Continuous Agrochemical Treatments in Agroecosystems Can Modify the Effects of Pendimethalin-Based Herbicide Exposure on Immunocompetence of a Beneficial Ground Beetle
Abstract
1. Introduction
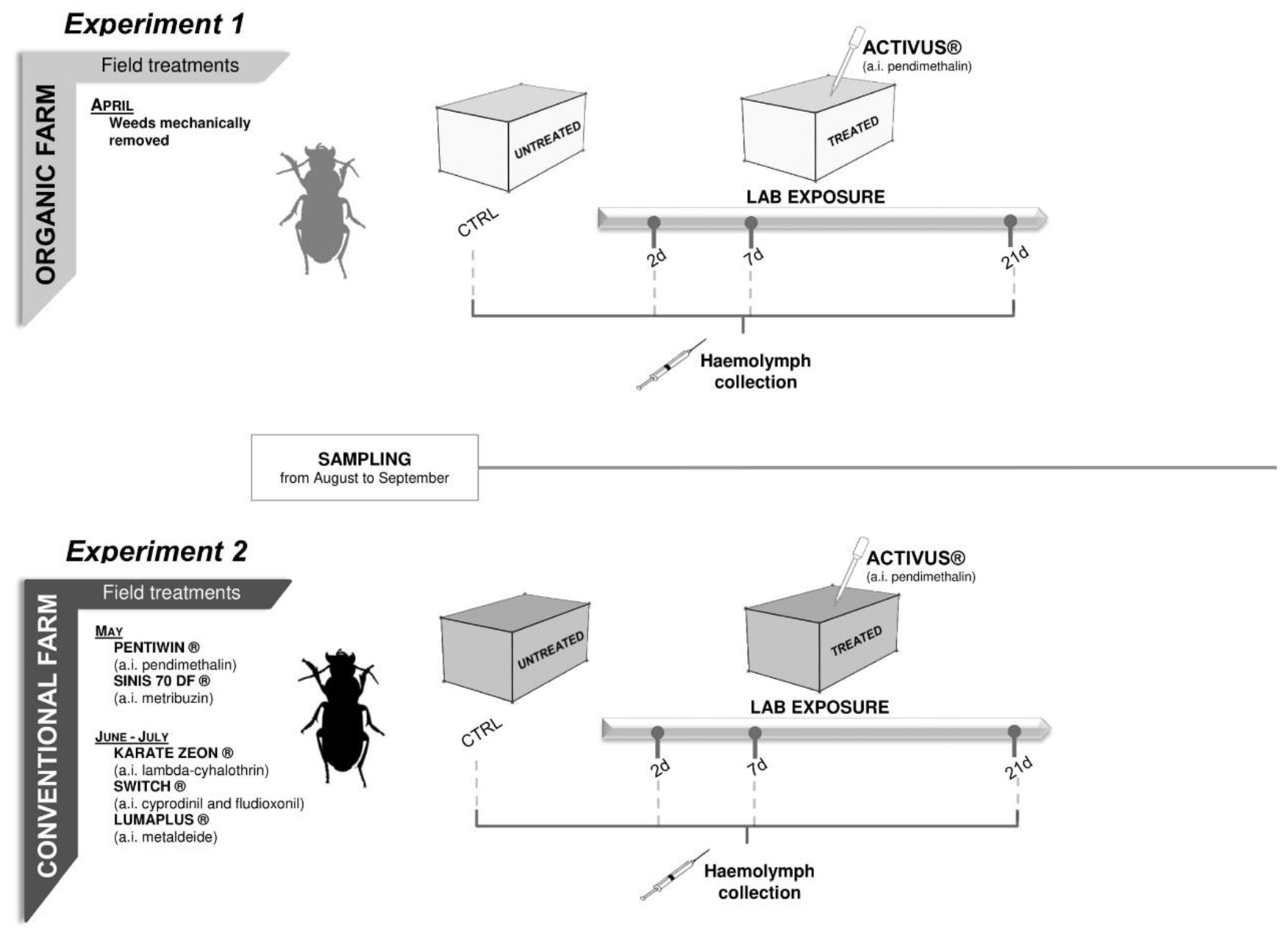
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Insect Sampling and Maintenance
2.2. Laboratory Toxicity Test Set up
2.3. Measured Parameters
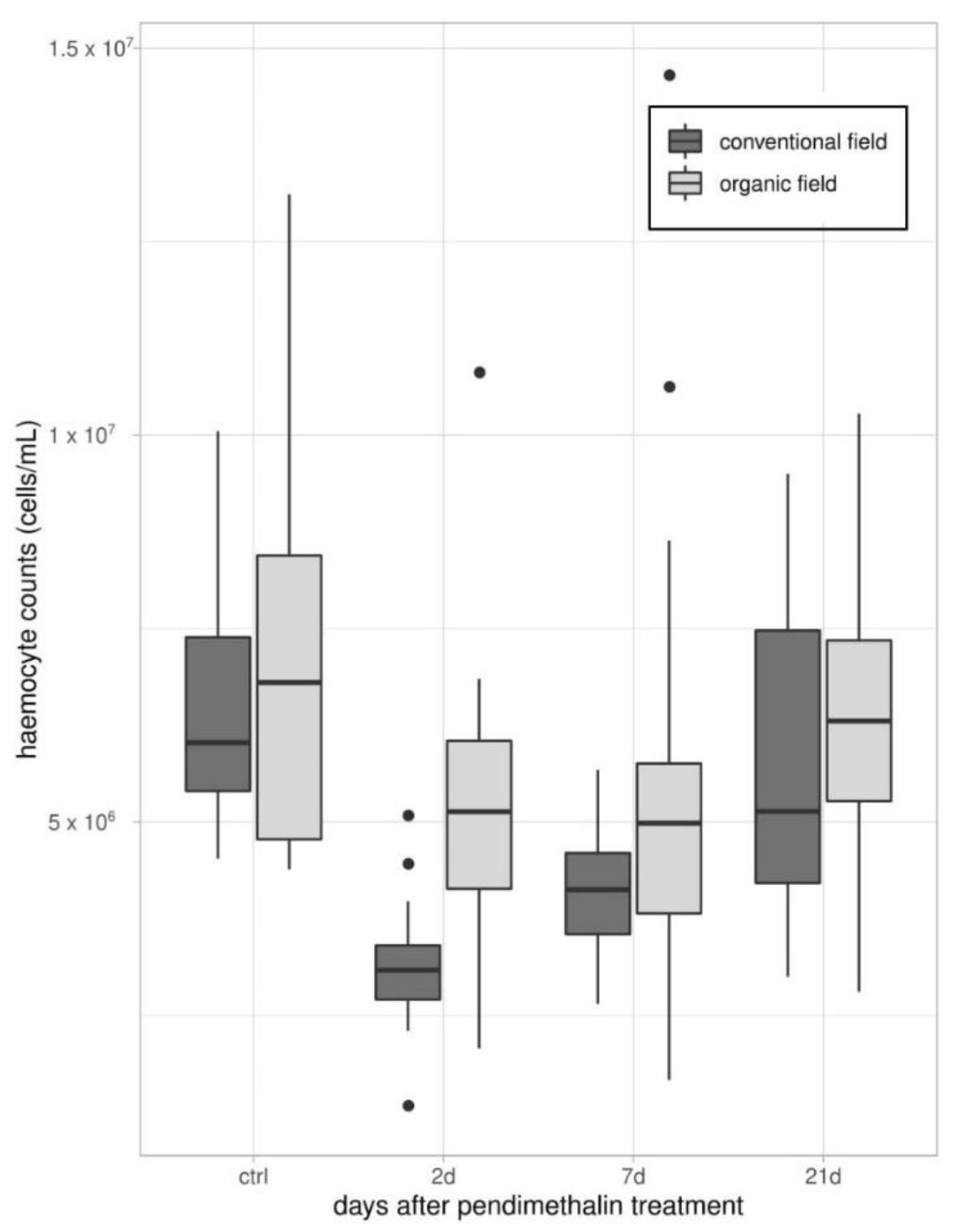
2.3.1. Total Hemocyte Counts (THCs)
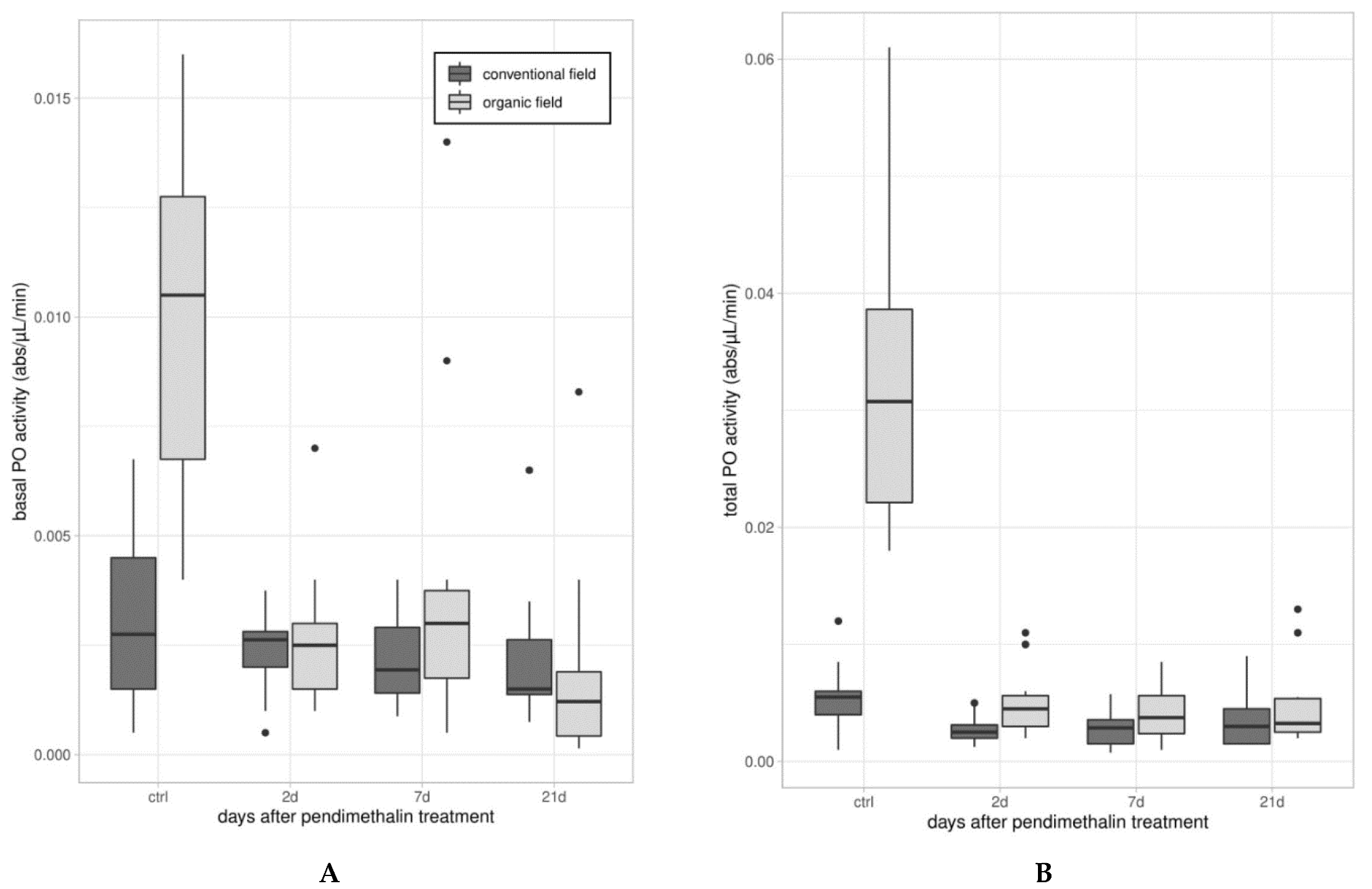
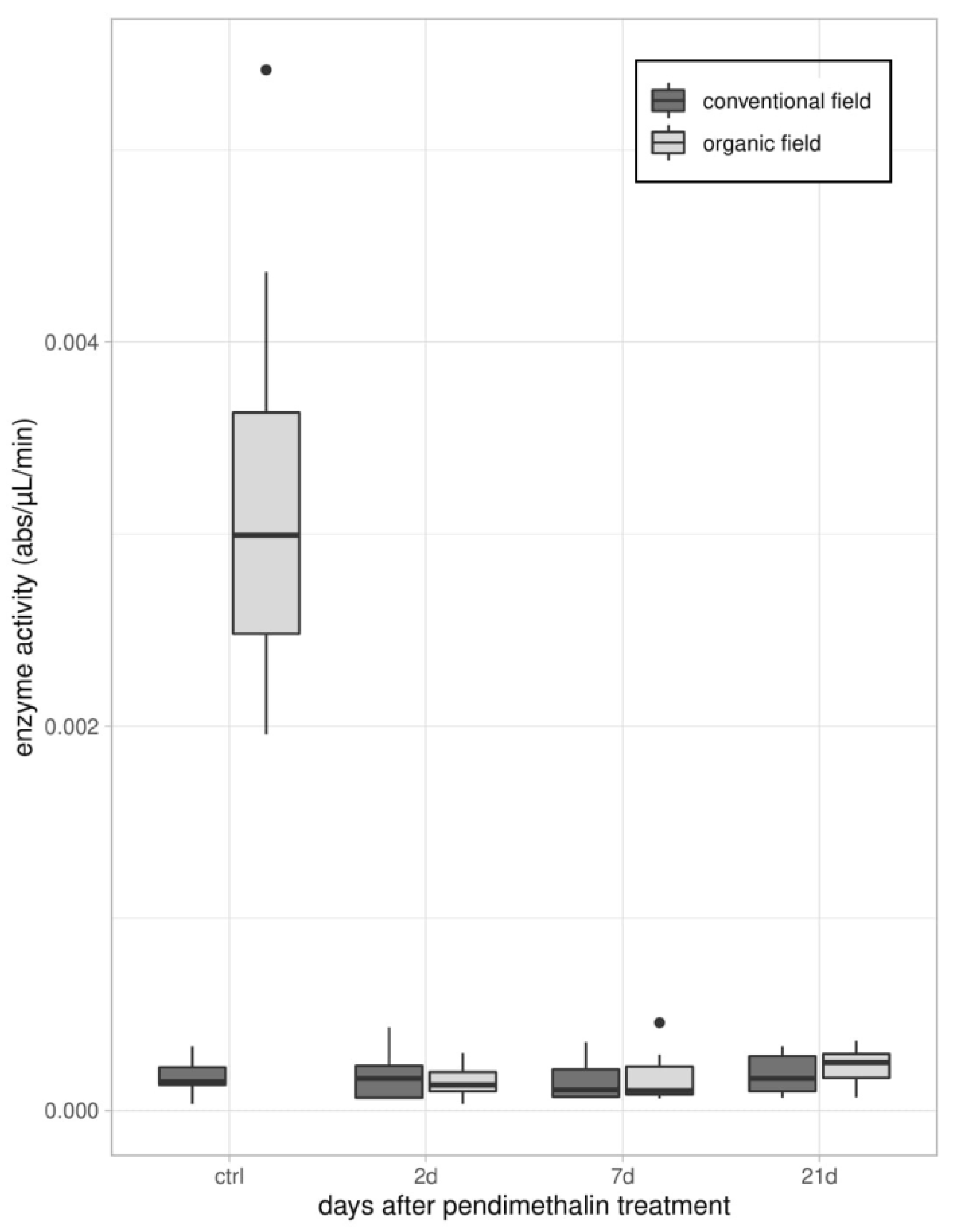
2.3.2. Enzymatic Assays
2.3.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Immune Parameters in Beetles from Organic and Conventional Fields
3.2. Immune Parameters Following the Laboratory Exposure to Sub-Lethal Dose of PDN
3.2.1. Experiment 1—Treated Beetles from Organic Untreated Field
3.2.2. Experiment 2—Treated Beetles from Conventional Field
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prosser, R.S.; Anderson, J.C.; Hanson, M.L.; Solomon, K.R.; Sibley, P.K. Indirect effects of herbicides on biota in terrestrial edge-of-field habitats: A critical review of the literature. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 232, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freemark, K.; Boutin, C. Impacts of agricultural herbicide use on terrestrial wildlife in temperate landscapes: A review with special reference to North America. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1995, 52, 67–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Moreno, S.; Castro, J.; Alonso-Prados, E.; Alonso-Prados, J.L.; García-Baudín, J.M.; Talavera, M.; Durán-Zuazo, V.H. Tillage and herbicide decrease soil biodiversity in olive orchards. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stellin, F.; Gavinelli, F.; Stevanato, P.; Concheri, G.; Squartini, A.; Paoletti, M.G. Effects of different concentrations of glyphosate (Roundup 360®) on earthworms (Octodrilus complanatus, Lumbricus terrestris and Aporrectodea caliginosa) in vineyards in the North-East of Italy. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 123, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemeyer, J.C.; de Santo, F.B.; Guerra, N.; Filho, A.M.R.; Pech, T.M. Do recommended doses of glyphosate-based herbicides affect soil invertebrates? Field and laboratory screening tests to risk assessment. Chemosphere 2018, 198, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalková, V.; Pekár, S. How glyphosate altered the behaviour of agrobiont spiders (Araneae: Lycosidae) and beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Biol. Control 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korenko, S.; Niedobová, J.; Kolářová, M.; Hamouzová, K.; Kysilková, K.; Michalko, R. The effect of eight common herbicides on the predatory activity of the agrobiont spider Pardosa agrestis. BioControl 2016, 61, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Jha, P.; Reddy, G.V.P. Multidimensional relationships of herbicides with insect-crop food webs. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1522–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O. Overview of herbicide mechanisms of action. Environ. Health Perspect. 1990, 87, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, M.T.; Cavagnaro, T.R.; Scanlan, C.A.; Rose, T.J.; Vancov, T.; Kimber, S.; Kennedy, I.R.; Kookana, R.S.; Van Zwieten, L. Impact of herbicides on soil biology and function. In Advances in Agronomy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 136, pp. 133–220. ISBN 0065-2113. [Google Scholar]
- Vighi, M.; Matthies, M.; Solomon, K.R. Critical assessment of pendimethalin in terms of persistence, bioaccumulation, toxicity, and potential for long-range transport. J. Toxicol. Environ. Heal. Part B 2017, 20, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandberg, M.; Scott-Fordsmand, J.J. Effects of pendimethalin at lower trophic levels—A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 57, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traoré, H.; Crouzet, O.; Mamy, L.; Sireyjol, C.; Rossard, V.; Servien, R.; Latrille, E.; Martin-Laurent, F.; Patureau, D.; Benoit, P. Clustering pesticides according to their molecular properties, fate, and effects by considering additional ecotoxicological parameters in the TyPol method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 4728–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Ahmad, M. Fresh water fish, Channa punctatus, as a model for pendimethalin genotoxicity testing: A new approach toward aquatic environmental contaminants. Environ. Toxicol. 2016, 31, 1520–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassum, H.; Afjal, M.A.; Khan, J.; Raisuddin, S.; Parvez, S. Neurotoxicological assessment of pendimethalin in freshwater fish Channa punctata Bloch. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 58, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belden, J.B.; Phillips, T.A.; Clark, B.W.; Coats, J.R. Toxicity of pendimethalin to nontarget soil organisms. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2005, 74, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, J.B.; Reding, M.E.; Moyseenko, J.J.; Klein, M.G.; Mannion, C.M.; Bishop, B. Survival of adult Tiphia vernalis (Hymenoptera: Tiphiidae) after insecticide, fungicide, and herbicide exposure in laboratory bioassays. J. Econ. Entomol. 2006, 99, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.M. Carabid beetles: Their ecology, survival and use in agroecosystems. In Agroecol. Carabid Beetles; Intercept Ltd.: Hanover, UK, 2002; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Kromp, B. Carabid beetles (Coleoptera, Carabidae) as bioindicators in biological and conventional farming in Austrian potato fields. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1990, 9, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honek, A.; Saska, P.; Martinkova, Z. Seasonal variation in seed predation by adult carabid beetles. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2006, 118, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kromp, B. Carabid beetles in sustainable agriculture: A review on pest control efficacy, cultivation impacts and enhancement. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1999, 74, 187–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.S.; Dosdall, L.M.; Willenborg, C.J. The Role of Ground Beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) in Weed Seed Consumption: A Review. Weed Sci. 2015, 63, 355–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainio, J.; Niemelä, J. Ground beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) as bioindicators. Biodivers. Conserv. 2003, 12, 487–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivula, M.J. Useful model organisms, indicators, or both? Ground beetles (Coleoptera, Carabidae) reflecting environmental conditions. Zookeys 2011, 100, 287–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brygadyrenko, V.V.; Reshetniak, D.Y. Trophic preferences of Harpalus rufipes (Coleoptera, Carabidae) with regard to seeds of agricultural crops in conditions of laboratory experiment. Balt. J. Coleopterol. 2014, 14, 179–190. [Google Scholar]
- Faly, L.; Brygadyrenko, V. Patterns in the horizontal structure of litter invertebrate communities in windbreak plantations in the steppe zone of the Ukraine. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2014, 54, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinós, G.P.; de la Poza, M.; Hernández-Crespo, P.; Ortego, F.; Castañera, P. Diversity and seasonal phenology of aboveground arthropods in conventional and transgenic maize crops in Central Spain. Biol. Control 2008, 44, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irmler, U. The spatial and temporal pattern of carabid beetles on arable fields in northern Germany (Schleswig-Holstein) and their value as ecological indicators. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 98, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lövei, G.L.; Sarospataki, M. Carabids in agricultural fields in Eastern Europe. In The Role of Ground Beetles in Ecological and Environmental Research; Stork, N.E., Ed.; Intercept Ltd.: Hanover, UK, 1990; pp. 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Miñarro, M.; Espadaler, X.; Melero, V.X.; Suárez-Álvarez, V. Organic versus conventional management in an apple orchard: Effects of fertilization and tree-row management on ground-dwelling predaceous arthropods. Agric. For. Entomol. 2009, 11, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Parkinson, L.; Griffiths, G.J.K.; Garcia, A.F.; Marshall, E.J.P. Aggregation and temporal stability of carabid beetle distributions in field and hedgerow habitats. J. Appl. Ecol. 2001, 38, 100–116. [Google Scholar]
- Zaller, J.G.; Moser, D.; Drapela, T.; Frank, T. Ground-dwelling predators can affect within-field pest insect emergence in winter oilseed rape fields. BioControl 2008, 54, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honek, A.; Martinkova, Z.; Saska, P. Post-dispersal predation of Taraxacum officinale (dandelion) seed. J. Ecol. 2005, 93, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honek, A.; Martinkova, Z.; Jarosik, V. Ground beetles (Carabidae) as seed predators. Eur. J. Entomol. 2003, 100, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshetniak, D.Y.; Pakhomov, O.Y.; Brygadyrenko, V. V Possibility of identifying plant components of the diet of Harpalus rufipes (Coleoptera, Carabidae) by visual evaluation. Regul. Mech. Biosyst. 2017, 8, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saska, P.; van der Werf, W.; de Vries, E.; Westerman, P.R. Spatial and temporal patterns of carabid activity-density in cereals do not explain levels of predation on weed seeds. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2008, 98, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saska, P.; Martinkova, Z.; Honek, A. Temperature and rate of seed consumption by ground beetles (Carabidae). Biol. Control 2010, 52, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talarico, F.; Giglio, A.; Pizzolotto, R.; Brandmayr, P. A synthesis of feeding habits and reproduction rhythm in Italian seed-feeding ground beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2016, 113, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Drummond, F.A.; Liebman, M.; Hartke, A. Phenology and dispersal of Harpalus rufipes DeGeer(Coleoptera: Carabidae) in agroecosystems in Maine. J. Agric. Entomol. 1997, 14, 171–186. [Google Scholar]
- Eyre, M.D.; Luff, M.L.; Leifert, C. Crop, field boundary, productivity and disturbance influences on ground beetles (Coleoptera, Carabidae) in the agroecosystem. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 165, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, F.; Brandmayr, P.; Giglio, A. DNA damage in haemocytes of Harpalus (Pseudophonus) rufipes (De Geer, 1774)(Coleoptera, Carabidae) as an indicator of sublethal effects of exposure to herbicides. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 98, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, R.R.; Xu, J. Mechanisms by which pesticides affect insect immunity. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 109, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St Clair, C.R.; Fuller, C.A. Atrazine Exposure Influences Immunity in the Blue Dasher Dragonfly, Pachydiplax longipennis (Odonata: Libellulidae). J. Insect Sci. 2018, 18, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-García, M.; Córdoba-Aguilar, A.; Condé, R.; Lanz-Mendoza, H. Current immunity markers in insect ecological immunology: Assumed trade-offs and methodological issues. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2013, 103, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, C.; Brehélin, M. Insect haemocytes: What type of cell is that? J. Insect Physiol. 2006, 52, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmaras, V.J.; Lampropoulou, M. Regulators and signalling in insect haemocyte immunity. Cell. Signal. 2009, 21, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosales, C. Phagocytosis, a cellular immune response in insects. Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2011, 8, 109–131. [Google Scholar]
- Strand, M.R. The insect cellular immune response. Insect Sci. 2008, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, J.P.; Kanost, M.R.; Trenczek, T. Biological mediators of insect immunity. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1997, 42, 611–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrinello, N.; Arizza, V.; Chinnici, C.; Parrinello, D.; Cammarata, M. Phenoloxidases in ascidian hemocytes: Characterization of the pro-phenoloxidase activating system. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 135, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerenius, L.; Lee, B.L.; Söderhäll, K. The proPO-system: Pros and cons for its role in invertebrate immunity. Trends Immunol. 2008, 29, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Santoyo, I.; Córdoba-Aguilar, A. Phenoloxidase: A key component of the insect immune system. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2012, 142, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B.; Wu, K.; Xie, W.; Luan, Y.-X.; Ling, E. Insect prophenoloxidase: The view beyond immunity. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillyer, J.F. Insect immunology and hematopoiesis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 58, 102–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratcliffe, N.A.; Rowley, A.F.; Fitzgerald, S.W.; Rhodes, C.P. Invertebrate immunity: Basic concepts and recent advances. In International Review of Cytology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1985; Volume 97, pp. 183–350. ISBN 0074-7696. [Google Scholar]
- Nappi, A.J.; Ottaviani, E. Cytotoxicity and cytotoxic molecules in invertebrates. Bioessays 2000, 22, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.A.; Zhang, L.; Dorrah, M.A.; Elmogy, M.; Yousef, H.A.; Bassal, T.T.M.; Duvic, B. Molecular characterization of a c-type lysozyme from the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria (Orthoptera: Acrididae). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 61, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.-Q.; Zhu, Y.-F.; Ma, C.; Fabrick, J.A.; Kanost, M.R. Pattern recognition proteins in Manduca sexta plasma. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 32, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiołka, M.J.; Ptaszyńska, A.A.; Czarniawski, W. Antibacterial and antifungal lysozyme-type activity in Cameraria ohridella pupae. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2005, 90, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Tan, L.; Hu, N.; Dong, Z.; Hu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, P.; Pan, M.; Lu, C. C-lysozyme contributes to antiviral immunity in Bombyx mori against nucleopolyhedrovirus infection. J. Insect Physiol. 2018, 108, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.M.; Potter, T.L.; Lima, I.M. Sugarcane and pinewood biochar effects on activity and aerobic soil dissipation of metribuzin and pendimethalin. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 74, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chiverton, P.A.; Sotherton, N.W. The effects of beneficial arthropods of the exclusion of herbicides from cereal crop edges. J. Appl. Ecol. 1991, 28, 1027–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, C.J.S. The effects of five herbicides on the numbers of certain invertebrate animals in grassland soil. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1964, 44, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, G.J.; Worsham, A.D.; Sheets, T.J.; Stinner, R.E. Herbicide effects on soil arthropod dynamics and wheat straw decomposition in a North Carolina no-tillage agroecosystem. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1987, 4, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolařík, P.; Rotrekl, J.; Barták, M.; Krupauerová, A.; Frydrych, J. A comparison of ground beetle assemblages (Coleoptera: Carabidae) in conventionally and ecologically managed alfalfa fields. J. Entomol. Acarol. Res. 2014, 46, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- VelcheVa, I.; PetroVa, S.; MolloV, I.; GecheVa, G.; GeorGIeV, D. Herbicides influence tHe community structure of tHe soil mezofauna. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 18, 742–748. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.X.; Drummond, F.A.; Leibman, M. Effect of crop habitat and potato management practices on the population abundance of adult Harpalus rufipes (Coleoptera: Carabidae) in Maine. J. Agric. Entomol. 1998, 15, 63–74. [Google Scholar]
- Kegel, B. Laboratory experiments on the side effects of selected herbicides and insecticides on the larvae of three sympatric Poecilus-species (Col., Carabidae). J. Appl. Entomol. 1989, 108, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Römbke, J.; Heimbach, U. Experiences derived from the carabid beetle laboratory test. Pestic. Sci. 1996, 46, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brust, G.E. Direct and indirect effects of four herbicides on the activity of carabid beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 1990, 30, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, M. Binding properties of pendimethalin herbicide to DNA: Multispectroscopic and molecular docking approaches. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 6476–6485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Bajpayee, M.; Pandey, A.K.; Parmar, D.; Dhawan, A. In vitro induction of cytotoxicity and DNA strand breaks in CHO cells exposed to cypermethrin, pendimethalin and dichlorvos. Toxicol. Vitr. 2007, 21, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıç, Z.S.; Aydın, S.; Bucurgat, Ü.Ü.; Başaran, N. In vitro genotoxicity assessment of dinitroaniline herbicides pendimethalin and trifluralin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 113, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, B.D.; Gadeva, P.G.; Benova, D.K.; Bineva, M. V Comparative genotoxicity of the herbicides Roundup, Stomp and Reglone in plant and mammalian test systems. Mutagenesis 2006, 21, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.M.; Saquib, Q.; Attia, S.M.; Abdel-Salam, E.M.; Alwathnani, H.A.; Faisal, M.; Alatar, A.A.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Musarrat, J. Pendimethalin induces oxidative stress, DNA damage, and mitochondrial dysfunction to trigger apoptosis in human lymphocytes and rat bone-marrow cells. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 149, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danion, M.; Le Floch, S.; Lamour, F.; Quentel, C. Effects of in vivo chronic exposure to pendimethalin on EROD activity and antioxidant defenses in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 99, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margus, A.; Rainio, M.; Lindström, L. Can indirect herbicide exposure modify the response of the colorado potato beetle to an organophosphate insecticide? J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 2316–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainio, M.J.; Margus, A.; Lehmann, P.; Helander, M.; Lindström, L. Effects of a glyphosate-based herbicide on survival and oxidative status of a non-target herbivore, the Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 215, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid-Hempel, P. Evolutionary ecology of insect immune defenses. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2005, 50, 529–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadd, B.M.; Schmid-Hempel, P. Ecological and evolutionary implications of specific immune responses. Insect Infect. Immun. Evol. Ecol. Mech. 2009, 25, 225. [Google Scholar]
- Rolff, J.; Siva-Jothy, M.T. Invertebrate ecological immunology. Science 2003, 301, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawniczak, M.K.N.; Barnes, A.I.; Linklater, J.R.; Boone, J.M.; Wigby, S.; Chapman, T. Mating and immunity in invertebrates. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmaras, V.J.; Charalambidis, N.D.; Zervas, C.G. Immune response in insects: The role of phenoloxidase in defense reactions in relation to melanization and sclerotization. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. Publ. Collab. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1996, 31, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, A.I.; Siva-Jothy, M.T. Density–dependent prophylaxis in the mealworm beetle Tenebrio molitor L.(Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae): Cuticular melanization is an indicator of investment in immunity. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2000, 267, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giglio, A.; Cavaliere, F.; Giulianini, P.G.; Kurtz, J.; Vommaro, M.L.; Brandmayr, P. Continuous Agrochemical Treatments in Agroecosystems Can Modify the Effects of Pendimethalin-Based Herbicide Exposure on Immunocompetence of a Beneficial Ground Beetle. Diversity 2019, 11, 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11120241
Giglio A, Cavaliere F, Giulianini PG, Kurtz J, Vommaro ML, Brandmayr P. Continuous Agrochemical Treatments in Agroecosystems Can Modify the Effects of Pendimethalin-Based Herbicide Exposure on Immunocompetence of a Beneficial Ground Beetle. Diversity. 2019; 11(12):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11120241
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiglio, Anita, Francesco Cavaliere, Piero Giulio Giulianini, Joachim Kurtz, Maria Luigia Vommaro, and Pietro Brandmayr. 2019. "Continuous Agrochemical Treatments in Agroecosystems Can Modify the Effects of Pendimethalin-Based Herbicide Exposure on Immunocompetence of a Beneficial Ground Beetle" Diversity 11, no. 12: 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11120241
APA StyleGiglio, A., Cavaliere, F., Giulianini, P. G., Kurtz, J., Vommaro, M. L., & Brandmayr, P. (2019). Continuous Agrochemical Treatments in Agroecosystems Can Modify the Effects of Pendimethalin-Based Herbicide Exposure on Immunocompetence of a Beneficial Ground Beetle. Diversity, 11(12), 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11120241





