Phylogenetic Signal of Indels and the Neoavian Radiation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
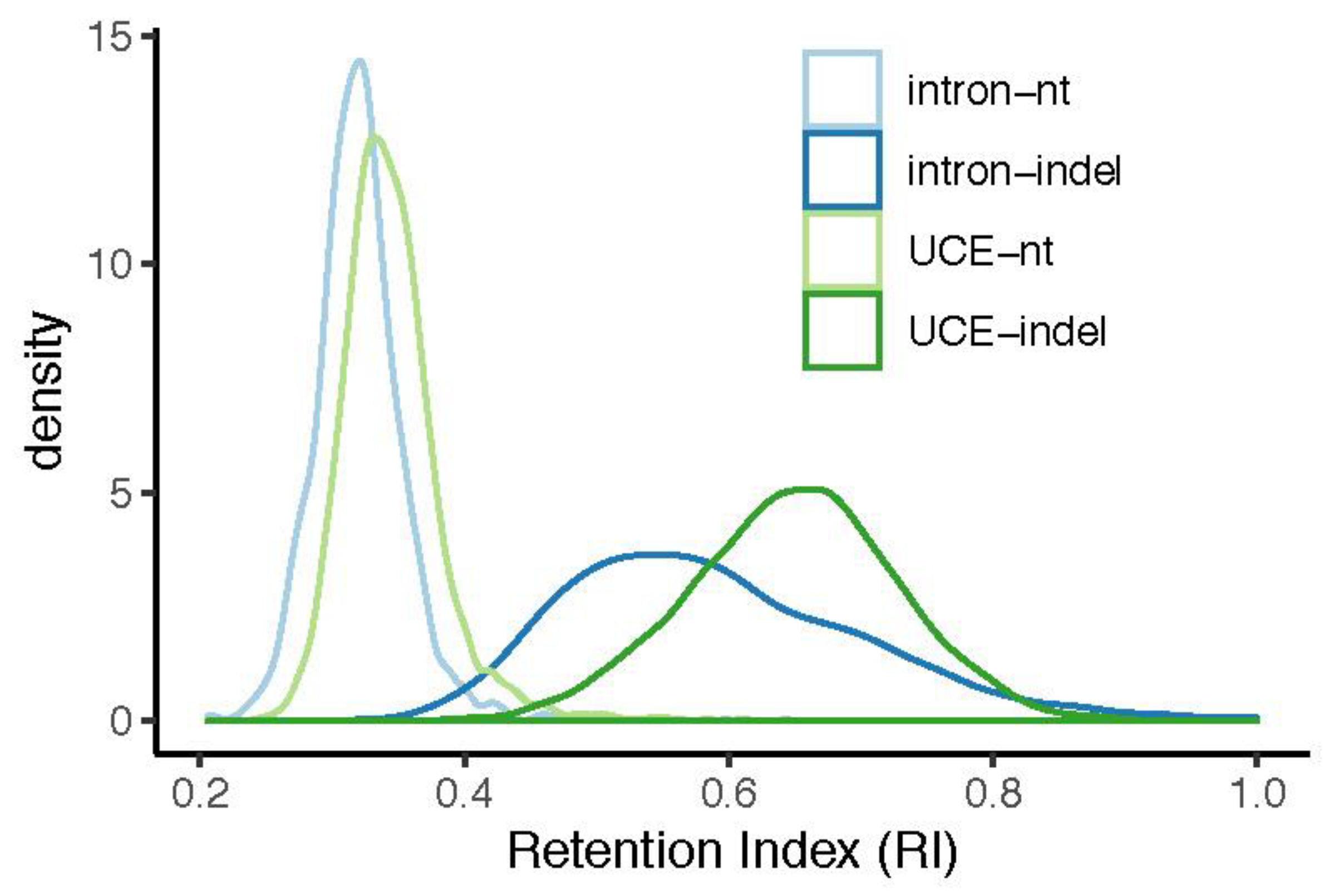
3.1. Indels Exhibit Less Homoplasy Than nt Substitutions
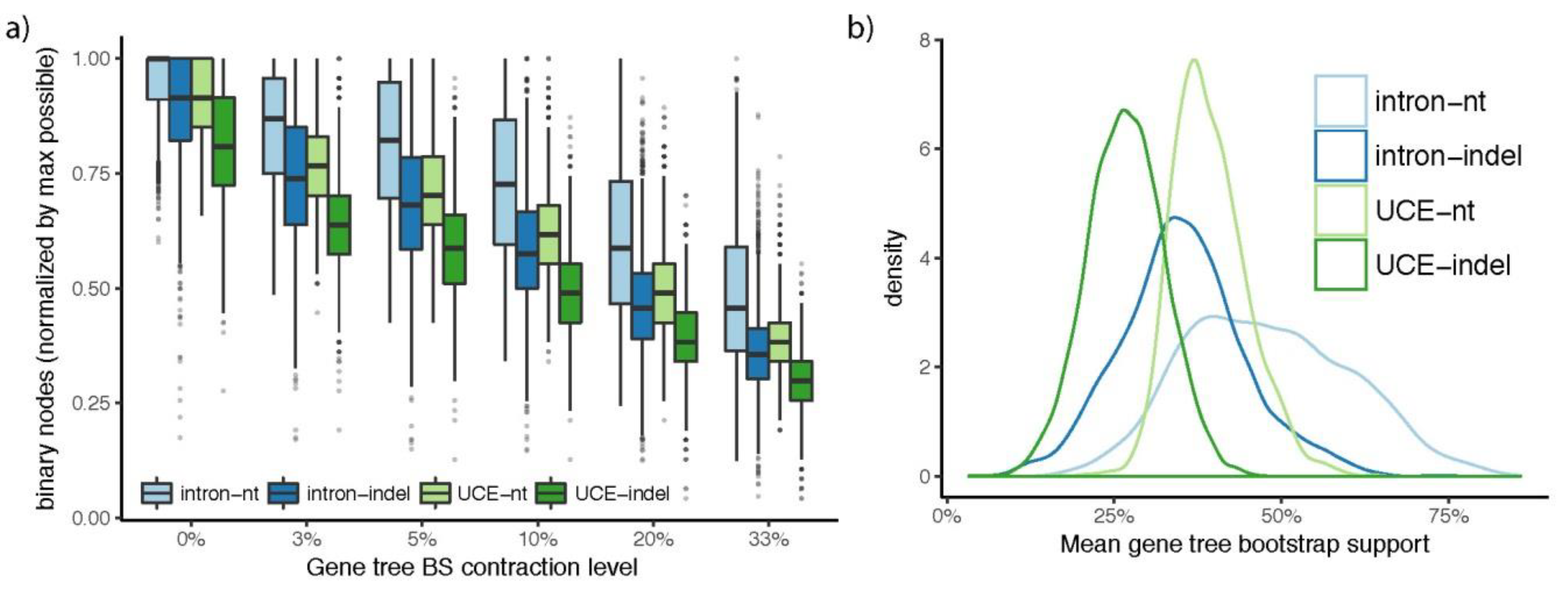
3.2. How Well Resolved Are Indel Trees in Comparison to nt Trees?
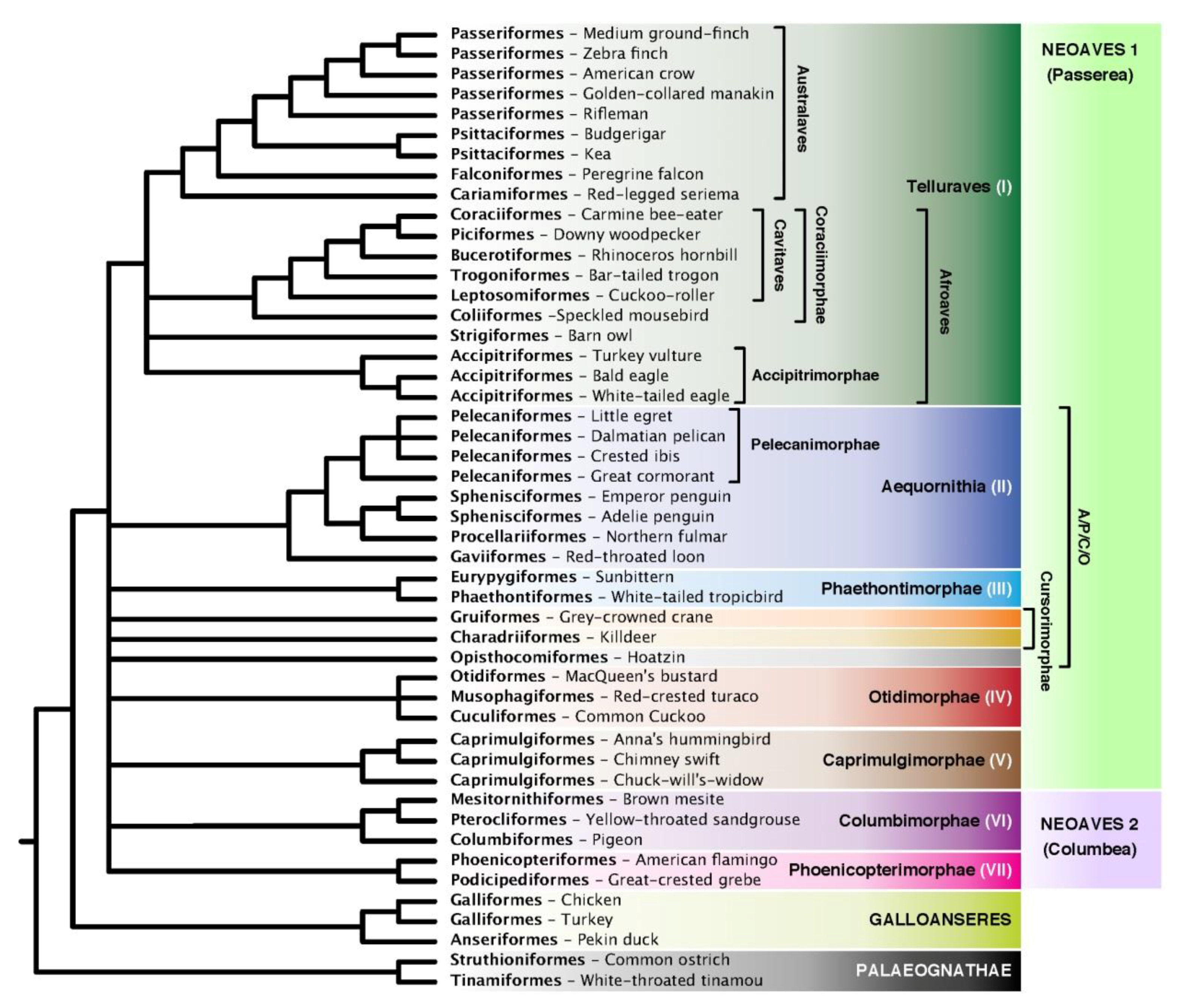
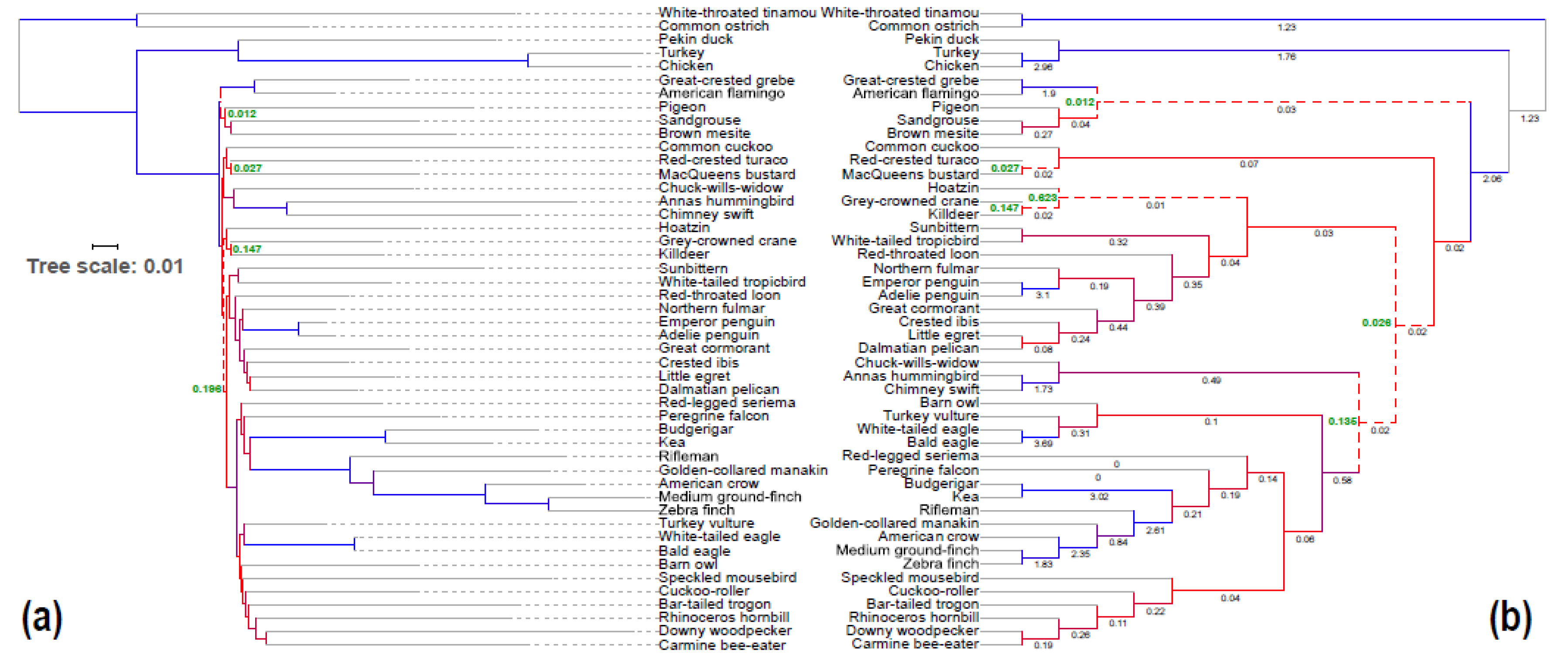
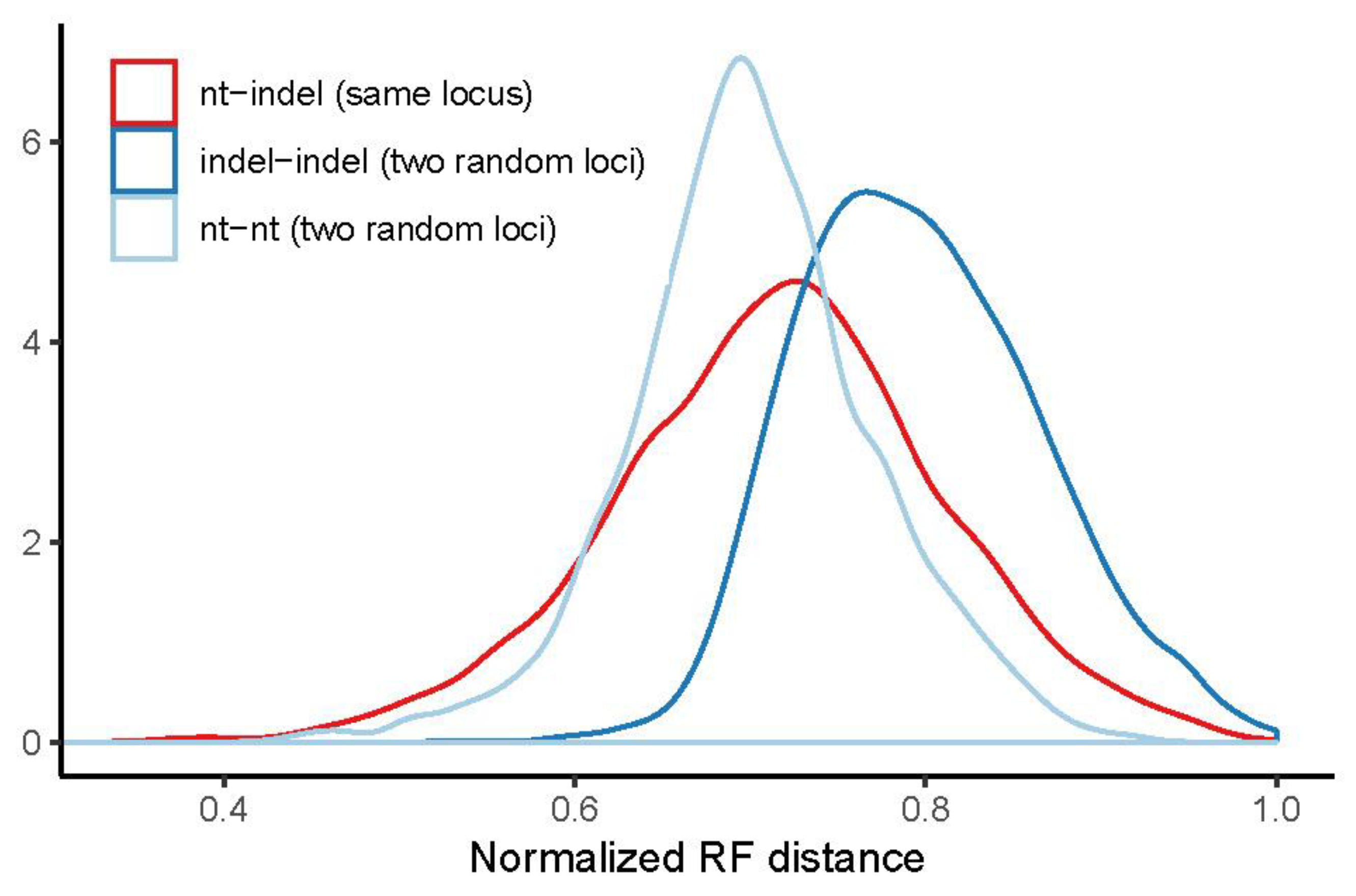
3.3. Congruence of Indel and nt Gene Trees
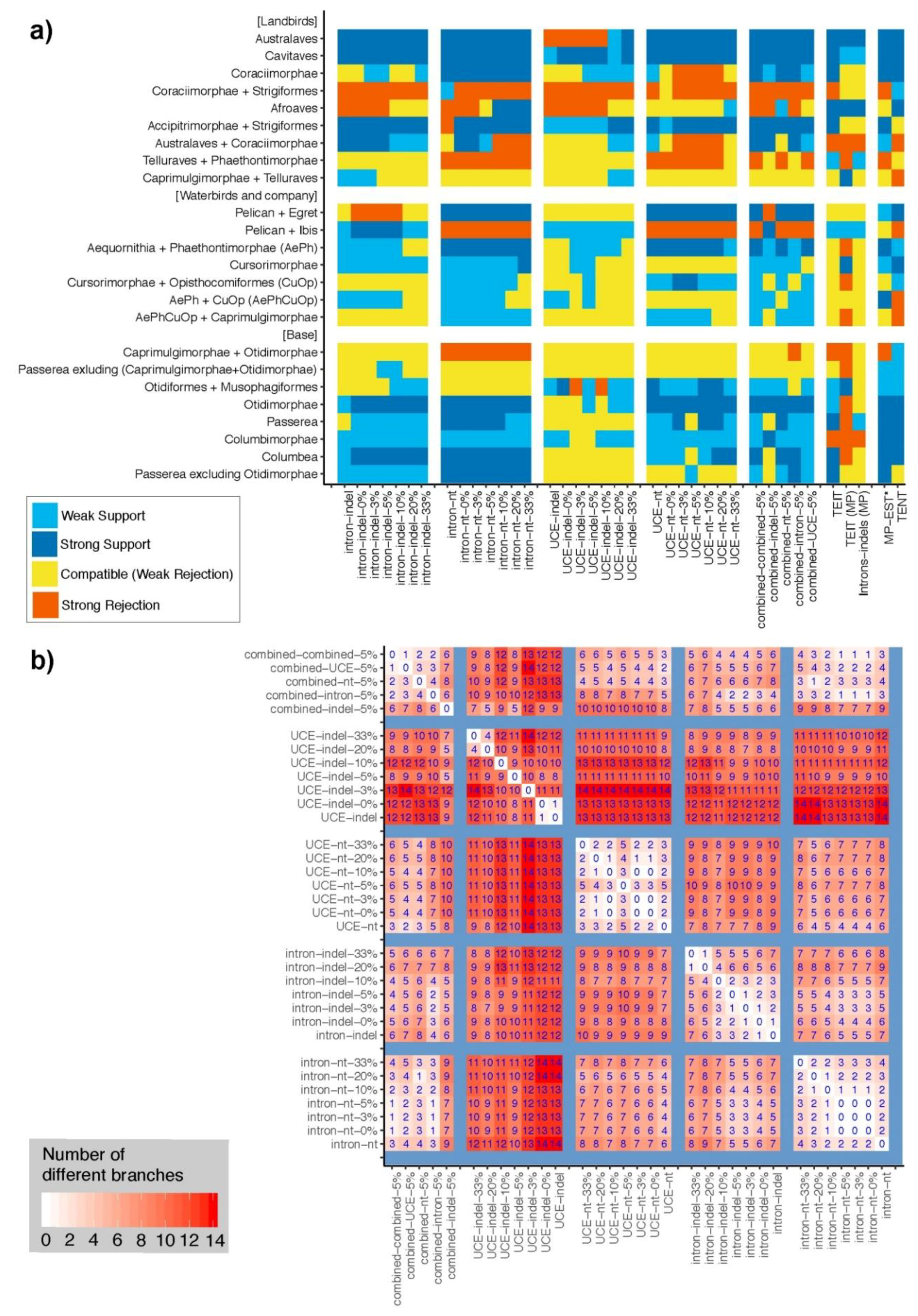
3.4. Congruence among Indel and nt Trees for Introns and UCEs
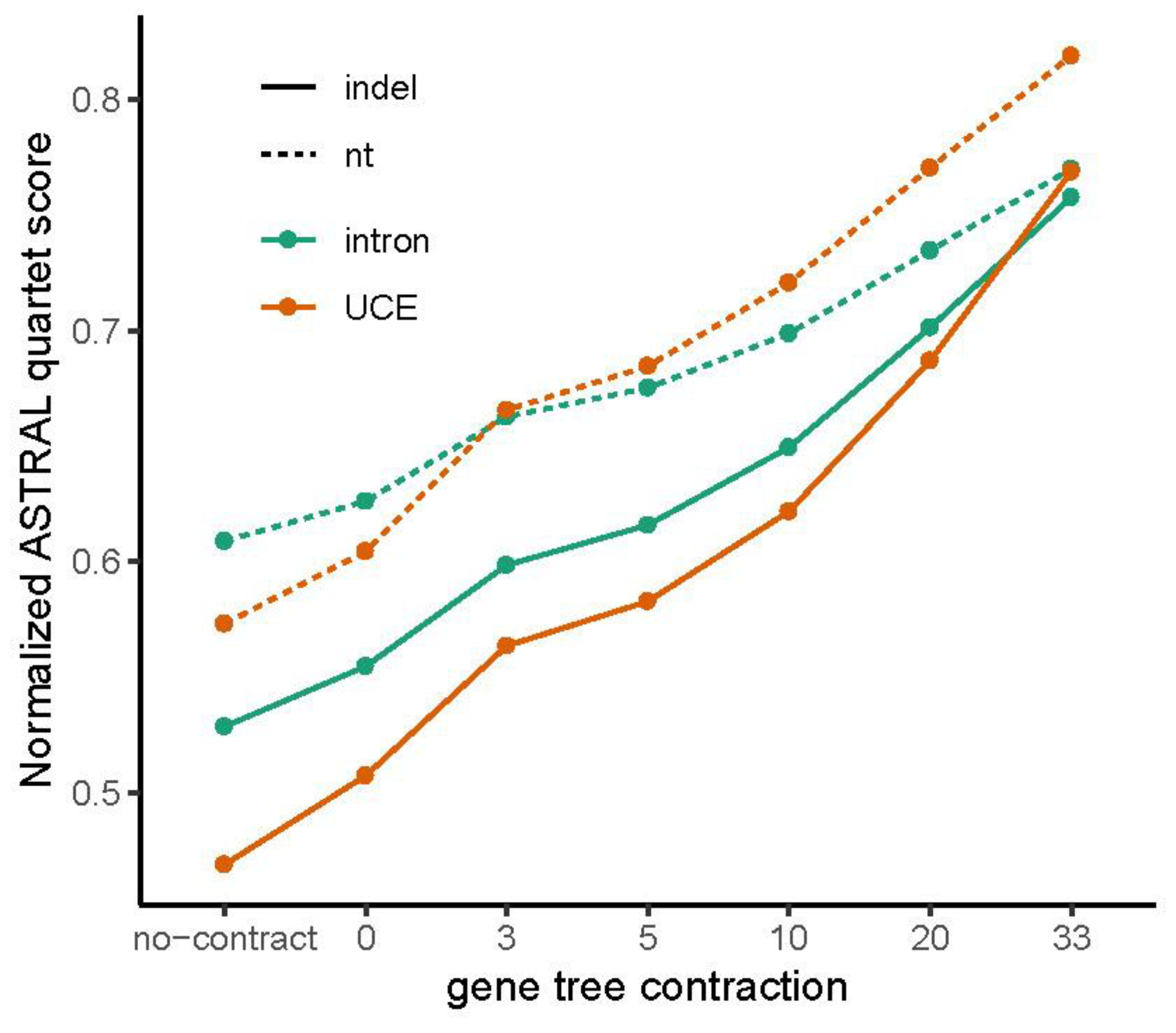
3.5. Are nt Trees Improved When Combined with Indel Trees?
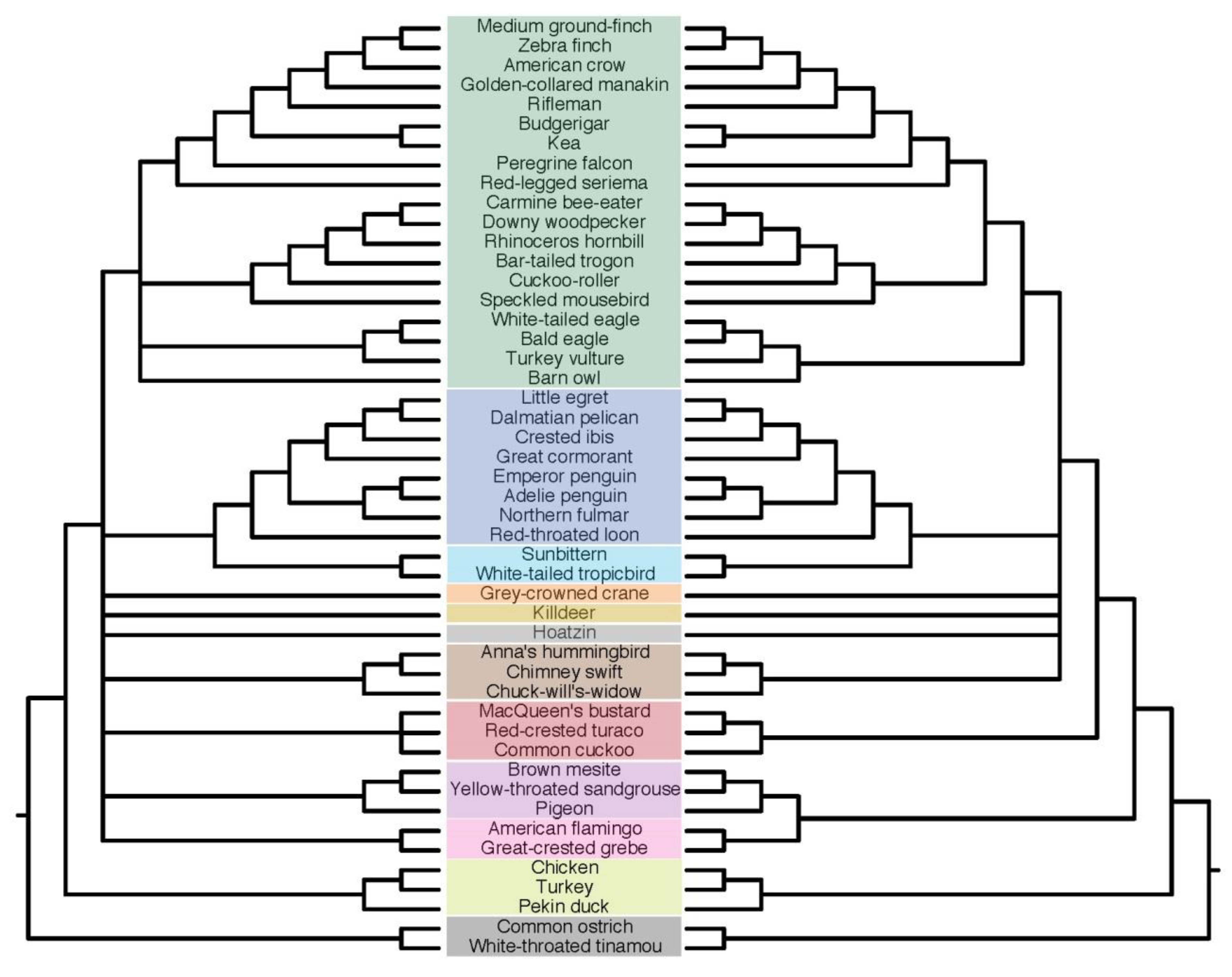
3.6. Indel ASTRAL Trees Are Largely Congruent with Concatenation Trees
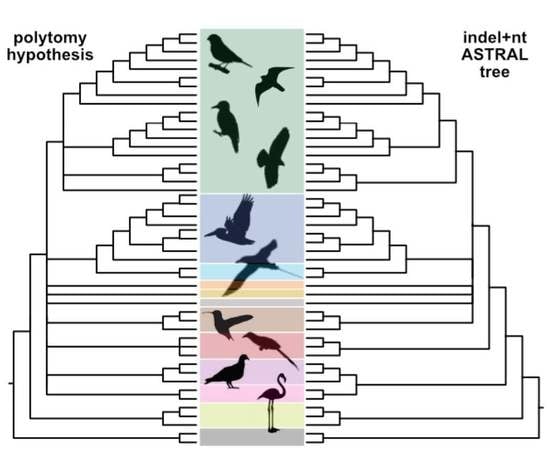
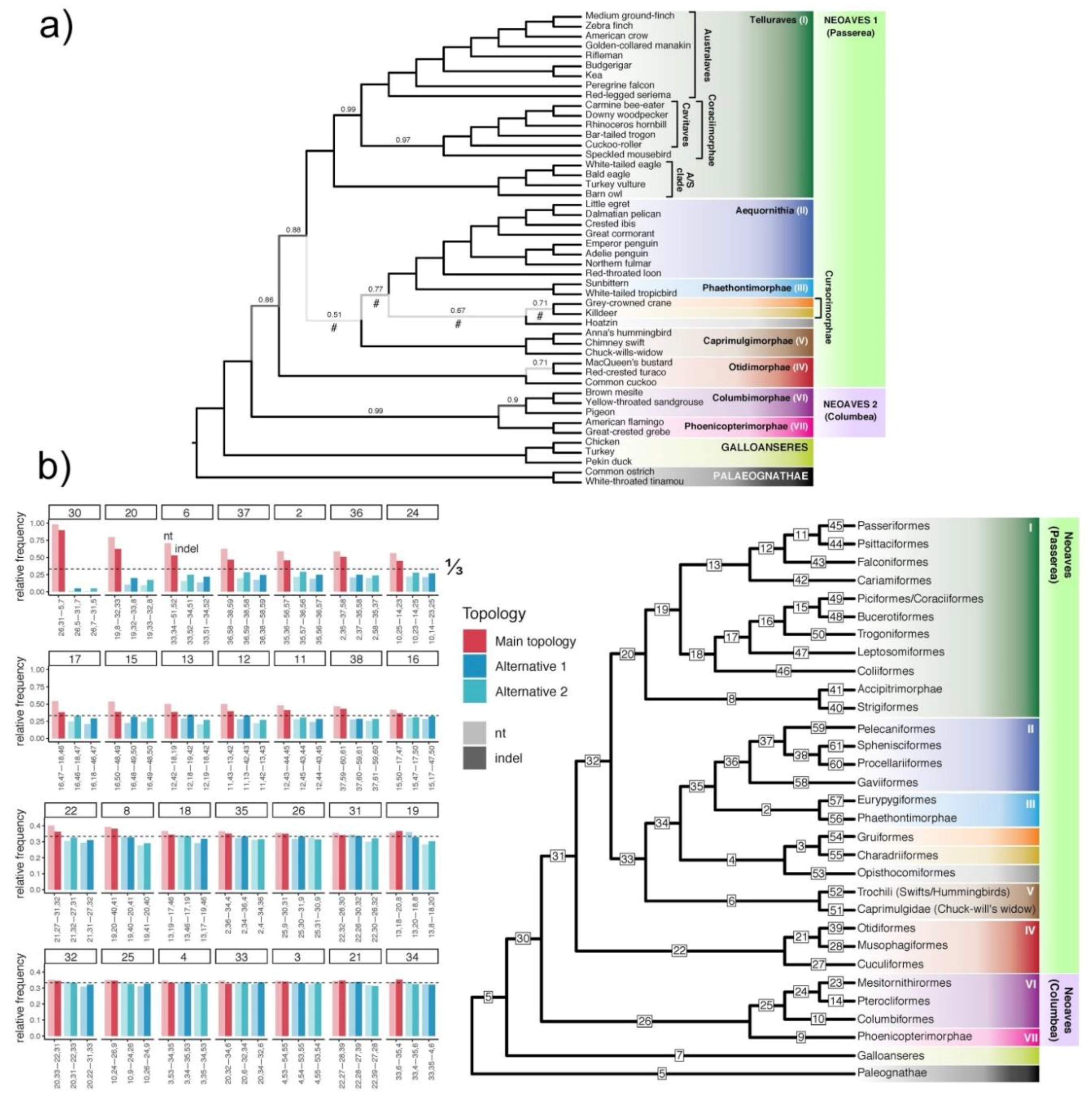
3.7. Can Indel Data Address the Neoaves Hard Polytomy Hypothesis?
4. Conclusions and Summary
5. Directions for Future Research
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Braun, E.L.; Cracraft, J.; Houde, P. Resolving the avian tree of life from top to bottom: The promise and potential boundaries of the phylogenomic era. In Avian Genomics in Ecology and Evolution—From the Lab into the Wild; Kraus, R.H.S., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mindell, D.P.; Sorenson, M.D.; Dimcheff, D.E.; Hasegawa, M.; Ast, J.C.; Yuri, T. Interordinal relationships of birds and other reptiles based on whole mitochondrial genomes. Syst. Biol. 1999, 48, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, E.L.; Kimball, R.T. Examining basal avian divergences with mitochondrial sequences: Model complexity, taxon sampling, and sequence length. Syst. Biol. 2002, 51, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibb, G.C.; Kardailsky, O.; Kimball, R.T.; Braun, E.L.; Penny, D. Mitochondrial genomes and avian phylogeny: Complex characters and resolvability without explosive radiations. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groth, J.G.; Barrowclough, G.F. Basal divergences in birds and the phylogenetic utility of the nuclear RAG-1 gene. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1999, 12, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubb, A.L. New nuclear evidence for the oldest divergence among neognath birds: The phylogenetic utility of ZENK (i). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2004, 30, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fain, M.G.; Houde, P. Parallel radiations in the primary clades of birds. Evolution 2004, 58, 2558–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericson, P.G.P.; Anderson, C.L.; Britton, T.; Elzanowski, A.; Johansson, U.S.; Källersjö, M.; Ohlson, J.I.; Parsons, T.J.; Zuccon, D.; Mayr, G. Diversification of Neoaves: Integration of molecular sequence data and fossils. Biol. Lett. 2006, 2, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojnowski, J.L.; Kimball, R.T.; Braun, E.L. Introns outperform exons in analyses of basal avian phylogeny using clathrin heavy chain genes. Gene 2008, 410, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poe, S.; Chubb, A.L. Birds in a bush: Five genes indicate explosive evolution of avian orders. Evolution 2004, 58, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackett, S.J.; Kimball, R.T.; Reddy, S.; Bowie, R.C.K.; Braun, E.L.; Braun, M.J.; Chojnowski, J.L.; Cox, W.A.; Han, K.-L.; Harshman, J.; et al. A phylogenomic study of birds reveals their evolutionary history. Science 2008, 320, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Braun, E.L.; Kimball, R.T. Testing hypotheses about the sister group of the passeriformes using an independent 30-locus data set. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimball, R.T.; Wang, N.; Heimer-McGinn, V.; Ferguson, C.; Braun, E.L. Identifying localized biases in large datasets: A case study using the avian tree of life. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 69, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormack, J.E.; Harvey, M.G.; Faircloth, B.C.; Crawford, N.G.; Glenn, T.C.; Brumfield, R.T. A phylogeny of birds based on over 1,500 loci collected by target enrichment and high-throughput sequencing. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, E.D.; Mirarab, S.; Aberer, A.J.; Li, B.; Houde, P.; Li, C.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Faircloth, B.C.; Nabholz, B.; Howard, J.T.; et al. Whole-genome analyses resolve early branches in the tree of life of modern birds. Science 2014, 346, 1320–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prum, R.O.; Berv, J.S.; Dornburg, A.; Field, D.J.; Townsend, J.P.; Lemmon, E.M.; Lemmon, A.R. A comprehensive phylogeny of birds (Aves) using targeted next-generation DNA sequencing. Nature 2015, 526, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, A. The phylogenomic forest of bird trees contains a hard polytomy at the root of Neoaves. Zool. Scr. 2016, 45, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.; Kimball, R.T.; Pandey, A.; Hosner, P.A.; Braun, M.J.; Hackett, S.J.; Han, K.-L.; Harshman, J.; Huddleston, C.J.; Kingston, S.; et al. Why do phylogenomic data sets yield conflicting trees? Data type influences the avian tree of life more than taxon sampling. Syst. Biol. 2017, 66, 857–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyari, E.; Mirarab, S. Testing for polytomies in phylogenetic species trees using quartet frequencies. Genes 2018, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degnan, J.H.; Rosenberg, N.A. Gene tree discordance, phylogenetic inference and the multispecies coalescent. Trends Ecol. Evol. (Amst.) 2009, 24, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, S.V. Is a new and general theory of molecular systematics emerging? Evolution 2009, 63, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyari, E.; Mirarab, S. Fast coalescent-based computation of local branch support from quartet frequencies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1654–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v4: Recent updates and new developments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Sayyari, E.; Mirarab, S. ASTRAL-III: Increased scalability and impacts of contracting low support branches. In Comparative Genomics; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Meidanis, J., Nakhleh, L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 10562, pp. 53–75. ISBN 978-3-319-67978-5. [Google Scholar]
- Rabiee, M.; Sayyari, E.; Mirarab, S. Multi-allele species reconstruction using ASTRAL. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019, 130, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, E.L.; Kimball, R.T. Polytomies, the power of phylogenetic inference, and the stochastic nature of molecular evolution: A comment on Walsh et al. (1999). Evolution 2001, 55, 1261–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsenstein, J. Cases in which parsimony or compatibility methods will be positively misleading. Syst. Biol. 1978, 27, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan-Richards, M.; Trewick, S.A.; Bartosch-Härlid, A.; Kardailsky, O.; Phillips, M.J.; McLenachan, P.A.; Penny, D. Bird evolution: Testing the Metaves clade with six new mitochondrial genomes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saurabh, K.; Holland, B.R.; Gibb, G.C.; Penny, D. Gaps: An elusive source of phylogenetic information. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Alfaro, M.E.; Suchard, M.A. Biologically inspired phylogenetic models strongly outperform the no common mechanism model. Syst. Biol. 2011, 60, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, J.L.; Kishino, H.; Felsenstein, J. An evolutionary model for maximum likelihood alignment of DNA sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1991, 33, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, J.L.; Kishino, H.; Felsenstein, J. Inching toward reality: An improved likelihood model of sequence evolution. J. Mol. Evol. 1992, 34, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, I.H. Solving the master equation for Indels. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alekseyenko, A.V.; Lee, C.J.; Suchard, M.A. Wagner and Dollo: A stochastic duet by composing two parsimonious solos. Syst. Biol. 2008, 57, 772–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, M.P.; Ochoterena, H.; Carr, T.G. Incorporation, relative homoplasy, and effect of gap characters in sequence-based phylogenetic analyses. Syst. Biol. 2001, 50, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossel, E. On the impossibility of reconstructing ancestral data and phylogenies. J. Comput. Biol. 2003, 10, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steel, M.; Penny, D. Two further links between MP and ML under the poisson model. Appl. Math. Lett. 2004, 17, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yuri, T.; Kimball, R.T.; Harshman, J.; Bowie, R.C.K.; Braun, M.J.; Chojnowski, J.L.; Han, K.-L.; Hackett, S.J.; Huddleston, C.J.; Moore, W.S.; et al. Parsimony and model-based analyses of indels in avian nuclear genes reveal congruent and incongruent phylogenetic signals. Biology 2013, 2, 419–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML-VI-HPC: Maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2688–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklós, I.; Lunter, G.A.; Holmes, I. A “Long Indel” model for evolutionary sequence alignment. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 21, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, M.; Penny, D. Maximum parsimony and the phylogenetic information in multistate characters. In Parsimony, Phylogeny, and Genomics; Albert, V.A., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 163–178. [Google Scholar]
- Chuzhanova, N.A.; Anassis, E.J.; Ball, E.V.; Krawczak, M.; Cooper, D.N. Meta-analysis of indels causing human genetic disease: Mechanisms of mutagenesis and the role of local DNA sequence complexity. Hum. Mutat. 2003, 21, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Diaz, M.; Kunkel, T.A. Mechanism of a genetic glissando: Structural biology of indel mutations. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2006, 31, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messer, P.W.; Arndt, P.F. The majority of recent short DNA insertions in the human genome are tandem duplications. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volfovsky, N.; Oleksyk, T.K.; Cruz, K.C.; Truelove, A.L.; Stephens, R.M.; Smith, M.W. Genome and gene alterations by insertions and deletions in the evolution of human and chimpanzee chromosome 22. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, J.V.; Yuhki, N.; Masuda, R.; Modi, W.; O’Brien, S.J. Numt, a recent transfer and tandem amplification of mitochondrial DNA to the nuclear genome of the domestic cat. J. Mol. Evol. 1994, 39, 174–190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qu, H.; Ma, F.; Li, Q. Comparative analysis of mitochondrial fragments transferred to the nucleus in vertebrate. J. Genet. Genom. 2008, 35, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Wang, N.; Li, N.; Kimball, R.T.; Braun, E.L. Comparative genomics reveals a burst of homoplasy-free numt insertions. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 2060–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, K.A.; Burns, K.H. Mobilizing diversity: Transposable element insertions in genetic variation and disease. Mob. DNA 2010, 1, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurka, J.; Bao, W.; Kojima, K.K. Families of transposable elements, population structure and the origin of species. Biol. Direct 2011, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzke, A.; Churakov, G.; Berkes, P.; Arms, E.M.; Kelsey, D.; Brosius, J.; Kriegs, J.O.; Schmitz, J. Retroposon insertion patterns of neoavian birds: Strong evidence for an extensive incomplete lineage sorting era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1497–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paśko, Ł.; Ericson, P.G.P.; Elzanowski, A. Phylogenetic utility and evolution of indels: A study in neognathous birds. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2011, 61, 760–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, E.D.; Mirarab, S.; Aberer, A.J.; Li, B.; Houde, P.; Li, C.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Faircloth, B.C.; Nabholz, B.; Howard, J.T.; et al. Avian Phylogenomics Consortium Phylogenomic analyses data of the avian phylogenomics project. Gigascience 2015, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, M.P.; Ochoterena, H. Gaps as characters in sequence-based phylogenetic analyses. Syst. Biol. 2000, 49, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, D.P. 2xread: A simple indel coding tool. Available online: https://www.nybg.org/files/scientists/2xread.html (accessed on 28 April 2019).
- Salinas, N.R.; Little, D.P. 2matrix: A utility for indel coding and phylogenetic matrix concatenation. Appl. Plant Sci. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, N.D.; Healy, J. GapCoder automates the use of indel characters in phylogenetic analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2003, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goloboff, P.A.; Farris, J.S.; Nixon, K.C. TNT, a free program for phylogenetic analysis. Cladistics 2008, 24, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farris, J.S. The retention index and the rescaled consistency index. Cladistics 1989, 5, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swofford, D.L. PAUP*. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and Other Methods); Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sayyari, E.; Whitfield, J.B.; Mirarab, S. DiscoVista: Interpretable visualizations of gene tree discordance. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 122, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericson, P.G.P. Evolution of terrestrial birds in three continents: Biogeography and parallel radiations. J. Biogeogr. 2012, 39, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cracraft, J.C. Avian higher-level relationships and classification: Nonpasseriforms. In The Howard and Moore Complete Checklist of the Birds of the World, 4th ed.; Dickinson, E.C., Remsen, J.V., Jr., Eds.; Aves Press: Eastbourne, UK, 2013; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Avise, J.C.; Robinson, T.J. Hemiplasy: A new term in the lexicon of phylogenetics. Syst. Biol. 2008, 57, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.-L.; Braun, E.L.; Kimball, R.T.; Reddy, S.; Bowie, R.C.K.; Braun, M.J.; Chojnowski, J.L.; Hackett, S.J.; Harshman, J.; Huddleston, C.J.; et al. Are transposable element insertions homoplasy free?: An examination using the avian tree of life. Syst. Biol. 2011, 60, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S. Error in phylogenetic estimation for bushes in the tree of life. J. Phylogenet. Evol. Biol. 2013, 01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, M.S.; Gatesy, J. The gene tree delusion. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 94, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobolth, A.; Dutheil, J.Y.; Hawks, J.; Schierup, M.H.; Mailund, T. Incomplete lineage sorting patterns among human, chimpanzee, and orangutan suggest recent orangutan speciation and widespread selection. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, J.J. The irrelevance of allele tree topologies for species delimitation, and a non-topological alternative. Syst. Bot. 1995, 20, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J. Trees within trees: Genes and species, molecules and morphology. Syst. Biol. 1997, 46, 537–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendy, M.D.; Penny, D. A framework for the quantitative study of evolutionary trees. Syst. Zool. 1989, 38, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. Slicing hyperdimensional oranges: The geometry of phylogenetic estimation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2000, 17, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, A.; Smeds, L.; Ellegren, H. The dynamics of incomplete lineage sorting across the ancient adaptive radiation of neoavian birds. PLoS Biol. 2015, 13, e1002224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doronina, L.; Reising, O.; Clawson, H.; Ray, D.A.; Schmitz, J. True homoplasy of retrotransposon insertions in primates. Syst. Biol. 2019, 68, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, H.E.; Kidd, M.G.; Moum, T.; Friesen, V.L. Polytomies and the power of phylogenetic inference. Evolution 1999, 53, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirarab, S.; Bayzid, M.S.; Boussau, B.; Warnow, T. Statistical binning enables an accurate coalescent-based estimation of the avian tree. Science 2014, 346, 1250463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Introns | Ultraconserved Elements (UCEs) | All Data | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number (#) of loci | 2515 | 3679 | 6194 |
| Total # of nts | 19,258,212 | 9,229,346 | 28,487,558 |
| Total # of indels | 3,918,322 | 1,242,014 | 5,160,336 |
| # Parsimony Informative nts | 10,855,614 | 3,908,476 | 14,764,090 |
| # Parsimony Informative indels | 942,169 | 315,393 | 1,257,562 |
| % Parsimony Informative nts | 56.37 | 42.35 | 51.83 |
| % Parsimony Informative indels | 24.05 | 25.39 | 24.37 |
| Indels per locus: | |||
| Minimum | 6 | 10 | 6 |
| Lower quartile | 431.5 | 266 | 284 |
| Upper quartile | 2065 | 406.5 | 704 |
| Median | 1014 | 333 | 389 |
| Mean | 1,557.98 | 337.6 | 833.12 |
| All | 1bp | 2–9bp | 10–49bp | 50–99bp | 100+bp | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # indels | 3,918,322 | 1,023,680 | 1,924,526 | 828,741 | 65,651 | 75,724 |
| # informative indels | 942,169 | 239,295 | 510,023 | 168,906 | 10,515 | 13,430 |
| % informative indels | 24.05 | 23.38 | 26.50 | 20.38 | 16.02 | 17.74 |
| Ensemble RI indels 1 | 0.52 | 0.54 | 0.49 | 0.56 | 0.73 | 0.86 |
| Ensemble RI nts 1 | 0.31 |
| Quartiles | indel–nt Same Locus | indel–indel Different Loci | nt–nt Different Loci |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st quartile | 0.658 | 0.744 | 0.659 |
| median | 0.721 | 0.791 | 0.698 |
| 3rd quartile | 0.775 | 0.842 | 0.743 |
| Tree Resolution | Same Locus Mean (SD) n = 2515 | Different Loci Mean (SD) n = 6322710 |
|---|---|---|
| Fully resolved | 30.06 (3.88) | 30.84 (2.90) |
| <34% contracted | 3.530 (2.61) | 4.138 (2.96) |
| <76% contracted | 0.192 (0.50) | 0.343 (0.72) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Houde, P.; Braun, E.L.; Narula, N.; Minjares, U.; Mirarab, S. Phylogenetic Signal of Indels and the Neoavian Radiation. Diversity 2019, 11, 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11070108
Houde P, Braun EL, Narula N, Minjares U, Mirarab S. Phylogenetic Signal of Indels and the Neoavian Radiation. Diversity. 2019; 11(7):108. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11070108
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoude, Peter, Edward L. Braun, Nitish Narula, Uriel Minjares, and Siavash Mirarab. 2019. "Phylogenetic Signal of Indels and the Neoavian Radiation" Diversity 11, no. 7: 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11070108
APA StyleHoude, P., Braun, E. L., Narula, N., Minjares, U., & Mirarab, S. (2019). Phylogenetic Signal of Indels and the Neoavian Radiation. Diversity, 11(7), 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11070108