Abstract
2,6-difluorobenzamides have been deeply investigated as antibacterial drugs in the last few decades. Several 3-substituted-2,6-difluorobenzamides have proved their ability to interfere with the bacterial cell division cycle by inhibiting the protein FtsZ, the key player of the whole process. Recently, we developed a novel family of 1,4-tetrahydronaphthodioxane benzamides, having an ethoxy linker, which reached sub-micromolar MICs towards Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis. A further investigation of their mechanism of action should require the development of a fluorescent probe, and the consequent definition of a synthetic pathway for its obtainment. In the present work, we report the obtainment of an unexpected bicyclic side product, 6-fluoro-3-(2,3,6,7,8,9-hexahydronaphtho[2,3-b][1,4]dioxin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxine-5-carboxamide, coming from the substitution of one aromatic fluorine by the in situ formed alkoxy group, in the final opening of an epoxide intermediate. This side product was similarly achieved, in good yields, by opening the ring of both erythro and threo epoxides, and the two compounds were fully characterized using HRMS, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, HPLC and DSC.
1. Introduction
The development of novel antibiotics able to modulate innovative targets represents one of the main pursued strategies to fight the worrying problem of antimicrobial resistance [1]. This phenomenon is caused by several human-related factors, such as over-prescription of antibiotics and low investments in the antibiotic resistance field [2].
With the aim of combatting this threat, one of the most exploited and promising bacterial targets is FtsZ (Filamenting temperature sensitive Z) [3], the main protein actor of the bacterial division process, the inhibition of which leads to cell filamentation and lysis [4,5,6,7]. Physiologically, GTP-dependent FtsZ polymerization represents the first step of the whole division process, leading to the formation of the Z-ring, a polymeric circular structure, at the site partition. Other division proteins then intervene, forming the mature divisome that allows cytokinesis and cellular division [8].
In the last years, a huge number of FtsZ inhibitors have been developed, belonging to different chemical classes and interacting with the protein on two different binding sites: the GTP-binding site or the Interdomain Cleft (IDC) [4,9,10,11].
Considering the high variety of FtsZ inhibitors, in terms of chemical structure, origin and interaction site, they are able to inhibit the FtsZ functionality through several mechanisms of actions. For instance, PC190723 (Figure 1), one of the most studied S. aureus and B. subtilis FtsZ inhibitors, is able to stabilize a high-affinity FtsZ conformation responsible for the assembly, thus exerting antimicrobial activity [12], while other derivatives can interfere with the GTPase activity of FtsZ polymers, evoking again their antimicrobial activity [13].
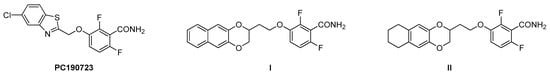
Figure 1.
Structures of PC190723, derivatives I and II.
Recently, our research group reported a novel class of 1,4-naphthodioxane- or 1,4-tetrahydronaphthodioxane-benzamides as strong antimicrobials [14], acting through the inhibition of FtsZ, which resulted to be more potent than other benzamides previously reported [5,15,16,17,18]. In particular, I and II (Figure 1) possess MIC values of 0.25 μg/mL and 0.1 μg/mL versus both Methicillin-sensitive and Methicillin-resistant S. Aureus, respectively. Moreover, I and II are both active vs. B. subtilis with MICs under 0.1 μg/mL [14].
After having proved their capability to interact and inhibit both S. aureus and B. subtilis FtsZ, the need of having a fluorescent analogue (Figure 2) of compound II, the strongest one, arose. An appropriate probe could indeed help to elucidate FtsZ inhibitors’ mechanism of action, as well as to understand any possible off-target interaction, to screen for novel antibiotics, to track antibiotic uptake throughout cells and organisms, and also to detect bacterial infections. Nonetheless, despite the clear and broad utility, the number of fluorescent FZ-probes so far available [19,20] is, to the best of our knowledge, now limited to only a couple of examples.
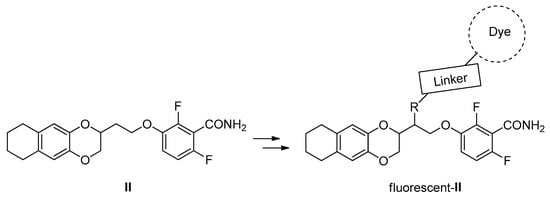
Figure 2.
Structures of II and of the desired fluorescent analogue.
When thinking how to properly introduce a fluorescent dye, a hydroxylated analogue of II, compound 1a, was designed (Scheme 1), taking inspiration from the work of Stokes and collaborators [21,22]. The introduction of the -OH was intended as a possible anchor point for the binding of a proper linker, and thus a fluorescent dye.
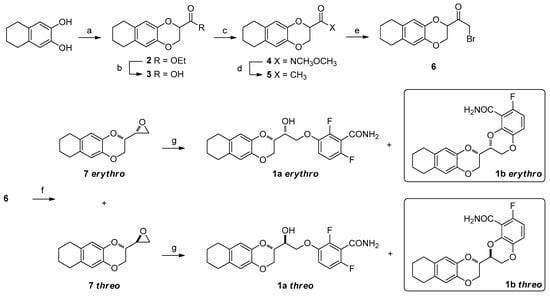
Scheme 1.
Synthetic pathway for the obtainment of both 1a and 1b. Reagents and conditions: (a) Ethyl 2,3-dibromopropionate, K2CO3, DMF, 70 °C, 1 h; (b) 10% aqueous NaOH, MeOH, RT, 30 min; (c) CDI, N,O-Dimethyl hydroxylamine hydrochloride, DMF, RT, 2 h; (d) CH3MgBr, THF, RT, 1.5 h; (e) Br2, diethyl ether, −5 °C, 3 h; (f) (I) NaBH4, MeOH, 0–5 °C, 30 min; (II) NaH, THF, RT, 18 h; (g) 2,6-difluoro-3-hydroxybenzamide, K2CO3, DMF, 70 °C, 18 h.
This substituent generates a second stereocenter, and the consequent formation of both erythro and threo isomers. The obtainment of 1a, for which we followed Scheme 1, involves the final ring opening of isolated erythro and threo epoxides. In the present work, we report how both these ring openings could surprisingly allow the achievement, in significant quantities, of the bicyclic side products 1b, the 6-fluoro-3-(2,3,6,7,8,9-hexahydronaphtho[2,3-b][1,4]dioxin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxine-5-carboxamides.
We further confirmed how the obtainment of these byproducts 1b erythro and threo is favored during the epoxide opening at quite high temperatures and keeping long reaction times, which are the usual conditions adopted in the final condensation for the preparation of FtsZ inhibitors [14,17,18]. On the contrary, the formation of these side products is partially retarded, keeping milder reaction conditions.
2. Results and Discussion
The synthetic scheme developed for achieving 1a is shown in Scheme 1 and started from the 5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalene-2,3-diol, obtained as previously described [14], which was treated with freshly prepared ethyl 2,3-dibromopropionate [23], giving racemic compound 2. The ester underwent basic hydrolysis, and the resulting carboxylic acid 3 was then converted into the Weinreb amide (4). Amide 4 was then quantitatively transformed into the corresponding methyl ketone 5, by treatment with methylmagnesium bromide, similarly to what was successfully done by our research group on structurally similar derivatives [24,25].
The bromination of methyl ketone 5 was conducted with a single equivalent of bromine at low temperature, to limit the formation of polybrominated side products, and to maximize the conversion into the bromoketone 6. Then, compound 6 underwent a tandem reaction: the first reduction of the carboxylic function with NaBH4, achieving the instable halohydrin that was soon treated with sodium hydride, affording the two epoxides 7, both erythro and threo isomers. The two spots of oxiranes 7 were easily distinguishable through TLC, and the two isomers were thus isolated by flash chromatography on silica gel. Their 1H-NMR spectra in CDCl3 revealed significant differences in terms of chemical shifts and multiplicity (Figure 3).
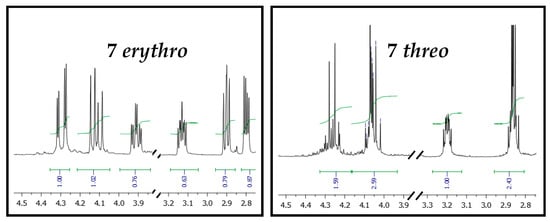
Figure 3.
1H-NMR Spectra extracts of 7 erythro and 7 threo.
In particular, the first eluted epoxide showed six different signals, with a very clear and defined multiplicity: four doublets of doublets (two at 4.29 and 4.12 ppm, referring to the CH2 the 1,4-dioxane portion, and two at 2.90 and 2.80 ppm, which are the two hydrogens of the epoxidic CH2), a doublet of triplets (at 3.91 ppm, diagnostic of the hydrogen of the dioxane CH), and a double of doublets of doublets (3.13 ppm, characteristic for the epoxidic CH). The second eluted oxirane, on the contrary, showed only four multiplets: at 4.26 (1H), 4.07 (2H), 3.19 (1H) and 2.85 (2H) ppm. Moreover, the two appearances were completely different: the first eluted compound was a wax, whereas the second one was a colorless oil. The absence of any literature data on tetrahydronaphthodioxane epoxides moved us to consider the scarce and quite old data on 1,4-dioxane oxiranes [26,27].
Indeed, the peculiar NMR data of the first eluted oxirane were completely in line with what was observed by Clark and coworkers when preparing the enantiopure erythro-2-oxiranyl-1,4-benzodioxanes (2R, 1′S) and (2S, 1′R). Moreover, also 1,4-benzodioxane threo and erythro epoxide isomers were strongly different in terms of physic state: enantiopure erythro was a solid with a defined melting point (63–64 °C [27]), while the racemic one was defined as oil or with a lower melting point [26,27]. The perfect NMR overlapping, and comparable physical state difference let us define, without doubts, the diastereoisomeric identity of the two epoxides 7.
The two 7 isomers were parallelly treated at 70 °C for 18 h in basic conditions, in the presence of 2,6-difluoro-3-hydroxybenzamide, to achieve the two final products 1a. Unexpectedly, the TLC of the two reaction mixtures revealed the presence of two main products, different in terms of chromatographic run. In addition to the one that should refer to the desired compound 1a, a higher spot was clearly visible in both the reactions, suggesting the formation of a more lipophilic side product.
The two reaction mixtures were worked up and the crudes purified by flash chromatography, letting the isolation, similarly in the two cases, of an undesired compound. Their 1H-NMR spectra showed a surprising pattern for the aromatic signals of the benzamide. We indeed expected to observe the two doublets of triplets, which were diagnostic of the presence of two different fluorine atoms. On the contrary, both the NMR spectra revealed a triplet and a doublet of doublets, suggesting us the absence of one of the two fluorine atoms. Considering the basic reaction conditions and the prolonged reaction times, we hypothesize the formation of the two 1b side products, in which the epoxide ring opening was soon followed by the in situ generation of the alcoholate, and the subsequent benzodioxane ring closure, achieving the bicyclic derivatives 1b erythro and 1b threo.
We further confirmed the identity of the two side products by evaluating their 13C-NMR spectra and their HRMS spectra. The presence of six doublets, instead of six doublets of doublets, was indeed the clear sign of the presence of a single fluorine atom. Moreover, the mass analysis confirmed the hypothesis and the elemental compositions.
We also repeated the final steps, by decreasing the reaction temperature or the reaction times, and we noticed how the side products yields were a little lower, further confirming the importance of the reaction conditions.
Finally, we also treated both 1a erythro and 1a threo while keeping the same reaction conditions used in the ring openings, and we noticed the formation of both 1b erythro and 1b threo, even with low yields.
The partial obtainment of these side products, directly from 1a erythro and 1a threo, suggests how these byproducts are most favored during the epoxides opening. In our opinion, the side products formation could be promoted by a concerted mechanism, in which the ring opening by the phenate is simultaneous to the cyclization due to nucleophilic substitution of the fluorine atom in phenate ortho position.
3. Materials and Methods
Starting materials and solvents were purchased from commercial suppliers (Merck, Darmstadt, DE, Fluorochem, Hadfield, UK, and TCI Europe N.V., Zwijndrecht, BE) and were used without further purification.
1H- and 13C-NMR spectra were acquired on a Varian 300 Mercury NMR spectrometer operating at 300 MHz for 1H-NMR, and 75 MHz for 13C-NMR; the chemical shifts are reported in ppm. Signal multiplicity is used according to the following abbreviations: s = singlet, bs = broad singlet, d = doublet, dd = doublet of doublets, ddd = doublet of doublets of doublets, td = triplet of doublets, t = triplet and m = multiplet.
Melting points were measured with a TA Q20 DSC system. TLC were performed on standard analytical silica gel layers (thickness 200 µm; aluminum support silica gel 60 matrix with fluorescent indicator 254 nm, Sigma-Aldrich/Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany). Chromatographic purifications were performed, in normal phase, using flash chromatography on Puriflash XS 420 (Sepachrom, Rho (Milan), Italy), and over different flash chromatography cartridges, filled with Merck high purity grade Silica Gel, 70–230 or 230–400 mesh particle size.
The final side products 1b erythro and 1b threo, as well as the benzamide derivatives 1a erythro and 1a threo, were analyzed by reverse-phase HPLC using a Waters XBridge C-18 column (5 μm, 4.6 mm × 150 mm) on an Elite LaChrom HPLC system with a diode array detector (Hitachi, San Jose, CA; USA). Mobile phase: A: H2O; B: acetonitrile; gradient, 90% A to 10% A in 25 min with 35 min run time and a flow rate of 1 mL/min. The purity was quantified at their λ max (289 nm) and was found to be >90% for all the compounds, and the relative retention time is reported in the experimental section. High-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) spectra were acquired on Q-Tof SYNAPT G2-Si HDMS 8K (Waters) coupled with an electrospray ionization (ESI) source in positive (ES+) ion mode. The characterization spectra of 1b erythro and 1b threo, in terms of NMR (both 1H and 13C) and HRMS, is reported in the Supplementary Material.
Ethyl 2,3,6,7,8,9-hexahydronaphtho[2,3-b][1,4]dioxine-2-carboxylate (2): A suspension of 5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalene-2,3-diol (1.50 g, 9.14 mmol) and K2CO3 (2.78 g, 20.1 mmol) in DMF (15 mL) was stirred at room temperature for 30 min. Ethyl 2,3-dibromoproprionate (2.61 g, 10.05 mmol) was added dropwise and the reaction mixture was stirred at 70 °C for 1 h, the volatile solvent evaporated under vacuum, the residue diluted with ethyl acetate (20 mL), washed with 10% aqueous NaCl (5 × 15 mL), dried with Na2SO4, filtered, and concentrated under vacuum to give 1.86 g (78 %) of 2 as a yellowish oil. 1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 6.70 (s, 1H), 6.56 (s, 1H), 4.77 (t, J = 3.8 Hz, 1H), 4.34 (m, 2H), 4.27 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 2.67 (m, 4H), 1.75 (m, 4H), and 1.29 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H).
2,3,6,7,8,9-Hexahydronaphtho[2,3-b][1,4]dioxine-2-carboxylic acid (3): 10% aqueous NaOH (5.7 mL) was added to a solution of 2 (1.86 g, 7.09 mmol) in methanol (20 mL). The reaction mixture was stirred for 30 min at RT, volatile solvents were evaporated, and the residue was diluted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with 10% aqueous HCl then with brine, dried over Na2SO4, then filtered and concentrated under vacuum to yield 1.58 g (95%) of 3 as a yellow oil. 1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.70 (s, 1H), 6.59 (s, 1H), 4.85 (dd, J = 5.1, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 4.41 (dd, J = 11.0, 5.1 Hz, 1H), 4.34 (dd, J = 11.0, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 2.66 (m, 4H), and 1.74 (m, 4H).
N-Methoxy-N-methyl-2,3,6,7,8,9-hexahydronaphtho[2,3-b][1,4]dioxine-2-carboxamide (4): 1,1′-Carbonyldiimidazole (1.64 g, 10.1 mmol) was added to a solution of 3 (1.58 g, 6.74 mmol) in DMF (16 mL). After stirring for 30 min, N,O-dimethyl hydroxylamine hydrochloride (0.99 g, 10 mmol) was added in portions, and the reaction mixture was stirred for 2 h. At completion, the DMF was evaporated, and the crude was diluted with ethyl acetate. The organic phase was washed with 10% aqueous NaHCO3, 10% aqueous HCl and finally with brine and then dried over Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated under vacuum to yield 1.76 g (95%) of 4 as a brownish oil. 1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, δ): δ 6.68 (s, 1H), 6.59 (s, 1H), 5.01 (dd, J = 6.7, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 4.37 (dd, J = 11.4, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 4.24 (dd, J = 11.4, 6.7 Hz, 1H), 3.78 (s, 3H), 3.26 (s, 3H), 2.66 (m, 4H), 1.74 (m, 4H).
1-(2,3,6,7,8,9-Hexahydronaphtho[2,3-b][1,4]dioxin-2-yl)ethanone (5): 3.0 M Methyl magnesium bromide in diethyl ether (3.2 mL) was added dropwise to a solution of 4 (1.76 g, 6.35 mmol) in dry THF (65 mL) at 0 °C under N2. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 1.5 h and poured into a 1/1 mixture of ethyl acetate and 10% aqueous HCl (50 + 50 mL). The organic phase was then washed twice with 10% aqueous NaCl, dried over Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated under vacuum to yield 1.34 g (92%) of 5 as a yellowish oil. 1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 6.69 (s, 1H), 6.58 (s, 1H), 4.56 (dd, J = 4.9, 3.5 Hz, 1H), 4.28 (dd, J = 11.4, 3.5 Hz, 1H), 4.25 (dd, J = 11.4, 4.9 Hz, 1H), 2.68 (m, 4H), 2.29 (s, 3H), and 1.75 (m, 4H).
2-Bromo-1-(2,3,6,7,8,9-hexahydronaphtho[2,3-b][1,4]dioxin-2-yl)ethanone (6): Bromine (0.30 mL, 5.8 mmol) was added dropwise to a solution of 5 (1.34 g, 5.77 mmol) in diethyl ether (40 mL) at −5.0 °C. The mixture was stirred at that temperature for 3 h, washed Na2S2O5 (10 mL), dried over Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated under vacuum, to obtain 1.80 g of 6 as a yellowish oil (quantitative yield). 1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 6.72 (s, 1H), 6.62 (s, 1H), 4.86 (dd, J = 4.7, 3.3 Hz, 1H), 4.40 (m, 2H), 4.33 (d, J = 14.0 Hz, 1H), 4.10 (d, J = 14.0 Hz, 1H), 2.70 (m, 4H), and 1.76 (m, 4H).
Erythro- and Threo- 2-(Oxiran-2-yl)-2,3,6,7,8,9-hexahydronaphtho[2,3-b][1,4]dioxine (7): NaBH4 (0.11 g, 2.9 mmol) was added in portions to a solution of 6 (1.80 g, 5.77 mmol) in MeOH (36 mL) at 0 °C. The reaction mixture was stirred at 0 °C for 30 min, then volatile solvents were removed under vacuum. The crude was diluted with THF (15 mL) and added dropwise to a suspension of 60% NaH (0.28 g, 6.92 mmol) in THF (5 mL) at 0°C under nitrogen atmosphere. After 30 min, the reaction mixture was warmed to RT and stirred for 18 h, then THF was evaporated, and the crude resumed with ethyl acetate (20 mL) and phosphate buffer pH = 7 (15 mL). The organic phase was washed with 10% aqueous NaCl, dried over Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated under vacuum to yield 1.40 g of a mixture of 7 isomers as a brown oil. Elution with 9/1 cyclohexane/ethyl acetate on silica gel gave 0.47 g of 7 erythro (first eluted) as white wax and 0.32 g of 7 threo (second eluted) as colorless oil (Cumulative yield of erythro and threo isomers = 59%).
7 Erythro:1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 6.60 (s, 2H), 4.29 (dd, J = 11.4, 2.4 Hz, 1H), 4.12 (dd, J = 11.4, 6.6 Hz, 1H), 3.91 (td, J = 6.6, 2.4 Hz, 1H), 3.13 (ddd, J = 6.6, 4.1, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 2.90 (dd, J = 4.9, 4.1 Hz, 1H), 2.80 (dd, J = 4.9, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 2.67 (m, 4H), and 1.73 (m, 4H).
7 Threo:1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 6.63 (s, 1H), 6.58 (s, 1H), 4.26 (m, 1H), 4.07 (m, 2H), 3.19 (m, 1H), 2.85 (m, 2H), 2.66 (m, 4H), and 1.74 (m, 4H).
Erythro 2,6-Difluoro-3-(2-(2,3,6,7,8,9-hexahydronaphtho[2,3-b][1,4]dioxin-2-yl)-2-hydroxyethoxy)benzamide (1a erythro) and erythro 6-Fluoro-3-(2,3,6,7,8,9-hexahydronaphtho[2,3-b][1,4]dioxin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxine-5-carboxamide (1b erythro): A solution of 3-Hydroxy-2,6-difluorobenzamide (0.37 g, 2.1 mmol) in DMF (3 mL) was added to a solution of 7 erythro (0.47 g, 2.0 mmol) and K2CO3 (0.31 g, 2.2 mmol) in DMF (2 mL) at RT. Heating and stirring at 70 °C for 18 h led to the obtainment of the side product 1b erythro in 24% yield. DMF evaporation under vacuum, dilution with ethyl acetate (20 mL), washing with 10% aqueous NaCl (5 × 10 mL), drying over Na2SO4, filtering and concentration under vacuum gave a brown residue. Elution with 6/4 to 4/6 cyclohexane/ethyl acetate on silica gel allowed the isolation of 0.32 g (Yield = 39%) of 1a erythro and of 0.19 g (Yield = 24%) of 1b erythro as white solids.
1a erythro: HPLC: Tr = 14.9 min. Mp = 155 °C.
1H-NMR (300 MHz, d6-DMSO): δ 8.10 (s, 1H), 7.81 (s, 1H), 7.24 (dt, J = 9.3, 5.3 Hz, 1H), 7.04 (dt, J = 9.0, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 6.52 (s, 1H), 6.51 (s, 1H), 5.68 (d, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 4.32 (d, J = 9.5 Hz, 1H), 4.15 (m, 4H), 3.94 (m, 1H), 2.55 (m, 4H), and 1.64 (m, 4H)
13C-NMR (75 MHz, d6-DMSO): δ 161.8, 152.3 (dd, J = 239.3, 6.7 Hz), 148.3 (dd, J = 246.8, 8.2 Hz), 143.7 (dd, J = 10.5, 3.0 Hz), 143.3, 140.8, 129.9, 129.7, 117.0 (dd, J = 24.6, 20.3 Hz), 117.0, 116.9, 116.8, 116.7, 116.0 (dd, J = 8.5, 1.7 Hz), 111.3 (dd, J = 23.1, 3.0 Hz), 73.1, 71.4, 67.8, 64.9, 28.5, and 23.2.
1b erythro: HPLC: Tr = 15.3 min. Mp = 266 °C. HRMS (TOF ES+, Na+-adduct): m/z 408.1229, 409.1263, and 410.1289. Calculated mass 408.1218, evaluated mass 408.1229.
1H-NMR (300 MHz, d6-DMSO): δ 7.91 (s, 1H), 7.63 (s, 1H), 6.92 (d, J = 9.0, 5.4 Hz, 1H), 6.73 (t, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 6.58 (s, 1H), 6.55 (s, 1H), 4.44 (dd, J = 11.6, 3.5 Hz, 1H), 4.33–4.28 (m, 4H), 4.17 (dd, J = 12.1, 6.5 Hz, 1H), 2.57 (m, 4H), and 1.64 (m, 4H).
13C-NMR (75 MHz, d6-DMSO): δ 163.4, 153.1 (d, J = 237.0 Hz), 141.1, 140.1, 139.7 (d, J = 3.0 Hz), 139.5 (d, J = 9.0 Hz), 130.24, 130.17, 117.6 (d, J = 9.0 Hz), 117.03, 117.01, 116.9 (d, J = 27.0 Hz), 108.3 (d, J = 25.5 Hz), 70.1, 70.0, 64.3, 63.6, 28.5, and 23.2.
Threo 2,6-Difluoro-3-(2-(2,3,6,7,8,9-hexahydronaphtho[2,3-b][1,4]dioxin-2-yl)-2-hydroxyethoxy)benzamide (1a threo) and threo 6-Fluoro-3-(2,3,6,7,8,9-hexahydronaphtho[2,3-b][1,4]dioxin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxine-5-carboxamide (1b threo): 1a and 1b threo were obtained from 7 threo (0.30 g, 1.3 mmol), following the same procedure of 1a erythro and 1b erythro, achieving 0.16 g (Yield = 31%) of 1a threo and 80 mg (Yield = 16%) of 1b threo as white solids.
1a threo: HPLC Tr = 14.5 min. Mp = 147 °C.
1H-NMR (300 MHz, d6-DMSO): δ 8.09 (s, 1H), 7.81 (s, 1H), 7.27 (dt, J = 9.4, 5.3 Hz, 1H), 7.05 (dt, J = 9.0, 1.9 Hz, 1H), 6.53 (s, 1H), 6.52 (s, 1H), 5.49 (d, J = 5.8 Hz, 1H), 4.33 (dd, J = 11.2, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 4.09 (m, 5H), 2.56 (m, 4H), and 1.64 (m, 4H).
13C-NMR (75 MHz, d6-DMSO): δ 161.8, 152.3 (dd, J = 239.3, 6.7 Hz), 148.3 (dd, J = 246.8, 8.2 Hz), 143.7 (dd, J = 10.5, 3.0 Hz), 143.3, 140.8, 129.9, 129.7, 117.0 (dd, J = 24.6, 20.3 Hz), 117.0, 116.9, 116.8, 116.7, 116.0 (dd, J = 8.5, 1.7 Hz), 111.3 (dd, J = 23.1, 3.0 Hz), 73.1, 71.4, 67.8, 64.9, 28.5, and 23.2.
1b threo: HPLC Tr = 13.3 min. Mp = 290 °C with decomposition. HRMS (TOF ES+, Na+-adduct): m/z 408.1222, 409.1253, and 410.1277. Calculated mass 408.1218, evaluated mass 408.1222.
1H-NMR (300 MHz, d6-DMSO): δ 7.75 (s, 1H), 7.56 (s, 1H), 6.91 (d, J = 8.9, 5.5 Hz, 1H), 6.71 (t, J = 8.9 Hz, 1H), 6.55 (s, 1H), 6.52 (s, 1H), 4.48-4.37 (m, 4H), 4.21 (dd, J = 11.9, 8.1 Hz, 1H), 4.08 (dd, J = 11.9, 8.3 Hz, 1H), 2.56 (m, 4H), and 1.64 (m, 4H).
13C-NMR (75 MHz, d6-DMSO): δ 163.4, 153.2 (d, J = 236.8 Hz), 141.0, 140.8 (d, J = 3.0 Hz), 140.4 (d, J = 10.1 Hz), 139.7, 130.1, 130.0, 117.61 (d, J = 9.0 Hz), 117.59, 117.5, 117.0 (d, J = 21.1 Hz), 108.2 (d, J = 22.3 Hz), 72.1, 71.7, 64.5, 64.2, 28.5, and 23.2.
Conversion of 1a erythro to 1b erythro: A solution of 1a erythro (0.10 g, 0.25 mmol) in DMF (1 mL) was added to a suspension of K2CO3 (0.070 g, 0.50 mmol) in DMF (1 mL) at RT. The mixture was heated at 70 °C and stirred for 18 h, then DMF was evaporated under vacuum. The residue was diluted with ethyl acetate (10 mL), washed with 10% aqueous NaCl (5 × 5 mL), dried over Na2SO4, then filtered and concentrated under vacuum, yielding a brown residue. Elution with 1/1 cyclohexane/ethyl acetate on silica gel allowed the isolation of 34 mg (35%) of 1b erythro as a white solid.
Conversion of 1a threo to 1b threo: 1b threo was obtained from 1a threo (0.10 g, 0.25 mmol), following the same procedure seen for 1b erythro, achieving 29 mg (30%) of 1b threo as a white solid.
4. Conclusions
The two threo and erythro isomers of the 6-fluoro-3-(2,3,6,7,8,9-hexahydronaphtho[2,3-b][1,4]dioxin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxine-5-carboxamide were obtained as a significant and abundant side product, when opening the two isomers of the 2-(oxiran-2-yl)-2,3,6,7,8,9-hexahydronaphtho[2,3-b][1,4]dioxines with a 2,6-difluorophenate, stirring at 70 °C and keeping overnight reaction times.
The structure of these two side products was firstly hypothesized by carefully evaluating the 1H-NMR spectra, which revealed the absence of a fluorine atom, and then confirmed by both 13C-NMR and HRMS spectra. The diastereoisomeric identity was defined after having characterized the isomer nature of the starting epoxides, by NMR comparison with literature enantiopure 1,4-benzodixoane oxiranes. The side products were further characterized by HPLC and DSC, fully detailing these novel and unexpected byproducts.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online: Compound 1b erythro; Figure S1: Copy of 1H-NMR spectrum in DMSO-d6; Figure S2: Copy of 13C-NMR spectrum in DMSO-d6; Figure S3: Copy of HRMS spectrum; Figure S4: Copy of Elemental Composition Report; Compound 1b threo; Figure S5: Copy of 1H-NMR spectrum in DMSO-d6; Figure S6: Copy of 13C-NMR spectrum in DMSO-d6; Figure S7: Copy of HRMS spectrum; and Figure S8: Copy of Elemental Composition Report.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.S., V.S. and E.V.; investigation, L.S. and G.L.; data curation, L.S. and V.S.; writing—original draft preparation, V.S. and L.S.; writing—review and editing, V.S. and E.V.; supervision, V.S. and E.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
Mass spectrometry analyses were performed at the Mass Spectrometry facility of Unitech COSPECT at the University of Milan (Italy). The authors acknowledge the support of the APC central fund of the University of Milan.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Sample Availability
Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
References
- World Health Organization. Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance. 2015. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241509763 (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- World Health Organization. Antibiotic Resistance: Prevention and Control. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antibiotic-resistance#:~:text=Antibiotic%20resistance%20is%20accelerated%20by,poor%20infection%20prevention%20and%20control (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- Pradhan, P.; Margolin, W.; Beuria, T.K. Targeting the Achilles Heel of FtsZ: The Interdomain Cleft. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 732796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casiraghi, A.; Suigo, L.; Valoti, E.; Straniero, V. Targeting Bacterial Cell Division: A Binding Site-Centered Approach to the Most Promising Inhibitors of the Essential Protein FtsZ. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straniero, V.; Pallavicini, M.; Chiodini, G.; Zanotto, C.; Volontè, L.; Radaelli, A.; Bolchi, C.; Fumagalli, L.; Sanguinetti, M.; Menchinelli, G.; et al. 3-(Benzodioxan-2-ylmethoxy)-2,6-difluorobenzamides bearing hydrophobic substituents at the 7-position of the benzodioxane nucleus potently inhibit methicillin-resistant Sa and Mtb cell division. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 120, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.W.; Wu, L.J.; Czaplewski, L.G.; Errington, J. Multiple effects of benzamide antibiotics on FtsZ function. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 80, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.W.; Wu, L.J.; Errington, J. A benzamide-dependent ftsZ mutant reveals residues crucial for Z-ring assembly. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 99, 1028–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeusser, D.P.; Margolin, W. Splitsville: Structural and functional insights into the dynamic bacterial Z ring. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carro, L. Recent Progress in the Development of Small-Molecule FtsZ Inhibitors as Chemical Tools for the Development of Novel Antibiotics. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.; Sahu, S.K. FtsZ inhibitors as a new genera of antibacterial agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 91, 103169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, T.; Da, T.; Mao, R.; Hao, Y.; Yang, N.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. Recent progress of bacterial FtsZ inhibitors with a focus on peptides. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 1091–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsen, N.L.; Lu, J.; Parthasarathy, G.; Reid, J.C.; Sharma, S.; Soisson, S.M.; Lumb, K.J. Mechanism of action of the cell-division inhibitor PC190723: Modulation of FtsZ assembly cooperativity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 12342–12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X.; Lu, Y.-J.; Yan, S.-C.; Wong, W.-L.; Chan, K.-F.; Wong, K.-Y.; Sun, N. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of a thiophenyl substituted pyrimidine derivative. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 10739–10744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straniero, V.; Sebastián-Pérez, V.; Suigo, L.; Margolin, W.; Casiraghi, A.; Hrast, M.; Zanotto, C.; Zdovc, I.; Radaelli, A.; Valoti, E. Computational Design and Development of Benzodioxane-Benzamides as Potent Inhibitors of FtsZ by Exploring the Hydrophobic Subpocket. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiodini, G.; Pallavicini, M.; Zanotto, C.; Bissa, M.; Radaelli, A.; Straniero, V.; Bolchi, C.; Fumagalli, L.; Ruggeri, P.; De Giuli Morghen, C.; et al. Benzodioxane-benzamides as new bacterial cell division inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 89, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straniero, V.; Zanotto, C.; Straniero, L.; Casiraghi, A.; Duga, S.; Radaelli, A.; De Giuli Morghen, C.; Valoti, E. 2,6-Difluorobenzamide Inhibitors of Bacterial Cell Division Protein FtsZ: Design, Synthesis, and Structure-Activity Relationships. ChemMedChem 2017, 12, 1303–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straniero, V.; Sebastián Pérez, V.; Hrast, M.; Zanotto, C.; Casiraghi, A.; Suigo, L.; Zdovc, I.; Radaelli, A.; De Giuli Morghen, C.; Valoti, E. Benzodioxane-benzamides as antibacterial agents: Computational and SAR studies to evaluate the influence of the 7-substitution in FtsZ interaction. ChemMedChem 2020, 2, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straniero, V.; Suigo, L.; Casiraghi, A.; Sebastián-Pérez, V.; Hrast, M.; Zanotto, C.; Zdovc, I.; De Giuli Morghen, C.; Radaelli, A.; Valoti, E. Benzamide Derivatives Targeting the Cell Division Protein FtsZ: Modifications of the Linker and the Benzodioxane Scaffold and Their Effects on Antimicrobial Activity. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artola, M.; Ruíz-Avila, L.B.; Ramírez-Aportela, E.; Martínez, R.F.; Araujo-Bazán, L.; Vázquez-Villa, H.; Martín-Fontecha, M.; Oliva, M.A.; Martín-Galiano, A.J.; Chacón, P.; et al. The structural assembly switch of cell division protein FtsZ probed with fluorescent allosteric inhibitors. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer-González, E.; Fujita, J.; Yoshizawa, T.; Nelson, J.M.; Pilch, A.J.; Hillman, E.; Ozawa, M.; Kuroda, N.; Al-Tameemi, H.M.; Boyd, J.M.; et al. Structure-Guided Design of a Fluorescent Probe for the Visualization of FtsZ in Clinically Important Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacterial Pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokes, N.R.; Baker, N.; Bennett, J.M.; Berry, J.; Collins, I.; Czaplewski, L.G.; Logan, A.; Macdonald, R.; Macleod, L.; Peasley, H.; et al. An improved small-molecule inhibitor of FtsZ with superior in vitro potency, drug-like properties, and in vivo efficacy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, N.R.; Baker, N.; Bennett, J.M.; Chauhan, P.K.; Collins, I.; Davies, D.T.; Gavade, M.; Kumar, D.; Lancett, P.; Macdonald, R.; et al. Design, synthesis and structure-activity relationships of substituted oxazole-benzamide antibacterial inhibitors of FtsZ. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casiraghi, A.; Valoti, E.; Suigo, L.; Artasensi, A.; Sorvillo, E.; Straniero, V. How Reaction Conditions May Influence the Regioselectivity in the Synthesis of 2,3-Dihydro-1,4-benzoxathiine Derivatives. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 13217–13227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suigo, L.; Lodigiani, G.; Straniero, V.; Valoti, E. (3-Methylene-2,3-dihydronaphtho[2,3-b][1,4]dioxin-2-yl)methanol. Molbank 2022, 2022, M1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straniero, V.; Casiraghi, A.; Fumagalli, L.; Valoti, E. How do reaction conditions affect the enantiopure synthesis of 2-substituted-1,4-benzodioxane derivatives? Chirality 2018, 30, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, R.D.; Caroon, J.M.; Kluge, A.F.; Repke, D.B.; Roszkowski, A.P.; Strosberg, A.M.; Baker, S.; Bitter, S.M.; Okada, M.D. Synthesis and antihypertensive activity of 4′-substituted spiro4H-3,1-benzoxazine-4,4′-piperidin-2(1H)-ones. J. Med. Chem. 1983, 26, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, R.D.; Kurz, L.J. Synthesis of the Enantiomers of Erythro-2-oxiranyl-1,4-benzodioxan. Heterocycles 1985, 23, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).