Correlated Effects of Ocean Acidification and Warming on Behavioral and Metabolic Traits of a Large Pelagic Fish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
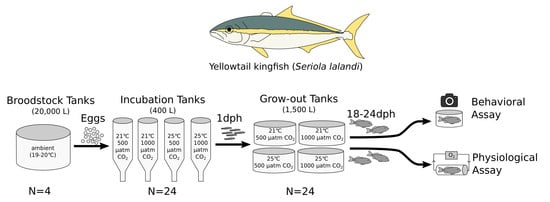
2.1. Study Species, Broodstock, Egg and Larval Maintenance
2.2. Carbonate Chemistry
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Behavioral Assay
2.5. Physiological Assay
2.6. Statistical Analyses
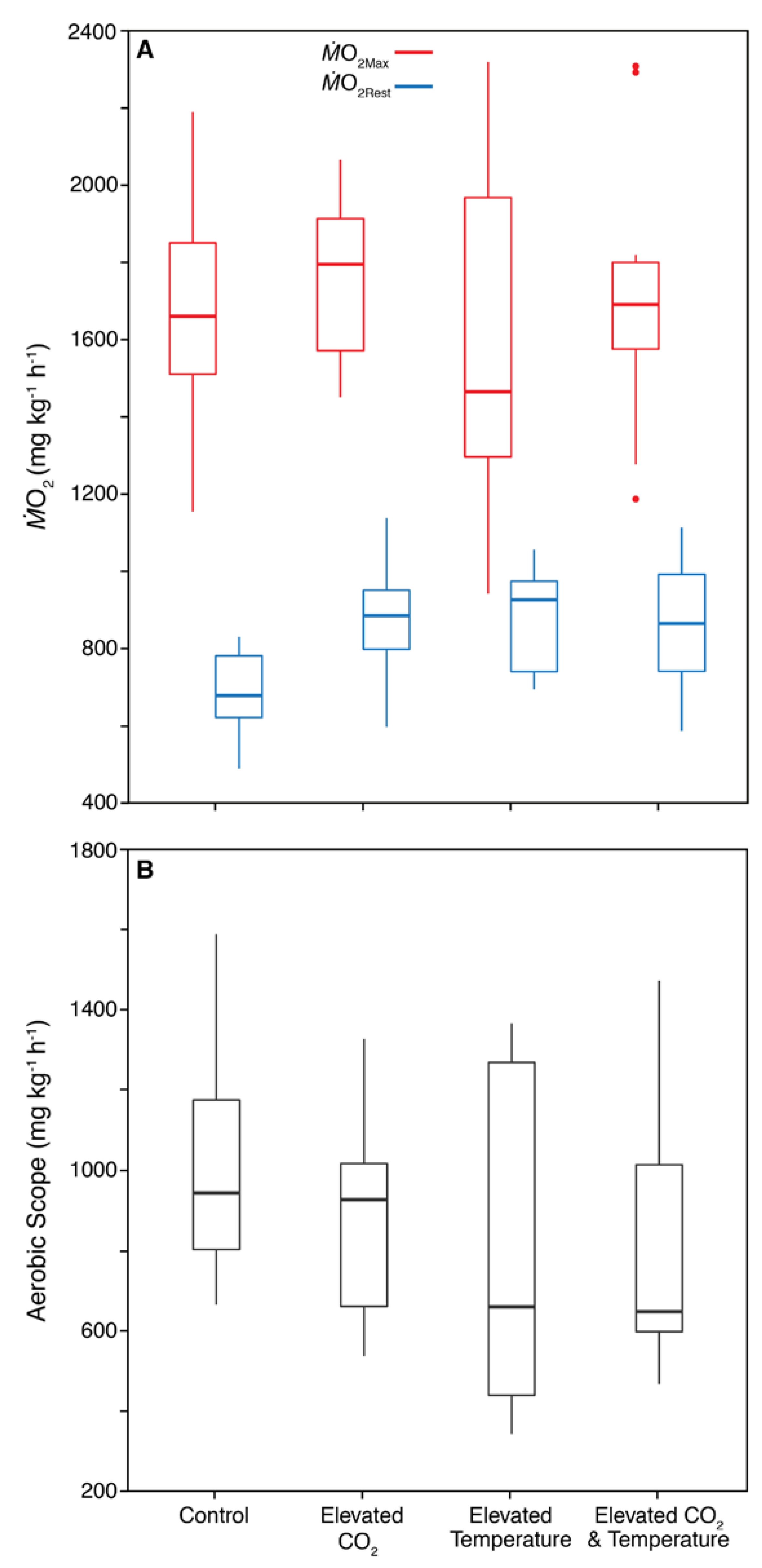
3. Results
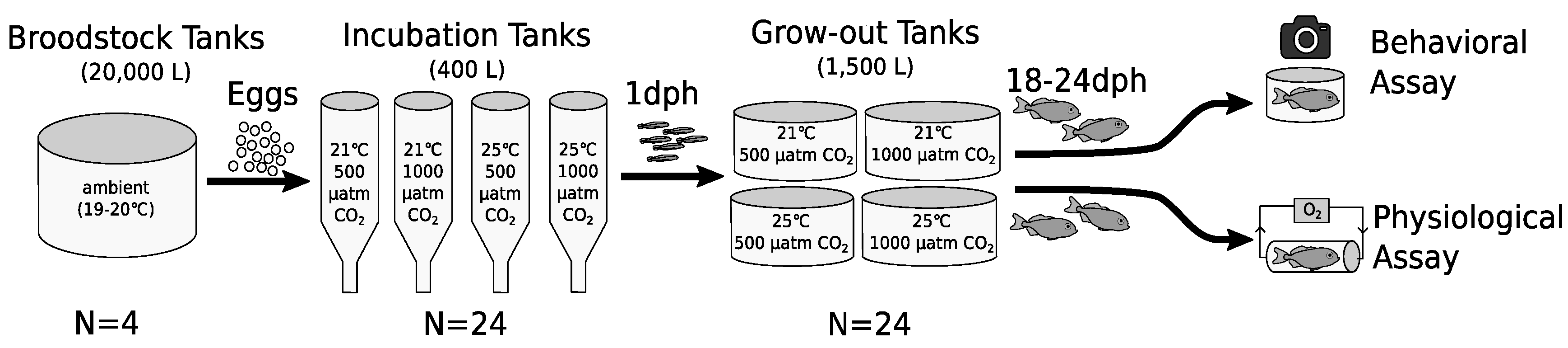
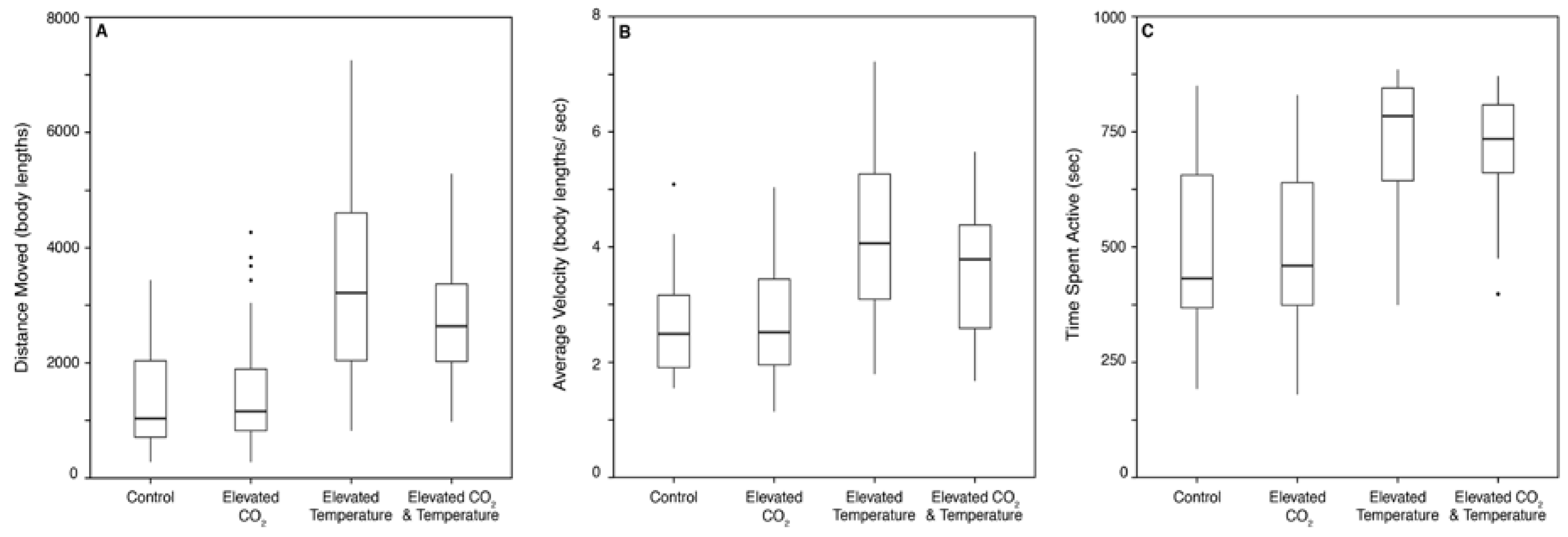
3.1. Behavior
3.2. Physiology
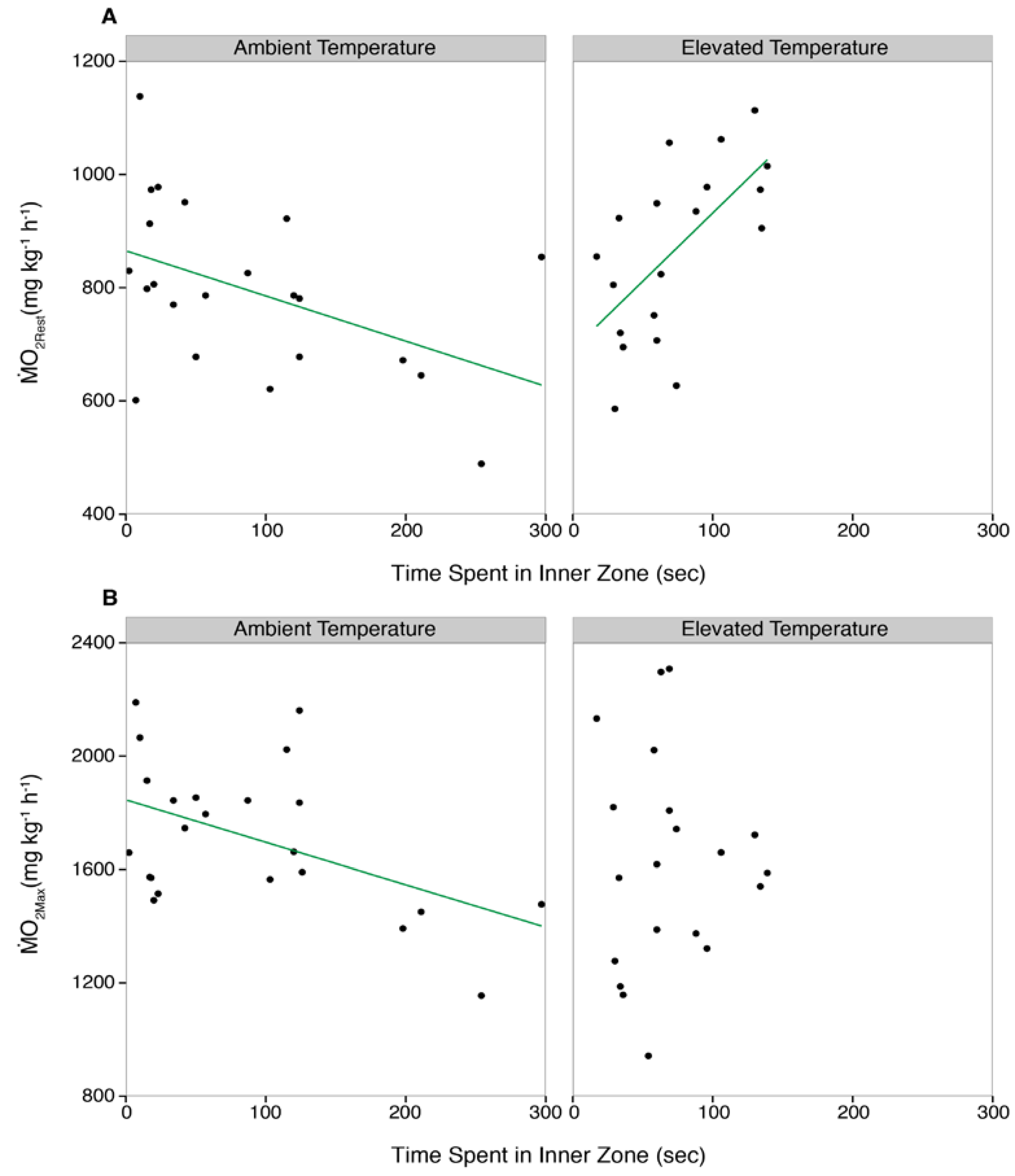
3.3. Correlations
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collins, M.; Knutti, R.; Arblaster, J.; Dufresne, J.-L.; Fichefet, T.; Friedlingstein, P.; Gao, X.; Gutowski, W.J.; Johns, T.; Krinner, G.; et al. Long-term climate change: Projections, commitments and irreversibility. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1029–1136. ISBN 9781107415324. [Google Scholar]
- Doney, S.C.; Fabry, V.J.; Feely, R.A.; Kleypas, J.A. Ocean acidification: The other CO2 problem. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2009, 1, 69–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendriks, I.E.; Duarte, C.M.; Álvarez, M. Vulnerability of marine biodiversity to ocean acidification: A meta-analysis. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 86, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittmann, A.C.; Pörtner, H.-O. Sensitivities of extant animal taxa to ocean acidification. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroeker, K.J.; Kordas, R.L.; Crim, R.N.; Singh, G.G. Meta-analysis reveals negative yet variable effects of ocean acidification on marine organisms. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 13, 1419–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doney, S.C.; Ruckelshaus, M.; Emmett Duffy, J.; Barry, J.P.; Chan, F.; English, C.A.; Galindo, H.M.; Grebmeier, J.M.; Hollowed, A.B.; Knowlton, N.; et al. Climate change impacts on marine ecosystems. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2012, 4, 11–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroeker, K.J.; Kordas, R.L.; Crim, R.; Hendriks, I.E.; Ramajo, L.; Singh, G.S.; Duarte, C.M.; Gattuso, J.P. Impacts of ocean acidification on marine organisms: Quantifying sensitivities and interaction with warming. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 1884–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riebesell, U.; Gattuso, J.P. Lessons learned from ocean acidification research. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuer, R.M.; Grosell, M. Physiological impacts of elevated carbon dioxide and ocean acidification on fish. AJP Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2014, 307, R1061–R1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clements, J.C.; Hunt, H.L. Marine animal behaviour in a high CO2 ocean. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 536, 259–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefevre, S. Are global warming and ocean acidification conspiring against marine ectotherms? A meta-analysis of the respiratory effects of elevated temperature, high CO2 and their interaction. Conserv. Physiol. 2016, 4, cow009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattano, C.; Claudet, J.; Domenici, P.; Milazzo, M. Living in a high CO2 world: A global meta-analysis shows multiple trait-mediated responses of fish to ocean acidification. Ecol. Monogr. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenici, P.; Allan, B.J.M.; Watson, S.-A.; McCormick, M.I.; Munday, P.L. Shifting from right to left: The combined effect of elevated CO2 and temperature on behavioural lateralization in a coral reef fish. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, P.L.; Crawley, N.E.; Nilsson, G.E. Interacting effects of elevated temperature and ocean acidification on the aerobic performance of coral reef fishes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 388, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.-A.; Allan, B.J.M.; McQueen, D.E.; Nicol, S.; Parsons, D.M.; Pether, S.M.J.; Pope, S.; Setiawan, A.N.; Smith, N.; Wilson, C.; et al. Ocean warming has a greater effect than acidification on the early life history development and swimming performance of a large circumglobal pelagic fish. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, B.J.M.; Domenici, P.; Watson, S.A.; Munday, P.L.; McCormick, M.I. Warming has a greater effect than elevated CO2 on predator–prey interactions in coral reef fish. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 284, 20170784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casini, M.; Hjelm, J.; Molinero, J.-C.; Lovgren, J.; Cardinale, M.; Bartolino, V.; Belgrano, A.; Kornilovs, G. Trophic cascades promote threshold-like shifts in pelagic marine ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, K.T.; Petrie, B.; Choi, J.S.; Leggett, W.C. Ecology: Trophic cascades in a formerly cod-dominated ecosystem. Science 2005, 308, 1621–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture. Contributing to Food Security and Nutrition for All; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Munday, P.L.; Jones, G.P.; Pratchett, M.S.; Williams, A.J. Climate change and the future for coral reef fishes. Fish Fish. 2008, 9, 261–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pörtner, H.O. Ecosystem effects of ocean acidification in times of ocean warming: A physiologist’s view. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 373, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, G.E.; Smith, J.E.; Johnson, K.S.; Send, U.; Levin, L.A.; Micheli, F.; Paytan, A.; Price, N.N.; Peterson, B.; Takeshita, Y.; et al. High-frequency dynamics of ocean pH: A multi-ecosystem comparison. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldbusser, G.G.; Salisbury, J.E. Ocean acidification in the coastal zone from an organism’s perspective: Multiple system parameters, frequency domains, and habitats. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2014, 6, 221–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houde, E.D. Subtleties and episodes in the early life of fishes. J. Fish Biol. 1989, 35, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowen, R.K.; Sponaugle, S. Larval dispersal and marine population connectivity. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2009, 1, 443–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, C.R.; Trippel, E.A. Early Life History and Recruitment in Fish Populations; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Rombough, P. The effects of temperature on embryonic and larval development. In Global Warming: Implications for Freshwater and Marine Fish; Wood, C., McDonald, D.G., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Melzner, F.; Gutowska, M.A.; Langenbuch, M.; Dupont, S.; Lucassen, M.; Thorndyke, M.C.; Bleich, M.; Pörtner, H.-O. Physiological basis for high CO2 tolerance in marine ectothermic animals: Pre-adaptation through lifestyle and ontogeny? Biogeosciences 2009, 2313–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinshausen, M.; Smith, S.J.; Calvin, K.; Daniel, J.S.; Kainuma, M.L.T.; Lamarque, J.; Matsumoto, K.; Montzka, S.A.; Raper, S.C.B.; Riahi, K.; et al. The RCP greenhouse gas concentrations and their extensions from 1765 to 2300. Clim. Chang. 2011, 109, 213–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biro, P.A.; Post, J.R.; Parkinson, E.A. From individuals to populations: Prey fish risk-taking mediates mortality in whole-system experiments. Ecology 2003, 84, 2419–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biro, P.A.; Post, J.R.; Parkinson, E.A. Density-dependent mortality is mediated by foraging activity for prey fish in whole-lake experiments. J. Anim. Ecol. 2003, 72, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, E.E.; Anholt, B.R. Ecological consequences of the trade-off between growth and mortality rates mediated by foraging activity. Am. Nat. 1993, 142, 242–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bignami, S.; Sponaugle, S.; Cowen, R.K. Response to ocean acidification in larvae of a large tropical marine fish, Rachycentron canadum. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bignami, S.; Sponaugle, S.; Cowen, R.K. Effects of ocean acidification on the larvae of a high-value pelagic fisheries species, Mahi-mahi Coryphaena hippurus. Aquat. Biol. 2014, 21, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, P.L.; Watson, S.A.; Parsons, D.M.; King, A.; Barr, N.G.; McLeod, I.M.; Allan, B.J.M.; Pether, S.M.J. Effects of elevated CO2 on early life history development of the yellowtail kingfish, Seriola lalandi, a large pelagic fish. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2015, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignami, S.; Sponaugle, S.; Hauff, M.; Cowen, R.K. Combined effects of elevated pCO2, temperature, and starvation stress on larvae of a large tropical marine fish. ICES J. Mar. Sci. J. Cons. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, M.; Pegado, M.; Repolho, T.; Rosa, R. Impact of ocean acidification in the metabolism and swimming behavior of the dolphinfish (Coryphaena hippurus) early larvae. Mar. Biol. 2014, 161, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biro, P.A.; Beckmann, C.; Stamps, J.A. Small within-day increases in temperature affects boldness and alters personality in coral reef fish. Proc. R. Soc. B 2010, 277, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuhara, O. Effects of temperature on yolk utilization, initial growth, and behaviour of unfed marine fish-larvae. Mar. Biol. 1990, 106, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biro, P.A.; Stamps, J.A. Do consistent individual differences in metabolic rate promote consistent individual differences in behavior? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, C.R.; Kearney, M.R. Metabolic scaling in animals: Methods, empirical results, and theoretical explanations. Compr. Physiol. 2014, 4, 231–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.; Jones, F.; Braithwaite, V. In situ examination of boldness-shyness traits in the tropical poeciliid, Brachyraphis episcopi. Anim. Behav. 2005, 70, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.S.; Clark, A.B.; Coleman, K.; Dearstyne, T. Shyness and boldness in humans and other animals. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1994, 9, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyomo, T.O.; Watt, P.J. The effect of variation in boldness and aggressiveness on the reproductive success of zebrafish. Anim. Behav. 2012, 83, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, P.L.; Dixson, D.L.; McCormick, M.I.; Meekan, M.; Ferrari, M.C.O.; Chivers, D.P.; Karl, D. Replenishment of fish populations is threatened by ocean acidification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12930–12934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biro, P.A.; Dingemanse, N.J. Sampling bias resulting from animal personality. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 66–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jutfelt, F.; Bresolin de Souza, K.; Vuylsteke, A.; Sturve, J. Behavioural disturbances in a temperate fish exposed to sustained high-CO2 levels. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lienart, G.D.H.; Mitchell, M.D.; Ferrari, M.C.O.; McCormick, M.I. Temperature and food availability affect risk assessment in an ectotherm. Anim. Behav. 2014, 89, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biro, P.A.; Stamps, J.A. Are animal personality traits linked to life-history productivity? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2008, 23, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, T.; Killen, S.S.; Armstrong, J.D.; Metcalfe, N.B. What causes intraspecific variation in resting metabolic rate and what are its ecological consequences? Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2011, 278, 3465–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metcalfe, N.B.; Van Leeuwen, T.E.; Killen, S.S. Does individual variation in metabolic phenotype predict fish behaviour and performance? J. Fish Biol. 2016, 88, 298–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norin, T.; Clark, T.D. Measurement and relevance of maximum metabolic rate in fishes. J. Fish Biol. 2016, 88, 122–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couturier, C.S.; Stecyk, J.A.W.; Rummer, J.L.; Munday, P.L.; Nilsson, G.E. Species-specific effects of near-future CO2 on the respiratory performance of two tropical prey fish and their predator. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2013, 166, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannan, K.D.; Rummer, J.L. Aquatic acidification: A mechanism underpinning maintained oxygen transport and performance in fish experiencing elevated carbon dioxide conditions. J. Exp. Biol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, F.E.J. The effect of environmental factors on the physiology of fish. Fish Physiol. 1971, 6, 1–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Careau, V.; Thomas, D.; Humphries, M.M.; Réale, D. Energy metabolism and animal personality. Oikos 2008, 117, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sih, A.; Bell, A.M.; Johnson, J.C.; Ziemba, R.E. Behavioral syndromes: An integrative overview. Q. Rev. Biol. 2004, 79, 241–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killen, S.S.; Marras, S.; Metcalfe, N.B.; McKenzie, D.J.; Domenici, P. Environmental stressors alter relationships between physiology and behaviour. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunday, J.M.; Calosi, P.; Dupont, S.; Munday, P.L.; Stillman, J.H.; Reusch, T.B.H. Evolution in an acidifying ocean. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2014, 29, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicuro, B.; Luzzana, U. The state of Seriola spp. other than yellowtail (S. quinqueradiata) farming in the world. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2016, 24, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, D.J. Seriola lalandi in Fishes of Australia. Available online: http://fishesofaustralia.net.au/home/species/1662 (accessed on 2 March 2018).
- Kailola, P.J.; Williams, M.J.; Stewart, P.C.; Reichelt, R.E.; McNee, A.; Grieve, C. Australian Fisheries Resources; Bureau of Resource Sciences and the Fisheries Research and Development Corporation: Canberra, Australia, 1993; ISBN 0642188769. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, C.D.; Stewart, A.L.; Struthers, C.D. The Fishes of New Zealand; Te Papa Press: Wellington, New Zealand, 2015; Volumes 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, D.; Smith, C.K.; Gara, B.; Poortenaar, C.W. Reproductive behaviour and early development in yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi Valenciennes 1833). Aquaculture 2007, 262, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrbach, C.; Culberson, C.H.; Hawley, J.E.; Pytkowitz, R.M. Measurement of the apparent dissociation constants of carbonic acid in seawater at atmospheric pressure. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1973, 18, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, A.G.; Millero, F.J. A comparison of the equilibrium constants for the dissociation of carbonic acid in seawater media. Deep Sea Res. Part A Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1987, 34, 1733–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, A.G. Standard potential of the reaction AgCl(aq) + H2(g) = Ag(s) + HCl(aq) and the standard acidity constant of the ion HSO4− in synthetic sea water from 273.15 K to 318.15 K. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 1990, 22, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.G. The validity of three tests of temperament in guppies (Poecilia reticulata). J. Comp. Psychol. 2008, 122, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, D.G.; Binning, S.A.; Bosiger, Y.; Johansen, J.L.; Rummer, J.L. Finding the best estimates of metabolic rates in a coral reef fish. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 2103–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rummer, J.L.; Binning, S.A.; Roche, D.G.; Johansen, J.L. Methods matter: Considering locomotory mode and respirometry technique when estimating metabolic rates of fishes. Conserv. Physiol. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niimi, A.J.; Beamish, W.H. Bioenergetics and growth of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) in relation to body weight and temperature. Can. J. Zool. 1974, 52, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, T.D.; Sandblom, E.; Jutfelt, F. Aerobic scope measurements of fishes in an era of climate change: Respirometry, relevance and recommendations. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 2771–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killen, S.S.; Mitchell, M.D.; Rummer, J.L.; Chivers, D.P.; Ferrari, M.C.O.; Meekan, M.G.; McCormick, M.I. Aerobic scope predicts dominance during early life in a tropical damselfish. Funct. Ecol. 2014, 28, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, S.; Prescott, L.J.; Hoey, A.S.; McMahon, S.A.; Wenger, A.S.; Rummer, J.L. Species-specific impacts of suspended sediments on gill structure and function in coral reef fishes. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 284, 20171279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, M.C.O.; Munday, P.L.; Rummer, J.L.; McCormick, M.I.; Corkill, K.; Watson, S.A.; Allan, B.J.M.; Meekan, M.G.; Chivers, D.P. Interactive effects of ocean acidification and rising sea temperatures alter predation rate and predator selectivity in reef fish communities. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 1848–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLeod, I.M.; Rummer, J.L.; Clark, T.D.; Jones, G.P.; McCormick, M.I.; Wenger, A.S.; Munday, P.L. Climate change and the performance of larval coral reef fishes: The interaction between temperature and food availability. Conserv. Physiol. 2013, 1, cot024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Found. Stat. Comput. Vienna Austria 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, W. The predator-prey interaction of planktivorous fish and zooplankton: Recent research with planktivorous fish and their zooplankton prey shows the evolutionary thrust. Am. Sci. 1979, 67, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llopiz, J.; Cowen, R.; Hauff, M.; Ji, R.; Munday, P.; Muhling, B.; Peck, M.; Richardson, D.; Sogard, S.; Sponaugle, S. Early life history and fisheries oceanography: New questions in a changing world. Oceanography 2014, 27, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.C.O.; Manassa, R.P.; Dixson, D.L.; Munday, P.L.; McCormick, M.I.; Meekan, M.G.; Sih, A.; Chivers, D.P. Effects of ocean acidification on learning in coral reef fishes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundin, J.; Jutfelt, F. 9–28 d of exposure to elevated pCO2 reduces avoidance of predator odour but had no effect on behavioural lateralization or swimming activity in a temperate wrasse (Ctenolabrus rupestris). ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2016, 73, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enzor, L.A.; Zippay, M.L.; Place, S.P. High latitude fish in a high CO2 world: Synergistic effects of elevated temperature and carbon dioxide on the metabolic rates of Antarctic notothenioids. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2013, 164, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodie, S.; Hobday, A.J.; Smith, J.A.; Everett, J.D.; Taylor, M.D.; Gray, C.A.; Suthers, I.M. Modelling the oceanic habitats of two pelagic species using recreational fisheries data. Fish. Oceanogr. 2015, 24, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, G.E.; Crawley, N.; Lunde, I.G.; Munday, P.L. Elevated temperature reduces the respiratory scope of coral reef fishes. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyomo, T.O.; Carter, M.; Watt, P.J. Heritability of boldness and aggressiveness in the zebrafish. Behav. Genet. 2013, 43, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.; Burgess, F.; Braithwaite, V.A. Heritable and experiential effects on boldness in a tropical poeciliid. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2007, 62, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, P.L.; Donelson, J.M.; Domingos, J.A. Potential for adaptation to climate change in a coral reef fish. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norin, T.; Malte, H. Intraspecific variation in aerobic metabolic rate of fish: Relations with organ size and enzyme activity in brown trout. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 2012, 85, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecl, G.T.; Araújo, M.B.; Bell, J.D.; Blanchard, J.; Bonebrake, T.C.; Chen, I.C.; Clark, T.D.; Colwell, R.K.; Danielsen, F.; Evengård, B.; et al. Biodiversity redistribution under climate change: Impacts on ecosystems and human well-being. Science 2017, 355, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| CO2 Treatment | Temperature Treatment | Temperature (°C) | Salinity | pHtotal | Total Alkalinity (µmol.kg−1 SW) | pCO2 (µatm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Broodstock–ambient | Broodstock–ambient | 19.4 (0.4) | 35.6 (0.1) | 7.906 (0.024) | 2329.6 (6.1) | 589.4 (38.0) |
| Control | 21 °C | 21.1 (0.1) | 35.6 (0.1) | 7.995 (0.025) | 2318.8 (7.2) | 462.0 (42.8) |
| Control | 25 °C | 24.8 (0.4) | 35.6 (0.1) | 7.938 (0.011) | 2319.9 (7.7) | 538.3 (15.6) |
| Elevated | 21 °C | 21.1 (0.1) | 35.6 (0.2) | 7.718 (0.028) | 2319.0 (3.8) | 959.8 (57.3) |
| Elevated | 25 °C | 24.9 (0.4) | 35.6 (0.1) | 7.700 (0.012) | 2320.0 (6.2) | 1010.6 (30.4) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laubenstein, T.D.; Rummer, J.L.; Nicol, S.; Parsons, D.M.; Pether, S.M.J.; Pope, S.; Smith, N.; Munday, P.L. Correlated Effects of Ocean Acidification and Warming on Behavioral and Metabolic Traits of a Large Pelagic Fish. Diversity 2018, 10, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/d10020035
Laubenstein TD, Rummer JL, Nicol S, Parsons DM, Pether SMJ, Pope S, Smith N, Munday PL. Correlated Effects of Ocean Acidification and Warming on Behavioral and Metabolic Traits of a Large Pelagic Fish. Diversity. 2018; 10(2):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/d10020035
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaubenstein, Taryn D., Jodie L. Rummer, Simon Nicol, Darren M. Parsons, Stephen M. J. Pether, Stephen Pope, Neville Smith, and Philip L. Munday. 2018. "Correlated Effects of Ocean Acidification and Warming on Behavioral and Metabolic Traits of a Large Pelagic Fish" Diversity 10, no. 2: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/d10020035
APA StyleLaubenstein, T. D., Rummer, J. L., Nicol, S., Parsons, D. M., Pether, S. M. J., Pope, S., Smith, N., & Munday, P. L. (2018). Correlated Effects of Ocean Acidification and Warming on Behavioral and Metabolic Traits of a Large Pelagic Fish. Diversity, 10(2), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/d10020035