boar Reveals Multiple Centers of Pig Domestication. Science 2005, 307, 1618–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ervynck, A.; Dobney, K.; Hongo, H.; Meadow, R. Born Free? New Evidence for the Status of Sus Scrofa at Neolithic Çayönü Tepesi (Southeastern Anatolia, Turkey). Paléorient 2001, 27, 47–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucchi, T.; Hulme-Beaman, A.; Yuan, J.; Dobney, K. Early Neolithic Pig Domestication at Jiahu, Henan Province, China: Clues from Molar Shape Analyses Using Geometric Morphometric Approaches. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2011, 38, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenen, M.A.M.; Archibald, A.L.; Uenishi, H.; Tuggle, C.K.; Takeuchi, Y.; Rothschild, M.F.; Rogel-Gaillard, C.; Park, C.; Milan, D.; Megens, H.-J.; et al. Analyses of Pig Genomes Provide Insight into Porcine Demography and Evolution. Nature 2012, 491, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frantz, L.A.F.; Schraiber, J.G.; Madsen, O.; Megens, H.-J.; Bosse, M.; Paudel, Y.; Semiadi, G.; Meijaard, E.; Li, N.; Crooijmans, R.P.M.A.; et al. Genome Sequencing Reveals Fine Scale Diversification and Reticulation History during Speciation in Sus. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, G.; Fuller, D.Q. The Evolution of Animal Domestication. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Systain. 2014, 45, 115–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeder, M.A. Others Pathways to Animal Domestication. Biodivers. Agric. Domest. Evol. Sustain. 2012, 227–259. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, G.; Liu, R.; Zhao, X.; Yuan, J.; Fuller, D.; Barton, L.; Dobney, K.; Fan, Q.; Gu, Z.; Liu, X.-H.; et al. Patterns of East Asian Pig Domestication, Migration, and Turnover Revealed by Modern and Ancient DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 7686–7691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megens, H.-J.; Crooijmans, R.P.M.A.; San Cristobal, M.; Hui, X.; Li, N.; Groenen, M.A.M. Biodiversity of Pig Breeds from China and Europe Estimated from Pooled DNA Samples: Differences in Microsatellite Variation between Two Areas of Domestication. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2008, 40, 103–128. [Google Scholar]
- Frantz, L.A.F.; Schraiber, J.G.; Madsen, O.; Megens, H.-J.; Cagan, A.; Bosse, M.; Paudel, Y.; Crooijmans, R.P.M.A.; Larson, G.; Groenen, M.A.M. Evidence of Long-Term Gene Flow and Selection during Domestication from Analyses of Eurasian Wild and Domestic Pig Genomes. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowley-Conwy, P.; Albarella, U.; Dobney, K. Distinguishing Wild Boar from Domestic Pigs in Prehistory: A Review of Approaches and Recent Results. J. World Prehistory 2012, 25, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evin, A.; Cucchi, T.; Cardini, A.; Strand Vidarsdottir, U.; Larson, G.; Dobney, K. The Long and Winding Road: Identifying Pig Domestication through Molar Size and Shape. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khederzadeh, S.; Kusza, S.; Huang, C.-P.; Markov, N.; Scandura, M.; Babaev, E.; Šprem, N.; Seryodkin, I.V.; Paule, L.; Esmailizadeh, A.; et al. Maternal Genomic Variability of the Wild Boar (Sus Scrofa) Reveals the Uniqueness of East-Caucasian and Central Italian Populations. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 9467–9478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, P.; Bhuiyan, A.A.; Chen, J.-H.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, S.; Du, X.; Li, H.; Yu, H.; Liu, X.; et al. De Novo Assembly of Mitochondrial Genomes Provides Insights into Genetic Diversity and Molecular Evolution in Wild Boars and Domestic Pigs. Genetica 2018, 146, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Du, H.; Jiang, L.; Zheng, X.; Feng, W.; Diao, C.; Zhou, L.; Liu, G.E.; Zhang, H.; Chamba, Y.; et al. PRE-1 Revealed Previous Unknown Introgression Events in Eurasian Boars during the Middle Pleistocene. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 12, 1751–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeola, A.C.; Oluwole, O.O.; Oladele, B.M.; Olorungbounmi, T.O.; Boladuro, B.; Olaogun, S.C.; Nneji, L.M.; Sanke, O.J.; Dawuda, P.M.; Omitogun, O.G.; et al. Analysis of the Genetic Variation in Mitochondrial DNA, Y-Chromosome Sequences, and MC1R Sheds Light on the Ancestry of Nigerian Indigenous Pigs. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2017, 49, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, G.; Albarella, U.; Dobney, K.; Rowley-Conwy, P.; Schibler, J.; Tresset, A.; Vigne, J.-D.; Edwards, C.J.; Schlumbaum, A.; Dinu, A.; et al. Ancient DNA, Pig Domestication, and the Spread of the Neolithic into Europe. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15276–15281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause-Kyora, B.; Makarewicz, C.; Evin, A.; Flink, L.G.; Dobney, K.; Larson, G.; Hartz, S.; Schreiber, S.; von Carnap-Bornheim, C.; von Wurmb-Schwark, N.; et al. Use of Domesticated Pigs by Mesolithic Hunter-Gatherers in Northwestern Europe. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottoni, C.; Flink, L.G.; Evin, A.; Geörg, C.; De Cupere, B.; Van Neer, W.; Bartosiewicz, L.; Linderholm, A.; Barnett, R.; Peters, J.; et al. Pig Domestication and Human-Mediated Dispersal in Western Eurasia Revealed through Ancient DNA and Geometric Morphometrics. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliebe, A.; Nebel, A.; Makarewicz, C.; Krawczak, M.; Krause-Kyora, B. Insights into Early Pig Domestication Provided by Ancient DNA Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vai, S.; Vilaça, S.T.; Romandini, M.; Benazzo, A.; Visentini, P.; Modolo, M.; Bertolini, M.; MacQueen, P.; Austin, J.; Cooper, A.; et al. The Biarzo Case in Northern Italy: Is the Temporal Dynamic of Swine Mitochondrial DNA Lineages in Europe Related to Domestication? Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, S.E.; Tautscher, B.; Pucher, E.; Kowarik, K.; Reschreiter, H.; Kern, A.; Haring, E. Bronze Age Meat Industry: Ancient Mitochondrial DNA Analyses of Pig Bones from the Prehistoric Salt Mines of Hallstatt (Austria). BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Evin, A.; Flink, L.G.; Bălăşescu, A.; Popovici, D.; Andreescu, R.; Bailey, D.; Mirea, P.; Lazăr, C.; Boroneanţ, A.; Bonsall, C.; et al. Unravelling the Complexity of Domestication: A Case Study Using Morphometrics and Ancient DNA Analyses of Archaeological Pigs from Romania. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20130616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, G.; Cucchi, T.; Fujita, M.; Matisoo-Smith, E.; Robins, J.; Anderson, A.; Rolett, B.; Spriggs, M.; Dolman, G.; Kim, T.-H.; et al. Phylogeny and Ancient DNA of Sus Provides Insights into Neolithic Expansion in Island Southeast Asia and Oceania. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4834–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, L.A.F.; Haile, J.; Lin, A.T.; Scheu, A.; Geörg, C.; Benecke, N.; Alexander, M.; Linderholm, A.; Mullin, V.E.; Daly, K.G.; et al. Ancient Pigs Reveal a near-Complete Genomic Turnover Following Their Introduction to Europe. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 17231–17238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasse, M.; Cucchi, T.; Evin, A.; Bălăşescu, A.; Frémondeau, D.; Horard-Herbin, M.-P. Wild game or farm animal? Tracking human-pig relationships in ancient times through stable isotope analysis. In Hybrid Communities; Routledge: London, UK, 2018; Volume 1, pp. 81–96. [Google Scholar]
- Minagawa, M.; Matsui, A.; Ishiguro, N. Patterns of Prehistoric Boar Sus Scrofa Domestication, and Inter-Islands Pig Trading across the East China Sea, as Determined by Carbon and Nitrogen Isotope Analysis. Chem. Geol. 2005, 218, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lösch, S.; Grupe, G.; Peters, J. Stable Isotopes and Dietary Adaptations in Humans and Animals at Pre-Pottery Neolithic Nevalli Cori, Southeast Anatolia. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2006, 131, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Kan, X.; Zhang, X. An Investigation into the Strategy of Pig Husbandry Combining Zooarchaeological and Stable Isotopic Approaches at Neolithic Houjiazhai, China. Int. J. Osteoarchaeol. 2019, 29, 772–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madgwick, R.; Mulville, J.; Stevens, R.E. Diversity in Foddering Strategy and Herd Management in Late Bronze Age Britain: An Isotopic Investigation of Pigs and Other Fauna from Two Midden Sites. Environ. Archaeol. 2012, 17, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, J.; Thomas, R. Pannage, Pulses and Pigs: Isotopic and Zooarchaeological Evidence for Changing Pig Management Practices in Later Medieval England. Mediev. Archaeol. 2012, 56, 234–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müldner, G.; Richards, M.P. Stable Isotope Evidence for 1500 Years of Human Diet at the City of York, UK. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2007, 133, 682–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Luan, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Richards, M.P. Preliminary Attempt to Distinguish the Domesticated Pigs from Wild Boars by the Methods of Carbon and Nitrogen Stable Isotope Analysis. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2009, 52, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechenkina, E.A.; Ambrose, S.H.; Xiaolin, M.; Benfer, R.A. Reconstructing Northern Chinese Neolithic Subsistence Practices by Isotopic Analysis. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2005, 32, 1176–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fuller, B.T.; Zhang, P.; Hu, S.; Hu, Y.; Shang, X. Millet Manuring as a Driving Force for the Late Neolithic Agricultural Expansion of North China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenner, J.N.; Gagan, M.K.; Cowley, J.; Armstrong, R.; Prasetyo, B. Investigating the Presence of Foreigners and Pig Husbandry in Ancient Bali: Stable Isotopes in Human and Domestic Animal Tooth Enamel. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2016, 10, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, L. Ancient Genomes Reveal Unexpected Horse Domestication and Management Dynamics. Bioessays 2020, 42, e1900164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlando, L.; Ginolhac, A.; Raghavan, M.; Vilstrup, J.; Rasmussen, M.; Magnussen, K.; Steinmann, K.E.; Kapranov, P.; Thompson, J.F.; Zazula, G.; et al. True Single-Molecule DNA Sequencing of a Pleistocene Horse Bone. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 1705–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, L.; Ginolhac, A.; Zhang, G.; Froese, D.; Albrechtsen, A.; Stiller, M.; Schubert, M.; Cappellini, E.; Petersen, B.; Moltke, I.; et al. Recalibrating Equus Evolution Using the Genome Sequence of an Early Middle Pleistocene Horse. Nature 2013, 499, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonardi, M.; Boschin, F.; Giampoudakis, K.; Beyer, R.M.; Krapp, M.; Bendrey, R.; Sommer, R.; Boscato, P.; Manica, A.; Nogues-Bravo, D.; et al. Late Quaternary Horses in Eurasia in the Face of Climate and Vegetation Change. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vershinina, A.O.; Heintzman, P.D.; Froese, D.G.; Zazula, G.; Cassatt-Johnstone, M.; Dalén, L.; Der Sarkissian, C.; Dunn, S.G.; Ermini, L.; Gamba, C.; et al. Ancient Horse Genomes Reveal the Timing and Extent of Dispersals across the Bering Land Bridge. Mol. Ecol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, L.A.F.; Bradley, D.G.; Larson, G.; Orlando, L. Animal Domestication in the Era of Ancient Genomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaunitz, C.; Fages, A.; Hanghøj, K.; Albrechtsen, A.; Khan, N.; Schubert, M.; Seguin-Orlando, A.; Owens, I.J.; Felkel, S.; Bignon-Lau, O.; et al. Ancient Genomes Revisit the Ancestry of Domestic and Przewalski’s Horses. Science 2018, 360, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.; Jónsson, H.; Chang, D.; Der Sarkissian, C.; Ermini, L.; Ginolhac, A.; Albrechtsen, A.; Dupanloup, I.; Foucal, A.; Petersen, B.; et al. Prehistoric Genomes Reveal the Genetic Foundation and Cost of Horse Domestication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E5661–E5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warmuth, V.; Eriksson, A.; Bower, M.A.; Barker, G.; Barrett, E.; Hanks, B.K.; Li, S.; Lomitashvili, D.; Ochir-Goryaeva, M.; Sizonov, G.V.; et al. Reconstructing the Origin and Spread of Horse Domestication in the Eurasian Steppe. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8202–8206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieslak, M.; Pruvost, M.; Benecke, N.; Hofreiter, M.; Morales, A.; Reissmann, M.; Ludwig, A. Origin and History of Mitochondrial DNA Lineages in Domestic Horses. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fages, A.; Hanghøj, K.; Khan, N.; Gaunitz, C.; Seguin-Orlando, A.; Leonardi, M.; McCrory Constantz, C.; Gamba, C.; Al-Rasheid, K.A.S.; Albizuri, S.; et al. Tracking Five Millennia of Horse Management with Extensive Ancient Genome Time Series. Cell 2019, 177, 1419–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooyman, B.; Newman, M.E.; Cluney, C.; Lobb, M.; Tolman, S.; McNeil, P.; Hills, L.V. Identification of Horse Exploitation by Clovis Hunters Based on Protein Analysis. Am. Antiq. 2001, 66, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Librado, P.; Gamba, C.; Gaunitz, C.; Der Sarkissian, C.; Pruvost, M.; Albrechtsen, A.; Fages, A.; Khan, N.; Schubert, M.; Jagannathan, V.; et al. Ancient Genomic Changes Associated with Domestication of the Horse. Science 2017, 356, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallner, B.; Palmieri, N.; Vogl, C.; Rigler, D.; Bozlak, E.; Druml, T.; Jagannathan, V.; Leeb, T.; Fries, R.; Tetens, J.; et al. Y Chromosome Uncovers the Recent Oriental Origin of Modern Stallions. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 2029–2035.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippold, S.; Knapp, M.; Kuznetsova, T.; Leonard, J.A.; Benecke, N.; Ludwig, A.; Rasmussen, M.; Cooper, A.; Weinstock, J.; Willerslev, E.; et al. Discovery of Lost Diversity of Paternal Horse Lineages Using Ancient DNA. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, J.L.; Sánchez, B.; Alberdi, M.T. Ancient Feeding Ecology Inferred from Stable Isotopic Evidence from Fossil Horses in South America over the Past 3 Ma. BMC Ecol. 2011, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.R.V.; Ventresca Miller, A.R.; Bragina, T.M.; Abil, Y.A.; Rulyova, M.M.; Makarewicz, C.A. Correction to: Pasture Usage by Ancient Pastoralists in the Northern Kazakh Steppe Informed by Carbon and Nitrogen Isoscapes of Contemporary Floral Biomes. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2019, 11, 3063–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczensky, P.; Šturm, M.B.; Sablin, M.V.; Voigt, C.C.; Smith, S.; Ganbaatar, O.; Balint, B.; Walzer, C.; Spasskaya, N.N. Stable Isotopes Reveal Diet Shift from Pre-Extinction to Reintroduced Przewalski’s Horses. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baca, M.; Popović, D.; Panagiotopoulou, H.; Marciszak, A.; Krajcarz, M.; Krajcarz, M.T.; Makowiecki, D.; Węgleński, P.; Nadachowski, A. Human-Mediated Dispersal of Cats in the Neolithic Central Europe. Heredity 2018, 121, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randi, E.; Pierpaoli, M.; Beaumont, M.; Ragni, B.; Sforzi, A. Genetic Identification of Wild and Domestic Cats (Felis Silvestris) and Their Hybrids Using Bayesian Clustering Methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001, 18, 1679–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, C.A.; Menotti-Raymond, M.; Roca, A.L.; Hupe, K.; Johnson, W.E.; Geffen, E.; Harley, E.H.; Delibes, M.; Pontier, D.; Kitchener, A.C.; et al. The Near Eastern Origin of Cat Domestication. Science 2007, 317, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driscoll, C.A.; Macdonald, D.W.; O’Brien, S.J. From Wild Animals to Domestic Pets, an Evolutionary View of Domestication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106 (Suppl. S1), 9971–9978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottoni, C.; Van Neer, W.; De Cupere, B.; Daligault, J.; Guimaraes, S.; Peters, J.; Spassov, N.; Prendergast, M.E.; Boivin, N.; Morales-Muñiz, A.; et al. The Palaeogenetics of Cat Dispersal in the Ancient World. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Hu, S.; Wang, W.; Wu, X.; Marshall, F.B.; Chen, X.; Hou, L.; Wang, C. Earliest Evidence for Commensal Processes of Cat Domestication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajcarz, M.; Krajcarz, M.T.; Baca, M.; Baumann, C.; Van Neer, W.; Popović, D.; Sudoł-Procyk, M.; Wach, B.; Wilczyński, J.; Wojenka, M.; et al. Ancestors of Domestic Cats in Neolithic Central Europe: Isotopic Evidence of a Synanthropic Diet. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 17710–17719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigne, J.-D.; Guilaine, J.; Debue, K.; Haye, L.; Gérard, P. Early Taming of the Cat in Cyprus. Science 2004, 304, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajcarz, M.; Makowiecki, D.; Krajcarz, M.T.; Masłowska, A.; Baca, M.; Panagiotopoulou, H.; Romańska, A.; Bednarczyk, J.; Gręzak, A.; Sudoł, M. On the Trail of the Oldest Domestic Cat in Poland. An Insight from Morphometry, Ancient DNA and Radiocarbon Dating. Int. J. Osteoarchaeol. 2016, 26, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiry, E.J.; Orchard, T.J.; Royle, T.C.A.; Cheung, C.; Yang, D.Y. Dietary Plasticity and the Extinction of the Passenger Pigeon (Ectopistes Migratorius). Quat. Sci. Rev. 2020, 233, 106225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlence, N.J.; Metcalf, J.L.; Wood, J.R.; Worthy, T.H.; Austin, J.J.; Cooper, A. The Effect of Climate and Environmental Change on the Megafaunal Moa of New Zealand in the Absence of Humans. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2012, 50, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
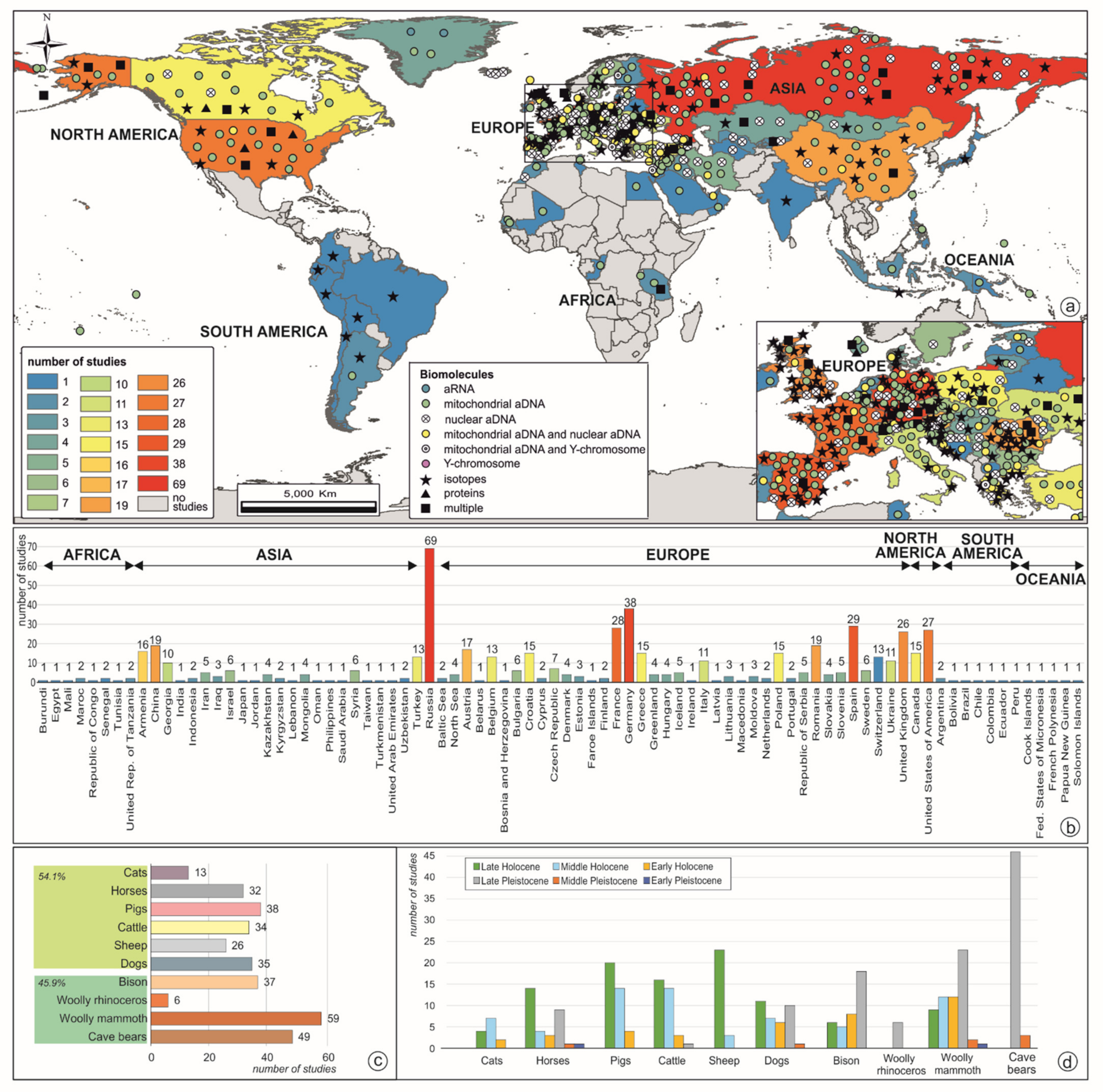
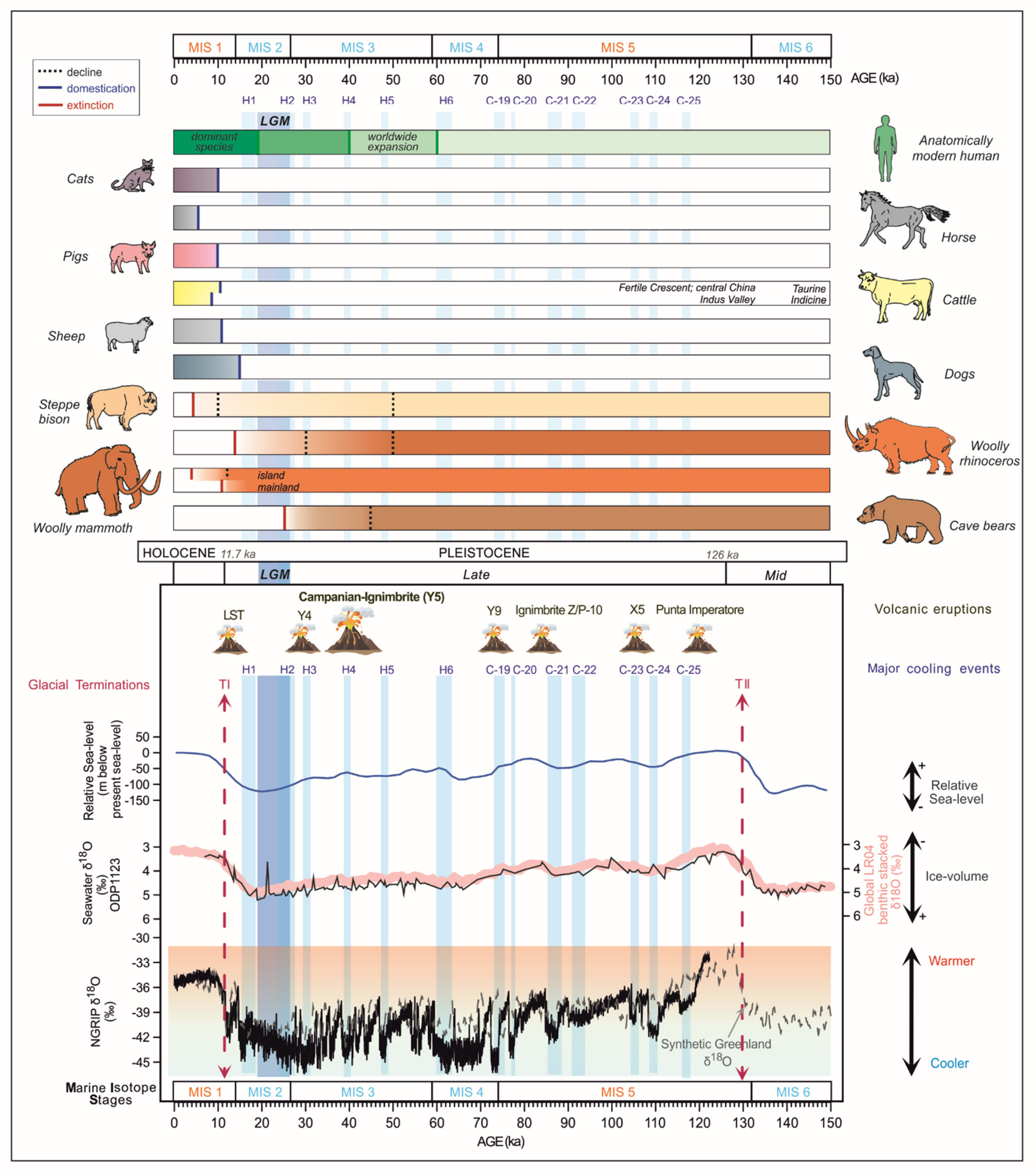
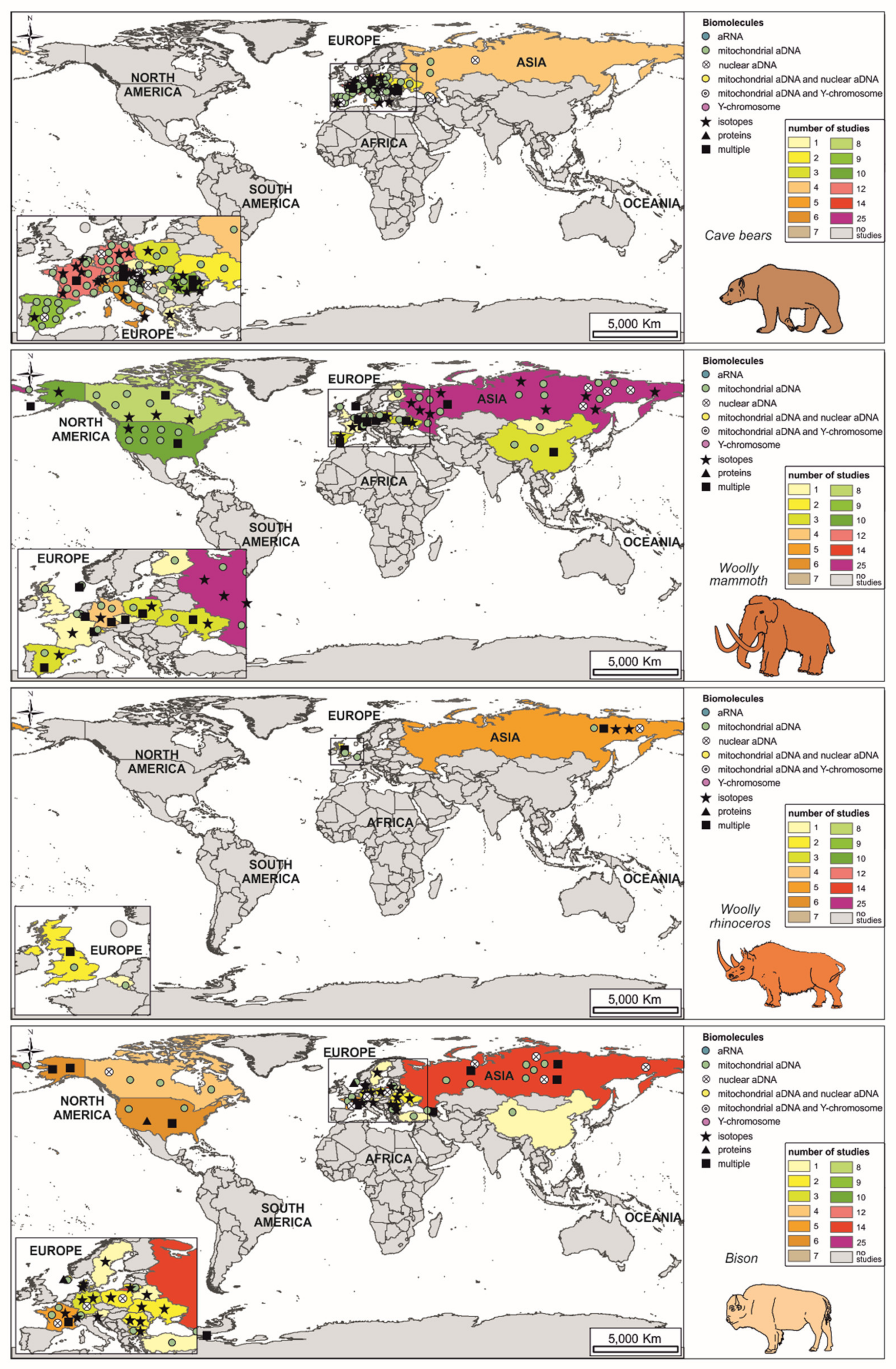

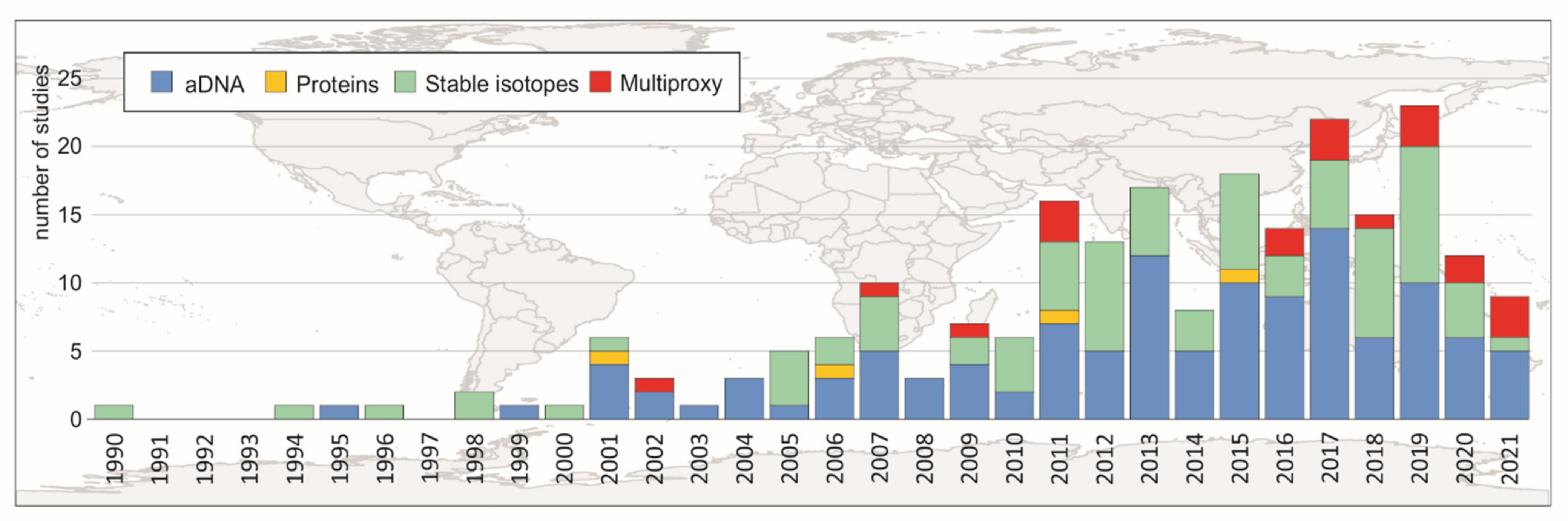
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosengren, E.; Acatrinei, A.; Cruceru, N.; Dehasque, M.; Haliuc, A.; Lord, E.; Mircea, C.I.; Rusu, I.; Mármol-Sánchez, E.; Kelemen, B.S.; et al. Ancient Faunal History Revealed by Interdisciplinary Biomolecular Approaches. Diversity 2021, 13, 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13080370
Rosengren E, Acatrinei A, Cruceru N, Dehasque M, Haliuc A, Lord E, Mircea CI, Rusu I, Mármol-Sánchez E, Kelemen BS, et al. Ancient Faunal History Revealed by Interdisciplinary Biomolecular Approaches. Diversity. 2021; 13(8):370. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13080370
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosengren, Erika, Arina Acatrinei, Nicolae Cruceru, Marianne Dehasque, Aritina Haliuc, Edana Lord, Cristina I. Mircea, Ioana Rusu, Emilio Mármol-Sánchez, Beatrice S. Kelemen, and et al. 2021. "Ancient Faunal History Revealed by Interdisciplinary Biomolecular Approaches" Diversity 13, no. 8: 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13080370
APA StyleRosengren, E., Acatrinei, A., Cruceru, N., Dehasque, M., Haliuc, A., Lord, E., Mircea, C. I., Rusu, I., Mármol-Sánchez, E., Kelemen, B. S., & Meleg, I. N. (2021). Ancient Faunal History Revealed by Interdisciplinary Biomolecular Approaches. Diversity, 13(8), 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13080370







