2-(2-(4-Methoxyphenyl)furo[3,2-h]quinolin-3-yl)acetic Acid
Abstract
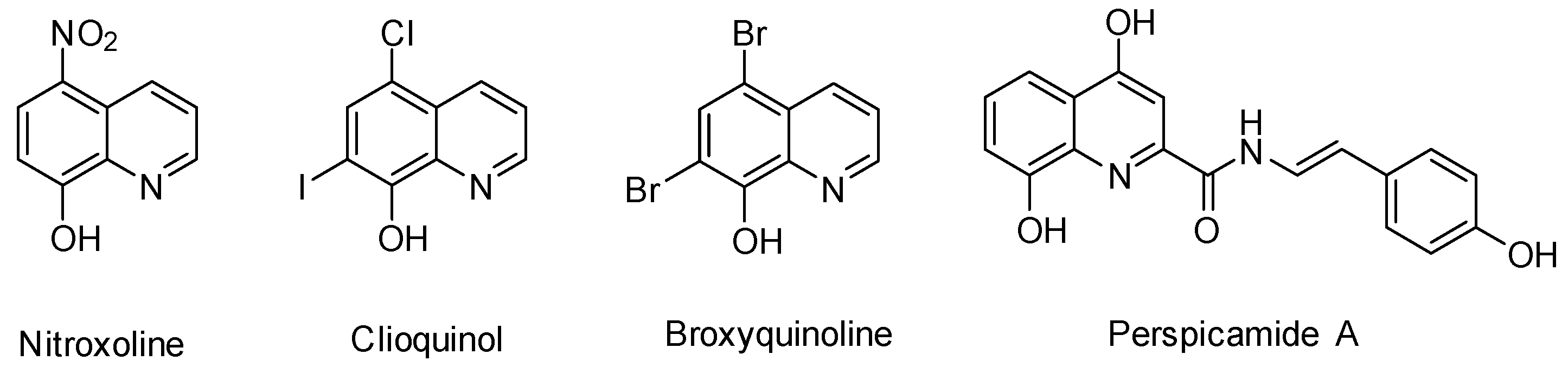
1. Introduction
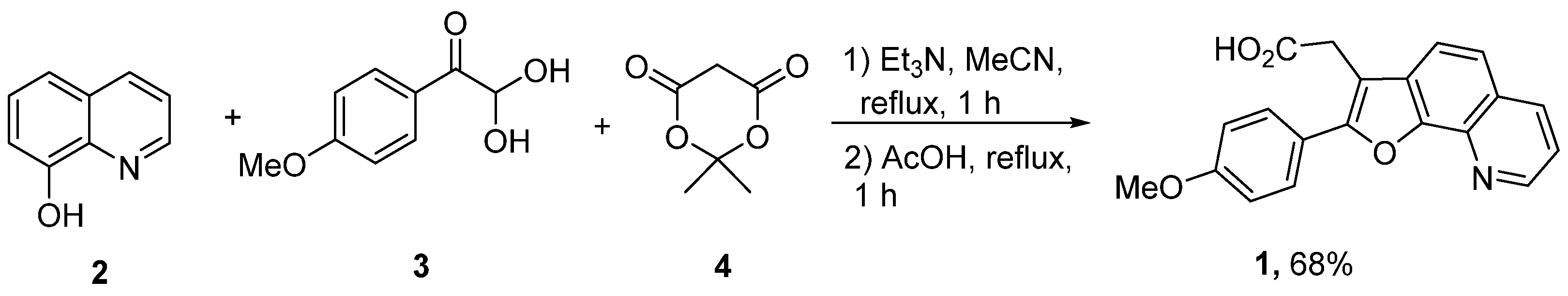
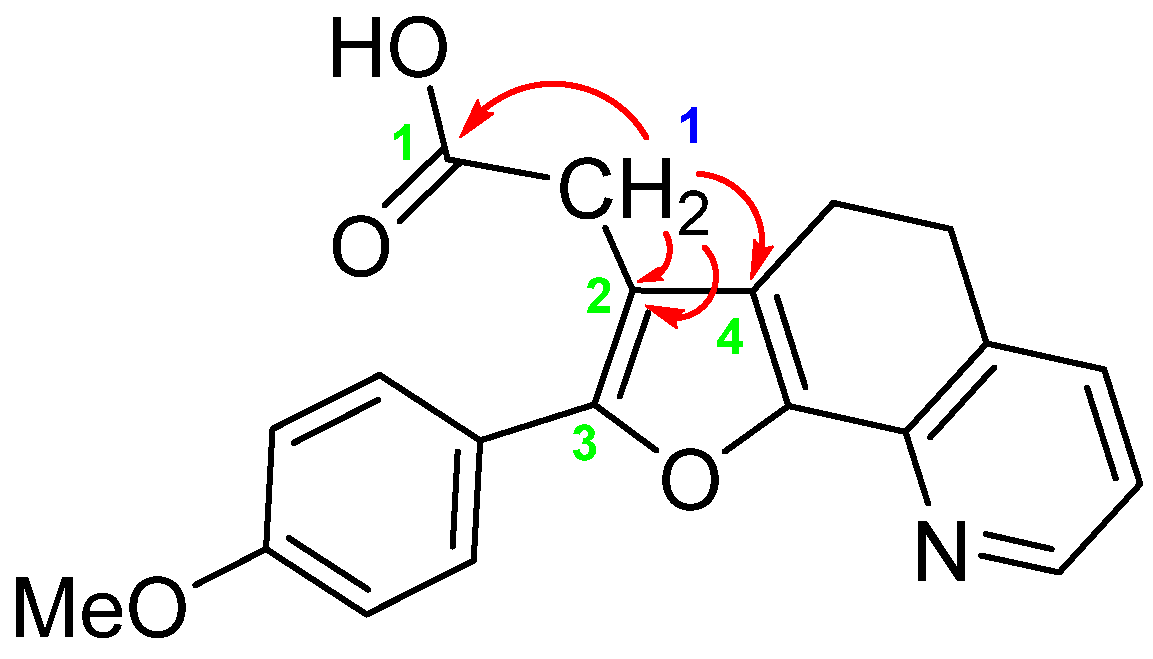
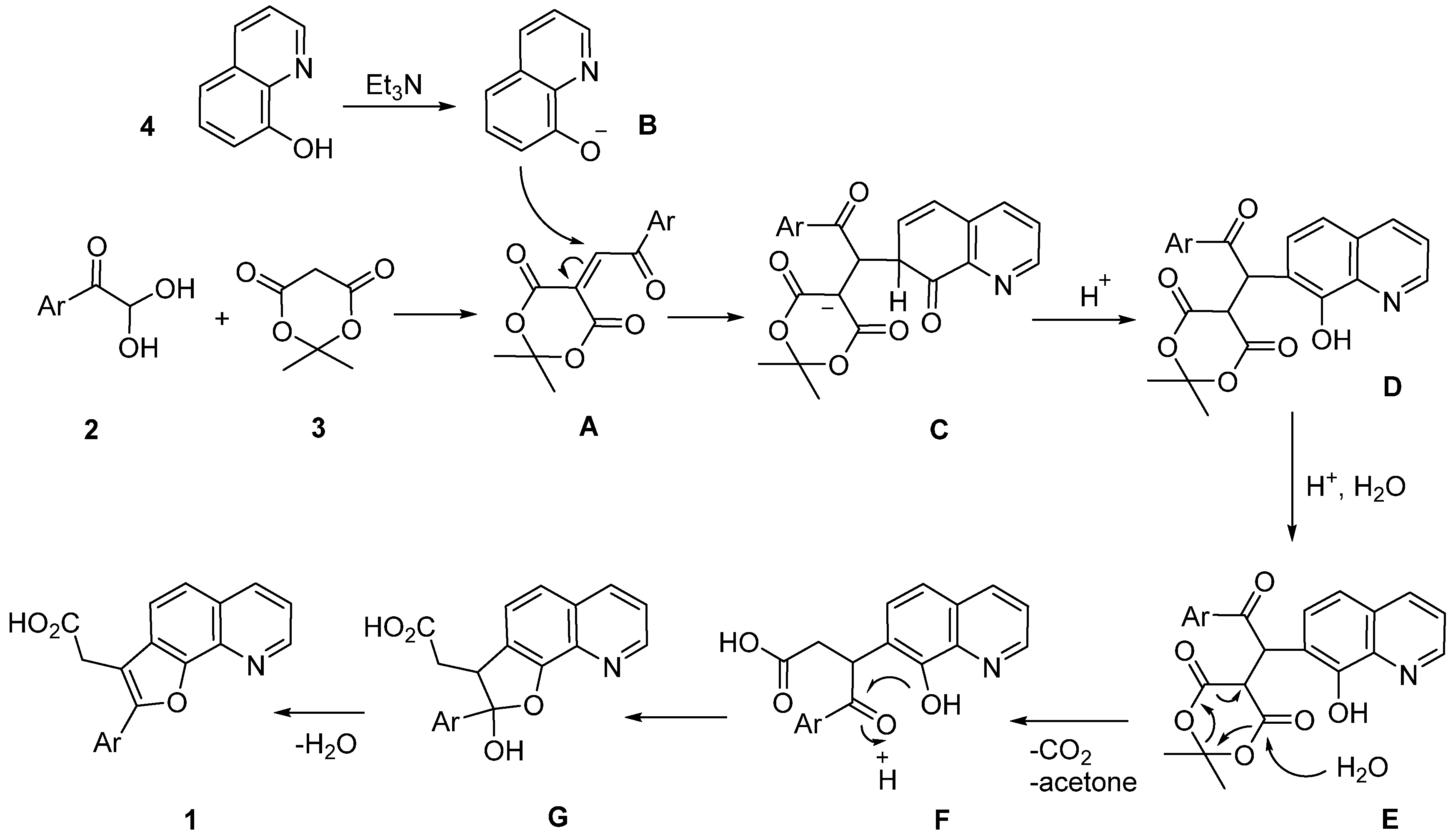
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
Experimental Procedure for the Synthesis of 2-(2-(4-Methoxyphenyl)furo[3,2-h]quinolin-3-yl)Acetic Acid 1
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, Y.; Xu, H.; Chen, W.; Zhan, P.; Liu, X. 8-Hydroxyquinoline: A privileged structure with a broad-ranging pharmacological potential. MedChemComm 2015, 6, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadeh, H.A.; Sweidan, K.A.; Mubarak, M.S. Recent Advances in the Synthesis and Biological Activity of 8-Hydroxyquinolines. Molecules 2020, 25, 4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Luxami, V.; Paul, K. Insights of 8-Hydroxyquinolines: A novel target in medicinal chemistry. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 108, 104633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savić-Gajić, I.M.; Savić, I.M. Drug design strategies with metal-hydroxyquinoline complexes. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2020, 15, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveri, V.; Vecchio, G. 8-Hydroxyquinolines in medicinal chemistry: A structural perspective. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 120, 252–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prachayasittikul, V.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Prachayasittikul, S.; Ruchirawat, S. 8-Hydroxyquinolines: A review of their metal chelating properties and medicinal applications. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2013, 7, 1157–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.S.; Thakur, G.A.; Shaikh, M.M. Synthesis, Characterization, and Antibacterial Studies of Mixed Ligand Dioxouranium Complexes with 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Some Amino Acids. ISRN Pharm. 2011, 2011, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cherdtrakulkiat, R.; Boonpangrak, S.; Sinthupoom, N.; Prachayasittikul, S.; Ruchirawat, S.; Prachayasittikul, V. Derivatives (halogen, nitro and amino) of 8-hydroxyquinoline with highly potent antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2016, 6, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joaquim, A.R.; Reginatto, P.; Lopes, M.S.; Bazana, L.C.G.; Gionbelli, M.P.; Cesare, M.A.D.; Kaminski, T.F.A.; Teixeira, M.L.; Abegg, M.A.; Fuentefria, A.M.; et al. New 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives highlight the potential of this class for treatment of fungal infections. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 18158–18170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joaquim, A.R.; Gionbelli, M.P.; Gosmann, G.; Fuentefria, A.M.; Lopes, M.S.; Andrade, S.F.D. Novel Antimicrobial 8-Hydroxyquinoline-Based Agents: Current Development, Structure–Activity Relationships, and Perspectives. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 16349–16379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shi, J.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, R.; Bai, Y.; Li, J.; Liang, F.; Tang, Y. An 8-Hydroxy-Quinoline Derivative Protects Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Lethality in Endotoxemia by Inhibiting HMGB1-Mediated Caspase-11 Signaling. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-R.; Liu, Y.-C.; Chen, Z.-F.; Meng, T.; Zou, B.-Q.; Liu, Y.-N.; Liang, H. Studies on the structures, cytotoxicity and apoptosis mechanism of 8-hydroxylquinoline rhodium(iii) complexes in T-24 cells. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 6005–6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, M.; Pastuch-Gawolek, G.; Mrozek-Wilczkiewicz, A.; Kuczak, M.; Skonieczna, M.; Musiol, R. Synthesis of 8-hydroxyquinoline glycoconjugates and preliminary assay of their β1,4-GalT inhibitory and anti-cancer properties. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 84, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choroba, K.; Raposo, L.R.; Palion-Gazda, J.; Malicka, E.; Erfurt, K.; Machura, B.; Fernandes, A.R. In vitro antiproliferative effect of vanadium complexes bearing 8-hydroxyquinoline-based ligands—the substituent effect. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 6596–6606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.H.; Chui, C.H.; Chan, S.W.; Kok, S.H.L.; Chan, D.; Tsoi, M.Y.T.; Leung, P.H.M.; Lam, A.K.Y.; Chan, A.S.C.; Lam, K.H.; et al. Synthesis of 8-Hydroxyquinoline Derivatives as Novel Antitumor Agents. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatova, M.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Markova, N.; Kukeva, R.; Stoyanova, R.; Georgieva, A.; Toshkova, R. 8-Hydroxyquinoline-5-Sulfonic Acid-Containing Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Chitosan Electrospun Materials and Their Cu2+ and Fe3+ Complexes: Preparation, Antibacterial, Antifungal and Antitumor Activities. Polymers 2021, 13, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.-D.; Sun, Y.; Lawoe, R.K.; Yang, G.-Z.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Shang, X.-F.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.-D.; Zhu, J.-K.; Huang, X.-L. Synthesis and anti-phytopathogenic activity of 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 30087–30099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pippi, B.; Lopes, W.; Reginatto, P.; Silva, F.É.K.; Joaquim, A.R.; Alves, R.J.; Silveira, G.P.; Vainstein, M.H.; Andrade, S.F.; Fuentefria, A.M. New insights into the mechanism of antifungal action of 8-hydroxyquinolines. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Vaira, M.; Bazzicalupi, C.; Orioli, P.; Messori, L.; Bruni, B.; Zatta, P. Clioquinol, a Drug for Alzheimer’s Disease Specifically Interfering with Brain Metal Metabolism: Structural Characterization of Its Zinc(II) and Copper(II) Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 43, 3795–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shachar, D.B.; Kahana, N.; Kampel, V.; Warshawsky, A.; Youdim, M.B.H. Neuroprotection by a novel brain permeable iron chelator, VK-28, against 6-hydroxydopamine lession in rats. Neuropharmacology 2004, 46, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bareggi, S.R.; Cornelli, U. Clioquinol: Review of Its Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Uses in Neurodegenerative Disorders. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2012, 18, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caglič, D.; Krutein, M.C.; Bompiani, K.M.; Barlow, D.J.; Benoni, G.; Pelletier, J.C.; Reitz, A.B.; Lairson, L.L.; Houseknecht, K.L.; Smith, G.R.; et al. Identification of Clinically Viable Quinolinol Inhibitors of Botulinum Neurotoxin A Light Chain. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohini; Paul, K.; Luxami, V. 8-Hydroxyquinoline Fluorophore for Sensing of Metal Ions and Anions. Chem. Rec. 2020, 20, 1430–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazaeli, Y.; Amini, M.M.; Najafi, E.; Mohajerani, E.; Janghouri, M.; Jalilian, A.; Ng, S.W. Synthesis and Characterization of 8-Hydroxyquinoline Complexes of Tin(IV) and Their Application in Organic Light Emitting Diode. J. Fluoresc. 2012, 22, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Wu, S.-L.; Xu, J.-X.; Chen, D.-S. An Efficient One-Pot Synthesis of 6,9-Dihydrofuro[3,2-f]Quinoline-8-Carbonitrile Derivatives under Catalyst-Free Conditions. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, X.-J.; Liu, J.-Q.; Wang, X.-S. One-Pot Three-Component Synthesis of 6H-Chromeno[4,3-b] or Cyclopenta[b]Furo[3,2-f]Quinoline Derivatives. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2017, 54, 2929–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Yu, Y.-L.; Zhao, L.; Ding, M.-W. One-pot and divergent synthesis of furo[3,2-c]quinolines and quinazolin-4(3H)-ones via sequential isocyanide-based three-component/Staudinger/aza-Wittig reaction. Tetrahedron 2021, 80, 131868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, S.E.; Gulati, S.; Shankaraiah, N. Recent advances in multi-component reactions and their mechanistic insights: A triennium review. Org. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 4237–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younus, H.A.; Al-Rashida, M.; Hameed, A.; Uroos, M.; Salar, U.; Rana, S.; Khan, K.M. Multicomponent reactions (MCR) in medicinal chemistry: A patent review (2010–2020). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2021, 31, 267–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graebin, C.S.; Ribeiro, F.V.; Rogério, K.R.; Kümmerle, A.E. Multicomponent Reactions for the Synthesis of Bioactive Compounds: A Review. Curr. Org. Synth. 2019, 16, 855–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touré, B.B.; Hall, D.G. Natural Product Synthesis Using Multicomponent Reaction Strategies. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4439–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaczyk-Lesanko, A.; Hall, D.G. Wanted: New multicomponent reactions for generating libraries of polycyclic natural products. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2005, 9, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, R.; Panday, A.K.; Choudhury, L.H.; Pal, J.; Subramanian, R.; Verma, A. Multicomponent Reactions of Arylglyoxal, 4-Hydroxycoumarin, and Cyclic 1,3-C,N-Binucleophiles: Binucleophile-Directed Synthesis of Fused Five- and Six-Membered N-Heterocycles. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 2017, 2789–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, A. Arylglyoxals as Versatile Synthons for Heterocycles Through Multi-Component Reactions. Curr. Org. Chem. 2019, 23, 1945–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komogortsev, A.N.; Lichitsky, B.V.; Melekhina, V.G. Straightforward One-step approach towards novel derivatives of 9-oxo-5,6,7,9-tetrahydrobenzo[9,10]heptaleno[3,2-b]furan-12-yl)acetic acid based on the multicomponent reaction of colchiceine, arylglyoxals and Meldrum’s acid. Tetrahedron Lett. 2021, 78, 153292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbunov, Y.O.; Lichitsky, B.V.; Komogortsev, A.N.; Mityanov, V.S.; Dudinov, A.A.; Krayushkin, M.M. Synthesis of Condensed Furylacetic Acids Based on Multicomponent Condensation of Heterocyclic Enols with Arylglyoxals and Meldrum’s Acid. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2018, 54, 692–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komogortsev, A.N.; Lichitsky, B.V.; Tretyakov, A.D.; Dudinov, A.A.; Krayushkin, M.M. Investigation of the multicomponent reaction of 5-hydroxy-2-methyl-4H-pyran-4-one with carbonyl compounds and Meldrum’s acid. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2019, 55, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichitsky, B.V.; Melekhina, V.G.; Komogortsev, A.N.; Minyaev, M.E. A new multicomponent approach to the synthesis of substituted furan-2(5H)-ones containing 4H-chromen-4-one fragment. Tetrahedron Lett. 2020, 61, 152602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichitsky, B.V.; Tretyakov, A.D.; Komogortsev, A.N.; Mityanov, V.S.; Dudinov, A.A.; Gorbunov, Y.O.; Daeva, E.D.; Krayushkin, M.M. Synthesis of substituted benzofuran-3-ylacetic acids based on three-component condensation of polyalkoxyphenols, arylglyoxals and Meldrum’s acid. Mendeleev Commun. 2019, 29, 587–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lichitsky, B.V.; Komogortsev, A.N.; Melekhina, V.G. 2-(2-(4-Methoxyphenyl)furo[3,2-h]quinolin-3-yl)acetic Acid. Molbank 2022, 2022, M1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1315
Lichitsky BV, Komogortsev AN, Melekhina VG. 2-(2-(4-Methoxyphenyl)furo[3,2-h]quinolin-3-yl)acetic Acid. Molbank. 2022; 2022(1):M1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1315
Chicago/Turabian StyleLichitsky, Boris V., Andrey N. Komogortsev, and Valeriya G. Melekhina. 2022. "2-(2-(4-Methoxyphenyl)furo[3,2-h]quinolin-3-yl)acetic Acid" Molbank 2022, no. 1: M1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1315
APA StyleLichitsky, B. V., Komogortsev, A. N., & Melekhina, V. G. (2022). 2-(2-(4-Methoxyphenyl)furo[3,2-h]quinolin-3-yl)acetic Acid. Molbank, 2022(1), M1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1315






