Abstract
The determination of the geographic distributions of orchid species and their relationships with environmental factors are considered fundamental to their conservation. Paphiopedilum subgenus Brachypetalum is one of the most primitive, ornamental, and threatened groups of Orchidaceae. However, little is known about the distribution of Brachypetalum orchids and how they are influenced by environmental factors. In this study, we developed a database on the geographical distribution of Brachypetalum orchids based on a large-scale field investigation in the Guangxi, Guizhou, and Yunnan provinces of southwest China (2019–2020). Using this database, we first adopted the nonparametric Mann–Whitney U test to analyze the differences in the geographical distributions and growth environments of Brachypetalum orchids. In addition, we also used the method of principal component analysis (PCA) to explore distribution patterns of Brachypetalum orchids in relation to environmental factors (topography, climate, anthropogenic disturbance, productivity, and soil) in southwest China. Our results indicated that Brachypetalum orchid species were mainly distributed in the karst limestone habitats of southwest China. In general, there were 194 existing localities with the occurrence of seven target orchids in the investigated area. Of the discovered species in our study, 176 locations (~90.7%) were distributed primarily in the karst habitat. Among them, the range of 780–1267 m was the most concentrated elevation of Brachypetalum orchids. In addition, the findings also suggested that the distribution of Brachypetalum orchids in southwest China was relatively scattered in geographical space. However, the density of the distribution of Brachypetalum orchids was high, between 104° and 108° E and between 25° and 26° N. The results of the Mann–Whitney U test revealed that there are obviously different geographical distributions and growth environments of Brachypetalum in southwest China. More specifically, we found some extremely significant differences (p < 0.001) in elevation, mean diurnal range, precipitation of coldest quarter, solar radiation, and exchangeable Ca2+ between the provinces of southwest China. The PCA analysis revealed that elevation, solar radiation, temperature (mean diurnal range, annual temperature range) and precipitation (precipitation seasonality, precipitation of the warmest quarter) were found to be the most significant factors in determining Brachypetalum orchids’ distribution. These findings have implications in assessing conservation effectiveness and determining niche breadth to better protect the populations of these Brachypetalum orchid species in the future.
1. Introduction
Orchidaceae is an exceptionally diverse family of the monocotyledons, including about 25,000 species worldwide, belonging to five subfamilies and 880 genera [1]. Significantly, orchids in China represent one of the most species-rich families and endangered plant groups [2]. In addition, most orchids (~90%) are distributed across only 2.7% of the Chinese landmass, consistent with areas of high general plant diversity [3]. Orchid species are mainly widespread in tropical and subtropical regions with different life forms [4]. In addition, southwest China is the distribution center and the differentiation center of orchids [5]. As one of the global biodiversity hotspots [6], southwest China has a high level of orchid diversity [2], but the majority of these species are under threat. Furthermore, many orchids are significant in the horticultural industry for their unique and attractive flowers, such as Paphiopedilum villosum [7] and Cypripedium macranthos [8]. Moreover, several orchid species, such as Dendrobium crepidatum [9] and Bletilla striata [10], also have relatively high medicinal value, particularly in traditional Chinese medicine. Considering this high amount of interest, their threatened conditions, and their endangered status in the wild, orchids are frequently used as one of the flagships and most crucial groups in conservation biology [11].
The genus of Paphiopedilum is a primitive group of Orchidaceae. Paphiopedilum, usually known as the “tropical slipper orchid”, is a fascinating genus of orchids [12]. Species of the genus Paphiopedilum have multiple life forms, including epiphytic, lithophytic, or terrestrial. There are about 80–85 species in the genus Paphiopedilum, of which 27 species (two endemics) grow in China [13]. Paphiopedilum has high ornamental value because of its peculiar and unusual flower shape [14]. However, because of its fragile growth environmental conditions, it is highly vulnerable to factors such as artificial excavation and habitat destruction [15]. Notably, the genera of Paphiopedilum and Cypripedium are closely associated in terms of their phylogeny, although they have contrasting distribution areas and habitats [16]. Most species of Cypripedium are found in temperate areas [8], whereas a majority of Paphiopedilum species are grown in the tropics or subtropics [17].
The genus Paphiopedilum is a rare and endangered category, listed in the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) [18]. Due to habitat destruction and over-collection, the wild populations are at risk of extinction [19]. Recent studies have supported the division of the genus Paphiopedilum into three subgenera, Brachypetalum, Paphiopedilum, and Parvisepalum [20,21]. In addition, the subgenus Brachypetalum is the most primitive, ornamental, and threatened group of Paphiopedilum. Currently, the research on the subgenus Brachypetalum involves many aspects, including phylogenetic analysis [20,21], trait evolution [12], the comparison of chromosome numbers and karyotypes [22], and the collection or description of several new species [23,24]. However, at present, little is known about the actual distribution and related factors affecting the distribution of Brachypetalum orchid species in the wild and its conservation status on a large scale.
Compared to plants of other families, orchids are extremely impressionable to habitat loss, fragmentation, and climate change [8,25,26]. The majority of orchids are narrowly distributed in specific and unique habitats because of their pollinator specialization, mycorrhizal specificity, and limited seed germination rate [2]. Understanding the many environmental factors that influence the spatial distribution and abundance patterns of species in natural habitats is one of the primary objectives in ecology and biogeography [2,27]. Furthermore, some recent studies have revealed that habitat availability and pollination limitation can jointly influence the distribution of orchid species [28]. In addition, the existence of specific mycorrhizal fungi has also partly contributed to the spatial distribution of these orchid species [27]. However, to our knowledge, no studies have been conducted on the impact of environmental factors on the geographical distribution of Brachypetalum species.
The purpose of this study was to analyze the distribution patterns and to investigate the influence of environmental and climatic factors on the distribution of Brachypetalum species in southwest China. To do this, we first carried out a wide range of field investigations to obtain habitat types and coordinates of species distribution. Furthermore, we also collected a large amount of environmental and climatic data from different sources. On the basis of these data, we attempted to (1) explore the patterns of Brachypetalum species in southwest China (Figure 1); (2) study the differences in the growing environments in geographical distribution sites of Brachypetalum species in southwest China; (3) identify the critical environmental variables constraining the distribution of Brachypetalum species in southwest China, and (4) evaluate the in situ conservation status of Brachypetalum species in southwest China.
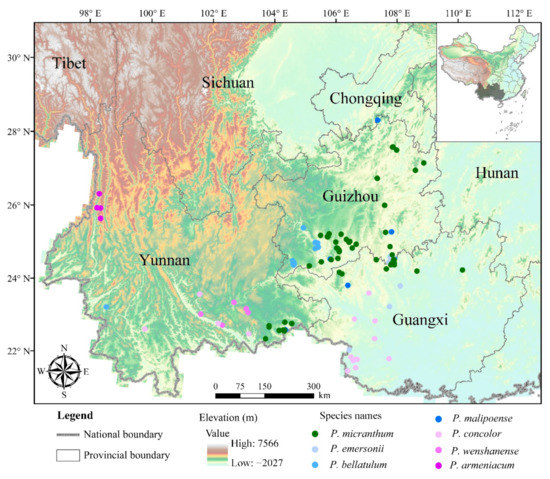
Figure 1.
Geographical distribution pattern of seven orchids in the subgenus Brachypetalum in southwest China.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Species
Paphiopedilum is a genus of flagship orchids and comprises some of the most popular orchids due to their beauty and rarity [29]. They are mainly distributed in areas from tropical Asia to the Pacific islands, with some species extending to subtropical areas [13]. Among them, southwest China is one of the distribution centers for this genus. Furthermore, the subgenus Brachypetalum is considered to be the more primitive type of the genus Paphiopedilum. In addition, the threatening situations of the subgenus Brachypetalum species are highly prevalent, such as Paphiopedilum armeniacum [30,31] and Paphiopedilum micranthum [32]. The problems of habitat fragmentation, unreasonable mining, and population decline of the Brachypetalum subgenus group are very prominent. We investigated seven species of the subgenus Brachypetalum that occurred in the wild of southwest China in this study. These species are Paphiopedilum micranthum, P. emersonii, P. bellatulum, P. malipoense, P. concolor, P. wenshanense, and P. armeniacum. In addition, because of the great ecological variation of Paphiopedilum malipoense, three varieties (Paphiopedilum malipoense var. jackii, Paphiopedilum malipoense var. hiepii, and Paphiopedilum malipoense var. angustatum) were classified as the protospecies of Paphiopedilum malipoense. According to the latest published version of The National Key Protected Wild Plants List [33], all these species were national first-class protected species, except for Paphiopedilum micranthum, which was placed on the second-class protected species list. For more detailed information on these species, please refer to Table 1. The scientific names of these species are consistent with the modern international databases (https://www.catalogueoflife.org/, accessed on 6 November 2021).

Table 1.
A checklist of the subgenus Brachypetalum from southwest China is presented based on recent field investigations of orchids. The Red List level was based on the global assessment scope of IUCN (https://www.iucnredlist.org/, accessed on 6 November 2021). The protected level was based on The National Key Protected Wild Plants List [33]. The CITES appendix was based on Endangered Species Scientific Commission, People’s Republic of China (http://www.cites.org.cn/, accessed on 5 November 2021). PSESP (which stands for plant species with extremely small populations) was based on Information System of Chinese Rare and Endangered Plants (ISCREP) (http://www.iplant.cn/rep/, accessed on 6 November 2021).
2.2. Study Area
Southwest China is a hotspot for biodiversity conservation, characterized by heterogeneous regional climates, complex topography, and rich flora [34]. The study area covers Guangxi, Guizhou, and Yunnan provinces in southwest China and occupies approximately 0.8 million square kilometers (Figure 1). The study area is entirely coincident with the administrative boundary. This area has a subtropical monsoon climate with the mean annual temperature ranging from −2.9 °C to 23.3 °C and mean annual precipitation ranging from 583 mm to 2608 mm per year. Because southwest China is located in a low-latitude area with huge elevation differences, and under the direct influence of the Indian Ocean Warm Current, the variety and quantity of plants are abundant in this area [35,36]. Furthermore, the mixed evergreen-deciduous broadleaf forest is a typical and representative vegetation type in southwest China, and it is also the main vegetation type we investigated. This type of forest has a complicated community structure, high habitat heterogeneity, rich biodiversity, and high productivity [37].
2.3. Data Collection
2.3.1. Distribution of Target Orchids
We first collected and compiled the historical occurrence data for target orchid species in southwest China using an online database (http://www.cfh.ac.cn/, accessed on 15 September 2021; http://www.sp2000.org.cn/, accessed on 16 September 2021; http://ppbc.iplant.cn/, accessed on 15 September 2021) and digital herbarium (https://www.cvh.ac.cn/, accessed on 5 November 2021), as well as various types of literature available (Flora of China, Provincial flora, research papers, and scientific investigation reports on Maolan, Mulun, and other relevant nature reserves). In addition, to conduct a more targeted survey and assessment of the target species, we also consulted with some relevant insiders. Finally, we collected a total of 69 historical distribution records of the subgenus Brachypetalum. However, these distribution records often lack detailed and specific location information, especially herbarium records. Based on the collected species distribution and habitat information, we used quadrat and line-transect methods to investigate the target species in the field. The field survey lasted for 139 days and was conducted between June 2019 and November 2020. We obtained longitude and latitude data for target orchids’ occurrence sites (point data) using Google Earth.
2.3.2. Environmental and Climatic Data
To explore the influences of environmental factors on the distribution of orchids of the subgenus Brachypetalum in southwest China, we obtained topographic, climate, anthropogenic, productivity, and soil data from WorldClim (https://www.worldclim.org/, accessed on 7 September 2021), Resource and Environment Science and Data Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences (RESDC) (https://www.resdc.cn/, accessed on 7 September 2021) and the National Tibetan Plateau Data Center (TPDC) (http://data.tpdc.ac.cn/, accessed on 7 September 2021) databases. The variables obtained are shown in Table S1. The geographical coordinate system of all environmental variables was GCS_WGS_1984. In addition, to avoid redundancy and multicollinearity of variables, a Spearman correlation analysis was conducted in R software. Furthermore, variables with a high correlation coefficient (|r| > 0.8) were not taken into account for subsequent analyses [38,39]. The Spearman correlation coefficient between each variable presented is in Table S2. Finally, we selected 27 environmental variables before conducting the analysis (Table 2).

Table 2.
The environmental factors associated with the distributions of target orchids in southwest China.
2.4. Data Analyses
2.4.1. Differences of Environmental Factors among Species Distribution Sites
In comparisons of two independent samples where the result is not normally distributed and the samples are small, a nonparametric test is applicable. One popular and approved nonparametric test for comparing results between two independent groups is the Mann–Whitney U test. In addition, the Mann–Whitney U test, also known as the Wilcoxon rank sum test or the Mann–Whitney–Wilcoxon test, is designed to compare if there is a difference in the dependent variable for two independent groups [47]. In this paper, we analyzed the differences in environmental factors using the Mann–Whitney U test. This was carried out in R and based on the package ‘ggpubr’, version 0.4.0 [48].
2.4.2. Relationship between Species Distribution and Environmental Factors
As a first step, correlation analyses were conducted between geographical distribution data (latitude and longitude) of seven orchid species and the values for the 27 environmental variables (correlation coefficients are presented in Table S2). Then, we took into account the dimension reduction of these environmental variables in each classification. Accordingly, we applied a principal component analysis (PCA), implemented using the package ‘factoextra’ version 1.0.7 in R [49,50]. We tested for correlations between environmental factors and species’ geographical distributions using correlation analysis in R. In addition, PCA allows us to summarize and visualize the information within a data set containing observations described by multiple quantitative variables. In other words, PCA reduces the dimensionality of multi-variate data to two or three main components, which can be visualized graphically, with a minimal loss of information [50]. In this study, we used correlation analysis and principal component analysis to identify the main environmental factors influencing the distribution patterns of Brachypetalum species. All statistical analyses in the study were conducted with R software version 4.1.0 (available from: https://www.r-project.org/, accessed on 6 September 2021).
3. Results
3.1. Distribution Pattern of Brachypetalum Species in Southwest China
Through field surveys conducted in 2019 and 2020, we confirmed the total number of locations with the presence of each target orchid species in southwest China (Table S3). Ultimately, a total of 194 existing geographical distribution locations of seven target orchids of the subgenus Brachypetalum were recorded in 50 counties (districts/cities) of southwest China (Figure 1). This resulted in a better understanding of the distribution and conservation status of each species in southwest China. As a whole, the number of extant distribution sites for Brachypetalum species in southwest China was highest in the Guizhou province, with 105 in total (Figure 2). The number of extant distribution sites was small in Guangxi and Yunnan provinces, with 44 and 45 respectively (Figure 2). For different Brachypetalum species, Paphiopedilum micranthum has shown a similar distribution pattern as Paphiopedilum bellatulum. However, Paphiopedilum concolor, Paphiopedilum wenshanense, and Paphiopedilum armeniacum were mainly distributed in Guangxi and/or Yunnan. In addition, Paphiopedilum emersonii was mostly distributed in Guangxi and Guizhou provinces, whereas the Paphiopedilum malipoense was mostly distributed in Guangxi, Guizhou, and Yunnan provinces of southwest China (Figure 2).
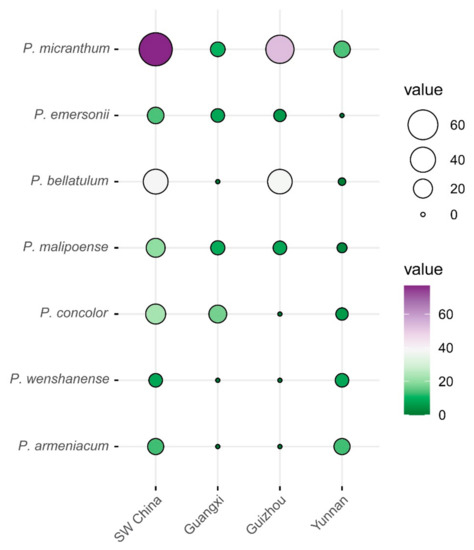
Figure 2.
The number of distribution sites detected in southwest China and different provinces for orchids in the subgenus of Brachypetalum.
In general, the distribution pattern of Brachypetalum species in southwest China was relatively scattered and sparse. However, the density of Brachypetalum species distribution was high, between 104° and 108° E and between 25° and 26° N in southwest China (Figure 3A). In addition, there was a very significant difference (p < 0.001) in the longitude of Brachypetalum species distributed in each province of southwest China (Figure 3B). Furthermore, there was a very significant difference (p < 0.001) in the latitude of Brachypetalum species distribution between Guangxi and Guizhou provinces, as well as Guizhou and Yunnan provinces. However, no significant difference (p > 0.05) was observed in the latitude of Brachypetalum species distributed in Guangxi and Yunnan provinces (Figure 3C).
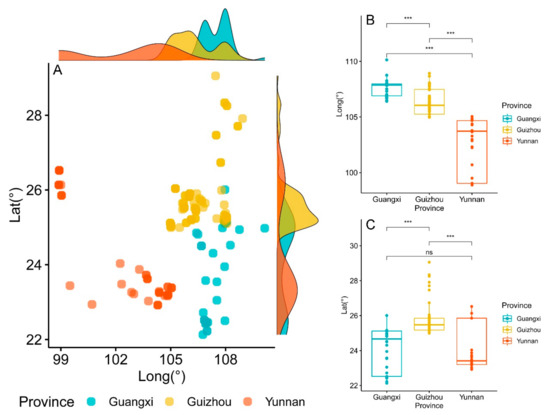
Figure 3.
Distribution of all orchids in the subgenus of Brachypetalum and the differences of longitude and latitude in different provinces. (A) Distribution of all orchids in the subgenus of Brachypetalum in Guangxi, Guizhou, and Yunnan provinces. The lines on the top and right are density curves. (B) The longitude differences in the distribution of orchids in the subgenus of Brachypetalum in Guangxi, Guizhou, and Yunnan provinces. (C) The latitude differences in the distribution of orchids in the subgenus of Brachypetalum in Guangxi, Guizhou, and Yunnan provinces. Note: ns represents not significant; *** represents 0.001 level of significance.
3.2. Differences in Geographical Distribution and Growth Environment of Brachypetalum Species
3.2.1. Differences in Topographic Factors
The Mann–Whitney U test indicated that there was a very significant difference (p < 0.001) between the elevation of growing Brachypetalum species in each province (Figure 4A). In terms of slope, there were some provinces with significant differences, except between Guangxi and Guizhou (Figure 4B). However, concerning aspect, there was no significant difference between each province (Figure 4C).
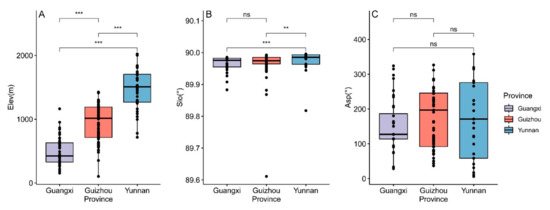
Figure 4.
Differences in topographic factors in the subgenus of Brachypetalum, distributed in different provinces. (A) The differences in elevation in each province. (B) The differences in slope in each province. (C) The differences in aspect in each province. Note: ns represents not significant; ** represents 0.01 level of significance; *** represents 0.001 level of significance.
3.2.2. Differences in Productive Factors
The Wilcoxon rank sum test revealed extremely significant differences (p < 0.001) in the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) between Guangxi and Guizhou, as well as Guangxi and Yunnan (Figure 5A). However, in terms of net primary production (NPP), there was only a significant difference (p < 0.01) between Guangxi and Guizhou (Figure 5B).
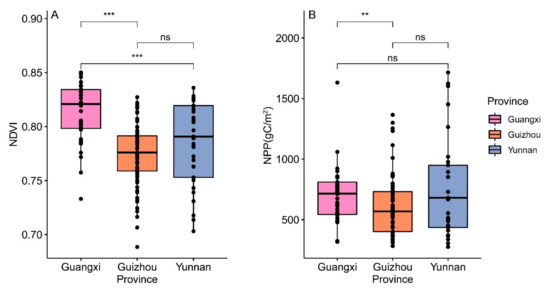
Figure 5.
The differences in productive factors in the subgenus of Brachypetalum, distributed in different provinces. (A) The differences in the normalized difference vegetation index in each province. (B) The differences in net primary production in each province. Note: ns represents not significant; ** represents 0.01 level of significance; *** represents 0.001 level of significance.
3.2.3. Differences in Human Interference Factors
In consideration of multicollinearity, we only introduced population density (POP) as a factor. The results indicated that no significant difference (p > 0.05) was observed in population density among Guangxi and Yunnan. However, there were very significant differences (p < 0.001) in population density between the other two provinces and Guizhou, respectively (Figure 6).
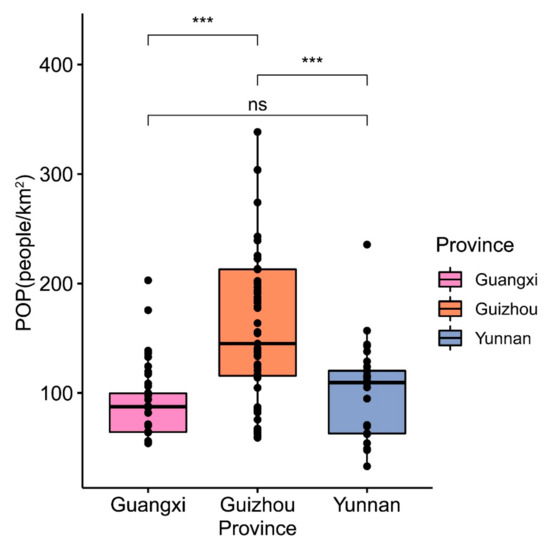
Figure 6.
The differences in the human interferential factor in the subgenus of Brachypetalum, distributed in different provinces. Note: ns represents not significant; *** represents 0.001 level of significance.
3.2.4. Differences in Climatic Factors
We found some significant differences (p < 0.001) in the mean diurnal range (Bio2) (Figure 7B), precipitation of coldest quarter (Bio19) (Figure 7F), and solar radiation (Srad) (Figure 7H) between the provinces of southwest China. Furthermore, the differences between provinces in terms of the climate factors mentioned above were higher than those in terms of the other climatic factors (Figure 7).
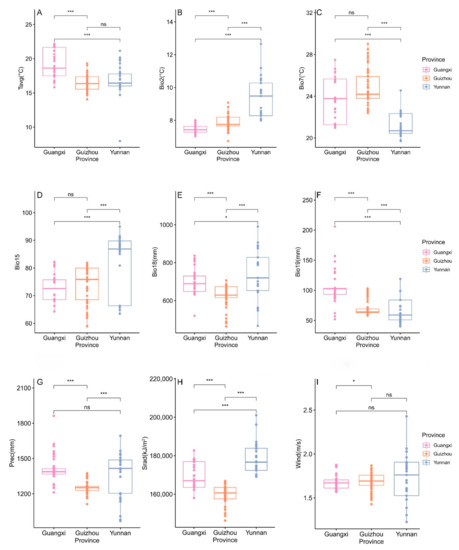
Figure 7.
The differences in climatic factors in the subgenus of Brachypetalum, distributed in different provinces. (A) The differences in average temperature in each province. (B) The differences in the mean diurnal range in each province. (C) The differences in the annual temperature range in each province. (D) The differences in precipitation seasonality in each province. (E) The differences in the precipitation of the warmest quarter in each province. (F) The differences in the precipitation of the coldest quarter in each province. (G) The differences in precipitation in each province. (H) The differences in solar radiation in each province. (I) The differences in wind speed in each province. Note: ns represents not significant; * represents 0.05 level of significance; *** represents 0.001 level of significance.
3.2.5. Differences in Edaphic Factors
Although there were some very significant differences (p < 0.001) between some provinces in terms of soil moisture (SMC), there was a minor difference (p < 0.05) between Guangxi and Guizhou (Figure 8B). Similarly, we found that there were some very significant differences (p < 0.001) between some provinces in terms of the available K (AK), but there was a minor difference (p < 0.05) between Guizhou and Yunnan (Figure 8I). The only extremely statistically significant difference (p < 0.001) that we found was in the area of exchangeable Ca2+ (Ca2+ex) (Figure 8J).
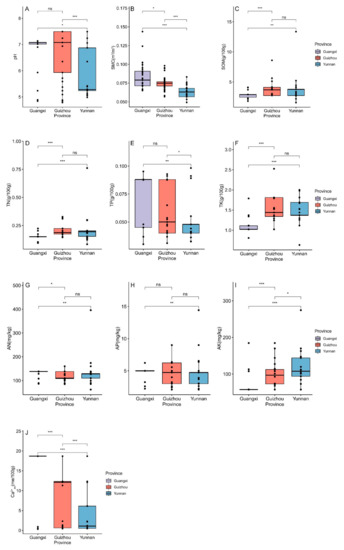
Figure 8.
The differences in edaphic factors in the subgenus of Brachypetalum, distributed in different provinces. (A) The differences in pH value in each province. (B) The differences in soil moisture in each province. (C) The differences in soil organic matter in each province. (D) The differences in total N in each province. (E) The differences in total P in each province. (F) The differences in total K in each province. (G) The differences in alkali-hydrolysable N in each province. (H) The differences in the available P in each province. (I) The differences in the available K in each province. (J) The differences in exchangeable Ca2+ in each province. Note: ns represents not significant; * represents 0.05 level of significance; ** represents 0.01 level of significance; *** represents 0.001 level of significance.
3.3. Environmental Factors Related to Distribution Patterns of Brachypetalum Species
The greater the variable (distance from the origin of the axis), the more fully the variable is explained by the PC represented in that dimension (axis). Obviously, the first two dimensions explain roughly 57% to 71% of the variation in the data (Figure 9). In this research, principal component analysis showed that the distribution patterns of Brachypetalum species were highly related to the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) (Figure 9B), elevation (Elev) (Figure 9C), average temperature (Tavg), solar radiation (Srad), water vapor pressure (Vapr), mean diurnal range (Bio2), annual temperature range (Bio7), precipitation seasonality (Bio15), precipitation of the warmest quarter (Bio18) (Figure 9D) and exchangeable Ca2+ (Ca2+ex) (Figure 9E).
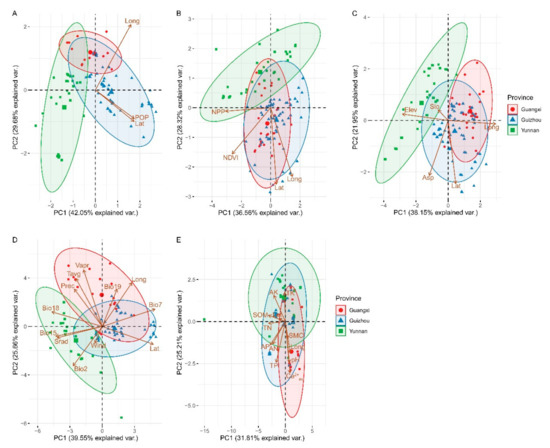
Figure 9.
Principal component analysis (PCA) of longitude, latitude, and environmental factors in the subgenus of Brachypetalum, distributed in different provinces. (A) PCA based on the human activity of different provinces. (B) Productivity-based PCA of different provinces. (C) Topography-based PCA of different provinces. (D) Climate-based PCA of different provinces. (E) Soil-based PCA of different provinces. In the figure above, the PC1 axis is the first principal direction along which the factors show the largest variation. The PC2 axis is the second important direction and is orthogonal to the PC1 axis.
4. Discussion
4.1. Distribution Patterns of Brachypetalum Orchids in Southwest China
The orchid family is one of the richest in the realm of flowering plants and includes a lot of rare, endangered, or threatened species [4,51]. In this study, we discovered that the distribution of Brachypetalum orchid species is uneven in southwest China. More orchids occurred in the Guizhou province, an area of typical karstic geomorphology in China, whereas fewer orchids occurred in the Guangxi and Yunnan provinces. This may be due to uneven sampling efforts in each province. In addition, Yunnan province had the most abundant Brachypetalum orchid species, with six species in total, except for Paphiopedilum emersonii (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Of course, Yunnan province was followed by Guangxi and Guizhou provinces, with four species of Brachypetalum orchids distributed in these two provinces, respectively (Figure 1 and Figure 2). These findings showed that the distribution of Brachypetalum orchid species richness almost followed a general pattern of all wild orchids at the province-level scale in southwest China [52]. Furthermore, almost all orchid species were found in mountainous areas, which is consistent with the findings of Tang et al. [53], probably because the mountains provide heterogeneous habitats for various orchid species [2].
Some studies have focused on the ecological preferences of orchid species at regional scales. For example, Tsiftsis et al. [51] revealed the differentiation of the ecological or habitat preferences of some orchid species of east Macedonia. In that study, the vegetation types of the typical distribution sites of Brachypetalum orchid species were mixed evergreen/deciduous broadleaf forests. This also illustrated that certain habitat types or associated vegetation types were important determinants of orchid distribution [51]. Furthermore, the results of our study indicated that Brachypetalum orchid species were mainly distributed in the karst limestone habitats of southwest China, especially in southeast Yunnan province, Nu River in Yunnan province, southwest Guizhou province, southwest Guangxi province, and the junction between southern Guizhou province and northern Guangxi province (Figure 1). In general, there were 194 existing localities with an occurrence of seven target orchids in the investigated area. Of the discovered localities in our study, about 90.7% were distributed primarily in the karst habitat. They accounted for 176 locations from a total of 194 mapped locations. This may be related to the fact that most orchids belong to the group of calcific to basophilic species [54]. Therefore, it is sufficient to demonstrate that Brachypetalum orchids have strong habitat and ecological preferences for karst landform in southwest China. This is consistent with the findings of Wittlinger and Petrikovičová [54], who also agreed that the presence of orchids was concentrated primarily in a portion of the karst area.
4.2. Relationships between Environmental Factors and the Distribution of Brachypetalum Orchids in Southwest China
Orchids are usually sensitive to the environment, and their distribution is highly associated with environmental factors [55]. Based on some previous studies, some environmental factors (e.g., climate factors, soil factors, etc.) could influence orchid performance, thus impacting species distribution and population dynamics [3,51,56]. In this study, we explored the relationships between environmental factors and distribution patterns of Brachypetalum orchid species in southwest China. Moreover, we also found that many environmental factors played a significant role in the distribution of Brachypetalum orchid species in southwest China (Figure 9), which was consistent with the findings of previous studies [54].
According to previous research, human pressure has had an important impact on the distribution of some Cypripedium orchid species [8]. In this study, we also found that the population density (POP)—an index of human pressure or human activity—was a crucial factor in explaining the distribution of Brachypetalum orchid species in southwest China. The population density may affect the distribution of orchid species in the following two ways. First, high population density means an increase in the illegal harvesting of orchids, which can reduce the population of orchids. Furthermore, illegal harvesting has become a threat to the orchid species in southwest China, which may lead to a decrease in the number of recruits and adult individuals [57]. Second, high population density can increase human activity or human disturbance, such as grazing and deforestation, thus increasing fragmentation or habitat loss, which is the most serious threat to the survival of orchid populations. This may be due to human disturbances, which may lead to the breakdown of ecological connections between orchids and their mycorrhiza and pollinators [57].
Climate was an important factor affecting the distribution of Brachypetalum orchids in southwest China (Figure 9D). In this study, we discovered that there were significant differences (p < 0.001) in the mean diurnal range (Bio2), precipitation of the coldest quarter (Bio19), and solar radiation (Srad) in the provinces of the study area. This indicated that the climatic niche of orchids distributed in various provinces is different, especially in terms of temperature, precipitation, and illuminance. This may be related to the difference between the growing altitudes of different orchid species, as altitude represents a complex variable associated with climate factors such as temperature and humidity [51]. Our study has scientific reference value for determining the ecological niche of Brachypetalum orchids in southwest China. Among the climatic factors, we revealed the relative significant roles of average temperature (Tavg), mean diurnal range (Bio2), annual temperature range (Bio7), precipitation seasonality (Bio15), precipitation of the warmest quarter (Bio18), solar radiation (Srad), and water vapor pressure (Vapr) in influencing the Brachypetalum orchid species in southwest China.
In addition to climate, productivity also contributed greatly to the distributions of Brachypetalum orchid species in southwest China. The productivity indexes of net primary production (NPP) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) were important factors in explaining the distribution of Brachypetalum orchids in southwest China. This may be due to the fact that NDVI and NPP are likely to reflect the diversity and abundance of insects by providing food and habitats for a variety of insects [58,59], thus affecting the distribution of orchids, since most orchids are pollinated by particular insects [60,61,62].
In agreement with numerous previous studies on the distribution patterns of the various groups [63,64], we discovered that the elevation was very important in affecting the species distribution of Brachypetalum orchid species in southwest China. Other researchers have also reported that altitude was considered to be one of the most significant factors in determining orchid distribution [51]. Since the habitat requirement may vary by orchid species [65], areas with a large elevation range could provide various habitat conditions, and therefore contain more species. In addition, we found that many environmental factors changed with elevation in our research. For example, average temperature, water vapor pressure, precipitation of the coldest quarter, normalized difference vegetation index, and soil moisture decreased with elevation. Hence, the elevation may be one of the crucial factors structuring the distribution patterns of orchids in southwest China as it is linked to climate, productivity, and some soil properties [66].
According to the results of many previous studies [28,67], the majority of orchid species have a symbiotic relationship with mycorrhizal fungi. In turn, the distribution of mycorrhizal fungi depends to a large extent on soil conditions such as soil moisture, pH, organic content, and nutrients [3,28]. According to a previous study, soil factors (organic carbon, pH) had a significant impact on the distribution of some Cypripedium orchid species [8]. In this study, we found that soil condition is also one of the abiotic factors affecting the distribution of orchid species, which is consistent with the findings of Liu et al. [8]. On the one hand, this may be partly due to the fact that soil can influence the distribution of mycorrhizal fungi, thus affecting the distribution of orchids [3,28]. On the other hand, this is possibly because soil conditions can promote or inhibit the seed germination rate of orchid species [67,68]. Furthermore, exchangeable calcium ion (Ca2+ex) has a significant influence on orchid species distribution (Figure 9E), which coincides with the findings of Hrivnák et al. [69] and the essential role of calcium ions in pollen germination and pollen tube growth [70].
4.3. Conservation of Brachypetalum Orchids in Southwest China
The orchid family is a significant group with respect to biological conservation [11,64], because many are threatened with extinction. In situ conservation is very important in order to protect threatened species and populations in their natural habitat [25]. In this study, we discovered that there were 67 existing distribution locations of Brachypetalum orchids in the range of protected areas (Table S3). They accounted for 34.5% of the total 194 existing distribution locations, which indicated that there were still a large number of Brachypetalum orchids distributed outside the protected area without effective conservation. In addition, in the investigation, we found that unreasonable harvest and habitat destruction were the main threat factors of Brachypetalum orchids. In this regard, establishing protection plots can be an effective approach to the in situ conservation of Brachypetalum orchids in southwest China. In addition, actively developing ex situ conservation and wild reintroduction are also important to the conservation of orchids.
Moreover, identifying the niche of plant species is considered essential for their conservation [51]. In this study, we discovered that the elevation of Brachypetalum orchids ranged from 103.1 to 2024 m, with an average elevation of 974.4 m. Among them, the range of 780–1267 m was the most concentrated elevation of Brachypetalum orchids. Furthermore, all species occurred at this elevation range except Paphiopedilum armeniacum, which was distributed within a range of 1696–2024 m (Table S3). The results indicated that ecological preferences and niche breadth vary among species, which is consistent with Tsiftsis et al. [51], possibly because orchid germination niches are complex [71]. A better understanding of how niche breadth is associated with environmental gradients is crucial to species conservation, especially when considering the distribution of orchids [72]. These results revealed the niche breadth and the amplitude of geographical distribution of different Brachypetalum orchid species, which would be beneficial to set conservation priorities for the Brachypetalum orchid species in southwest China.
5. Conclusions
The geographical coordinates of Brachypetalum orchids obtained through this investigation strengthen our understanding of the distribution patterns and conservation status of each species in southwest China. Our findings showed that the distribution pattern of Brachypetalum species in southwest China was relatively scattered and sparse. In addition, Brachypetalum orchid species were mainly distributed in the karst limestone habitats of southwest China. In addition, more than 65% of Brachypetalum orchid sites were located outside protected areas and have not been effectively protected. Our preliminary but comprehensive non-parametric and correlative analysis implied that environmental factors play a significant role in determining the spatial distribution pattern of Brachypetalum orchids in southwest China. The PCA analysis also revealed that the distribution patterns of Brachypetalum orchids were most related to elevation, solar radiation, temperature (mean diurnal range, annual temperature range), and precipitation (precipitation seasonality, precipitation of the warmest quarter). Based on these results, we suggest that more in-depth investigations of orchids’ ecological preferences and niche breadth will be necessary to confirm its future conservation methods and programs, especially in the context of increasing anthropogenic disturbance and climate variability.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d13120634/s1, Table S1: Environmental variables used to explain the geographical distribution of Brachypetalum orchids in southwest China. Table S2: The Spearman correlation coefficient between each environmental variable. Table S3: The population and distribution status of each target orchid species in southwest China.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.Y. and J.W.; methodology, P.Y.; software, P.Y. and X.Z.; formal analysis, P.Y.; investigation, M.A., J.W., X.J., H.C., P.Y. and X.Z.; data curation, J.W., M.A. and P.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, P.Y.; writing—review and editing, P.Y. and J.W.; visualization, P.Y.; supervision, J.W.; project administration, J.W., H.C., X.Z., P.Y. and Q.S.; funding acquisition, J.W. and M.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Biodiversity Survey, Observation and Assessment Program of Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China (Grant No. 2019HJ2096001006), and Major Project of Biodiversity Conservation of Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors are very thankful to the editors and anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and valuable suggestions on this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Niu, Z.T.; Xue, Q.Y.; Zhu, S.Y.; Sun, J.; Liu, W.; Ding, X.Y. The complete plastome sequences of four orchid species: Insights into the evolution of the orchidaceae and the utility of plastomic mutational hotspots. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Yan, Y.J.; Tian, Y.; Li, J.S.; He, J.S.; Tang, Z.Y. Distribution and conservation of orchid species richness in China. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 181, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaskett, A.C.; Gallagher, R.V. Orchid diversity: Spatial and climatic patterns from herbarium records. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 11235–11245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cribb, P.J.; Kell, S.P.; Dixon, K.W.; Barrett, R.L. Orchid conservation: A global perspective. In Orchid Conservation; Natural History Publications: Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia, 2003; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.L.; Wang, L.F. The horizontal distribution pattern of Orchidaceae in China along latitude and longitude. J. Biol. 2013, 30, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.J.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Xiao, Y. Priority area of biodiversity conservation in Southwest China. Chin. J. Ecol. 2018, 37, 3721–3728. [Google Scholar]
- Medhi, R.P.; Chakrabarti, S. Traditional knowledge of NE people on conservation of wild orchids. Indian J. Tradit. Knowl. 2009, 8, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Jacquemyn, H.; He, X.Y.; Chen, W.; Huang, Y.Q.; Yu, S.; Lu, Y.P.; Zhang, Y. The impact of human pressure and climate change on the habitat availability and protection of Cypripedium (Orchidaceae) in Northeast China. Plants 2021, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, P.; Kumaria, S.; Job, N.; Tandon, P. En-masse production of elite clones of Dendrobium crepidatum: A threatened, medicinal orchid used in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2016, 3, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Qi, C.; Wang, H.; Xiao, X.F.; Zhuang, Y.; Gu, S.J.; Zhou, Y.S.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.J.; Xu, W.L. Biocompatible and degradable Bletilla striata polysaccharide hemostasis sponges constructed from natural medicinal herb Bletilla striata. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 226, 115304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillon, Y.; Chase, M. Taxonomic exaggeration and its effects on orchid conservation. Conserv. Biol. 2006, 21, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.P.; Huang, J.L.; Zhang, S.B. Trait evolution in the slipper orchid Paphiopedilum (Orchidaceae) in China. Plant Signal. Behav. 2016, 11, e1149668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.J.; Chen, S.C.; Phillip, J.C. Flora of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009; Volume 25, pp. 33–44. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.Y.; Wu, Y.L.; Peng, K. Micro-morphological characters of leaf epidermis of ten species in genus Paphiopedilum. Bull. Bot. Res. 2014, 34, 723–729. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.Z.; Chen, H.; An, M.T.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, C.; Wu, J.Y. Analyses on distribution characteristics and protection effect of wild Paphiopedilum in Guizhou Province. Guihaia 2021. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/45.1134.Q.20210324.1433.012.html (accessed on 29 July 2021).
- Guan, Z.J.; Zhang, S.B.; Guan, K.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Hu, H. Leaf anatomical structures of Paphiopedilum and Cypripedium and their adaptive significance. J. Plant Res. 2011, 124, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Yang, Z.L.; Li, S.Y.; Hu, H.; Huang, J.L. Mycorrhizal specificity, preference, and plasticity of six slipper orchids from South Western China. Mycorrhiza 2010, 20, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evonne, T. Conversion of RAPD Markers to Co-Dominant Based Sequence Characterized Amplified Region (SCAR) Markers in Three Paphiopedilum Species; Universiti Malaysia Sabah: Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia, 2007; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.I. The asymbiotic seed germination of six Paphiopedilum species in relation to the time of seed collection and seed pretreatment. Acta Hortic. 2007, 755, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chochai, A.; Leitch, I.J.; Ingrouille, M.J.; Fay, M.F. Molecular phylogenetics of Paphiopedilum (Cypripedioideae; Orchidaceae) based on nuclear ribosomal ITS and plastid sequences. Bot. J. Linnean Soc. 2012, 170, 176–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tsai, C.C.; Liao, P.C.; Ko, Y.Z.; Chen, C.H.; Chiang, Y.C. Phylogeny and historical biogeography of Paphiopedilum Pfitzer (Orchidaceae) based on nuclear and plastid DNA. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.J.; Zhu, G.F.; Lü, F.B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, B.Q. Studies on the karyotypes of eight species of Paphiopedilum subgenus Brachypetalum. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2006, 33, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.J.; Chen, S.C. Paphiopedilum angustatum, a new orchid from Yunnan, China. Acta Phytotaxon. Sin. 2000, 38, 464–466. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.J.; Zhang, J.Y. Paphiopedilum singchii sp. nov., an addition to the subgenus Brachypetalum of Paphiopedilum (Orchidaceae). Acta Phytotaxon. Sin. 2000, 38, 467–470. [Google Scholar]
- Juiling, S.; Leon, S.K.; Jumian, J.; Tsen, S.; Lee, Y.L.; Khoo, E.; Sugau, J.B.; Nilus, R.; Pereira, J.T.; Damit, A.; et al. Conservation assessment and spatial distribution of endemic orchids in Sabah, Borneo. Nat. Conserv. Res. 2020, 5, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štípková, Z.; Kindlmann, P. Orchid extinction over the last 150 years in the Czech Republic. Diversity 2021, 13, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemyn, H.; Brys, R.; Lievens, B.; Wiegand, T. Spatial variation in below-ground seed germination and divergent mycorrhizal associations correlate with spatial segregation of three co-occurring orchid species. J. Ecol. 2012, 100, 1328–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, M.K.; Jacquemyn, H. What constrains the distribution of orchid populations? New Phytol. 2014, 202, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, M.C.; Yong, C.S.Y.; Go, R. The differences between Paphiopedilum barbatum (Lindl.) and Papiopedilum callosum (Rchb.f.) Stein var. sublaeve (Rchb.f.) P.J. Cribb. In Proceedings of the Malaysia International Biology Symposium 2016, Putrajaya, Malaysia, 26–27 October 2016; p. 26. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.J.; Liu, K.W.; Chen, L.J.; Lei, S.P.; Li, L.Q.; Shi, X.C.; Huang, L.Q. Conservation ecology of endangered species Paphiopedilum armeniacum (Orchidaceae). Acta Ecol. Sin. 2006, 26, 2791–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.N.; Li, S.Z.; Chen, L.J.; Li, J.; Li, L.Q.; Rao, W.H.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.B.; Ren, H. Conservation and reintroduction of the rare and endangered orchid Paphiopedilum armeniacum. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2021, 7, 1903817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Li, M.Y. Study on phenotypic variation of Paphiopedilum micranthum population. J. Plant Genet. Resour. 2015, 16, 765–771. [Google Scholar]
- National Forestry and Grassland Administration, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. The National Key Protected Wild Plants List. 2021. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2021-09/09/content_5636409.htm (accessed on 23 September 2021).
- Wang, B.S.; Mao, J.F.; Zhao, W.; Wang, X.R. Impact of geography and climate on the genetic differentiation of the subtropical pine Pinus yunnanensis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Chen, G.H.; He, J.X.; Yu, G.C. Factors about shallow biogenic gas reservoir and evidence of its migration and accumulation in the Qujing basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2007, 18, 673–677. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, X.Z.; Yu, D.S.; Wang, H.J.; Zhao, Y.C.; Sun, W.X. Effects of the linkage between spatial data and attribute data on estimates of soil organic carbon. Adv. Earth Sci. 2008, 23, 840–847. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.; Hu, F.; Zeng, F.P.; Wang, K.L.; Peng, W.X.; Zhang, Z.X.; Song, T.Q. Spatial distribution of tree species in evergreen-deciduous broadleaf karst forests in southwest China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, S.; Cabral, H.N. Predicting fish species distribution in estuaries: Influence of species’ ecology in model accuracy. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 180, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.C.; Zhang, G.F.; Zhao, X.; Chen, H.; Si, Q.; Wu, J.Y. Potential geographical distribution and environmental explanations of rare and endangered plant species through combined modelling: A case study of Northwest Yunnan, China. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 13052–13067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, S.E.; Hijmans, R.J. WorldClim 2: New 1 km spatial resolution climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4302–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.L. China Population Spatial Distribution Kilometer Grid Dataset; Data Registration and Publishing System of Resource and Environmental Science Data Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.L. China Annual Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) Spatial Distribution Dataset; Data Registration and Publishing System of Resource and Environmental Science Data Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K. SMC Dataset: Soil Moisture in China Dataset (2002–2018); National Tibetan Plateau Data Center: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Mao, K.; Meng, F.; Shi, J.; Zeng, J.; Shen, X.; Cui, Y.; Jiang, L.; Guo, Z. A fine-resolution soil moisture dataset for China in 2002–2018. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3239–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, W.; Dai, Y.J.; Liu, B.Y.; Zhu, A.X.; Duan, Q.Y.; Wu, L.Z.; Ji, D.Y.; Ye, A.Z.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, Q.; et al. A China dataset of soil properties for land surface modeling. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2013, 5, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Shangguan, W. Dataset of Soil Properties for Land Surface Modeling over China; National Tibetan Plateau Data Center: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaMorte, W.W. Mann Whitney U Test (Wilcoxon Rank Sum Test). Boston University School of Public Health, 4 May 2017. Available online: https://sphweb.bumc.bu.edu/otlt/MPH-Modules/BS/BS704_Nonparametric/BS704_Nonparametric4.html (accessed on 28 September 2021).
- Kassambara, A. R Package ‘Ggpubr’ Version 0.4.0: ‘Ggplot2’ Based Publication Ready Plots. 2020. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ggpubr/ggpubr.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2021).
- Ding, C.; He, X.F. K-means clustering via principal component analysis. In Proceedings of the Twenty-First International Conference on Machine Learning ACM, Banff, AB, Canada, 4–8 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kassambara, A. Practical Guide to Principal Component Methods in R. 2017. Available online: https://www.bibsonomy.org/bibtex/25f79c00df4524ae5b9455539b6b00c0f/asalber (accessed on 22 November 2021).
- Tsiftsis, S.; Tsiripidis, I.; Karagiannakidou, V.; Alifragis, D. Niche analysis and conservation of the orchids of east Macedonia (NE Greece). Acta Oecol. Int. J. Ecol. 2008, 33, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Du, H.D.; Jin, X.H.; Ma, K.P. Species diversity and geographic distribution of wild Orchidaceae in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 179–188. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, C.; Fang, J. Biodiversity in China’s mountains. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2006, 4, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittlinger, L.; Petrikovičová, L. Phytogeographical analysis and ecological factors of the distribution of Orchidaceae taxa in the Western Carpathians (Local study). Plants 2021, 10, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.C.; Zhang, G.F.; Wu, J.Y. Hotspots and conservation gaps: A case study of key higher plant species from Northwest Yunnan, China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 23, e01005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, T.J.; Bowles, M.L.; Zettler, L.W.; Pollack, C.A.; Ibberson, J.E. Environmental and management effects on demographic processes in the U.S. threatened Platanthera leucophaea (Nutt.) Lindl. (Orchidaceae). Plants 2021, 10, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapagain, D.J.; Meilby, H.; Baniya, C.B.; Budha-Magar, S.; Ghimire, S.K. Illegal harvesting and livestock grazing threaten the endangered orchid Dactylorhiza hatagirea (D. Don) Soó in Nepalese Himalaya. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 6672–6687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettorelli, N.; Ryan, S.; Mueller, T.; Bunnefeld, N.; Jędrzejewska, B.; Lima, M.; Kausrud, K. The Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI): Unforeseen successes in animal ecology. Clim. Res. 2011, 46, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLucia, E.H.; Gomez-Casanovas, N.; Greenberg, J.A.; Hudiburg, T.W.; Kantola, I.B.; Long, S.P.; Miller, A.D.; Ort, D.R.; Parton, W.J. The theoretical limit to plant productivity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 9471–9477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.D.; Morita, S. Lying to Pinocchio: Floral deception in an orchid pollinated by long-proboscid flies. Bot. J. Linnean Soc. 2010, 152, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pansarin, E.R.; Pansarin, L.M. Reproductive biology of Trichocentrum pumilum: An orchid pollinated by oil-collecting bees. Plant Biol. 2011, 13, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, M.M.; Toft, R.J.; Gaskett, A.C. Pollination and insect visitors to the putatively brood-site deceptive endemic spurred helmet orchid, Corybas cheesemanii. N. Z. J. Bot. 2013, 51, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.F.; Liang, J.C.; Hu, Y.M.; Zhou, Z.X.; Sun, H.B.; Liu, L.N.; Liu, H.J.; Hu, H.J.; Si, X.F. Different responses of avian feeding guilds to spatial and environmental factors across an elevation gradient in the central Himalaya. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 4116–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiftsis, S.; Štípková, Z.; Kindlmann, P. Role of way of life, latitude, elevation and climate on the richness and distribution of orchid species. Biodivers. Conserv. 2019, 28, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, F.; Chase, M.W. Orchid biology: From Linnaeus via Darwin to the 21st century. Ann. Bot. 2009, 104, 359–364. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.L.; Li, X.Z.; Craft, C.; Ma, Z.G.; Sun, Y.G. Relationships between vegetation zonation and environmental factors in newly formed tidal marshes of the Yangtze River estuary. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2011, 19, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez, J.M. Hierarchical patterns of symbiotic orchid germination linked to adult proximity and environmental gradients. J. Ecol. 2007, 95, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figura, T.; Weiser, M.; Ponert, J. Orchid seed sensitivity to nitrate reflects habitat preferences and soil nitrate content. Plant Biol. 2020, 22, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrivnák, M.; Slezák, M.; Galvánek, D.; Vlčko, J.; Belanová, E.; Rízová, V.; Senko, D.; Hrivnák, R. Species richness, ecology, and prediction of orchids in Central Europe: Local-scale study. Diversity 2020, 12, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewbaker, J.L.; Kwack, B.H. The essential role of calcium ion in pollen germination and pollen tube growth. Am. J. Bot. 1963, 50, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izuddin, M.; Yam, T.W.; Webb, E.L. Germination niches and seed persistence of tropical epiphytic orchids in an urban landscape. J. Plant Res. 2019, 132, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štípková, Z.; Kindlmann, P. Factors determining the distribution of orchids–A review with examples from the Czech Republic. Eur. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 11, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).