Abstract
Extreme environmental features can drive the evolution of extreme phenotypes. Over the course of evolution, certain environmental changes may be so drastic that they lead to extinction. Conversely, if an organism adapts to harsh environmental changes, the adaptations may permit expansion of a novel niche. The interaction between environmental stressors and adaptive changes is well-illustrated by the blind Mexican cavefish, Astyanax mexicanus, which has recurrently adapted to the stark subterranean environment. The transition from terrestrial rivers and streams (occupied by extant surface morphs of the same species) to the cave has been accompanied by the resorption of eyes, diminished pigmentation and reduced metabolism in cave-dwelling morphs. The principal features of caves most often associated with evolution of these common cave features are the absence of light and limited nutrition. However, a putatively essential cave feature that has received less attention is the frequently low concentration of oxygen within natural karst environments. Here, we review the potential role of limited oxygen as a critical environmental feature of caves in the Sierra de El Abra. Additionally, we review evidence that Astyanax cavefish may have evolved adaptive features enabling them to thrive in lower oxygen compared to their surface-dwelling counterparts.
1. Introduction
Extreme environmental changes can have dramatic consequences on organismal form and physiology. The freshwater teleost species Astyanax mexicanus is a ”natural” model system that has provided novel insight to interactions between environment and phenotype. This species exists as two distinct morphotypes—an extant ”ancestral surrogate” surface form and an obligate cave-dwelling form (Figure 1b,c). Over the course of several hundred thousand years, multiple discrete cave invasions occurred in which surface morphs of this species colonized the limestone caves of the Sierra de El Abra region in northeastern Mexico (Figure 1a [1]). Numerous common troglobitic traits accompanied this surface-to-cave transition, including complete eye regression [2,3], lack of pigmentation [4,5] and reduced metabolism [6,7]. These divergent phenotypes are often linked to common features of the cave microenvironment, including complete darkness and scarce nutritional resources [8,9]. Interestingly, however, few investigations in this system have focused on the putatively low levels of oxygen (hypoxia) present within caves as an important environmental feature.
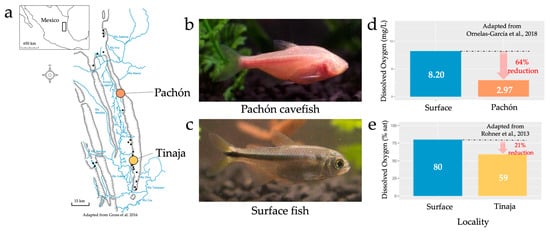
Figure 1.
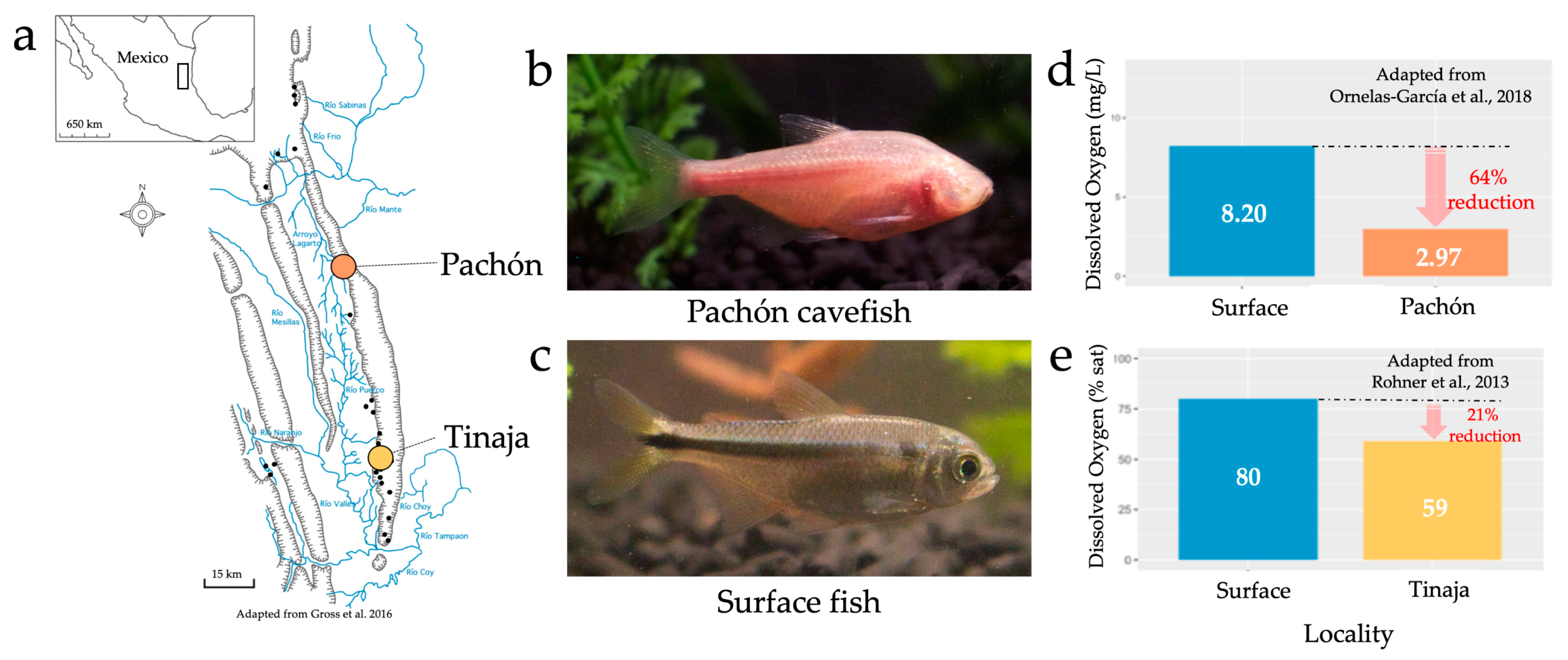
The numerous caves, fish and oxygen measurements found in the Sierra de El Abra and surrounding regions. 30 named caves are located in this region of northeastern Mexico (a). The species Astyanax mexicanus is composed of two morphotypes, the cavefish (b) and surface fish (c). Oxygen measurements taken with the Pachón cave (d) and Tinaja cave (e) show reduced levels of oxygen compared to surrounding surface environments.
The number of aquatic environments with reduced concentrations of oxygen are growing, likely as a consequence of climate change. For instance, recent studies indicate that hypoxic zones in both freshwater and marine environments are expanding globally [10,11,12]. The dramatic switch from normoxia (well-oxygenated) to hypoxia can be devastating for native fauna and has already decimated aquatic populations around the world [13,14,15,16]. Further, subterranean environments have long been appreciated as having less oxygen compared to the above-ground terrestrial environment [17]. The question of how certain aquatic species have adapted to low oxygen has been examined in certain contexts. However, the cavefish model system, Astyanax mexicanus, presents the opportunity to examine interspecific differences in oxygen metabolism in two morphs of the same species. This powerful comparative paradigm has enabled broad insights to the developmental, genetic and morphological differences that underlie adaptation to the cave environment. Here, we argue that despite having received less attention in the literature, reduced oxygen has likely had a meaningful impact on the evolutionary history of the cave morphotype. Since numerous ecological factors differ across the many caves of the Sierra de El Abra, this model system may provide improved resolution for understanding how differences in oxygen levels across similar cave networks explain subtle differences in oxygen metabolism and respiratory physiology. This review has two principal aims: First, we examine the available evidence of low oxygen in the caves of the Sierra de El Abra. Second, we assess whether Astyanax mexicanus cavefish exhibit phenotypes consistent with ”hypoxia-tolerant” species. In sum, we propose that reduced oxygen is a critical driver of cave-associated phenotypes, and that Astyanax cavefish have adapted to the low oxygen concentrations in the cave environment.
2. Determinants of Dissolved Oxygen Concentration and Their Status in Subterranean Environments
The concentration of dissolved oxygen in a body of water is influenced by a number of factors. Thus, the dissolved oxygen concentration can vary according to the magnitude of these diverse features. For instance, if the environmental conditions surrounding a body of water vary, so too will the concentration of dissolved oxygen within that body of water. Alternatively, if those factors remain stable, so too will the concentration of dissolved oxygen. Here, we review key factors determining dissolved oxygen concentrations in natural bodies of water, including how these factors may differentially influence the cave and surface environments of the Sierra de El Abra. We note that the level of reduced oxygen in caves likely varies over both time and space, and therefore should be regarded as a dynamic feature. Moreover, karstic systems are known to be quite dynamic, rendering one’s ability to generalize from other cave complexes (e.g., in temperate regions) quite challenging. Nonetheless, the caves of the Sierra de El Abra have likely experienced reduced level(s) of oxygen, in a manner consistently lower than terrestrial environments, across vast geologic and evolutionary timescales.
2.1. Low Dissolved Oxygen in Subterranean Environments and the Sierra de El Abra
Considerable research has been conducted on hypoxia tolerance in a variety of species, owing to increasingly common environmental oxygen limitations [18,19,20]. Additionally, studies relating to dissolved oxygen in subterranean environments (including caves) have revealed the presence of low dissolved oxygen compared to surface waters [21]. These observations have mostly been recorded since the early 1970s, when trends of reduced dissolved oxygen in subterranean environments were first appreciated by numerous ecologists [17]. Similarly, direct measurements of reduced oxygen have been recorded in the Sierra de El Abra. For example, Rohner et al. [22] reported less oxygen in the Tinaja cave compared to the surrounding surface waters (Figure 1e, 80% air saturation in surface waters, 59% air saturation in the Tinaja cave). Additionally, Ornelas-García et al. [23] reported substantially less oxygen in Pachón cave pools (2.97 mg/L), compared to two river locations: Micos River (4.43 mg/L) and Rascón (8.2 mg/L; Figure 1d). Remarkably, one historical measurement in the Sierra de El Abra found dissolved oxygen concentrations as low as 0.9 mg/L [24]; however, it should be noted that cavefish are not believed to be present at this locality. Interestingly, a recent measurement reported by Krishnan et al. [25] found much higher dissolved oxygen concentrations in the Pachón cave (~6.9 mg/L on average) compared to previous measurements. We believe this finding provides evidence that dissolved oxygen levels may fluctuate across time and space within the dynamic karst environment. It is difficult to say whether stable reductions in oxygen, or long-term fluctuations, are more stressful depending on how physiological stress is defined. Regardless of ”reduced” versus ”variable” oxygen levels, we would argue that either factor will have been at play over extensive geological periods, and therefore either feature (but hypoxia more saliently) represents a challenging environmental factor likely driving changes in oxygen metabolism. Further, although direct measurements of dissolved oxygen in the region are limited, environmental features that contribute to low levels of oxygen are frequently reported in caves. Although less is known of the specific factors contributing to hypoxia (e.g., water depth of different cave pools), the following sections examine those environmental features that most likely influence oxygen levels in the El Abra cave complex.
2.2. Atmospheric Composition and Mixing
A key determinant of oxygen concentration within a body of water is the amount of oxygen in the surrounding atmosphere. Exchange occurs at the surface of the water, where oxygen can enter or leave depending on the concentration in either substrate. In principle, oxygen in a body of water and in the atmosphere will either be at equilibrium or moving towards equilibrium [26]. If a body of water is in complete equilibrium with the ambient atmosphere, then the body of water has 100% air saturation. However it is important to note that if the ambient atmosphere has limited levels of oxygen, the body of water will likely also have limited levels of oxygen (even at 100% air saturation). Many factors impact the efficiency of this exchange, such as temperature, atmospheric pressure, water pressure and salinity. Further, diffusion of oxygen is also impacted by turbulence of the water body. Accordingly, a greater flow velocity (increased turbulence) increases the diffusion rate [27]. Thus, stagnant water mixes poorly with the ambient atmosphere, leading to a slower oxygen diffusion into the body of water. Not surprisingly, many pools within the caves of the Sierra de El Abra are reportedly stagnant [28,29], and therefore likely do not mix efficiently with atmospheric oxygen. We note that many of these features likely differ across the El Abra cave complex, even for cave localities that are geographically close to one another.
Beyond stagnation of the water, some cave environments in the Sierra de El Abra are characterized by ”bad air” [30]. Even if a body of water is able to maintain 100% air saturation, if the level of oxygen in the ambient atmosphere is low, the level of oxygen in the local body of water will also be low. The pioneering El Abra caver William Elliott recounted an anecdote relating to low oxygen in the air of the Tinaja cave, which created a dangerous environment for a group of explorers. In 1972, a group of technical cavers entered the Tinaja cave with the hope of finding an underground connection to a nearby cave, Sótano del Arroyo. During this expedition, the only diving gear brought along was a rope and flashlight—no scuba or diving gear. Don Broussard dove into a sump and found a pocket of air into which he swam. There, after an estimated four deep breaths, the other explorers saw the light coming from Don’s flashlight begin to sink in the cave pool—a sign that he was unconscious. The group frantically pulled him from the water and discovered he was not breathing. Following CPR to remove the water from his lungs, he regained consciousness [31].
”Bad air” is frequently present in caves [30]. Many cavers utilize the ”Bic” test as an empirical way to sample atmospheric oxygen in an unknown cave. If a Bic brand handheld lighter ignites properly and retains its flame, there is enough oxygen to breathe. However, if the lighter cannot light or maintain its flame, one could be in a dangerous spot with little oxygen. Elliott [30] recounted some of his experiences and mentioned that ”normal people” may be turned off by the fact that frequent cavers develop a ”body expectation” to the bad air of caves. He continued, “Maybe it also causes minor brain damage and that’s why we continue to go caving…hmmm. Maybe it also causes minor brain damage and that’s why we continue to go caving…Wait, I already said that. That’s all for now.”
2.3. Photosynthesis
One primary input of dissolved oxygen into a body of water is photosynthesis [26]. Vegetation, phytoplankton and other algae within a body of water utilize natural light to produce energy, and oxygen is released as a byproduct. Thus, the presence of these species in a natural environment is normally crucial for maintaining sufficient oxygen for aquatic organisms. Since natural light is necessary for photosynthesis, daily fluctuations occur in most terrestrial bodies of water, with the concentration of oxygen being highest near the end of the day, and lowest just before sunrise [32]. However, these fluctuations are typically not sufficient to cause hypoxia around sunrise in typical terrestrial bodies of water [32].
Given that the Sierra de El Abra and surrounding regions are filled with dense vegetation, robust photosynthesis occurs within this over-ground environment. In fact, vegetation is so dense in some areas that it has caused cavers to get lost [33]. However, caves experience limited light beyond the entrance, and therefore are essentially devoid of photosynthetic activity. This lack of photosynthesis is described many times in the Astyanax literature; however, few published works link this commonly reported cave feature to low levels of dissolved oxygen. Some even discuss the benefit of seasonal flooding for cavefish as the main influx of energy [2,7,34,35,36]. We propose that these floods may also provide an essential input of oxygen into the cave pools. In this context, we also note that it will be interesting to determine if cave morphs demonstrate direct genetic or physiological changes such as differences in mitochondrial function and/or DNA repair mechanisms in cavefish compared to surface morphs.
2.4. Respiration and Organic Matter
Just as photosynthesis is the major driver of oxygen input in water, aerobic respiration is regarded as the principal consumer of oxygen in a body of water [26]. Many caves and most surface aquatic environments of the Sierra de El Abra harbor organisms that consume oxygen. Further, oxygen is consumed by microbes that respire during decomposition of organic material [17]. Organic material is present within the caves of the El Abra, even when actively flowing water is absent. For instance, many caves harbor sizable bat populations providing bat guano, as well as deceased bats, to the cave waters below [31]. These substrates undergo decomposition through a process that ultimately serves to further reduce oxygen levels within the cave.
An additional factor affecting the cave environment is methane gas. Methane is known to displace oxygen in water; thus, concentrations of methane and other substances should be considered when determining levels of oxygen deficiency [37]. Elliott [31] recalled a striking anecdote relating to methane in the Arroyo cave of the Sierra de El Abra. After navigating through “Strickland’s Bad Air Passage” and “The Wallow,” cave explorers will come upon “Methane Passage,” so named for the bubbles of methane that can be seen floating up from the muddy sediment of the cave pools. The concentration of methane in these bubbles is so high that they can be ignited, producing blueish and yellowish flames. A video of “tourist” cavers in Arroyo posted to YouTube in 2008 illustrated the combustible nature of methane gas. At first, small bubbles only produced a small, brief flame. However, later in the video, enough methane was released above the surface of the water that a dangerous amount of fire was produced. Instinctively, the person in the water panicked and tried to exit the water as quickly as possible. This only caused more methane to be released, increasing the surface area of the flame. Luckily, the cavers were not harmed. This remarkably high amount of methane in and near the cave pools clearly impacts oxygen concentration within the Arroyo cave pools. At present, it remains unclear if the concentration of methane is similar across all cave environments, or between different pools within a single cave locality.
3. Adaptation to Low Oxygen across Teleost Fish Taxa
Many aquatic animals encounter hypoxic water and must emigrate or adapt to the reduced levels of oxygen. However, certain species are able to tolerate low oxygen better than others. These animals are regarded as hypoxia-tolerant, -resistant or -acclimated (particularly in controlled experiments). Many adaptations have evolved to permit survival in low oxygen conditions [38]. Here, we discuss adaptive phenotypes that may be relevant to cave-dwelling organisms, such as Astyanax mexicanus.
3.1. Metabolism
A well-known response of hypoxia-acclimated fish is the suppression of metabolic rate. Typically, the metabolic rate is established experimentally via respiration. Therefore, respirometric methods are used to determine metrics as a proxy for metabolic change. These metrics include maximum metabolic rate (MMR), standard metabolic rate (SMR) and routine metabolic rate (RMR). Additionally, the critical oxygen tension (Pcrit) metric is often reported in hypoxia resistance studies, which is the minimum amount of oxygen required to maintain the standard metabolic rate [39]. Fish with lower Pcrit values are considered to be more hypoxia-resistant compared to individuals with higher Pcrit values [40]. To determine the extent to which hypoxia-resistant goldfish (Carassius auratus) could suppress their standard metabolic rate, Fu et al. [41] determined the critical oxygen tension of this species. Juvenile fish were commercially bought and reared under normoxic conditions. Prior to the start of the experiment, half the population was exposed to hypoxia. After 48 h of exposure to extreme hypoxia (0.3 mg/L) the critical oxygen tension was calculated. The critical oxygen tension of hypoxia-acclimated goldfish was nearly half that of the control group, illustrating how the standard metabolic rate can be suppressed as an adaptation to lower oxygen environments.
Beyond suppression of aerobic metabolic rate, some teleost species are capable of utilizing anaerobic metabolism to survive in low-oxygen conditions [42,43]; however, this phenomenon is less understood. An example of ”paradoxical anaerobism” is observed in the desert pupfish [44]. Following the last ice age, the groundwater table began receding in the Mojave desert, trapping this species in several distinct springs. These springs are located below the surface of the desert and are characterized by limited light during winters, resulting in limited primary production and scarce food sources. During testing, anaerobic metabolisms could not be activated ”on-demand” and even occurred randomly in environments with ample ambient oxygen—hence ”paradoxical.“ One individual went over two hours consuming negligible amounts of oxygen. Ultimately however, the authors could not rule out the possibility that ”paradoxical anaerobism” provides any real benefit and that it may simply be the indirect consequence, or component, of another underlying physiological mechanism. Additional studies of potential adaptations to hypoxia in animals living in extreme aquatic environments will provide further insight to the underlying mechanisms of this unusual respiratory feature.
3.2. Gill Morphology
Fish may also adapt to low oxygen through alterations in gill morphology. Gills are the primary surfaces of gas exchange in fish, and morphological alterations to the structure of gill organs can impact oxygen capture from the environment. Some examples of alterations to gill morphology are quite astounding. For example, the crucian carp (Carassius carassius), a hypoxia-tolerant species, dramatically changes the morphology of its gills in response to hypoxic stress [45]. Interestingly, this species displays a unique gill morphology trait even in normoxic conditions—the lack of protruding lamella. Teleost fish gills are composed of many gill arches. Attached to these gill arches are fingerlike projections known as gill filaments. Each gill filament has numerous disklike protrusions called lamella. The surfaces of these lamella are the sites of gas exchange. Thus, fish with expanded lamella have greater overall surface area available for respiration and are able to capture more oxygen. Although during normoxic conditions the crucian carp has lower-than-average lamella surface area, during hypoxic conditions the crucian carp increases the surface area of its lamella via apoptosis of the interlamellar cell mass (ILCM). Strikingly, these changes can be visualized via scanning electron microscopy within 24 h of low-oxygen exposure. Additionally, this feature of gill remodeling is reversible. Upon returning the carp to well-oxygenated water, lamella reverted to an intact ILCM within seven days. This study provided evidence of a remarkable morphological adaptation to low oxygen, but also indicates that adaptations to hypoxia may persist in a population even if hypoxia is no longer present.
3.3. Hemoglobin
The ability of teleosts to inhabit such a wide range of environmental conditions may be attributed, in part, to the teleost-specific whole genome duplication event that occurred ~350 million years ago [46]. This whole genome duplication event also impacted syntenic regions of the genome housing the hemoglobin superfamily of genes. Beyond a few anomalies [47], all teleost hemoglobin genes are organized into two distinct genomic regions named for the genes that flank them [48]. The MN region (flanking genes: mpg and nprl3) is generally larger and contains the majority of hemoglobin genes, compared to the LA cluster (flanking genes: lcmt1 and aqp8).
An important adaptation to life in hypoxic environments involves changes to the structure and function of the heterotetramer hemoglobin protein. In principle, modifications can also impact the genetic sequence, organization and regulation of the hemoglobin gene repertoire. For instance, a survey of multiple Gadiformes (codfish) species revealed that the number of hemoglobin genes can vary among even closely related species [49]. This discrepancy was largely explained by certain aquatic features, namely the water depth at which each species resides. Phylogenetically older species, living in deeper waters, possessed fewer hemoglobin genes than the phylogenetically younger species living in shallower waters. The authors explained this finding based on the characteristic that the deep ocean is “an extreme, yet stable environment” and that environmental conditions are more variable near the surface. Therefore, an expanded hemoglobin repertoire, capable of producing a more diverse set of proteins, could be advantageous for animals that live in fluctuating oxygen conditions.
Simply having a diverse repertoire of hemoglobin genes does not confer hypoxic tolerance. Conceivably, efficient regulation of the repertoire is vital for producing the most effective hemoglobin protein(s) for a given environmental condition. The phenomena of hemoglobin ”switching” as a response to hypoxia was fortuitously discovered by Rutjes et al. [50] in African cichlids. Three species were utilized in multiple split-brood style experiments. Half of each brood was reared under either normoxic or hypoxic conditions for ~15 months. Through the use of isoelectric focusing, diverse isoforms of hemoglobin protein within each blood sample were separated on a polyacrylamide gel using electrophoresis. This approach enables one to identify and quantify the number of isoforms and their relative abundance. Of the three species examined, two displayed no differences in hemoglobin isoform diversity in response to varying oxygen concentration. However, the third species, Haplochromis ishmaeli, showed robust differences in both identity and relative abundance of hemoglobin isoforms in response to diverse oxygen conditions.
It was noted in this study that one defining characteristic of H. ishmaeli is that it is native to Lake Victoria in southeastern Africa while the others, although closely related, are native to different regions [51]. The authors argued that the adaptation of hemoglobin ”switching” may have originated in the ancestors of these fish during an extreme desiccation event ~15,000 years ago. To test this notion, van den Thillart et al. [51] conducted isoelectric focusing on three species of African cichlids all native to Lake Victoria. These species were characterized by varying likelihood of experiencing hypoxia in the wild, as well as having diverse nutritional requirements. Interestingly, all of the examined species exhibited hemoglobin switching when reared under hypoxic conditions in captivity. They also found that the hemoglobin molecules produced by H. ishmaeli had a higher oxygen binding affinity at lower concentrations of ambient oxygen. In sum, changes to hemoglobin genomic organization may provide robust paths towards adaptation in hypoxic environments. These changes could be accomplished through alterations in splicing that enable the production of hemoglobin molecules with improved binding efficiency, and/or through changes in the structure and expression of hemoglobin family members.
4. Evidence of Adaptation to Low Oxygen in Astyanax mexicanus
Teleosts have evolved a number of interesting adaptations to endure the challenge of low oxygen. To this point, few studies on hypoxia tolerance have been conducted in Astyanax mexicanus. Here, we review prior work that may indicate differences in respiration and/or hypoxic tolerance in the blind Mexican cavefish.
4.1. Metabolism
Several respirometric studies have examined metabolic differences between Astyanax cave and surface morphs [6,36,52,53]. These studies measured the rate at which oxygen was consumed per hour. Although the experimental design of each study varied, a consistent finding across different studies revealed that cave morphs consume far less oxygen compared to surface fish. Hüppop [6] found that for both routine consumption (average consumption over 24 h) and standard consumption (i.e., the minimum consumption recorded), Pachón cavefish consumed significantly less oxygen compared to their surface fish counterparts. Although the Micos and Chica populations did not differ significantly from the surface population, qualitatively they consumed less oxygen as well. Salin et al. [52] largely confirmed these results several years later. Over the course of a two-month fast, cavefish consumed roughly half the oxygen of surface morphs. Moran et al. [53] similarly investigated metabolic differences; however, they also examined photic condition as an environmental cue during measurements. They discovered surface fish increase mean oxygen consumption during the day, but cavefish retain stable consumption across the 24 h day. As a result, they concluded that cavefish use ~27% less energy than surface fish per day.
Respiration has also been measured across early development in Astyanax mexicanus. Bilandžija et al. [36] investigated differences in respiration rates of Pachón cavefish and surface fish when reared on a 12:12h light dark/cycle versus being reared in complete darkness. Regardless of lighting conditions at 7.5 days post-fertilization, Pachón cavefish consumed less oxygen than light/dark-reared surface fish. Interestingly, however, surface fish reared in constant darkness consumed less oxygen and did not significantly differ from Pachón cavefish. In sum, these studies provide direct evidence that cavefish likely consume less oxygen than surface fish, and these alterations were likely driven by life in complete darkness.
4.2. Gill Morphology
Few studies have examined differences in gill morphology between Astyanax mexicanus morphs. However, Moran et al. [54] reported a greater percentage of body weight was appropriated to the gills of Pachón cavefish compared to surface fish. Specifically, the gills of the Pachón cavefish, on average, accounted for 3.1% of wet body weight, while surface fish gills accounted for only 2.0% of wet body weight. Further, the gills of Pachón x surface F2 hybrids accounted for an intermediate (mean) percentage of 2.6%. Although the authors found this difference in gills, they did not find similar results in other organs (excluding eyes and brain). Accordingly, this unique difference in wet weight proportion could be the result of selection for larger gills as a consequence of lower oxygen concentrations in caves. This increased gill size in cavefish most likely provides greater surface area to augment the efficiency of gas exchange during respiration.
4.3. Hemoglobin
Recently, two independent studies examined differences in hemoglobin expression in Astyanax cavefish [55,56]. To our knowledge, these studies represent the only published works examining hemoglobin in this model system. Sears et al. [55] examined global changes to the transcriptome using RNA sequencing of adult surface and Pachón Astyanax morphs reared under different lighting conditions (i.e., 12:12 h light/dark conditions and constant darkness). When comparing gene expression patterns under natural photic conditions (light/dark for surface, total darkness for cavefish), several hemoglobin genes demonstrated significantly higher expression values in cavefish compared to surface fish. One gene, hemoglobin subunit adult alpha 1 (hbaa1), demonstrated the largest fold-change difference within this transcriptomic comparison, expressed 20× higher in cave compared to surface morphs. Further, a Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis of highly expressed genes in dark-reared cavefish revealed terms such as “oxygen transport”, “oxygen binding” and “hemoglobin complex”. The functional and adaptive significance of this upregulation remains unclear, but it is intriguing to consider that hemoglobin gene expression may be influenced by photic conditions.
Additionally, van der Weele and Jeffery [56] measured expression of two hemoglobin genes in developing Pachón cavefish and surface fish (~10–84 h post-fertilization) under normoxic conditions, using qPCR and whole-mount in situ hybridization. They found that embryonic Pachón cavefish have increased expression of these two hemoglobin genes under normoxic conditions. Further, based on in situ gene expression, developing cavefish have more mature red blood cells (erythrocytes) compared to surface fish. The authors noted a stark contrast in the response of multiple other genes to hypoxia. Many genes associated with hypoxic pathways, and metabolic processes impacted by hypoxia, increased expression in both morphotypes compared to normoxic rearing. Interestingly, the extent of this increased expression was significantly higher in Pachón cavefish than in surface fish. These recent studies suggest that cavefish have evolved resistance to hypoxia, and these changes can be observed in both development and adulthood.
5. Conclusions
Over the last few decades, the blind Mexican cavefish Astyanax mexicanus has been utilized to investigate diverse adaptive phenotypes, such as vision loss, sleep reduction and changes in nutrient metabolism evolving in cave organisms [57]. Certain cave features such as total darkness and limited food are regarded as having clear regressive impacts at the genetic, developmental and morphological levels. However, one environmental feature that has received less attention is the oxygen level within the caves inhabited by these fish. Low oxygen has commonly been reported in other temperate cave and subterranean environments around the globe [17]. Hypoxia is not limited to hypogean habitats, and the number of affected habitats is increasing as a consequence of climate change [10]. Therefore, in order to anticipate potential impacts on natural populations, it is essential that we improve our understanding of how certain taxa have evolved strategies to cope with limited oxygen. We propose that this question can be robustly examined using the natural model system, Astyanax mexicanus. Given the powerful paradigm of intra-specific comparisons, prior work reveals that this system has evolved hypoxic adaptations as a consequence of life in a low-oxygen environment. Future work, designed to parse the adaptations to low oxygen as a selective pressure, position Astyanax as an emerging model system that could reveal key insights that enable them to flourish in hypoxic environments.
Author Contributions
Scholarly review, T.B.; manuscript creation, T.B. and J.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Daniel Berning for his assistance in photographing Astyanax cavefish and surface fish. The authors also wish to thank current and former members of the Gross lab for many intriguing discussions, particularly Alyssa Hamm, Cody Kisner and Jessica Friedman. We are grateful to two anonymous reviewers who provided helpful comments on an earlier version of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Herman, A.; Brandvain, Y.; Ornelas-García, C.P.; Yoshizawa, M.; Carlson, B.; Maldonado, E.; Gross, J.B.; Cartwright, R.; Rohner, N.; Warren, W.C.; et al. The Role of Gene Flow in Rapid and Repeated Evolution of Cave-Related Traits in Mexican Tetra, Astyanax mexicanus. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 4397–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protas, M.; Conrad, M.; Gross, J.B.; Tabin, C.; Borowsky, R.L. Regressive Evolution in the Mexican Cave Tetra, Astyanax mexicanus. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 452–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Quin, K.E.; Yoshizawa, M.; Doshi, P.; Jeffery, W.R. Quantitative Genetic Analysis of Retinal Degeneration in the Blind Cavefish Astyanax mexicanus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffery, W.R. Regressive Evolution of Pigmentation in the Cavefish Astyanax. Isr. J. Ecol. Evol. 2006, 52, 405–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J.B.; Borowsky, R.; Tabin, C.J. A Novel Role for Mc1r in the Parallel Evolution of Depigmentation in Independent Populations of the Cavefish Astyanax mexicanus. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hüppop, K. Oxygen consumption of Astyanax fasciatus (Characidae, Pisces): A Comparison of Epigean and Hypogean Populations. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1986, 17, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddle, M.R.; Aspiras, A.C.; Borowsky, R.; Tabin, C.J.; Rohner, N.; Gaudenz, K.; Peuß, R.; Sung, J.Y.; Martineau, B.; Peavey, M.; et al. Insulin Resistance in Cavefish as an Adaptation to a Nutrient-Limited Environment. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 555, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, W.R. Regressive Evolution in AstyanaxCavefish. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2009, 43, 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culver, D.C. Cave Life: Evolution and Ecology; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, R.J.; Breitburg, D.L. The hypoxic environment. In Fish Physiology; Richards, J.G., Farrell, A.P., Brauner, C.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; Volume 27, pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, R.J.; Rosenberg, R. Introduction to Environmental and Economic Consequences of Hypoxia. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2011, 27, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramma, L.; Johnson, G.C.; Sprintall, J.; Mohrholz, V. Expanding Oxygen-Minimum Zones in the Tropical Oceans. Science 2008, 320, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.R.; Howell, T.; Watson, S.B.; Abernethy, S. On Hypoxia and Fish Kills along the North Shore of Lake Erie. J. Great Lakes Res. 2014, 40, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, K.; Kopf, R.K.; Watts, R.J.; Howitt, J.A. Hypoxia, Blackwater and Fish Kills: Experimental Lethal Oxygen Thresholds in Juvenile Predatory Lowland River Fishes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, J.; Janssen, F.; Gilli, A.; Gomoiu, M.T.; Hall, P.O.J.; Hansson, D.; He, Y.; Holtappels, M.; Kirf, M.K.; Kononets, M.; et al. Investigating Hypoxia in Aquatic Environments: Diverse Approaches to Addressing a Complex Phenomenon. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 1215–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Mahajan, A.K.; Kumar, P. Determining Limiting Factors Influencing Fish Kills at Rewalsar Lake: A Case Study with Reference to Dal Lake (Mcleodganj), Western Himalaya, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervant, F.; Malard, F. Adaptations: Low Oxygen. In Encyclopedia of Caves; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, R.J.; Nestlerode, J.; Diaz, M.L. A Global Perspective on the Effects of Eutrophication and Hypoxia on Aquatic Biota and Water Quality. In Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Fish Physiology, Toxicology and Water Quality, Tallinn, Estonia, 12–15 May 2003; Rupp, G., White, M.D., Eds.; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Ecosystems Research Division: Athens, GA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Pollock, M.; Clarke, L.; Dubé, M. The Effects of Hypoxia on Fishes: From Ecological Relevance to Physiological Effects. Environ. Rev. 2007, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenny, J.P.; Francus, P.; Normandeau, A.; Lapointe, F.; Perga, M.E.; Ojala, A.E.K.; Schimmelmann, A.; Zolitschka, B. Global Spread of Hypoxia in Freshwater Ecosystems During the Last Three Centuries is Caused by Rising Local Human Pressure. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüppop, K. How Do Cave Animals Cope with Food Scarcity in Caves? In Ecosystems of the World: Subterranean Ecosystem, 1st ed.; Wilkens, H., Culver, D.C., Humphreys, W.F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 172–188. [Google Scholar]
- Rohner, N.; Jarosz, D.F.; Kowalko, J.E.; Yoshizawa, M.; Jeffery, W.R.; Borowsky, R.L.; Lindquist, S.; Tabin, C.J. Cryptic Variation in Morphological Evolution: HSP90 as a Capacitor for Loss of Eyes in Cavefish. Science 2013, 342, 1372–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornelas-Garcia, P.; Pajares, S.; Sosa-Jiménez, V.M.; Rétaux, S.; Miranda-Gamboa, R.A. Microbiome Differences Between River-Dwelling and Cave-Adapted Populations of the Fish Astyanax mexicanus (De Filippi, 1853). PeerJ 2018, 6, e5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos, J.L.; Alvarez, F.; Iliffe, T.M. New Species of Troglobitic Shrimps from Mexico, with the Description of Troglomexicanus, New Genus (Decapoda: Palaemonidae). J. Crustac. Biol. 1999, 19, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, J.; Persons, J.L.; Peuss, R.; Hassan, H.; Kenzior, A.; Xiong, S.; Olsen, L.; Maldonado, E.; Kowalko, J.E.; Rohner, N. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Wild and Lab Populations of Astyanax mexicanus Uncovers Differential Effects of Environment and Morphotype on Gene Expression. J. Exp. Zool. Part B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2020, 334, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, W.K.; Whiles, M.R. Aquatic Chemistry and Factors Controlling Nutrient Cycling; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 289–321. [Google Scholar]
- Demars, B.O.L.; Manson, J. Temperature Dependence of Stream Aeration Coefficients and the Effect of Water Turbulence: A Critical Review. Water Res. 2013, 47, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinasa, L.; Heintz, C.; Rétaux, S.; Yoshisawa, M.; Agnès, F.; Ornelas-Garcia, P.; Balogh-Robinson, R. Vibration Attraction Response is a Plastic Trait in Blind Mexican Tetra (Astyanax mexicanus), Variable within Subpopulations Inhabiting the Same Cave. J. Fish. Biol. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, M.; Fumey, J.; Lejeune, C.; Policarpo, M.; Leclercq, J.; Père, S.; Torres-Paz, J.; Pierre, C.; Imarazene, B.; Rétaux, S. Diversity of Olfactory Responses and Skills in Astyanax mexicanus Cavefish Populations Inhabiting Different Caves. Diversity 2020, 12, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, W.R. Bad Air in Caves. Am. Caving Accid. NSS News 1997, 55, 396–397. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, W.R. The Astyanax Caves of Mexico: Cavefishes of Tamaulipas, San Luis Potosí, and Guerrero; Múzquiz, J.L.L.M., McNatt, L., Eds.; Association for Mexican Cave Studies: Austin, TX, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel, R.G. Oxygen. In Limnology; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 151–168. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, R. The Second Great Sierra de El Abra Caving Expedition. In AMCS Activities Newsletter, 41st ed.; Mixon, B., Ed.; Asso-ciation for Mexican Cave Studies: Austin, TX, USA, 2018; pp. 174–207. [Google Scholar]
- Borowsky, R. Astyanax Mexicanus, the Blind Mexican Cave Fish: A Model for Studies in Development and Morphology. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2008, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rétaux, S.; Casane, D. Evolution of Eye Development in the Darkness of Caves: Adaptation, Drift, or Both? Evo. Dev. 2013, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilandžija, H.; Hollifield, B.; Jeffery, W.R.; Steck, M.; Meng, G.; Ng, M.; Koch, A.D.; Gračan, R.; Ćetković, H.; Porter, M.L.; et al. Phenotypic Plasticity as a Mechanism of Cave Colonization and Adaptation. eLife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennak, R.W.; Cole, G.A. Textbook of Limnology. Trans. Am. Microsc. Soc. 1982, 101, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.G. Metabolic and Molecular Responses of Fish to Hypoxia. In Fish Physiology; Richards, J.G., Farrell, A.P., Brauner, C.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; Volume 27, pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Negrete, B., Jr.; Esbaugh, A.J. A Methodological Evaluation of the Determination of Critical Oxygen Threshold in an Estuarine Teleost. Biol. Open 2019, 8, bio045310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandic, M.; Todgham, A.E.; Richards, J.G. Mechanisms and Evolution of Hypoxia Tolerance in Fish. Proc. R. Soc. B. Biol. Sci. 2008, 276, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.J.; Brauner, C.J.; Cao, Z.D.; Richards, J.G.; Peng, J.L.; Dhillon, R.; Wang, Y.X. The Effect of Acclimation to Hypoxia and Sustained Exercise on Subsequent Hypoxia Tolerance and Swimming Performance in Goldfish (Carassius Auratus). J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 2080–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lema, S.C.; Chow, M.I.; Resner, E.J.; Westman, A.A.; May, D.; Dittman, A.H.; Hardy, K.M. Endocrine and Metabolic Impacts of Warming Aquatic Habitats: Differential Responses between Recently Isolated Populations of a Eurythermal Desert Pupfish. Conserv. Physiol. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuton, M.; Ayala, L.; Morante, A.; Dayton, K.; Jones, A.C.; Hunt, J.R.; McKenna, A.; Van Breukelen, F.; Hillyard, S. Oxygen Consumption of Desert Pupfish at Ecologically Relevant Temperatures Suggests a Significant Role for Anaerobic Metabolism. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2018, 188, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuton, M.; Ayala, L.; Van Breukelen, F.; Burg, C.; Dayton, K.; McKenna, K.; Morante, A.; Puentedura, G.; Urbina, N.; Hillyard, S.; et al. Paradoxical Anaerobism in Desert Pupfish. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 3739–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sollid, J.; De Angelis, P.; Gundersen, K.; Nilsson, G.E. Hypoxia Induces Adaptive and Reversible Gross Morphological Changes in Crucian Carp Gills. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 3667–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opazo, J.C.; Butts, G.T.; Nery, M.F.; Storz, J.F.; Hoffman, F. Whole-Genome Duplication and the Functional Diversification of Teleost Fish Hemoglobins. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 30, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidell, B.D. When Bad Things Happen to Good Fish: The Loss of Hemoglobin and Myoglobin Expression in Antarctic Icefishes. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 1791–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardison, R.C. Globin Genes on the Move. J. Biol. 2008, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baalsrud, H.T.; Voje, K.L.; Tørresen, O.K.; Solbakken, M.H.; Matschiner, M.; Malmstrøm, M.; Hanel, R.; Salzburger, W.; Jakobsen, K.S.; Jentoft, S. Evolution of Hemoglobin Genes in Codfishes Influenced by Ocean Depth. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutjes, H.A.; Nieveen, M.C.; Weber, R.E.; Witte, F.; van den Thillart, G.E.E.J.M. Multiple Strategies of Lake Victoria Cichlids to Cope with Lifelong Hypoxia Include Hemoglobin Switching. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 293, R1376–R1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Thillart, G.; Wilms, I.; Nieveen, M.; Weber, R.E.; Witte, F. Hypoxia-Induced Changes in Hemoglobins of Lake Victoria Cichlids. J. Exp. Biol. 2018, 221, jeb177832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salin, K.; Voituron, Y.; Mourin, J.; Hervant, F. Cave Colonization without Fasting Capacities: An Example with the Fish Astyanax fasciatus mexicanus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2010, 156, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, D.; Softley, R.; Warrant, E.J. Eyeless Mexican Cavefish Save Energy by Eliminating the Circadian Rhythm in Metabolism. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, D.; Softley, R.; Warrant, E.J. The Energetic Cost of Vision and the Evolution of Eyeless Mexican Cavefish. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sears, C.R.; Boggs, T.E.; Gross, J.B. Dark-Rearing Uncovers Novel Gene Expression Patterns in an Obligate Cave-Dwelling Fish. J. Exp. Zool. Part B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2020, 334, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Weele, C.M.; Jeffery, W.R. Cavefish Increase Red Blood Cell Development and Reprogram Metabolism as Adaptations to Environmental Hypoxia. bioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J.B.; Meyer, B.; Perkins, M. The Rise of Astyanax Cavefish. Dev. Dyn. 2015, 244, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).