Abstract
Dendropoma lebeche is a prosobranch gastropod belonging to the family Vermetidae, which calcifies its shell on hard substrates in dense aggregates, forming biogenic constructions along the western Mediterranean intertidal habitat. It is an important ecosystem engineer and, due to its ecological value, is protected by international convention. The aim of this study is to investigate the mollusc composition and diversity occurring within Spanish vermetid bioconstructions. During the late summer 2013, three distant sites along the Mediterranean coast of Spain were sampled by scraping off the vermetid shells to study their associated assemblages. A total of 600 molluscs were identified within the classes of Polyplacophora (four species), Gastropoda (35 spp.) and Bivalvia (18 spp.). Multivariate analyses revealed significant differences in composition and trophic diversity of mollusc assemblages among the three sites, highlighting a clear geographical gradient. Overall, both herbivores (grazers and deposit feeders) and omnivores were the quantitatively dominant trophic groups, while carnivores (predators and ectoparasites) were very scarce. Our results point out that mollusc assemblages associated with vermetid bioconstructions are rich and diversified, both in populations structure and trophic diversity, confirming the important role of vermetid gastropods as ecosystem engineers and biodiversity enhancers in shallow coastal waters.
1. Introduction
Marine coastal areas and continental shelves are generally characterized by highly productive ecosystems with elevated levels of biodiversity. The Mediterranean Sea, despite its relatively small dimensions [1], is known as a hotspot of biodiversity [2,3]. In its shallow waters several biogenic structures (bioconstructions) play an important role in the high level of biodiversity, even though they are less known than those flourishing in tropical seas [4].
The bioconstructions built by gastropods belonging to the genus Dendropoma (Vermetidae) are commonly distributed along the shallow warm-water coasts of the Mediterranean Sea and are particularly important as biological markers of sea level fluctuations, they protect the underlying rock from the coastal erosion processes and increase the hard-bottom complexity [5,6,7].
The sessile and gregarious habits of vermetids along with their capability of secreting calcium carbonate are the main features through which the biogenic structures are built up along shallow rocky coasts; these concretions attract and become colonized by a particular associated community [8,9,10]. The vermetid shells overgrow each other, starting from the hard substrate on which the species primarily settled. The result is a complex bioconstruction that hosts a large number of small invertebrates, enhancing local density and species richness. The vermetid shells are structural components of habitats (sensu Jones [11]) and play a multiple functional role: (i) providing protection to the organisms against the physical disturbance caused by water movement and the physiological stress caused by desiccation during low tide; (ii) constituting a suitable substrate for colonization as well as a refuge from predation; (iii) supporting high resources availability at different trophic levels [12,13].
Current research works are mainly focused on the reproductive biology of vermetid species from different areas along the Mediterranean coasts (e.g., Spain [14], Italy [15], Israel [16,17], western and central Mediterranean [18]). Conversely, there are few studies regarding fauna associated with the vermetid bioconstructions. In the eastern Mediterranean, along the Israeli shore, the polychaete assemblage living among vermetid shells was composed of 70 species [13], while fish biodiversity was represented by 36 species [19]. In the central Mediterranean, along the Sicilian shore, the algal community was represented by more than 100 species [20], fish biodiversity by 39 taxa belonging to 15 families [21] and the mollusc community by 46 taxa [22] and by 28 gastropod species [10]. Along the Western Mediterranean coast, the fauna associated with these biogenic structures is still poorly documented [23], while recent research deals mainly with algal assemblages, represented by over 100 taxa [24,25].
The main purpose of the present study is therefore to investigate the role of the vermetid bioconstructions, formed by the endemic prosobranch Dendropoma lebeche Templado, Richter and Calvo 2016, in modeling the structural and functional (trophic) diversity of the associated mollusc assemblage along the Spanish Mediterranean coast.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Design
Study area was located along the Alicante and Murcia coast of southern Spain (western Mediterranean) (Figure 1), in three rocky intertidal sites: Cabo de Palos (CP; 37°37′ N, 0°42′ W), Punta Prima (PP; 37°56′ N, 0°42′ W) and Jávea (Ja; 38°46′ N, 0°12′ E). In this area the winter surface temperature does not fall below 14 °C [14]. The selected sites are at considerable distance apart: Cabo de Palos is located approximately 35 km from Punta Prima and 150 km from Jávea. The three sites were surveyed between late September and early October 2013. Three randomly selected replicates from each site were collected by scraping off the substratum, consisting of a dense vermetid shells layer of about 2 cm in thickness, within a 10 × 10 cm frame using hammer and chisel. Since D. lebeche is a threatened and ecologically significant species, included (as D. petraeum) in the SPA/BIO Protocol (Barcelona Convention) and in the Habitats Directive 92/43/EEC, the sampling effort was reduced at a total of 9 replicates for the analysis of the associated mollusc assemblages.
Figure 1.
Map of the Mediterranean Spanish coast showing the geographical position of the three sampling sites: Cabo de Palos (CP), Punta Prima (PP) and Jávea (Ja).
In the laboratory samples were fixed in 4% formalin-seawater solution and transferred, after 48 h, into 70% ethanol for future species observation. They were then carefully checked under the stereomicroscope and all the macrobenthic invertebrates (>0.5 mm) found among and inside the empty shells of vermetids were removed for further identification. The samples were split into small fragments and checked again under the stereomicroscope and additional invertebrates found were sorted out. Molluscs were selected and identified at species level whenever possible. Mollusc nomenclature follows the World Register of Marine Species database [26].
2.2. Data Analysis
Mollusc assemblages were analysed using community indices such as total abundance of individuals (N) per dm2, species richness (SR), the Shannon-Weaver diversity (H’) and the Pielou’s Evenness (J’). The quantitative (%DI: percentage of individuals of a particular species upon total individuals collected in the sample) and qualitative (%DQ: percentage of species for one particular taxon [Polyplacophora, Gastropoda or Bivalvia] upon total of species collected in the sample) dominances and frequency (%F: percentage of number of replicates in which a particular species is present) were also calculated.
Each mollusc species was assigned to a trophic group and a feeding guild as listed in Table 1, according to Purchon [27], Hughes [28], Fretter and Graham [29] and Dame [30].

Table 1.
List of trophic groups and description of relative feeding guilds with codes used in the species characterization.
To estimate biodiversity values of the vermetid habitat on a reduced number of available samples (n = 9), the nonparametric richness estimators Chao1 and Chao2 [31] were calculated as follows:
where SRobs is the number of species observed in a sample, f1 is the number of species represented by a single individual and f2 by two individuals, while q1 is the number of unique species in the sample, for each site, and q2 the number of species occurring twice.
SRChao1 = SRobs + f12/2f2 and SRChao2 = SRobs + q12/2q2
Permutational analysis of variance (PERMANOVA [32]) based on Euclidean distance was performed as univariate analysis [33] in order to assess differences on each community index among sites. A one-way model was used with Site (CP versus PP versus Ja) as a fixed factor. With the same design, PERMANOVA analysis based on Bray-Curtis similarity was performed in order to assess differences in the structure of mollusc assemblages among sites. 4999 permutations of residuals under a reduced model were applied [34] and a pairwise was used in order to evaluate differences between pairs of sites. Prior to analysis, data were log (x + 1) transformed [35] to reduce the effect of the dominant taxa in the samples.
The compositional differences of mollusc assemblages among the three distant sites were visualised using a nonmetric multidimensional scaling ordination (nMDS), based on the Bray-Curtis similarity. Similarity percentage (SIMPER) was performed to identify those species that better contributed to the similarity among the three sites, as well as the species that mostly characterized each one. All multivariate analyses were undertaken using the PRIMER-PERMANOVA+ v.6 software (PRIMER-E Ltd, Plymouth, UK) package [36,37].
3. Results
3.1. Composition of Mollusc Assemblages
A total of 600 individuals represented by 57 species and 31 families associated with vermetid bioconstructions were recorded. They belong to the classes of Polyplacophora (three families; four species; 37 individuals), Gastropoda (18 families; 35 species; 288 individuals) and Bivalvia (10 families; 18 species; 275 individuals) (Table 2). These three taxa were mainly represented respectively by the families Acanthochitonidae, Rissoidae and Mytilidae, which displayed the highest number of species, while 16 families were just represented by a single species.

Table 2.
Taxonomic list of mollusc species with their trophic categories (TC) and feeding guilds (FG: MG micro- and macro-grazers, DF deposit feeders, E ectoparasites, P predators, SF suspension feeders), their abundance (N) at each site (CP Cabo de Palos, PP Punta Prima and Ja Jávea), and their overall quantitative dominance (%DI) and frequency (%F).
At each site there was one taxonomic group that was substantially more species rich or more abundant than the other taxonomic groups. At CP, gastropods were dominant both in species richness (%DQ 74.07%, 20 sp.) and abundance (%DI 72.09%, 124 ind.), followed by bivalves (%DQ 14.81%, four spp.; %DI 13.37%, 23 ind.) and polyplacophorans (%DQ 11.11%, three spp.; %DI 14.53%, 25 ind.). The most abundant and frequent species, belonging to these three taxa, were respectively the gastropod Tricolia tingitana (%DI 20.93%; %F 100%), the bivalve Mytilaster solidus (%DI 9.30%; %F 100%) and the polyplacophoran Lepidochitona sp. (%DI 4.07%; %F 100%).
At PP, gastropods and bivalves showed the same species richness (%DQ 45.45%, 10 sp.) with an abundance of 76.19% (64 ind.) and 15.47% (13 ind.) respectively, followed by polyplacophorans (%DQ 9.09%, two spp.; %DI 8.33%, seven ind.). The most abundant and frequent species were respectively the gastropod Crisilla semistriata (%DI 50%; %F 66.6%), the bivalve M. solidus (%DI 3.57%; %F 100%) and the polyplacophoran Acanthochitona fascicularis (%DI 4.76%; %F 66.6%).
At Ja, gastropods were dominant in species richness (%DQ 51.28%, 20 sp.), with an abundance of 29.06% (100 ind.), followed by bivalves (%DQ 41.02%, 16 sp.), with an abundance of 69.47% (239 ind.), while polyplacophorans were poorly represented (%DQ 7.69%, three spp.; %DI 1.45%, five ind.). The most abundant and frequent species respectively for the three taxa were the gastropod Gibbula drepanensis (%DI 7.56%; %F 100%), the bivalve M. solidus (%DI 43.60%; %F 100%) and the polyplacophoran A. fascicularis (%DI 0.58%; %F 66.6%).
3.2. Trophic Diversity
The mollusc assemblage was dominated for 51% by herbivores (MG 155 ind.; 20 spp. and DF 151 ind.; nine spp.) and 45.83% by omnivores (SF 275 ind.; 18 spp.), followed for 3.17% by carnivores (P 14 ind.; nine spp. and E five ind.; one sp.).
At each site, a single feeding guild showed a higher dominance upon the others (Figure 2). At CP, the feeding guild MG was dominant both in abundance and species richness (%DI 52.91%, 91 ind.; %DQ 51.85%, 14 spp.) and was mainly represented by the gastropod T. tingitana (36 ind.). At PP, the feeding guild DF was dominant in abundance (%DI 61.90%; 52 ind.), while SF was dominant in species richness (%DQ 43.48%; 10 spp.). These guilds were mainly represented by the gastropod C. semistriata (42 ind.) and the bivalve M. solidus (three ind.) respectively. At Ja, the dominant feeding guild was SF, both in abundance and species richness (%DI 69.48%, 239 ind.; %DQ 41.03%, 16 spp.) and it was mainly represented by the bivalve M. solidus (150 ind.).
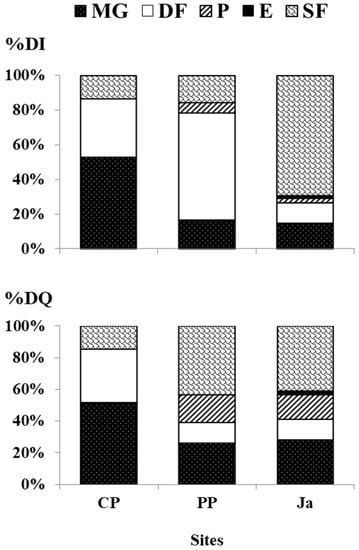
Figure 2.
Trophic contribution of each feeding guild (MG micro- and macro-grazers, DF deposit feeders, P predators, E ectoparasites, SF suspension feeders) to quantitative (%DI) and qualitative (%DQ) dominances, obtained by pooling data of the three replicates per each site (CP Cabo de Palos, PP Punta Prima and Ja Jávea).
3.3. Structural Analysis of Mollusc Assemblage
A mean value of 66.66 ± 47.22 individuals/dm2 was recorded. The maximum abundance (N) occurred at the Ja site, an intermediate value occurred at CP and the minimum value at PP. This same trend was found for species richness (SR). PERMANOVA test highlighted significant differences both for mollusc abundance and species richness among sites. Diversity indices (H’, J’), instead, resulted higher at CP than at the other two sites (Table 3).

Table 3.
Mollusc assemblage. Number of individuals (N) per dm2, species richness (SR) and diversity indices (H’, J’) measured for the three sampled sites (CP Cabo de Palos, PP Punta Prima and Ja Jávea) (mean ± SD), and results of PERMANOVA test on Euclidean distance (F: F-value, p(perm): calculated probability value, Unique perms: the number of unique permutations).
The richness estimators (Chao1 and Chao2; Figure 3) revealed that the efficiency of sampling was higher at PP than at CP and at Ja, for both the expected number of individuals and the expected number of species.
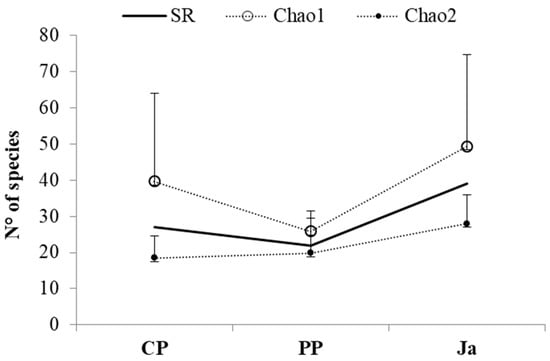
Figure 3.
Comparison between the species richness (SR) observed in every site (CP Cabo de Palos, PP Punta Prima and Ja Jávea) and the species richness expected by using the non-parametric estimator Chao 1, for abundance data, and Chao 2, for replicated incidence data (dots with S.D. bars).
PERMANOVA test highlighted significant differences in structure of mollusc assemblage among the three sites, with a highly significant p-value between CP and Ja (Table 4). These differences were evident in the nMDS plot (Figure 4). CP and Ja were clearly separated and replicates formed a consistent cluster for each site, while PP showed a high dispersion of replicates between the two other sites.

Table 4.
Results from PERMANOVA on Bray-Curtis similarity of mollusc assemblages among the three sites (CP Cabo de Palos, PP Punta Prima and Ja Jávea) after log (x + 1) transformation and pair-wise comparison using 4999 permutations (df: degrees of freedom, SS: sum of squares, MS: mean square, F: F-value, Unique perms: the number of unique permutations, p(perm): calculated probability value).
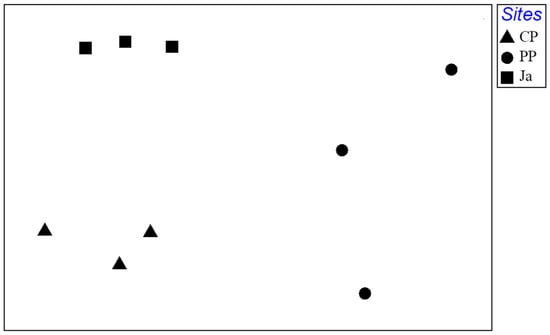
Figure 4.
Nonmetric multidimensional scaling (nMDS) ordination, based on Bray-Curtis similarity matrix, for all replicates collected at each site (CP Cabo de Palos, PP Punta Prima and Ja Jávea).
SIMPER analysis, based on the mollusc composition, indicated that the highest average similarities among the replicates occurred for the sites Ja (61.88%) and CP (58.06%), while that for PP replicates was only 29.94% (Table 5). The species that concurred for about 50% of similarity were mainly represented: at Ja by the suspension feeders, such as M. solidus, Rocellaria dubia, Gregariella semigranata and Hiatella arctica; at CP by the deposit feeder Sinezona cingulata and grazer species T. tingitana and Lepidochitona sp.; at PP by the deposit feeders, such as Setia amabilis and Rissoa similis.

Table 5.
Summary of SIMPER results for similarities in the three sites (CP Cabo de Palos, PP Punta Prima and Ja Jávea): Average similarity among replicates within each site and their average abundance of the species (Av.Abund), average similarity among replicates (Av.Sim), standard deviation of similarity (Sim/SD), percentage of contribution to similarity (Contrib%), percentage of cumulated contribution to similarity (Cum.%–50% cut-off).
On the other hand, the average similarity among the three sites was 31.39% (Table 6), mainly due to the suspension feeder M. solidus and deposit feeders R. similis, S. cingulata and S. amabilis.

Table 6.
Average abundance of the species (Av.Abund) most contributing to the Bray-Curtis similarity value among the sites, their average similarity among replicates (Av.Sim), standard deviation of similarity (Sim/SD), percentage of contribution to similarity (Contrib%), percentage of cumulated contribution to similarity (Cum.%–50% cut-off).
4. Discussion
It is well known that the complex surface of vermetid bioconstructions creates semi-sheltered microhabitats, promoting an extremely diversified benthic assemblage in intertidal zone exposed to water movement. Our results showed that the mollusc assemblage occurring on the intertidal vermetid bioconstructions was composed by 600 individuals grouped in 57 species. Even though data are based on a limited number of samples, the results reflect the highest species richness ever found in vermetid bioconstructions investigations [10,22,23].
Among the three taxonomic groups recorded in this study, polyplacophorans were poorly represented both in number of individuals and species richness, among which the grazers A. fascicularis and Acanthochitona crinita were the main representative. As highlighted in the present study, species belonging to this taxon fall into the “meso-littoral benthic component” described by Pandolfo et al. [22] in association with the most exposed portion of Sicilian vermetid bioconstructions.
By contrast, gastropods were represented by a high abundance, species richness and trophic diversity. The grazers G. drepanensis and T. tingitana and the deposit feeders S. cingulata and C. semistriata were the most dominant herbivore species. Predators and ectoparasites were instead poorly represented, among which Marshallora adversa and Vitreolina philippi were respectively the main dominant species.
A high abundance and a rather high species richness were also detected for bivalves, such as M. solidus, R. dubia, G. semigranata, H. arctica and Striarca lactea, even though they belong to a single trophic category represented by omnivores suspension feeders, which are relevant constituents of benthic communities of hard bottoms [38].
The dominance of herbivores associated with bioconstruction is an indirect effect of the functional role of the vermetid ecosystem engineer in sustaining biodiversity. Previous studies [39,40,41,42] reported that the abundance and diversity of molluscan assemblages are closely related to the algal types and architecture, which represent an important food resource. This is also corroborated by Fernández et al. [25]. They revealed a rich phytobenthic diversity inhabiting vermetid platforms of the southeastern Iberian Peninsula, with the lack of a persistent dominant group and a scarcity of grazers’ coverage where the algal cover was low. Therefore, high algal diversity growing on vermetid shells and sand coated with bacteria and organic detritus traps in the pores and crevices of bioconstruction were the main drivers of the dominant feeding guilds, such as grazers and deposit feeders.
In Sicily, Pandolfo et al. [9] reported the bivalve Mytilaster minimus as an important constituent of the mollusc assemblage associated with bioconstructions built up by the vermetid species Dendropoma cristatum (Biondi 1859). Other bivalves found, such as Lithophaga lithophaga, Irus irus and Petricola lithophaga, were also previously reported in association with the vermetids, both in Sicilian [9] and Alicante coasts [23]. These are rock-boring and filter-feeding bivalves which are especially favoured by crevice, empty vermetid shells of bioconstructions and the degree of coast exposure to the water movement. According to Österling and Pihl [43], high water movement promotes a low algal cover that favours bivalves such as suspension feeders; while low water movement promotes a rich algal cover that favours gastropods such as grazers and their species diversity.
Even though in the three sites the vermetid bioconstructions were always sampled along the rocky shore more exposed to the water movement, different mollusc assemblages occurred and consisted of algal cover associated with the vermetid platforms reported by Fernández [24].
Some previous studies suggested that benthic assemblages are strongly affected by environmental conditions, which changes at broader spatial scales [44,45,46,47]. Therefore, the significant difference in mollusc composition within the three sites (SIMPER, pairwise comparisons), besides bioconstructions algal covers, could be attributable to the geographical distance among the sites. Indeed, Cabo de Palos and Jávea were extremely distant sampling sites.
The westernmost site (Cabo de Palos), where vermetid bioconstructions were dominated by brown and red algae (e.g., Padina pavonica and Jania sp. [24]), was mainly characterized by herbivore gastropods including species such as Fossarus ambiguous, Tubbreva micrometrica, Pisinna glabrata, Tricolia punctura and T. tingitana which were exclusively found there. Moreover, this latter species was reported by Gofas [48,49] exclusively for the coasts of southern Spain (Straits of Gibraltar area), even though it was recently detected by Scuderi and Russo [50] along the coasts of southern Italy, both as living and fossil species.
On the other hand, the easternmost site (Jávea), where bioconstructions were dominated by red algae (e.g., Laurencia spp. [24]), was mainly characterized by bivalve suspension feeders such as Mytilus galloprovincialis, Musculus costulatus, R. dubia, Arca noae and P. lithophaga which were exclusive to this site and were previously reported for the same study area by Boronat et al. [23].
The presence of a geographic gradient in mollusc populations, from a dominance of gastropods, at Cabo de Palos, to a dominance of bivalves, at Jávea, is confirmed by the structure of mollusc assemblage at Punta Prima. Indeed, in this latter site, located between the westernmost and the easternmost site, the mollusc assemblage was characterized by a high abundance of gastropods and high species richness of bivalves.
5. Conclusions
Overall, data shown in this study describe the role of vermetid bioconstructions in structuring the mollusc composition which was a poorly investigated topic until now. Our findings also demonstrate that the distance between the vermetid bioconstructions plays a major role in forming different assemblages from site to site, confirming the existence of a geographical variability of benthic fauna at medium spatial scale, possibly due to biogeographic factors associated with the local variation of the environmental parameters [40,51]. Moreover, macroalgae provide additional substrate for grazer gastropods, in agreement with Ape et al. [52] who found a significant relation between meiofauna and algal community associated with vermetid bioconstructions.
Finally, the study points out the role of vermetids as important ecosystem engineers, such as other benthic bioconstructions (e.g., sabellariid reefs [53,54], mussel beds [55,56]), hosting a very heterogeneous assemblage of small invertebrates, crucial for an efficient coastal ecosystem functioning.
Author Contributions
Author Contributions: L.D. and R.S. wrote the manuscript. L.D. provided samples from the field and taxonomic analysis. L.D. and L.A. performed statistical analysis. J.L.S.L. and G.F.R. provided the sampling design and improved the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Italian Ministry for Education, Universities and Research (Z8HJ5M_008; P.R.I.N. Program 2010–2011: project “Marine bioconstructions: structure, function and management”), and by a Ph.D. fellowship of the first author L.D. (Doctorate in Marine, Terrestrial and Climate Sciences, University of Naples Parthenope).
Acknowledgments
This study is part of the Ph.D. thesis of L.D. We wish to thank the staff of the Marine Biology Laboratory at the University of Alicante for their assistance with this work. We are particularly grateful to M.T. Fernández for logistical and field support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Bianchi, C.N.; Morri, C. Marine biodiversity of the Mediterranean Sea: Situation, problems and prospects for future research. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, M.; Piroddi, C.; Steenbeek, J.; Kaschner, K.; Ben Rais Lasram, F.; Danovaro, R. The Biodiversity of the Mediterranean Sea: Estimates, Patterns, and Threats. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; Da Fonseca, G.A.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kružić, P. Bioconstructions in the Mediterranean: Present and Future. In The Mediterranean Sea; Goffredo, S., Dubinsky, Z., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 435–447. ISBN 978-94-007-6703-4. [Google Scholar]
- Antonioli, F.; Chemello, R.; Improta, S.; Riggio, S. Dendropoma lower intertidal reef formations and their palaeoclimatological significance NW Sicily. Mar. Geol. 1999, 161, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silenzi, S.; Antonioli, F.; Chemello, R. A new marker for sea surface temperature trend during the last centuries in temperate areas: Vermetid reef. Glob. Planet Chang. 2004, 40, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnarumma, L.; Sandulli, R.; Appolloni, L.; Di Stefano, F.; Russo, G.F. Morpho-structural and ecological features of a shallow vermetid bioconstruction in the Tyrrhenian Sea (Mediterranean Sea, Italy). J. Sea Res. 2018, 131, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Eliahu, M.N.; Safriel, U.N. A comparison between species diversities of polychaetes from tropical and temperate structurally similar rocky intertidal habitats. J. Biogeogr. 1982, 9, 371–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandolfo, A.; Chemello, R.; Riggio, S. Notes sur la signification écologique de la malacofaune d’un “Trottoir à Vermets” le long de la côte de Palerme (Sicile). Rapp. Comm. Int. Mer. Medit. 1992, 33, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Chemello, R.; Ciuna, I.; Pandolfo, A.; Riggio, S. Molluscan assemblages associated with intertidal vermetid formations: A morpho-functional approach. Boll. Malacol. 1998, 33, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, C.G.; Lawton, J.H.; Shachak, M. Organisms as ecosystem engineers. Oikos 1994, 69, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menge, B.A.; Sutherland, J.P. Species diversity gradients: Synthesis of the roles of predation, competition, and temporal heterogeneity. Am. Nat. 1976, 110, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safriel, U.N.; Ben Eliahu, M.N. The influence of habitat structure and environmental stability on the species diversity of polychaetes in vermetid reefs. In Habitat Structure. The Physical Arrangement of Objects in Space; Bell, S.S., McCoy, E.D., Mushinsky, H.R., Eds.; Chapman and Hall, Ltd.: London, UK, 1991; pp. 349–369. ISBN 978-94-011-3076-9. [Google Scholar]
- Calvo, M.; Templado, J.; Penchaszadeh, P.E. Reproductive biology of the gregarious Mediterranean vermetid gastropod Dendropoma petraeum. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 1998, 78, 525–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ancona Lunetta, G.; Damiani, F. Spermiogenesis in the vermetid gastropod Dendropoma petraeum (Gastropoda, Prosobranchia). Eur. J. Histochem. 2002, 46, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klerman, A.; Fine, M.; Galil, B.S. Reproductive biology of a threatened reef building vermetid (Mollusca: Gastropoda) off the coast of Israel. Rapp. Comm. Int. Mer. Médit. 2004, 37, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Usvyatsov, S. Dendropoma petraeum (Monterosato, 1884): A Mediterranean species complex based on reproductive characteristics? In Proceedings of the 38th CIESM (the Mediterranean Science Commission) Congress, Istanbul, Turkey, 9–13 April 2007; p. 629. [Google Scholar]
- Templado, J.; Richter, A.; Calvo, M. Reef building Mediterranean vermetid gastropods: Disentangling the Dendropoma petraeum species complex. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2016, 17, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goren, M.; Galil, B.S. Fish biodiversity in the vermetid reef of Shiqmona (Israel). Mar. Ecol. 2001, 22, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannino, A.M. Studio fitosociologico della vegetazione mesolitorale a Lithophyllum lichenoides PHILIPPI (Rhodophyceae, Corallinales). Nat. Sicil. 1992, 16, 3–25. [Google Scholar]
- Consoli, P.; Romeo, T.; Giongrandi, U.; Andaloro, F. Differences among fish assemblages associated with a nearshore vermetid reef and two other rocky habitats along the shores of Cape Milazzo (northern Sicily, central Mediterranean Sea). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2008, 88, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandolfo, A.; Chemello, R.; Riggio, S. Prime note sui popolamenti associati ai “trottoir” a vermetidi delle coste siciliane: I Molluschi. Oebalia 1992, 17, 379–382. [Google Scholar]
- Boronat, J.; Acuna, D.; Fresneda, M. Ensayo de caracterizacion malacologica de tres unidades bionomicas en las costas de Jávea (Alicante). Bol. Inst. Esp. Oceanogr. 1985, 2, 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, M.T. Caracterización de las fitocenosis de las plataformas de abrasión con vermétidos del sureste ibérico. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Alicante, Alicante, Spain, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, M.T.; Gómez, C.B.; Urrea, M.V.; Zubcoff, J.J.; Espla, A.R. The dynamics of phytobenthos and its main drivers on abrasion platforms with vermetids (Alicante, Southeastern Iberian Peninsula). Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2018, 19, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WoRMS Editorial Board—World Register of Marine Species. Available online: http://www.marinespecies.org at VLIZ (accessed on 19 June 2018).
- Purchon, R.D. The Biology of the Mollusca, 2nd ed.; Pergamon Press Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1977; p. 587. ISBN 1483285421. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, R.N. A Functional Biology of Marine Gastropods; Croom Helm: London, UK; Sydney, Australia, 1986; p. 245. ISBN 0 7099 3746 6. [Google Scholar]
- Fretter, V.; Graham, A. British Prosobranch Molluscs. Their Functional Anatomy and Ecology; The Ray Society: London, UK, 1994; ISBN 0-903874-23-7. [Google Scholar]
- Dame, R.F. Ecology of Marine Bivalves: An Ecosystem Approach, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; p. 283. ISBN 1439839123. [Google Scholar]
- Gotelli, N.J.; Colwell, R.K. Estimating species richness. In Frontiers in Measuring Biodiversity; Magurran, A.E., McGill, B.J., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 39–54. ISBN 9780199580675. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.J. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Terlizzi, A.; Anderson, M.J.; Fraschetti, S.; Benedetti-Cecchi, L. Scales of spatial variation in Mediterranean subtidal sessile assemblages at different depths. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 332, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. Permutation tests for univariate or multivariate analysis of variance and regression. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 58, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation, 2nd ed.; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2010; ISBN 1855311402. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. PRIMER v.6: User Manual/Tutorial; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.J.; Gorley, R.N.; Clarke, K.R. PERMANOVA+ for PRIMER: Guide to Software and Statistical Methods; PRIMER-E Ltd.: Plymouth, UK, 2008; p. 214. [Google Scholar]
- Gabriele, M.; Bellot, A.; Gallotti, D.; Brunetti, R. Sublittoral hard substrate communities of the northern Adriatic Sea. Cah. Biol. Mar. 1999, 40, 65–76. [Google Scholar]
- Chemello, R.; Russo, G.F. The molluscan taxocoene of photophilic algae from the Island of Lampedusa (Strait of Sicily, southern Mediterranean). Boll. Malacol. 1997, 33, 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Moyano, J.E.; Estacio, F.J.; García-Adiego, E.M.; García-Gómez, J.C. The molluscan epifauna of the alga Halopteris scoparia in Southern Spain as a bioindicator of coastal environmental conditions. J. Mollus. Stud. 2000, 66, 431–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemello, R.; Milazzo, M. Effect of algal architecture on associated fauna: Some evidence from phytal molluscs. Mar. Biol. 2002, 140, 981–990. [Google Scholar]
- Pitacco, V.; Orlando-Bonaca, M.; Mavrič, B.; Popović, A.; Lipej, L. Mollusc fauna associated with the Cystoseira algal associations in the Gulf of Trieste (Northern Adriatic Sea). Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2014, 15, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Österling, M.; Pihl, L. Effects of filamentous green algal mats on benthic macrofaunal functional feeding groups. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2001, 263, 159–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, A.J.; Chapman, M.G. Scales of spatial patterns of distribution of intertidal invertebrates. Oecologia 1996, 107, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetti-Cecchi, L. Variability in abundance of algae and invertebrates at different spatial scales on rocky sea shores. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 215, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraschetti, S.; Terlizzi, A.; Benedetti-Cecchi, L. Patterns of distribution of marine assemblages from rocky shores: Evidence of relevant scales of variation. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 296, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mykrä, H.; Heino, J.; Muotka, T. Scale-related patterns in the spatial and environmental components of stream macroinvertebrate assemblage variation. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2007, 16, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gofas, S. The genus Tricolia in the Eastern Atlantic and the Mediterranean. J. Mollus. Stud. 1982, 48, 182–213. [Google Scholar]
- Gofas, S. Notes on some Ibero-Moroccan and Mediterranean Tricolia (Gastropoda, Tricoliidae), with descriptions of new species. J. Mollus. Stud. 1993, 59, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuderi, D.; Russo, G.F. Due nuovi Gasteropodi per le acque italiane: Melibe fimbriata Alder e Hancock, 1864 e Tricolia tingitana Gofas 1982 (Mollusco, Gastropoda). Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2003, 10, 618–621. [Google Scholar]
- Soininen, J.; McDonald, R.; Hillebrand, H. The distance decay of similarity in ecological communities. Ecography 2007, 30, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ape, F.; Gristina, M.; Chemello, R.; Sarà, G.; Mirto, S. Meiofauna associated with vermetid reefs: The role of macroalgae in increasing habitat size and complexity. Coral Reefs 2018, 37, 875–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, S.; Commito, J.A.; Olivier, F.; Retière, C. Effects of epibionts on Sabellaria alveolata (L.) biogenic reefs and their associated fauna in the Bay of Mont Saint-Michel. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 68, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Porta, B.; Nicoletti, L. Sabellaria alveolata (Linnaeus) reefs in the central Tyrrhenian Sea (Italy) and associated polychaete fauna. Zoosymposia 2009, 2, 527–536. [Google Scholar]
- Karatayev, A.Y.; Burlakova, L.E.; Padilla, D.K. Impacts of zebra mussels on aquatic communities and their role as ecosystem engineers. In Invasive Aquatic Species of Europe. DISTRIBUTION, Impacts and Management; Leppäkoski, E., Gollasch, S., Olenin, S., Eds.; Kluwer Accademic Publishers: London, UK, 2002; pp. 433–446. ISBN 978-94-015-9956-6. [Google Scholar]
- Arribas, L.P.; Donnarumma, L.; Palomo, M.G.; Scrosati, R.A. Intertidal mussels as ecosystem engineers: Their associated invertebrate biodiversity under contrasting wave exposures. Mar. Biodivers. 2014, 44, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).