A National Survey of Managed Honey Bee Colony Winter Losses (Apis mellifera) in China (2013–2017)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
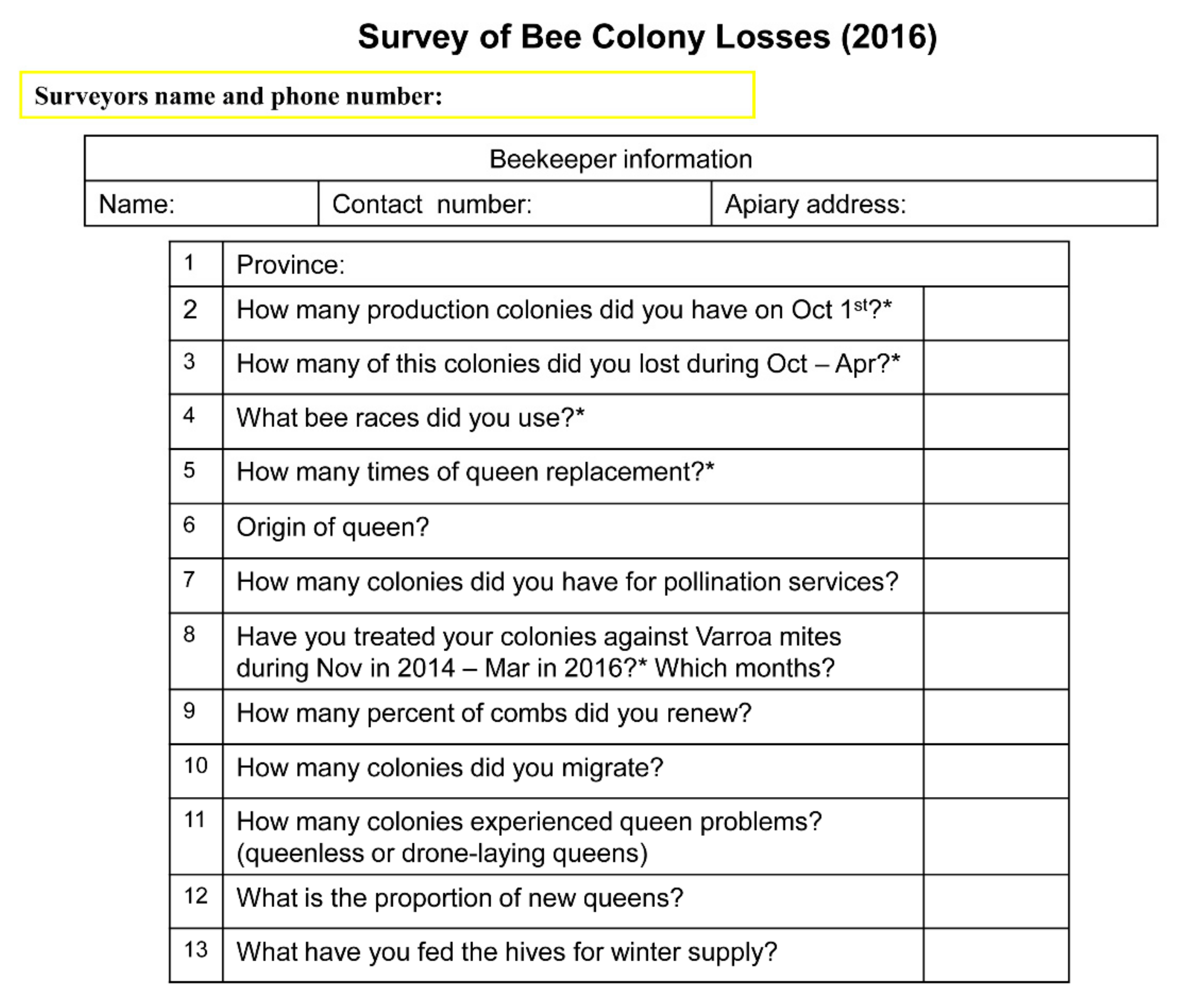
2.1. Survey and Data Acquisition
2.2. Calculation and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Survey Data
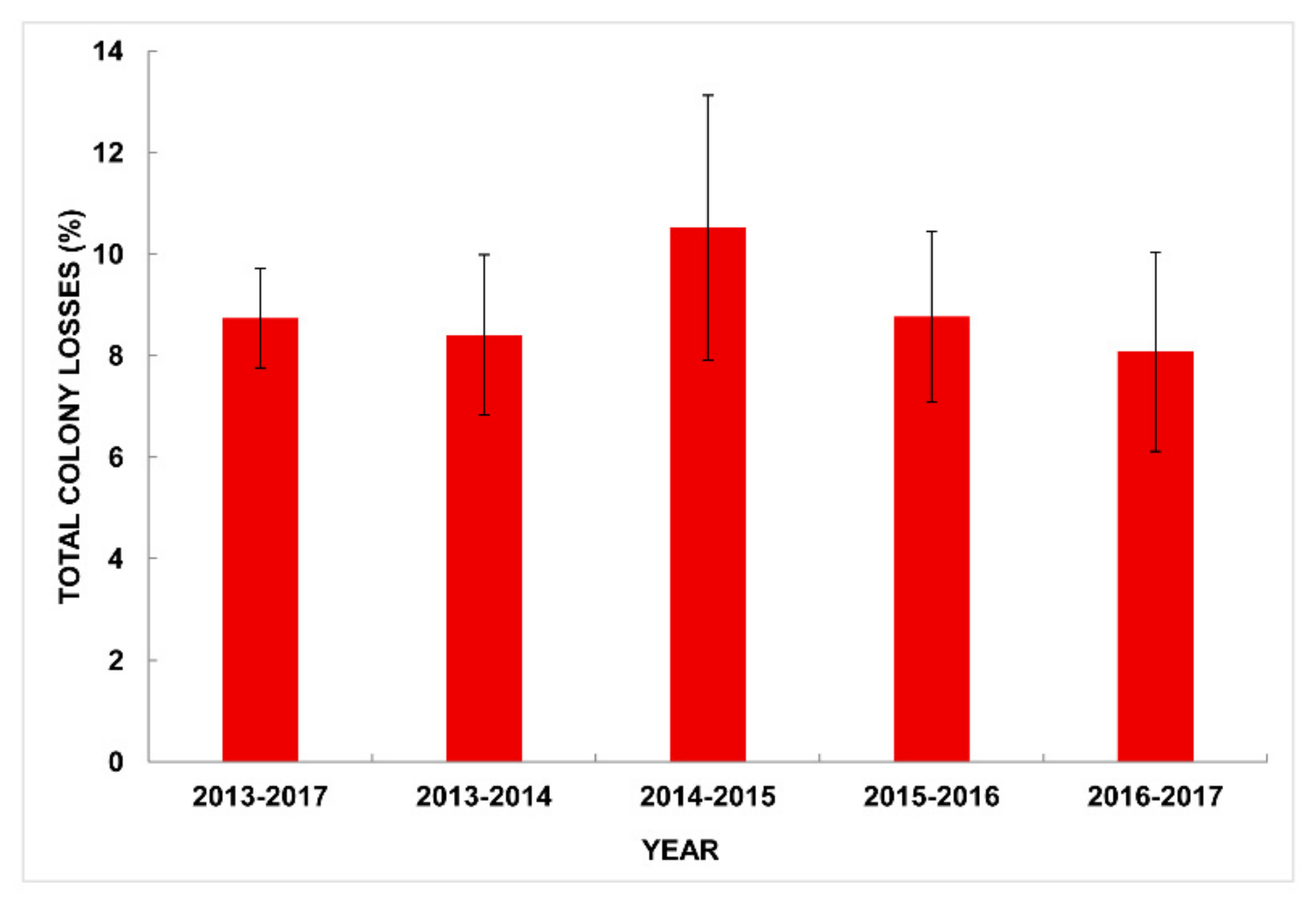
3.2. National Total Losses in Winter
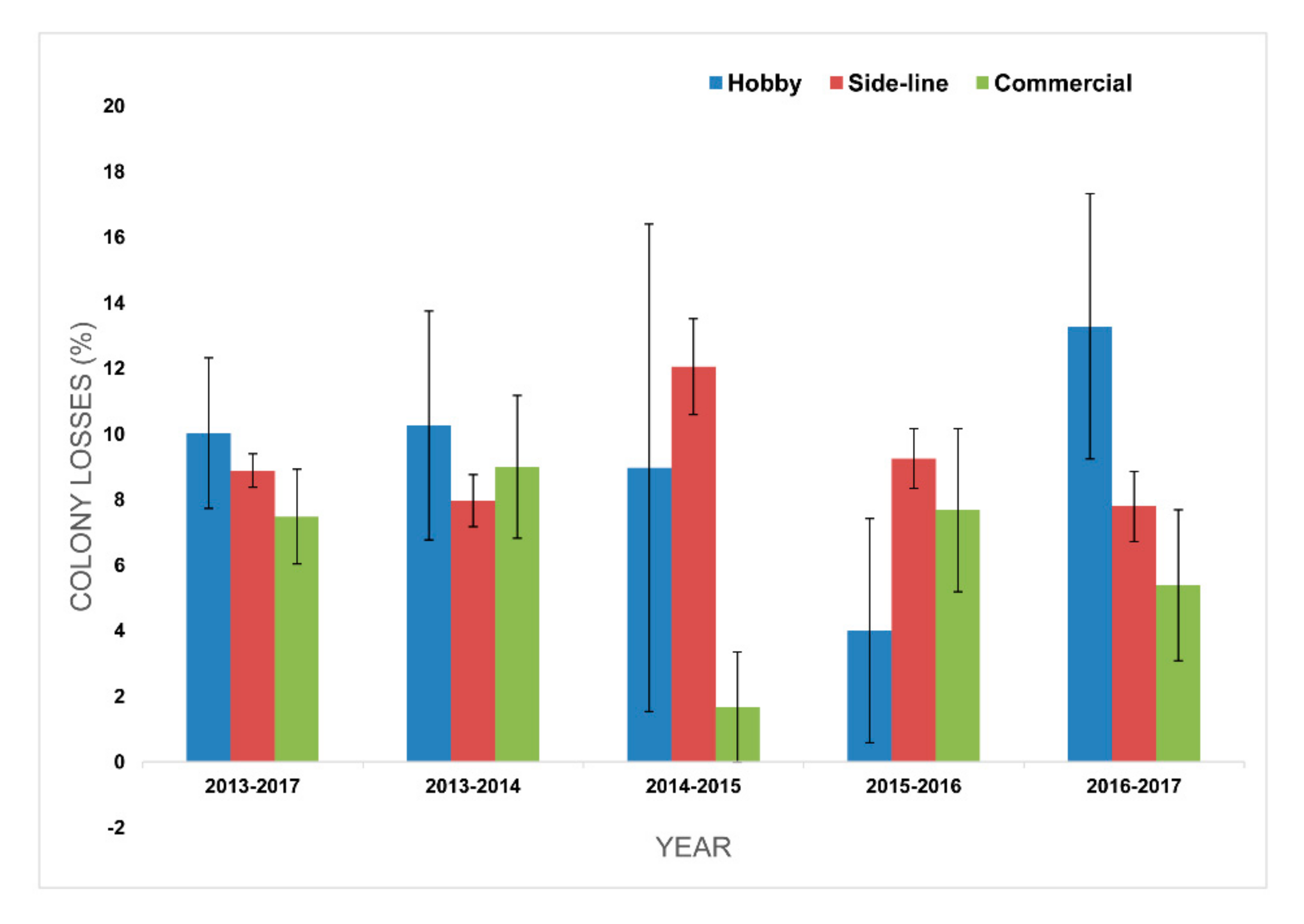
3.3. Losses by Operation Size (Apiary Size)
3.4. Losses by Province
3.5. Potential Risk Factor
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations:
References
- Klein, A.M.; Vaissiere, B.E.; Cane, J.H.; Steffan-Dewenter, I.; Cunningham, S.A.; Kremen, C.; Tscharntke, T. Importance of pollinators in changing landscapes for world crops. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 274, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potts, S.G.; Biesmeijer, J.C.; Kremen, C.; Neumann, P.; Schweiger, O.; Kunin, W.E. Global pollinator declines: Trends, impacts and drivers. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulson, D.; Nicholls, E.; Botias, C.; Rotheray, E.L. Bee declines driven by combined stress from parasites, pesticides, and lack of flowers. Science 2015, 347, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Zee, R.; Pisa, L.; Andonov, S.; Brodschneider, R.; Charriere, J.D.; Chlebo, R.; Coffey, M.F.; Crailsheim, K.; Dahle, B.; Gajda, A.; et al. Managed honey bee colony losses in Canada, China, Europe, Israel and Turkey, for the winters of 2008–9 and 2009–10. J. Apic. Res. 2012, 51, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Zee, R.; Brodschneider, R.; Brusbardis, V.; Charriere, J.D.; Chlebo, R.; Coffey, M.F.; Dahle, B.; Drazic, M.M.; Kauko, L.; Kretavicius, J.; et al. Results of international standardised beekeeper surveys of colony losses for winter 2012–2013: Analysis of winter loss rates and mixed effects modelling of risk factors for winter loss. J. Apic. Res. 2014, 53, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodschneider, R.; Gray, A.; Adjlane, N.; Ballis, A.; Brusbardis, V.; Charriere, J.D.; Chlebo, R.; Coffey, M.F.; Dahle, B.; de Graaf, D.C.; et al. Multi-country loss rates of honey bee colonies during winter 2016/2017 from the COLOSS survey. J. Apic. Res. 2018, 57, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilhos, D.; Bergamo, G.C.; Gramacho, K.P.; Goncalves, L.S. Bee colony losses in Brazil: A 5-year online survey. Apidologie 2019, 50, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, R.W.; Pernal, S.F.; Guzman-Novoa, E. Honey bee colony losses in Canada. J. Apic. Res. 2010, 49, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanengelsdorp, D.; Caron, D.; Hayes, J.; Underwood, R.; Henson, M.; Rennich, K.; Spleen, A.; Andree, M.; Snyder, R.; Lee, K.; et al. A national survey of managed honey bee 2010–11 winter colony losses in the USA: Results from the bee informed partnership. J. Apic. Res. 2012, 51, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spleen, A.M.; Lengerich, E.J.; Rennich, K.; Caron, D.; Rose, R.; Pettis, J.S.; Henson, M.; Wilkes, J.T.; Wilson, M.; Stitzinger, J.; et al. A national survey of managed honey bee 2011–12 winter colony losses in the United States: Results from the bee informed partnership. J. Apic. Res. 2013, 52, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhauer, N.A.; Rennich, K.; Wilson, M.E.; Caron, D.M.; Lengerich, E.J.; Pettis, J.S.; Rose, R.; Skinner, J.A.; Tarpy, D.R.; Wilkes, J.T.; et al. A national survey of managed honey bee 2012–2013 annual colony losses in the USA: Results from the bee informed partnership. J. Apic. Res. 2014, 53, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.V.; Steinhauer, N.; Rennich, K.; Wilson, M.E.; Tarpy, D.R.; Caron, D.M.; Rose, R.; Delaplane, K.S.; Baylis, K.; Lengerich, E.J.; et al. A national survey of managed honey bee 2013–2014 annual colony losses in the USA. Apidologie 2015, 46, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, N.; Traynor, K.S.; Steinhauer, N.; Rennich, K.; Wilson, M.E.; Ellis, J.D.; Rose, R.; Tarpy, D.R.; Sagili, R.R.; Caron, D.M.; et al. A national survey of managed honey bee 2014–2015 annual colony losses in the USA. J. Apic. Res. 2016, 54, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulhanek, K.; Steinhauer, N.; Rennich, K.; Caron, D.M.; Sagili, R.R.; Pettis, J.S.; Ellis, J.D.; Wilson, M.E.; Wilkes, J.T.; Tarpy, D.R.; et al. A national survey of managed honey bee 2015–2016 annual colony losses in the USA. J. Apic. Res. 2017, 56, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajger, I.T.; Tomljanovic, Z.; Petrinec, Z. Monitoring health status of Croatian honey bee colonies and possible reasons for winter losses. J. Apic. Res. 2015, 49, 107–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topolska, G.; Gajda, A.; Iminska, U. Temporal and spatial patterns of honeybee colony winter losses in Poland from autumn 2006 to spring 2012; Survey based on self-selected samples. J. Apic. Sci. 2018, 62, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawetz, L.; Koglberger, H.; Griesbacher, A.; Derakhshifar, I.; Crailsheim, K.; Brodschneider, R.; Moosbeckhofer, R. Health status of honey bee colonies (Apis mellifera) and disease-related risk factors for colony losses in Austria. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberreiter, H.; Brodschneider, R. Austrian COLOSS survey of honey bee colony winter losses 2018/19 and analysis of hive management practices. Diversity 2020, 12, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.G.; Chen, C.; Niu, Q.S.; Qi, W.Z.; Yuan, C.Y.; Su, S.K.; Liu, S.D.; Zhang, Y.S.; Zhang, X.W.; Ji, T.; et al. Survey results of honey bee (Apis mellifera) colony losses in China (2010–2013). J. Apic. Res. 2016, 55, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, Z.G.; Luo, Y.X.; Xu, Z.; Wang, S.H.; Zhang, X.W.; Dai, R.G.; Gao, J.L.; Chen, X.; Guo, H.K.; et al. Managed honeybee colony losses of the Eastern honeybee (Apis cerana) in China (2011–2014). Apidologie 2017, 48, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirk, C.W.W.; Human, H.; Crewe, R.M.; vanEngelsdorp, D. A survey of managed honey bee colony losses in the Republic of South Africa—2009 to 2011. J. Apic. Res. 2014, 53, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajger, I.T.; Sakac, M.; Gregorc, A. Impact of thiamethoxam on honey bee queen (Apis mellifera carnica) reproductive morphology and physiology. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 99, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajger, I.T.; Svecnjak, L.; Bubalo, D.; Zorat, T. Control of Varroa destructor mite infestations at experimental apiaries situated in Croatia. Diversity 2020, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Zee, R.; Gray, A.; Holzmann, C.; Pisa, L.; Brodschneider, R.; Chlebo, R.; Coffey, M.F.; Kence, A.; Kristiansen, P.; Mutinelli, F.; et al. Standard survey methods for estimating colony losses and explanatory risk factors in Apis mellifera. J. Apic. Res. 2013, 52, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- vanEngelsdorp, D.; Tarpy, D.R.; Lengerich, E.J.; Pettis, J.S. Idiopathic brood disease syndrome and queen events as precursors of colony mortality in migratory beekeeping operations in the eastern United States. Prev. Vet. Med. 2013, 108, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, E.; Strand, M.K.; Rueppell, O.; Tarpy, D.R. Queen quality and the impact of honey bee diseases on queen health: Potential for interactions between two major threats to colony health. Insects 2017, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyol, E.; Yeninar, H.; Karatepe, M.; Karatepe, B.; Ozkok, D. Effects of queen ages on Varroa (Varroa destructor) infestation level in honey bee (Apis mellifera caucasica) colonies and colony performance. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 6, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricigliano, V.A.; Mott, B.M.; Floyd, A.S.; Copeland, D.C.; Carroll, M.J.; Anderson, K.E. Honey bees overwintering in a southern climate: Longitudinal effects of nutrition and queen age on colony-level molecular physiology and performance. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeunovic, P.; Stevanovic, E.; Cirkovic, D.; Radojicic, S.; Lakic, N.; Stanisic, L.; Stanimirovic, Z. Nosema ceranae and queen age influence the reproduction and productivity of the honey bee colony. J. Apic. Res. 2015, 53, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, A.; Brodschneider, R.; Adjlane, N.; Ballis, A.; Brusbardis, V.; Charrire, J.D.; Chlebo, R.; Coffey, M.F.; Cornelissen, B.; da Costa, C.A.; et al. Loss rates of honey bee colonies during winter 2017/18 in 36 countries participating in the COLOSS survey, including effects of forage sources. J. Apic. Res. 2019, 58, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Anderson, D.L.; Huang, Z.Y.; Huang, S.X.; Yao, J.; Ken, T.; Zhang, Q.W. Identification of Varroa mites (Acari: Varroidae) infesting Apis cerana and Apis mellifera in China. Apidologie 2004, 35, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, J.L.; Qin, H.R.; Wu, J.; Sadd, B.M.; Wang, X.H.; Evans, J.D.; Peng, W.J.; Chen, Y.P. The prevalence of parasites and pathogens in Asian honeybees Apis cerana in China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genersch, E.; von der Ohe, W.; Kaatz, H.; Schroeder, A.; Otten, C.; Buchler, R.; Berg, S.; Ritter, W.; Muhlen, W.; Gisder, S.; et al. The German bee monitoring project: A long term study to understand periodically high winter losses of honey bee colonies. Apidologie 2010, 41, 332–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarpy, D.R. Genetic diversity within honeybee colonies prevents severe infections and promotes colony growth. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarpy, D.R.; Seeley, T.D. Lower disease infections in honeybee (Apis mellifera) colonies headed by polyandrous vs monandrous queens. Sci. Nat. 2006, 93, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.; Lodesani, M.; Bienefeld, K. Differences in colony phenotypes across different origins and locations: Evidence for genotype by environment interactions in the Italian honeybee (Apis mellifera ligustica)? Apidologie 2012, 43, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchler, R.; Costa, C.; Hatjina, F.; Andonov, S.; Meixner, M.D.; Le Conte, Y.; Uzunov, A.; Berg, S.; Bienkowska, M.; Bouga, M.; et al. The influence of genetic origin and its interaction with environmental effects on the survival of Apis mellifera L. colonies in Europe. J. Apic. Res. 2014, 53, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Conte, Y.; Ellis, M.; Ritter, W. Varroa mites and honey bee health: Can Varroa explain part of the colony losses? Apidologie 2010, 41, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodschneider, R.; Moosbeckhofer, R.; Crailsheim, K. Surveys as a tool to record winter losses of honey bee colonies: A two year case study in Austria and South Tyrol. J. Apic. Res. 2010, 49, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, H.R.; Seeley, T.D. Genetic diversity in honey bee colonies enhances productivity and fitness. Science 2007, 317, 362–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldroyd, B.P.; Fewell, J.H. Genetic diversity promotes homeostasis in insect colonies. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarpy, D.R.; vanEngelsdorp, D.; Pettis, J.S. Genetic diversity affects colony survivorship in commercial honey bee colonies. Sci. Nat. 2013, 100, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacobino, A.; Molineri, A.; Cagnolo, N.B.; Merke, J.; Orellano, E.; Bertozzi, E.; Masciangelo, G.; Pietronave, H.; Pacini, A.; Salto, C.; et al. Queen replacement: The key to prevent winter colony losses in Argentina. J. Apic. Res. 2016, 55, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Province | No. of Apiaries (2013–2014) | No. of Apiaries (2014–2015) | No. of Apiaries (2015–2016) | No. of Apiaries (2016–2017) | No. of Apiaries (2013–2017) | Total Losses (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hainan (HN) | 20 | 16 | 17 | * | 53 | 7.9 (2.8–13.1) |
| Zhejiang (ZJ) | 83 | * | 61 | * | 144 | 9.8 (7.7–11.9) |
| Shanxi (SX) | 88 | * | 50 | * | 138 | 14.2 (11.6–16.8) |
| Beijing (BJ) | 52 | 37 | * | * | 89 | 11.3 (8.7–13.8) |
| Gansu (GS) | 48 | * | 45 | 44 | 137 | 1.8 (1.1–2.5) |
| Anhui (AH) | 51 | * | * | * | 51 | 10.7 (8.5–12.8) |
| Yunnan (YN) | 50 | * | 1 | * | 51 | 0.9 (−0.06–1.9) |
| Sichuan (SC) | 73 | 52 | 37 | * | 162 | 4.3 (3.1–5.6) |
| Jilin (JL) | 36 | 100 | 101 | 77 | 314 | 5.5 (4.8–6.3) |
| Liaoning (LN) | 67 | * | 100 | 92 | 259 | 7.6 (6.9–8.2) |
| Guangdong (GD) | 4 | * | 0 | 23 | 27 | 4.7 (0.9–8.5) |
| Jiangsu (JS) | 104 | * | * | * | 104 | 4.1 (2.8–5.3) |
| Xinjiang (XJ) | 181 | * | 2 | * | 183 | 11.8 (8.7–14.9) |
| Jiangxi (JX) | * | * | * | 16 | 16 | 22.0 (13.2–30.8) |
| Heilongjiang (HLJ) | 96 | 77 | * | * | 173 | 7.7 (5.6–9.8) |
| Shandong (SD) | 81 | * | * | 48 | 129 | 5.8 (4.2–7.4) |
| Henan (HEN) | 98 | 80 | * | 20 | 198 | 19.4 (18.4–20.5) |
| Guangxi (GX) | * | * | 39 | 77 | 116 | 12.9 (10.3–15.5) |
| Chongqing (CQ) | 34 | * | * | 9 | 43 | 7.8 (3.8–11.9) |
| Province | Year | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013–2014 | 2014–2015 | 2015–2016 | 2016–2017 | |
| Hainan (HN) | 4.5 (−4.9–13.8) | 7.9 (−4.2–20.0) | 12.1 (5.5–18.7) | * |
| Sichuan (SC) | 5.2 (3.4–7.0) | 0.6 (0.1–1.1) | 7.9 (4.4–11.5) | * |
| Gansu (GS) | 0.6 (0.2–1.1) | * | 1.2 (0.5–1.8) | 3.8 (1.8–5.7) |
| Henan (HEN) | 18.1 (16.4–19.8) | 22.5 (21.4–23.7) | * | 13.7 (12.0–15.4) |
| Jilin (JL) | 7.9 (2.7–13.1) | 5.1 (4.5–5.7) | 4.9 (4.4–5.5) | 5.8 (4.2–7.3) |
| Liaoning (LN) | 9.1 (7.6–10.7) | * | 7.5 (6.9–8.1) | 6.5 (5.4–7.5) |
| Effects | Regression Coefficient | t Value | Pr (>|t|) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Null | −3.4738 (−4.2896–(−2.6580)) | −8.35 | <2 × 10−16 *** |
| Apiary Size | −0.0017 (−0.0019–(−0.0016)) | −23.98 | <2 × 10−16 *** |
| Proportion of New Queen | 0.9292 (0.8218–1.0366) | 16.97 | <2 × 10−16 *** |
| Queen Problem | 0.0407 (0.0379–0.0435) | 28.68 | <2 × 10−16 *** |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, J.; Ma, C.; Shi, W.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, C. A National Survey of Managed Honey Bee Colony Winter Losses (Apis mellifera) in China (2013–2017). Diversity 2020, 12, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12090318
Tang J, Ma C, Shi W, Chen X, Liu Z, Wang H, Chen C. A National Survey of Managed Honey Bee Colony Winter Losses (Apis mellifera) in China (2013–2017). Diversity. 2020; 12(9):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12090318
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Jiao, Cuiyan Ma, Wei Shi, Xiao Chen, Zhiguang Liu, Huihua Wang, and Chao Chen. 2020. "A National Survey of Managed Honey Bee Colony Winter Losses (Apis mellifera) in China (2013–2017)" Diversity 12, no. 9: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12090318
APA StyleTang, J., Ma, C., Shi, W., Chen, X., Liu, Z., Wang, H., & Chen, C. (2020). A National Survey of Managed Honey Bee Colony Winter Losses (Apis mellifera) in China (2013–2017). Diversity, 12(9), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12090318





