The Composition and Assembly of Bacterial Communities across the Rhizosphere and Phyllosphere Compartments of Phragmites Australis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Site and Sample Collection
2.2. Processing of the Collected Samples
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.4. Processing of the Sequencing Data
2.5. Definition of Abundant and Rare Operating Taxonomic Units (OTUs)
2.6. Statistical Analyses
2.7. Phylogenetic Structure of Bacterial Community
2.8. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Numbers
3. Results
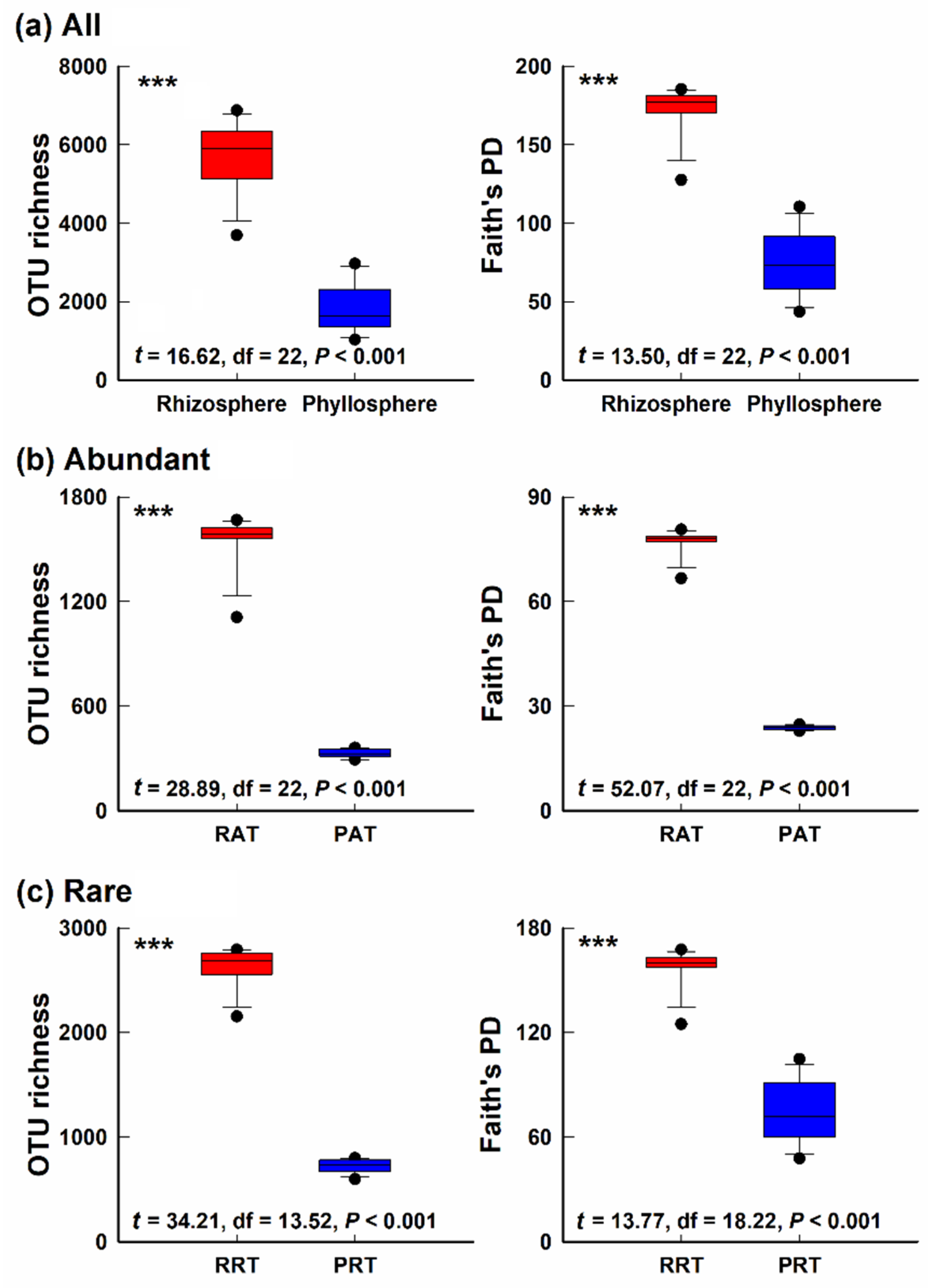
3.1. Alpha-Diversity of Bacterial Community in Different Epiphytic Compartments
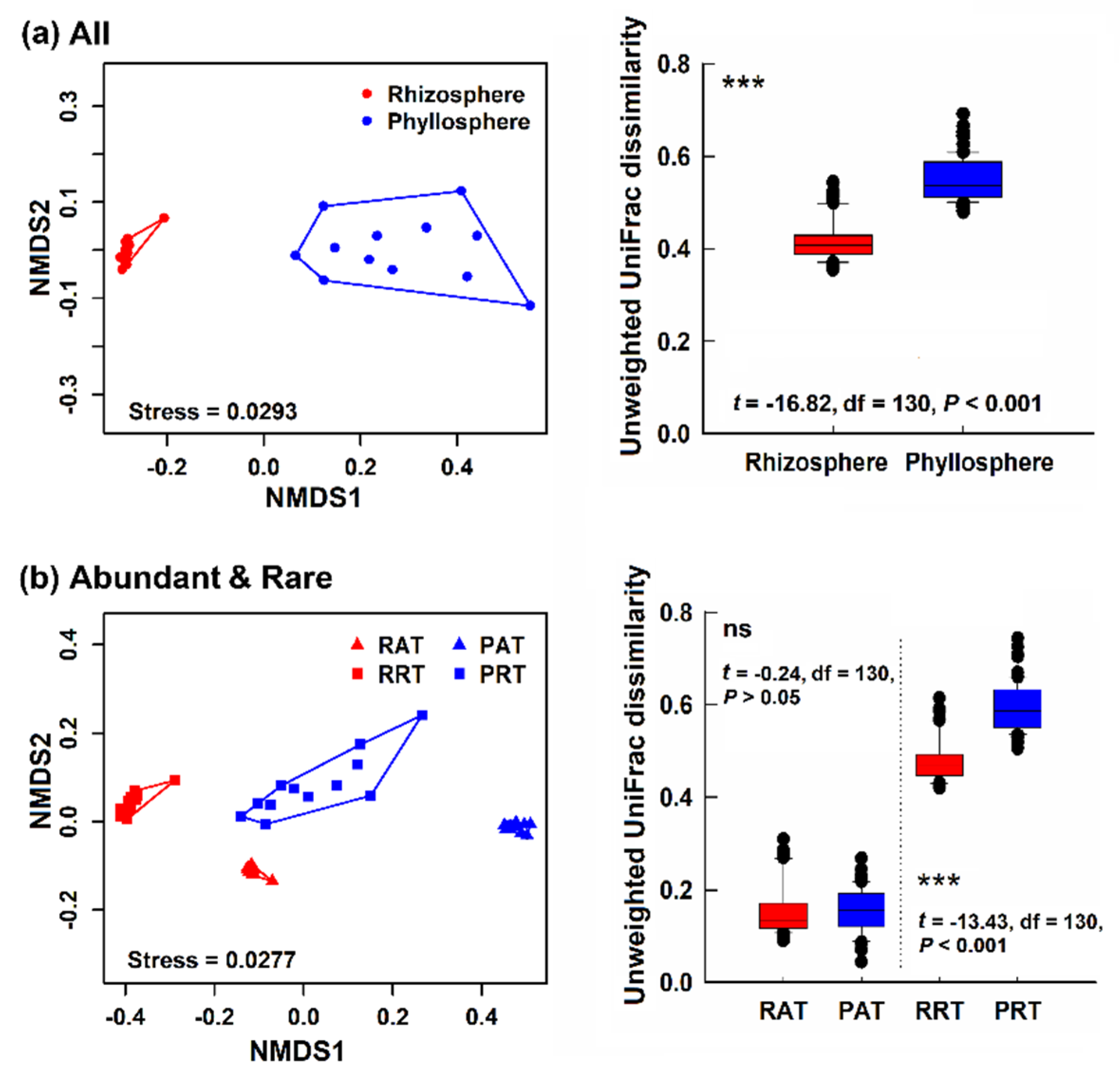
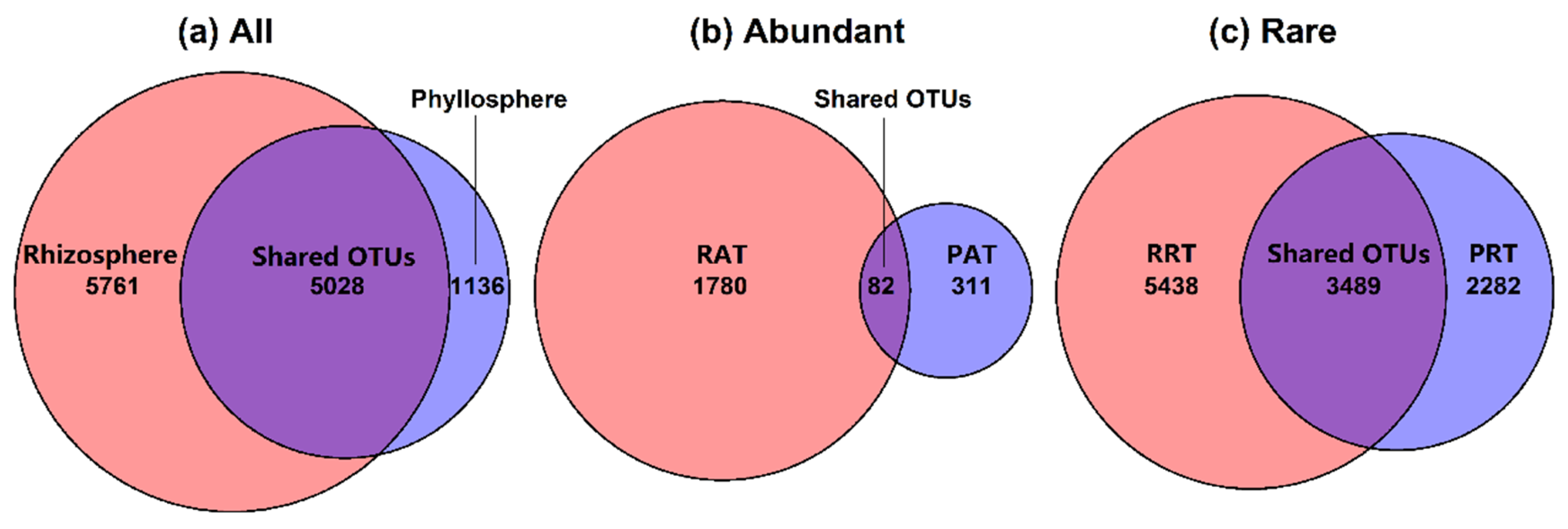
3.2. Bacterial Community Structure in Different Epiphytic Compartments
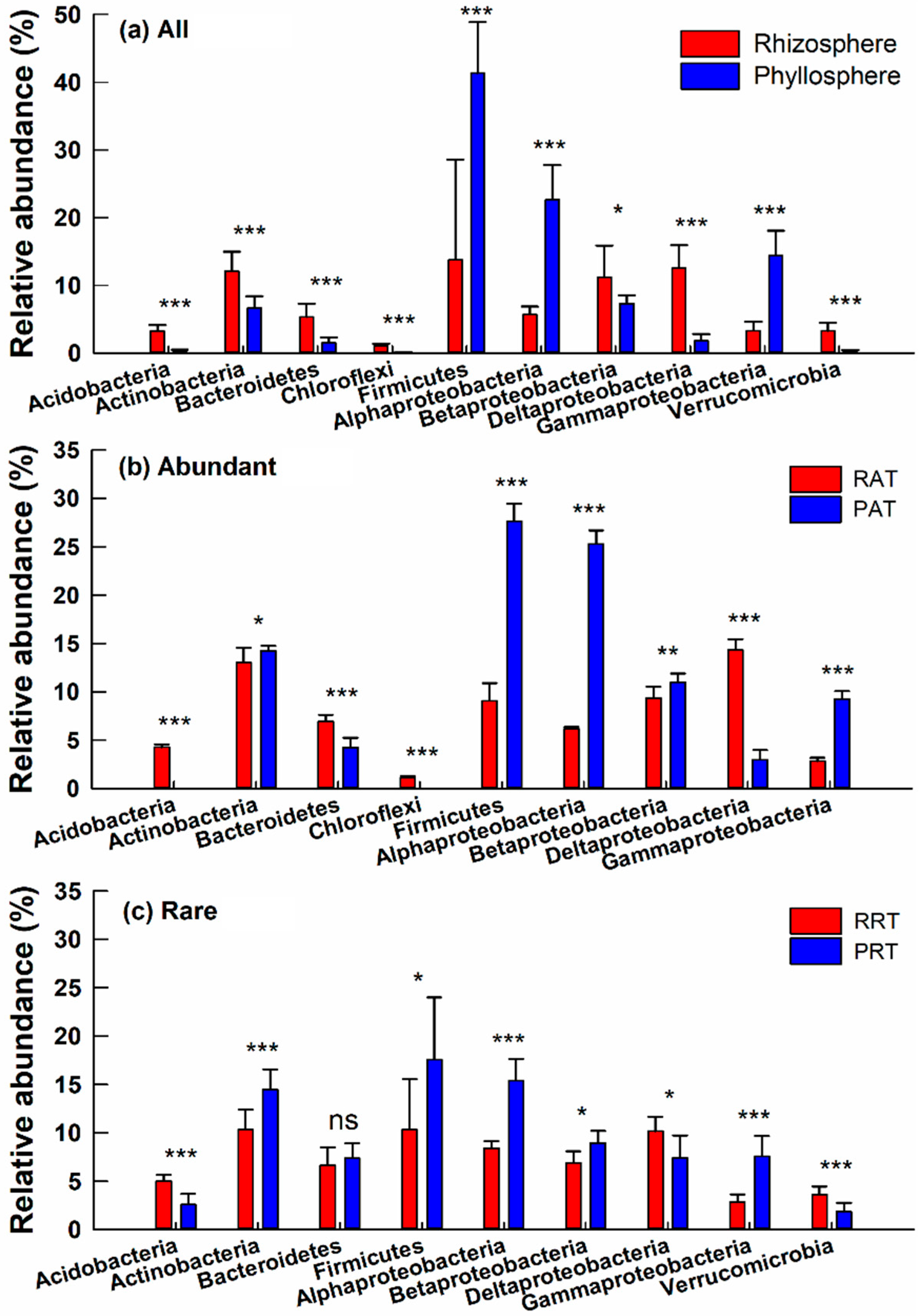
3.3. Taxonomic Differences of Bacterial Community across Different Groups
3.4. Phylogenetic Structure of Bacterial Community
4. Discussion
4.1. Differences of Alpha- and Beta- Diversity in Bacterial Community of Two Epiphytic Compartments
4.2. Similar Taxonomic Composition and Distinct Individual Classes or Genera Across Different Groups
4.3. Diversity and Composition of Abundant Taxa and Rare Taxa
4.4. Phylogenetic Structure of Bacterial Community in Different Epiphytic Compartments
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chambers, R.M.; Meyerson, L.A.; Saltonstall, K. Expansion of Phragmites australis into tidal wetlands of North America. Aquat. Bot. 1999, 64, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, J.L.; Kearns, P.J.; Byrnes, J.E.K.; Wigginton, S.; Allen, W.J.; Greenwood, M.; Tran, K.; Yu, J.; Cronin, J.T.; Meyerson, L.A. Lineage overwhelms environmental conditions in determining rhizosphere bacterial community structure in a cosmopolitan invasive plant. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyerson, L.A.; Cronin, J.T.; Pyšek, P. Phragmites australis as a model organism for studying plant invasions. Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 2421–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achenbach, L.; Lambertini, C.; Brix, H. Phenotypic traits of Phragmites australis clones are not related to ploidy level and distribution range. AoB Plants 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eller, F.; Skalova, H.; Caplan, J.S.; Bhattarai, G.P.; Burger, M.K.; Cronin, J.T.; Guo, W.Y.; Guo, X.; Hazelton, E.L.G.; Kettenring, K.M.; et al. Cosmopolitan species as models for ecophysiological responses to global change:the common reed Phragmites australis. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.P.; Han, W.X.; Thevs, N.; Jia, X.H.; Ji, C.J.; Jin, D.M.; He, P.; Schmitt, A.O.; Cirella, G.T.; Zerbe, S. A comparison of the functional traits of common reed (Phragmites australis) in Northern China: Aquatic vs. terrestrial ecotypes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.L.; Li, X.Y.; Yang, F.; Lu, X.R.; Li, X.J.; Yang, F.Y. Growth and physiology responses of Phragmites australis to combined drought-flooding condition in inland saline-alkaline marsh, Northeast China. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 108, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgarelli, D.; Schlaeppi, K.; Spaepen, S.; Ver Loren van Themaat, E.; Schulze-Lefert, P. Structure and functions of the bacterial microbiota of plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2013, 64, 807–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippot, L.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Lemanceau, P.; van der Putten, W.H. Going back to the roots: The microbial ecology of the rhizosphere. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knief, C.; Ramette, A.; Frances, L.; Alonso-Blanco, C.; Vorholt, J.A. Site and plant species are important determinants of the Methylobacterium community composition in the plant phyllosphere. ISME J. 2010, 4, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacher, C.; Hampe, A.; Porte, A.J.; Sauer, U.; Compant, S.; Morris, C.E. The phyllosphere: Microbial jungle at the plant-climate interface. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2016, 47, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorholt, J.A. Microbial life in the phyllosphere. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 828–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, M.R.; Lundberg, D.S.; Del Rio, T.G.; Tringe, S.G.; Dangl, J.L.; Mitchell-Olds, T. Host genotype and age shape the leaf and root microbiomes of a wild perennial plant. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rico, L.; Ogaya, R.; Terradas, J.; Peñuelas, J. Community structures of N2-fixing bacteria associated with the phyllosphere of a Holm oak forest and their response to drought. Plant Biol. 2014, 16, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckers, B.; Op De Beeck, M.; Weyens, N.; Boerjan, W.; Vangronsveld, J. Structural variability and niche differentiation in the rhizosphere and endosphere bacterial microbiome of field-grown poplar trees. Microbiome 2017, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, J.; Johnson, C.; Santos-Medellin, C.; Lurie, E.; Podishetty, N.K.; Bhatnagar, S.; Eisen, J.A.; Sundaresan, V. Structure, variation, and assembly of the root-associated microbiomes of rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E911–E920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, K.K.; Cardona, C.; Li, Y.T.; Shi, Y.; Xiang, X.J.; Shen, C.C.; Wang, H.F.; Gilbert, J.A.; Chu, H.Y. Rhizosphere-associated bacterial network structure and spatial distribution differ significantly from bulk soil in wheat crop fields. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 113, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofek-Lalzar, M.; Sela, N.; Goldman-Voronov, M.; Green, S.J.; Hadar, Y.; Minz, D. Niche and host-associated functional signatures of the root surface microbiome. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peiffer, J.A.; Spor, A.; Koren, O.; Jin, Z.; Tringe, S.G.; Dangl, J.L.; Buckler, E.S.; Ley, R.E. Diversity and heritability of the maize rhizosphere microbiome under field conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6548–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Xu, J.; Riera, N.; Jin, T.; Li, J.Y.; Wang, N. Huanglongbing impairs the rhizosphere-to-rhizoplane enrichment process of the citrus root-associated microbiome. Microbiome 2017, 5, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgarelli, D.; Rott, M.; Schlaeppi, K.; Ver Loren van Themaat, E.; Ahmadinejad, N.; Assenza, F.; Rauf, P.; Huettel, B.; Reinhardt, R.; Schmelzer, E.; et al. Revealing structure and assembly cues for Arabidopsis root-inhabiting bacterial microbiota. Nature 2012, 488, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlaeppi, K.; Dombrowski, N.; Oter, R.G.; Ver Loren van Themaat, E.; Schulze-Lefert, P. Quantitative divergence of the bacterial root microbiota in Arabidopsis thaliana relatives. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.D.; Pan, Y.B.; Yu, L.Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.J. Patterns and processes in marine microeukaryotic community biogeography from Xiamen coastal waters and intertidal sediments, Southeast China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logares, R.; Audic, S.; Bass, D.; Bittner, L.; Boutte, C.; Christen, R.; Claverie, J.M.; Decelle, J.; Dolan, J.R.; Dunthorn, M.; et al. Patterns of rare and abundant marine microbial eukaryotes. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrós-Alió, C. The rare bacterial biosphere. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2012, 4, 449–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sogin, M.L.; Morrison, H.G.; Huber, J.A.; Mark Welch, D.; Huse, S.M.; Neal, P.R.; Arrieta, J.M.; Herndl, G.J. Microbial diversity in the deep sea and the underexplored “rare biosphere”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12115–12120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.S.; Jeong, J.Y.; Wells, G.F.; Park, H.D. General and rare bacterial taxa demonstrating different temporal dynamic patterns in an activated sludge bioreactor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 1755–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galand, P.E.; Casamayor, E.O.; Kirchman, D.L.; Lovejoy, C. Ecology of the rare microbial biosphere of the Arctic Ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 22427–22432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, J.R.; Liu, M.; Huang, B.; Yang, J. Distinct patterns and processes of abundant and rare eukaryotic plankton communities following a reservoir cyanobacterial bloom. ISME J. 2018, 12, 2263–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debroas, D.; Hugoni, M.; Domaizon, I. Evidence for an active rare biosphere within freshwater protists community. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 1236–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.D.J.; Neufeld, J.D. Ecology and exploration of the rare biosphere. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, B.J.; Yu, L.Y.; Heidelberg, J.F.; Kirchman, D.L. Activity of abundant and rare bacteria in a coastal ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 12776–12781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jousset, A.; Bienhold, C.; Chatzinotas, A.; Gallien, L.; Gobet, A.; Kurm, V.; Küsel, K.; Rillig, M.C.; Rivett, D.W.; Salles, J.F.; et al. Where less may be more: How the rare biosphere pulls ecosystems strings. ISME J. 2017, 11, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shade, A.; Hogan, C.S.; Klimowicz, A.K.; Linske, M.; McManus, P.S.; Handelsman, J. Culturing captures members of the soil rare biosphere. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 2247–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, C.C.; Zhao, D.Y.; Huang, R.; Cao, X.Y.; Zeng, J.; Lin, Y.Q.; Zhao, W.J. Abundant and rare bacterioplankton in freshwater lakes subjected to different levels of tourism disturbances. Water 2018, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, D.S.; Lebeis, S.L.; Paredes, S.H.; Yourstone, S.; Gehring, J.; Malfatti, S.; Tremblay, J.; Engelbrektson, A.; Kunin, V.; del Rio, T.G.; et al. Defining the core Arabidopsis thaliana root microbiome. Nature 2012, 488, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redford, A.J.; Bowers, R.M.; Knight, R.; Linhart, Y.; Fierer, N. The ecology of the phyllosphere: Geographic and phylogenetic variability in the distribution of bacteria on tree leaves. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 2885–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laforest-Lapointe, I.; Messier, C.; Kembel, S.W. Tree leaf bacterial community structure and diversity differ along a gradient of urban intensity. MSystems 2017, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.T.; Highlander, S.K.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a Dual-Index Sequencing Strategy and Curation Pipeline for Analyzing Amplicon Sequence Data on the MiSeq Illumina Sequencing Platform. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunin, V.; Engelbrektson, A.; Ochman, H.; Hugenholtz, P. Wrinkles in the rare biosphere: Pyrosequencing errors can lead to artificial inflation of diversity estimates. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D. The Effects of Alignment Quality, Distance Calculation Method, Sequence Filtering, and Region on the Analysis of 16S rRNA Gene-Based Studies. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2010, 6, e1000844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naïve Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Subramanian, S.; Faith, J.J.; Gevers, D.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.; Mills, D.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree: Computing large minimum evolution trees with profiles instead of a distance matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Shi, F.; Ma, B.; Dong, J.; Pachiadaki, M.; Zhang, X.; Edgcomb, V.P. Depth shapes alpha- and beta-diversities of microbial eukaryotes in surficial sediments of coastal ecosystems. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 3722–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Luo, Y.T.; Lu, M.M.; Xiao, X.; Lin, Y.B.; Chen, W.M.; Wei, G.H. Distinct succession patterns of abundant and rare bacteria in temporal microcosms with pollutants. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Yu, Z.; Wilkinson, D.M. The biogeography of abundant and rare bacterioplankton in the lakes and reservoirs of China. ISME J. 2015, 9, 2068–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. UniFrac: A new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8228–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 13 April 2019).
- Deng, W.K.; Wang, Y.B.; Liu, Z.X.; Cheng, H.; Xue, Y. HemI: A toolkit for illustrating heatmaps. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.J.; Konopka, A.E.; Fredrickson, J.K. Stochastic and deterministic assembly processes in subsurface microbial communities. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, C.O.; Ackerly, D.D.; McPeek, M.A.; Donoghue, M.J. Phylogenies and community ecology. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2002, 33, 475–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kembel, S.W.; Cowan, P.D.; Helmus, M.R.; Cornwell, W.K.; Morlon, H.; Ackerly, D.D.; Blomberg, S.P.; Webb, C.O. Picante: R tools for integrating phylogenies and ecology. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1463–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Soininen, J.; He, J.Z.; Shen, J. Phylogenetic clustering increases with elevation for microbes. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2012, 4, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, P.V.A.; Kembel, S.W. Phylogenetic community structure and phylogenetic turnover across space and edaphic gradients in western Amazonian tree communities. Ecography 2011, 34, 552–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Z.; Ning, D.L. Stochastic community assembly: Does it matter in microbial ecology? Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, O.J. Testing the spatial phylogenetic structure of local communities: Statistical performances of different null models and test statistics on a locally neutral community. J. Ecol. 2008, 96, 914–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.J.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Chen, X.Y.; Kennedy, D.W.; Murray, C.J.; Rockhold, M.L.; Konopka, A. Quantifying community assembly processes and identifying features that impose them. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, J.; Kao-Kniffin, J. Microbial group dynamics in plant rhizospheres and their implications on nutrient cycling. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindow, S.E.; Brandl, M.T. Microbiology of the phyllosphere. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 1875–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahlgren, C.; Hagstrom, A.; Nilsson, D.; Zweifel, U.L. Annual variations in the diversity, viability, and origin of airborne bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 3015–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, R.M.; Jones, A.M.; Biggins, P.D.E.; Pomeroy, N.; Cox, C.S.; Kidd, S.P.; Hobman, J.L.; Brown, N.L.; Beswick, A. Climate factors influencing bacterial count in background air samples. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2005, 49, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maron, P.A.; Lejon, D.P.H.; Carvalho, E.; Bizet, K.; Lemanceau, P.; Ranjard, L.; Mougel, C. Assessing genetic structure and diversity of airborne bacterial communities by DNA fingerprinting and 16S rDNA clone library. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3687–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitman, W.B.; Coleman, D.C.; Wiebe, W.J. Prokaryotes: The unseen majority. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6578–6583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, N.; Murray, R. Proposals concerning the higher taxa of bacteria. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1978, 28, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, A.S.; Hertel, C.; Holzapfel, W.H.; Franz, C.M. Antibiotic resistances of starter and probiotic strains of lactic acid bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, S.; Singh, R. Antibiotic resistance in food lactic acid bacteria—A review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 105, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.Y.D.; Zhu, D.; Giles, M.; Yang, X.R.; Daniell, T.; Neilson, R.; Zhu, Y.G. Phyllosphere of staple crops under pig manure fertilization, a reservoir of antibiotic resistance genes. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albuquerque, L.; Franca, L.; Rainey, F.A.; Schumann, P.; Nobre, M.F.; da Costa, M.S. Gaiella occulta gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel representative of a deep branching phylogenetic lineage within the class Actinobacteria and proposal of Gaiellaceae fam. nov. and Gaiellales ord. nov. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 34, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novello, G.; Gamalero, E.; Bona, E.; Boatti, L.; Mignone, F.; Massa, N.; Cesaro, P.; Lingua, G.; Berta, G. The Rhizosphere Bacterial Microbiota of Vitis vinifera cv. Pinot Noir in an Integrated Pest Management Vineyard. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severino, R.; Froufe, H.J.C.; Barroso, C.; Albuquerque, L.; Lobo-da-Cunha, A.; da Costa, M.S.; Egas, C. High-quality draft genome sequence of Gaiella occulta isolated from a 150 m deep mineral water borehole and comparison with the genome sequences of other deep-branching lineages of the phylum Actinobacteria. MicrobiologyOpen 2019, e840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vreeland, R.H.; Anderson, R.; Murray, R.G. Cell wall and phospholipid composition and their contribution to the salt tolerance of Halomonas elongata. J. Bacteriol. 1984, 160, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata, J.A.; Martinez-Canovas, J.; Quesada, E.; Bejar, V. A detailed phenotypic characterisation of the type strains of Halomonas species. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 25, 360–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, O.M.; Burch, A.Y.; Lindow, S.E.; Post, A.F.; Belkin, S. Geographical Location Determines the Population Structure in Phyllosphere Microbial Communities of a Salt-Excreting Desert Tree. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7647–7655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, D.R.; Lovley, D.R. Electricity production by Geobacter sulfurreducens attached to electrodes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 1548–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childers, S.E.; Ciufo, S.; Lovley, D.R. Geobacter metallireducens accesses insoluble Fe(III) oxide by chemotaxis. Nature 2002, 416, 767–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambright, K.D.; Beyer, J.E.; Easton, J.D.; Zamor, R.M.; Easton, A.C.; Hallidayschult, T.C. The niche of an invasive marine microbe in a subtropical freshwater impoundment. ISME J. 2015, 9, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dini-Andreote, F.; de Cássia Pereira e Silva, M.; Triadó-Margarit, X.; Casamayor, E.O.; van Elsas, J.D.; Salles, J.F. Dynamics of bacterial community succession in a salt marsh chronosequence: Evidences for temporal niche partitioning. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1989–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orrock, J.L.; Watling, J.I. Local community size mediates ecological drift and competition in metacommunities. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 2185–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kragelund, C.; Levantesi, C.; Borger, A.; Thelen, K.; Eikelboom, D.; Tandoi, V.; Kong, Y.H.; van der Waarde, J.; Krooneman, J.; Rossetti, S.; et al. Identity, abundance and ecophysiology of filamentous Chloroflexi species present in activated sludge treatment plants. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 59, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chase, J.M. Drought mediates the importance of stochastic community assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 17430–17434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Patel, S.N. Community assembly in the presence of disturbance: A microcosm experiment. Ecology 2008, 89, 1931–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Q.; Zhang, X.; He, R.; Wang, S.; Jiao, C.; Huang, R.; He, X.; Zeng, J.; Zhao, D. The Composition and Assembly of Bacterial Communities across the Rhizosphere and Phyllosphere Compartments of Phragmites Australis. Diversity 2019, 11, 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11060098
Zhou Q, Zhang X, He R, Wang S, Jiao C, Huang R, He X, Zeng J, Zhao D. The Composition and Assembly of Bacterial Communities across the Rhizosphere and Phyllosphere Compartments of Phragmites Australis. Diversity. 2019; 11(6):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11060098
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Qi, Xiaomin Zhang, Rujia He, Shuren Wang, Congcong Jiao, Rui Huang, Xiaowei He, Jin Zeng, and Dayong Zhao. 2019. "The Composition and Assembly of Bacterial Communities across the Rhizosphere and Phyllosphere Compartments of Phragmites Australis" Diversity 11, no. 6: 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11060098
APA StyleZhou, Q., Zhang, X., He, R., Wang, S., Jiao, C., Huang, R., He, X., Zeng, J., & Zhao, D. (2019). The Composition and Assembly of Bacterial Communities across the Rhizosphere and Phyllosphere Compartments of Phragmites Australis. Diversity, 11(6), 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11060098






