Impact of Hinoki Cypress Wood on Diversity of Microflora: A Case Study from Owase City Hall
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Influence of Hinoki Cypress on the Growth of Airborne Microorganisms (Culture Method)
2.2. Influence of Hinoki Cypress on Airborne Bacterial Community Structure (PCR-DGGE Method)
3. Results
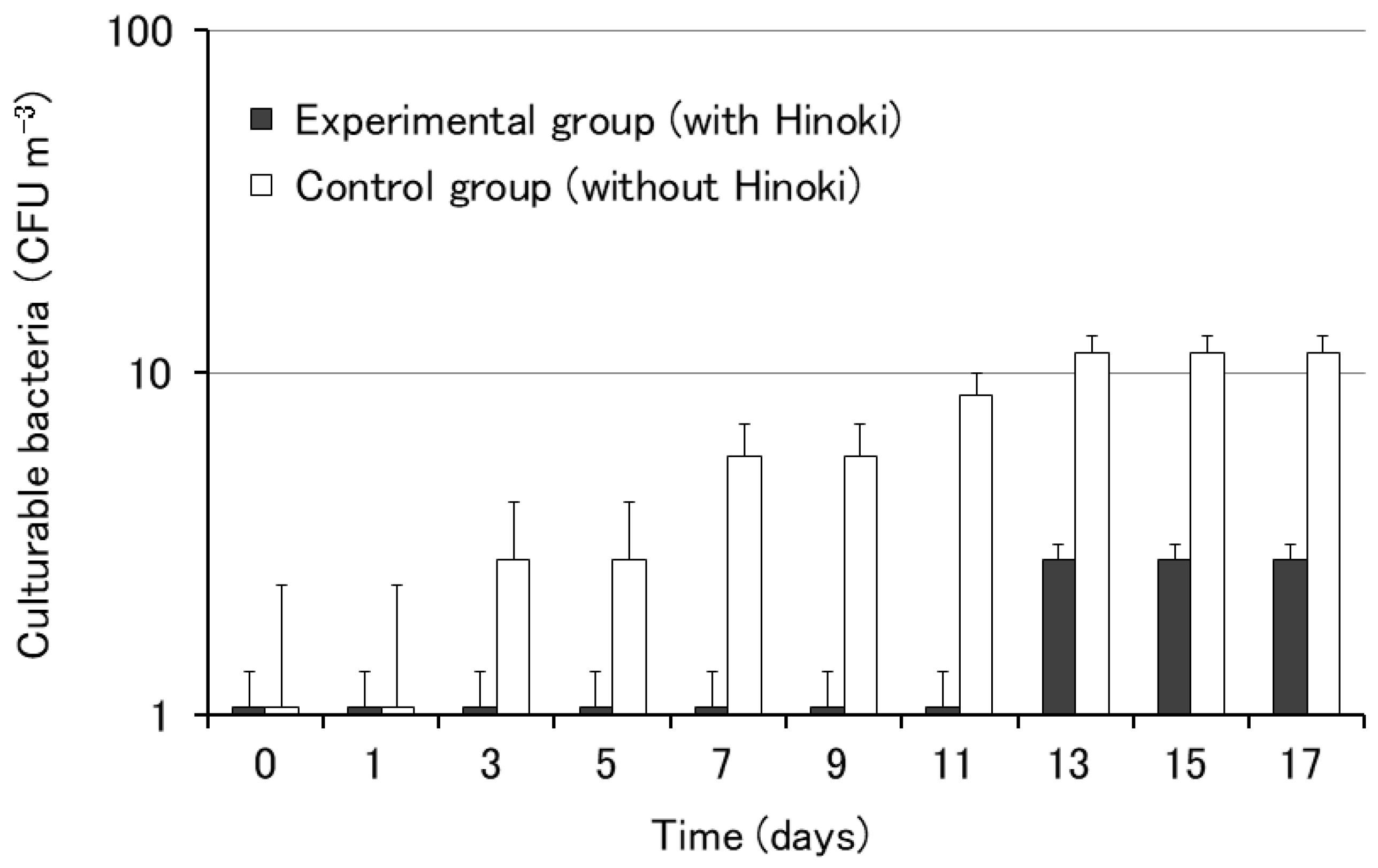
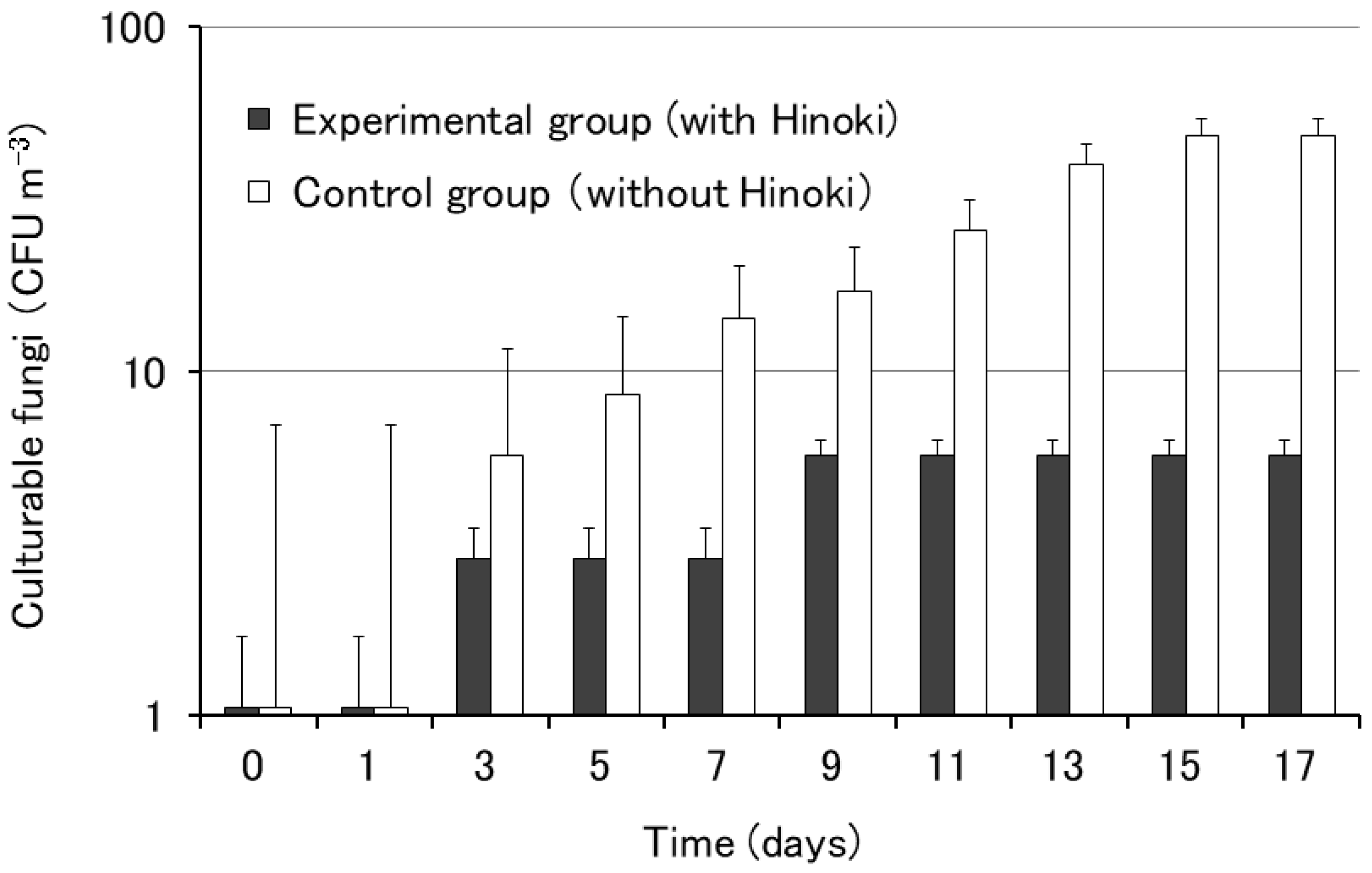
3.1. Influence of Hinoki Cypress on the Growth of Airborne Microorganisms (Culture Method)
3.2. Influence of Hinoki Cypress on the Community Structure of Airborne Bacteria (PCR-DGGE Method)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, M.J.; Choi, W.S.; Kang, H.Y.; Gwak, K.S.; Lee, G.S.; Jeung, E.B.; Choi, I.G. Inhibitory effect of the essential oil from Chamaecyparis obtusa on the growth of food-borne pathogens. J. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, T.; Kiyono, Y. The potential of hinoki (Chamaecyparis obtusa [Sieb. et Zucc.] Endlicher) plantation forests for the restoration of the original plant community in Japan. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 255, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikei, H.; Song, C.; Miyazaki, Y. Physiological Effects of Touching the Wood of Hinoki Cypress (Chamaecyparis obtusa) with the Soles of the Feet. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ito, K.; Uchiyama, Y.; Kurokami, N.; Sugano, K.; Nakanishi, Y. Soil acidification and decline of trees in forests within the precincts of shrines in Kyoto (Japan). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 214, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikei, H.; Song, C.; Miyazaki, Y. Physiological effect of olfactory stimulation by Hinoki cypress (Chamaecyparis obtusa) leaf oil. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 2015, 34, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bae, D.; Seol, H.; Yoon, H.G.; Na, J.R.; Oh, K.; Choi, C.Y.; Lee, D.W.; Jun, W.; Youl Lee, K.; Lee, J.; et al. Inhaled essential oil from Chamaecyparis obtuse ameliorates the impairments of cognitive function induced by injection of β-amyloid in rats. Pharm. Biol. 2012, 50, 900–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arima, Y.; Nakai, Y.; Hayakawa, R.; Nishino, T. Antibacterial effect of beta-thujaplicin on staphylococci isolated from atopic dermatitis: Relationship between changes in the number of viable bacterial cells and clinical improvement in an eczematous lesion of atopic dermatitis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 51, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishimatsu, S.; Oga, Y.; Ishida, T.; Hori, H. Antibacterial properties of hinokitiol against Legionella pneumophila. J. UOEH 2003, 25, 435–439. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.K.; Choi, M.S.; Seo, W.T.; Rinker, D.L.; Han, S.W.; Cheong, G.W. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of Chamaecyparis obtusa leaf essential oil. Fitoterapia 2007, 78, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, E.J.; Na, K.J.; Choi, I.G.; Choi, K.C.; Jeung, E.B. Antibacterial and antifungal effects of essential oils from coniferous trees. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morikawa, T.; Ashitani, T.; Sekine, N.; Kusumoto, N.; Takahashi, K. Bioactivities of extracts from Chamaecyparis obtusa branch heartwood. J. Wood Sci. 2012, 58, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyzer, G.; de Waal, E.C.; Uitterlinden, A.G. Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muyzer, G.; Smalla, K. Application of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) and temperature gradient gel electrophoresis (TGGE) in microbial ecology. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 73, 127–141. [Google Scholar]
- Hanning, I.B.; Ricke, S.C. Prescreening of microbial populations for the assessment of sequencing potential. In High-Throughput Next Generation Sequencing; Kwon, Y.M., Ricke, S.C., Eds.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 733, pp. 159–170. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, D.; Terada, Y.; Nakashima, T.; Sakatoku, A.; Nakamura, S. Seasonal variations in airborne bacterial community structures at a suburban site of central Japan over a 1-year time period using PCR-DGGE method. Aerobiologia 2015, 31, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Choi, B.; Yi, S.M.; Ko, G. Characterization of microbial community during Asian dust events in Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 5308–5314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maki, T.; Susuki, S.; Kobayashi, F.; Kakikawa, M.; Tobo, Y.; Yamada, M.; Higashi, T.; Matsuki, A.; Hong, C.; Hasegawa, H.; et al. Phylogenetic analysis of atmospheric halotolerant bacterial communities at high altitude in an Asian dust (KOSA) arrival region, Suzu City. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4556–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, X.; Li, G.; Yang, W.; Li, D. Distribution characteristics of microbial community structure in atmospheric particulates of the typical industrial city in Jiangsu province, China. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, R.; Garcia-Alcega, S.; Coulon, F.; Dumbrell, A.J.; Whitby, C.; Colbeck, I. Bioaerosol biomonitoring: Sampling optimization for molecular microbial ecology. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 19, 672–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, D.; Tokuyama, Y.; Terada, Y.; Kunimochi, K.; Mizumaki, C.; Tamura, S.; Wakabayashi, M.; Aoki, K.; Shimada, W.; Tanaka, H.; et al. Bacterial communities in Asian dust-containing snow layers on Mt. Tateyama, Japan. Bull. Glaciol. Res. 2011, 29, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiodjio, R.E.; Sakatoku, A.; Nakamura, A.; Tanaka, D.; Fantong, W.Y.; Tchakam, K.B.; Tanyileke, G.; Ohba, T.; Hell, V.J.; Kusakabe, M. Bacterial and archaeal communities in Lake Nyos (Cameroon, Central Africa). Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 30 July 2021).
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package, R Package Version 2.5–7. 2020. Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 30 July 2021).
- Tanaka, D.; Takahashi, T.; Yamashiro, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Kimochi, Y.; Nishio, M.; Sakatoku, A.; Nakamura, S. Seasonal variations in bacterioplankton community structures in two small rivers in the Himi region of central Japan and their relationships with environmental factors. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorquera, M.A.; Maruyama, F.; Ogram, A.V.; Navarrete, O.U.; Lagos, L.M.; Inostroza, N.G.; Acuña, J.J.; Rilling, J.I.; de La Luz Mora, M. Rhizobacterial Community Structures Associated with Native Plants Grown in Chilean Extreme Environments. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 72, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.G.; Yang, J.I.; Kim, E.; Geum, S.W.; Park, J.H.; Yeo, M.K. Investigation of bacterial and fungal communities in indoor and outdoor air of elementary school classrooms by 16S rRNA gene and ITS region sequencing. Indoor Air 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiyoshi, S.; Tanaka, D.; Maruyama, F. Transmission of airborne bacteria across built environments and its measurement standards: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hospodsky, D.; Qian, J.; Nazaroff, W.W.; Yamamoto, N.; Bibby, K.; Rismani-Yazdi, H.; Peccia, J. Human occupancy as a source of indoor airborne bacteria. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Staley, J.T.; Irgens, R.L.; Brenner, D.J. Enhydrobacter aerosaccus gen. nov., sp. nov., a Gas-Vacuolated, Facultatively Anaerobic, Heterotrophic Rod. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1987, 37, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, Y.; Fujiwara, N.; Naka, T.; Mitani, A.; Kubota, H.; Tomida, J.; Morita, Y.; Hitomi, J. Genus Enhydrobacter Staley et al. 1987 should be recognized as a member of the family Rhodospirillaceae within the class Alphaproteobacteria. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 56, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premalatha, N.; Gopal, N.O.; Jose, P.A.; Anandham, R.; Kwon, S.W. Optimization of cellulase production by Enhydrobacter sp. ACCA2 and its application in biomass saccharification. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.H.; Oh, D.H.; Jung, J.Y.; Kim, J.C.; Jeon, C.O. Comparative ocular microbial communities in humans with and without blepharitis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 5585–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, P.; Sharma, S.; Maurya, R.K.; Das De, T.; Thomas, T.; Lata, S.; Singh, N.; Pandey, K.C.; Valecha, N.; Dixit, R. Salivary glands harbor more diverse microbial communities than gut in Anopheles culicifacies. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gaüzère, C.; Moletta-Denat, M.; Blanquart, H.; Ferreira, S.; Moularat, S.; Godon, J.J.; Robine, E. Stability of airborne microbes in the Louvre Museum over time. Indoor Air 2014, 24, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.K.; Kim, J.; Ha, S.M.; Oh, H.S.; Chun, J.; Sohn, J.; Yi, H. Metagenomic insights into the bioaerosols in the indoor and outdoor environments of childcare facilities. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydogdu, H.; Asan, A.; Tatman Otkun, M. Indoor and outdoor airborne bacteria in child day-care centers in Edirne City (Turkey), seasonal distribution and influence of meteorological factors. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 164, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brągoszewska, E.; Biedroń, I.; Kozielska, B.; Pastuszka, J.S. Microbiological indoor air quality in an office building in Gliwice, Poland: Analysis of the case study. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2018, 11, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brągoszewska, E.; Biedroń, I. Indoor Air Quality and Potential Health Risk Impacts of Exposure to Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria in an Office Rooms in Southern Poland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


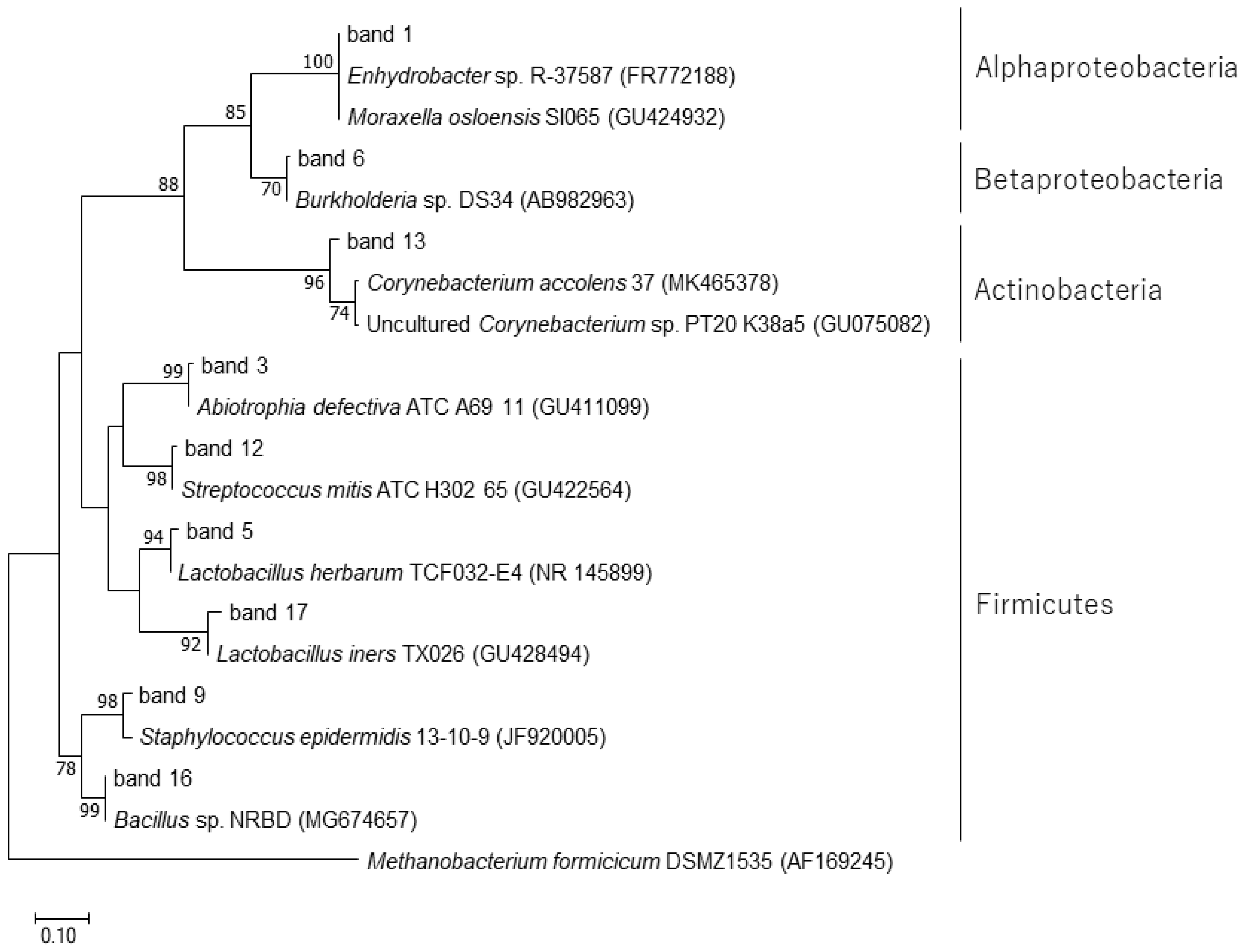
| DGGE Band | Closest Relative (Accession Number) | Source | Identity | Phylogenetic Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (2, 7, 8, 10, 11, 14, 18) | Enhydrobacter sp. R-37587 (FR772188) | Aquatic microbial mat | 136/136 (100%) | Alphaproteobacteria |
| 3 (4, 15) | Abiotrophia defectiva ATC_A69_11 (GU411099) | Human oral cavity | 141/142 (99%) | Firmicutes |
| 5 | Lactobacillus herbarum TCF032-E4 (NR_145899) | Traditional Chinese fermented radish | 128/130 (98%) | Firmicutes |
| 6 | Burkholderia sp. DS34 (AB982963) | Soil, Japan | 143/144 (99%) | Betaproteobacteria |
| 9 | Staphylococcus epidermidis 13-10-9 (JF920005) | 143/145 (99%) | Firmicutes | |
| 12 | Streptococcus mitis ATC_H302_65 (GU422564) | Human oral cavity | 141/144 (98%) | Firmicutes |
| 13 | Corynebacterium segmentosum NCTC934 (LR134408) | Nose | 116/123 (94%) | Actinobacteria |
| 16 | Bacillus sp. NRBD (MG674657) | Rhizosphere of fluoride contaminated site | 151/151 (100%) | Firmicutes |
| 17 | Lactobacillus iners TX026 (GU428494) | Human oral cavity | 124/127 (98%) | Firmicutes |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanaka, D.; Uei, D.; Matsui, J.; Matsunaga, M.; Morimoto, M.; Maruyama, F. Impact of Hinoki Cypress Wood on Diversity of Microflora: A Case Study from Owase City Hall. Diversity 2021, 13, 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13100473
Tanaka D, Uei D, Matsui J, Matsunaga M, Morimoto M, Maruyama F. Impact of Hinoki Cypress Wood on Diversity of Microflora: A Case Study from Owase City Hall. Diversity. 2021; 13(10):473. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13100473
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanaka, Daisuke, Daisuke Uei, Jun Matsui, Masahiro Matsunaga, Masaaki Morimoto, and Fumito Maruyama. 2021. "Impact of Hinoki Cypress Wood on Diversity of Microflora: A Case Study from Owase City Hall" Diversity 13, no. 10: 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13100473
APA StyleTanaka, D., Uei, D., Matsui, J., Matsunaga, M., Morimoto, M., & Maruyama, F. (2021). Impact of Hinoki Cypress Wood on Diversity of Microflora: A Case Study from Owase City Hall. Diversity, 13(10), 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13100473






