4-(1H-Tetrazol-5-yl)-2-(p-tolyl)quinoline
Abstract
1. Introduction
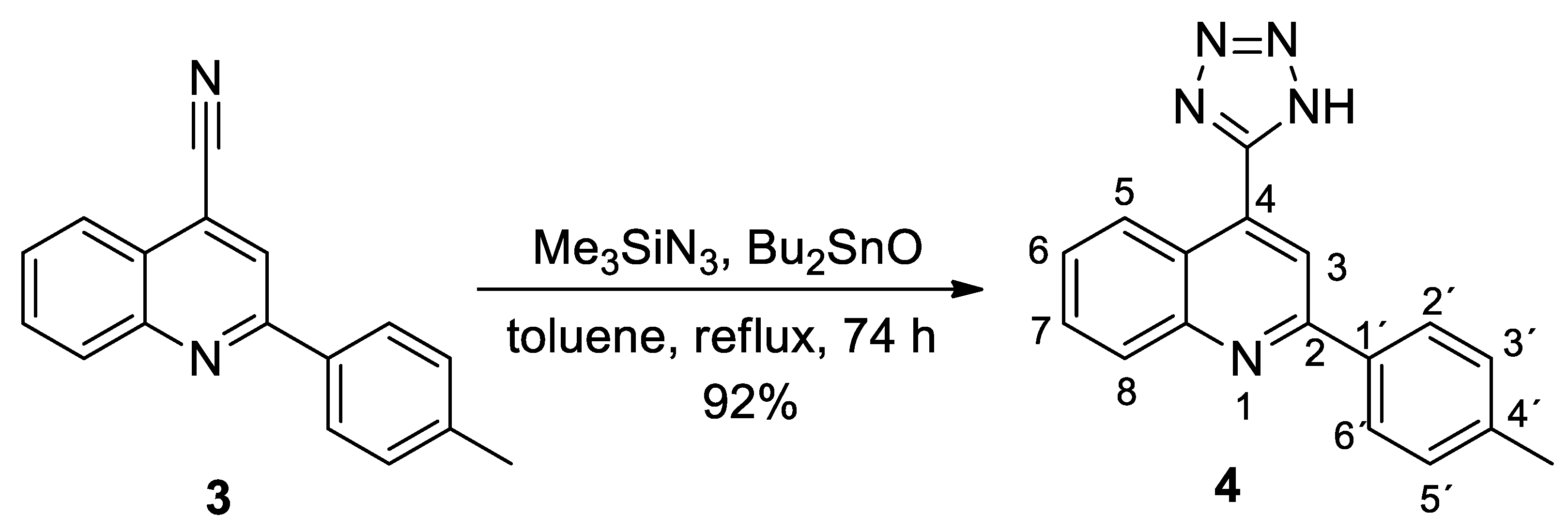
2. Results and Discussion
Synthesis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.2. Synthesis of 4-(1H-Tetrazol-5-yl)-2-(p-tolyl)quinoline (4)
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naik, P.; Murumkar, P.; Giridhar, R.; Yadav, M.R. Angiotensin II receptor type 1 (AT1) selective nonpeptidic antagonists—A perspective. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 8418–8456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavromoustakos, T.; Agelis, G.; Durdagi, S. AT1 antagonists: A patent review (2008–2012). Expert Opin. Ther. Patents 2013, 23, 1483–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncia, J.V.; Carini, D.J.; Chiu, A.T.; Johnson, A.L.; Price, W.A.; Wong, P.C.; Wexler, R.R.; Timmermans, P.B.M.W.M. The discovery of DuP 753, a potent, orally active nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonist. Med. Res. Rev. 1992, 12, 149–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncia, J.V.; Chiu, A.T.; Carini, D.J.; Gregory, G.B.; Johnson, A.L.; Price, W.A.; Wells, G.J.; Wong, P.C.; Calabrese, J.C.; Timmermns, P.B.M.W.M. The discovery of potent nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists: A new class of potent antihypertensives. J. Med. Chem. 1990, 33, 1312–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garudachari, B.; Satyanarayana, M.N.; Thippeswamy, B.; Shivakumar, C.K.; Shivananda, K.N.; Hegde, G.; Isloor, A.M. Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial studies of some new quinoline incorporated benzimidazole derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 54, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velu, A.B.; Chen, G.W.; Hsieh, P.T.; Horng, J.T.; Hsu, J.T.; Hsieh, H.P.; Chen, T.C.; Weng, K.F.; Shih, S.R. BPR-3P0128 inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase elongation and VPg uridylylation activities of Enterovirus 71. Antivir. Res. 2014, 112, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boa, A.N.; Canavan, S.P.; Hirst, P.R.; Ramsey, C.; Stead, A.M.W.; McConkey, G.A. Synthesis of brequinar analogue inhibitors of malaria parasite dihydroorotate dehydrogenase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 1945–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarghi, A.; Ghodsi, R. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of ketoprofen analogs as potent cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 5855–5860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinakaran, M.; Senthilkumar, P.; Yogeeswari, P.; China, A.; Nagaraja, V.; Sriram, D. Synthesis, antimycobacterial activities and phototoxic evaluation of 5H-thiazolo [3,2-a]quinoline-4-carboxylic Acid Derivatives. Med. Chem. 2008, 4, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strigacova, J.; Hudecova, D.; Varecka, L.; Lasikova, A.; Vegh, D. Some biological properties of new quinoline-4-carboxylic acid and quinoline-4-carboxamide derivatives. Folia Microbiol. 2000, 45, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, X.; Cai, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.; He, M. Design, synthesis and antibacterial evaluation of some new 2-phenyl-quinoline-4-carboxylic acid derivatives. Molecules 2016, 21, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matada, B.S.; Pattanashettar, R.; Yernale, N.G. A comprehensive review on the biological interest of quinoline and its derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 32, 115973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giardina, G.A.M.; Sarau, H.M.; Farina, C.; Medhurst, A.D.; Grugni, M.; Foley, J.J.; Raveglia, L.F.; Schmidt, D.B.; Rigolio, R.; Vassallo, M.; et al. 2-Phenyl-4-quinolinecarboxamides: A novel class of potent and selective non-peptide competitive antagonists for the human neurokinin-3 receptor. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 2281–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldham, A.A.; Allott, C.P.; Major, J.S.; Pearce, R.J.; Roberts, D.A.; Russell, S.T. ICI D8731, a novel, potent and orally-effective angiotensin II antagonist. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1992, 105, 83. [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury, R.H.; Allott, C.P.; Dennis, M.; Fisher, E.; Major, J.S.; Masek, B.B.; Oldham, A.A.; Rearce, R.J.; Rankine, N.; Revill, J.M.; et al. New nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. 2. Synthesis, biological properties, and structure-activity relationships of 2-alkyl-4-(biphenylylmethoxy)quinoline derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 1992, 35, 4027–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, J.; Ryono, D.E.; Bird, J.E.; Buote, J.; Delaney, C.L.; Dejneka, T.; Dickinson, K.E.J.; Moreland, S.; Normandin, D.E.; Skwish, S.; et al. Quinoline-4-carboxylic acids as angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1994, 4, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryono, D.E.; Lloyd, J.; Poss, M.A.; Bird, J.E.; Buote, J.; Chong, S.; Dejneka, T.; Dickinson, K.E.J.; Gu, Z.; Mathers, P.; et al. Orally active prodrugs of quinoline-4-carboxylic acid angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1994, 4, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebisu, H.; Nishikawa, M.; Tanaka, M.; Okazoe, T.; Morizawa, Y.; Shinyama, H.; Nakamura, N. Pharmacologic profiles of GA0113, a novel quinoline derivative angiotensin II AT1-receptor antagonist. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1999, 34, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, E.A.; Trifonov, R.E.; Ostrovskii, V.A. Tetrazoles for biomedicine. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2019, 88, 644–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittenberger, S.J.; Donner, B.G. Dialkyltin oxide mediated addition of trimethylsilyl azide to nitriles. A novel preparation of 5-substituted tetrazoles. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 4139–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lásiková, A.; Végh, D. Synthetic use of the Pfitzinger reaction in preparation of 2(3)-(di)substituted derivatives of quinoline-4-carboxylic acids. Chem. Papers 1997, 51, 408–411. [Google Scholar]
- Rickborn, B.; Jensen, F.R. α-Carbon isomerization in amide dehydrations. J. Org. Chem. 1962, 27, 4608–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lásiková, A.; Végh, D. 4-(1H-Tetrazol-5-yl)-2-(p-tolyl)quinoline. Molbank 2024, 2024, M1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1897
Lásiková A, Végh D. 4-(1H-Tetrazol-5-yl)-2-(p-tolyl)quinoline. Molbank. 2024; 2024(4):M1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1897
Chicago/Turabian StyleLásiková, Angelika, and Daniel Végh. 2024. "4-(1H-Tetrazol-5-yl)-2-(p-tolyl)quinoline" Molbank 2024, no. 4: M1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1897
APA StyleLásiková, A., & Végh, D. (2024). 4-(1H-Tetrazol-5-yl)-2-(p-tolyl)quinoline. Molbank, 2024(4), M1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1897




