New Intranuclear Symbiotic Bacteria from Macronucleus of Paramecium putrinum—“Candidatus Gortzia Yakutica”
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Identification of Paramecium
2.2. Phenotypic Characterization of the Symbionts
2.3. Purification and Sequencing of Symbionts
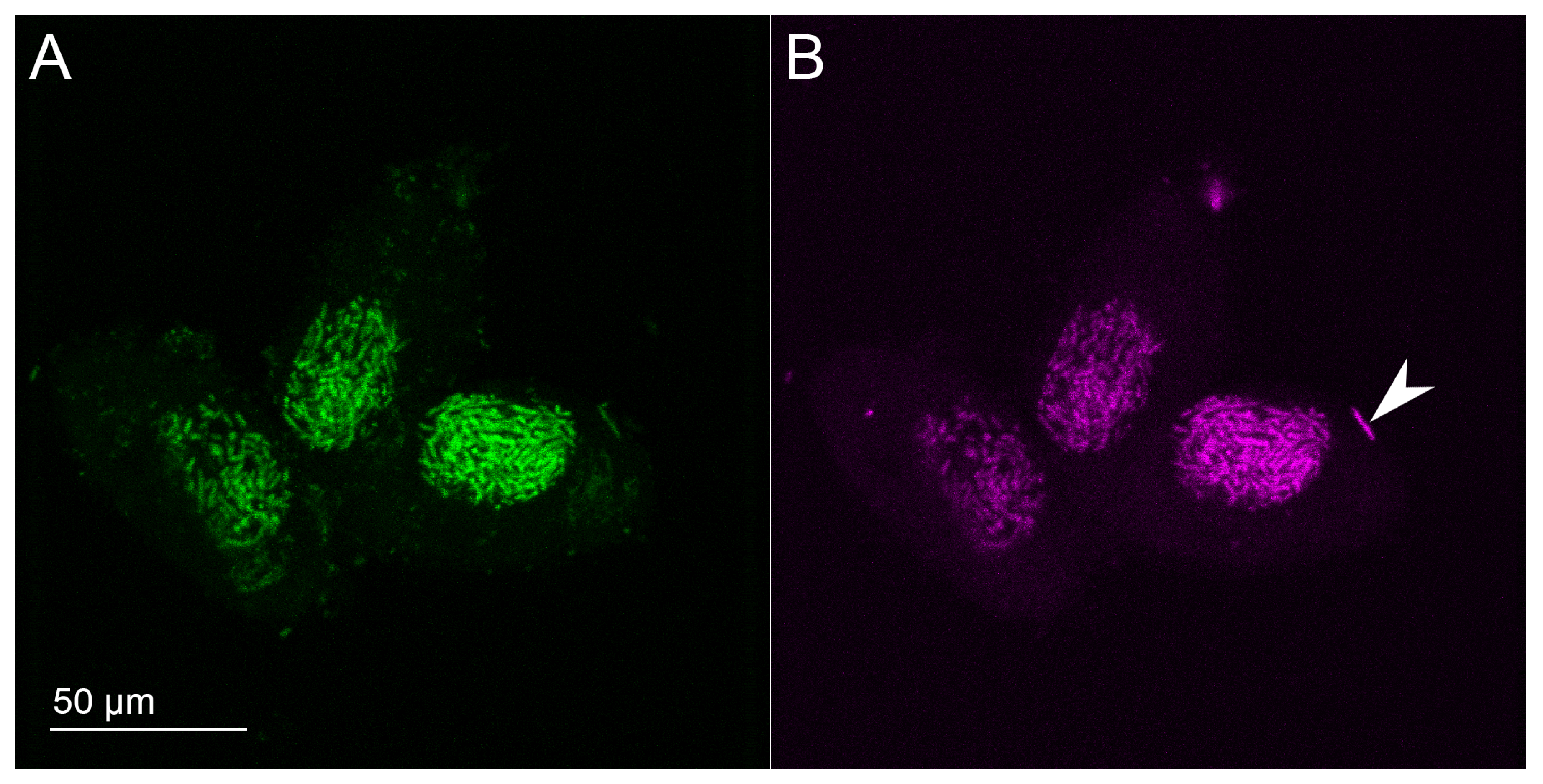
2.4. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH)
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
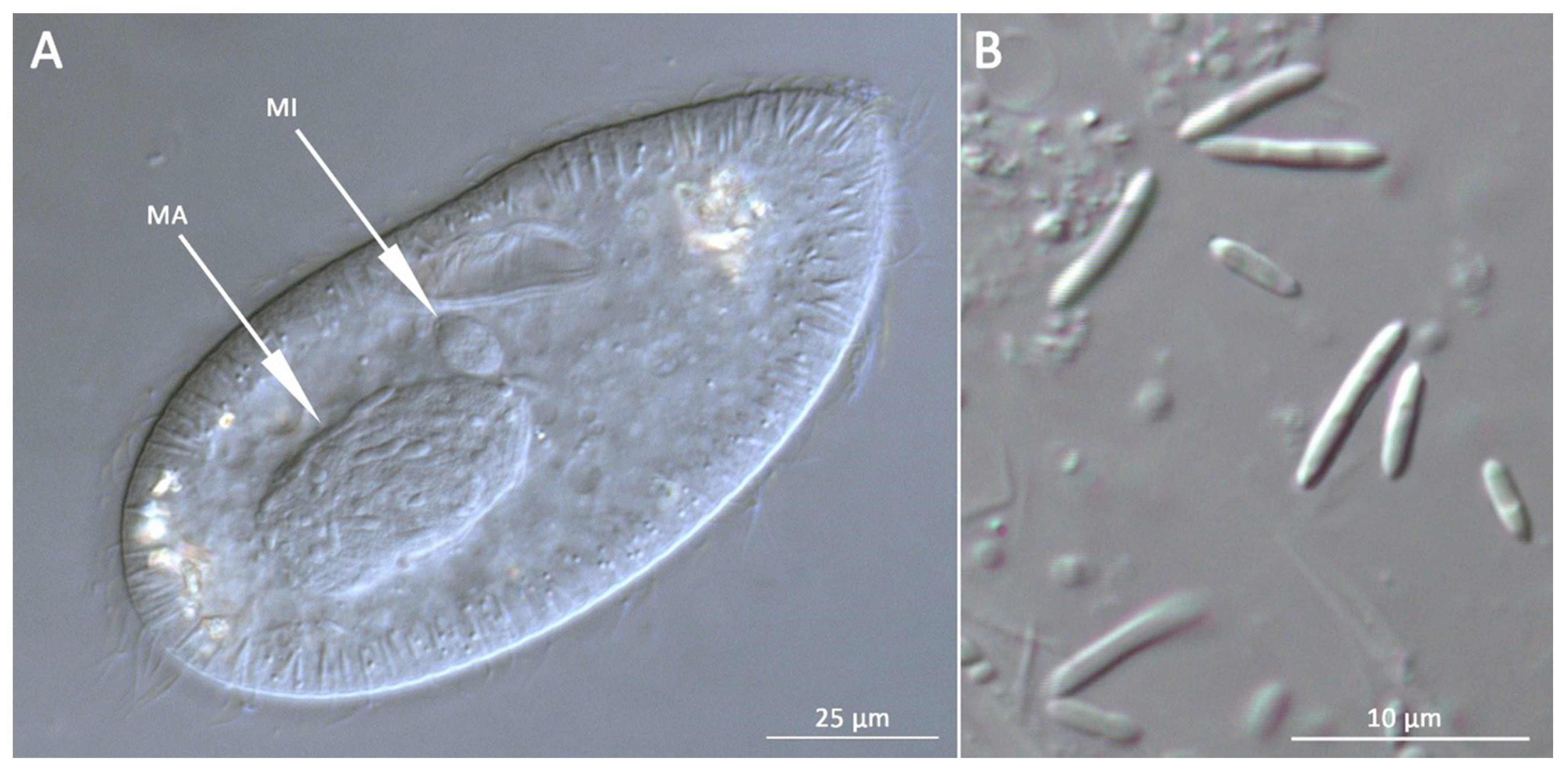
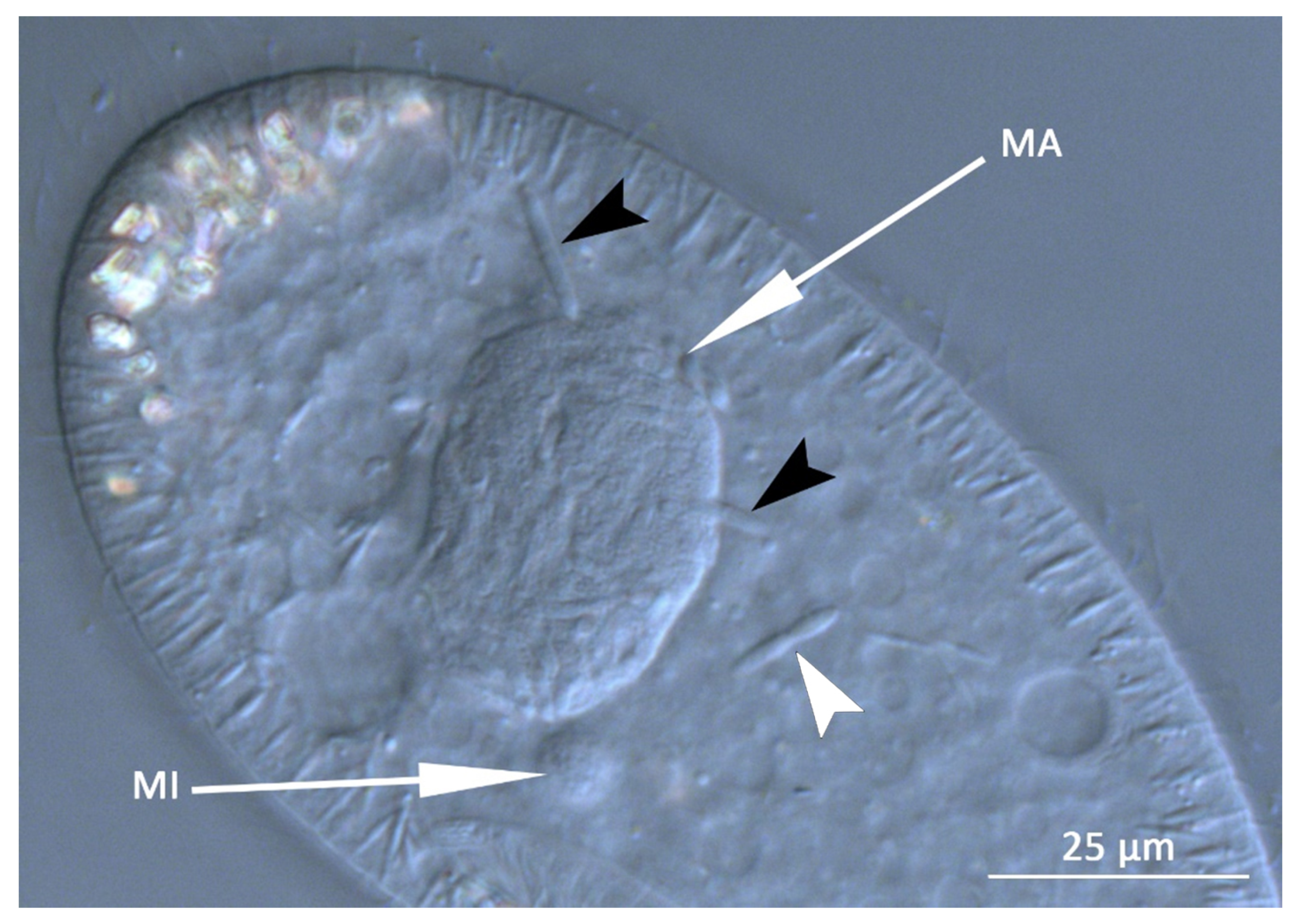
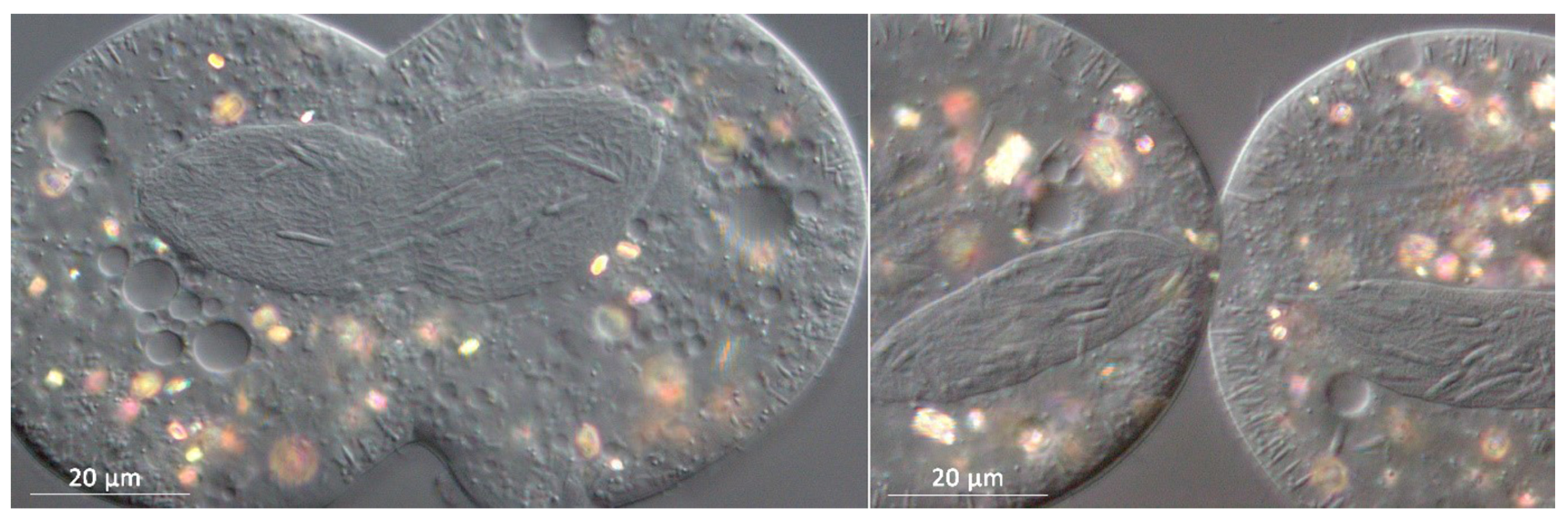
3.1. Bacterial Morphology and Localization
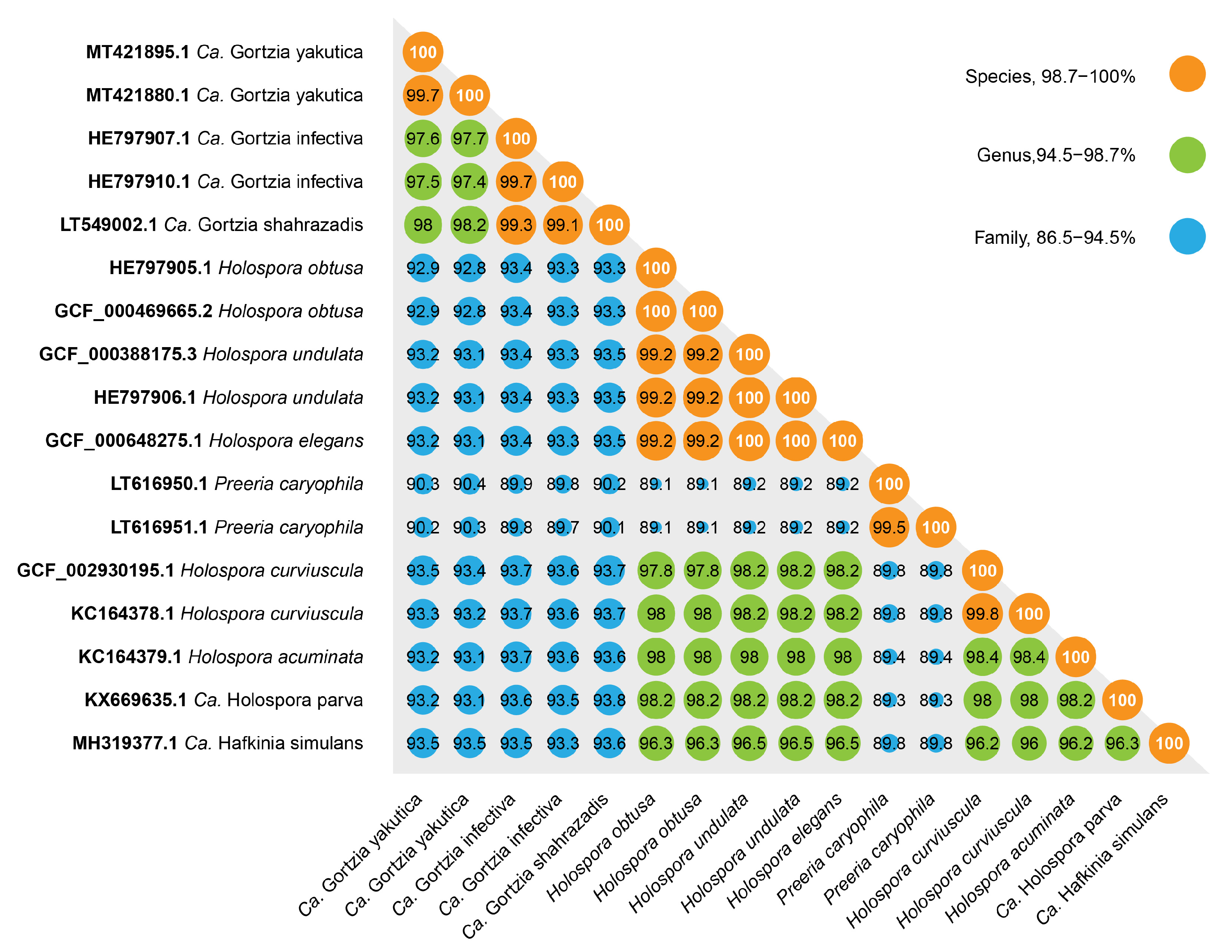
3.1.1. Molecular Characterization
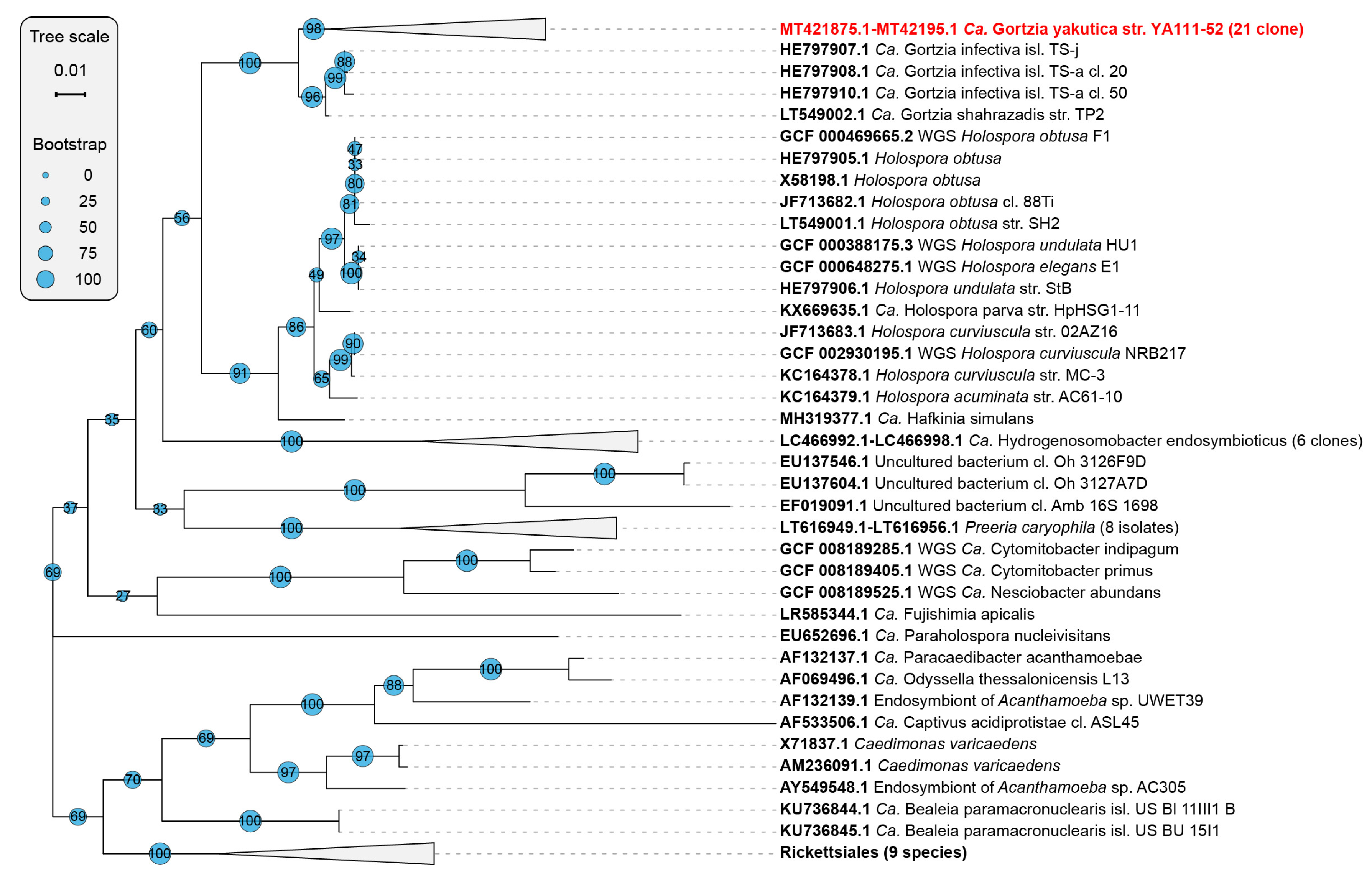
3.1.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Description of “Candidatus Gortzia yakutica” sp. nov.
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HLB | Holospora-like bacteria |
| RF | reproductive form |
| IF | infectious form |
| Ma | macronucleus |
| Mi | micronucleus |
References
- Görtz, H.D.; Fokin, S.I. Diversity of Endosymbiotic Bacteria in Paramecium. In Endosymbionts in Paramecium; Fujishima, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germnay, 2009; Volume 12, pp. 131–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, M. Infection and Maintenance of Holospora Species in Paramecium caudatum. In Endosymbionts in Paramecium; Fujishima, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germnay, 2009; Volume 12, pp. 201–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preer, J.R.; Preer, L.B.; Jurand, A. Kappa and Other Endosymbionts in Paramecium aurelia. In Bacteriological Reviews; American Society for Microbiology USA: Washington, DC, USA, 1974; Volume 38. [Google Scholar]
- Gortz, H.D. Symbiotic Associations Between Ciliates and Prokaryotes. In The Prokaryotes; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 364–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görtz, H.D.; Wiemann, M. Route of infection of the bacteria Holospora elegans and Holospora obtusa into the nuclei of Paramecium caudatum. Eur. J. Protistol. 1989, 24, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrity, G. (Ed.) Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology; The Proteobacteria; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Wiemann, M.; Görtz, H.D. Release of the endonucleobiotic bacterium Holospora elegans from its host cell Paramecium caudatum. Eur. J. Protistol. 1989, 25, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokin, S.I.; Brigge, T.; Brenner, J.; Gortz, H.D. Holospora species infecting the nuclei of Paramecium appear to belong into two groups of bacteria. Eur. J. Protistol. 1996, 32, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzoni, O.; Fokin, S.I.; Lebedeva, N.; Migunova, A.; Petroni, G.; Potekhin, A. Rare Freshwater Ciliate Paramecium chlorelligerum Kahl, 1935 and Its Macronuclear Symbiotic Bacterium “Candidatus Holospora parva”. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potekhin, A.; Schweikert, M.; Nekrasova, I.; Vitali, V.; Schwarzer, S.; Anikina, A.; Kaltz, O.; Petroni, G.; Schrallhammer, M. Complex life cycle, broad host range and adaptation strategy of the intranuclear Paramecium symbiont Preeria caryophila comb. nov. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscaro, V.; Fokin, S.I.; Schrallhammer, M.; Schweikert, M.; Petroni, G. Revised Systematics of Holospora-Like Bacteria and Characterization of “Candidatus Gortzia infectiva”, a Novel Macronuclear Symbiont of Paramecium jenningsi. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, V.; Fokin, S.I.; Castelli, M.; Basuri, C.K.; Nitla, V.; Verni, F.; Sandeep, B.V.; Kalavati, C.; Petroni, G. “Candidatus Gortzia shahrazadis”, a Novel Endosymbiont of Paramecium multimicronucleatum and a Revision of the Biogeographical Distribution of Holospora-Like Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautian, M.S.; Wackerow-Kouzova, N.D. Phylogenetic placement of two previously described intranuclear bacteria from the ciliate Paramecium bursaria (Protozoa, Ciliophora): ‘Holospora acuminata’ and ’Holospora curviuscula’. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 1930–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokin, S.I.; Serra, V.; Ferrantini, F.; Modeo, L.; Petroni, G. “Candidatus Hafkinia simulans” gen. nov., sp. nov., a Novel Holospora-Like Bacterium from the Macronucleus of the Rare Brackish Water Ciliate Frontonia salmastra (Oligohymenophorea, Ciliophora): Multidisciplinary Characterization of the New Endosymbiont and Its Host. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 77, 1092–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarza, P.; Yilmaz, P.; Pruesse, E.; Glöckner, F.O.; Ludwig, W.; Schleifer, K.H.; Whitman, W.B.; Euzéby, J.; Amann, R.; Rosselló-Móra, R. Uniting the classification of cultured and uncultured bacteria and archaea using 16S rRNA gene sequences. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonneborn, T. Chapter 12 Methods in Paramecium Research. In Methods in Cell Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1970; Volume 4, pp. 241–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichterman, R. The Biology of Paramecium; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Fokin, S.I. Paramecium genus: Biodiversity, some morphological features and the key to the main morphospecies discrimination. Protistology 2010, 6, 227–235. [Google Scholar]
- Tarcz, S.; Rautian, M.; Potekhin, A.; Sawka, N.; Beliavskaya, A.; Kiselev, A.; Nekrasova, I.; Przyboś, E. Paramecium putrinum (Ciliophora, Protozoa): The first insight into the variation of two DNA fragments—Molecular support for the existence of cryptic species. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2014, 73, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiselev, A. Genetic, Physiological and Morphological Diversity of Paramecium Putrinum. Ph.D. Thesis, Saint Petersburg State University, St Petersburg, Russia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Garushyants, S.K.; Beliavskaia, A.Y.; Malko, D.B.; Logacheva, M.D.; Rautian, M.S.; Gelfand, M.S. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Holospora spp., Intranuclear Symbionts of Paramecia. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, D. 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In Nucleic acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics; Modern Microbiological Methods; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, R.; Springer, N.; Ludwig, W.; Görtz, H.D.; Schleifer, K.H. Identification in situ and phylogeny of uncultured bacterial endosymbionts. Nature 1991, 351, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowiol mounting medium. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2006. [CrossRef]
- Benson, D.A.; Cavanaugh, M.; Clark, K.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J.; Sayers, E.W. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D36–D42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coordinators, N.R. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 46, D8–D13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinlan, A.R.; Hall, I.M. BEDTools: A flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawrocki, E.P. Structural RNA Homology Search and Alignment Using Covariance Models. Ph.D. Thesis, Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Criscuolo, A.; Gribaldo, S. BMGE (Block Mapping and Gathering with Entropy): A new software for selection of phylogenetic informative regions from multiple sequence alignments. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Darriba, D.; Posada, D.; Kozlov, A.M.; Stamatakis, A.; Morel, B.; Flouri, T. ModelTest-NG: A New and Scalable Tool for the Selection of DNA and Protein Evolutionary Models. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 37, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v4: Recent updates and new developments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W256–W259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference and Model Choice across a Large Model Space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huson, D.H.; Richter, D.C.; Rausch, C.; Dezulian, T.; Franz, M.; Rupp, R. Dendroscope: An interactive viewer for large phylogenetic trees. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rautian, M.S.; Skoblo, I.I.; Lebedeva, N.A.; Ossipov, D.V. Genetics of symbiotic interactions between Paramecium bursaria and the intranuclear bacterium Holospora acuminata, natural genetic variability by infectivity and susceptibility. Acta Protozool. 1993, 32, 165–173. [Google Scholar]
- Fokin, S.; Brigge, T.; Görtz, H. An infectious bacterium inhabiting the macronucleus of Paramecium putrinum. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1999, 46, 11a. [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita, K.; Yamada, T.; Kawahara, Y.; Narihiro, T.; Ito, M.; Kamagata, Y.; Shinzato, N. Tripartite Symbiosis of an Anaerobic Scuticociliate with Two Hydrogenosome-Associated Endosymbionts, a Holospora -Related Alphaproteobacterium and a Methanogenic Archaeon. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e00854-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Větrovský, T.; Baldrian, P. The Variability of the 16S rRNA Gene in Bacterial Genomes and Its Consequences for Bacterial Community Analyses. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, C.; Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Phillippy, A.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Aluru, S. High throughput ANI analysis of 90K prokaryotic genomes reveals clear species boundaries. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, M.A.; Gelfand, M.S. Pangenomic Definition of Prokaryotic Species and the Phylogenetic Structure of Prochlorococcus spp. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beliavskaia, A.Y.; Predeus, A.V.; Garushyants, S.K.; Logacheva, M.D.; Gong, J.; Zou, S.; Gelfand, M.S.; Rautian, M.S. New Intranuclear Symbiotic Bacteria from Macronucleus of Paramecium putrinum—“Candidatus Gortzia Yakutica”. Diversity 2020, 12, 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12050198
Beliavskaia AY, Predeus AV, Garushyants SK, Logacheva MD, Gong J, Zou S, Gelfand MS, Rautian MS. New Intranuclear Symbiotic Bacteria from Macronucleus of Paramecium putrinum—“Candidatus Gortzia Yakutica”. Diversity. 2020; 12(5):198. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12050198
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeliavskaia, Alexandra Y., Alexander V. Predeus, Sofya K. Garushyants, Maria D. Logacheva, Jun Gong, Songbao Zou, Mikhail S. Gelfand, and Maria S. Rautian. 2020. "New Intranuclear Symbiotic Bacteria from Macronucleus of Paramecium putrinum—“Candidatus Gortzia Yakutica”" Diversity 12, no. 5: 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12050198
APA StyleBeliavskaia, A. Y., Predeus, A. V., Garushyants, S. K., Logacheva, M. D., Gong, J., Zou, S., Gelfand, M. S., & Rautian, M. S. (2020). New Intranuclear Symbiotic Bacteria from Macronucleus of Paramecium putrinum—“Candidatus Gortzia Yakutica”. Diversity, 12(5), 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12050198




