The Chemoautotrophically Based Movile Cave Groundwater Ecosystem, a Hotspot of Subterranean Biodiversity
Abstract
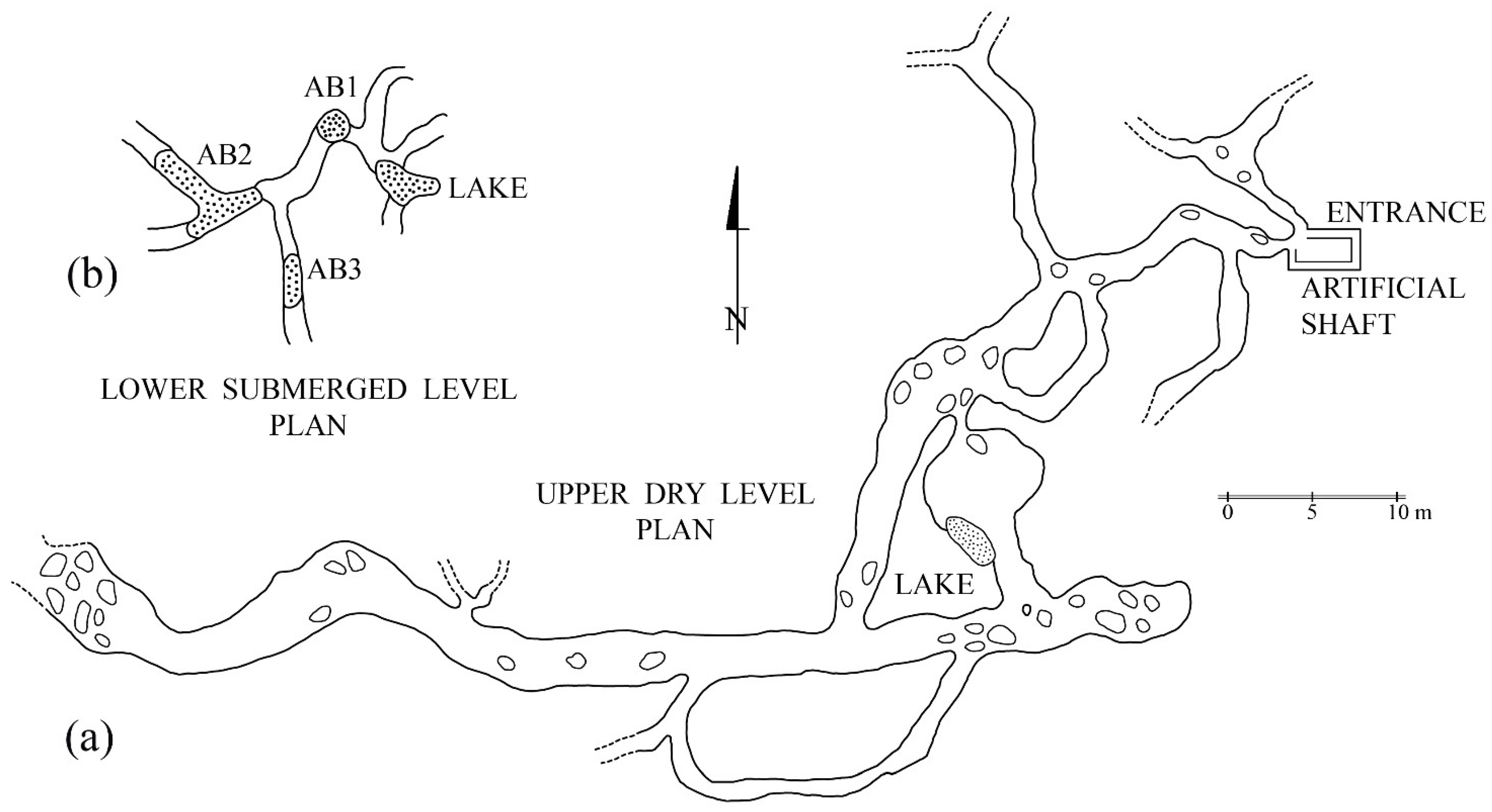
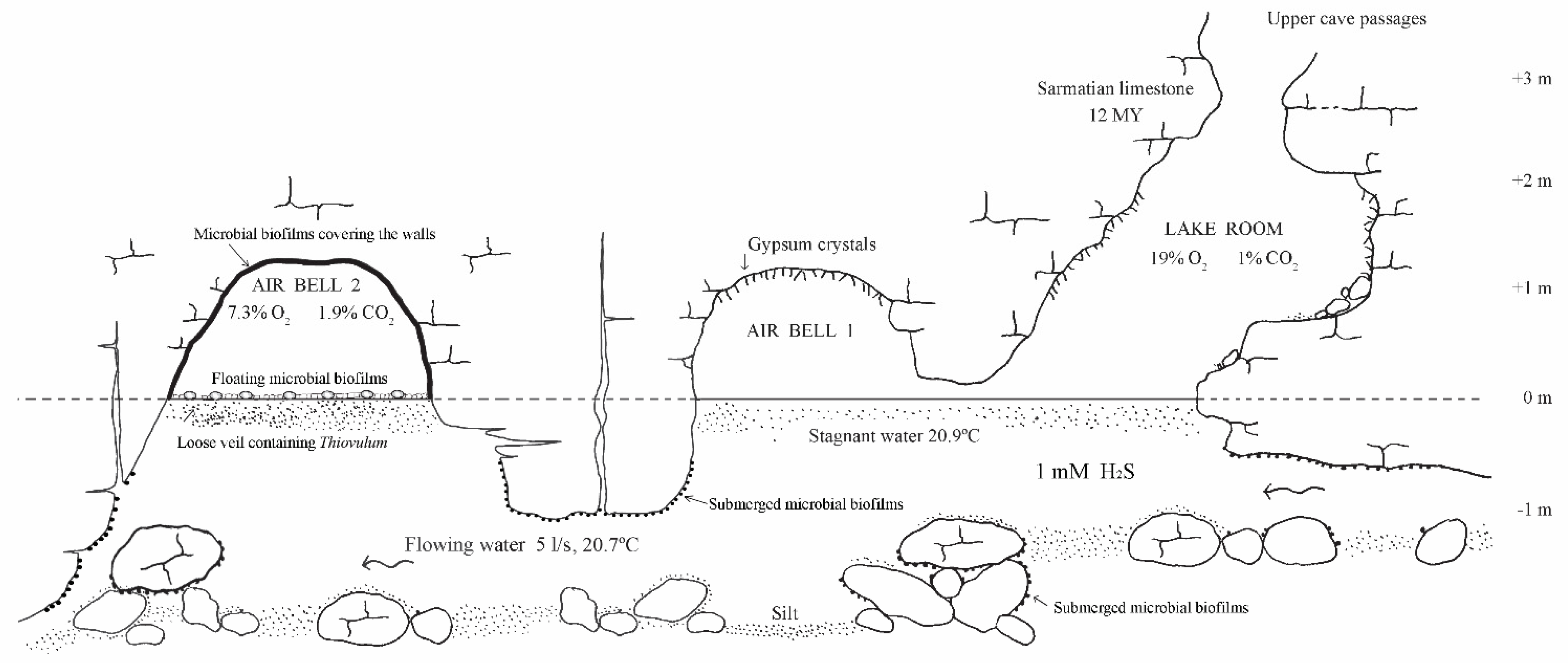
1. Introduction
2. Movile Cave Fauna
2.1. Aquatic Fauna
2.2. Terrestrial Fauna
| Aquatic/Terrestrial | Species | Taxonomic Affiliation | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Aquatic | Dendrocoelum obstinatum *; Stocchino et al., 2017 | Platyhelminthes, Dendrocoelidae | [30] |
| 2 | Aquatic | Panagrolaimus cf. thienemani * | Nematoda, Panagrolaimidae | [34] |
| 3 | Aquatic | Chronogaster troglodytes *; Poinar and Sarbu, 1994 | Nematoda, Chronogasteridae | [35] |
| 4 | Aquatic | Haemopis caeca *,#; Manoleli et al., 1998 | Annelida, Hirudinea, Haemopidae | [36] |
| 5 | Aquatic | Helodrilus sp. nov. * | Annelida, Clitellata, Lumbricidae | Martin, P., pers. comm. |
| 6 | Aquatic | Heleobia dobrogica *; Grossu and Negrea, 1989 | Gastropoda, Moitessieriidae | [29] |
| 7 | Aquatic | Pseudocandona sp. nov. * | Crustacea, Ostracoda, Cyprididae | Danielopol, D., pers. comm. |
| 8 | Aquatic | Eucyclops graeteri scythicus *; Plesa, 1989 | Crustacea, Copepoda, Cyclopidae | [37] |
| 9 | Aquatic | Parapseudoleptomesochra italica; Pesce and Petkovski, 1980 | Crustacea, Copepoda, Harpacticoida | Rouch, pers. comm. |
| 10 | Aquatic | Niphargus racovitzai *; Dancau, 1970 | Crustacea, Amphipoda, Niphargidae | [38] |
| 11 | Aquatic | Niphargus dancaui *,#; Brad et al., 2015 | Crustacea, Amphipoda, Niphargidae | [39] |
| 12 | Aquatic | Asellus aquaticus infernus *,#; Turk-Prevorčnik and Blejec, 1998 | Crustacea, Isopoda, Asellidae | [40] |
| 13 | Terrestrial | Caucasonethes vandeli pygmaeus *; Giurginca, 2020 | Crustacea, Isopoda, Trichoniscidae | [41] |
| 14 | Terrestrial | Haplophthalmus movilae *; Gruia and Giurginca, 1998 | Crustacea, Isopoda, Trichoniscidae | [42] |
| 15 | Terrestrial | Trachelipus troglobius *; Tabacaru and Boghean, 1989 | Crustacea, Isopoda, Trachelipodidae | [43] |
| 16 | Terrestrial | Armadillidium tabacarui *; Gruia et al., 1994 | Crustacea, Isopoda, Armadillidiidae | [44] |
| 17 | Terrestrial | Chthonius monicae *; Boghean, 1989 | Arachnida, Pseudoscorpiones, Chthoniidae | [45] |
| 18 | Terrestrial | Chthonius borissketi *; Curčić et al., 2014 | Arachnida, Pseudoscorpiones, Chthoniidae | [46] |
| 19 | Terrestrial | Roncus dragobete *; Curčić et al., 1993 | Arachnida, Pseudoscorpiones, Neobisiidae | [47] |
| 20 | Terrestrial | Roncus ciobanmos *; Curčić et al., 1993 | Arachnida, Pseudoscorpiones, Neobisiidae | [47] |
| 21 | Terrestrial | Palliduphantes constantinescui *; Georgescu, 1989 | Arachnida, Araneae, Linyphiidae | [48] |
| 22 | Terrestrial | Agraecina cristiani *,#; Georgescu, 1989 | Arachnida, Araneae, Liocranidae | [48] |
| 23 | Terrestrial | Kryptonesticus georgescuae *; Nae, Sarbu, and Weiss, 2018 | Arachnida, Araneae, Nesticidae | [49] |
| 24 | Terrestrial | Hahnia caeca *; Georgescu and Sarbu, 1992 | Arachnida, Araneae, Hahniidae | [50] |
| 25 | Terrestrial | Labidostomma motasi *; Iavorschi, 1992 | Arachnida, Acarina, Labidostommatidae | [51] |
| 26 | Terrestrial | Geophilus sp. nov. * | Chilopoda, Geophilidae | Baba, St., pers. comm. |
| 27 | Terrestrial | Cryptops speleorex *,#; Vahtera et al., 2020 | Chilopoda, Cryptopidae | [31] |
| 28 | Terrestrial | Archiboreoiulus serbansarbui *,#; Giurginca et al., 2020 | Diplopoda, Julida, Julidae | [52] |
| 29 | Terrestrial | Onychiurus movilae *; Gruia, 1989 | Collembola, Onychiuridae | [53] |
| 30 | Terrestrial | Oncopodura vioreli *; Gruia, 1989 | Collembola, Oncopoduridae | [53] |
| 31 | Terrestrial | Plusiocampa isterina *; Condé, 1993 | Diplura, Campodeidae | [54] |
| 32 | Terrestrial | Plusiocampa euxina *; Condé, 1996 | Diplura, Campodeidae | [55] |
| 33 | Terrestrial | Medon dobrogicus *; Decu and Georgescu, 1994 | Coleoptera, Staphylinidae | [56] |
| 34 | Terrestrial | Tychobythinus sulphydricus *; Poggi and Sarbu, 2013 | Coleoptera, Staphylinidae | [57] |
| 35 | Terrestrial | Decumarellus sarbui *; Poggi, 1994 | Coleoptera, Staphylinidae | [58] |
| 36 | Terrestrial | Bryaxis dolosus *; Poggi and Sarbu, 2013 | Coleoptera, Staphylinidae | [57] |
| 37 | Terrestrial | Clivina subterranea *; Decu et al., 1994 | Coleoptera, Clivinidae | [59] |
| 38 | Aquatic | Nepa anophthalma *; Dedu et al., 1994 | Hemiptera, Nepidae | [60] |
| Aquatic/Terrestrial | Species | Taxonomic Affiliation | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Aquatic | Udonchus tenuicaudatus; Cobb, 1913 | Nematoda, Rhabdolaimidae | [34] |
| 2 | Aquatic | Poikilolaimus sp. | Nematoda, Rhabditidae | [34] |
| 3 | Aquatic | Monhystrella sp. | Nematoda, Monhysteridae | [34] |
| 4 | Aquatic | Habrotrocha rosa; Donner, 1949 | Rotatoria, Habrotrochidae | Ricci, C., pers. comm. |
| 5 | Aquatic | Habrotrocha bidens; Gosse, 1851 | Rotatoria, Habrotrochidae | Ricci, C., pers. comm. |
| 6 | Aquatic | Aelosoma hyalinum; Bunke, 1967 | Annelida, Aeolosomatidae | Dumnicka, E., pers. comm. |
| 7 | Aquatic | Aelosoma italica; Bunke, 1967 | Annelida, Aeolosomatidae | Dumnicka, E., pers. comm. |
| 8 | Aquatic | Tropocyclops prasinus; Fischer, 1860 | Crustacea, Copepoda, Cyclopidae | [37] |
| 9 | Terrestrial | Carniella brignolii; Thaler and Steinberger, 1988 | Arachnida, Araneae, Theridiiae | [48] |
| 10 | Terrestrial | Dysdera hungarica; Kulczynski, 1897 | Arachnida, Araneae, Dysderidae | Weiss, L., pers. comm. |
| 11 | Terrestrial | Clinopodes carinthiacus; Latzel, 1880 | Chilopoda, Geophilidae | Zapparoli, M., pers. comm. |
| 12 | Terrestrial | Strongylosoma jaqueti; Verhoeff, 1898 | Diplopoda, Paradoxosomatidae | Tajovsky K., pers comm. |
| 13 | Terrestrial | Pygmarrhopalites pygmaeus; Wankel, 1860 | Collembola, Arrhopalitidae | [55] |
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarbu, S.; Lascu, C.; Brad, T. Dobrogea: Movile Cave; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 429–436. ISBN 978-3-319-90745-1. [Google Scholar]
- Lascu, C.; Popa, R.; Sarbu, S.M. Le Karst de Movile (Dobrogea de Sud). Rev. Roum. Geogr. 1994, 38, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Sarbu, S.M.; Lascu, C. Condensation Corrosion in Movile Cave, Romania. J. Cave Karst Stud. 1997, 59, 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Sarbu, S.M.; Popa, R. A unique chemoautotrophically based cave ecosystem. In The Natural History of Biospeleology; Camacho, A.I., Ed.; Mus. Nat. de Hist. Naturales: Madrid, Spain, 1992; pp. 637–666. [Google Scholar]
- Sarbu, S.M. Movile Cave: A chemoautotrophically based groundwater ecosystem. In Subterranean Ecosystems; Wilken, H., Culver, D.C., Humphreys, W.F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 319–343. [Google Scholar]
- Riess, W.; Giere, O.; Kohls, O.; Sarbu, S. Anoxic Thermomineral Cave Waters and Bacterial Mats as Habitat for Freshwater Nematodes. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1999, 18, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbu, S.M.; Kane, T.C.; Kinkle, B.K. A Chemoautotrophically Based Cave Ecosystem. Science 1996, 272, 1953–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumaresan, D.; Wischer, D.; Stephenson, J.; Hillebrand-Voiculescu, A.; Murrell, J.C. Microbiology of Movile Cave—A Chemolithoautotrophic Ecosystem. Geomicrobiol. J. 2014, 31, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohwerder, T.; Sand, W.; Lascu, C. Preliminary Evidence for a Sulphur Cycle in Movile Cave, Romania. Acta Biotechnol. 2003, 23, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, L.; Boden, R.; Hillebrand, A.; Kumaresan, D.; Moussard, H.; Baciu, M.; Lu, Y.; Colin Murrell, J. Life without Light: Microbial Diversity and Evidence of Sulfur- and Ammonium-Based Chemolithotrophy in Movile Cave. ISME J. 2009, 3, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flot, J.-F.; Bauermeister, J.; Brad, T.; Hillebrand-Voiculescu, A.; Sarbu, S.M.; Dattagupta, S. Niphargus-Thiothrix Associations May Be Widespread in Sulphidic Groundwater Ecosystems: Evidence from Southeastern Romania. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 1405–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarbu, S.M.; Galdenzi, S.; Menichetti, M.; Gentile, G. Geology and Biology of Grotte Di Frasassi (Frasassi Caves) in Central Italy, an Ecological Multi-Disciplinary Study of a Hypogenic Underground Karst System. Subterr. Ecosyst. Ecosyst. World 2000, 30, 359–378. [Google Scholar]
- Galassi, D.M.P.; Fiasca, B.; Di Lorenzo, T.; Montanari, A.; Porfirio, S.; Fattorini, S. Groundwater Biodiversity in a Chemoautotrophic Cave Ecosystem: How Geochemistry Regulates Microcrustacean Community Structure. Aquat. Ecol. 2017, 51, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, D.; Finger, K.; Iepure, S.; Mariani, S.; Montanari, A.; Namiotko, T. Ostracod Assemblages in the Frasassi Caves and Adjacent Sulfidic Spring and Sentino River in the Northeastern Apennines of Italy. J. Cave Karst Stud. Natl. Speleol. Soc. Bull. 2013, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, I.; Brad, T.; Vaxevanopoulos, M.; Giurginca, A.; Baba, S.C.; Iepure, S.; Plaiasu, R.; Sarbu, S. Rich and Diverse Subterranean Invertebrate Communities Inhabiting Melissotrypa Cave in Central Greece. Trav. Inst. Spéol. «Émile Racovitza» 2019, 58, 65–78. [Google Scholar]
- Por, F.D.; Dimentman, C.; Frumkin, A.; Naaman, I. Animal Life in the Chemoautotrophic Ecosystem of the Hypogenic Groundwater Cave of Ayyalon (Israel): A Summing Up. Nat. Sci. 2013, 5, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frumkin, A.; Dimentman, C.; Naaman, I. Biogeography of Living Fossils as a Key for Geological Reconstruction of the East Mediterranean: Ayyalon-Nesher Ramla System, Israel. Quat. Int. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, Y.; Malek Hosseini, M.-J.; Falniowski, A.; Hofman, S.; Kuntner, M.; Grego, J. Description of a New Genus and Species as the First Gastropod Species from Caves in Iran. J. Cave Karst Stud. 2019, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi-Sabet, H.; Vatandoust, S.; Fatemi, Y.; Eagderi, S. Tashan Cave a New Cave Fish Locality for Iran; and Garra tashanensis, a New Blind Species from the Tigris River Drainage (Teleostei: Cyprinidae). Fishtaxa 2016, 1, 133–148. [Google Scholar]
- Khalaji-Pirbalouty, V.; Fatemi, Y.; Malek-Hosseini, M.J.; Kuntner, M. A New Species of Stenasellus Dollfus, 1897 from Iran, with a Key to the Western Asian Species (Crustacea, Isopoda, Stenasellidae). ZooKeys 2018, 766, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emerson, B.C.; Kolm, N. Species Diversity Can Drive Speciation. Nature 2005, 434, 1015–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchens, E.; Radajewski, S.; Dumont, M.G.; McDonald, I.R.; Murrell, J.C. Analysis of Methanotrophic Bacteria in Movile Cave by Stable Isotope Probing. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirmack, J.; Mangelsdorf, K.; Ganzert, L.; Sand, W.; Hillebrand-Voiculescu, A.; Wagner, D. Methanobacterium movilense Sp. Nov., a Hydrogenotrophic, Secondary-Alcohol-Utilizing Methanogen from the Anoxic Sediment of a Subsurface Lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganzert, L.; Schirmack, J.; Alawi, M.; Mangelsdorf, K.; Sand, W.; Hillebrand-Voiculescu, A.; Wagner, D. Methanosarcina spelaei Sp. Nov., a Methanogenic Archaeon Isolated from a Floating Biofilm of a Subsurface Sulphurous Lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizic, M.; Brad, T.; Barbu-Tudoran, L.; Aerts, J.; Ionescu, D.; Popa, R.; Ody, J.; Flot, J.-F.; Tighe, S.; Vellone, D.; et al. Genomic and Morphologic Characterization of a Planktonic Thiovulum (Campylobacterota) Dominating the Surface Waters of the Sulfidic Movile Cave, Romania. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nováková, A.; Hubka, V.; Valinová, Š.; Kolařík, M.; Hillebrand-Voiculescu, A.M. Cultivable Microscopic Fungi from an Underground Chemosynthesis-Based Ecosystem: A Preliminary Study. Folia Microbiol. (Praha) 2018, 63, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboul, G.; Moreira, D.; Bertolino, P.; Hillebrand-Voiculescu, A.M.; López-García, P. Microbial Eukaryotes in the Suboxic Chemosynthetic Ecosystem of Movile Cave, Romania. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2019, 11, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muschiol, D.; Marković, M.; Threis, I.; Traunspurger, W. Predatory Copepods Can Control Nematode Populations: A Functional-Response Experiment with Eucyclops subterraneus and Bacterivorous Nematodes. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. Arch. Für Hydrobiol. 2008, 172, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falniowski, A.; Szarowska, M.; Sîrbu, I.; Hillebrand-Voiculescu, A.; Baciu, M. Heleobia dobrogica (Grossu & Negrea, 1989)(Gastropoda: Rissooidea: Cochliopidae) and the Estimated Time of Its Isolation in a Continental Analogue of Hydrothermal Vents. Molluscan Res. 2008, 28, 165. [Google Scholar]
- Stocchino, G.; Sluys, R.; Kawakatsu, M.; Sarbu, S.; Manconi, R. A New Species of Freshwater Flatworm (Platyhelminthes, Tricladida, Dendrocoelidae) Inhabiting a Chemoautotrophic Groundwater Ecosystem in Romania. Eur. J. Taxon. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahtera, V.; Stoev, P.; Akkari, N. Five Million Years in the Darkness: A New Troglomorphic Species of Cryptops Leach, 1814 (Chilopoda, Scolopendromorpha) from Movile Cave, Romania. ZooKeys 2020, 1004, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruia, M. Quelques Considérations Sur La Faune de Collemboles de La Grotte de Movile, Roumanie. Mém. Biospéol. 1996, 23, 105–109. [Google Scholar]
- Gruia, M. Sur La Faune de Collemboles de l’écosystème Exokarstique et Karstique de Movilé (Dobrogea Du Sud, Mangalia, Romania). Mém. Biospéol. 1998, 25, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Muschiol, D.; Giere, O.; Traunspurger, W. Population Dynamics of a Cavernicolous Nematode Community in a Chemoautotrophic Groundwater System: Cavernicolous Nematode Community. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2015, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poinar, G.; Sarbu, S.M. Chronogaster troglodytes Sp. n.(Nemata: Chronogasteridae) from Movile Cave, with a Review of Cavernicolous Nematodes. Appl. Nematol. 1994, 17, 231–237. [Google Scholar]
- Manoleli, D.G.; Klemm, D.J.; Sarbu, S.M. Haemopis caeca (Annelida: Hirudinea: Arhynchobdellida: Haemopidae), A New Species Of Troglobitic Leech From A Chemoautotrophically Based Groundwater Ecosystem In Romania. Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 1998, 111, 222–229. [Google Scholar]
- Plesa, C. Étude Préliminaire Des Cyclopides (Crustacea, Copepoda) de La Grotte “Peştera de La Movile”, Mangalia (Roumanie). Misc. Speologica Romanica 1989, 1, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Dancau, D. Sur un nouvel amphipode souterrain de Roumanie, Pontoniphargus racovitzai n.g., n.sp. In Livre du Centenaire. Emile G. Racovitza 1868–1968; Académie de la République Socialiste de Roumanie: Bucharest, Romania, 1970; pp. 275–285. [Google Scholar]
- Brad, T.; Fišer, C.; Flot, J.-F.; Sarbu, S. Niphargus dancaui Sp. Nov. (Amphipoda, Niphargidae) - A New Species Thriving in Sulfidic Groundwaters in Southeastern Romania. Eur. J. Taxon. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Turk-Prevorčnik, S.; Blejec, A. Asellus aquaticus infernus, New Subspecies (Isopoda: Asellota: Asellidae), From Romanian Hypogean Waters. J. Crustac. Biol. 1998, 18, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giurginca, A.; Sarbu, S.M. Caucasonethes vandeli pygmaeus n.Ssp. (Crustacea, Isopoda, Oniscidea) from Movile Cave (Southern Dobrogea, Romania). Trav. Inst. Spéol. «Émile Racovitza» 2020, 59, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Gruia, M.; Giurginca, A. Haplophthalmus movilae (Isopoda, Trichoniscidae), a New Troglobitic Species from Movile Cave, Dobrogea, Romania. Mitteilungen Hambg. Zool. Mus. Inst. 1998, 95, 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Tabacaru, I.; Boghean, V. Découverte En Dobrogea (Roumanie) D´ Une Espèce Troglobie Du Genre Trachelipus (Isopoda Oniscoidea Trachelipidae). Misc. Speologica Romanica 1989, 1, 53–75. [Google Scholar]
- Gruia, M.; Iavorschi, V.; Sarbu, S. Armadillidium tabacarui (Isopoda, Oniscidea, Armadillidiidae), A New Troglobitic Species From A Sulfurous Cave In Romania; Biological Society of Washington: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Boghean, V. Sur Un Pseudoscorpion Cavernicole Nouveau, Chthonius (C.) monicae n.Sp. (Arachnida Pseudoscorpionida Chthonidae). Misc. Speologica Romanica 1989, 1, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Curcic, B.P.M.; Sarbu, S.; Dimitrijevic, R.; Ćurčić, S. A New Cave Pseudoscorpion from the Region of Mangalia (Romania): Chthonius (Ephippiochthonius) borissketi n. Sp. (Chthoniidae, Pseudoscorpiones). Arch. Biol. Sci. 2014, 66, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćurčić, B.; Poinar, G.; Sarbu, S. New and Little-Known Species of Chthoniidae and Neobisiidae (Pseudoscorpiones, Arachnida) from the Movile Cave in Southern Dobrogea, Romania. Bijdr. Tot Dierkd. 1993, 63, 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgescu, M. Sur Trois Taxa Nouveaux d’Araneides Troglobies de Dobrogea (Roumanie). Misc. Speol. Romanica 1989, 1, 85–102. [Google Scholar]
- Nae, A.; Sarbu, S.; Weiss, I. Kryptonesticus georgescuae Spec. Nov. from Movile Cave, Romania (Araneae: Nesticidae). Arachnol. Mitteilungen 2018, 55, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Georgescu, M.; Sarbu, S.M. Description d’un Noveau Taxon: Iberina caeca de La Grotte: “Peștera de La Movile” (Araneae - Hahniidae). Mém. Biospéol. 1992, 19, 139–141. [Google Scholar]
- Iavorschi, V. Labidostoma motasi n.Sp. (Nicoletiellidae) a New Species of the Mite of Romania. Trav. Inst. Spéol. «Émile Racovitza» 1992, 31, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Giurginca, A.; Vanoaica, L.; Sustr, V.; Tajovský, K. A New Species of the Genus Archiboreoiulus Brolemann, 1921 (Diplopoda, Julida) from Movile Cave (Southern Dobrogea, Romania). Zootaxa 2020, 4802, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruia, M. Nouvelles Espèces Troglobiontes Des Collemboles de Roumanie. Misc. Speol. Romanica 1989, 1, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Conde, B. Une lignée danubienne du genre Plusiocampa (Diploures Campodéidés); A Danubian lineage in the genus Plusiocampa (Diplura Campodeidae). Rev. Suisse Zool. 1993, 100, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condé, B. Diploures Campodéidés de La Pestera de La Movile (Movile Cave), Dobroudja Méridionale (Roumanie). Rev. Suisse Zool. 1996, 103, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decu, V.; Georgescu, M. Deux Espèces Nouvelles de Medon (M. Dobrogicus et M. Paradobrogicus) (Coleoptera, Staphylinidae) de La Grotte “Peștera de La Movile”, Dobrogea Meridionale, Roumanie. Mém. Biospéol. 1994, 21, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Poggi, R.; Sarbu, S. Two New Pselaphine Beetles from Movile Cave (Romania) (Coleoptera, Staphylinidae, Pselaphinae). Ann. Mus. Civ. Storia Nat. Giacomo Doria 2013, 105, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Poggi, R. Descrizione Di Un Nuovo Pselafide Rumeno, Primo Rappresentante Cavernicolo Della Tribù Tyrini (Coleoptera Pselaphidae). Boll. Della Soc. Entomol. Ital. 1994, 125, 221–228. [Google Scholar]
- Decu, V.; Nitu, E.; Juberthie, C. Clivina subterranea (Caraboidea, Scaritidae) Nouvelle Espèce de La Grotte “Pestera de La Movile”, Dobrogea Meridionale, Roumanie. Mém. Biospéol. 1994, 21, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Decu, V.; Gruia, M.; Keffer, S.L.; Sarbu, S.M. Stygobiotic Waterscorpion, Nepa anophthalma, n. Sp. (Heteroptera: Nepidae), from a Sulfurous Cave in Romania. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1994, 87, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaler-Knoflach, B.; Hänggi, A.; Kielhorn, K.-H.; von Broen, B. Revisiting the Taxonomy of the Rare and Tiny Comb-footed Spider Carniella brignolii (Araneae, Theridiidae). Arachnologische Mitteilungen 2014, 47, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruia, M. Collembola from Romanian Caves. Trav. Mus. Nat. Hist. Nat. “Grigore Antipa” 2003, 35, 139–158. [Google Scholar]
- Sarbu, S.M.; Vlasceanu, L.; Popa, R.; Sheridan, P.; Kinkle, B.K.; Kane, T.C. Microbial Mats in a Thermomineral Sulfurous Cave. In Proceedings of the Microbial Mats; Stal, L.J., Caumette, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; pp. 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Kumaresan, D.; Stephenson, J.; Doxey, A.; Bandukwala, H.; Brooks, E.; Hillebrand-Voiculescu, A.; Whiteley, A.; Murrell, J. Aerobic Proteobacterial Methylotrophs in Movile Cave: Genomic and Metagenomic Analyses. Microbiome 2018, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
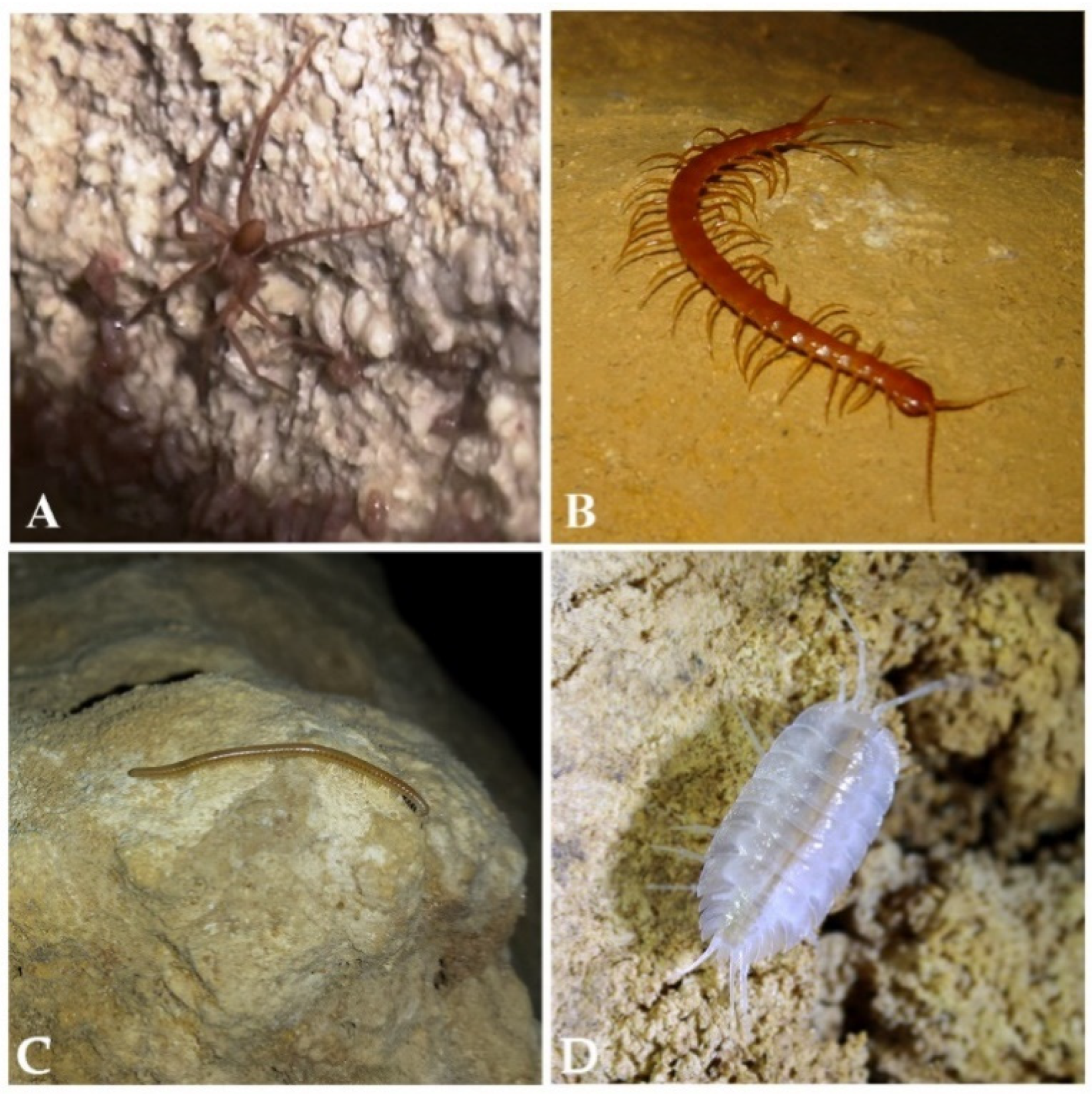
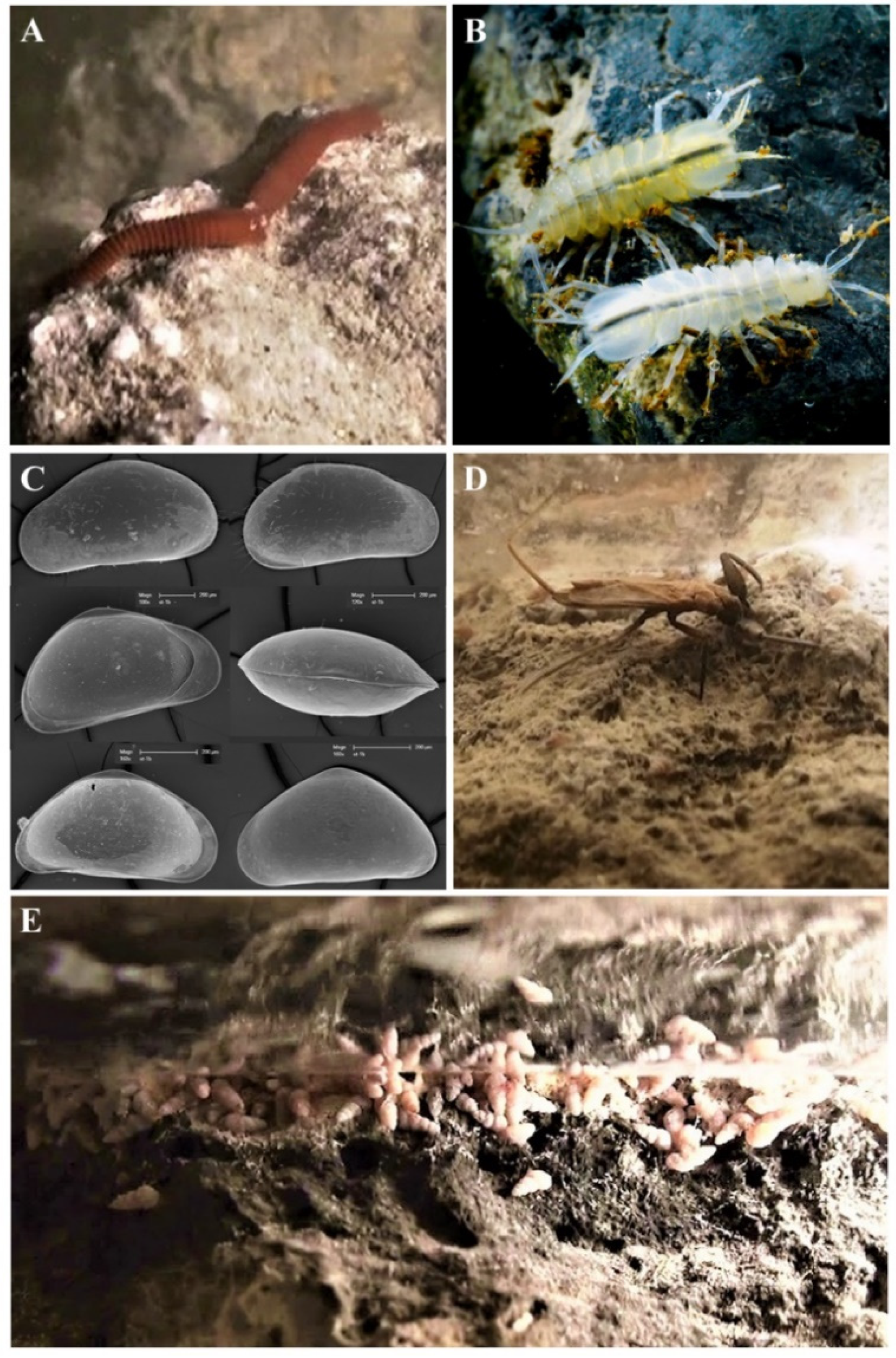

| Cave | Species Present | Endemic Species |
|---|---|---|
| Movile Cave (Romania) | 52 | 37 |
| Frasassi caves (Italy) | 56 | 16 |
| Melissotrypa Cave (Greece) | 30 | 8 |
| Ayyalon Cave (Israel) | 8 | 7 |
| Tashan Cave (Iran) | 3 | 3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brad, T.; Iepure, S.; Sarbu, S.M. The Chemoautotrophically Based Movile Cave Groundwater Ecosystem, a Hotspot of Subterranean Biodiversity. Diversity 2021, 13, 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13030128
Brad T, Iepure S, Sarbu SM. The Chemoautotrophically Based Movile Cave Groundwater Ecosystem, a Hotspot of Subterranean Biodiversity. Diversity. 2021; 13(3):128. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13030128
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrad, Traian, Sanda Iepure, and Serban M. Sarbu. 2021. "The Chemoautotrophically Based Movile Cave Groundwater Ecosystem, a Hotspot of Subterranean Biodiversity" Diversity 13, no. 3: 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13030128
APA StyleBrad, T., Iepure, S., & Sarbu, S. M. (2021). The Chemoautotrophically Based Movile Cave Groundwater Ecosystem, a Hotspot of Subterranean Biodiversity. Diversity, 13(3), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13030128







