How Roads Affect the Spatial Use of the Guanaco in a South American Protected Area: Human Connectivity vs Animal Welfare
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
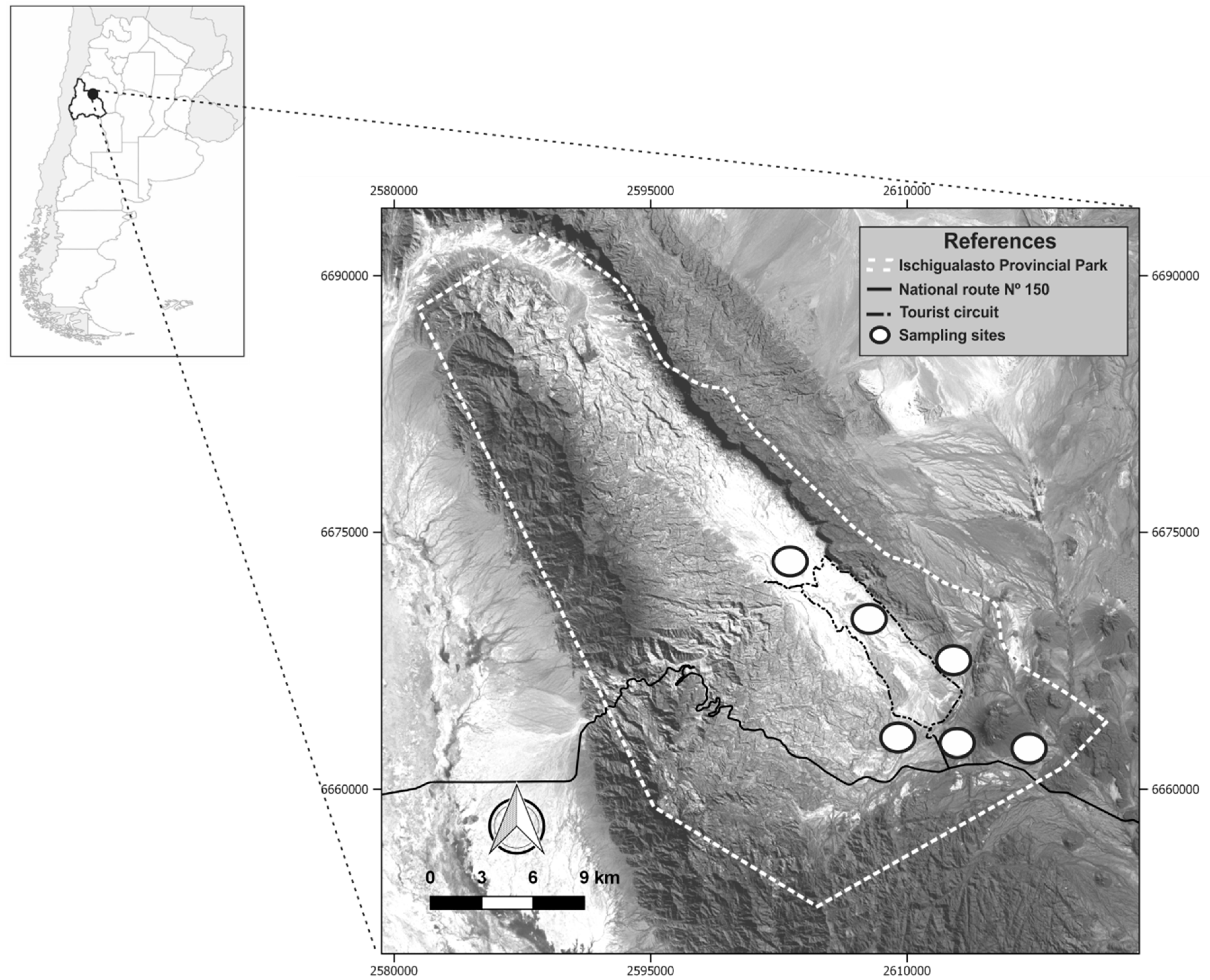
2.1. Study area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
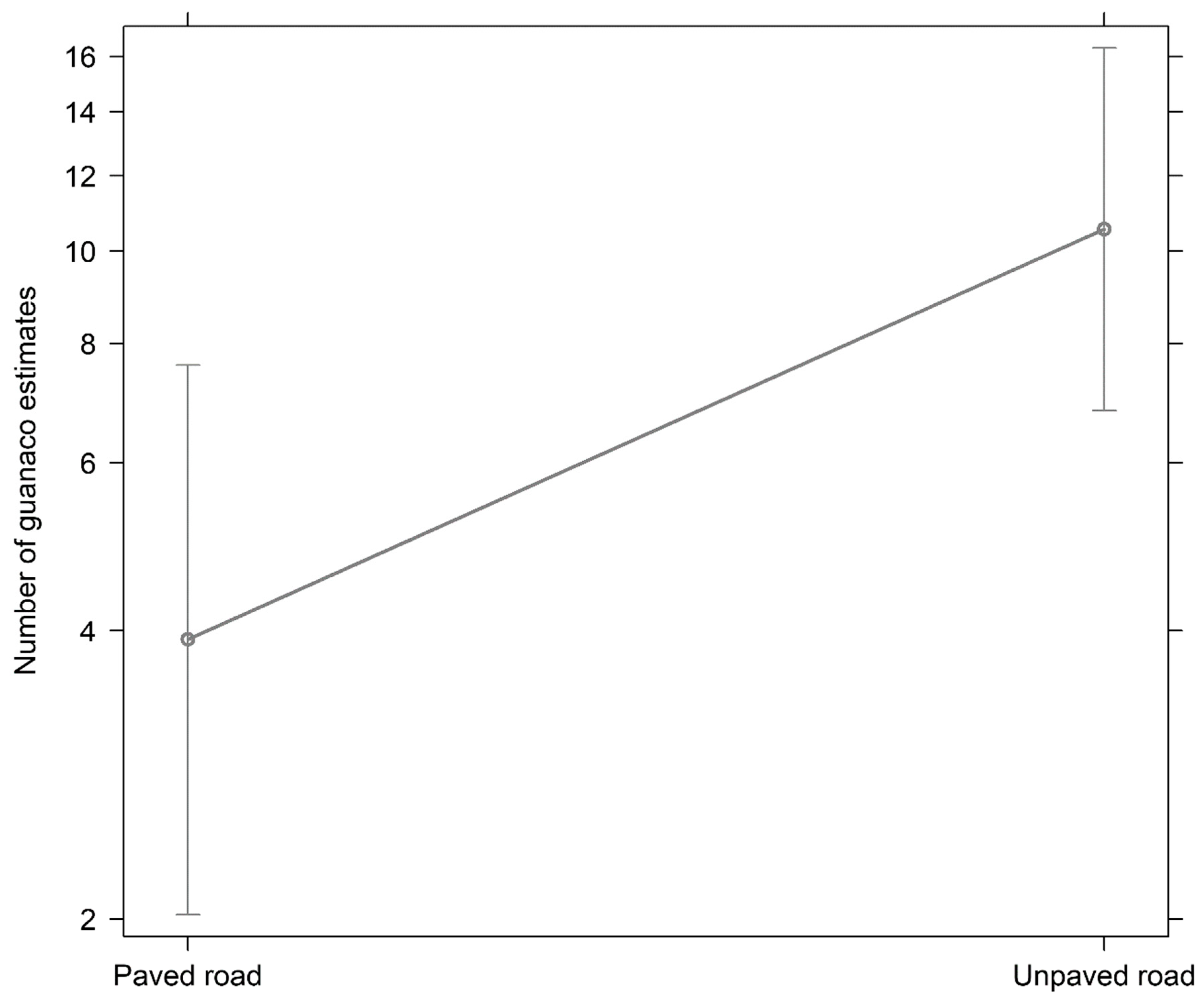
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forman, R.T.T.; Sperling, D.; Bissonette, J.; Clevenger, A.; Cutshall, C.; Dale, V.; Fahrig, L.; France, R.; Goldman, C.; Heanue, K.; et al. Road Ecology: Science and Solutions; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnot, N.; Morellet, N.; Verheyden, H.; Cargnelutti, B.; Lourtet, B.; Klein, F.; Hewison, A.J.M. Habitat use under predation risk: Hunting, roads and human dwellings influence the spatial behaviour of roe deer. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2013, 59, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rost, G.R.; Bailey, J.A. Distribution of mule deer and elk in relation to road. J. Wildl. Manag. 1979, 43, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manor, R.; Saltz, D. Effects of human disturbance on use of space and Flight distance of mountain gazelles. J. Wildl. Manag. 2005, 69, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, N.; Ovejero, R.; Moreno, P.; Gregorio, P.; Taraborelli, P.; Mateucci, S.D.; Carmanchahi, P.D. Including species interactions in resource selection of guanacos and livestock in Northern Patagonia. J. Zool. 2013, 291, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulac, J. Global Land Transport Infrastructure Requirements. In Estimating Road and Railway Infrastructure Capacity and Costs to 2050; International Energy Agency: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell, S.L.; Fuller, R.A.; Brooks, T.M.; Watson, J.E.M. Biodiversity The ravages of guns, nets and bulldozers. Nature 2016, 536, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, R.T.T.; Alexander, L.E. Roads and their major ecological effects. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 1998, 29, 207–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, J.; Paranhos Filho, A.C. The influence of highway BR262 on the loss of Cerrado vegetation cover in southwestern Brazil. Oecol. Aust. 2013, 17, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dyer, S.J.; O’neill, J.P.; Wasel, S.M.; Boutin, S. Quantifying barrier effects of roads and seismic lines on movements of female woodland caribou in northeastern Alberta. Can. J. Zool. 2002, 80, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, J.A.G.; Bowman, J.; Brennan, J.; Fahrig, L.; Dan Bert, D.; Bouchard, J.; Charbonneau, N.; Frank, K.; Gruber, B.; von Toschanowitz, K.T. Predicting when animal populations are at risk from roads: An interactive model of road avoidance behavior. Ecol. Modell. 2005, 185, 329–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laporte, M.; Beaudry, C.O.S.; Angers, B. Effects of road proximity on genetic diversity and reproductive success of the painted turtle (Chrysemy spicta). Conserv. Genet. 2012, 14, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, L.W.; Fahrig, L. Effect of road traffic on two amphibian species of differing vagility. Conserv. Biol. 2001, 15, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytwinski, T.; Fahrig, L. Reproductive rate and body size predict road impacts on mammal abundance. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forman, R.T.T.; Deblinger, R.D. The Ecological Road-Effect Zone of a Massachusetts (U.S.A.) Suburban Highway. Conserv. Biol. 2000, 14, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, R.T.T. Estimate of the Area Affected Ecologically by the Road System in the United States. Conserv. Biol. 2000, 14, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez-López, A.; Alkemade, R.; Verweij, P.A. The impacts of roads and other infrastructure on mammal and bird populations: A meta-analysis. Biol. Conserv. 2010, 143, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot Bruinderink, G.W.T.A.; Hazebroek, E. Ungulate traffic collisions in Europe. Conserv. Biol. 1996, 10, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, A. Trends and spatial patterns in ungulate-vehicle collisions in Sweden. Wildl. Biol. 2004, 10, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taraborelli, P.; Ovejero, R.; Mosca Torres, M.E.; Schroeder, N.M.; Moreno, P.; Gregorio, P.; Marcotti, E.; Marozzi, A.; Carmanchahi, P. Different factors that modify anti-predator behaviour in guanacos (Lama guanicoe). Acta Theriol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, N.M.; González, A.; Wisdom, M.; Nielson, R.; Rowland, M.M.; Novaro, A.J. Roads have no effect on guanaco habitat selection at a Patagonian site with limited poaching. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2018, 14, e00394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, W.L. Contrasting socioecologies of South America’s wild camelids: The vicugna and the guanaco. Spec. Publ. J. Mammal 1983, 7, 573–629. [Google Scholar]
- Baldi, R.; de Lamo, D.; Failla, M.; Ferrando, P.; Funes, D.; Nugent, P.; Puig, S.; Rivera, S.; Von Thüngen, J. Plan Nacional de Manejo del Guanaco (Lama guanicoe)-República Argentina-Secretaria de Ambiente y Desarrollo Sustentable de la Nación; Anexo I: 2006. Available online: http://www.produccion-animal.com.ar/produccion_de_camelidos/guanacos/65-plan_guanaco.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2019).
- Marín, J.C.; Saucedo, C.E.; Corti, P.; González, B.A. Application of DNA Forensic Techniques for Identifying Poached Guanacos (Lama guanicoe) in Chilean Patagonia. J. Forensic Sci. 2009, 54, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puig, S.; Videla, F.; Monge, S.; Roig, V. Seasonal variations in guanaco diet (Lama guanicoe Müller 1776) and food availability in Northern Patagonia, Argentina. J. Arid Environ. 1996, 34, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reus, M.L.; Cappa, F.M.; Andino, N.; Campos, V.E.; de los Ríos, C.; Campos, C.M. Trophic interactions between the native guanaco (Lama guanicoe) and the exotic donkey (Equus asinus) in the hyper-arid Monte desert (Ischigualasto Park, Argentina). Stud. Neotrop. Fauna Environ. 2014, 49, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappa, F.M.; Borghi, C.E.; Campos, V.E.; Andino, N.; Reus, M.L.; Giannoni, S.M. Guanacos in the Desert Puna: A trade-off between drinking and the risk of being predated. J. Arid Environ. 2014, 107, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, A.; Baldi, R. Ecological Correlates of Group-Size Variation in a Resource-Defense Ungulate, the Sedentary Guanaco. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera Soto, F. Situación de Lama guanicoe en el Parque Nacional Llanos de Challe y su potencial como producto turístico. Rev. Interam. Ambient. Turism. 2014, 10, 181–188. [Google Scholar]
- Radovani, N.I.; Funes, M.C.; Walker, R.S.; Gader, R.; Novaro, A.J. Guanaco Lama guanicoe numbers plummet in an area subject to poaching from oil-exploration trails in Patagonia. Oryx 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappa, F.M.; Giannoni, S.M.; Borghi, C.E. Effects of roads on the behaviour of the largest South American artiodactyl (Lama guanicoe) in an Argentine reserve. Anim. Behav. 2017, 131, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortéz, E.; Borghi, C.E.; Giannoni, S.M. Plan de Manejo Parque Provincial Ischigualasto Fase I; Informe inédito, Ente Autárquico Ischigualasto: Gobierno de San Juan, Argentina, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Giannoni, S.M. Plan de Manejo del Parque Natural Provincial Ischigualasto Patrimonio Natural de la Humanidad—Provincia de San Juan, 2015.
- Baigún, R.J.; Bolkovic, M.L.; Aved, M.B.; Li Puma, M.C.; Scandalo, R.P. Primer censo Nacional de Camélidos Silvestres al Norte del Río Colorado. In Buenos Aires: Secretaría de Ambiente y Desarrollo Sustentable de la Nación, 1st ed.; 2008; ISBN 978-987-23836-6-4. Print in Argentina. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, L.S. Conservation of Wildlife Populations: Demography, Genetics, and Management; Blackwell Plublishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Boo, E. Ecotourism: The Potentials and Pitfalls, Vol. 2 Country Case Studies; World Wildlife Fund: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Kerbiriou, C.; Leviol, I.; Robert, A.; Porcher, E.; Gourmelon, F.; Julliard, R. Tourism in protected areas can threaten wild populations: From individual response to population viability of the chough Pyrrhocorax pyrrhocorax. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 46, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghi, C.E.; Campos, C.M.; Ortuño, N.; Beninato, V.; Andino, N.; Campos, V.; de los Ríos, C.; Cappa, F.; Giannoni, S.M. Efeitos Indiretos Sobre a Fauna do Corredor Bioceánico Central em uma Área Protegida do Deserto do Monte: P. P. Ischigualasto; Bager, A., Lavras, U.F.L.A., Eds.; Ecologia de Estradas: Tendências e pesquisas, Lavras, Brazil, 2012; pp. 237–252. [Google Scholar]
- Bager, A.; Borghi, C.E.; Secco, H. The influence of economics, politics and environment on road ecology in South America. In Handbook of Road Ecology, 1st ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; Chapter 50. [Google Scholar]
- Fahrig, L.; Rytwinski, T. Effects of roads on animal abundance: An empirical review and synthesis. Ecol. Soc. 2009, 14, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves Da Rosa, C.; Bager, A. Review of the factors underlying the mechanisms and effects of roads on vertebrates. Oecol. Aust. 2013, 17, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acebes, P.; Traba, J.; Malo, J.E. Co-occurrence and potential for competition between wild and domestic large herbivores in a South American desert. J. Arid Environ. 2012, 77, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkart, R.; Barbaro, N.O.; Sánchez, R.O.; Gómez, D.A. Ecoregiones de la Argentina; Administración de Parques Nacionales: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 1999.
- Márquez, J.; Martínez Carretero, E.; Dalmasso, A.; Pastrán, G.; Ortiz, S. Las áreas protegidas de la provincia de San Juan (Argentina) II. La vegetación del Parque Provincial de Ischigualasto. Multequina 2005, 14, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Acebes, P.; Ovejero, R.; Traba, J.; Malo, J.E.; Borghi, C.E. Density and habitat use at different spatial scales of a guanaco population (Lama guanicoe) in the Monte desert of Argentina. Mammalia 2010, 74, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestre, F.T.; Escudero, A. Is the patch size distribution of vegetation a suitable indicator of desertification processes? Ecology 2009, 90, 1729–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiberger, R.M.; Holland, B. Statistical Analysis and Data Display: An Intermediate Course with Examples in S-Plus, R, and SAS; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zuur, A.; Leno, E.N.; Walker, N.; Saveliev, A.A.; Smith, G.M. Mixed Effects Models and Extensions in Ecology with R; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Crawley, M.J. The R Book, 1st ed.; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; ISBN 13: 978-0-470-51024-7. [Google Scholar]
- Schielzeth, H. Simple means to improve the interpretability of regression coefficients: Interpretation of regression coefficients. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2010, 1, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Model selection and multimodel inference. In A Practical Information—Theoretic Approach; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, D.A.; Skaug, H.J.; Ancheta, J.; Ianelli, J.; Magnusson, A.; Maunder, M.; Nielsen, A.; Sibert, J. AD Model Builder: Using automatic differentiation for statistical inference of highly parameterized complex nonlinear models. Optim. Methods Softw. 2012, 27, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D.; Debroy, S.; Sarkar, D.; EISPACK; Heisterkamp, S.; Van Willigen, B.; R-core Team. nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models. R Package Version 2014, 3, 117. [Google Scholar]
- Karlson, M.; Mörtberg, U.; Balfors, B. Road ecology in environmental impact assessment. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2014, 48, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffin, A.W. From roadkill to road ecology: A review of the ecological effects of roads. J. Transp. Geogr. 2007, 15, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblond, M.; Dussault, J.C.; Ouellet, P. Avoidance of roads by large herbivores and its relation to disturbance intensity. J. Zool. 2012, 289, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cromsigt, J.P.G.M.; Prins, H.H.T.; Olff, H. Habitat heterogeneity as a driver of ungulate diversity and distribution patterns: Interaction of body mass and digestive strategy. Divers. Distrib. 2009, 15, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Buzzard, P.; Jiang, X. Habitat associations of four ungulates in mountain forests of southwest China, based on camera trapping and dung counts data. Res. Popul. Ecol. 2014, 56, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsberg, J.; Stol, J. Spatial distribution of sheep, feral goats and kangaroos in woody rangeland paddocks. Rangel. J. 1996, 18, 270–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrote, G.; Pérez de Ayala, R.; Tellería, J.L. A comparison of scat counts and camera-trapping as means of assessing Iberian lynx abundance. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Model | k | AICc | ∆AICc | wi |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dist + Roads + Dist*Roads | 8 | 953.62 | 0.00 | 0.22 |
| Dist + Cov | 6 | 954.06 | 0.44 | 0.17 |
| Dist + Roads + Cov + Dist*Roads | 9 | 954.20 | 0.59 | 0.16 |
| Dist + Roads + Height + Dist*Roads | 9 | 955.26 | 1.65 | 0.10 |
| Dist + Roads + Cov + Height + Dist*Roads | 10 | 955.56 | 1.95 | 0.08 |
| Dist + Roads + Cov | 7 | 955.80 | 2.18 | 0.07 |
| NULL | 3 | 963.04 | 9.42 | 0.00 |
| Explanatory Variable | Parameter Likelihood | Parameter Estimate ±SE | CL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||
| Intercept | 0.19 ± 0.33 | -0.38 | 1.39 | |
| Dist | 0.99 | |||
| 500 m | 0.09 ± 0.28 | -0.46 | 0.64 | |
| 1500 m | 1.19 ± 0.30 | 0.60 | 1.77 | |
| Roads | 0.68 | 0.29 ± 0.56 | -0.81 | 1.38 |
| Dist*Roads | 0.56 | |||
| Paved road*500m | -0.09 ± 0.47 | -1.02 | 0.83 | |
| Paved road*1500m | -1.34 ± 0.49 | -2.30 | -0.39 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cappa, F.M.; Borghi, C.E.; Giannoni, S.M. How Roads Affect the Spatial Use of the Guanaco in a South American Protected Area: Human Connectivity vs Animal Welfare. Diversity 2019, 11, 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11070110
Cappa FM, Borghi CE, Giannoni SM. How Roads Affect the Spatial Use of the Guanaco in a South American Protected Area: Human Connectivity vs Animal Welfare. Diversity. 2019; 11(7):110. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11070110
Chicago/Turabian StyleCappa, Flavio M., Carlos E. Borghi, and Stella M. Giannoni. 2019. "How Roads Affect the Spatial Use of the Guanaco in a South American Protected Area: Human Connectivity vs Animal Welfare" Diversity 11, no. 7: 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11070110
APA StyleCappa, F. M., Borghi, C. E., & Giannoni, S. M. (2019). How Roads Affect the Spatial Use of the Guanaco in a South American Protected Area: Human Connectivity vs Animal Welfare. Diversity, 11(7), 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11070110





