Biodiversity and Community Structure of Mesozooplankton in the Marine and Coastal National Park Areas of Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mesozooplankton Sample and Spatial and Environmental Data Collection
2.2. Morphological Identification and Metabarcoding Process
2.3. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
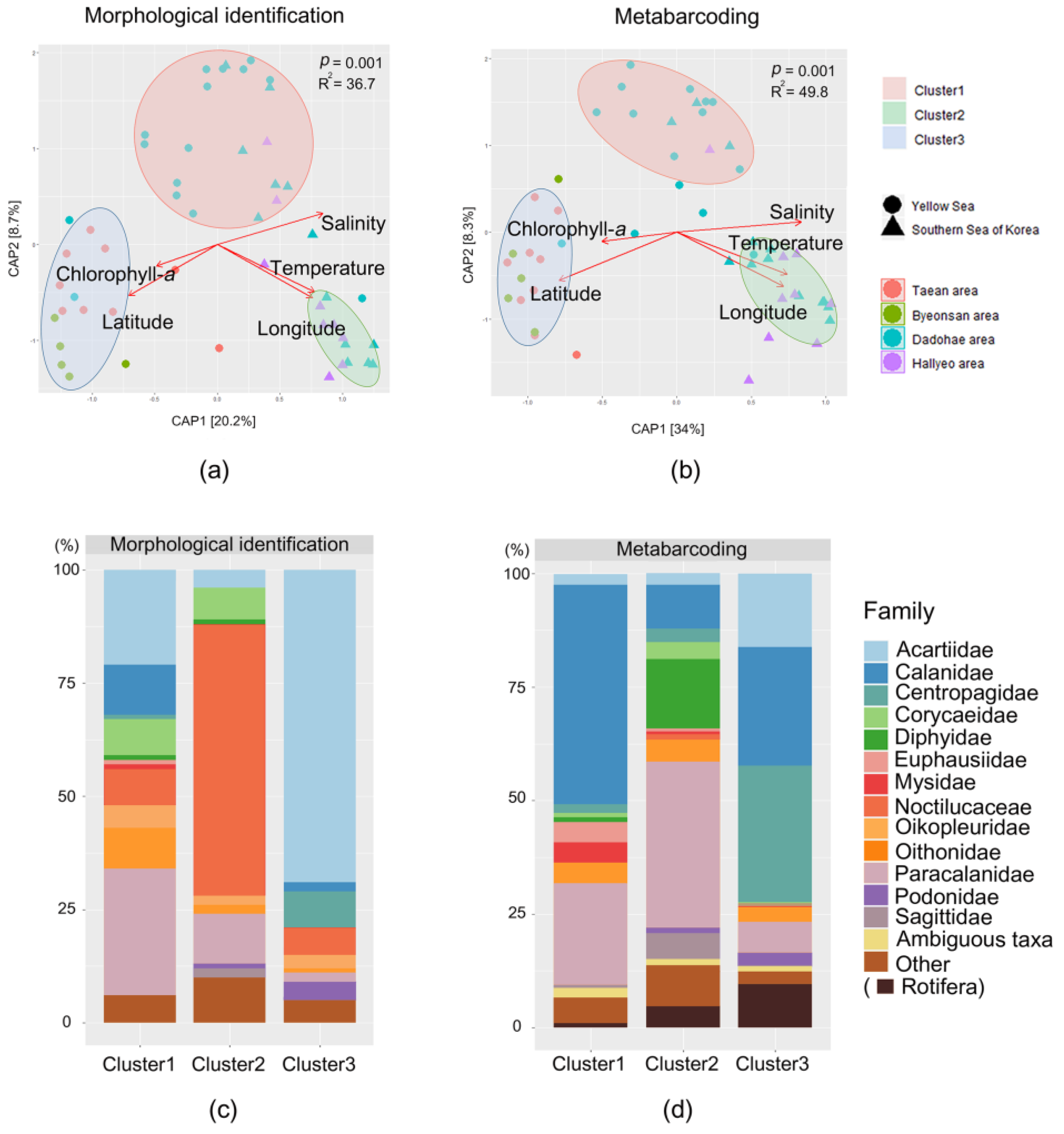
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Characteristics in the Marine and Coastal National Park Areas in Korea
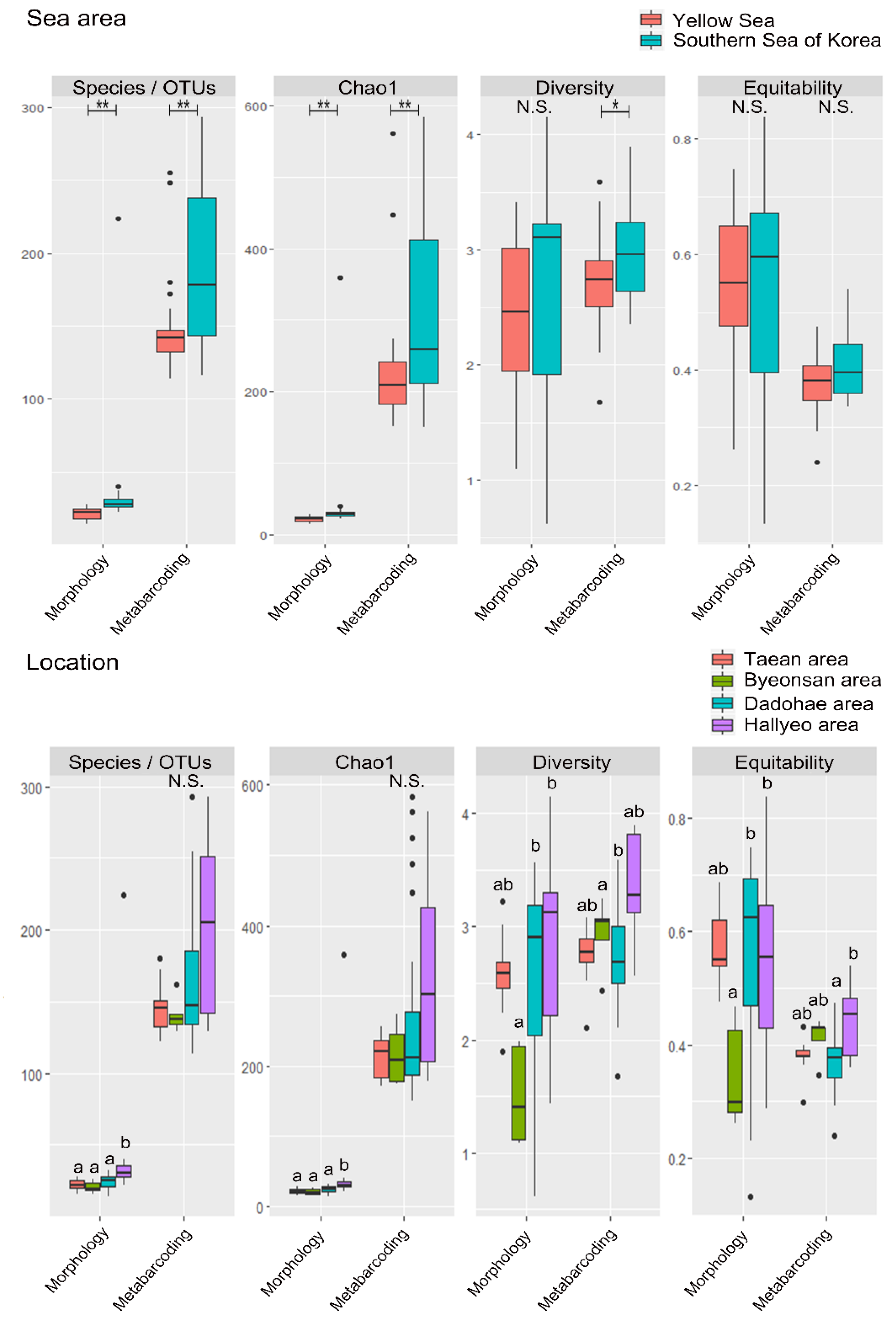
3.2. Mesozooplankton Biodiversity Analysis
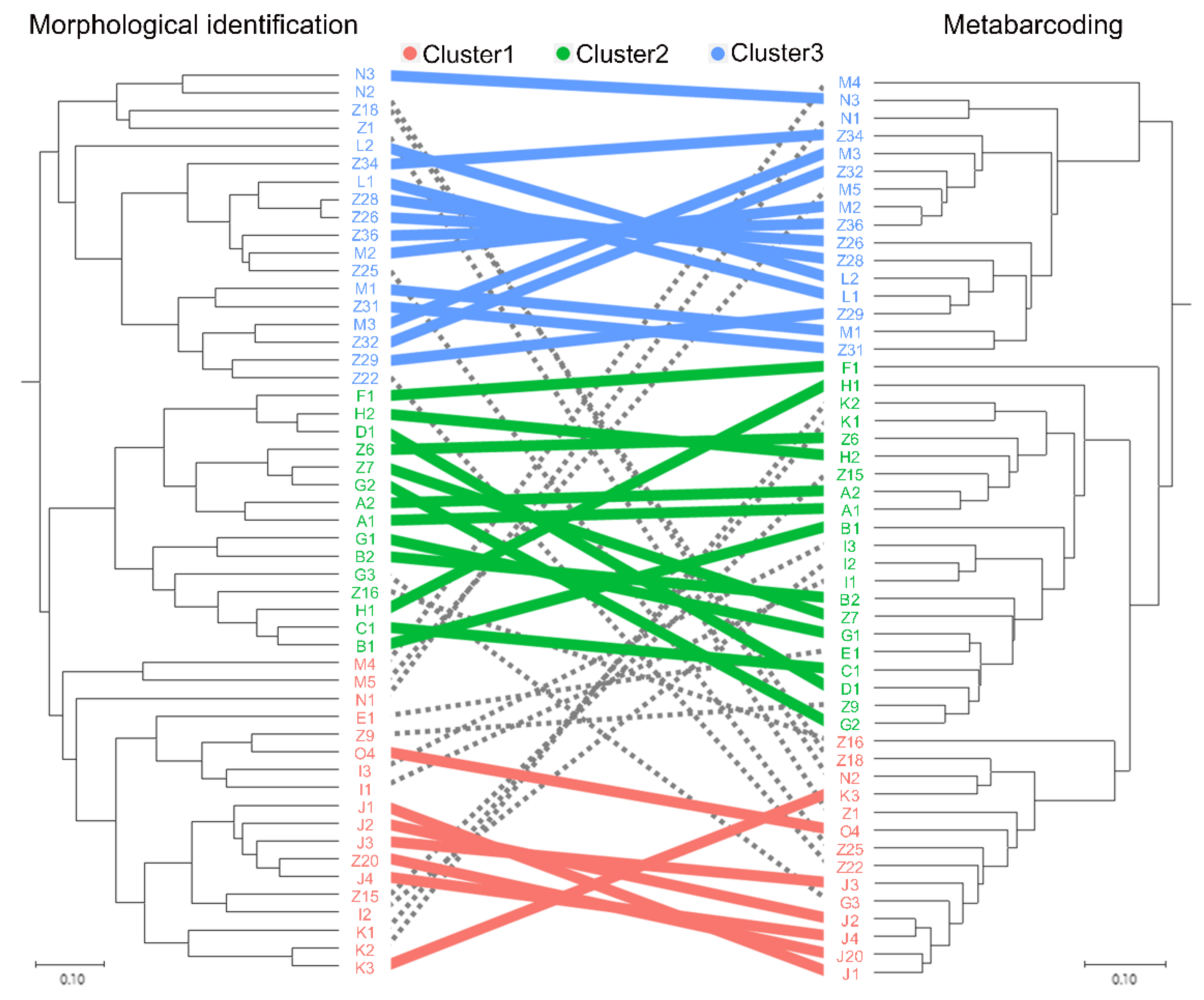
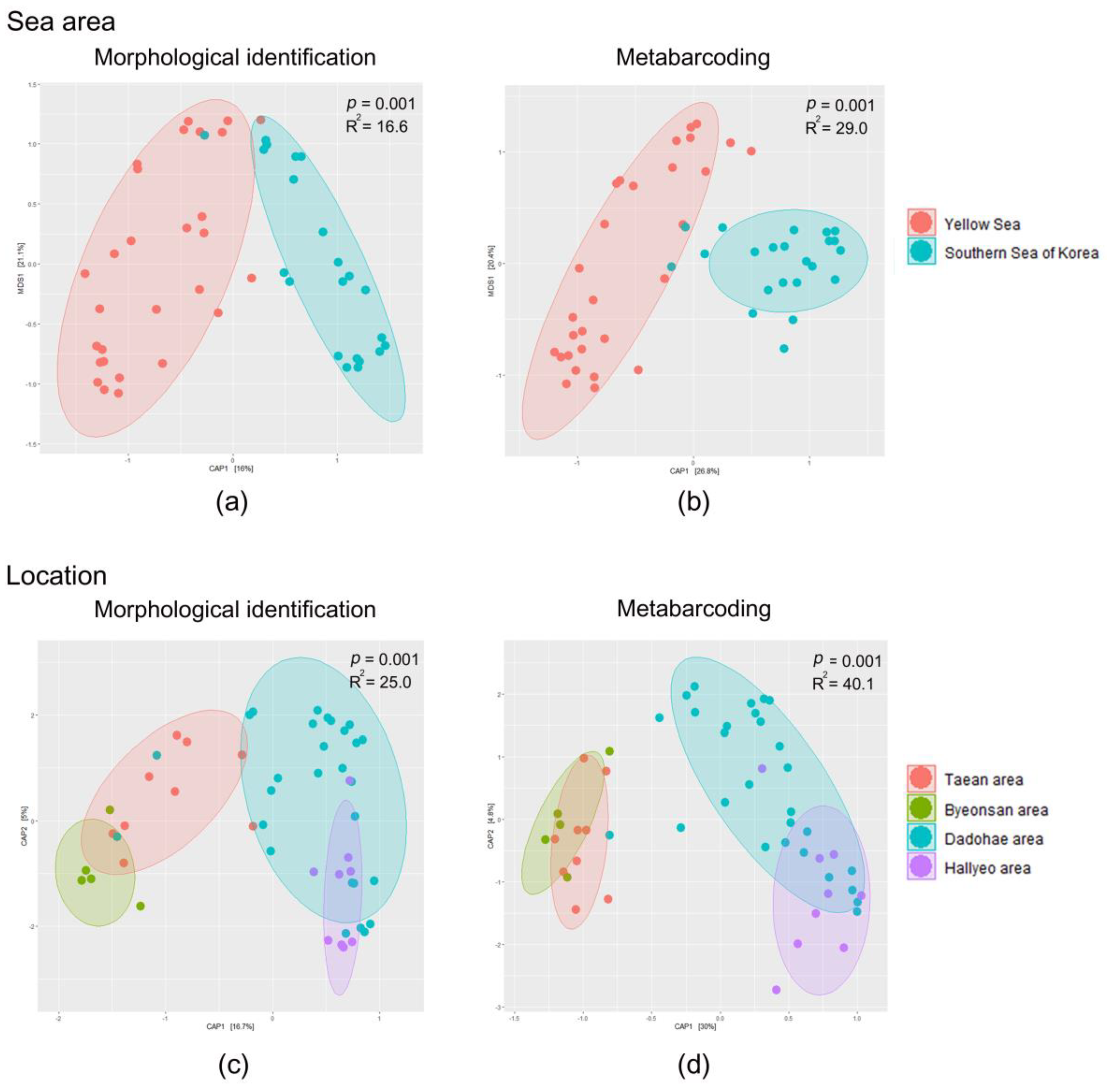
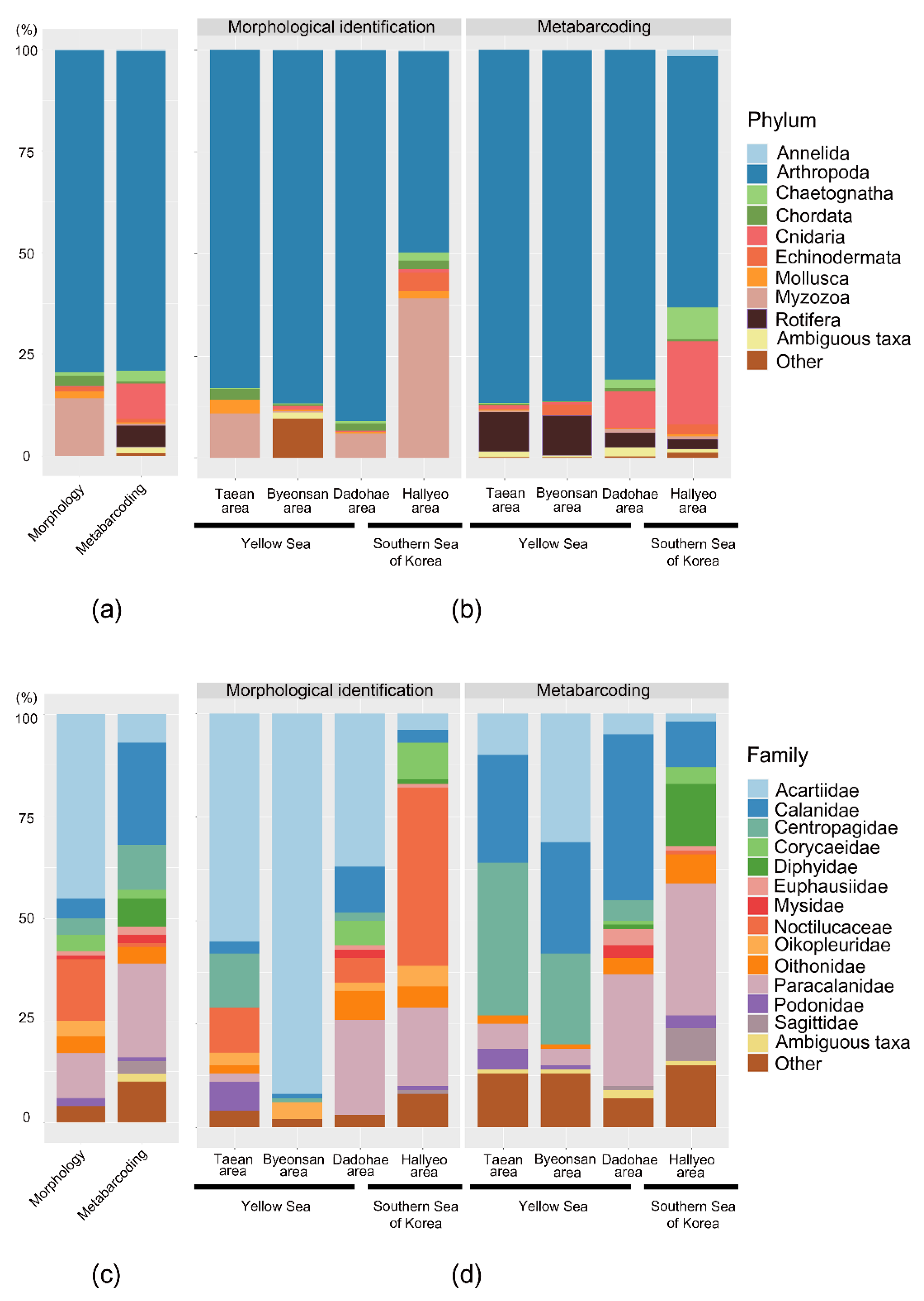
3.3. Mesozooplankton Community Analysis
3.4. Potential Bioindicator Taxa Detection Using Metabarcoding
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison between the Morphological Identification and Metabarcoding Results
4.2. Potential Bioindicator Taxa in the Marine and Coastal National Park Areas of Korea in Spring
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bortone, S.A.; Davis, W.P.; Bundrick, C.M. Morphological and behavioral characters in mosquitofish as potential bioindication of exposure to kraft mill effluent. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1989, 43, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, E.; Soto, J.M.; García, P.C.; López-Lefebre, L.R.; Rivero, R.M.; Ruiz, J.M.; Romero, L. Phenolic and Oxidative Metabolism as Bioindicators of Nitrogen Deficiency in French Bean Plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L. cv. Strike). Plant Biol. 2000, 2, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongers, T.; Ferris, H. Nematode community structure as a bioindicator in environmental monitoring. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1999, 14, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, T.K.; Rawtani, D.; Agrawal, Y.K. Bioindicators: The natural indicator of environmental pollution. Front. Life Sci. 2016, 9, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuklina, I.; Kouba, A.; Kozák, P. Real-time monitoring of water quality using fish and crayfish as bio-indicators: A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 185, 5043–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, A.J. In hot water: Zooplankton and climate change. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, B.A.; Dutkiewicz, S.; Jahn, O.; Follows, M.J. A size-structured food-web model for the global ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 1877–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochon, X.; Bott, N.J.; Smith, K.F.; Wood, S.A. Evaluating Detection Limits of Next-Generation Sequencing for the Surveillance and Monitoring of International Marine Pests. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purushothama, R.; Sayeswara, H.; Goudar, M.A.; Harishkumar, K. Physicochemical profile and zooplankton community composition in Brahmana Kalasi Tank, Sagar, Karnataka, India. Ecoscan 2011, 5, 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Gili, J.M.; Sabatés, A.; Pages, F. Relationship between zooplankton distribution, geographic characteristics and hydrographic patterns off the Catalan coast (Western Mediterranean). Mar. Biol. 1989, 103, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, G. Zooplankton community structure in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea in autumn. Braz. J. Oceanogr. 2015, 63, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Li, S. Marine Planktology; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, C.-H.; Chiu, T.-S.; Shih, C.-T. Copepod diversity and composition as indicators of intrusion of the Kuroshio Branch Current into the Northern Taiwan Strait in Spring 2000. Zool. Stud. 2004, 43, 393–403. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Qi, Y.; Liu, G. Spatial and temporal variations of macro- and mesozooplankton community in the Huanghai Sea (Yellow Sea) and East China Sea in summer and winter. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2011, 30, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casé, M.; Leça, E.E.; Neumann-Leitão, S.; Sant’anna, E.E.; Schwamborn, R.; Junior, A.T.D.M. Plankton community as an indicator of water quality in tropical shrimp culture ponds. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 1343–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thierstein, H.R.; Cortés, M.Y.; Haidar, A. Plankton community behavior on ecological and evolutionary time-scales: When models confront evidence. In Coccolithophores; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 455–479. [Google Scholar]
- Sawaya, N.A.; Djurhuus, A.; Closek, C.J.; Hepner, M.; Olesin, E.; Visser, L.; Kelble, C.; Hubbard, K.; Breitbart, M. Assessing eukaryotic biodiversity in the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary through environmental DNA metabarcoding. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimeier, D.; Lavery, S.D.; Sewell, M.A. Using DNA barcoding and phylogenetics to identify Antarctic invertebrate larvae: Lessons from a large scale study. Mar. Genom. 2010, 3, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusch, D.B.; Halpern, A.L.; Sutton, G.; Heidelberg, K.; Williamson, S.; Yooseph, S.; Wu, D.; Eisen, J.A.; Hoffman, J.M.; Remington, K.; et al. The Sorcerer II Global Ocean Sampling Expedition: Northwest Atlantic through Eastern Tropical Pacific. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, N.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N.; Owens, S.M.; Betley, J.; Fraser, L.; Bauer, M.; et al. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucklin, A.; Lindeque, P.K.; Rodriguez-Ezpeleta, N.; Albaina, A.; Lehtiniemi, M. Metabarcoding of marine zooplankton: Prospects, progress and pitfalls. J. Plankton Res. 2016, 38, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormontt, E.; Van Dijk, K.-J.; Bell, K.L.; Biffin, E.; Breed, M.F.; Byrne, M.; Caddy-Retalic, S.; Encinas-Viso, F.; Nevill, P.G.; Shapcott, A.; et al. Advancing DNA Barcoding and Metabarcoding Applications for Plants Requires Systematic Analysis of Herbarium Collections—An Australian Perspective. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taberlet, P.; Coissac, E.; Pompanon, F.; Brochmann, C.; Willerslev, E. Towards next-generation biodiversity assessment using DNA metabarcoding. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 2045–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamowicz, S.J.; Boatwright, J.S.; Chain, F.; Fisher, B.L.; Hogg, I.D.; Leese, F.; Lijtmaer, D.A.; Mwale, M.; Naaum, A.M.; Pochon, X.; et al. Trends in DNA barcoding and metabarcoding. Genome 2019, 62, v–viii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrana, J.M.; Miyake, Y.; Gamboa, M.; Watanabe, K. Comparison of DNA metabarcoding and morphological identification for stream macroinvertebrate biodiversity assessment and monitoring. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-K.; Park, K.; Jo, H.; Kwak, I.S. Comparison of Water Sampling between Environmental DNA Metabarcoding and Conventional Microscopic Identification: A Case Study in Gwangyang Bay, South Korea. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clare, E.L.; Chain, F.J.J.; Littlefair, J.E.; Cristescu, M.E. The effects of parameter choice on defining molecular operational taxonomic units and resulting ecological analyses of metabarcoding data. Genome 2016, 59, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, J.; Glöckner, G.; Jahn, R.; Enke, N.; Gemeinholzer, B. Metabarcoding vs. morphological identification to assess diatom diversity in environmental studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2014, 15, 526–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowart, D.A.; Pinheiro, M.; Mouchel, O.; Maguer, M.; Grall, J.; Miné, J.; Arnaud-Haond, S. Metabarcoding Is Powerful yet Still Blind: A Comparative Analysis of Morphological and Molecular Surveys of Seagrass Communities. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korea National Park Service. Available online: http://www.knps.or.kr (accessed on 30 March 2020).
- Go, W.-J.; Kim, S.-W.; Jang, L.-H. Relationship between ocean-meteorological factors and snowfall in the western coastal region of Korea in winter. J. Korean Soc. Mar. Environ. Saf. 2009, 15, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, P.; Gao, S.; Bokuniewicz, H. Net sediment transport patterns over the Bohai Strait based on grain size trend analysis. Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 60, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, I.-C.; Hyun, K.-H. Seasonal variation of water mass distributions in the eastern Yellow Sea and the Yellow Sea Warm Current. J. Korean Soc. Oceanogr. 1998, 33, 41–52. [Google Scholar]
- Albaina, A.; Aguirre, M.; Abad, D.; Santos, M.; Estonba, A. 18S rRNA V9 metabarcoding for diet characterization: A critical evaluation with two sympatric zooplanktivorous fish species. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 1809–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral-Zettler, L.A.; McCliment, E.A.; Ducklow, H.W.; Huse, S.M. A method for studying protistan diversity using massively parallel sequencing of V9 hypervariable regions of small-subunit ribosomal RNA genes. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearman, J.K.; El-Sherbiny, M.M.; Al-Aidaroos, A.M.; Irigoien, X.; Lanzén, A. Zooplankton diversity across three Red Sea reefs using pyrosequencing. Front. Mar. Sci. 2014, 1, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vargas, C.; Audic, S.; Henry, N.; Decelle, J.; Mahé, F.; Logares, R.; Lara, E.; Berney, C.; Le Bescot, N.; Probert, I.; et al. Eukaryotic plankton diversity in the sunlit ocean. Science 2015, 348, 1261605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanni, S.; Stanković, D.; Borme, D.; De Olazabal, A.; Juretić, T.; Pallavicini, A.; Tirelli, V. Multi-marker metabarcoding approach to study mesozooplankton at basin scale. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abad, D.; Albaina, A.; Aguirre, M.; Estonba, A. 18S V9 metabarcoding correctly depicts plankton estuarine community drivers. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 584, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djurhuus, A.; Pitz, K.; Sawaya, N.A.; Rojas-Márquez, J.; Michaud, B.; Montes, E.; Muller-Karger, F.; Breitbart, M. Evaluation of marine zooplankton community structure through environmental DNA metabarcoding. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2018, 16, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Kobert, K.; Flouri, T.; Stamatakis, A. PEAR: A fast and accurate Illumina Paired-End reAd mergeR. Bioinformatics 2013, 30, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Xiong, J.; Yu, Y. Taxonomic Resolutions Based on 18S rRNA Genes: A Case Study of Subclass Copepoda. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- McMurdie, P.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dray, S.; Dufour, A.B.; Chessel, D. The ade4 package-II: Two-table and K-table methods. R News 2007, 7, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, J.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; O’Hara, B.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Oksanen, M.J.; Suggests, M. The vegan package. Commun. Ecol. Package 2007, 10, 631–637. [Google Scholar]
- Pairwise.Adonis: Pairwise Multilevel Comparison Using Adonis. R Package Version 0.0.1. Available online: https://github.com/pmartinezarbizu/pairwiseAdonis (accessed on 16 October 2019).
- Package ‘dunn. test’. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/dunn.test/index.html (accessed on 27 October 2017).
- Package ‘rcompanion’. Available online: http://rcompanion.org/handbook/ (accessed on 24 July 2017).
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabaldón, C.; Fontaneto, D.; Carmona, M.J.; Montero-Pau, J.; Serra, M. Ecological differentiation in cryptic rotifer species: What we can learn from the Brachionus plicatilis complex. Hydrobiologia 2016, 796, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.-J.; Krogh, P.H.; Jeong, H.-G.; Joo, G.-J.; Kwak, I.-S.; Hwang, S.-J.; Gim, J.-S.; Chang, K.-H.; Jo, H. Pretreatment Method for DNA Barcoding to Analyze Gut Contents of Rotifers. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aylagas, E.; Borja, Á.; Irigoien, X.; Rodriguez-Ezpeleta, N. Benchmarking DNA Metabarcoding for Biodiversity-Based Monitoring and Assessment. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiebelhut, L.M.; Abboud, S.S.; Daglio, L.E.G.; Swift, H.F.; Dawson, M.N. A comparison of DNA extraction methods for high-throughput DNA analyses. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 17, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, P.D.; Hunter, E.; Pinnegar, J.K.; Creer, S.; Davies, R.G.; Taylor, M.I. How quantitative is metabarcoding: A meta-analytical approach. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 28, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Li, M.; Lin, S. An Improved DNA Extraction Method for Efficient and Quantitative Recovery of Phytoplankton Diversity in Natural Assemblages. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrell, Y.J.; Miralles, L.; Huu, H.D.; Mohammed-Geba, K.; Garcia-Vazquez, E. DNA in a bottle—Rapid metabarcoding survey for early alerts of invasive species in ports. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, H.; Fukaya, K.; Oka, S.-I.; Sato, K.; Kondoh, M.; Miya, M. Evaluation of detection probabilities at the water-filtering and initial PCR steps in environmental DNA metabarcoding using a multispecies site occupancy model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andruszkiewicz, E.A.; Starks, H.A.; Chavez, F.P.; Sassoubre, L.M.; Block, B.A.; Boehm, A.B. Biomonitoring of marine vertebrates in Monterey Bay using eDNA metabarcoding. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacoursière-Roussel, A.; Howland, K.; Normandeau, E.; Grey, E.K.; Archambault, P.; Deiner, K.; Lodge, D.M.; Hernandez, C.; LeDuc, N.; Bernatchez, L. eDNA metabarcoding as a new surveillance approach for coastal Arctic biodiversity. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 7763–7777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wurzbacher, C.; Attermeyer, K.; Kettner, M.T.; Flintrop, C.; Warthmann, N.; Hilt, S.; Grossart, H.; Monaghan, M.T. DNA metabarcoding of unfractionated water samples relates phyto-, zoo- and bacterioplankton dynamics and reveals a single-taxon bacterial bloom. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2017, 9, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, T.; Hirai, J.; Tamura, S.; Takahashi, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Ishihara, T.; Tawa, A.; Morimoto, H.; Ohshimo, S. Diet composition and feeding habits of larval Pacific bluefin tuna Thunnus orientalis in the Sea of Japan: Integrated morphological and metagenetic analysis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 583, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Huang, X.; Chen, Y.; Fu, R.; Du, X.; Chen, X.; Zhan, A. Zooplankton biodiversity monitoring in polluted freshwater ecosystems: A technical review. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2020, 1, 100008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Kim, S.; Lee, B.; Noh, H.; Jeong, J.; Song, S.; Kim, T. Hydrographical characteristics and distribution of mesozooplankton in the Chilbal is. and the Yeoseo is. J. Nation. Park Res. 2012, 3, 64–74. [Google Scholar]
- Oscar, K. Satellite observations and the annual cycle of surface circulation in the Yellow Sea, East China Sea and Korea Strait. La Mer 1982, 20, 210–222. [Google Scholar]
- Lie, H.-J.; Cho, C.-H. Seasonal circulation patterns of the Yellow and East China Seas derived from satellite-tracked drifter trajectories and hydrographic observations. Prog. Oceanogr. 2016, 146, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, H.M.P. Distribution of paracalanidae species (Copepoda, Crustacea) in the continental shelf off Sergipe and Alagoas States, Northeast Brazil. Braz. J. Oceanogr. 2006, 54, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kang, J.-H.; Kim, W.-S. Spring dominant copepods and their distribution pattern in the yellow sea. Ocean Sci. J. 2008, 43, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.-C.; Baek, S.-H.; Jang, P.-G.; Lee, W.-J.; Shin, K.-S. Patterns of Zooplankton Distribution as Related to Water Masses in the Korea Strait during Winter and Summer. Ocean Polar Res. 2012, 34, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.-S. Redescription of Paracalanus parvus and P. indicus (Copepoda: Paracalanidae) recorded in the Korean waters. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1996, 29, 409–413. [Google Scholar]
- Blackett, M.; Licandro, P.; Coombs, S.H.; Lucas, C.H. Long-term variability of the siphonophores Muggiaea atlantica and M. kochi in the Western English Channel. Prog. Oceanogr. 2014, 128, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackie, G.; Pugh, P.; Purcell, J. Siphonophore Biology. In Advances in Marine Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1988; Volume 24, pp. 97–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buecher, E. Appearance of Chelophyes appendiculata and Abylopsis tetragona (Cnidaria, Siphonophora) in the Bay of Villefranche, northwestern Mediterranean. J. Sea Res. 1999, 41, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, M.; Lindsay, D.J. Diversity and distribution of the Siphonophora (Cnidaria) in Sagami Bay, Japan, and their association with tropical and subarctic water masses. J. Oceanogr. 2013, 69, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noblezada, M.M.P.; Campos, W.L. Spatial distribution of chaetognaths off the northern Bicol Shelf, Philippines (Pacific coast). ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.B.; Terazaki, M. Species composition and depth distribution of chaetognaths in a Kuroshio warm-core ring and Oyashio water. J. Plankton Res. 2003, 25, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaguchi, H.; Fujiki, T.; Kikuchi, T.; Kuwahara, V.S.; Toda, T. Relationship between the bloom of Noctiluca scintillans and environmental factors in the coastal waters of Sagami Bay, Japan. J. Plankton Res. 2006, 28, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dela-Cruz, J.; Middleton, J.H.; Suthers, I. Population growth and transport of the red tide dinoflagellate, Noctiluca scintillans, in the coastal waters off Sydney Australia, using cell diameter as a tracer. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 656–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-H. Distributional Characteristics and Carrying Capacity of the Potentially Risky Species Noctiluca scintillans at International Korean Seaports. Ocean Polar Res. 2010, 32, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.H.; Kim, D.; Choi, H.-W.; Kim, Y.-O. Hydrographical and Bio-ecological Characteristics of Heterotrophic Red Tide Dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans in Semi-enclosed Gwangyang Bay, Korea. Environ. Biol. Res. 2013, 31, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.-K.; Jeong, J.-H.; Nam, E.-J.; Jeong, K.-M.; Lee, S.-W.; Myung, C.-S. Zooplankton Community and Distribution in Relation to Water Quality in the Saemangeum Area, Korea: Change in Zooplankton Community by the Construction of Sea Dyke. Ocean Polar Res. 2006, 28, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, C.-R.; Kang, H.-K.; Noh, J.-H. Temporal and Spatial Variation of Zooplankton Community Structure Post Construction of Saemangeum Dyke. Ocean Polar Res. 2009, 31, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Xu, Z.; Zhuang, P. The relation between distribution of zooplankton and salinity in the Changjiang Estuary. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2008, 26, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paturej, E.; Gutkowska, A. The effect of salinity levels on the structure of zooplankton communities. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2015, 67, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, W.D. Salinity as a determinant of the structure of biological communities in salt lakes. Hydrobiologia 1998, 381, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.E.; Remfert, J.L.; Gelembiuk, G.W. Evolution of Physiological Tolerance and Performance During Freshwater Invasions. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2003, 43, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soh, H.Y.; Suh, H.-L. A new species of Acartia (Copepoda, Calanoida) from the Yellow Sea. J. Plankton Res. 2000, 22, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, A.S.Y.; Seo, M.-H.; Shin, Y.-S.; Soh, H.-Y. Seasonal Variation of Mesozooplankton Communities in the Semi-enclosed Muan Bay, Korea. Ocean Polar Res. 2012, 34, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, H. Zooplankton investigations in Shijiki bay [Japan], 2: Zooplankton communities from September 1975 to April 1976, with special reference to distributional characteristics of inlet copepods. Bull. Seikai Reg. Fish. Res. Lab. 1982, 58, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Shim, M.-B.; Choi, J.-K. A review on the microstructures and taxonomy of the Acartia bifilosa (Crustacea: Copepoda) in Kyeonggi Bay, Yellow Sea. Ocean Sci. J. 1996, 31, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Põllupüü, M.; Simm, M.; Ojaveer, H. Life history and population dynamics of the marine cladoceran Pleopis polyphemoides (Leuckart) (Cladocera, Crustacea) in a shallow temperate Parnu Bay (Baltic Sea). J. Plankton Res. 2010, 32, 1459–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segers, H. Global diversity of rotifers (Rotifera) in freshwater. In Freshwater Animal Diversity Assessment; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 49–59. [Google Scholar]

| Sea Area/Location | Water Temperature | Salinity | Chlorophyll a | Depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yellow Sea | 13.25 (1.94) | 32.35 (0.80) | 1.77 (1.28) | 24.86 (18.44) |
| Southern Sea of Korea | 17.39 (1.86) | 33.30 (0.66) | 0.87 (0.47) | 25.00 (18.03) |
| Taean area | 12.13 (1.80) | 31.79 (0.08) | 1.57 (0.80) | 21.73 (20.12) |
| Byeonsan area | 15.56 (0.99) | 31.64 (0.17) | 3.31 (1.36) | 13.16 (3.89) |
| Dadohae area | 14.94 (2.64) | 33.05 (0.77) | 1.18 (0.95) | 26.74 (16.65) |
| Hallyeo area | 17.94 (1.31) | 33.44 (0.39) | 0.84 (0.29) | 29.0 (23.78) |
| Variables | Morphological Identification | Metabarcoding | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sea area | Yellow Sea | 55 | 629 |
| Southern Sea of Korea | 73 | 728 | |
| Location | Taean area | 37 | 336 |
| Byeonsan area | 30 | 244 | |
| Dadohae area | 57 | 730 | |
| Hallyeo area | 61 | 522 | |
| Taxonomic rank | Phylum | 10 | 20 |
| Class | 18 | 38 | |
| Order | 27 | 86 | |
| Family | 36 | 187 | |
| Genus | 43 | 230 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.; Lee, C.-R.; Lee, S.-k.; Oh, S.-Y.; Kim, W. Biodiversity and Community Structure of Mesozooplankton in the Marine and Coastal National Park Areas of Korea. Diversity 2020, 12, 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12060233
Kim H, Lee C-R, Lee S-k, Oh S-Y, Kim W. Biodiversity and Community Structure of Mesozooplankton in the Marine and Coastal National Park Areas of Korea. Diversity. 2020; 12(6):233. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12060233
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Heesoo, Chang-Rae Lee, Sang-kyu Lee, Seung-Yoon Oh, and Won Kim. 2020. "Biodiversity and Community Structure of Mesozooplankton in the Marine and Coastal National Park Areas of Korea" Diversity 12, no. 6: 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12060233
APA StyleKim, H., Lee, C.-R., Lee, S.-k., Oh, S.-Y., & Kim, W. (2020). Biodiversity and Community Structure of Mesozooplankton in the Marine and Coastal National Park Areas of Korea. Diversity, 12(6), 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12060233






